Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) as Green Bioinoculants: Recent Developments, Constraints, and Prospects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biofertilizers
3. Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR)—The Phyto-Friendly Soil Microbes
3.1. Characteristics of an Ideal PGPR
- (1)
- It should be highly rhizosphere-competent and eco-friendly.
- (2)
- It should colonize the plant roots in significant numbers upon inoculation.
- (3)
- It should be able to promote plant growth.
- (4)
- It should exhibit a broad spectrum of action.
- (5)
- It should be compatible with other bacteria in the rhizosphere.
- (6)
- It should be tolerant of physicochemical factors like heat, desiccation, radiations, and oxidants.
- (7)
- It should demonstrate better competitive skills over the existing rhizobacterial communities.
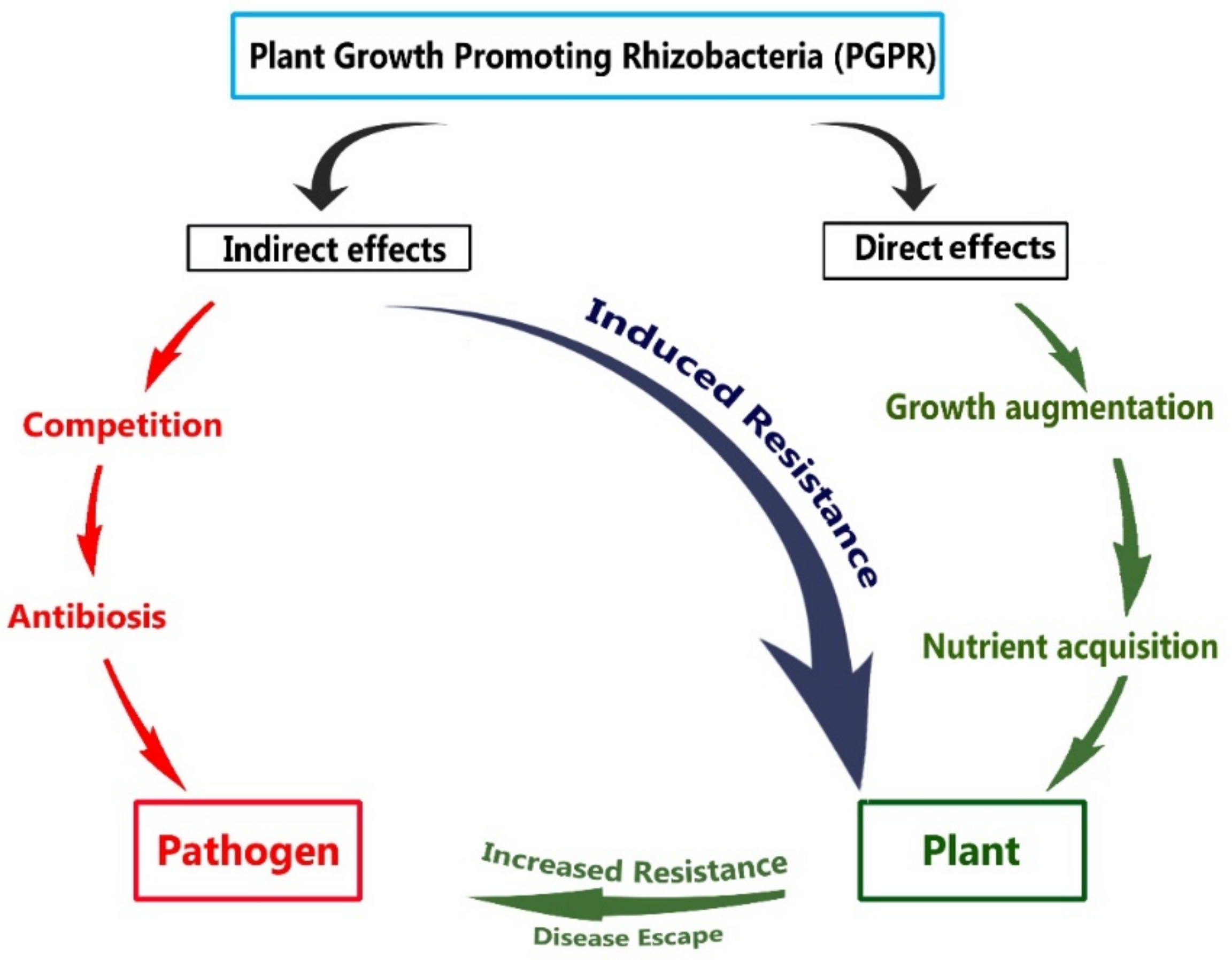
3.2. Mechanisms of PGPR Action
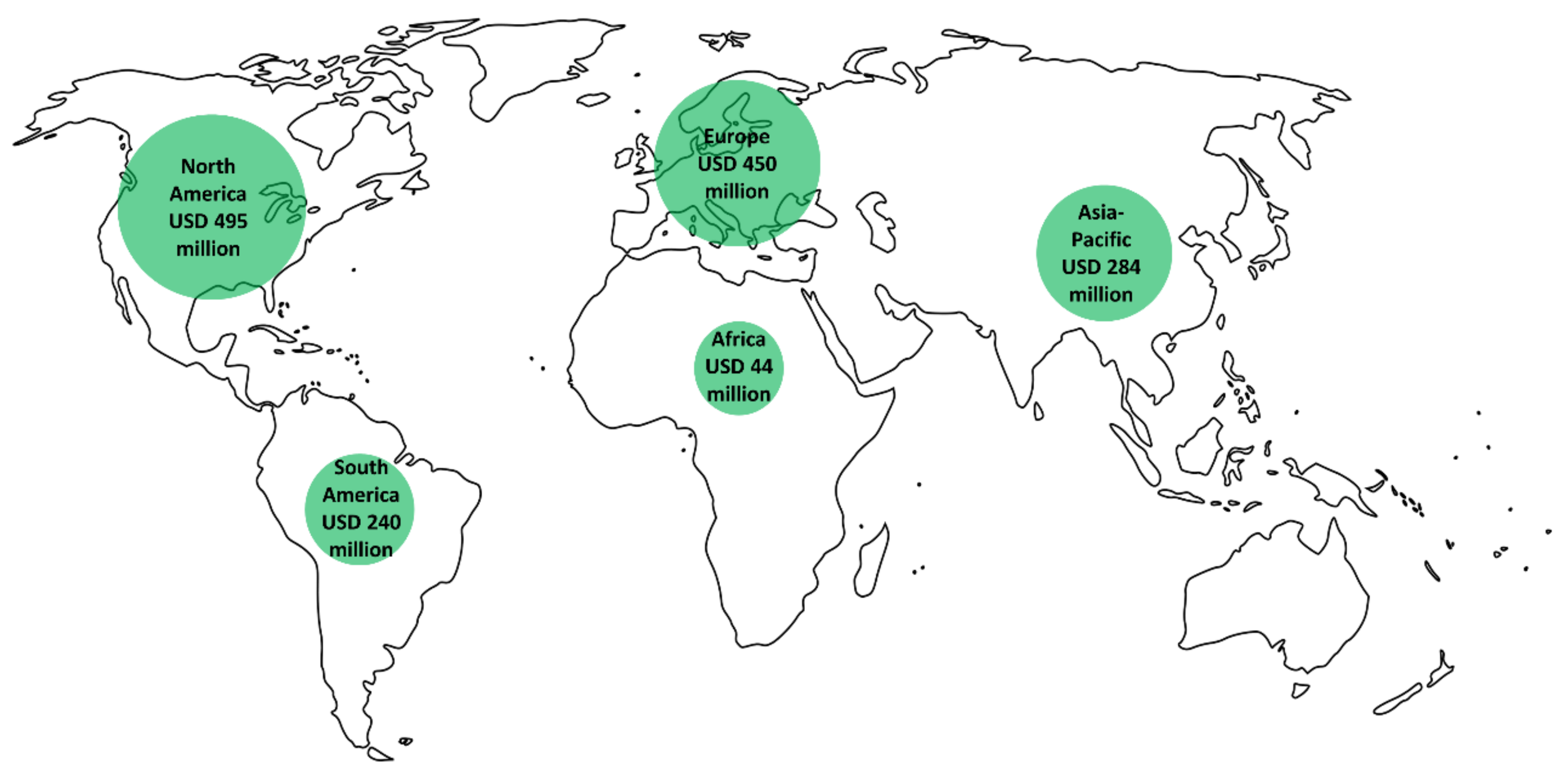
4. Global Biofertilizer Market
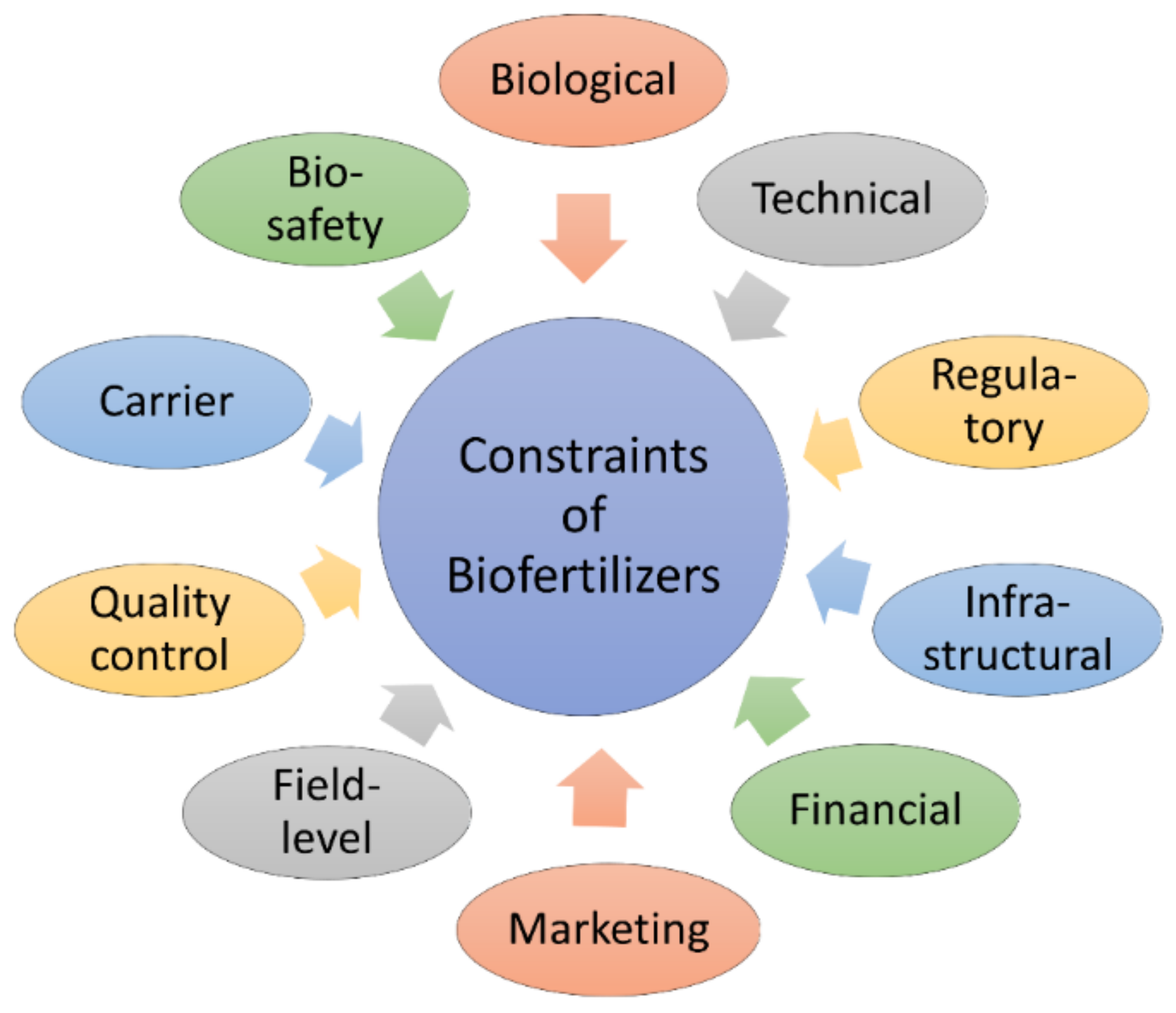
5. Challenges and Constraints with PGPR-Based Biofertilizers
5.1. Biological Constraints
5.2. Technical Constraints
5.3. Regulatory Constraints
5.4. Infrastructural Constraints
5.5. Financial Constraints
5.6. Marketing Constraints
5.7. Field-Level Constraints
5.8. Quality Control Constraints
5.9. Biofertilizer Carrier
5.10. Biosafety of PGPRs
6. Guidelines and Precautions for Using PGPRs as Biofertilizers
- (1)
- It is essential that the supplied biofertilizer to be used in fields is of good quality, contains 107 viable cells per gram as an inoculum, and is purchased from a reputed manufacturer only.
- (2)
- Since the biofertilizer exhibits specificity, it should only be used for the crop(s) specified on the commercially available product packet.
- (3)
- The culture bag should have a tag of the name of the crop for which it has to be used.
- (4)
- While inoculating, excess culture should be inoculated, or any remnants/residual culture should be immediately put in grooves of the field so that inoculum microorganisms start interacting with other microbiota in the rhizosphere and begin colonizing the rhizosphere.
- (5)
- Since the biofertilizers are microbial products, for achieving better shelf life, before their application in fields, they should be stored in cool and shady places, preferably at room temperature (25–28 °C).
- (6)
- During storage or application, direct contact of the biofertilizers with agrochemicals (herbicides/weedicides/pesticides) should be strictly avoided.
- (7)
- Generally speaking, 200g biofertilizer can be effectively used to treat 10 kg of seeds.
- (8)
- In the case of unfavorable soil conditions, especially where the soil is strongly acidic, soil amendments such as lime or rock phosphate, are usually preferred.
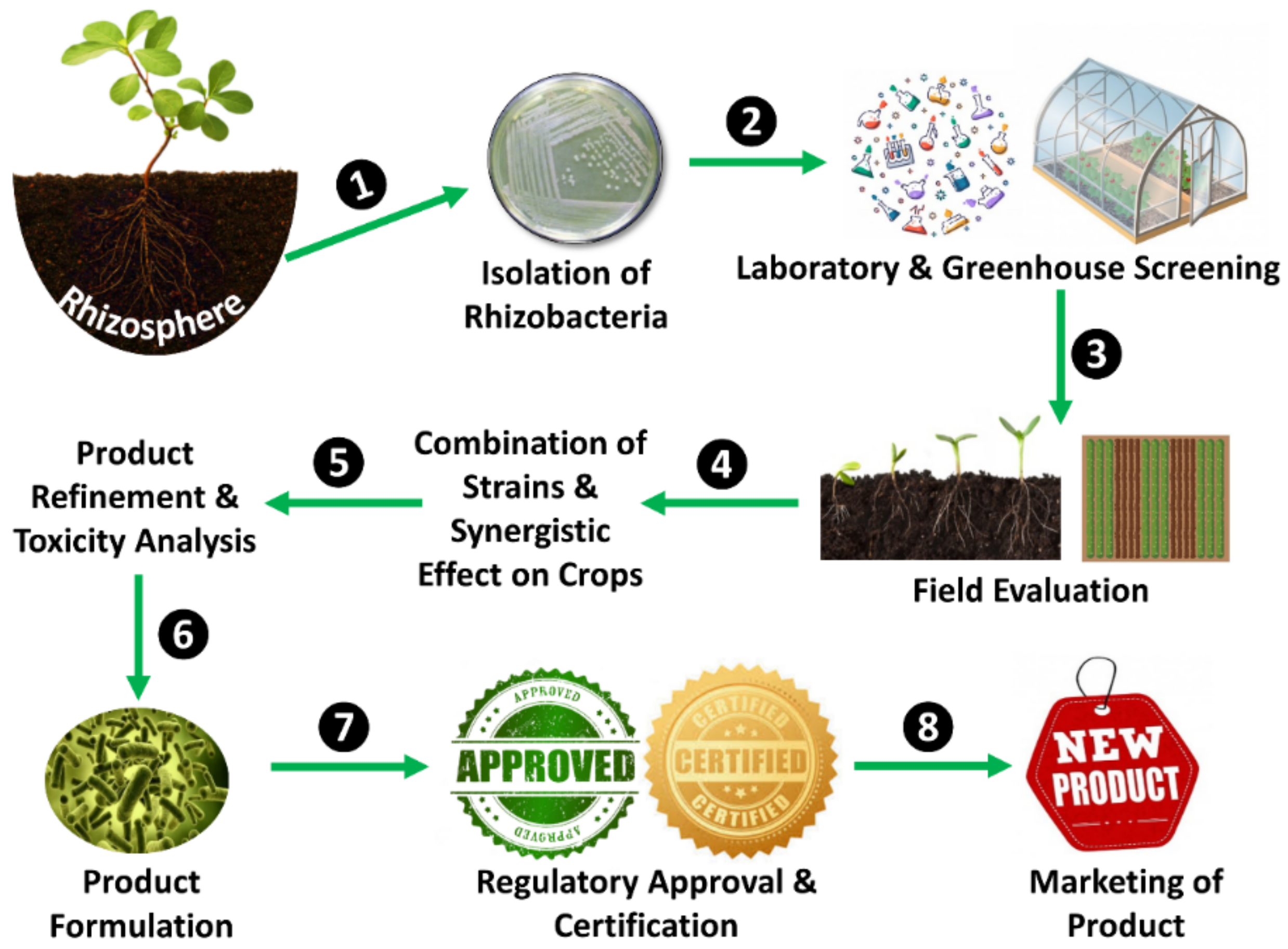
7. Roadmap to the Commercialization of PGPR-Based Biofertilizers
8. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kesavan, P.C.; Swaminathan, M.S. Modern technologies for sustainable food and nutrition security. Curr. Sci. 2018, 115, 1876–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingali, P.L. Green revolution: Impacts, limits, and the path ahead. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12302–12308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Fang, S. Practices, perceptions, and implications of fertilizer use in East-Central China. Ambio 2015, 44, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishnoi, U. Agriculture and the dark side of chemical fertilizers. Environ. Anal. Ecol. Stud. 2018, 3, EAES.000552.2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fascella, G.; Montoneri, E.; Ginepro, M.; Francavilla, M. Effect of urban biowaste derived soluble substances on growth, photosynthesis and ornamental value of Euphorbia × lomi. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 197, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fascella, G.; Montoneri, E.; Francavilla, M. Biowaste versus fossil sourced auxiliaries for plant cultivation: The Lantana case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 185, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, K.; Ciais, P.; Polasky, S. Reducing human nitrogen use for food production. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilangumaran, G.; Smith, D.L. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in amelioration of salinity stress: A systems biology perspective. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, R.; Ambrosini, A.; Passaglia, L.M.P. Plant growth-promoting bacteria as inoculants in agricultural soils. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2015, 38, 401–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Wang, K.-H.; Sipes, B.S.; Tian, M. Suppression of root-knot nematode by vermicompost tea prepared from different curing ages of vermicompost. Plant Dis. 2017, 101, 734–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arancon, N.Q.; Owens, J.D.; Converse, C. The effects of vermicompost tea on the growth and yield of lettuce and tomato in a non-circulating hydroponics system. J. Plant Nutr. 2019, 42, 2447–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinnuoye-Adelabu, D.B.; Steenhuisen, S.; Bredenhand, E. Improving pea quality with vermicompost tea and aqueous biochar: Prospects for sustainable farming in Southern Africa. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2019, 123, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raklami, A.; Bechtaoui, N.; Tahiri, A.; Anli, M.; Meddich, A.; Oufdou, K. Use of rhizobacteria and mycorrhizae consortium in the open field as a strategy for improving crop nutrition, productivity and soil fertility. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabborova, D.; Wirth, S.; Kannepalli, A.; Narimanov, A.; Desouky, S.; Davranov, K.; Sayyed, R.Z.; El Enshasy, H.; Malek, R.A.; Syed, A.; et al. Co-Inoculation of rhizobacteria and biochar application improves growth and nutrients in soybean and enriches soil nutrients and enzymes. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.B.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Trivedi, M.H.; Gobi, T.A. Phosphate solubilizing microbes: Sustainable approach for managing phosphorus deficiency in agricultural soils. Springerplus 2013, 2, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vessey, J.K. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria as biofertilizers. Plant Soil 2003, 255, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anli, M.; Baslam, M.; Tahiri, A.; Raklami, A.; Symanczik, S.; Boutasknit, A.; Ait-El-Mokhtar, M.; Ben-Laouane, R.; Toubali, S.; Ait Rahou, Y.; et al. Biofertilizers as strategies to improve photosynthetic apparatus, growth, and drought stress tolerance in the date palm. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 516818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, J.; Wei, G.; Shen, L.; Ding, W.; Chen, S. Biofertilizers regulate the soil microbial community and enhance Panax ginseng yields. Chin. Med. 2019, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atieno, M.; Herrmann, L.; Nguyen, H.T.; Phan, H.T.; Nguyen, N.K.; Srean, P.; Than, M.M.; Zhiyong, R.; Tittabutr, P.; Shutsrirung, A.; et al. Assessment of biofertilizer use for sustainable agriculture in the Great Mekong Region. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 275, 111300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dineshkumar, R.; Kumaravel, R.; Gopalsamy, J.; Sikder, M.N.A.; Sampathkumar, P. Microalgae as bio-fertilizers for rice growth and seed yield productivity. Waste Biomass Valorization 2018, 9, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanty, T.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Goswami, M.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Das, B.; Ghosh, A.; Tribedi, P. Biofertilizers: A potential approach for sustainable agriculture development. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 3315–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandi, P.; Basu, S.K. Role of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) as biofertilizers in stabilizing agricultural ecosystems. In Organic Farming for Sustainable Agriculture; Nandwani, D., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, D.; Ansari, M.W.; Sahoo, R.K.; Tuteja, N. Biofertilizers function as key player in sustainable agriculture by improving soil fertility, plant tolerance and crop productivity. Microb. Cell Fact. 2014, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritika, B.; Utpal, D. Biofertilizer, a way towards organic agriculture: A review. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 8, 2332–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkar, S.G. Microbes as Bio-Fertilizers and Their Production Technology, 1st ed.; WPI Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.M.; Reddy, C.G.; Phogat, M.; Korav, S. Role of bio-fertilizers towards sustainable agricultural development: A review. J. Pharm. Phytochem. 2018, 7, 1915–1921. [Google Scholar]
- Itelima, J.; Bang, W.J.; Onyimba, I.A.; Sila, M.D.; Egbere, O.J. Bio-fertilizers as key player in enhancing soil fertility and crop productivity: A review. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Rep. 2018, 2, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.S.; Pandey, V.C.; Singh, D.P. Efficient soil microorganisms: A new dimension for sustainable agriculture and environmental development. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 140, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Bai, Z.; Bao, L.; Xue, L.; Zhang, S.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhuang, G.; Zhuang, X. Bacillus subtilis biofertilizer mitigating agricultural ammonia emission and shifting soil nitrogen cycling microbiomes. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 105989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backer, R.; Rokem, J.S.; Ilangumaran, G.; Lamont, J.; Praslickova, D.; Ricci, E.; Subramanian, S.; Smith, D.L. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria: Context, mechanisms of action, and roadmap to commercialization of biostimulants for sustainable agriculture. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Gupta, R.D. Bio-fertilizers: Their kinds and requirement in India. In Integrated Nutrient Management (INM) in a Sustainable Rice—Wheat Cropping System; Mahajan, A., Gupta, R.D., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 75–100. [Google Scholar]
- Meena, M.; Swapnil, P.; Divyanshu, K.; Kumar, S.; Tripathi, Y.N.; Zehra, A.; Marwal, A.; Upadhyay, R.S. PGPR-mediated induction of systemic resistance and physiochemical alterations in plants against the pathogens: Current perspectives. J. Basic Microbiol. 2020, 60, 828–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmusk, S.; Kim, S.-B.; Nevo, E.; Abd El Daim, I.; Ek, B.; Bergquist, J.; Behers, L. Sfp-type PPTase inactivation promotes bacterial biofilm formation and ability to enhance wheat drought tolerance. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, N.; Pandey, S.S.; Barnawal, D.; Patel, V.K.; Kalra, A. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria Dietzia natronolimnaea modulates the expression of stress responsive genes providing protection of wheat from salinity stress. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Kulkarni, J.; Jha, B. Halotolerant rhizobacteria promote growth and enhance salinity tolerance in peanut. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmusk, S.; Abd El-Daim, I.A.; Copolovici, L.; Tanilas, T.; Kännaste, A.; Behers, L.; Nevo, E.; Seisenbaeva, G.; Stenström, E.; Niinemets, Ü. Drought-tolerance of wheat improved by rhizosphere bacteria from harsh environments: Enhanced biomass production and reduced emissions of stress volatiles. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schütz, L.; Gattinger, A.; Meier, M.; Müller, A.; Boller, T.; Mäder, P.; Mathimaran, N. Improving crop yield and nutrient use efficiency via biofertilization—A global meta-analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 8, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Fuente Cantó, C.; Simonin, M.; King, E.; Moulin, L.; Bennett, M.J.; Castrillo, G.; Laplaze, L. An extended root phenotype: The rhizosphere, its formation and impacts on plant fitness. Plant J. 2020, 103, 951–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalam, S.; Das, S.N.; Basu, A.; Podile, A.R. Population densities of indigenous Acidobacteria change in the presence of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) in rhizosphere. J. Basic Microbiol. 2017, 57, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buée, M.; de Boer, W.; Martin, F.; van Overbeek, L.; Jurkevitch, E. The rhizosphere zoo: An overview of plant-associated communities of microorganisms, including phages, bacteria, archaea, and fungi, and of some of their structuring factors. Plant Soil 2009, 321, 189–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Podile, A.R. Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR): The bugs to debug the root zone. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 36, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshru, B.; Mitra, D.; Khoshmanzar, E.; Myo, E.M.; Uniyal, N.; Mahakur, B.; Mohapatra, P.K.; Panneerselvam, P.; Boutaj, H.; Alizadeh, M.; et al. Current scenario and future prospects of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria: An economic valuable resource for the agriculture revival under stressful conditions. J. Plant Nutr. 2020, 43, 3062–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahemad, M.; Kibret, M. Mechanisms and applications of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: Current perspective. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2014, 26, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parray, J.A.; Jan, S.; Kamili, A.N.; Qadri, R.A.; Egamberdieva, D.; Ahmad, P. Current perspectives on plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2016, 35, 877–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejan, P.; Abdullah, R.; Khadiran, T.; Ismail, S.; Nasrulhaq Boyce, A. Role of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in agricultural sustainability - A review. Molecules 2016, 21, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalam, S.; Basu, A.; Podile, A.R. Functional and molecular characterization of plant growth promoting Bacillus isolates from tomato rhizosphere. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swarnalakshmi, K.; Yadav, V.; Tyagi, D.; Dhar, D.W.; Kannepalli, A.; Kumar, S. Significance of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in grain legumes: Growth promotion and crop production. Plants 2020, 9, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopalakrishnan, S.; Sathya, A.; Vijayabharathi, R.; Varshney, R.K.; Gowda, C.L.L.; Krishnamurthy, L. Plant growth promoting rhizobia: Challenges and opportunities. 3 Biotech 2015, 5, 355–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, P.N.; Jha, D.K. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): Emergence in agriculture. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 1327–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaikuntapu, P.R.; Dutta, S.; Samudrala, R.B.; Rao, V.R.V.N.; Kalam, S.; Podile, A.R. Preferential promotion of Lycopersicon esculentum (tomato) growth by plant growth promoting bacteria associated with tomato. Indian J. Microbiol. 2014, 54, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, D.; Thakker, J.N.; Dhandhukia, P.C. Portraying mechanics of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): A review. Cogent Food Agric. 2016, 2, 1127500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankati, S.; Podile, A.R. Understanding plant-beneficial microbe interactions for sustainable agriculture. J. Spices Aromat. Crop. 2018, 27, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Ahmad, I.; Khan, M.S. Screening of free-living rhizospheric bacteria for their multiple plant growth promoting activities. Microbiol. Res. 2008, 163, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Song, L.; Xiao, Y.; Ge, W. Drought-tolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria associated with foxtail millet in a semi-arid agroecosystem and their potential in alleviating drought stress. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lima, B.C.; Moro, A.L.; Santos, A.C.P.; Bonifacio, A.; Araujo, A.S.F.; de Araujo, F.F. Bacillus subtilis ameliorates water stress tolerance in maize and common bean. J. Plant Interact. 2019, 14, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresson, J.; Varoquaux, F.; Bontpart, T.; Touraine, B.; Vile, D. The PGPR strain Phyllobacterium brassicacearum STM196 induces a reproductive delay and physiological changes that result in improved drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2013, 200, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, M.V.B.; Burity, H.A.; Martínez, C.R.; Chanway, C.P. Alleviation of drought stress in the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) by co-inoculation with Paenibacillus polymyxa and Rhizobium tropici. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2008, 40, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kloepper, J.W.; Ryu, C.M. Rhizosphere bacteria help plants tolerate abiotic stress. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, N.; Mumtaz, K.; Akhtar, N.; Yasmin, H.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Khan, W.; El Enshasy, H.A.; Dailin, D.J.; Elsayed, E.A.; Ali, Z. Exopolysaccharides producing bacteria for the amelioration of drought stress in wheat. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayak, S.; Tirosh, T.; Glick, B.R. Plant growth-promoting bacteria confer resistance in tomato plants to salt stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2004, 42, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, N.; Yadav, D.; Barnawal, D.; Maji, D.; Kalra, A. Exiguobacterium oxidotolerans, a halotolerant plant growth promoting rhizobacteria, improves yield and content of secondary metabolites in Bacopa monnieri (L.) Pennell under primary and secondary salt stress. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 29, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marulanda, A.; Azcón, R.; Chaumont, F.; Ruiz-Lozano, J.M.; Aroca, R. Regulation of plasma membrane aquaporins by inoculation with a Bacillus megaterium strain in maize (Zea mays L.) plants under unstressed and salt-stressed conditions. Planta 2010, 232, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasciglione, G.; Casanovas, E.M.; Quillehauquy, V.; Yommi, A.K.; Gõ Ni, M.G.; Roura, S.I.; Barassi, C.A. Azospirillum inoculation effects on growth, product quality and storage life of lettuce plants grown under salt stress. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 195, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, A.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Ramteke, P.W.; Sharma, S.; Marraiki, N.; Elgorban, A.M.; Syed, A. ACC deaminase and antioxidant enzymes producing halophilic Enterobacter sp. PR14 promotes the growth of rice and millets under salinity stress. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2020, 26, 1847–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, P.; Yadav, A.N.; Khannam, K.S.; Kumar, S.; Saxena, A.K.; Suman, A. Molecular diversity and multifarious plant growth promoting attributes of Bacilli associated with wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) rhizosphere from six diverse agro-ecological zones of India. J. Basic Microbiol. 2016, 56, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.; Bist, V.; Srivastava, S.; Singh, P.C.; Trivedi, P.K.; Asif, M.H.; Chauhan, P.S.; Nautiyal, C.S. Unraveling aspects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens mediated enhanced production of rice under biotic stress of Rhizoctonia solani. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vasconcellos, R.L.F.; Cardoso, E.J.B.N. Rhizospheric streptomycetes as potential biocontrol agents of Fusarium and Armillaria pine rot and as PGPR for Pinus taeda. Biocontrol 2009, 54, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowtham, H.G.; Hariprasad, P.; Nayak, S.C.; Niranjana, S.R. Application of rhizobacteria antagonistic to Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici for the management of Fusarium wilt in tomato. Rhizosphere 2016, 2, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Mishra, A.; Nautiyal, C.S. Paenibacillus lentimorbus B-30488 r controls early blight disease in tomato by inducing host resistance associated gene expression and inhibiting Alternaria solani. Biol. Control 2012, 62, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshma, P.; Naik, M.K.; Aiyaz, M.; Niranjana, S.K.; Chennappa, G.; Shaikh, S.S.; Sayyed, R.Z. Induced systemic resistance by 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol positive fluorescent Pseudomonas strains against rice sheath blight. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2018, 56, 207–212. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, S. Identification and characterization of the phosphate-solubilizing bacterium Pantoea sp. S32 in reclamation soil in Shanxi, China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pii, Y.; Mimmo, T.; Tomasi, N.; Terzano, R.; Cesco, S.; Crecchio, C. Microbial interactions in the rhizosphere: Beneficial influences of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on nutrient acquisition process. A review. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2015, 51, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Aguilar, C.; Garruña, R.; Zúñiga-Aguilar, J.J.; Guzmán-Antonio, A.A. PGPR inoculation improves growth, nutrient uptake and physiological parameters of Capsicum chinense plants. Phyton Int. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 86, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaghrabi, O.A.; Abdelmoneim, T.S.; Albishri, H.M.; Moussa, T.A. Enhancement of maize growth using some plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) under laboratory conditions. Life Sci. J. 2014, 11, 764–772. [Google Scholar]
- Nezarat, S.; Gholami, A. Screening plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for improving seed germination, seedling growth and yield of maize. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2009, 12, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, A.; Saharan, B.; Joshi, M.; Prasanna, R.; Kumar, K.; Nain, L. Identification of multi-trait PGPR isolates and evaluating their potential as inoculants for wheat. Ann. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassán, F.D.; Lucangeli, C.D.; Bottini, R.; Piccoli, P.N. Azospirillum spp. metabolize [17,17-2H2] gibberellin A20 to [17,17-2H2] gibberellin A1 in vivo in dy rice mutant seedlings. Plant Cell Physiol. 2001, 42, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, H.A.S.; Gu, Q.; Wu, H.; Raza, W.; Hanif, A.; Wu, L.; Colman, M.V.; Gao, X. Plant growth promotion by volatile organic compounds produced by Bacillus subtilis SYST2. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnawal, D.; Bharti, N.; Pandey, S.S.; Pandey, A.; Chanotiya, C.S.; Kalra, A. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria enhance wheat salt and drought stress tolerance by altering endogenous phytohormone levels and TaCTR1/TaDREB2 expression. Physiol. Plant. 2017, 161, 502–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.H.; Woo, S.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Khaine, I.; Kwak, M.J.; Lee, H.K.; Lee, T.Y.; Lee, W.Y. Effects of increased soil fertility and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria inoculation on biomass yield, energy value, and physiological response of poplar in short-rotation coppices in a reclaimed tideland: A case study in the Saemangeum area of Korea. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 107, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Akanda, A.M.; Prova, A.; Islam, M.T.; Hossain, M.M. Isolation and identification of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria from cucumber rhizosphere and their effect on plant growth promotion and disease suppression. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Zahir, Z.A.; Asghar, H.N.; Asghar, M. Inducing salt tolerance in mung bean through coinoculation with rhizobia and plant-growth promoting rhizobacteria containing 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase. Can. J. Microbiol. 2011, 57, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Ghosh, P.K.; Ghosh, S.; De, T.K.; Maiti, T.K. Role of heavy metal resistant Ochrobactrum sp. and Bacillus spp. strains in bioremediation of a rice cultivar and their PGPR like activities. J. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Bano, A. Role of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and Ag-nano particle in the bioremediation of heavy metals and maize growth under municipal wastewater irrigation. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2016, 18, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.J.; Kumar, R. Bioremediation of petroleum contaminated soil to combat toxicity on Withania somnifera through seed priming with biosurfactant producing plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 174, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalam, S.; Basu, A.; Ankati, S. Plant root-associated biofilms in bioremediation. In Biofilms in Plant and Soil Health; Ahmad, I., Husain, F.M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2017; pp. 337–355. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, P.; Shaikh, S.; Sayyed, R. Dynamism of PGPR in bioremediation and plant growth promotion in heavy metal contaminated soil. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 54, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sayyed, R.Z.; Patel, P.R.; Shaikh, S.S. Plant growth promotion and root colonization by EPS producing Enterobacter sp. RZS5 under heavy metal contaminated soil. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 53, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Banchio, E.; Xie, X.; Zhang, H.; Paré, P.W. Soil bacteria elevate essential oil accumulation and emissions in sweet basil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordookhani, K.; Sharafzadeh, S.; Zare, M. Influence of PGPR on growth, essential oil and nutrients uptake of sweet basil. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2011, 5, 672–677. [Google Scholar]
- Etesami, H.; Maheshwari, D.K. Use of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPRs) with multiple plant growth promoting traits in stress agriculture: Action mechanisms and future prospects. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 156, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, I.; Fahsi, N.; Hafidi, M.; Allaoui, A.; Biskri, L. Plant growth enhancement using rhizospheric halotolerant phosphate solubilizing bacterium Bacillus licheniformis QA1 and Enterobacter asburiae QF11 isolated from Chenopodium quinoa willd. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etesami, H.; Alikhani, H.A.; Mirseyed Hosseini, H. Indole-3-acetic acid and 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase: Bacterial traits required in rhizosphere, rhizoplane and/or endophytic competence by beneficial bacteria. In Bacterial Metabolites in Sustainable Agroecosystem; Maheshwari, D.K., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 183–258. [Google Scholar]
- Umesha, S.; Singh, P.K.; Singh, R.P. Microbial biotechnology and sustainable agriculture. In Biotechnology for Sustainable Agriculture: Emerging Approaches and Strategies; Singh, R.L., Mondal, S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 185–205. [Google Scholar]
- Gouda, S.; Kerry, R.G.; Das, G.; Paramithiotis, S.; Shin, H.-S.; Patra, J.K. Revitalization of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for sustainable development in agriculture. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 206, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, Z.; Huang, S.; Rafique, M.; Fakhar, A.; Kamran, M.A.; Santoyo, G. Unlocking the potential of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on soil health and the sustainability of agricultural systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 273, 111118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleńska, E.; Małek, W.; Wójcik, M.; Swiecicka, I.; Thijs, S.; Vangronsveld, J. Beneficial features of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria for improving plant growth and health in challenging conditions: A methodical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beneduzi, A.; Ambrosini, A.; Passaglia, L.M.P. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): Their potential as antagonists and biocontrol agents. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2012, 35, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glick, B.R. Plant growth-promoting bacteria: Mechanisms and applications. Scientifica 2012, 2012, 963401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glick, B.R. Bacteria with ACC deaminase can promote plant growth and help to feed the world. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 169, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, I. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) and their various mechanisms for plant growth enhancement in stressful conditions: A review. Eur. J. Biol. Res. 2018, 8, 191–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Bahadur, I.; Maurya, B.R.; Raghuwanshi, R.; Meena, V.S.; Singh, D.K.; Dixit, J. Does a plant growth promoting rhizobacteria enhance agricultural sustainability? J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 9, 715–724. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, G.; Köberl, M.; Rybakova, D.; Müller, H.; Grosch, R.; Smalla, K. Plant microbial diversity is suggested as the key to future biocontrol and health trends. Fems Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyed, R.Z.; Seifi, S.; Patel, P.R.; Shaikh, S.S.; Jadhav, H.P.; El Enshasy, H. Siderophore production in groundnut rhizosphere isolate, Achromobacter sp. RZS2 influenced by physicochemical factors and metal ions. Environ. Sustain. 2019, 2, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fraile, P.; Menéndez, E.; Rivas, R. Role of bacterial biofertilizers in agriculture and forestry. Aims Bioeng. 2015, 2, 183–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacheron, J.; Desbrosses, G.; Bouffaud, M.L.; Touraine, B.; Moënne-Loccoz, Y.; Muller, D.; Legendre, L.; Wisniewski-Dyé, F.; Prigent-Combaret, C. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and root system functioning. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmusk, S.; Behers, L.; Muthoni, J.; Muraya, A.; Aronsson, A.C. Perspectives and challenges of microbial application for crop improvement. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soumare, A.; Diedhiou, A.G.; Thuita, M.; Hafidi, M.; Ouhdouch, Y.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Kouisni, L. Exploiting biological nitrogen fixation: A route towards a sustainable agriculture. Plants 2020, 9, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, B.J.; Mens, C.; Hastwell, A.H.; Zhang, M.; Su, H.; Jones, C.H.; Chu, X.; Gresshoff, P.M. Legume nodulation: The host controls the party. Plant. Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Fraile, P.; Menéndez, E.; Celador-Lera, L.; Díez-Méndez, A.; Jiménez-Gómez, A.; Marcos-García, M.; Cruz-González, X.A.; Martínez-Hidalgo, P.; Mateos, P.F.; Rivas, R. Bacterial probiotics: A truly green revolution. In Probiotics and Plant Health; Kumar, V., Kumar, M., Sharma, S., Prasad, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 131–162. [Google Scholar]
- Dal Cortivo, C.; Ferrari, M.; Visioli, G.; Lauro, M.; Fornasier, F.; Barion, G.; Panozzo, A.; Vamerali, T. Effects of seed-applied biofertilizers on rhizosphere biodiversity and growth of common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in the field. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aloo, B.N.; Makumba, B.A.; Mbega, E.R. Plant growth promoting rhizobacterial biofertilizers for sustainable crop production: The past, present, and future. Preprints 2020, 2020090650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleke, R.A.; Raimi, A.R.; Roopnarain, A.; Mokubedi, S.M. Status and prospects of bacterial inoculants for sustainable management of agroecosystems. In Biofertilizers for Sustainable Agriculture and Environment; Giri, B., Prasad, R., Wu, Q.-S., Varma, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 137–172. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, S.; Kabir, S.; Shabbir, U.; Batool, R. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in sustainable agriculture: From theoretical to pragmatic approach. Symbiosis 2019, 78, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mącik, M.; Gryta, A.; Frąc, M. Biofertilizers in agriculture: An overview on concepts, strategies and effects on soil microorganisms. In Advances in Agronomy; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; Volume 162, pp. 31–87. [Google Scholar]
- Artyszak, A.; Gozdowski, D. The effect of growth activators and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on the soil properties, root yield, and technological quality of sugar beet. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, D.; Sánchez-Nieves, J.; Vanegas, J. Role of microbial biofertilizers in the development of a sustainable agriculture in the Tropics. In Soil Biology and Agriculture in the Tropics; Dion, P., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 235–250. [Google Scholar]
- Mehnaz, S. An overview of globally available bioformulations. In Bioformulations: For Sustainable Agriculture; Arora, N., Mehnaz, S., Balestrini, R., Eds.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2016; pp. 268–281. [Google Scholar]
- Sessitsch, A.; Mitter, B. 21st century agriculture: Integration of plant microbiomes for improved crop production and food security. Microb. Biotechnol. 2015, 8, 32–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, M.; Ratering, S.; Suarez, C.; Zapata Montoya, A.M.; Geissler-Plaum, R.; Schnell, S. Paradox of plant growth promotion potential of rhizobacteria and their actual promotion effect on growth of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) under salt stress. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 181, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, U.; Khalid, R.; Hayat, R. Soil bacteria and phytohormones for sustainable crop production. In Bacterial Metabolites in Sustainable Agroecosystem; Maheshwari, D.K., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamilova, F.; Okon, Y.; Deweert, S.; Horal, K. Commercialization of microbes: Manufacturing, inoculation, best practice for objective field testing, and registration. In Principles of Plant-Microbe Interactions: Microbes for Sustainable Agriculture; Lugtenberg, B., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.; Singh, I. Microbial biofertilizers: Types and applications. In Biofertilizers for Sustainable Agriculture and Environment; Giri, B., Prasad, R., Wu, Q.S., Varma, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, N.K.; Khare, E.; Maheshwari, D.K. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: Constraints in bioformulation, commercialization, and future strategies. In Plant Growth and Health Promoting Bacteria; Maheshwari, D., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 97–116. [Google Scholar]
- Du Jardin, P. Plant biostimulants: Definition, concept, main categories and regulation. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barea, J.M. Future challenges and perspectives for applying microbial biotechnology in sustainable agriculture based on a better understanding of plant-microbiome interactions. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2015, 15, 261–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnell, J.J.; Berka, R.; Young, H.A.; Sturino, J.M.; Kang, Y.; Barnhart, D.M.; Dileo, M.V. From the lab to the farm: An industrial perspective of plant beneficial microorganisms. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndeddy Aka, R.J.; Babalola, O.O. Effect of bacterial inoculation of strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Alcaligenes feacalis and Bacillus subtilis on germination, growth and heavy metal (Cd, Cr, and Ni) uptake of Brassica juncea. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2016, 18, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Verma, H.; Singh, V.K.; Singh, P.P.; Singh, S.K.; Ansari, W.A.; Yadav, A.; Singh, P.K.; Pandey, K.D. Role of Pseudomonas sp. in sustainable agriculture and disease management. In Agriculturally Important Microbes for Sustainable Agriculture; Meena, V.S., Mishra, P.K., Bisht, J.K., Pattanayak, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; Volume 2, pp. 195–215. [Google Scholar]
- Malusà, E.; Pinzari, F.; Canfora, L. Efficacy of biofertilizers: Challenges to improve crop production. In Microbial Inoculants in Sustainable Agricultural Productivity; Singh, D.P., Singh, H.B., Prabha, R., Eds.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2016; pp. 17–40. [Google Scholar]
- Dangi, S.R.; Tirado-Corbalá, R.; Gerik, J.; Hanson, B.D. Effect of long-term continuous fumigation on soil microbial communities. Agronomy 2017, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashan, Y.; de-Bashan, L.E.; Prabhu, S.R.; Hernandez, J.P. Advances in plant growth-promoting bacterial inoculant technology: Formulations and practical perspectives (1998–2013). Plant Soil 2014, 378, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Benefits of PGPR Inoculation to Plants | PGPR Strain(s) | Tested Plant(s) | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tolerance to drought stress | Pseudomonas fluorescens DR11, Enterobacter hormaechei DR16, Pseudomonas migulae DR35, Bacillus subtilis, Achromobacter piechaudii ARV8, Phyllobacterium brassicacearum, Paenibacillus polymyxa, Rhizobium tropici, Azospirillum brasilense | Foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.), Maize (Zea mays L.), Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.), Arabidopsis thaliana, Tomato (Lycopersicum esculentum Mill cv. F144), Pepper (Capsicum annuum L. cv. Maor), Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) | [36,54,55,56,57,58,59] |
| Tolerance to salinity stress | Bacillus pumilus, Exiguobacterium oxidotolerans, Bacillus megaterium, Azospirillum sp., Achromobacter piechaudii, Eneterobacter sp. PR14 | Brahmi (Bacopa monnieri L.), Maize (Zea mays L.), Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.), Tomato (Lycopersicum esculentum Mill.), Rice (Oryza sativa cv. Sahbhagi), Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor), Finger Millets (Eleusine coracana) | [60,61,62,63,64] |
| Tolerance to biotic stress (biocontrol) | Paenibacillus xylanexedens, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, Streptomyces sp., Ochrobacttrum intermedium, Paenibacillus lentimorbus, Pseudomonas spp. | Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), Rice (Oryza sativa), Pine (Pinus taeda L.), Tomato (Lycopersicum esculentum Mill.) | [65,66,67,68,69,70] |
| Increased nutrient absorption | Pantoea sp. S32, Paenibacillus polymyxa | Rice (Oryza sativa L.), Habanero pepper (Capsicum chinense) | [71,72,73] |
| Seed germination enhancement | Serratia marcences, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Azospirillum lipoferum, Pseudomonas putida, Bacillus subtilis, Providencia sp., Brevundimonas diminuta | Maize (Zea mays L.), Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) | [74,75,76] |
| Biostimulation by phytohormone(s) production | Azospirillum lipoferum, Bacillus subtilis, Arthrobacter protophormiae, Dietzia natronolimnaea, Bacillus sp. | Rice (Oryza sativa L.), Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.), Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) | [46,77,78,79] |
| Soil fertility enhancement | Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus cereus, Rhizobium spp. | Poplar (Populus sp.), Mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) | [80,81,82] |
| Bioremediation of heavy metals and pollutants | Ochrobactrum sp., Bacillus spp., Pseudomonas spp., Pseudomonas fluorescens, Bacillus cereus, Alcaligenes feacalis RZS2, Pseudomonas aeruginosa RZS3, Enterobacter sp. RZS5 | Rice (Oryza sativa L.), Groundnut (Arachis hypogaea), Maize (Zea mays L.), Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) | [83,84,85,86,87,88] |
| Modulation of plant secondary metabolites | Bacillus subtilis, Azotobacter chroococcum, Pseudomonas putida, Bacillus pumilus, Exiguobacterium oxidotolerans | Basil (Ocimum basilicum), Brahmi (Bacopa monnieri L.) | [89,90] |
| Type of Biofertilizer | Name of Biofertilizer | PGPR Strain(s) | Manufacturer’s Country | Market Region | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen fixer | Nitragin Gold® | Rhizobia | USA | North America | [110] |
| Cell-Tech® | Rhizobia | USA | North America | [110] | |
| TagTeam® | Rhizobia, Penicillium bilaii | USA | North America | [110] | |
| Custom N2 | Paenibacillus polymyxa | USA | North America | [110] | |
| Nodulator® | Bradyrhizobium japonicum | Canada | North America | [110] | |
| Nodulator® PRO | Bacillus subtilis, Bradyrhizobium japonicum | Canada | North America | [110] | |
| Bioboots® | Delftia acidovorans, Bradyrhizobium sp. | Canada | North America | [105,110] | |
| Azofer® | Azospirillum brasilense | Mexico | North America | [110] | |
| Rhizofer® | Rhizobium etli | Mexico | North America | [110] | |
| Nitrofix® | Azospirillum sp. | Cuba | North America | [105,110] | |
| Rhizosum N® | Azotobacter vinelandii, Rhizophagus irregularis | Spain | Europe | [110,111] | |
| Rhizosum Aqua | Azospirillum sp. | Spain | Europe | [105,110] | |
| Legume Fix | Rhizobium sp., Bradyrhizobium japonicum | UK | Europe | [112,113] | |
| BactoFil® A10 | Azospirillum brasilense, Azotobacter vinelandii, Bacllius megaterium | Hungary | Europe | [112] | |
| BactoFil® Soya | Bradyrhizobium japonicum | Hungary | Europe | [114] | |
| Phylazonit M | Azotobacter chroococcum, Bacillus megaterium | Hungary | Europe | [115] | |
| Azotobacterin® | Azospirillum brasilense B-4485 | Russia | Europe | [105,110] | |
| Azoter | Azotobacter chroococcum, Azospirillum brasilense, Bacillus megaterium | Slovakia | Europe | [116] | |
| TwinN® | Azorhizobium sp., Azoarcus sp., Azospirillum sp. | Australia | Asia-Pacific | [113] | |
| TripleN® | Azorhizobium spp., Azoarcus spp., Azospirillum spp. | Australia | Asia-Pacific | [111] | |
| Bio-N | Azospirillum spp. | Philippines, Australia | Asia-Pacific | [112,117] | |
| BioGro® | Pseudomonas fluorescens / putida, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Citrobacter freundii | Vietnam | Asia-Pacific | [117] | |
| Mamezo® | Rhizobia | Japan | Asia-Pacific | [105,110] | |
| Agrilife Nitrofix | Azotobacter chroococcum, A. vinelandii, Acetobacter diazotrophicus, Azospirillum lipoferum, Rhizobium japonicum | India | Asia-Pacific | [118] | |
| Ajay Azospirillum | Azospirillum sp. | India | Asia-Pacific | [112] | |
| Symbion N | Azospirillum sp., Rhizobium sp., Acetobacter sp., Azotobacter sp. | India | Asia-Pacific | [115] | |
| Zadspirillum | Azospirillum brasilense | Argentina | South America | [112] | |
| Rizo-Liq | Bradyrhizobium sp., Mesorhizobium ciceri, Rhizobium spp. | Argentina | South America | [112,113] | |
| Nodulest 10 | Bradyrhizobium japonicum | Argentina | South America | [118] | |
| Rizo-Liq Top | Bradyrhizobium japonicum | Argentina | South America | [113] | |
| BiAgro 10® | Bradyrhizobium japonicum | Argentina, Brazil, Bolivia | South America | [117] | |
| Dimargon® | Azotobacter chroococcum | Colombia | South America | [117] | |
| Nitrasec | Rhizobium sp. | Uruguay | South America | [112] | |
| Biofix | Rhizobia | Kenya | Africa | [112,113] | |
| Nodumax | Bradyrhizobium spp. | Nigeria | Africa | [112,113] | |
| Azo-N | Azospirillum brasilense, A. lipoferum | South Africa | Africa | [113] | |
| Azo-N Plus | Azospirillum brasilense, A. lipoferum, Azotobacter chroococcum | South Africa | Africa | [113] | |
| Phosphate solubilizer | Fosforina® | Pseudomonas fluorescens | Cuba | North America | [117] |
| Rhizosum PK® | Bacillus megaterium, Frateuria aurantia, Rhizophagus irregularis | Spain | Europe | [110,111] | |
| Phosphobacterin | Bacillus megaterium var. phosphaticum | Russia | Europe | [31] | |
| CataPult | Bacillus spp., Glomus intraradices | Australia | Asia-Pacific | [118] | |
| Symbion van Plus | Bacillus megaterium | India | Asia-Pacific | [112] | |
| P Sol B | Pseudomonas striata, Bacillus polymyxa, B. megaterium | India | Asia-Pacific | [115,118] | |
| CBF | Bacillus mucilaginosus, B. subtilis | China | Asia-Pacific | [117] | |
| Bio Phos® | Bacillus megaterium | Sri Lanka | Asia-Pacific | [115,118] | |
| Potassium solubilizer | Rhizosum K | Frateuria aurantia | Spain | Europe | [105,110] |
| K Sol B | Frateuria aurantia | India | Asia-Pacific | [118] | |
| Zinc solubilizer | Biozink® | PGPR consortia | India | Asia-Pacific | [110] |
| Zn Sol B | Thiobacillus thiooxidans | India | Asia-Pacific | [118] | |
| Phytostimulator | EVL Coating® | PGPR consortia | Canada | North America | [105] |
| Amase® | Pseudomonas azotoformans | Sweden | Europe | [114,118] | |
| Bio Gold | Azotobacter chroococcum, Pseudomonas fluorescens | Sri Lanka | Asia-Pacific | [115,118] | |
| Bioativo | PGPR consortia | Brazil | South America | [112] | |
| Biocontrol | Cedomon® | Pseudomonas chlororaphis | Sweden | Europe | [114] |
| Cedress® | Pseudomonas chlororaphis | Sweden | Europe | [114] | |
| Cerall® | Pseudomonas chlororaphis | Sweden | Europe | [114] | |
| Biotilis | Bacillus subtilis | India | Asia-Pacific | [118] | |
| Soilfix | Brevibacillus laterosporus, Paenibacillus chitinolyticus | South Africa | Africa | [112] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basu, A.; Prasad, P.; Das, S.N.; Kalam, S.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Reddy, M.S.; El Enshasy, H. Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) as Green Bioinoculants: Recent Developments, Constraints, and Prospects. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031140
Basu A, Prasad P, Das SN, Kalam S, Sayyed RZ, Reddy MS, El Enshasy H. Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) as Green Bioinoculants: Recent Developments, Constraints, and Prospects. Sustainability. 2021; 13(3):1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031140
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasu, Anirban, Priyanka Prasad, Subha Narayan Das, Sadaf Kalam, R. Z. Sayyed, M. S. Reddy, and Hesham El Enshasy. 2021. "Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) as Green Bioinoculants: Recent Developments, Constraints, and Prospects" Sustainability 13, no. 3: 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031140
APA StyleBasu, A., Prasad, P., Das, S. N., Kalam, S., Sayyed, R. Z., Reddy, M. S., & El Enshasy, H. (2021). Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) as Green Bioinoculants: Recent Developments, Constraints, and Prospects. Sustainability, 13(3), 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031140







