Abstract
The increasing number of cyber-attacks has become a serious threat to organizations, organizations that are not prepared to face cyber-attacks on their organizational resources will experience huge losses and reduce organizational performance. It is a big challenge for organizations to combat cyber-attacks by improving cyber security, but there is still little research examining the factors that affect an organization’s cyber security readiness from a holistic point of view. This study integrates a framework based on technology, organization, environment, and technology readiness to examine various factors that affect cyber security readiness in organizations, as well as their impact on organizational performance, where the impact is in the form of tangible and intangible benefits. This study proposes 4 hypotheses to test the framework that has been built. A total of 260 data have been validated from an online questionnaire survey given to organizations and companies. This study applied quantitative approach, while the main method used was SEM-PLS and the software involved was SmartPLS V2. The results of the study indicate that the overall hypotheses proposed have a significant impact, cyber security readiness and technology have a positive impact on organizational security performance, which in turn has an impact on the intangible benefits and tangible benefits. The results of this study can be used by organizations as a guide in improving cyber security to achieve superior performance in organizations and improve understanding of references related to cyber security in organizations. Meanwhile, this research has impact to the society because the good cooperation and good organization will be achieved. it also increases the social cooperation responsibility.
1. Introduction
Over time, the development of information technology continues to progress, this changes the paradigm of conventional activities into digital activities. Digital transformation provides benefits for organizations or companies and even governments such as increasing the speed and accessibility of communication, performance effectiveness, and operational cost efficiency [1]. Of course, this is a new opportunity for organizations or companies to be able to improve product quality by utilizing digital technology. However, in addition to providing benefits, digital transformation in business processes also opens up opportunities for information technology security threats such as cyber-attacks on their assets [2]. Cyber-attacks can range from individual attacks to attacks on confidential company data that can cripple the business processes of an organization or company. To perform unauthorized intrusion into the organization’s existing information technology (IT) or information systems (IS) infrastructure, this can be done through the spread of malware, viruses, ransom ware, and spam on users’ emails, resulting in attempted theft of sensitive data. Data or attacks that are easier to carry out.
The National Cyber Security Operations Center in Indonesia noted that there were millions of cases of cyber-attacks in less than 1 year. Based on these figures, shows the high number of cyber-attacks, and the number of these attacks may continue to increase in the future. The complexity of cyber-attacks continues to grow over time [3], and the results of a survey conducted on several previous studies show that more than 90% of the security administration staff of organizations have not been able to deal with and make good efforts in dealing with cyber-attacks despite warnings [4].
The impact and losses caused by cyber-attacks on organizations or companies are very large [5]. The loss of sensitive data for companies [6], resulting in a decline in organizational reputation [7], these are some of the impacts of cyber-attacks that cause economic losses for organizations, both in terms of very high costs and revenues [8], even greater the impact of losses incurred. It is felt and based on available data, many organizations do not report incidents of cyber-attacks, and this is done to protect the good name of the organization or company [9].
The high frequency of cyber-attacks and the magnitude of the losses and impacts that must be borne by the organization or company shows how important it is for the organization or company to have good and appropriate cyber security to protect organizational resources. Organizations or companies that have good and appropriate cyber security can improve their reputation [10] and facilitate the achievement of competitive advantage and organizational performance [11]. Cyber security is an effort to protect IT and IS assets from illegal access that can damage or alter confidential data and also paralyze business processes [12]. Cyber security also requires the participation of people, processes, and technology within the organization to protect the organization, people, and IT infrastructure collectively from cyber-attacks [13]. However, described by Smith et al. [10] that it takes awareness and shared commitment within organizations to prevent, detect, and counter cyber-attacks before organizations can have cyber security [13]. This study describes cyber security readiness as the level of cognition, readiness, and organizational support to prevent and fight cyber-attacks [14]. Organizations that have high IT security readiness, can be sure to have a high level of organizational security to protect their resources. And conversely, the indifference of the organization to cyber security readiness, the more vulnerable and the higher the risk of the threat of cyber-attacks on organizational assets. The reluctance of organizations to adopt cyber security will be a big challenge for organizations to meet the resource requirements to create a level of cyber security to protect company assets [5]. This situation can harm organizational performance towards organizational profits [2,15].
Literature studies show that there are not many previous studies that discuss the effect of cyber security readiness and technology on organizational performance, previous studies tend to examine the role of cyber security in reducing threats and attacks and examine the role of information security management in investment decision making [16] and updating system security administrative information [17]. Organizational compliance with cyber security regulations and standards can empower organizations to perform security checks, system checks, backup recovery, and contingency planning [18,19,20,21]. In previous studies, it was stated that organizations can gain profits and a better reputation if organizations can ensure cyber security within their organizations [10,22]. And despite the importance of cyber security readiness and technology readiness in improving organizational performance, there has been no empirical research to determine the impact of cyber security and technology readiness on organizational performance.
Based on previous research focusing on factors that enhance cyber security, several general factors affect cyber security readiness, such as adequate IT infrastructure [21], executive management commitment [17], business capabilities [22], traditions within the organization [23], collaborating with competitors [24], establishing relationships with partners [25], government policies [26], government support [27], and industry benchmarks [28]. The use of the above factors is also based on several theories including institutional theory and macro ergonomics theory, which includes internal organizational factors and ignores the external environment [17,21,27] and prevention theory [29]. In his research, Quinnley et al. [30], mentions that the internal and external environmental factors of the organization need to be included in cyber security research. Wang et al. [31] argued that high-tech people are comfortable with innovative technology, while low-tech people tend to avoid new technology. There are limitations to the research carried out which is the gap between this research and previous research that has not fully understood the broad set of factors to determine its impact on cyber security readiness. This is realized well because of the limitations of the researcher’s perspective which is only based on individual theories from previous research.
Therefore, to solve the problems and limitations presented in this study, a conceptual model was developed to examine all the common factors that affect an organization’s cyber security readiness and their impact on performance at the same time. Thus, this study examines more deeply two perspectives, the first is how an organization’s cyber security readiness affects organizational performance from a security perspective, tangible benefits, and intangible benefits. Then secondly we examine how technology readiness affects organizational performance from the perspective of security, tangible benefits, and intangible benefits.
To find out the main factors that have an impact on the cyber security readiness of an organization, this study uses three variables, namely technology, organization, and environment [32,33,34,35,36], while from the aspect of technology readiness it uses four variables, namely optimism, innovation, discomfort, and insecurity. These variables are then integrated into a holistic, robust, and flexible framework that is used at the organizational level [33] which covers all perspectives of the organization both internal and external. Furthermore, the use and technology aspects of this framework are supported by strong empirical methods in previous studies of corporate information systems [17,37,38,39,40,41]. Furthermore, the flexible nature of this framework allows for the addition of new variables and theories within a single study.
To answer whether organizational cyber security readiness and technology readiness affect organizational performance from a security perspective [42,43], tangible and intangible benefits, it is necessary to examine the impact of organizational cyber security readiness and technology readiness on the performance of tangible and intangible benefits [44], mediated by cyber security performance.
Therefore, this research is expected to be able to examine in depth the key factors that affect an organization’s cyber security readiness, so that it can contribute and provide recommendations to organizations that use cyber security to protect assets and improve company performance.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Concept and Introduction to Organizational Security Adoption
The institutional theory developed by DiMaggio and Powell [45] explains that within each institution they have structures, cultures, and actions that can influence technology initiatives [46]. DiMaggio and Powell [45] also explain that there are three isomorphic mechanisms, namely mimetic, coercive, and normative pressures, these three mechanisms are believed to be able to encourage internal changes in an institution. In line with Hasan et al. [5] statement that the three mechanisms of institutional theory affect the internal environment. In previous research related to information security, researchers used the institutional theory as a theoretical lens to explore the impact of internal institutional factors on technology initiatives [17,18,21,47]. Likewise, Hsu et al. [17] used organizational culture factors and top management support in institutional theory to determine the impact of the internal environment on information security.
In an organization, interaction with other parties is needed to carry out the organization’s business processes. Such other parties may include competitors, suppliers, and business partners. Neumann and Morgenstern [48] developed a game theory to understand the relationship between organizations and competitors, suppliers, and business partners, they mention competitors, suppliers, and business partners as a single player who must follow a set of rules to manage cooperation within the organization. [49]. Mohebbi and Li [50] explain that organizational collaboration with game players can be done in the form of exchanging knowledge, assets, and needs to optimize profits and minimize uncertainty. Previous studies have used game theory to examine the relationship between collaboration with competitors and cyber security investments [24,51].
Furthermore, prevention theory was proposed by criminologist researchers which were later adopted by information systems researchers to test compliance with information security policies [29]. In his research, Wall et al. [34] examined the enforcement of rules and sanctions by organizations using deterrence theory. In his proposal, Gibbs [52] explains that the theory of prevention can be used to understand the laws and benchmarks of organizational practice that have been set by governments and international organizations [43]. Meanwhile, Hasan et al. [5] states that prevention theory can be used to determine the influence of external forces such as government regulations and industry standards on organizational cyber security.
2.2. Theory of Cyber Security Readiness
The availability and utilization of IT infrastructure are important to support business processes in an organization. IT infrastructure, capability, and investment are important technical factors that need to be considered by organizations both in terms of availability and utilization [5]. Tornatzky et al. [38] also describe the technology context including the characteristics of technology and information systems that can influence organizations in adopting digital innovations. Kong et al. [16] and Angst et al. [23] in their research discussing the impact of IT infrastructure on information security stated that if an organization has good IT resources, it will improve information system security and reduce the number of security breaches and incidents. Hsu et al. [17] and Kong et al. [16] also conveyed the same thing that organizations that have good IT skills have good information security management.
Organizational decision-making in adopting digital innovation is not only influenced by technological factors but also influenced by organizational factors which refer to organizational features and organizational characteristics [32]. Hsu et al. [17] and Kraemer et al. [25] mention in their research that management support, skills, and organizational culture are organizational factors that influence organizations in adopting digital innovations or new technologies. As shown by previous studies [17,18,23,53] proved that executive management support can affect information security such as reducing cyber-attacks. Daud, et al. [20] and Kraemer [23] also emphasized that organizational information security can be improved if there is support from top management to comply with information security policies. Top management support in information security management can be demonstrated by identifying information security management best practices and leading to the appropriate information security implementation for the organization [17].
In several previous studies, it is known that another theory used is cyber security theory to determine the effect of cyber security skills on organizational cyber security [22,52,53]. In another study, researchers said that upgrading employees’ skills in cyber security training courses strengthen organizations’ defenses to protect company assets and information, increases employee discipline to comply with security regulations, and reduces the risk of cyber-attacks. And the last factor in the organizational context is organizational culture, based on previous research.
Next is the organizational culture factor in influencing the organization’s information security. Previous research investigating the influence of culture on organizational cyber security management has been conducted by [17,23,54,55,56], they agree that organizational culture support can affect information system security which includes security governance, control, and coordination as well as reduce the threat of cyber-attack for organizational assets.
Tornatzky et al. [38] explains the environmental context in terms of external factors that can influence organizational decision-making when introducing an innovation. There have been many studies that examine the importance of cooperation with external parties to maintain information security, cooperation can be done by sharing information and cooperation in information security investment [24,57]. In line with that stated by Smith et al. [29] that organizations can improve information security by exchanging knowledge and cooperating with suppliers and business partners. In another study, several researchers tried to examine the impact of government policies on organizational cyber security risks [58,59]. Previous studies have been conducted to determine the effect of government support in improving information system security [30,37]. The next external factor studied in previous research related to its effect on information system security is the role of cyber security industry standards. Another study was also conducted to examine the role of cyber security industry standards in improving organizational cyber security using deterrence theory and neutralization theory to examine each influencing factor [32,34].
Although there have been many studies examining the key factors that have a significant impact on organizational cyber security, there are still few studies that integrate various factors that affect organizational cyber security [60]. Hasan et al. [5] also stated that to fully study the impact of all the main factors affecting cyber security and the importance of each factor, a comprehensive framework that combines these factors is needed. It is also confirmed in different studies that to understand the various factors that can improve organizational information security from various perspectives [61,62], it is not enough to consider only one aspect, but a more comprehensive model is needed that combines all the main factors that can affect the organization’s information security organizational cyber security [63].
2.3. Theory of Technology Readiness
Parasuraman [64] defines technology readiness as a personality trait that can increase the acceptance of new technology, which is not only to achieve personal goals but also work-related. Meanwhile [65,66] describe technology readiness as a multi-asset construction that can be divided into 2 driving components and 2 inhibiting components in technology adaptation. Chang and Chen [67] explained that technology readiness can be used as a parameter of individual readiness to use new technology. The dimensions of optimism, innovation, discomfort, and insecurity are the four sub-dimensions of technology readiness. Optimism and innovation are components that support technology readiness, while discomfort and insecurity are components that hinder technology readiness. Parasuraman and Colby [68] and Parasuraman [64] have shown that together these four dimensions are strong predictors of technology-related behavior.
Therefore, this study will build a conceptual model to examine all the comprehensive factors that affect an organization’s cyber security readiness and technology readiness and their impact on performance simultaneously [69]. Eilts [70] explains that no previous research has examined cyber security readiness in small businesses, and investigated the impact of cyber security readiness and organizational technology readiness on organizational performance. This study focuses on cyber security readiness and technology readiness of organizations, assessing the impact of cyber security readiness and technology readiness on security performance, tangible and intangible benefits.
3. Research Model and Hypothesis Development
3.1. Cyber Security Readiness
Eilts [70] explained that the cyber security Framework can be used to measure cyber security readiness and also improve cyber security [71]. The framework consists of five functions, namely identification, protection, detection, response, and recovery. Identification is an organizational activity to understand cyber security risks [56], by conducting vulnerability assessments and controlling computer ports for the identification of cyber-attacks [72].
Protect is the protection of cyber infrastructure and services [72], encrypting data and installing anti-virus software, and using strong passwords to protect IT infrastructure from cyber-attacks [73]. Detection is defined as the process of identifying the occurrence of a cyber-attack [74]. The process of identifying cyber-attacks can be carried out by organizations by conducting an operational and strategic analysis of incidents and monitoring security alerts regularly [75]. The response is the reaction caused by the detection of a cyber-attack [75]. Organizations need to have a failover monitoring system in place to respond to failures [76] and a recovery plan for cyber-attacks that occur [77].
Recover is the activity of recovering failures and damages caused by cyber-attacks [78]. To respond to cyber-attacks, organizations need to have clear recovery plan procedures [60] and backup databases [79]. This study examines the organization’s readiness to detect, take preventive action, catch, respond and make improvements from cyber-attacks under the framework that we have built. Assessing the impact of factors on cyber security readiness as a guide for organizations to improve the security of IT infrastructure and cyber services by increasing the factors that have the most significant effect on cyber security readiness. We thus propose the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis (H1).
The better the organization’s readiness to combat cyber-attacks, the better the organization’s security performance.
3.2. Technology Readiness Aspect
Represents the supporting components of technology readiness, optimism, and innovation that represent a positive response to new technologies that can provide users flexibility, increased control, and efficiency to become early adopters and thought leaders of new technologies. On the other hand, representing the inhibiting components of technology readiness, discomfort and insecurity indicate a sense of anticipation and overwhelm over the lack of mastery of new technologies, resulting in distrust of new technologies and doubts about their skills in getting the job done properly [50,54,61,62,79]. Wang, et al [31] claim that people with high technology readiness scores will feel comfortable with innovative technology while individuals with low technology readiness will try to resist new technology. This is in line with what was conveyed by Parasuraman [64] which states that a high value of optimism and innovation can increase overall technology readiness, but on the contrary, if the value of discomfort and insecurity is high it can cause a decrease in it. So this research will investigate the impact of technology readiness for organizations to improve the security of IT infrastructure and cyber services.
The decrease in the number of violations over time can be used as a benchmark for organizations to have cyber security readiness and performance achieved in protecting organizational assets [21,80]. Organizations need to measure the performance of the organization’s internal processes because this is an important part of organizational performance. Therefore, internal process safety should be measured in this study [63]. Tsuu and Hsu [22] added an item in measuring organizational performance, namely a good reputation so that in this study security reputation becomes an item that needs to be measured. While Bharadwaj [79] explains that the most important items in measuring organizational performance are systems and databases, therefore this research will add system capabilities and database availability to measure security performance. Based on the description previously described, both an organization’s cyber security readiness and technology readiness can significantly reduce cyber-attacks and affect an organization’s security performance. Therefore, in this study the following hypothesis is proposed:
Hypothesis (H2).
The higher the technological readiness of an organization to adopt new technology, the higher the security performance of the organization.
3.3. Tangible and Intangible Benefits Post-Adoption of Organization Security
Several studies that have been conducted consistently state that there are two types of company resources, namely tangible and intangible [81]. In previous studies, it is generally explained that tangible resources are divided into 2 types, namely financial and physical [82,83], while intangible resources such as knowledge [84], ability to innovate, trademarks, marketing capabilities [70], and intellectual capital of employees skilled [85]. Therefore, the performance of tangible and intangible earnings can also be interpreted as financial and non-financial performance [86]. Tsou and Hsu [20] explain that real profit performance can be measured by increasing product sales, profits received, and expanding market share. Bharadwaj [79] found that the effect of IT on the company’s real profit performance increases the company’s profit. While the measurement of the performance of intangible profits can be measured by the competitive advantage achieved, the good name of the organization, customer loyalty, and new customers who come [20,71]. Eccles et al. [87] explained that financial and non-financial performance can be achieved well for a long period if the organization has good system security. Thus et al. [88] share the same opinion that an organization can achieve high financial performance and reputation if it has a secure block chain within its organization. Based on the description above, it is suspected that there is an effect of high-security performance on the performance of tangible and intangible benefits [89,90]. Therefore, we propose the third and fourth hypotheses as follows.
Hypothesis (H3).
Good security performance of an organization results in high tangible benefits for the organization.
Hypothesis (H4).
Good security performance of an organization results in high intangible benefits for the organization.
Furthermore, the overall research framework and hypotheses in this study are shown in Figure 1, while Table 1 is a summary of the operating definitions for the constructs used in this study and Table 2 of the construct measurement items used.
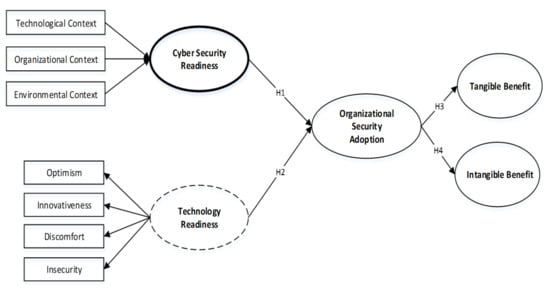
Figure 1.
Research model.

Table 1.
Operation definition.

Table 2.
Measurement items of constructs.
4. Research Method
This research was conducted to examine the readiness of cyber security and organizational technology at the organizational level. To determine the impact of organizational readiness in dealing with cyber-attacks and the relationship between model construction, a quantitative approach, and empirical model hypothesis testing were used. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct a survey, survey questionnaires distributed online to collect samples. The measurement elements used in this study were formulated based on construct items in the previous research literature. The measurement items for all constructs used in this study are as shown in Table 2. Each construct item will be measured with a 7-scale Likert scale, the measurement starts from a scale of 1 which means strongly disagree to a scale of 7 which means strongly agree. As for the questionnaire survey period from January–August 2021, the survey was given to IT professionals who were randomly selected from various organizations in Indonesia. The determination of respondents is based on the respondent’s level of knowledge about cyber security within the organization, this aims to ensure that the data collected is valid and accurate because not all organizations have cyber security experts. There were 289 responses received from the distributed questionnaire survey and 260 data were declared valid and represent acceptable sample size. As stated by Gefen et al. [91], for modeling structural equations in management information systems research the appropriate minimum sample size is 200 participants. Of the 260 respondents, 235 were male and 25 were female, and respondents came from various age groups, education levels, positions, and work experience. In addition, respondents are also grouped based on the organization where the respondent works. Overall, the demographics of the respondents, both the respondent’s profile and the organizational profile are presented in Table 3; Table 4.

Table 3.
Demographics sample.

Table 4.
Organizational profile.
5. Data Analysis
This study has a high complexity in the model we built, which consists of five construct variables, namely the second-order formative construct (CSR) and the second-order reflexive construct (TR), where the least-squares partial data analysis method (PLS) is used to overcome the complexity this. Data analysis using SmartPLS software version 2.0.1, this method is very suitable in overcoming problems related to data obtained from abnormal distributions, besides that PLS can analyze both second-order formative models as well as second-order reflective models simultaneously, then PLS not only can analyze large data but can also analyze relatively small data with high accuracy [92]. In this study, the analytical step used consisted of 2 stages, namely testing the measurement model and the structural model [93].
5.1. Measurement Model Evaluation
The first step in this phase is to measure each item variable and construct in the model, this is used as a reference to ensure that both are under the criteria of convergent and discriminant validity. But the main thing must be ensured that the variable or construct must be declared reliable first. For this reason, the indicators used to show that the variables or constructs built are reliable, then the composite reliability value must be greater than 0.7 [94,95]. Next, we analyzed the items for each loading factor and Average Variance Extracted (AVE) to measure the level of convergent validity. In this study, it was found that the value of each loading factor was greater than 0.7, while the value we obtained from the AVE was greater than 0.5, so we conclude that this value meets the standards and criteria to be declared as convergent validity for evaluation measurement models [96,97]. The results of the analysis of the reliability test and the convergent validity test are described in Table 5.

Table 5.
Results of the measurement model.
To measure the degree of discriminant validity, in this study using a correlation matrix, where if the square root of the AVE is greater than the correlation coefficient, it is concluded that it has met the discriminant validity standard, in Table 6 it can be seen that this study has met and can be declared discriminant validity. The two test steps that we have done above, shows that the measurement items have been declared valid and reliable so that at the next stage an assessment of the existing hypothesis can be made.

Table 6.
Number of correlations matrix.
5.2. Structural Models
In this study, we use three indicators in assessing the structural model that has been made, namely by using the value of variance (R2), then assessing the path coefficient and the results of the t-statistic assessment [96,97]. The standard used to measure the hypothesis is to use a bootstrap procedure of 5000 samples used to produce a value that is relatively valid against the t-statistic. From the results of the analysis and calculation of the existing data, we confirm that the 4 hypotheses proposed are positive and have significance. Overall the results of this research hypothesis are summarized in Table 7.

Table 7.
Summary of the hypothesis test.
Hypothesis 1 shows that the cyber security readiness variable is positive and has a strong relationship with the organizational security adoption variable (H1; CSR-OSA = 0.439, T-Statistics = 5.364). Hypothesis 2 shows the results that the technology readiness variable is positive and has a correlation and importance to the organizational security adoption variable (H2; TR-OSA = 0.492, T-Statistics = 6.011). For hypothesis 3, we find that the organizational security adoption variable has a positive value and a significant correlation with the real benefit variable (H3; OSA-TB = 0.719, T-Statistic = 11.719). And next is hypotension 4, we confirm that the organizational security adoption variable is positive and has a significant correlation with the intangible benefit variable (H4; OSA-IB = 0.835, T-Statistics = 6.335). Furthermore, the R2 value for the organizational security adoption variable is 0.810, the R2 value for the tangible benefit variable is 0.517, while the R2 value for the intangible benefit variable is 0.698.
6. Discussion
To answer the question in this study, namely whether organizational cyber security readiness and technology readiness affect organizational performance from a security perspective, tangible and intangible benefits. So the findings in this study will be discussed in detail in the following discussion:
Technological factors, the test results show the influence of technological factors on the readiness of the organization to maintain its cyber infrastructure and services. This is in line with the research of Kong et al. [16] that a good IT infrastructure can encourage organizations to increase their preparedness in the face of cyber-attacks. Therefore, the organization’s special attention to the development of IT infrastructure is an important factor that can be utilized by organizations to increase organizational readiness to protect organizational resources from cyber-attacks. Organizations can grow their IT infrastructure by ensuring the availability of IT experts, IT tools, and software applications that businesses need to maintain and manage cyber security. Organizations can also improve cyber security readiness by making the most of their IT resources.
Organizational factors, the test results show that organizational factors influence organizational readiness to maintain cyber security infrastructure and services. This finding is in line with the results of previous studies which explained that organizations need to ensure top management provides support and commitment to security [17,20,25,56]. Top management’s contribution as a form of support for the organization’s cyber security can be demonstrated in the form of cyber security regulations, policies, strategies, and standards. Hsu et al. [17] in their research explained that compliance with information security behavior is influenced by competence and commitment, and compliance with cyber security policies and intention to violate among employees affects cyber security readiness [24,57,95]. Therefore, the results of this study support the results of studies in previous studies that having skilled human resources in cyber security management can affect the cyber security readiness of an organization. Therefore, organizations can improve employee skills in managing cyber security by providing cyber security skills training to the IS team regularly and ensuring the availability of resources that support the training process.
This study also shows the results that an organization’s cyber security readiness is influenced by organizational culture, where organizations that have good cultural support will be better prepared to face cyber-attacks. These findings support the findings of previous studies examining cyber security innovations [17,25,60]. Organizations that are ready to face cyber-attacks and secure organizational resources are organizations that can manage organizational values, beliefs, and habits related to improving organizational cyber security well. Providing support for activities and collaboration across groups and encouraging team members to contribute to cyber security are various ways that organizations can improve organizational culture. In addition, organizations need to provide information about cyber security incidents and failures that occurred in various units, this is to prevent similar incidents from happening again in the future.
Environmental factors, the test results prove that there is an environmental influence on the organization’s readiness to maintain the organization’s cyber infrastructure and services. This finding supports the findings of previous research which explains that good cooperation between organizations, suppliers, and business partners can increase organizational readiness to face cyber-attacks [29,96,97]. Activities that can be carried out to create good relations between the organization and stakeholders in addition to helping each other but can also be done by communicating openly for security accountability. In addition to the organization’s collaboration with suppliers and partners in this study, it was found that government regulations and organizational compliance with industry standards have a significant impact on the organization’s cyber security readiness. This finding supports the findings of previous studies examining cyber security rule violations and the protection of critical infrastructure [30,34]. Organizational compliance with cyber security laws and regulations as well as compliance with industry standards have proven to make organizations better prepared for the threat of cyber-attacks. The organization believes that government support and industry-standard guidance can reduce the risk of cyber-attack incidents. This shows the important role of government support for cyber security readiness which is manifested in regulations and laws as well as organizational compliance with business rules and laws that have been issued by the government. In addition, it is also important for organizations to follow industry standards that have been set as best practices and guidelines for combating cyber-attacks and it is proven that compliant organizations are better prepared to deal with cyber-attacks and increase organizational readiness to protect their IT resources.
Furthermore, it is seen that both cyber security and technology readiness have a significant influence on organizational security performance. This finding is in line with the research results of Angst et al. [23], and Wang, et al [31]. The findings also suggest that increased cyber security readiness and technology readiness can help organizations to gain an edge in organizational security performance. Reduced data breaches, good security reputation, increased security of internal processes, and reliable systems for processing information, are some of the security performance advantages that companies achieve by increasing cyber security and technology readiness. In addition, this study proved that there is a significant effect of organizational security performance on the performance of tangible and intangible benefits, this result is under the findings of Eccles et al. [72]. The results show that achieving superior performance in organizational security brings with it superior material benefits such as sales and revenue growth and intangible performance, namely good corporate image and reputation, customer loyalty, and competitive position.
7. Conclusions and Research Implications
Organizations are expected to have cyber security preparedness, given the risk of cyber-attack threats that continue to increase all the time. This study examines the factors that affect cyber security readiness as well as technology readiness by integrating these factors into a comprehensive framework. This finding proves that all factors have a significant impact on cyber security and technology readiness. Therefore, the findings of this study have provided new knowledge for organizations to properly manage and maintain key factors to ensure organizational cyber security readiness. In addition, this study also proves that cyber security readiness and technology have a significant influence on the performance of organizational tangible and intangible benefits mediated by organizational security readiness. And overall, this research adds to cyber security research and practice. In this study, there are still shortcomings that need to be corrected in further research. Some of the shortcomings in this study are the limited scope of research which is only limited to Indonesia, so that future research can consider organizations from other countries when the factors studied in this study have different levels of meaning and context. Furthermore, based on the test results, collaboration with competitors is known to have a significant impact on cyber security readiness, there is no concern and suspicion of fraud attempts by competitors, avoidance of sharing knowledge of security ideas and skills with competitors and privacy concerns allow collaboration with competitors to have a significant impact about cyber security readiness. Therefore, studies that will be carried out in the future can examine in depth the influence of competitor collaboration on cyber security readiness. In this study using a quantitative approach where data collection is done through online questionnaires, further research can complement it with qualitative research to increase a deeper understanding of various factors that can affect organizational security readiness and performance. And lastly, further research is expected to be able to examine more deeply cyber security readiness, technology readiness, and its influence on overall organizational performance.
In the research conducted, the researcher proposes a conceptual model to determine cyber security readiness, organizational technology readiness, and its impact on organizational security performance. This research contributes knowledge for other researchers who will study cyber security can use the conceptual model proposed in this study by combining several theories. Therefore, this study also helps future researchers to more easily understand the relationship between cyber security readiness, technology readiness, and performance by conducting an empirical study on the effect of cyber security readiness on the performance of tangible and intangible benefits mediated by organizational security performance. Meanwhile, this research has impact to the society because the good cooperation and good organization will be achieved. it also increases the social cooperation responsibility. This research can complement previous research that has been done and prove that cyber security readiness and organizational technology readiness can improve security performance, tangible and intangible benefits of organizations. In addition, this research also practically highlights the importance of three factors that empirically show the impact on cyber security readiness, as well as the four main factors that influence technology readiness. If the organization wants the organization’s cyber security to be well maintained, then the organization must pay more attention to managing these important factors. In addition, organizations must also ensure that there is support from executive management and organizational culture that is directed at cyber security attacks to reduce the risk of threats of attacks on company resources that can negatively impact company performance. Top management support can motivate for organizations to be able to develop appropriate strategies and guidelines for managing organizational cyber security. An organization’s compliance with industry standards, regulations, and laws set by the government to protect an organization from cyber-attacks can improve an organization’s cyber security preparedness. Ultimately, the results of this study can help organizations determine the relationship between cyber security readiness, technology readiness, tangible benefits, and intangible benefits. This is to encourage organizations to pay more attention to cyber security management strategies and cyber security guidelines that are right for business so that organizations are better prepared to face cyber-attacks and provide positive business benefits by achieving superior business performance.
Furthermore, this study limited the constructed variable of cyber security adoption to the three concept variables, namely technology context, organizational context, and environment context. In the future, other contexts such as the government context can be added, government is considered as the important variable since it cannot be separated from the basic of public policy which in turn has a significant impact on the in fluency of cyber security adoption. At the same time, it is possible to the future research to compare the state in different countries, even different continents, it gives the possibility of comparison depending on the level of development of the country as well as other factors that influence the level of cyber security, such as regional conflicts on local or international scope.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.H. and A.R.; methodology, T.H. and T.N.; software, S. and B.; validation, T.H., A.R. and T.N.; formal analysis, T.H. and B.; investigation, T.H. and T.N.; resources, A.R. and T.H.; data curation, S. and B.; writing original draft preparation, T.H. and A.R.; writing review and editing, A.R. and T.N; visualization, T.H.; supervision, A.R.; project administration, S. and B.; funding acquisition, A.R. and T.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for this study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent from the patients/participants was not required to participate in this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation, to any qualified researchers.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Park, Y.; El Sawy, O.A.; Fiss, P.C. The role of business intelligence and communication technologies in organizational agility: A configurational approach. J. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2017, 18, 648–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rîndașu, S.-M. Emerging Information Technologies in Accounting and Related Security Risks—What is the Impact on the Romanian Accounting Profession. J. Account. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2017, 16, 581–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Publikasi—Laporan Tahunan GOV-CSIRT. Available online: https://https://bssn.go.id/publikasi/ (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Security Intel, McAfee Labs Report Finds 93 Percent of Security Operations Center Managers Overwhelmed by Alerts and Unable to Triage Potential Threats. Available online: https://newsroom.intel.com (accessed on 12 June 2021).
- Hasan, S.; Ali, M.; Kurnia, S.; Thurasamy, R. Evaluating the cyber security readiness of organizations and its influence on performance. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2021, 58, 102726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, S. How ethical hacking can protect organisations from a greater threat. Comput. Fraud Secur. 2019, 2019, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pala, A.; Zhuang, J. Information sharing in cyber security: A review. Decis. Anal. 2019, 16, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.H.; Ali, M.H.; Hassan, M.K. Cybersecurity hazards and financial system vulnerability: A synthesis of literature. Risk Manag. 2020, 22, 239–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, N. A larger problem: Financial and reputational risks. Comput. Fraud Secur. 2014, 2014, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.; Winchester, D.; Bunker, D.; Jamieson, R. Circuits of power: A study of mandated compliance to an information systems security de jure standard in a government organization. MIS Q. 2010, 34, 463–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, T.; Lertwongsatien, C. Effect of information systems resources and capabilities on firm performance: A resource-based perspective. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2005, 21, 237–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Solomon, M.G. Fundamentals of Information Systems Security, 3rd ed.; Jones and Bartlett Learning: Burlington, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, E.M. Modelling information and communications technology cyber security externalities Spillover EFFECTS on sustainable economic growth. J. Knowl. Econ. 2021, 12, 412–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaikh, M.; Adamson, B. From awareness to influence: Toward a model for improving employees’ security behaviour. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2021, 25, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenia, S.; Angelini, M.; Nonino, F.; Palombi, G.; Schlitzer, M.F. A dynamic simulation approach to support the evaluation of cyber risks and security investments in SMEs. Decis. Support Syst. 2021, 147, 113580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.-K.; Kim, T.-S.; Kim, J. An analysis on effects of information security investments: A BSC perspective. J. Intell. Manuf. 2012, 23, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.; Lee, J.-N.; Straub, D.W. Institutional influences on information systems security innovations. Inf. Syst. Res. 2012, 23, 918–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.T.; Tho, N.X. Purchasing power parity between Vietnam and United States. Int. J. Appl. Inf. Manag. 2022, 2, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Lesma, V.B.; Okada, H. Effect of textual errors on the evaluation of a foreign online store. Int. J. Inform. Inf. Syst. 2020, 3, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, M.; Rasiah, R.; George, M.; Asirvatham, D.; Thangiah, G. Bridging the gap between organisational practices and cyber security compliance: Can cooperation promote compliance in organisations. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2018, 19, 161–180. [Google Scholar]
- Herold, R. Addressing privacy issues during disaster recovery. Inf. Syst. Secur. 2006, 14, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, H.-T.; Hsu, S.H.-Y. Performance effects of technology-organization-environment openness, service co-production, and digital-resource readiness: The case of the IT industry. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2015, 35, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, C.M.; Block, E.S.; D’Arcy, J.; Kelley, K. When do it security investments matter? Accounting for the influence of institutional factors in the context of healthcare data breaches. MIS Q. 2017, 41, 893–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puhakainen, P.; Siponen, M. Improving employees’ compliance through information systems security training: An action research study. MIS Q. 2010, 34, 757–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kraemer, S.; Carayon, P.; Clem, J. Human and organizational factors in computer and information security: Pathways to vulnerabilities. Comput. Secur. 2009, 28, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhong, W. A differential game approach to security investment and information sharing in a competitive environment. IIE Trans. Institute Ind. 2016, 48, 511–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.J. An exploration into trust and privacy management in a digital age. Int. J. Appl. Inf. Manag. 2022, 2, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, T.-T. Determinants of trade balance in Vietnam during the period 1989–2013. Int. J. Appl. Inf. Manag. 2022, 2, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.E.; Watson, K.J.; Baker, W.H.; Pokorski, J.A. A critical balance: Collaboration and security in the IT-enabled supply chain. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2007, 45, 2595–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, K.; Burns, C.; Stallard, K. Cyber gurus’: A rhetorical analysis of the language of cyber security specialists and the implications for security policy and critical infrastructure protection. Gov. Inf. Q. 2015, 32, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; So, K.K.F.; Sparks, B.A. Technology readiness and customer satisfaction with travel technologies: A cross-country investigation. J. Travel Res. 2017, 56, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Njenga, K.; Jordaan, P. We want to do it our way: The neutralisation approach to managing information systems security by small businesses. Afr. J. Inf. Syst. 2015, 8, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, T.-H. The empirical study of usability and credibility on Intention usage of government-to-citizen services. J. Appl. Data Sci. 2021, 2, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, J.D.; Lowry, P.B.; Barlow, J.B. Organizational violations of externally governed privacy and security rules: Explaining and predicting selective violations under conditions of strain and excess. J. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2016, 7, 39–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; He, W.; Xu, L.; Ash, I.; Anwar, M.; Yuan, X. Investigating the impact of cyber security policy awareness on employees’ cyber security behavior. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2018, 45, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.-J. The effects of safety management systems, attitude and commitment on safety behaviors and performance. Int. J. Appl. Inf. Manag. 2021, 1, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K.; Choi, M. Effects of innovation-supportive culture and organizational citizenship behavior on e-government information system security stemming from mimetic isomorphism. Gov. Inf. Q. 2017, 34, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radanliev, P.; De Roure, D.C.; Nurse, J.R.C.; Mantilla Montalvo, R.; Cannady, S.; Santos, O.; Maddox, L.T.; Burnap, P.; Maple, C. Future developments in standardisation of cyber risk in the Internet of Things (IoT). SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruohonen, J. An acid test for europeanization: Public cyber security procurement in the European Union. Eur. J. Secur. Res. 2020, 5, 349–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estetikha, A.K.A.; Gutama, D.H.; Pradana, M.G.; Wijaya, D.P. Comparison of K-means clustering & logistic regression on university data to differentiate between public and private university. Int. J. Inform. Inf. Syst. 2021, 4, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Hitoshi, H.; Shogo, K.; Masakazu, O. The effectiveness of the body of knowledge process in the startup analysis of efficiency by applying startup management body of knowledge (SUBOK) guide. Int. J. Appl. Inf. Manag. 2021, 1, 28–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, M. Study of career education for women: Development of global human resources. Int. J. Appl. Inf. Manag. 2021, 1, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, K.K.Y.; Chau, P.Y.K. A perception-based model for EDI adoption in small businesses using a technology-organization-environment framework. Inf. Manag. 2001, 38, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.J.; Jang, W.Y. Determinants of the adoption of enterprise resource planning within the technology-organization-environment framework: Taiwan’s communications industry. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 2008, 48, 94–102. [Google Scholar]
- DiMaggio, P.J.; Powell, W.W. The iron cage revisited institutional isomorphism and collective rationality in organizational fields. Adv. Strateg. Manag. 2000, 17, 143–166. [Google Scholar]
- Thelen, G. Leadership in a global world management training requirement using the example of the Asian studies program at University of Applied Sciences (HTWG) Konstanz. Int. J. Appl. Inf. Manag. 2021, 1, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, T.; Martins, M.F. Information technology adoption models at firm level: Review of literature. In Proceedings of the 4th European Conference on Information Systems Management, Lisbon, Portugal, 9–10 September 2010; pp. 312–322. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, J.V.; Morgenstern, O. Theory of Games and Economic Behavior; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1944. [Google Scholar]
- Osborne, M.J. An Introduction to Game Theory; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mohebbi, S.; Li, X. Coalitional game theory approach to modeling suppliers’ collaboration in supply networks. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 169, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagurney, A.; Shukla, S. Multifirm models of cyber security investment competition vs. cooperation and network vulnerability. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 260, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, J.P. Crime, Punishment, and Deterrence; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Kasperskylab. KSN Report: Ransomware and Malicious Cryptominers 2016–2018. Retrieved from Kaspersky Business Hub. 2018. Available online: https://cloud.kaspersky.com (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- Maillard, D. The obsolescence of man in the digital society. Int. J. Appl. Inf. Manag. 2021, 1, 99–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ky Vien, N. Modelling the relationship of perceived quality, destination image, and tourist satisfaction at the destination level. Int. J. Appl. Inf. Manag. 2021, 1, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankanhalli, A.; Teo, H.H.; Tan, B.C.Y.; Wei, K.K. An integrative study of information systems security effectiveness. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2003, 23, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskal, E.J. A model for establishing a cyber security center of excellence. Inf. Syst. Educ. Conf. 2015, 13, 97–108. [Google Scholar]
- Ruighaver, A.B.; Maynard, S.B.; Chang, S. Organisational security culture: Extending the end-user perspective. Comput. Secur. 2007, 26, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakuwa, K. Difficulties of integrating human resources management globally by Japanese corporations. Int. J. Appl. Inf. Manag. 2021, 1, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Li, M.; Zhang, T. The impacts of organizational culture on information security culture: A case study. Inf. Technol. Manag. 2016, 17, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.E.; Ho, C.B. Organizational factors to the effectiveness of implementing information security management. Ind. M. Dat. Sys. 2006, 106, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, H.S.; Kim, C.; Ryu, Y.U. Self-efficacy in information security: Its influence on end users’ information security practice behavior. Comput. Secur. 2009, 28, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umami, I. Comparing Epsilon greedy and Thompson sampling model for multi-armed bandit algorithm on marketing dataset. J. Appl. Data Sci. 2021, 2, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, A. Technology readiness index (TRI): A multiple item scale to measure readiness to embrace new technologies. J. Serv. Res. 2000, 2, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Shih, H.Y.; Sher, P.J. Integrating technology readiness into technology acceptance: The TRAM model. Psychol. Mark. 2007, 24, 641–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.S.C.; Hsieh, P.L. The influence of technology readiness on satisfaction and behavioral intentions toward self-service technologies. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2007, 23, 1597–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.W.; Chen, J. What motivates customers to shop in smart shops? The impacts of smart technology and technology readiness. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2021, 58, 102325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, A.; Colby, C.L. An updated and streamlined technology readiness index: TRI 2.0. J. Serv. Res. 2015, 18, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradana, M.G.; Ha, H.T. Maximizing strategy improvement in mall customer segmentation using K-means clustering. J. Appl. Data Sci. 2021, 2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilts, D. An Empirical Assessment of Cybersecurity Readiness and Resilience in Small Businesses. Ph.D. Thesis, Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 16 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Vance, A.; Benjamin Lowry, P.; Wilson, D.W. Using trust and anonymity to expand the use of anonymizing systems that improve security across organizations. Secur. J. 2017, 30, 979–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten, C.W.; Manimaran, G.; Liu, C.C. Cyber security for critical infrastructures: Attack and defense modeling. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A Syst. Hum. 2010, 40, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, M. Information security threats: A comparative analysis of impact, probability, and preparedness. Inf. Syst. Manag. 2009, 26, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skopik, F.; Settanni, G.; Fiedler, R. A problem shared is a problem halved: A survey on the dimensions of collective cyber defense through security information sharing. Comput. Secur. 2016, 60, 154–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariguna, T. An Empirical Study to Understanding Students Continuance Intention Use of Multimedia Online Learning. Int. J. Appl. Inf. Manag. 2021, 1, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Balaji, M.; Quazi, A.; Quaddus, M. Predictors of customer acceptance of and resistance to smart technologies in the retail sector. Predict. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2018, 42, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nugroho, M.A.; Fajar, M.A. Effects of technology readiness towards acceptance of mandatory web-based attendance system. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 124, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Kraemer, K.L. Post-adoption variations in usage and value of e-business by organizations: Cross-country evidence from the retail industry. Inf. Syst. Res. 2005, 16, 61–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bharadwaj, A.S. A resource-based perspective on information technology capability and firm performance: An empirical investigation. MIS Q. 2000, 24, 169–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirodkar, V.; Mohr, A.T. Resource tangibility and foreign firms’ corporate political strategies in emerging economies: Evidence from India. Manag. Int. Rev. 2015, 55, 801–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, M.; Haase, H. Firm resources and entrepreneurial orientation as determinants for collaborative entrepreneurship. Manag. Decis. 2013, 51, 680–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, J.A.; Reed, R. Firm resources and joint ventures: What determines zero-sum versus positive-sum outcomes? Manag. Decis. Econ. 2000, 21, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, C.W.; Schendel, D. Strategy Formulation: Analytic Concepts; West Publishing: West St. Paul, MN, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Das, T.K.; Teng, B.S. A resource-based theory of strategic alliances. J. Manag. 2000, 26, 31–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Wernerfelt, B. The link between resources and type of diversification: Theory and evidence. Strateg. Manag. J. 1991, 12, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazevic, V.; Lievens, A. Learning during the new financial service innovation process-Antecedents and performance effects. J. Bus. Res. 2004, 57, 374–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eccles, R.G.; Ioannou, I.; Serafeim, G. The impact of corporate sustainability on organizational processes and performance. Manag. Sci. 2014, 60, 2835–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demirkan, S.; Demirkan, I.; McKee, A. Blockchain technology in the future of business cyber security and accounting. J. Manag. Anal. 2020, 7, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Integrating technology readiness into business technology: The TRAM model. Psychol. Mark. 2010, 31, 224–238.
- Lin, J.S.C.; Hsieh, P.L. Refinement of the technology readiness index scale: A replication and cross-validation in the self-service technology context. J. Serv. Manag. 2012, 23, 34–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gefen, D.; Rigdon, E.E.; Straub, D.; Quarterly, S.M.I.S.; June, N. Editor’s comments: An update and extension to SEM guidelines for administrative and social science research. MIS Q. 2019, 35, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringle, C.M.; Wende, S.; Will, A. SmartPLS 2.0. 2005. Available online: www.smartpls.de (accessed on 4 June 2021).
- Hoc, L.; Fong, N.; Law, R. A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). Eur. J. Tour. Res. 2014, 6, 211–213. [Google Scholar]
- Ramayah, T.; Cheah, J.; Francis, C.; Hiram, T.; Mumtaz, A.M. Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) using SmartPLS 3.0: An updated guide and practical guide to statistical analysis. Handb. Mark. Res. 2021, 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- D’Arcy, J.; Herath, T.; Shoss, M.K. Understanding employee responses to stressful information security requirements: A coping perspective. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2014, 31, 285–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, R.; Martin, X.; Noorderhaven, N.G. When does trust matter to alliance performance? Acad. Manag. J. 2006, 49, 894–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Bala, H. Adoption and impacts of interorganizational business process standards: Role of partnering synergy. Inf. Syst. Res. 2012, 23, 1131–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).