Limited Demand or Unreliable Supply? A Bibliometric Review and Computational Text Analysis of Research on Energy Policy in India
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
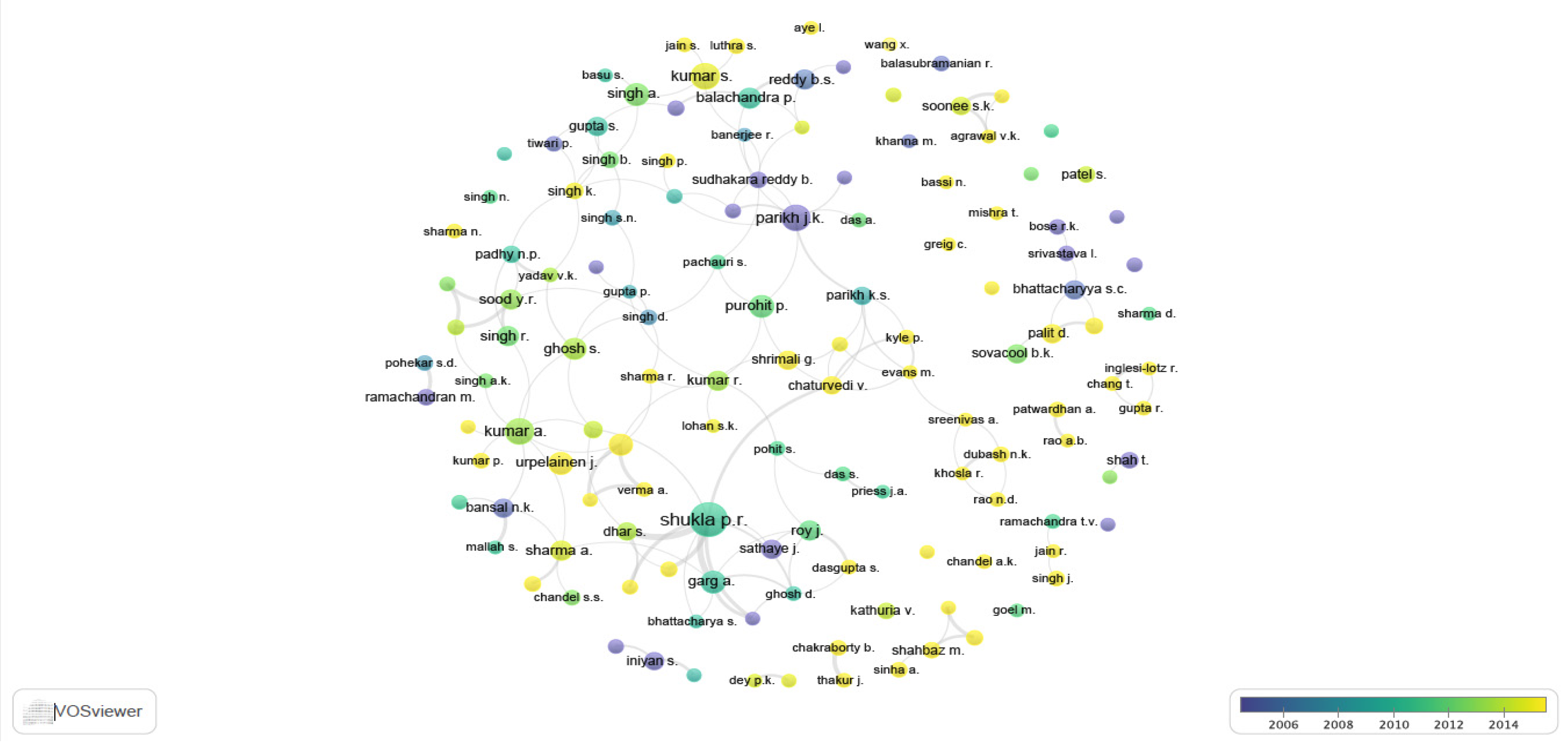
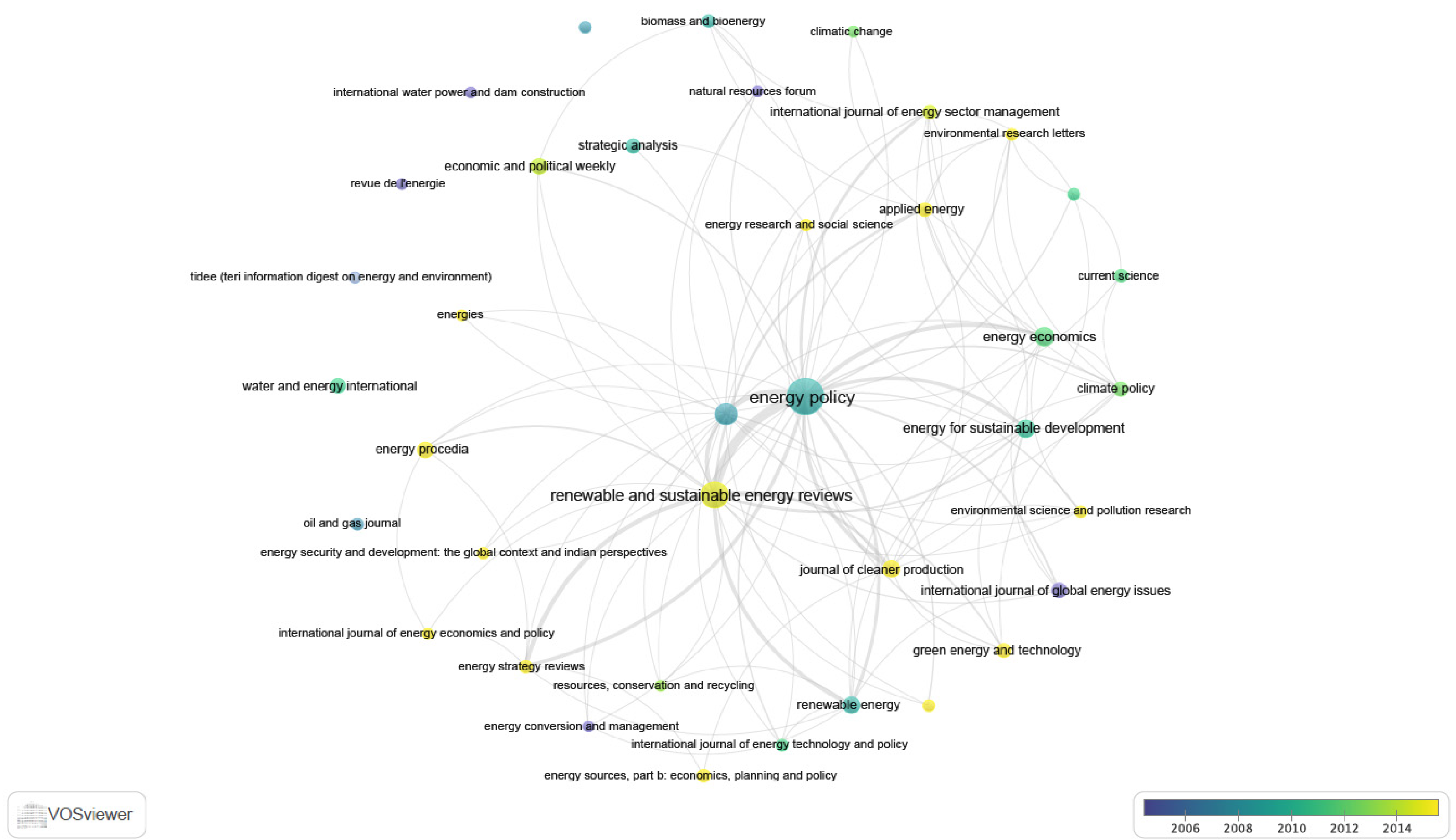
3. Overview of the Research on Energy Policy in India
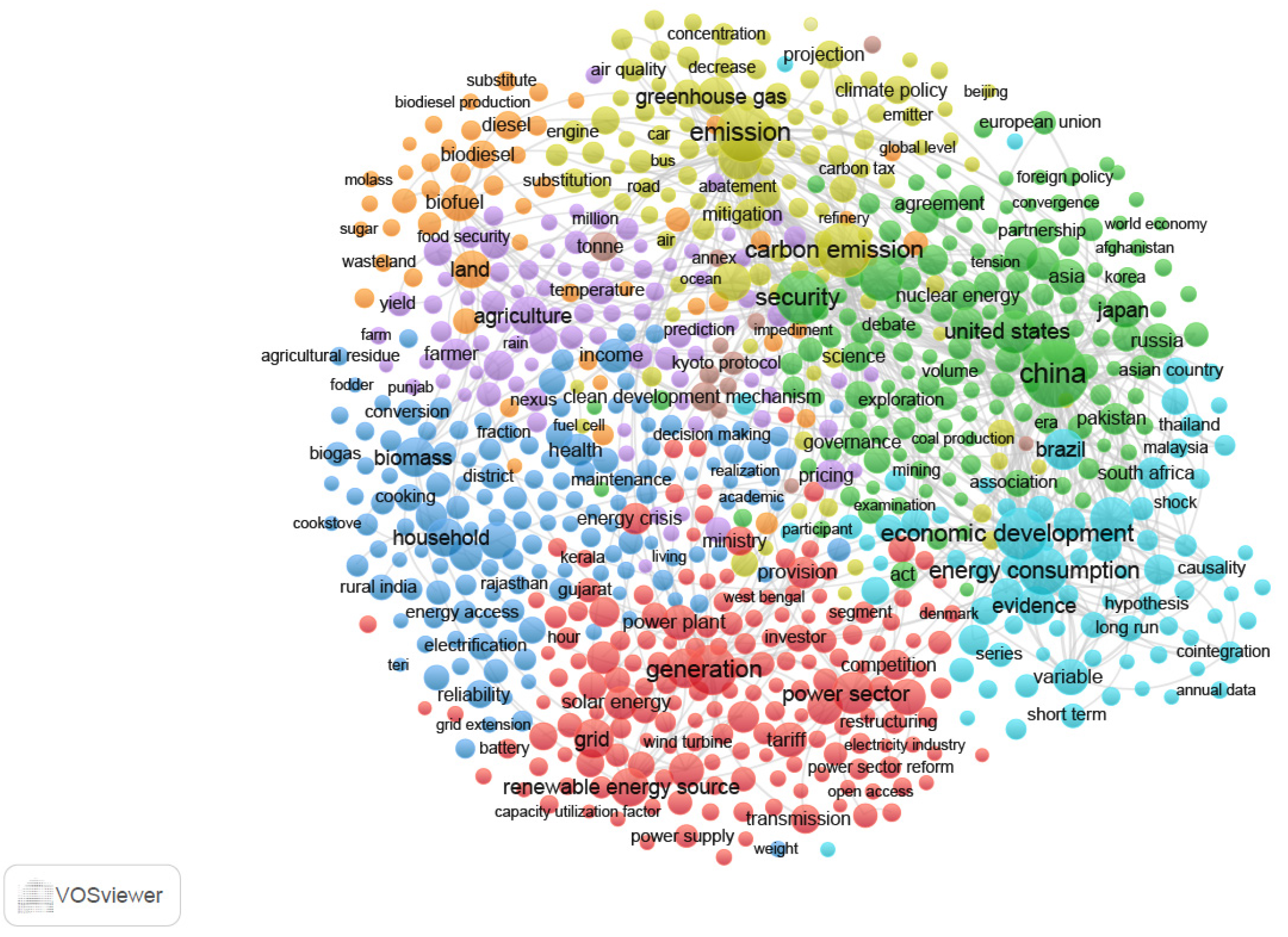
4. The Thematic Foci of the Research
5. The Geographies in the Research
6. The Locus of Public Policy
7. Discussion and Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chunekar, A.; Sreenivas, A. Towards an understanding of residential electricity consumption in India. Build. Res. Inf. 2019, 47, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, S.; Jain, A.; Tripathi, S.; Gould, C.F. The drivers of sustained use of liquified petroleum gas in India. Nat. Energy 2020, 5, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AEEE and BEE. AEEE and BEE State Energy Efficiency Index; Alliance for an Energy Efficient Economy (AEEE) and the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE): New Delhi, India, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Natarajan, B.; Kumar, S.; Rajah, V.; Cherail, K. State of Energy Efficiency in India: A Compilation of Policies, Priorities and Potential; Alliance for an Energy Efficient Economy: New Delhi, India, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dawn, S.; Tiwari, P.K.; Goswami, A.K.; Singh, A.K.; Panda, R. Wind power: Existing status, achievements and government’s initiative towards renewable power dominating India. Energy Strategy Rev. 2019, 23, 178–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, G.; Sinha, S. Outlook on the Indian scenario of solar energy strategies: Policies and challenges. Energy Strategy Rev. 2019, 24, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles Rajesh Kumar, J.; Majid, M.A. Renewable energy for sustainable development in India: Current status, future prospects, challenges, employment, and investment opportunities. Energy Sustain. Soc. 2020, 10, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Swain, S.S.; Mishra, P. Determinants of adoption of cleaner cooking energy: Experience of the Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana in rural Odisha, India. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Gupta, E.; Sarangi, G.K. Household Energy Poverty Index for India: An analysis of inter-state differences. Energy Policy 2020, 144, 111592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Singh, G.; Sodhi, G.P.S. Energy auditing and optimization approach for improving energy efficiency of rice cultivation in south-western Punjab, India. Energy 2019, 174, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Henriques, C.O.; Martins, A.G. Assessment of energy-efficient appliances: A review of the technologies and policies in India’s residential sector. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Energy Environ. 2019, 8, e330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phadke, A.; Park, W.Y.; Abhyankar, N. Providing reliable and financially sustainable electricity access in India using super-efficient appliances. Energy Policy 2019, 132, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.; Mishra, P.P. Benchmarking energy use of iron and steel industry: A data envelopment analysis. Benchmarking 2019, 26, 1314–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.; Danish, M.S.; Sharma, R. Assessing energy efficiency of Indian paper industry and influencing factors: A slack-based firm-level analysis. Energy Econ. 2019, 81, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardhan, R.; Debnath, R.; Jana, A. Evolution of sustainable energy policies in India since 1947: A review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Energy Environ. 2019, 8, e340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graus, W.H.J.; Voogt, M.; Worrell, E. International comparison of energy efficiency of fossil power generation. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 3936–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behuria, P. The politics of late late development in renewable energy sectors: Dependency and contradictory tensions in India’s National Solar Mission. World Dev. 2020, 126, 104726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasiya, P.K.; Warudkar, V.; Ahmed, S. Wind energy development and policy in India: A review. Energy Strategy Rev. 2019, 24, 342–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Sinha, S. Indian wind energy & its development-policies-barriers: An overview. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2019, 1, 100003. [Google Scholar]
- Malav, L.C.; Yadav, K.K.; Gupta, N.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, G.K.; Krishnan, S.; Rezania, S.; Kamyab, H.; Pham, Q.B.; Yadav, S.; et al. A review on municipal solid waste as a renewable source for waste-to-energy project in India: Current practices, challenges, and future opportunities. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PFCL. The Performance of State Power Utilities for the Years 2013-14 to 2015-16; Power Finance Corporation Ltd., Government of India: New Delhi, India, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- CEA. Load Generation Balance Report 2016-17; Central Electricity Authority, Ministry of Power, Government of India: New Delhi, India, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- CEA. Reliability Index of the Cities/Towns/Villages—DISCOM Wise; Central Electricity Authority, Ministry of Power, Government of India: New Delhi, India, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chunekar, A.; Varshney, S.; Dixit, S. Residential Electricity Consumption in India: What do We Know? Prayas (Energy Group): Pune, India, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- National Sample Survey Office, Ministry of Statistics, National Sample Survey (NSS) Data (Unit Level). 2016, Harvard Dataverse. Available online: https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/K8BSDU (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Chindarkar, N.; Goyal, N. One price doesn’t fit all: An examination of heterogeneity in price elasticity of residential electricity in India. Energy Econ. 2019, 81, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elavarasan, R.M.; Shafiullah, G.M.; Padmanaban, S.; Kumar, N.M.; Annam, A.; Vetrichelvan, A.M.; Mihet-Popa, L.; Holm-Nielsen, J.B. A Comprehensive Review on Renewable Energy Development, Challenges, and Policies of Leading Indian States with an International Perspective. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 74432–74457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Yu, Z.G.; Klemeš, J.J.; Bokhari, A. A state-of-the-art review of greenhouse gas emissions from Indian hydropower reservoirs. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 320, 128806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasswell, H.D. The Decision Process: Seven Categories of Functional Analysis; University of Maryland Press: College Park, MD, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Lindblom, C.E. The science of muddling through. Public Adm. Rev. 1959, 19, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasswell, H.D. The emerging conception of the policy sciences. Policy Sci. 1970, 1, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pressman, J.L.; Wildavsky, A. Implementation: How Great Expectations in Washington are Dashed in Oakland; Or, Why It’s Amazing that Federal Programs Work at All, This Being a Saga of the Economic Development Administration as Told by Two Sympathetic Observers Who Seek to Build Morals on A Foundation; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1984; Volume 708. [Google Scholar]
- Kingdon, J.W. Agendas, Alternatives, and Public Policies; Little, Brown: Boston, MA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Sabatier, P.A. An Advocacy Coalition Framework of Policy Change and the Role of Policy-Oriented Learning Therein. Policy Sci. 1988, 21, 129–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, P.A. Policy Paradigms, Social Learning, and the State: The Case of Economic Policymaking in Britain. Comp. Politics 1993, 25, 275–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, F. Reframing Public Policy: Discursive Politics and Deliberative Practices; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hajer, M. Discourse analysis and the study of policy making. Eur. Political Sci. 2002, 2, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, D.A. Policy Paradox: The Art of Political Decision Making; ww Norton: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Volume 13. [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi, V.; Dwivedi, P.; Gupta, A. Critical review of business models for grid connected rooftop solar PV systems in India. Water Energy Int. 2021, 63r, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Mathew, N.; Varaprasad, G. A review on factors affecting adoption of electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Advances in Computing, Control, and Telecommunication Technologies, Hyderabad, India, 8–15 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, M.K.; Mukherjee, V.; Yadav, V.K.; Ghosh, S. Indian power distribution sector reforms: A critical review. Energy Policy 2020, 144, 111672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Ghosal, A.; Rabbi, M.T. Proposed amendment of electricity distribution in India: A review. Water Energy Int. 2021, 63r, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Smirnova, E.; Kot, S.; Kolpak, E.; Shestak, V. Governmental support and renewable energy production: A cross-country review. Energy 2021, 230, 120903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Verma, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Gaur, A.; Mohapatra, S.; Dwivedi, G.; Verma, P. A comprehensive review on developments in electric vehicle charging station infrastructure and present scenario of India. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.; Sabharwal, S.P. A conceptual review of green buildings in India: Importance and need. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2016, 15, 799–804. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Jamwal, A.; Sharma, N.; Agrawal, R. Opportunities and Issues with Clean Renewable Energy Development in India: A Review. In Advances in Fluid and Thermal Engineering. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Sikarwar, B.S., Sundén, B., Wang, Q., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyshnavi, P.; Venkatesan, N.; Samad, A.; Avital, E.J. Tidal current energy for Indian Coastal lines—A state art of review. In Proceedings of the 2020 National Science, Engineering and Technology Conference, NCSET 2020, Chennai, India, 11–12 May 2020; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Chennai, India, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, S.; Dhingra, T.; Sengupta, A. Status of Electricity Act, 2003: A systematic review of literature. Energy Policy 2017, 102, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, U.E.; Nygaard, I.; Morris, M.; Robbins, G. The effects of local content requirements in auction schemes for renewable energy in developing countries: A literature review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 127, 109843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeek, A.; Debackere, K.; Luwel, M.; Zimmermann, E. Measuring progress and evolution in science and technology—I: The multiple uses of bibliometric indicators. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2002, 4, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijssen, R.J. Cartography of Science: Scientometric Mapping with Multidimensional Scaling Methods. Ph.D. Thesis, Leiden University, Leiden, The Netherlands, 1992. Available online: https://philpapers.org/rec/TIJCOS (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Visualizing bibliometric networks. In Measuring Scholarly Impact; Ding, Y., Rousseau, R., Wolfram, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 285–320. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10377-8_13 (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. VOS: A New Method for Visualizing Similarities Between Objects. In Advances in Data Analysis: Proceedings of the 30th Annual Conference of the Gesellschaft für Klassifikation e.V., Freie Universität Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 8–10 March 2006; Decker, R., Lenz, H.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 299–306. [Google Scholar]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, P.D. India: The Energy Sector; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Parikh, J.K.; Parikh, K.S. Mobilization and impacts of bio-gas technologies. Energy 1977, 2, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, K.S. Scope for Energy Substitution Policy in India. Rev. De L’energie 1977, 28, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Masih, A.M.M.; Masih, R. Energy consumption, real income and temporal causality: Results from a multi-country study based on cointegration and error-correction modelling techniques. Energy Econ. 1996, 18, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pao, H.T.; Tsai, C.M. CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in BRIC countries. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 7850–7860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S. Electricity consumption and economic growth in India. Energy Policy 2002, 30, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebaraj, S.; Iniyan, S. A review of energy models. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2006, 10, 281–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejat, P.; Jomehzadeh, F.; Taheri, M.M.; Gohari, M.; Majid, M.Z. A global review of energy consumption, CO2 emissions and policy in the residential sector (with an overview of the top ten CO2 emitting countries). Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 43, 843–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorda, G.; Banse, M.; Kemfert, C. An overview of biofuel policies across the world. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 6977–6988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fraiture, C.; Giordano, M.; Liao, Y. Biofuels and implications for agricultural water use: Blue impacts of green energy. Water Policy 2008, 10 (Suppl. 1), 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drèze, J.; Sen, A. An Uncertain Glory: India and its Contradictions; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–434. [Google Scholar]
- Leach, M.; Scoones, I.; Stirling, A. Dynamic Sustainabilities: Technology, Environment, Social Justice; Routledge: London, UK, 2010; pp. 1–212. [Google Scholar]
- Ackerman, J. Co-governance for accountability: Beyond “exit” and “voice”. World Dev. 2004, 32, 447–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, K.R.; Kulshreshtha, P. Efficiency analysis of coal-based thermal power generation in India during post-reform era. Int. J. Glob. Energy Issues 2005, 23, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.K.; Tiwari, P.K.; Sood, Y.R. Solar energy in India: Strategies, policies, perspectives and future potential. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, G.; Kathuria, V. Utility reforms in developing countries: Learning from the experiences of Delhi. Util. Policy 2014, 29, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossani, R. Reorganization of the power distribution sector in India. Energy Policy 2004, 320, 1277–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, J.K.; Reddy, B.S.; Banerjee, R.; Koundinya, S. DSM survey in India: Awareness, barriers and implementability. Energy 1996, 21, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananda Kumar, V.; Pandey, K.K.; Punia, D.K. Cyber security threats in the power sector: Need for a domain specific regulatory framework in India. Energy Policy 2014, 65, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, G. The development of renewable energy power in India: Which policies have been effective? Energy Policy 2012, 45, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, T.; Deshmukh, S.G.; Kaushik, S.C.; Kulshrestha, M. Impact assessment of the Electricity Act 2003 on the Indian power sector. Energy Policy 2005, 33, 1187–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umamaheswaran, S.; Seth, R. Financing large scale wind and solar projects-A review of emerging experiences in the Indian context. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 48, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, A.; Shrimali, G. The effectiveness of domestic content criteria in India’s Solar Mission. Energy Policy 2013, 62, 1470–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Shahidehpour, M. Restructuring choices for the Indian power sector. IEEE Power Eng. Rev. 2002, 22, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.P.; Nair, P.S.C.; Balasubramanian, R. Performance of Indian power sector during a decade under restructuring: A critique. Energy Policy 2005, 33, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahgat, G. Energy Security: An Interdisciplinary Approach; John Wiley and Sons: Chichester, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sovacool, B.K.; Mukherjee, I.; Drupady, I.M.; D’Agostino, A.L. Evaluating energy security performance from 1990 to 2010 for eighteen countries. Energy 2011, 36, 5846–5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.B.; Qin, P.; Chen, X. Strategic oil stockpiling for energy security: The case of China and India. Energy Econ. 2017, 61, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandian, S. The political economy of trans-Pakistan gas pipeline project: Assessing the political and economic risks for India. Energy Policy 2005, 33, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Valle, A.; Furlan, C. Diffusion of nuclear energy in some developing countries. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2014, 81, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, O. The US-India nuclear deal: The end of universal non-proliferation efforts? Int. Polit. Und Ges. 2006, 4, 28–43. [Google Scholar]
- Cronshaw, I. World Energy Outlook 2014 projections to 2040: Natural gas and coal trade, and the role of China. Aust. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 2015, 59, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D. Uranium trade and its security implications for India. South Asian Surv. 2010, 17, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Kumar, J. Fugitive Methane Emissions from Indian Coal Mining and Handling Activities: Estimates, Mitigation and Opportunities for its Utilization to Generate Clean Energy. Energy Procedia 2016, 90, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Kalirajan, K. A decade of economic reforms in India: The mining sector. Resour. Policy 2004, 29, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, R.B. Policy initiatives by the Government of India to accelerate the growth of installed nuclear power capacity in the coming years. Energy Procedia 2011, 7, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.S. Strategic Importance of Turkmenistan for India. Strateg. Anal. 2011, 35, 661–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jörgensen, K.; Wagner, C. Low Carbon Governance in Multi-level Structures: EU–India relations on energy and climate. Environ. Policy Gov. 2017, 27, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narula, K. Comparative assessment of energy sources for attaining sustainable energy security (SES): The case of India’s residential sector. Int. J. Sustain. Energy Plan. Manag. 2015, 5, 27–40. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Ravindranath, N.H. Financial analysis of cooking energy options for India. Energy Convers. Manag. 1997, 38, 1869–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, H.Y.; Nixon, J.D. A multi-criteria analysis of options for energy recovery from municipal solid waste in India and the UK. Waste Manag. 2015, 46, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, N.D. Kerosene subsidies in India: When energy policy fails as social policy. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2012, 16, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeuland, M.A.; Bhojvaid, V.; Kar, A.; Lewis, J.J.; Patange, O.; Pattanayak, S.K.; Ramanathan, N.; Rehman, I.H.; Soo, J.T.; Ramanathan, V. Preferences for improved cook stoves: Evidence from rural villages in north India. Energy Econ. 2015, 52, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakar, Y. Evaluating the role of rural electrification in expanding people’s capabilities in India. Energy Policy 2018, 114, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakara Reddy, B.; Nathan, H.S.K. Energy in the development strategy of Indian households—The missing half. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 18, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.R. The modelling of policy options for greenhouse gas mitigation in India. AMBIO 1996, 25, 240–248. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, D.; Shukla, P.R.; Garg, A.; Ramana, P.V. Renewable energy technologies for the Indian power sector: Mitigation potential and operational strategies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2002, 6, 481–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, B.; Blanco, H.; Dubash, N.K.; Dukkipati, S.; Khosla, R.; Scrieciu, S.; Stewart, T.; Torres-Gunfaus, M. Multi-criteria decision analysis in policy-making for climate mitigation and development. Clim. Dev. 2019, 11, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathuria, V. Impact of CNG on vehicular pollution in Delhi: A note. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2004, 9, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurjar, B.R.; Ravindra, K.; Nagpure, A.S. Air pollution trends over Indian megacities and their local-to-global implications. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 142, 475–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panday, A.; Bansal, H.O. Green transportation in India: Need analysis and solution. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and Embedded Systems (CARE), Jabalpur, India, 16–18 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Anand, S.; Vrat, P.; Dahiya, R.P. Application of a system dynamics approach for assessment and mitigation of CO2 emissions from the cement industry. J. Environ. Manag. 2006, 79, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Roy, J. Analysing energy intensity trends and decoupling of growth from energy use in Indian manufacturing industries during 1973–1974 to 2011–2012. Energy Effic. 2017, 10, 925–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, W.R., III; Hasanbeigi, A.; Sathaye, J.; Xu, T. Assessment of energy efficiency improvement and CO2 emission reduction potentials in India’s cement and iron & steel industries. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- <monospace>J</monospace>umani, S.; Rao, S.; Machado, S.; Prakash, A. Big concerns with small projects: Evaluating the socio-ecological impacts of small hydropower projects in India. Ambio 2017, 46, 500–511. [Google Scholar]
- Yuksel, I. Hydroelectric power in developing countries. Energy Sources Part B Econ. Plan. Policy 2009, 4, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkon, M.; Urpelainen, J. Trust in Government and Subsidy Reform: Evidence from a Survey of Indian Farmers. Stud. Comp. Int. Dev. 2018, 53, 449–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, J.K.; Ramanathan, R. Linkages among energy, agriculture and environment in rural India. Energy Econ. 1999, 21, 561–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, C.A.; Shah, T. Groundwater overdraft reduction through agricultural energy policy: Insights from India and Mexico. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2004, 20, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halsnæs, K.; Verhagen, J. Development based climate change adaptation and mitigation—Conceptual issues and lessons learned in studies in developing countries. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2007, 12, 665–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devasenapathy, P.; Senthilkumar, G.; Shanmugam, P.M. Energy management in crop production. Indian J. Agron. 2009, 54, 80–89. [Google Scholar]
- Bassi, N. Irrigation and energy nexus solar pumps are not viable. Econ. Political Wkly. 2015, 50, 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Closas, A.; Rap, E. Solar-based groundwater pumping for irrigation: Sustainability, policies, and limitations. Energy Policy 2017, 104, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, M.K. Reforming fossil fuel prices in India: Dilemma of a developing economy. Energy Policy 2016, 92, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Bhattacharya, R.N. Causality between energy consumption and economic growth in India: A note on conflicting results. Energy Econ. 2004, 26, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Mallick, H.; Mahalik, M.K.; Sadorsky, P. The role of globalization on the recent evolution of energy demand in India: Implications for sustainable development. Energy Econ. 2016, 55, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdouli, M.; Kamoun, O.; Hamdi, B. The impact of economic growth, population density, and FDI inflows on CO2 emissions in BRICTS countries: Does the Kuznets curve exist? Empir. Econ. 2018, 54, 1717–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Moerkerk, M.; Crijns-Graus, W. A comparison of oil supply risks in EU, US, Japan, China and India under different climate scenarios. Energy Policy 2016, 88, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lin, S.X. Do emerging markets matter in the world oil pricing system? Evidence of imported crude by China and India. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 4624–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, P.; Hari, K. Bio-Fuel Market Scenario in India. Sugar Tech 2011, 13, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Biswas, P.; Pohit, S. What ails India’s biodiesel programme? Energy Policy 2013, 52, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gmünder, S.M.; Zah, R.; Bhatacharjee, S.; Classen, M.; Mukherjee, P.; Widmer, R. Life cycle assessment of village electrification based on straight jatropha oil in Chhattisgarh, India. Biomass Bioenergy 2010, 34, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Elzen, M.; Lucas, P.; van Vuuren, D. Abatement costs of post-Kyoto climate regimes. Energy Policy 2005, 33, 2138–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.M.; Kirkman, G.A. Costs of certified emission reductions under the Clean Development Mechanism of the Kyoto Protocol. Energy Econ. 2015, 47, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, M.K.; Gupta, S.; Bhandari, P. Annex I commitments: Adverse economic impacts on developing countries: Myth or reality? Energy Policy 2000, 28, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddle, B. Consumption-based accounting and the trade-carbon emissions nexus. Energy Econ. 2018, 69, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, S. An empirical analysis on the adoption of alternative fuel vehicles: The case of natural gas vehicles. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 5865–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Worrell, E. International comparison of CO2 emission trends in the iron and steel industry. Energy Policy 2002, 30, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, U. A cross-country comparison of the building energy consumptions and their trends. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 123, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timilsina, G.R.; Shrestha, A. Transport sector CO2 emissions growth in Asia: Underlying factors and policy options. Energy Policy 2009, 37, 4523–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.; Malik, I.A.; Abdullah, A.B.; Hassan, A.; Awan, U.; Ali, G.; Zaman, K.; Naseem, I. Does financial development contribute to SAARC’S energy demand? from energy crisis to energy reforms. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, W.N.; Chang, T.; Inglesi-Lotz, R.; Gupta, R. The nexus of electricity consumption, economic growth and CO2 emissions in the BRICS countries. Energy Policy 2014, 66, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucher, J.; Peng, Z.R.; Mittal, N.; Zhu, Y.; Korattyswaroopam, N. Urban transport trends and policies in China and India: Impacts of rapid economic growth. Transp. Rev. 2007, 27, 379–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.K. Energy geopolitics and Iran-Pakistan-India gas pipeline. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 3280–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ummadisingu, A.; Soni, M.S. Concentrating solar power—Technology, potential and policy in India. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 5169–5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, I.; Purohit, P. Techno-economic evaluation of concentrating solar power generation in India. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 3015–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höffken, J.I. A closer look at small hydropower projects in India: Social acceptability of two storage-based projects in Karnataka. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 34, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.; Taylor, J.E.; Mahalingam, A. Strategic structure matrix: A framework for explaining the impact of superstructure organizations on the diffusion of wind energy infrastructure. Energy Policy 2013, 63, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.; Painuly, J.P. Diffusion of renewable energy technologies-barriers and stakeholders’ perspectives. Renew. Energy 2004, 29, 1431–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.F.; Khan, M.R. Wind power generation in india: Evolution, trends and prospects. Int. J. Renew. Energy Dev. 2013, 2, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenneti, K.; Day, R. Procedural (in)justice in the implementation of solar energy: The case of Charanaka solar park, Gujarat, India. Energy Policy 2015, 86, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J. Management of the agricultural biomass on decentralized basis for producing sustainable power in India. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 3985–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, T.; Bhatt, S.; Shah, R.K.; Talati, J. Groundwater governance through electricity supply management: Assessing an innovative intervention in Gujarat, western India. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painuly, J.P.; Rao, H.; Parikh, J. A rural energy-agriculture interaction model applied to Karnataka state. Energy 1995, 20, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.; Rogers, P.; Lall, U. Demand management of groundwater with monsoon forecasting. Agric. Syst. 2006, 90, 293–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherji, A. Political ecology of groundwater: The contrasting case of water-abundant West Bengal and water-scarce Gujarat, India. Hydrogeol. J. 2006, 14, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, P. Testing viability of cross subsidy using time-variant price elasticities of industrial demand for electricity: Indian experience. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aklin, M.; Bayer, P.; Harish, S.P.; Urpelainen, J. Information and energy policy preferences: A survey experiment on public opinion about electricity pricing reform in rural India. Econ. Gov. 2014, 15, 305–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Garg, A.; Kapshe, M.; Shukla, P.R.; Ghosh, D. Large point source (LPS) emissions from India: Regional and sectoral analysis. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttikunda, S.K.; Goel, R.; Mohan, D.; Tiwari, G.; Gadepalli, R. Particulate and gaseous emissions in two coastal cities—Chennai and Vishakhapatnam, India. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2015, 8, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovacool, B.K.; Brown, M.A. Twelve metropolitan carbon footprints: A preliminary comparative global assessment. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 4856–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadian, R.; Dahiya, R.P.; Garg, H.P. Energy-related emissions and mitigation opportunities from the household sector in Delhi. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 6195–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Baiocchi, G.; Creutzig, F. CO2 Emissions from Direct Energy Use of Urban Households in India. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11312–11320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.K.N.; Reddy, B.S. Substitution of energy carriers for cooking in Bangalore. Energy 1994, 19, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, K.; Iyer, P.P. Decentralized demand-supply matching using community microgrids and consumer demand response: A scenario analysis. Energy 2014, 76, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, B. Energy services for the urban poor: NGO participation in slum electrification in India. Environ. Plan. C Gov. Policy 2010, 28, 1011–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirmani, S.; Jamil, M.; Akhtar, I. Economic feasibility of hybrid energy generation with reduced carbon emission. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2018, 12, 934–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Parikh, J. Transport scenarios in two metropolitan cities in India: Delhi and Mumbai. Energy Convers. Manag. 2004, 45, 2603–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibin, K.T.; Gunasekaran, A.; Papadopoulos, T.; Childe, S.J.; Dubey, R.; Singh, T. Energy sustainability in operations: An optimization study. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 86, 2873–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Purohit, I.; Purohit, P.; Shekhar, S. Evaluating the potential of concentrating solar power generation in Northwestern India. Energy Policy 2013, 62, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhu, S.; Nehra, V.; Luthra, S. Investigation of feasibility study of solar farms deployment using hybrid AHP-TOPSIS analysis: Case study of India. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 73, 496–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, M.A.; Iyer, M.; Meyers, S.; Letschert, V.E.; McMahon, J.E. Potential benefits from improved energy efficiency of key electrical products: The case of India. Energy Policy 2008, 36, 3467–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usha Rao, K.; Kishore, V.V.N. Wind power technology diffusion analysis in selected states of India. Renew. Energy 2009, 34, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulal, H.B.; Akbar, S. Greenhouse gas emission reduction options for cities: Finding the “Coincidence of Agendas” between local priorities and climate change mitigation objectives. Habitat Int. 2013, 38, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quitzow, R. Assessing policy strategies for the promotion of environmental technologies: A review of India’s National Solar Mission. Res. Policy 2015, 44, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, T.; Deshmukh, S.G.; Kaushik, S.C. Efficiency evaluation of the state owned electric utilities in India. Energy Policy 2006, 34, 2788–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halsnæs, K.; Garg, A. Assessing the Role of Energy in Development and Climate Policies-Conceptual Approach and Key Indicators. World Dev. 2011, 39, 987–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmacharya, S.B.; de Vries, L.J. Addressing the supply-demand gap in India’s electricity market: Long and short-term policy options. In Proceedings of the 2009 Second International Conference on Infrastructure Systems and Services: Developing 21st Century Infrastructure Networks (INFRA), SNN, Nager, India, 9–11 December 2009; IEEE: Tamil Nadu, India, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rohankar, N.; Jain, A.K.; Nangia, O.P.; Dwivedi, P. A study of existing solar power policy framework in India for viability of the solar projects perspective. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 56, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongia, R.; Banerjee, R. Price of power in India. Energy Policy 1998, 26, 557–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Sathaye, J.; Barnes, D. Urban household energy use in India: Efficiency and policy implications. Energy Policy 1998, 26, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sishodia, R.P.; Shukla, S.; Wani, S.P.; Graham, W.D.; Jones, J.W. Future irrigation expansion outweigh groundwater recharge gains from climate change in semi-arid India. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 725–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosla, R.; Dukkipati, S.; Dubash, N.K.; Sreenivas, A.; Cohen, B. Towards methodologies for multiple objective-based energy and climate policy. Econ. Political Wkly. 2015, 50, 49–59. [Google Scholar]
- Kale, S.S. Current reforms: The politics of policy change in India’s electricity sector. Pac. Aff. 2004, 77, 467–491. [Google Scholar]
- Chaliganti, R.; Müller, U. Policy Discourses and Environmental Rationalities Underpinning India’s Biofuel Programme. Environ. Policy Gov. 2016, 26, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.; Ruysenaar, S. Burning desires: Untangling and interpreting ‘pro-poor’ biofuel policy processes in India and South Africa. Environ. Plan. A 2014, 46, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K. A Comparative Policy Analysis of Coalition Strategies: Case Studies of Nuclear Energy and Forest Management in India. J. Comp. Policy Anal. Res. Pract. 2014, 16, 356–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, K.L.; Katz, J.; Costie, D.P.; Heikkila, T.; Weible, C.M. A dominant coalition and policy change: An analysis of shale oil and gas politics in India. J. Environ. Policy Plan. 2018, 20, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depuru, S.S.; Wang, L.; Devabhaktuni, V. Electricity theft: Overview, issues, prevention and a smart meter based approach to control theft. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giljum, S.; Behrens, A.; Hinterberger, F.; Lutz, C.; Meyer, B. Modelling scenarios towards a sustainable use of natural resources in Europe. Environ. Sci. Policy 2008, 11, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Sathaye, J.; Akbari, H.; Garg, V.; Tetali, S. Quantifying the direct benefits of cool roofs in an urban setting: Reduced cooling energy use and lowered greenhouse gas emissions. Build. Environ. 2012, 48, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandra, P. Modern energy access to all in rural India: An integrated implementation strategy. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 7803–7814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhu, S.; Nehra, V.; Luthra, S. Identification and analysis of barriers in implementation of solar energy in Indian rural sector using integrated ISM and fuzzy MICMAC approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 62, 70–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raha, D.; Mahanta, P.; Clarke, M.L. The implementation of decentralised biogas plants in Assam, NE India: The impact and effectiveness of the National Biogas and Manure Management Programme. Energy Policy 2014, 68, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapar, S.; Sharma, S.; Verma, A. Economic and environmental effectiveness of renewable energy policy instruments: Best practices from India. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 66, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Kathuria, V. The effect of regulatory governance on efficiency of thermal power generation in India: A stochastic frontier analysis. Energy Policy 2016, 89, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creutzig, F.; Roy, J.; Lamb, W.F.; Azevedo, I.M.; De Bruin, W.B.; Dalkmann, H.; Edelenbosch, O.Y.; Geels, F.W.; Grubler, A.; Hepburn, C.; et al. Towards demand-side solutions for mitigating climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, T.; Coenen, F.; van den Berg, M. Illustrating the use of concepts from the discipline of policy studies in energy research: An explorative literature review. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2016, 21, 12–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, I.S.; van Daalen, C.E.; Bots, P.W.G. Perspectives on Policy Analysis: A Framework for Understanding and Design. In Public Policy Analysis: New Developments; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 41–64. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, N.; Howlett, M.; Chindarkar, N. Who coupled which stream(s)? Policy entrepreneurship and innovation in the energy–water nexus in Gujarat, India. Public Adm. Dev. 2020, 40, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, N. Explaining Policy Success Using the Multiple Streams Framework: Political Success Despite Programmatic Failure of the Solar Energy Policy in Gujarat, India. Politics Policy 2021, 49, 1021–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, N. A “review” of policy sciences: Bibliometric analysis of authors, references, and topics during 1970–2017. Policy Sci. 2017, 50, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, N. Promoting Policy Innovation for Sustainability: Leaders, Laggards and Learners in the Indian Electricity Transition; National University of Singapore: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Moss, T.; Becker, S.; Naumann, M. Whose energy transition is it, anyway? Organisation and ownership of the Energiewende in villages, cities and regions. Local Environ. 2015, 20, 1547–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Späth, P.; Rohracher, H. ‘Energy regions’: The transformative power of regional discourses on socio-technical futures. Res. Policy 2010, 39, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.L. The Diffusion of Innovations among the American States. Am. Political Sci. Rev. 1969, 63, 880–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, R. What is lesson-drawing? J. Public Policy 1991, 11, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, N. Policy Diffusion Through Multiple Streams: The (Non-)Adoption of Energy Conservation Building Code in India. Policy Stud. J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, R.; Sanger, J. The Text Mining Handbook: Advanced Approaches in Analyzing Unstructured Data; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Montes-y-Gómez, M.; Gelbukh, A.; López-López, A. Discovering association rules in semi-structured data sets. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Knowledge Discovery from Distributed, Dynamic, Heterogeneous, Autonomous Data and Knowledge Source at 17th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intel-ligence (IJCAI’2001), Seattle, WA, USA, 4–10 August 2001; AAAI Press: Menlo Park, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Allahyari, M.; Pouriyeh, S.; Assefi, M.; Safaei, S.; Trippe, E.D.; Gutierrez, J.B.; Kochut, K. A brief survey of text mining: Classification, clustering and extraction techniques. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.02919. [Google Scholar]
- Collobert, R.; Weston, J.; Bottou, L.; Karlen, M.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Kuksa, P. Natural language processing (almost) from scratch. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2493–2537. [Google Scholar]
- Blei, D.M.; Ng, A.Y.; Jordan, M.I. Latent dirichlet allocation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2003, 3, 993–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Ravi, K.; Ravi, V. A survey on opinion mining and sentiment analysis: Tasks, approaches and applications. Knowl. -Based Syst. 2015, 89, 14–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowlin, M.C. Modeling Issue Definitions Using Quantitative Text Analysis. Policy Stud. J. 2016, 44, 309–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawcett, P.; Jensen, M.J.; Ransan-Cooper, H.; Duus, S. Explaining the “ebb and flow” of the problem stream: Frame conflicts over the future of coal seam gas (“fracking”) in Australia. J. Public Policy 2019, 39, 521–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohr, J. Key events and challenges: A computational text analysis of the 115th house of representatives on Twitter. Environ. Politics 2021, 30, 399–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollibaugh, G.E. The Use of Text as Data Methods in Public Administration: A Review and an Application to Agency Priorities. J. Public Adm. Res. Theory 2018, 29, 474–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, C.A.; Kamkhaji, J.C.; Radaelli, C.M.; Taffoni, G. Measuring design diversity: A new application of Ostrom’s rule types. Policy Stud. J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, N.; Howlett, M. “Measuring the Mix” of Policy Responses to COVID-19: Comparative Policy Analysis Using Topic Modelling. J. Comp. Policy Anal. Res. Pract. 2021, 23, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, N.; Howlett, M. Combining internal and external evaluations within a multilevel evaluation framework: Computational text analysis of lessons from the Asian Development Bank. Evaluation 2019, 25, 366–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.C.; Cheung, L.Y.; Wang, S.; Li, V.O. Stakeholder concerns of air pollution in Hong Kong and policy implications: A big-data computational text analysis approach. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 101, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Hansen, F.; Callaghan, M.W.; Lee, Y.T.; Leipprand, A.; Flachsland, C.; Minx, J.C. Who cares about coal? Analyzing 70 years of German parliamentary debates on coal with dynamic topic modeling. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2021, 72, 101869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, R.; Bardhan, R.; Reiner, D.M.; Miller, J.R. Political, economic, social, technological, legal and environmental dimensions of electric vehicle adoption in the United States: A social-media interaction analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 152, 111707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Source | Publications | Citations |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Policy | 317 | 9448 |
| Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews | 130 | 4479 |
| Energy | 73 | 1888 |
| Energy Economics | 45 | 1446 |
| Energy for Sustainable Development | 41 | 637 |
| Renewable Energy | 33 | 754 |
| The Journal of Cleaner Production | 33 | 472 |
| Energy Procedia | 29 | 123 |
| Economic and Political Weekly | 27 | 131 |
| International Journal of Global Energy Issues | 25 | 66 |
| Authors | Title | Year | Source | Cites |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Masih A.M.M., Masih R. | Energy consumption, real income and temporal causality: Results from a multi-country study based on cointegration and error-correction modelling techniques | 1996 | Energy Economics | 419 |
| Dreze J., Sen A. | An uncertain glory: India and its contradictions | 2013 | - | 414 |
| Jebaraj S., Iniyan S. | A review of energy models | 2006 | Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews | 378 |
| Nejat P., Jomehzadeh F., Taheri M.M., Gohari M., Abd. Majid M.Z. | A global review of energy consumption, CO2 emissions and policy in the residential sector (with an overview of the top ten CO2 emitting countries) | 2015 | Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews | 347 |
| Leach M., Scoones I., Stirling A. | Dynamic sustainabilities: Technology, environment, social justice | 2010 | - | 335 |
| Pao H.-T., Tsai C.-M. | CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in BRIC countries | 2010 | Energy Policy | 283 |
| Ghosh S. | Electricity consumption and economic growth in India | 2002 | Energy Policy | 281 |
| Sorda G., Banse M., Kemfert C. | An overview of biofuel policies across the world | 2010 | Energy Policy | 279 |
| De Fraiture C., Giordano M., Liao Y. | Biofuels and implications for agricultural water use: Blue impacts of green energy | 2008 | Water Policy | 265 |
| Ackerman J. | Co-governance for accountability: Beyond “exit” and “voice” | 2004 | World Development | 223 |
| State | Occurrences |
|---|---|
| Gujarat | 44 |
| Tamil Nadu | 37 |
| Maharashtra | 30 |
| Karnataka | 28 |
| Uttar Pradesh | 27 |
| Andhra Pradesh | 25 |
| Rajasthan | 25 |
| Odisha | 22 |
| Kerala | 20 |
| City | Occurrences |
|---|---|
| (New) Delhi | 90 |
| Mumbai | 31 |
| Bengaluru | 18 |
| Chennai | 9 |
| Hyderabad | 9 |
| Ahmedabad | 7 |
| Vishakhapatnam | 6 |
| Pune | 5 |
| Kolkata | 5 |
| Policy Area | Occurrences |
|---|---|
| Energy policy | 217 |
| Bioenergy/biofuel policy | 37 |
| Energy conservation/efficiency policy | 28 |
| Electricity policy | 17 |
| New (gas) exploration licensing policy | 10 |
| Solar power policy | 3 |
| Oil policy | 3 |
| Climate (change) policy | 96 |
| Climate change mitigation policy | 26 |
| Emissions reduction policy | 7 |
| Low carbon policy | 4 |
| Economic policy | 22 |
| Development policy | 18 |
| Fiscal policy | 8 |
| Industrial policy | 7 |
| Trade policy | 5 |
| Environmental policy | 36 |
| Foreign policy | 24 |
| Science, technology, and innovation policy | 5 |
| Social policy | 5 |
| Urban policy | 5 |
| Agricultural policy | 4 |
| Term | Occurrences |
|---|---|
| Pertaining to policy relevance | |
| Policy implication | 83 |
| Policy recommendation | 38 |
| Policy relevance | 9 |
| Policy prescription | 8 |
| Policy perspective | 12 |
| Policy suggestion | 7 |
| Pertaining to policy analysis | |
| Policy option | 39 |
| Policy analysis | 23 |
| Policy scenario | 20 |
| Policy choice | 7 |
| Policy alternative | 6 |
| Policy modelling | 3 |
| Pertaining to policy instruments | |
| Policy measure | 49 |
| Policy initiative | 41 |
| Policy intervention | 41 |
| Policy instrument | 36 |
| Policy mechanism | 10 |
| Policy tool | 9 |
| Policy action | 7 |
| Pertaining to policy objectives | |
| Policy issue | 32 |
| Policy challenge | 4 |
| Policy formulation | 17 |
| Policy goal | 15 |
| Policy objective | 15 |
| Policy priority | 6 |
| Policy framework | 43 |
| Policy approach | 9 |
| Policy strategy | 8 |
| Policy design | 7 |
| Pertaining to the policy process | |
| Policy-making | 40 |
| Policy change | 29 |
| Policy decision | 18 |
| Policy reform | 11 |
| Policy process | 4 |
| Pertaining to implementation | |
| Implementation | 266 |
| Policy implementation | 10 |
| Implementation strategy | 8 |
| Project implementation | 4 |
| Pertaining to evaluation | |
| Evaluation | 120 |
| Outcome | 80 |
| Effectiveness | 64 |
| Efficacy | 14 |
| Impact assessment | 11 |
| Policy failure | 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goyal, N. Limited Demand or Unreliable Supply? A Bibliometric Review and Computational Text Analysis of Research on Energy Policy in India. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13421. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132313421
Goyal N. Limited Demand or Unreliable Supply? A Bibliometric Review and Computational Text Analysis of Research on Energy Policy in India. Sustainability. 2021; 13(23):13421. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132313421
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoyal, Nihit. 2021. "Limited Demand or Unreliable Supply? A Bibliometric Review and Computational Text Analysis of Research on Energy Policy in India" Sustainability 13, no. 23: 13421. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132313421
APA StyleGoyal, N. (2021). Limited Demand or Unreliable Supply? A Bibliometric Review and Computational Text Analysis of Research on Energy Policy in India. Sustainability, 13(23), 13421. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132313421






