A Comprehensive Exploration on Pollution Characteristics and Ecological Risks of Heavy Metals in Surface Paddy Soils around a Large Copper Smelter, Southeast China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
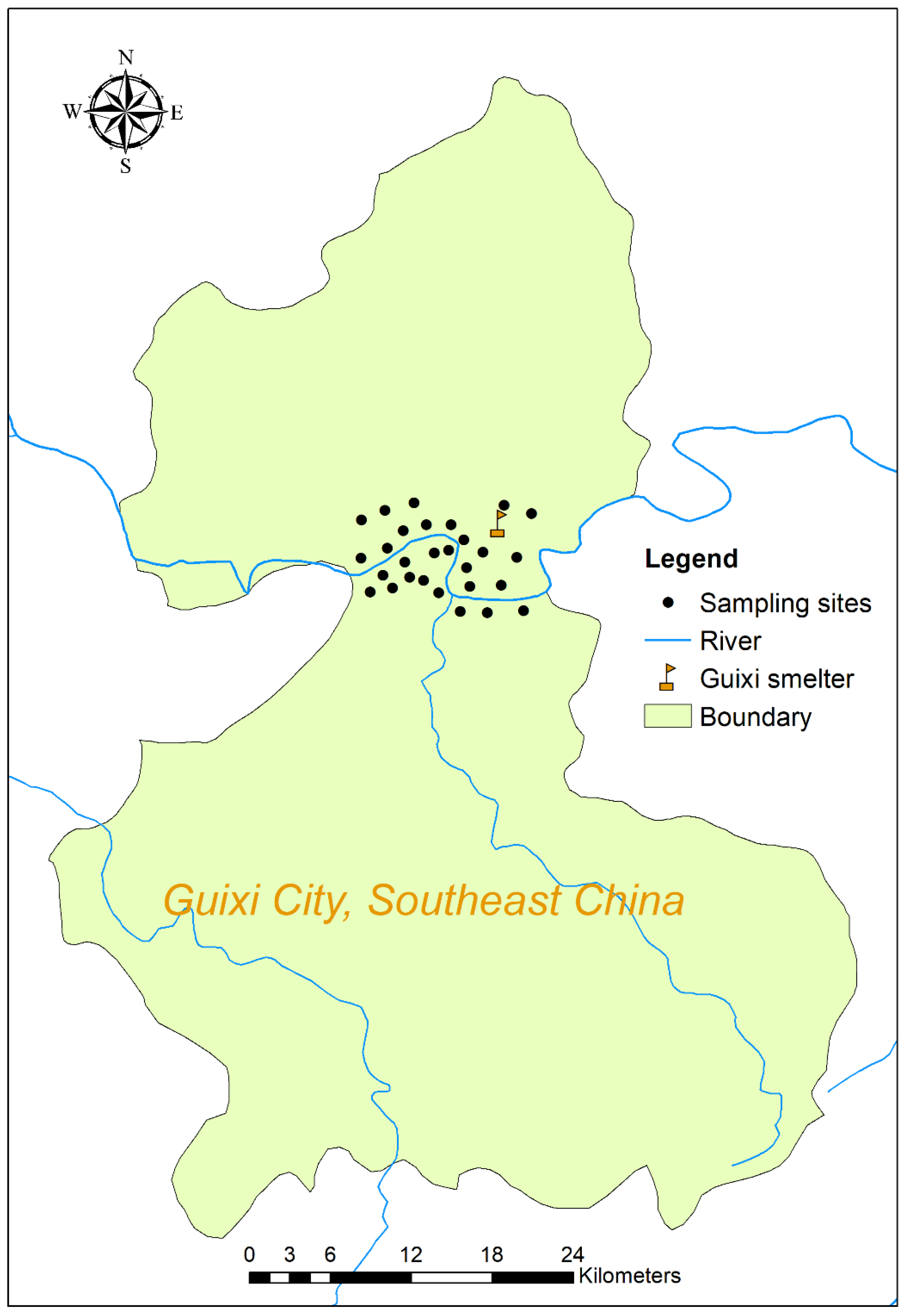
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Soil Sampling and Analysis
2.3. Soil Heavy Metal Pollution Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
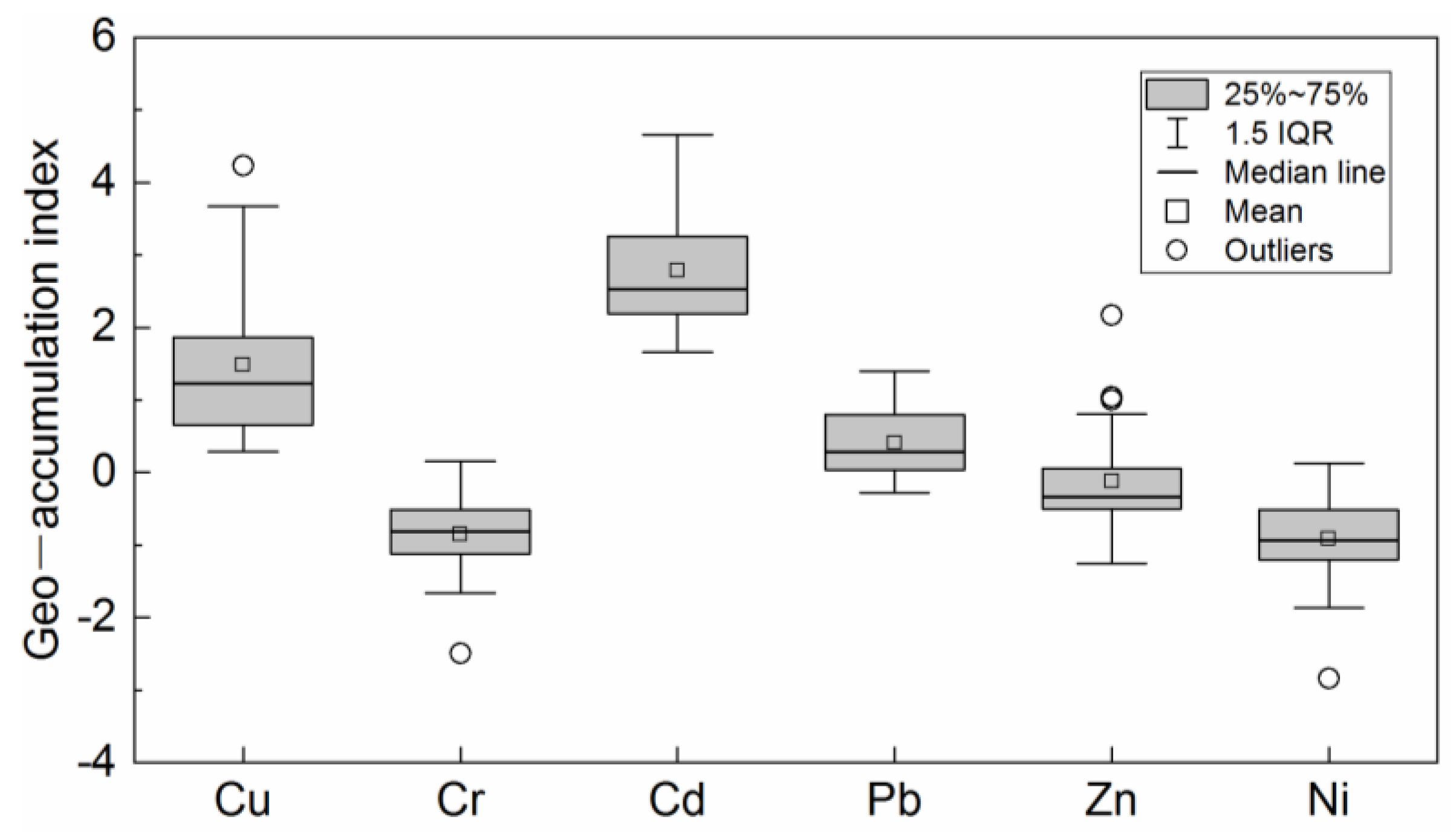
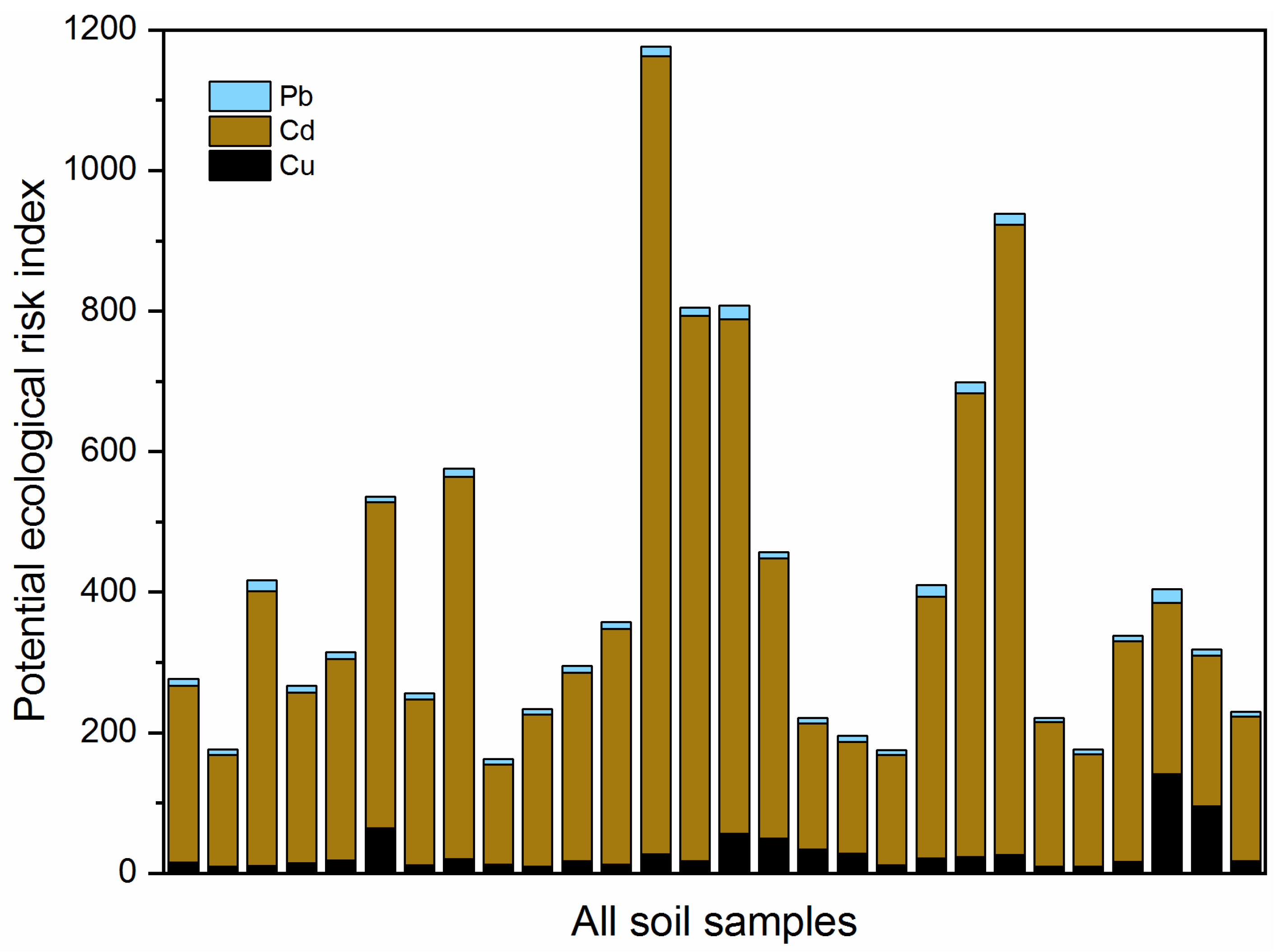
3.1. Characteristics of Heavy Metal Pollution
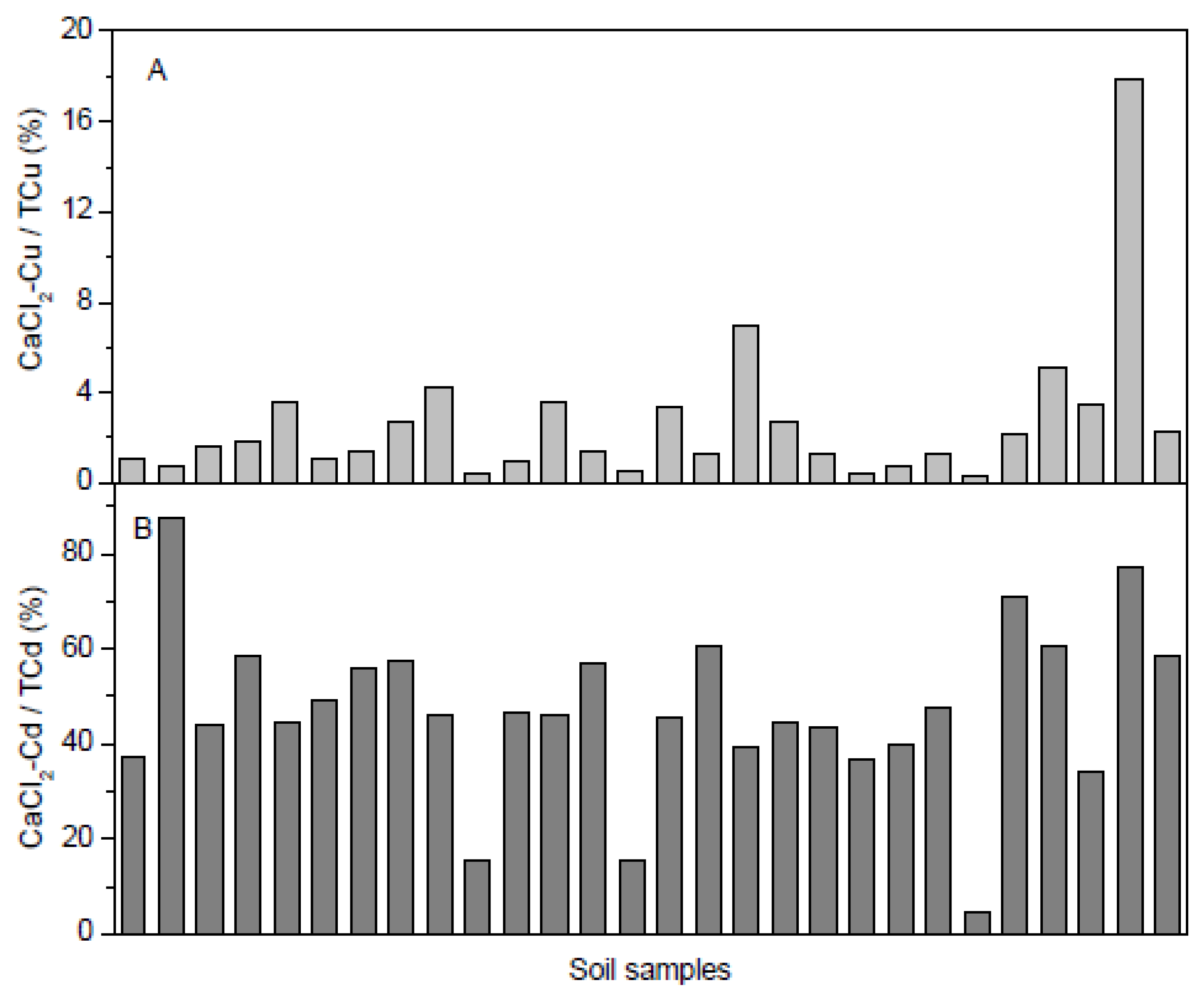
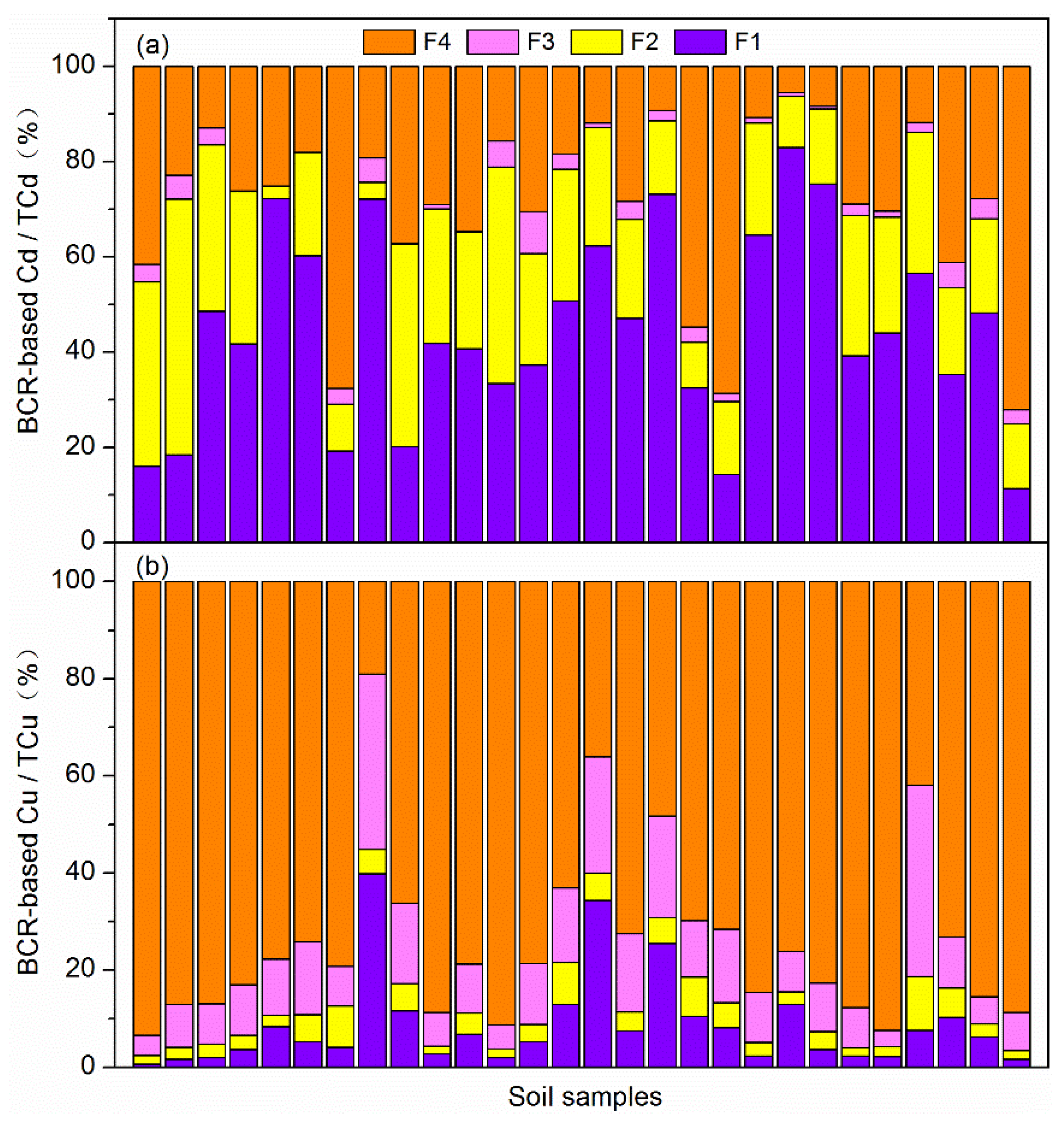
3.2. Speciation Analysis of Cu and Cd in Soil
3.3. Relationships of Cu and Cd Species with Soil Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Pollution Characteristics and Risk Assessment
4.2. Effects of Soil Properties on Heavy Metal Species
4.3. Implications for Sustainable Agricuture and Heavy Metal Contamination Control
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Koda, E.; Miszkowska, A.; Sieczka, A.; Osiński, P. Heavy metals contamination within restored landfill site in Poland. Environ. Geotech. 2020, 7, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gworek, B.; Dmuchowski, W.; Koda, E.; Marecka, M.; Baczewska, A.H.; Brągoszewska, P.; Sieczka, A.; Osiński, P. Impact of the Municipal Solid Waste Łubna Landfill on Environmental Pollution by Heavy Metals. Water 2016, 8, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Yang, F.; Li, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, F.; Ba, Y.; Cui, L.; Sun, L.; Lv, T.; Wang, N.; et al. Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of agricultural soil near a smelter in an industrial city in China. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2020, 30, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Ding, C.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X. A tillering application of zinc fertilizer based on basal stabilization reduces Cd accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2019, 167, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhong, T.; Liu, L.; Ouyang, X. Impact of soil heavy metal pollution on food safety in China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, M.; Hu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhou, J. Study of the bioavailability of heavy metals from atmospheric deposition on the soil-pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 362, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.J.; Li, Z.Q.; Huang, P.; Tao, C. Chemical forms of heavy metals in sewage-irrigated paddy soil in Guixi city. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2004, 23, 683–686. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J. Present situation and prospects of technologies for remediation of heavy-metal-contaminated soil around Jiangxi Guixi Smelter. World Environ. 2016, 161, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, H.; Fan, Y.; Yang, J.; Xu, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, Z. In situ phytoextraction of copper and cadmium and its biological impacts in acidic soil. Chemosphere 2016, 161, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Cui, H.; Zheng, X.; Zhu, Z.; Liang, J.; Zhou, J. Immobilization of copper and cadmium by hydroxyapatite combined with phytoextraction and changes in microbial community structure in a smelter-impacted soil. Rsc. Adv. 2016, 6, 103955–103964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, N.F.; El Zokm, G.M.; Okbah, M.A. Risk assessment and chemical fractionation of selected elements in surface sediments from Lake Qarun, Egypt using modified BCR technique. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabarrón, M.; Zornoza, R.; Martínez-Martínez, S.; Muñoz, V.A.; Faz, Á.; Acosta, J.A. Effect of land use and soil properties in the feasibility of two sequential extraction procedures for metals fractionation. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, L.; He, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Tsang, D.; Hu, Q.; Hu, B.; Tang, Y. Evaluation of the BCR sequential extraction scheme for trace metal fractionation of alkaline municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ennaji, W.; Barakat, A.; Baghdadi, M.E.; Rais, J. Heavy metal contamination in agricultural soil and ecological risk assessment in the northeast area of Tadla plain, Morocco. J. Sediment. Environ. 2020, 5, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Ding, C.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, G.; Wang, X. Stability of immobilization remediation of several amendments on cadmium contaminated soils as affected by simulated soil acidification. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 161, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.J.; Xie, X.; Liu, Y.D.; Wang, C.; Yang, M.; Huang, Y. Effects of digestate DOM on chemical behavior of soil heavy metals in an abandoned copper mining areas. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.X.; Zhu, G.; Ge, X.; Xu, G.; Guan, Y. Novel insights into heavy metal pollution of farmland based on reactive heavy metals (RHMs): Pollution characteristics, predictive models, and quantitative source apportionment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 360, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Yuan, Z.; Li, D.; Zheng, M.; Nie, X.; Liao, Y. Effects of soil particle size on the adsorption, distribution, and migration behaviors of heavy metal (loid) s in soil: A review. Environ. Sci. Proc. Imp. 2020, 22, 1596–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaswar, M.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Liu, K.; Mudasir, M.; Lv, Z.; Hou, H.; Lan, X.; Ji, J.; Ahmed, W.; et al. Soil nutrients and heavy metal availability under long-term combined application of swine manure and synthetic fertilizers in acidic paddy soil. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 2093–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Min, F.; Yu, D.; Xin, Z.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Sun, X.; Pan, J. Mean residence times of active and slow soil organic carbon pools in croplands across China. CATENA 2021, 202, 105271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhou, X.; Zeng, M.; Liao, B.; Liu, L.; Yang, W.; Wu, Y.; Qiu, Q.; Wang, Y. Effects of combined amendments on heavy metal accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) planted on contaminated paddy soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 101, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.K. Analytical Methods for Soil and Agro-Chemistry; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.R.; Wang, Z.Q. Soil Analytical Chemistry; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1988. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.; Zhao, W.; Guan, D.X.; Teng, H.H.; Ji, J.; Ma, L.Q. Comparing CaCl2, EDTA and DGT methods to predict Cd and Ni accumulation in rice grains from contaminated soils. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, G. Indice of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhime River. GeoJournal 1969, 2, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Förstner, U.; Ahlf, W.; Calmano, W. Sediment quality objectives and criteria development in Germany. Water Sci. Technol. 1993, 28, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk indice for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.Q.; Ni, S.J.; Tuo, X.G.; Zhang, C.J. Calculation of heavy metals’ toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk indice. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 31, 112–115. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.J.; Ali, A.; DeLaune, R.D. Physico-chemical forms of copper in water and sediments of Lake Pontchartrain basin, USA. Chemosphere 2018, 195, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leech, N.L.; Barret, K.K.C.; Morgan, G. SPSS for Intermediate Statistics; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: New York, NY, USA, 2008; p. 270. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Gong, X.; Liu, C.; Chen, C.; Zeng, H.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Zheng, L. Ecological risk assessment and pollution analysis on the heavy mentals contaminated soil around Guixi smeltery. J. Nanchang Univ. 2015, 39, 96–102. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Giannakis, I.; Emmanouil, C.; Mitrakas, M.; Manakou, V.; Kungolos, A. Chemical and ecotoxicological assessment of sludge-based biosolids used for corn field fertilization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 3797–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Deng, M.; Japenga, J.; Li, T.; Yang, X.; He, Z. Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of agricultural soils in a typical peri-urban area in southeast China. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 207, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Heavy Metal | Maximum Value (mg·kg−1) | Minimum Value (mg·kg−1) | Mean (mg·kg−1) | CV | Background Value (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | 586.21 | 38.14 | 118.78 | 1.04 | 20.80 |
| Cd | 3.79 | 0.48 | 1.23 | 0.69 | 0.10 |
| Cr | 80.28 | 12.79 | 42.46 | 0.34 | 48.00 |
| Pb | 127.00 | 39.79 | 67.86 | 0.38 | 32.10 |
| Zn | 465.03 | 43.30 | 110.72 | 0.75 | 69.10 |
| Ni | 31.09 | 3.99 | 16.66 | 0.43 | 19.00 |
| Dependent Variable | Independent Variable | Linear Regression Model | Adjusted R2 | p Value (F-Test) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCd | SOC | TCd = 0.11 × SOC − 0.04 | 0.14 | 0.029 * |
| ResC | TCd = 0.12 × ResC + 0.32 | 0.16 | 0.019 * | |
| F2Cd | SOC | F2Cd = 0.01 × SOC − 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.034 * |
| ResC | F2Cd = 0.01 × ResC − 0.00 | 0.17 | 0.018 * | |
| CEC | F2Cd = 0.02 × CEC − 0.03 | 0.29 | 0.002 ** | |
| F3Cd | CEC | F3Cd = 0.001 × CEC + 0.00 | 0.14 | 0.028 * |
| F4Cd | CEC | F4Cd = 0.01 × CEC + 0.01 | 0.29 | 0.002 ** |
| TCu | TK | TCu = –14.62 × TK + 427.10 | 0.57 | 0.000 ** |
| CaCl2Cu | TK | CaCl2Cu = −1.26 × TK + 31.66 | 0.33 | 0.001 ** |
| F1Cu | TK | F1Cu = −1.41 × TK + 36.43 | 0.48 | 0.000 ** |
| F2Cu | TK | F2Cu = −0.77 × TK + 20.17 | 0.29 | 0.002 ** |
| F3Cu | TK | F3Cu = −1.53 × TK + 41.54 | 0.63 | 0.000 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Li, L.; Guo, N.; Xin, Z.; Li, X.; Sun, X.; Li, Y. A Comprehensive Exploration on Pollution Characteristics and Ecological Risks of Heavy Metals in Surface Paddy Soils around a Large Copper Smelter, Southeast China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13359. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132313359
Wang X, Li L, Guo N, Xin Z, Li X, Sun X, Li Y. A Comprehensive Exploration on Pollution Characteristics and Ecological Risks of Heavy Metals in Surface Paddy Soils around a Large Copper Smelter, Southeast China. Sustainability. 2021; 13(23):13359. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132313359
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiyang, Liang Li, Naijia Guo, Zaijun Xin, Xiaohui Li, Xiaoyan Sun, and Ya Li. 2021. "A Comprehensive Exploration on Pollution Characteristics and Ecological Risks of Heavy Metals in Surface Paddy Soils around a Large Copper Smelter, Southeast China" Sustainability 13, no. 23: 13359. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132313359
APA StyleWang, X., Li, L., Guo, N., Xin, Z., Li, X., Sun, X., & Li, Y. (2021). A Comprehensive Exploration on Pollution Characteristics and Ecological Risks of Heavy Metals in Surface Paddy Soils around a Large Copper Smelter, Southeast China. Sustainability, 13(23), 13359. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132313359






