The Role of Research and Innovation in Europe for the Decarbonisation of Waterborne Transport
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- to provide an overview of waterborne transport projects focusing on decarbonisation, financed through the latest European Framework Programmes (FPs) for research and innovation through a quantitative assessment;
- to qualitatively assess the related project’s technologies and measures in the areas of control and reduction of waterborne CO2 emissions; and,
- to identify research gaps which will help with providing relevant recommendations for future research and policy developments.
2. Material and Methods
- Hull design which includes projects focusing on lightweight composite materials for structural components, innovative hull repair methods and hull surface protection;
- Power and propulsion which covers projects focusing on wind assisted propulsion, increases in engine efficiency and recycling of waste heat for use elsewhere in the vessel;
- Fuels and alternative energy sources which covers projects focusing on the use of electrification (batteries, hybrid systems), use of hydrogen, LNG or compressed natural gas (CNG) or liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) as a fuel;
- Operational measures which identifies projects focusing on topics such as improved vessel navigation, vessel allocation systems and robotic container handling systems;
- Coordination and support measures, including research, networking activities: which covers projects focusing on the dissemination and consolidation of research in the waterborne transport sector, as well as planning and investigating future strategy for the sector, including both vessel and port design.
3. Results
3.1. Quantitative Assessment
3.2. Qualitative Assessment
3.2.1. Sub-Theme 1—Hull Design
3.2.2. Sub-Theme 2—Power and Propulsion
3.2.3. Sub-Theme 3—Fuels and Alternative Energy Sources
3.2.4. Sub-Theme 4—Operational Measures
3.2.5. Sub-Theme 5—Coordination and Support Measures
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Glossary
| ATU | After Treatment Unit |
| CNG | Compressed natural gas |
| CORSIA | Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme for International Aviation |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease 2019 |
| CPC | Cooperative patent classification |
| DG MOVE | Directorate-General for Mobility and Transport |
| DG RTD | Directorate-General for Research and Innovation |
| EC | European Commission |
| EEDI | Energy Efficiency Design Index |
| EPO | European patent office |
| EROI | Energy Return of Investment |
| EU | European Union |
| EU-27 | 27 EU Member States |
| EU ETS | EU Emissions Trading System |
| FP | European Framework Programme for research and innovation |
| FP7 | 7th Framework Program for Research |
| GHG | Greenhouse gas |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite Systems |
| H2020 | Horizon 2020 Framework Program for Research and Innovation |
| HFO | Heavy fuel oil |
| ICAO | International Civil Aviation Organisation |
| IMO | International Maritime Organisation |
| JRC | Joint Research Centre |
| LNG | Liquefied natural gas |
| LPG | Liquefied petroleum gas |
| MARPOL | International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships |
| MRV | Monitoring, reporting and verification |
| NASA | National Aeronautics and Space Administration |
| PATSTAT | EPO Worldwide Patent Statistical Database |
| R&I | Research and Innovation |
| REGEX | Regular expression |
| SEEMP | Ship energy efficiency management plan |
| STRIA | Strategic Transport Research and Innovation Agenda |
| TRIMIS | Transport Research and Innovation Monitoring and Information System |
| TRL | Technology readiness level |
| WASP | Wind-assisted ship propulsion |
Appendix A. Regular Expressions (REGEX) Used for Scopus Database Keywords Analysis
| Waterborne Transport Sub-Theme | Regular Expressions |
|---|---|
| Hull design | ((DOCTYPE(ar) or DOCTYPE(cp)) and TITLE-ABS ((“hull design” or “hull structure” or “Hull weight” or “Bulbous bow” or “Hull shape”) and (boat or ship or ferry or vessel) and not “electric field”) AND PUBYEAR > 2009 AND PUBYEAR < 2020 and not SUBJAREA(MEDI OR NURS OR VETE OR DENT OR HEAL OR MULT)) |
| Power and propulsion | ((DOCTYPE(ar) or DOCTYPE(cp)) and TITLE-ABS(engine or power or propulsion and (boat or ship or ferry or vessel)) AND PUBYEAR > 2009 AND PUBYEAR < 2020 and not SUBJAREA(MEDI OR NURS OR VETE OR DENT OR HEAL OR MULT)) |
| Fuels and alternative energy sources | ((DOCTYPE(ar) or DOCTYPE(cp)) and TITLE-ABS ((electric or lpg or batter* or hybrid or hydrogen or methanol) and (boat or ship or ferry or vessel) and not “electric field” and not “pressure vessel” and not “spherical vessel”) AND PUBYEAR > 2009 AND PUBYEAR < 2020 and not SUBJAREA(MEDI OR NURS OR VETE OR DENT OR HEAL OR MULT)) |
| Operational measures | ((DOCTYPE(ar) or DOCTYPE(cp)) and TITLE-ABS ((electric or lpg or batter* or hybrid or hydrogen or methanol) and (boat or ship or ferry or vessel) and not “electric field” and not “pressure vessel” and not “spherical vessel”) AND PUBYEAR > 2009 AND PUBYEAR < 2020 and not SUBJAREA(MEDI OR NURS OR VETE OR DENT OR HEAL OR MULT)) |
| Coordination and support measures | ((DOCTYPE(ar) or DOCTYPE(cp)) and TITLE-ABS(standardization or “Market instrument” or Regulation or “Trading market” or “Emission Trading” and (boat or ship or ferry)) AND PUBYEAR > 2009 AND PUBYEAR < 2020 and not SUBJAREA(MEDI OR NURS OR VETE OR DENT OR HEAL OR MULT)) |
References
- UNCTAD. Review of Maritime Transport 2019; United Nations Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Directorate-General for Mobility and Transport; Statistical Pocketbook 2019-Transport in Figures; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2019; Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/transport/facts-fundings/statistics/pocketbook-2019_en (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- European Commission. The EU Blue Economy Report; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- IMO. Fourth IMO GHG Study 2020; International Maritime Organization (IMO): London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Psaraftis, H.N.; Kontovas, C.A. Decarbonization of Maritime Transport: Is There Light at the End of the Tunnel? Sustainability 2021, 13, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, P.; Fancello, G. Towards the IMO’s GHG goals: A critical overview of the perspectives and challenges of the main op-tions for decarbonizing international shipping. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Commission. The European Green Deal, Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the European Council, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions; COM(2019)640 Final; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Sustainable and Smart Mobility Strategy—Putting European transport on track for the future, Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions; COM/2020/789 Final; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Integrating Maritime Transport Emissions in the EU’s Greenhouse gas Reduction policies, Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the European Council, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions; COM(2013) 479 Final; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bouman, E.A.; Lindstad, E.; Rialland, A.I.; Strømman, A.H. State-of-the-art technologies, measures, and potential for reducing GHG emissions from shipping–A review. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 52, 408–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Spence, S.; Chen, H. A comprehensive review on countermeasures for CO2 emissions from ships. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 134, 110222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, R.A.; Kirstein, L.; Merk, O.; Martinez, L.M. Decarbonisation pathways for international maritime transport: A model-based policy impact assessment. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, H.; Ding, Y.; Sui, C. Influence of EEDI (Energy Efficiency Design Index) on ship–engine–propeller matching. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faber, J.; Nelissen, D.; Hon, G.; Wang, H.; Tsimplis, M. Regulated Slow Steaming in Maritime Transport; An assessment of Options, Costs and Benefits: 2012. Available online: https://cedelft.eu/publications/regulated-slow-steaming-in-maritime-transport/ (accessed on 11 August 2021).
- Miola, A.; Ciuffo, B. Estimating air emissions from ships: Meta-analysis of modelling approaches and available data sources. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2242–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wik, C.; Niemi, S. Low emission engine technologies for future tier 3 legislations-options and case studies. J. Shipp. Trade 2016, 1, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindstad, E.; Eskeland, G.S.; Rialland, A.; Valland, A. Decarbonizing Maritime Transport: The Importance of Engine Technology and Regulations for LNG to Serve as a Transition Fuel. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, A.; Mancini, S.; Pensa, C.; Calise, G.; De Luca, F. Flettner Rotor Concept for Marine Applications: A Systematic Study. Int. J. Rotating Mach. 2016, 2016, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chou, T.; Kosmas, V.; Acciaro, M.; Renken, K. A Comeback of Wind Power in Shipping: An Economic and Operational Re-view on the Wind-Assisted Ship Propulsion Technology. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prussi, M.; Scarlat, N.; Acciaro, M.; Kosmas, V. Potential and limiting factors in the use of alternative fuels in the European maritime sector. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 291, 125849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Aboosi, F.Y.; El-Halwagi, M.M.; Moore, M.; Nielsen, R.B. Renewable ammonia as an alternative fuel for the shipping industry. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2021, 31, 100670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaramonti, D.; Talluri, G.; Scarlat, N.; Prussi, M. The challenge of forecasting the role of biofuel in EU transport decarbonisation at 2050: A meta-analysis review of published scenarios. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 139, 110715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psaraftis, H.N. Speed optimization vs speed reduction: The choice between speed limits and a Bunker Levy. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2249. Available online: www.mdpi.com/journal/sustainability (accessed on 1 April 2021). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faber, J.; Huigen, T.; Nelissen, D. Regulating speed: A Short-term Measure to Reduce Maritime GHG Emissions; CE Delft Publication: Delft, The Netherlands, 2017; Available online: www.cedelft.eu (accessed on 25 February 2021).
- Frontier Economics. Reducing the UK Maritime Sector’s Contribution to Climate Change and Air Pollution; Frontier Economics: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lagouvardou, S.; Psaraftis, H.N.; Zis, T. A literature survey on market-based measures for the decarbonization of shipping. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme for International Aviation (CORSIA). Available online: https://www.icao.int/environmental-protection/CORSIA/Pages/default.aspx (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- European Commission. Directive to Enhance Cost-Effective Emission Reductions and Low-Carbon Investments; Directive (EU) 2018/410; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Regulation (EU) 2015/757 of the European Parliament and the Council of 29 April 2015 on the Monitoring, Reporting and Verification of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Maritime Transport, and Amending; Directive 2009/16/EC; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- THETIS-MRV. Available online: https://mrv.emsa.europa.eu/#public/emission-report (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Panagakos, G.; Pessôa, T.D.S.; Dessypris, N.; Barfod, M.B.; Psaraftis, H.N. Monitoring the carbon footprint of dry bulk shipping in the EU: An early assessment of the MRV regulation. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Commission. Strategic Transport Research and Innovation Agenda (STRIA). In Towards Clean, Competitive and Connected Mobility: The Contribution of Transport Research and Innovation to the Mobility Package; Staff Working Document; SWD(2017)223 Final; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tsakalidis, A.; van Balen, M.; Gkoumas, K.; Pekar, F. Catalyzing sustainable transport innovation through policy support and monitoring: The case of TRIMIS and the European green deal. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsakalidis, A.; Gkoumas, K.; Grosso, M.; Pekár, F. TRIMIS: Modular Development of an Integrated Policy-Support Tool for Forward-Oriented Transport Research and Innovation Analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, M.; Marques Dos Santos, F.; Gkoumas, K.; Ortega Hortelano, A.; Stepniak, M.; Tsakalidis, A.; Pekar, F. Waterborne transport in Europe—The role of Research and Innovation in Decarbonization; EUR 30636 EN; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Z.; El Makhloufi, A.; Chen, Y.; Tang, J. Decarbonizing the international shipping industry: Solutions and policy recommendations. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 126, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balcombe, P.; Brierley, J.; Lewis, C.; Skatvedt, L.; Speirs, J.; Hawkes, A.; Staffell, I. How to decarbonise international shipping: Options for fuels, technologies and policies. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 182, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehurek, R.; Sojka, P. Software Framework for Topic modelling with Large Corpora. In Proceedings of the LREC 2010 Workshop on New Challenges for NLP Frameworks. 2010. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.695.4595 (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- Mihalcea, R.; Tarau, P. Textrank: Bringing Order into Text. In Proceedings of the 2004 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. 2004. Available online: https://aclanthology.org/W04-3252.pdf (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- Scopus. 2020. Available online: www.scopus.com (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Gkoumas, K.; Tsakalidis, A. A framework for the taxonomy and assessment of new and emerging transport technologies and trends. Transport 2019, 34, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Héder, M. From NASA to EU: The evolution of the TRL scale in Public Section Innovation. Innov. J. Public Sect. Innov. J. 2017, 22, 3. [Google Scholar]
- De Castro, C.; Carpintero, Ó.; Frechoso, F.; Mediavilla, M.; de Miguel, L.J. A top-down approach to assess physical and ecological limits of biofuels. Energy 2014, 64, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterborne Technology Platform. 2020. Available online: https://www.waterborne.eu/images/documents/201021_SRIA_Zero_Emission_Waterborne_Transport_spread.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2021).
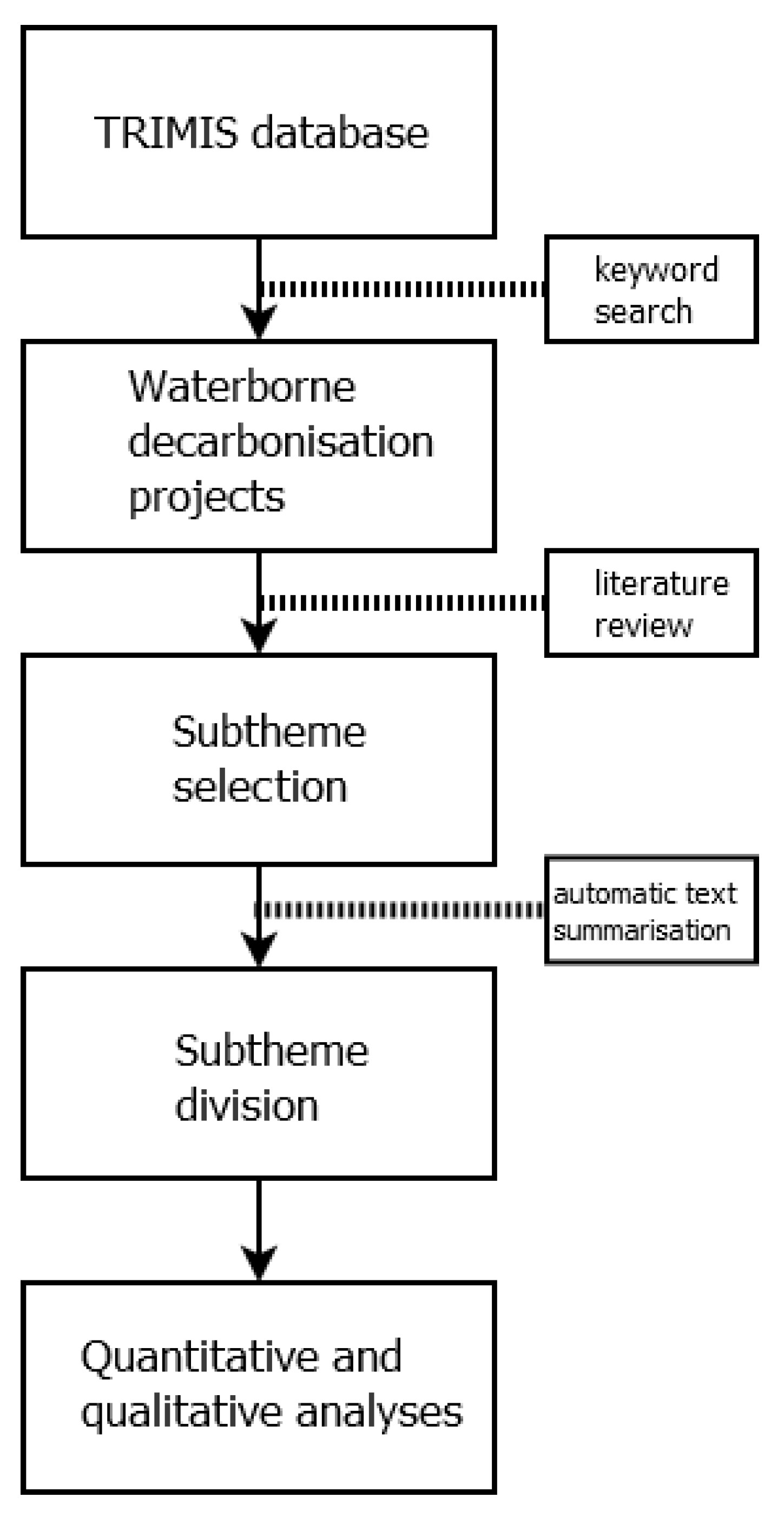

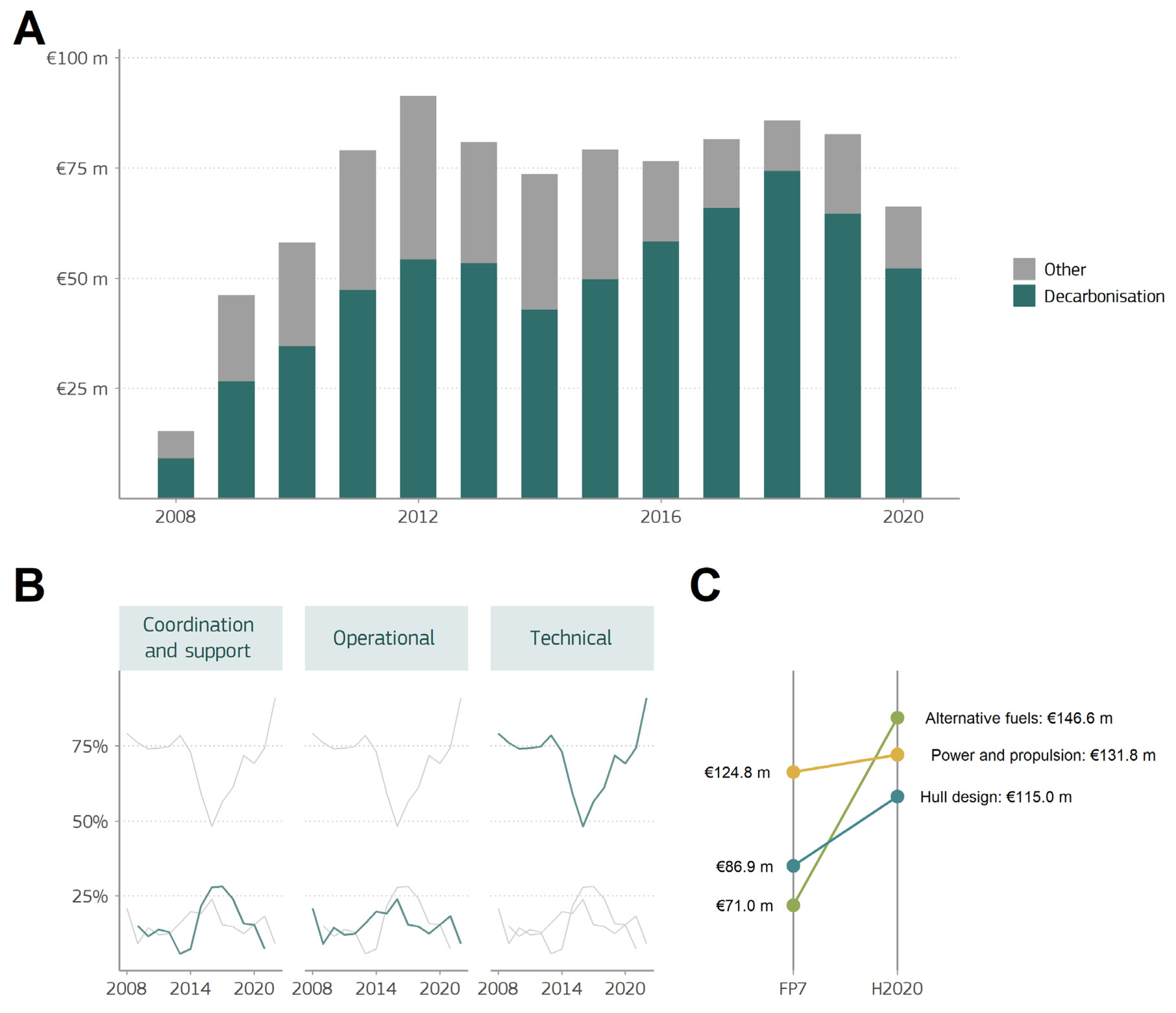
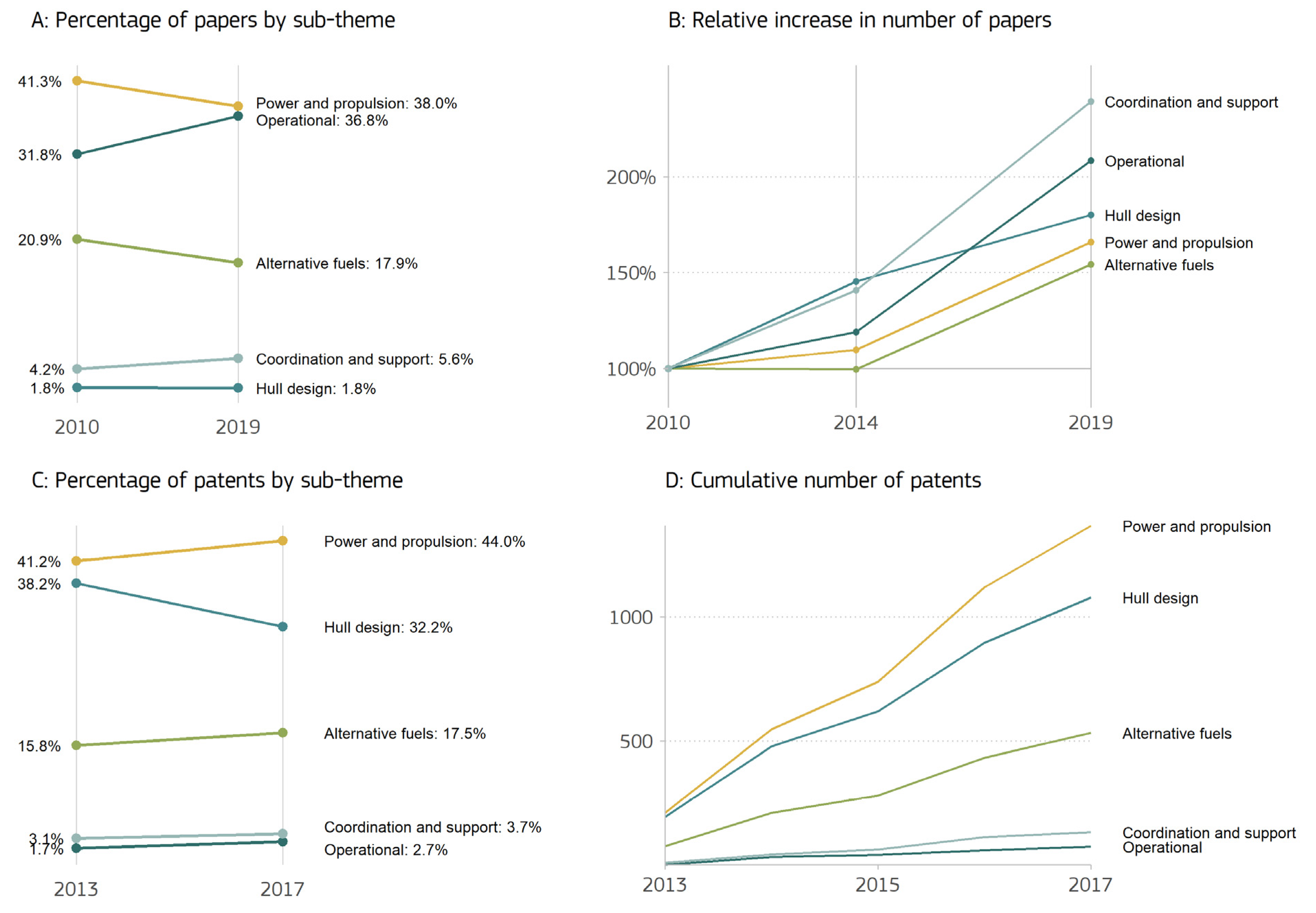
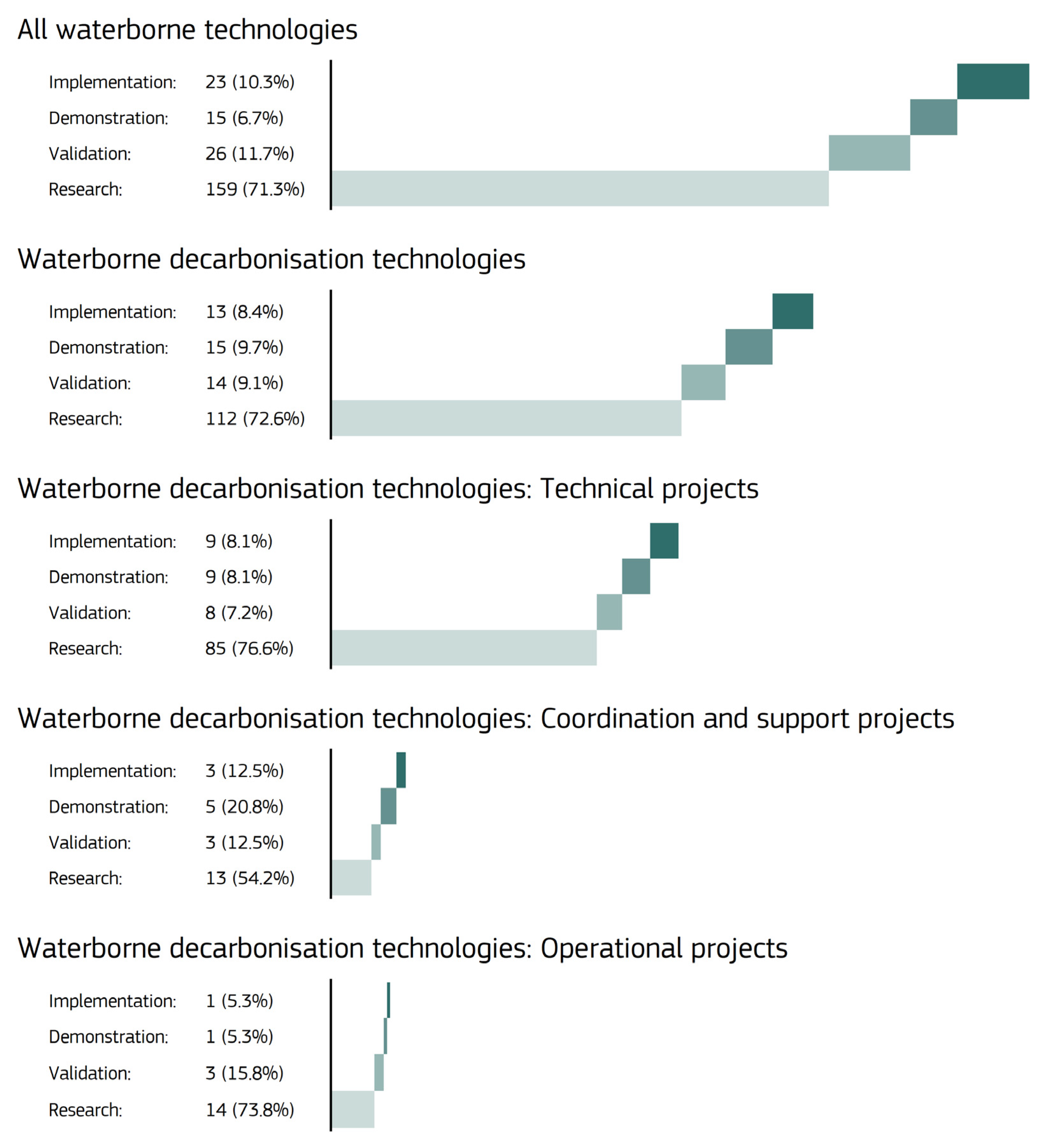
| Subtheme | Project Acronym | Key Themes | Funding Programme | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hull design | ADAM4EVE | Adaptive hull structures; smart materials | FP7-TRANSPORT | 2013–2015 |
| HILDA | Friction stir welding | FP7-TRANSPORT | 2012–2015 | |
| LEAF | Hull surface antifouling technology | FP7-TRANSPORT | 2012–2015 | |
| MOSAIC | High-strength low-alloy steels | FP7-TRANSPORT | 2012–2015 | |
| FIBRESHIP | Fibre reinforce polymers | H2020 | 2017–2020 | |
| COMPA 2GO | Smart repair service | H2020 | 2018–2020 | |
| Power and propulsion | RotorDEMO | Wind assisted propulsion | H2020 | 2017–2018 |
| GFF | Fully electric ferry | H2020 | 2016–2018 | |
| EEECSM-2 | Waste heat to energy | H2020 | 2016–2018 | |
| LeanShips | Increased engine efficiency, emissions abatement technologies | H2020 | 2015–2019 | |
| HERCULES-2 | Increased engine efficiency, fuel-flexible engines | H2020 | 2015–2018 | |
| RotorDEMO | Wind assisted propulsion | H2020 | 2017–2018 | |
| Fuels and alternative energy sources | BB Green | Vessel electrification; reduced hull resistance | FP7-TRANSPORT | 2011–2014 |
| PURE | Fuel-cell auxiliary power unit | FP7-JTI | 2013–2016 | |
| E-ferry | Fully-electric ferry | H2020 | 2015–2019 | |
| MARANDA | Hybrid fuel-cell powertrain system | H2020 | 2017–2021 | |
| HyMethShip | Hydrogen-methanol propulsion system | H2020 | 2018–2021 | |
| Operational measures | RCMS | Robotic container management system | H2020 | 2015–2017 |
| CLOUD-VAS | Cloud-based vessel allocation | H2020 | 2015–2017 | |
| LOGIMATIC | Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS); route planning | H2020 | 2016–2019 | |
| SHIPLYS | Virtual prototyping, life-cycle assessment | H2020 | 2016–2019 | |
| H2H | Safe vessel navigation | H2020 | 2017–2020 | |
| AUTOSHIP | Autonomous vessels | H2020 | 2019–2022 | |
| Coordination and support measures | MESA | Dissemination of research | FP7-TRANSPORT | 2013–2016 |
| VDRConnect | Market assessment of technology | H2020 | 2016–2016 | |
| Prominent | Assessment of technology development areas | H2020 | 2015–2018 | |
| DocksTheFuture | Port technology standardisation, dissemination, networking | H2020 | 2018–2020 | |
| MarTERA | Coordination of technologies | H2020 | 2016–2021 |
| Total Funding Action | Number Projects | Total Funding | EU Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hull design | 34 | EUR 199,585,618 | EUR 147,391,833 |
| Power and propulsion | 43 | EUR 238,664,870 | EUR 163,747,778 |
| Fuels and alternative energy sources | 37 | EUR 196,232,303 | EUR 144,362,260 |
| Operational measures | 22 | EUR 96,995,701 | EUR 80,040,301 |
| Coordination and support measures | 23 | EUR 118,709,260 | EUR 81,659,851 |
| Project Acronym | Key Themes | Expected/Proved Benefits | Main Benefits Estimation |
|---|---|---|---|
| ADAM4EVE | Adaptive hull structures; smart materials | Fuel savings due to: retractable stern flap, lightweight panels, adaptive bulbous bow. | Yearly fuel saving of ~5.6% of retractable stern flap |
| HILDA | Friction stir welding | System and software for using friction stir welding in industrial settings | Potential cost saving per welder per year: -€390 no molten metal injuries; -€160 no UV exposure; -€750 reduced training and certification |
| LEAF | Hull surface antifouling technology | New antifouling technology without biocide emission and low adhesion | Antifouling efficiency for a wide range of organisms; low biocide release rates; lower environmental impact (global warming, acidification, eutrophication potentials; lower production costs. |
| MOSAIC | High-strength low-alloy steels | High Strength Low Alloyed Steels and replacement of ship’s structural parts with composite materials. | Weight savings of ~30%; reduced material wastage and repair costs due to no corrosion of composite materials |
| FIBRESHIP | Fibre reinforce polymers | Design and construction of vessels greater than 500 GT in lightweight fibre reinforce polymers | Up to 36% overall weight reduction; bunkering consumption reduction; lower GHG Emissions; increasing payload/passenger capacity |
| COMPA 2GO | Smart repair service | Composite patch repair for damaged ship pipes | DNV GL certification |
| Project Acronym | Key Themes | Expected/Proved Benefits | Main Benefits Estimation |
|---|---|---|---|
| RotorDEMO | Wind assisted propulsion | Implementation, validation, update of commercialisation plan of Norsepower Rotor Sail Solution in full scale on a RoPax vessel. | Fuel savings of between 231 to 315 tonnes per year, resulting in ~900 tonnes less of CO2 per year (for RoPax) |
| GFF | Fully electric ferry | Implementation, validation, update of commercialisation plan of the GFF for potential customers | Zero emissions ferry able to sail at a 55 km/h speed, with autonomy of 26 km routes in 30 min and fast recharge at port <20 min. Reduced energy consumption by up to 40%. |
| EEECSM-2 | Waste heat to energy | Reuse waste heat to power heating and cooling systems, optimise on board energy circulation | Fuel savings of ~340 tonnes per year, resulting in ~1200 tonnes less of CO2 per year. Cooling operating expenses reduced by up to 94%. |
| LeanShips | Increased engine efficiency, emissions abatement technologies | Multiple technology demonstrators (e.g., conversion of a diesel engine to a dual-fuel engine with methanol) | Energy savings of 12%, CO2 savings of 14%, Reduction of 60% NOx, 70% SOx and 77% PM. |
| HERCULES-2 | Increased engine efficiency, fuel-flexible engines | Fuel flexibility, new materials for high temperature component applications, adaptive control methodologies, achieving near-zero emissions, combining an integrated approach after treatment of exhaust gases. | Up to a 25% reduction in GHG emissions using a fuel flexible engine. A 50% longer engine lifetime using new materials. Total of 80% NOx emissions reduction with the integration of an After Treatment Unit (ATU) into existing engine structure in very large engines. |
| Project Acronym | Key Themes | Expected/Proved Benefits | Main Benefits Estimation |
|---|---|---|---|
| BB Green | Vessel electrification; reduced hull resistance | New vessel to run entirely on renewable energy, with an on-board battery | 40% reduction of hull water resistance |
| PURE | Fuel-cell auxiliary power unit | Delivery of electrical power sufficient to cover power demand from heating/cooling, etc., of a small yacht | ~25% system efficiency, low noise and no smells |
| E-ferry | Fully-electric ferry | Design concept and demonstrate a 100% electric, emission free, medium sized ferry for passengers and cargo in full-scale operation on longer distances than previously seen (>5 nautical miles) | Annual vessel reduction of CO2 emissions by 2000 tonnes, 41,500 kg NOx, 1350 kg SO2 and 2500 kg PM |
| MARANDA | Hybrid fuel-cell powertrain system | Hydrogen fuelled proton exchange membrane fuel cell hybrid powertrain system for maritime applications with a powertrain power of around 165 kW. | ~50% system efficiency, freeze start capabilities from −35 °C, operating temperature from −32° to +50°, fuel cell stack life of 15,000 h |
| HyMethShip | Hydrogen-methanol propulsion system | Develop a hydrogen-methanol ship propulsion system using on-board pre-combustion carbon capture. | Target: GHG emissions by more than 97%, compared to conventional fuels, eliminating SOx and PM emissions. Increased energy efficiency of 45% compared to best available technology |
| Project Acronym | Key Themes | Expected/Proved Benefits | Main Benefits Estimation |
|---|---|---|---|
| RCMS | Robotic container management system | Efficient terminal design, validated and quantified benefits also related to noise and air pollution | Costs can be reduced by around 20%. RCMS can be the only solution for specific ports. |
| CLOUD-VAS | Cloud-based vessel allocation | Flexible and affordable optimisation platform to minimise operational costs and fuel consumption | Up to 75% timesaving compared to traditional vessel allocation tools |
| LOGIMATIC | Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS); route planning | Continuous, reliable and accurate estimation of the position and velocity of platforms, enabling resource and space optimisation. | Use of electric mechanical traction, reducing fuel consumption and CO2 by ~50% |
| SHIPLYS | Virtual prototyping, life-cycle assessment | Increase production efficiency, reduce energy consumption, environmental impacts and production costs both in shipyards and vessels in operation | Benefits reported for different scenarios |
| H2H | Safe vessel navigation | Increase navigation safety when in the proximity of other vessels or objects. | Benefits not directly quantified |
| AUTOSHIP | Autonomous vessels | Demonstration of autonomous vessels in real short sea shipping and inland waterway environments. | Benefits not directly quantified |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grosso, M.; Marques dos Santos, F.L.; Gkoumas, K.; Stępniak, M.; Pekár, F. The Role of Research and Innovation in Europe for the Decarbonisation of Waterborne Transport. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10447. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810447
Grosso M, Marques dos Santos FL, Gkoumas K, Stępniak M, Pekár F. The Role of Research and Innovation in Europe for the Decarbonisation of Waterborne Transport. Sustainability. 2021; 13(18):10447. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810447
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrosso, Monica, Fabio Luis Marques dos Santos, Konstantinos Gkoumas, Marcin Stępniak, and Ferenc Pekár. 2021. "The Role of Research and Innovation in Europe for the Decarbonisation of Waterborne Transport" Sustainability 13, no. 18: 10447. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810447
APA StyleGrosso, M., Marques dos Santos, F. L., Gkoumas, K., Stępniak, M., & Pekár, F. (2021). The Role of Research and Innovation in Europe for the Decarbonisation of Waterborne Transport. Sustainability, 13(18), 10447. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810447







