Effects of Controlled Drainage on the Content Change and Migration of Moisture, Nutrients, and Salts in Soil and the Yield of Oilseed Sunflower in the Hetao Irrigation District
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
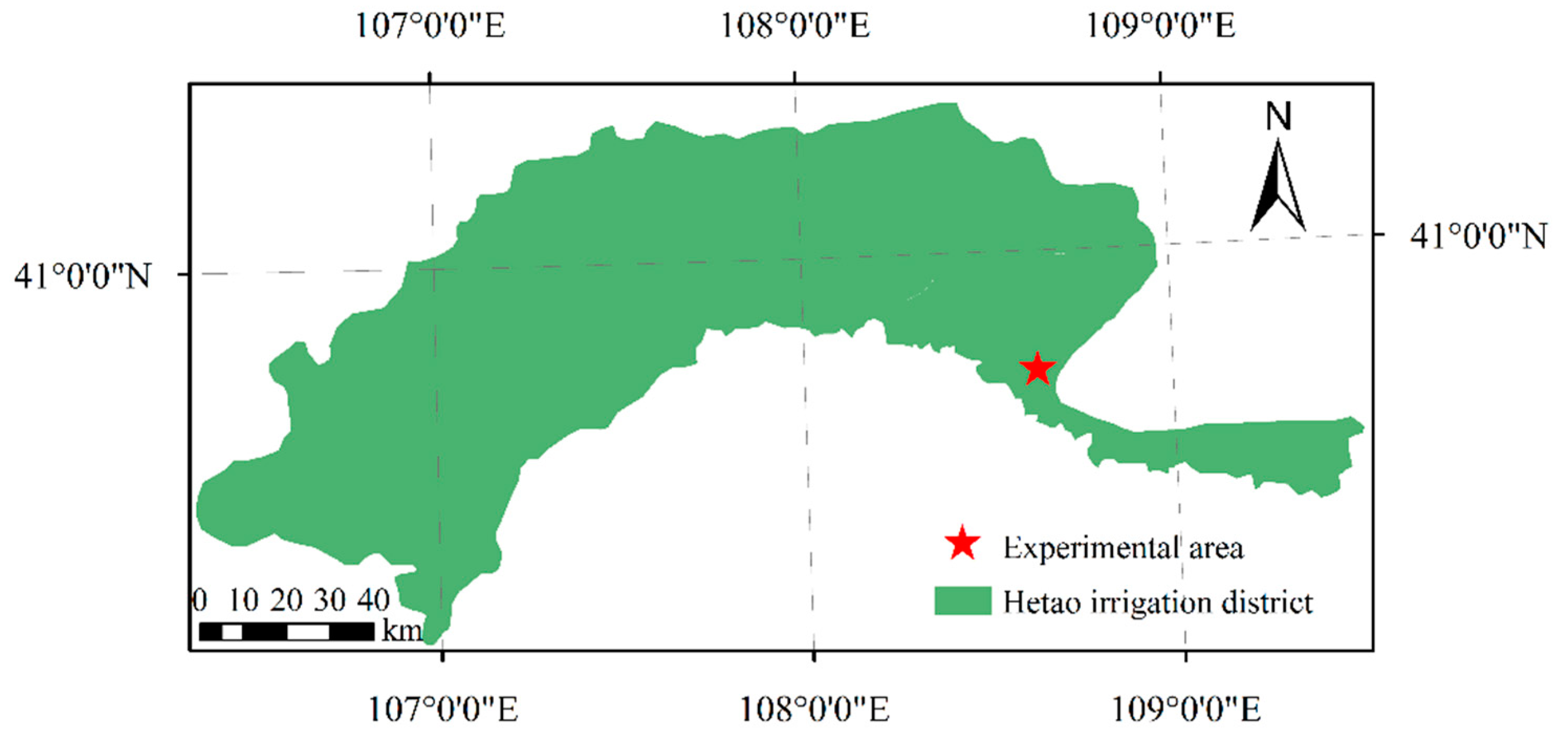
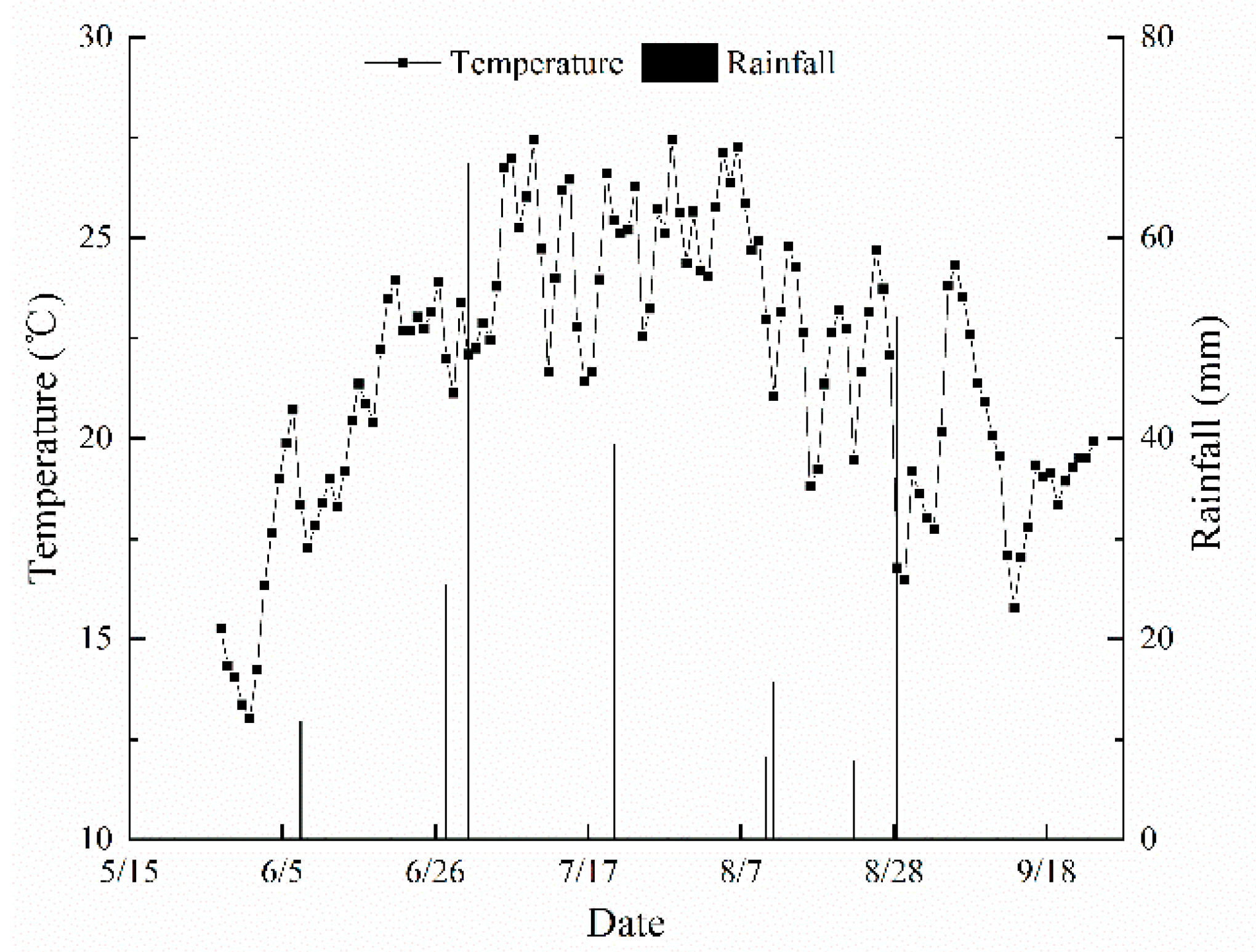
2.1. Overview of the Experimental Area
2.2. Soil Properties
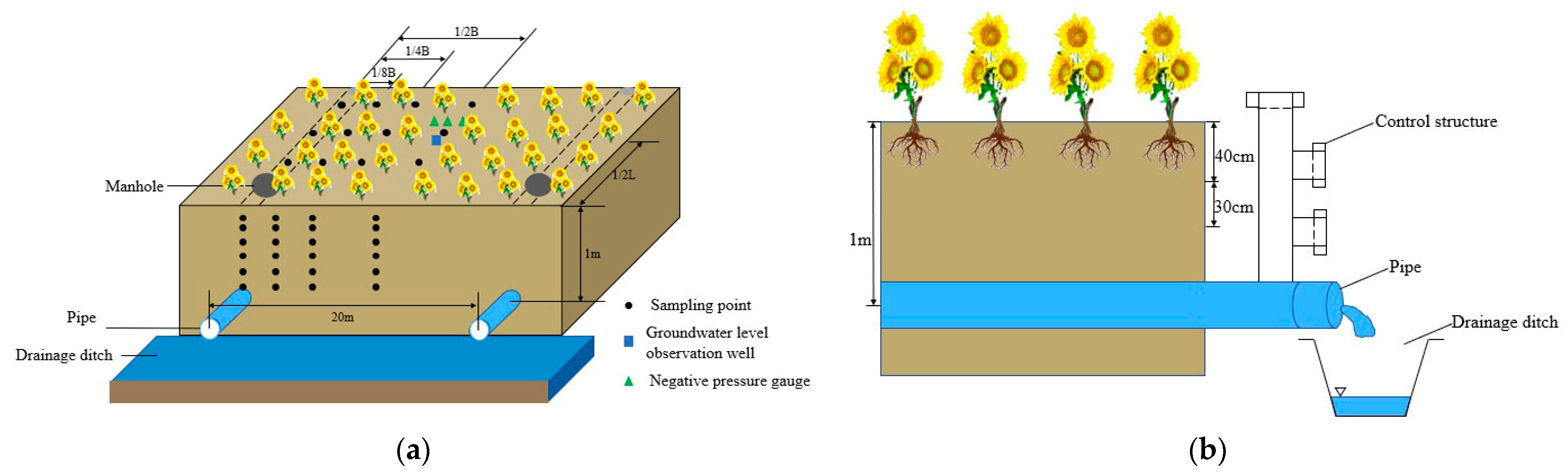
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Data Collection and Measurement Methods
2.4.1. Determination of Soil Salinity, Water Content, and Mineral Nitrogen Content
2.4.2. Record of Seedling Emergence and Yield Test
2.5. Data Processing and Analysis
2.5.1. Calculation of the Seedling Emergence Rate and Survival Rate
2.5.2. Water-Use Efficiency
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Controlled Drainage on Farmland Soil Water Content
3.2. Effect of Controlled Drainage on Farmland Soil Salinity (EC)
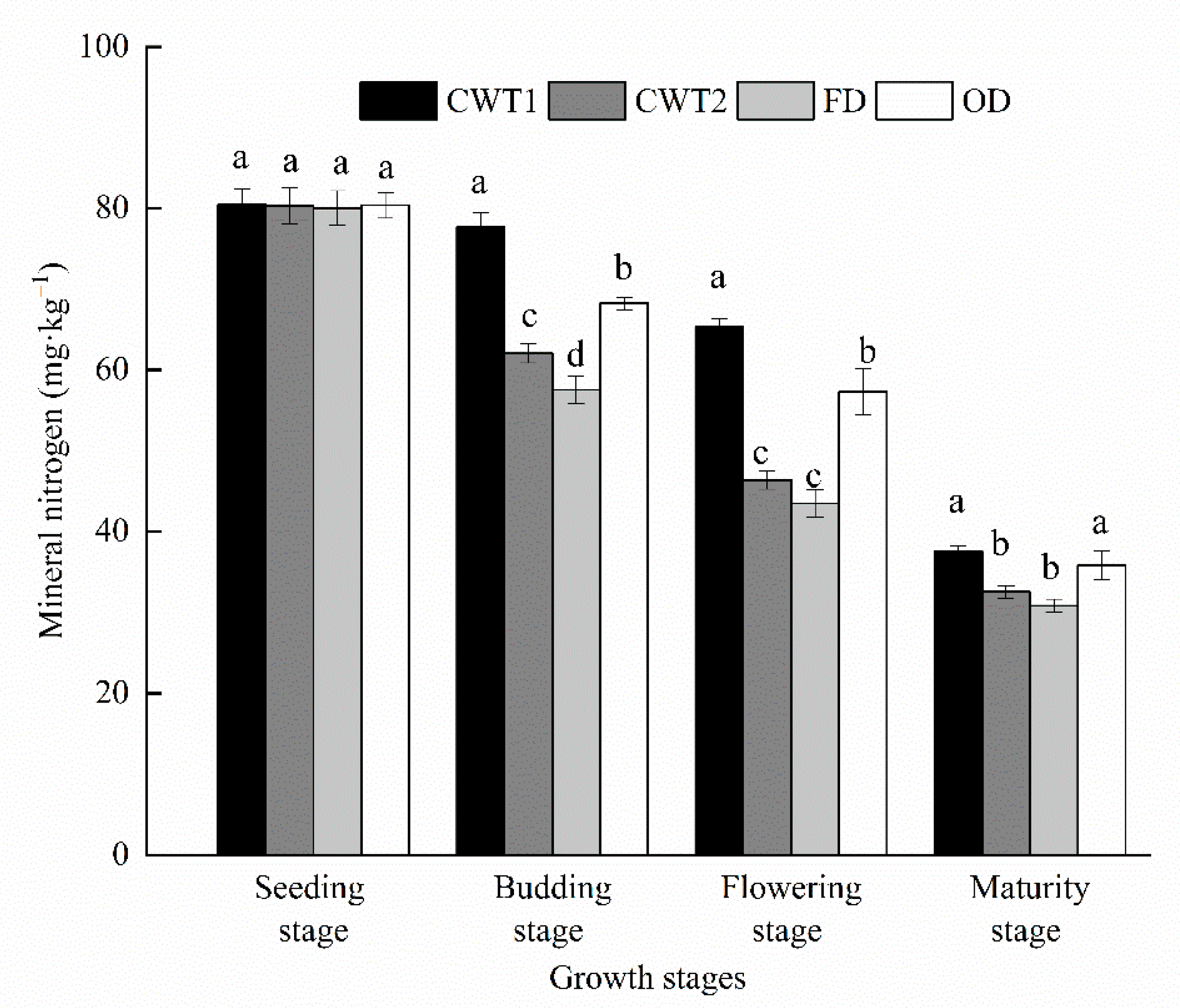
3.3. Effect of Controlled Drainage on Soil Mineral Nitrogen Content
3.4. Effect of Controlled Drainage on the Amount and Quality of Drainage Water and Nitrogen Loss
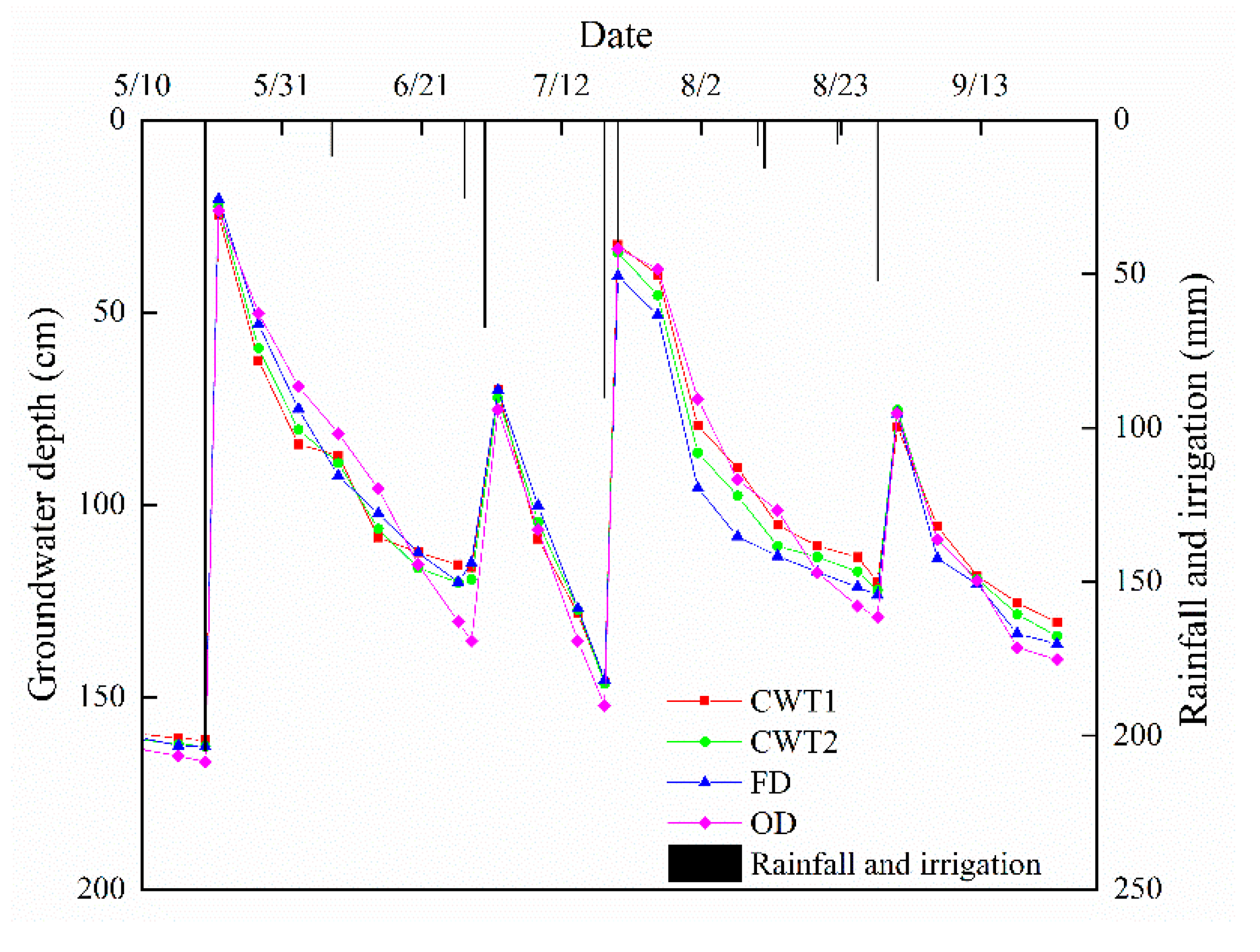
3.5. Effect of Controlled Drainage on the Groundwater Level of Farmlands
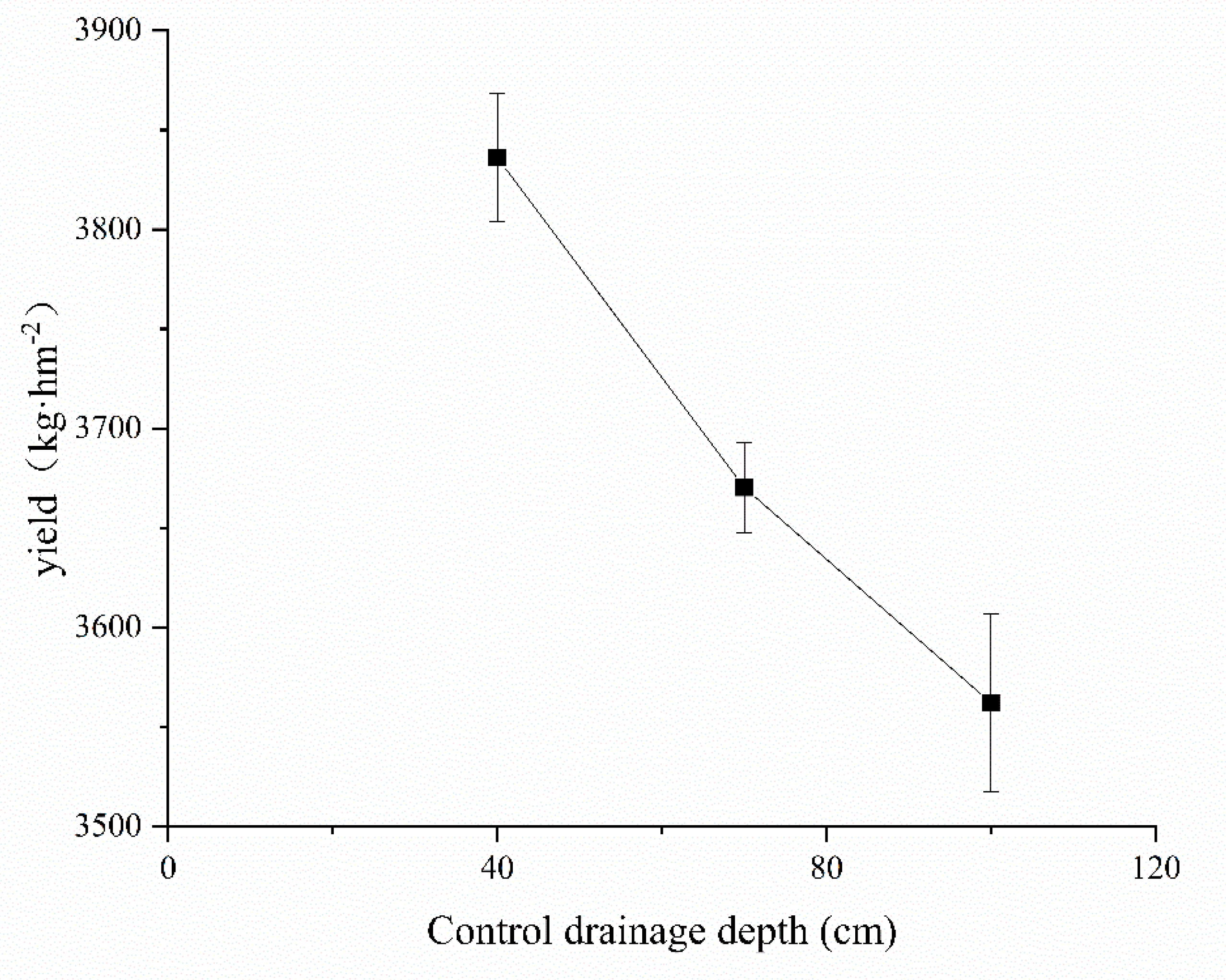
3.6. Effect of Controlled Drainage on Oilseed Sunflower Yield
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Controlled Drainage on the Water Content and Salinity of Farmland Soil
4.2. Effect of Controlled Drainage on Soil Nitrogen and Nitrogen Loss
4.3. Effect of Controlled Drainage on Crop Yield
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skaggs, R.W.; Breve, M.A.; Gilliam, J.W. Hydrologic and water quality impacts of agricultural drainage. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 24, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaggs, R.W.; Breve, M.A.; Gilliam, J.W. Predicting effects of water table management on loss of nitrogen from poorly drained soils. Eur. J. Agron. 1995, 4, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.O.; Skaggs, R.W.; Gilliam, J.W. Controlled versus Conventional Drainage Effects on Water Quality. J. Irrig. Drainage. Eng. 1995, 121, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.J.; Fausey, N.R.; Subler, S.E.; Brown, L.C.; Bierman, P.M. Water Table Management, Nitrogen Dynamics, and Yields of Corn and Soybean. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 1786–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritzema, H.P. Drain for Gain: Managing salinity in irrigated lands A-review. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 176, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sloan, B.P.; Basu, N.B.; Mantilla, R. Hydrologic impacts of subsurface drainage at the field scale: Climate, landscape and anthropogenic controls. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 165, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.R.; King, K.W.; Fausey, N.R. Drainage water management effects on tile discharge and water quality. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 148, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Rossi, C.G.; Arnold, J.G.; Tomer, M.D. Evaluating hydrology of the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) with new tile drain equations. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 67, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golmohammadi, G.; Rudra, R.P.; Prasher, S.O.; Madani, A.; Goel, P.K.; Mohammadi, K. Modeling the impacts of tillage practices on water table depth, drain outflow and nitrogen losses using DRAINMOD. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 124, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Sands, G.R.; Youssef, M.; Strock, J.S.; Song, I.; Canelon, D. Modeling the impact of alternative drainage practices in the northern Corn-belt with DRAINMOD-NII. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Helmers, M.; Crumpton, W.G.; Lemke, D.W. Predicting effects of drainage water management in Iowa’s subsurface drained landscapes. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 92, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Shi, H.B.; Li, R.P.; Miao, Q.F.; Tian, F.; Yu, D.D. Effects of Spring Irrigation Quotas on Soil Water and Salt Transport under Condition of Subsurface Drainage. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2020, 51, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.C.; Ren, S.M.; Yang, P.L.; Wang, Y.; He, X.; Xu, Z.; Wei, R.; Wang, S.J.; Chi, Y.B.; Zhang, M.T. Effects of irrigation methods and salinity on CO2 emissions from farmland soil during growth and fallow periods. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.C.; Li, F.H.; Yang, P.L.; Ren, S.M.; Wang, S.J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wei, R.; Zhang, Y.X. Effects of Irrigation Water Salinity on Soil Properties, N2O Emission and Yield of Spring Maize under Mulched Drip Irrigation. Water 2019, 11, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qadir, M.; Ghafoor, A.; Murtaza, G. Amelioration strategies for sodic soils: A review. Land Degrad. Dev. 2001, 11, 501–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritzema, H.P.; Nijland, H.J.; Croon, F.W. Subsurface drainage practices: From manual installation to large-scale implementation. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 86, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghumman, A.R.; Ghazaw, Y.M.; Hashmi, H.N.; Kamal, M.A.; Niazi, M.F. Environmental and socio-economic impacts of pipe drainage in Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 1671–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Van Leeuwen, H.M.; Koopmans, R.K. Benefits of Draining Agricultural Land in Egypt: Results of Five Years’ Monitoring of Drainage Effects and Impacts. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2001, 17, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Luo, W.; Jia, Z.; Tang, S.; Chen, C. The effect of natural rainfall on salt leaching under watertable management. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 1953–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayars, J.E.; Christen, E.W.; Hornbuckle, J.W. Controlled drainage for improved water management in and regions irrigated agriculture. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 86, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shao, G.; Lu, J.; Zhang, K.; Gao, Y.; Ding, J. Effects of controlled drainage on crop yield, drainage water quantity and quality: A meta-analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 239, 106253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, M.A.; Abdelbaki, A.M.; Negm, L.M.; Skaggs, R.W.; Thorp, K.R.; Jaynes, D.B. DRAINMOD-simulated performance of controlled drainage across the US Midwest. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 197, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, B.X.; Shi, H.B.; Xu, D.; Jiao, P.J. Distribution and variation of water and salt in soil profile under controlling subsurface drainage. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.Z.; Xu, X.; Lü, L.J.; Ren, D.Y.; Ke, J.D.; Xiong, Y.W.; Huo, Z.L.; Huang, G.H. Soil salinity distribution based on remote sensing and its effect on crop growth in Hetao Irrigation District. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.J.; Chen, X.L.; Wen, X.Y.; Chen, F.; Zhang, H.L.; Chu, Q.Q.; Dikgwatlhe, S.B. Applying a salinity response function and zoning saline land for three field crops: A case study in the Hetao Irrigation District, Inner Mongolia, China. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.J.; Mao, F.; Yang, X.H. Soil Salinization and Its Improvement in Arid Hetao Plain, Inner Mongolia: Irrigation Roles. Chin. For. Sci. Technol. 2010, 184, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Houba, V.J.G.; Novozamsky, I.; Huybregts, A.W.M.; Van der lee, J.J. Comparison of soil extractions by 0.01M CaCl2, by EUF and by some conventional extraction procedures. Plant Soil 1986, 96, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Healy, R.W.; Cook, P.G. Choosing appropriate techniques for quantifying groundwater recharge. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayars, J.E.; Christen, E.W.; Soppe, R.W.; Meyer, W.S. The resource potential of in-situ shallow ground water use in irrigated agriculture: A review. Irrig. Sci. 2006, 24, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, E.; Skehan, D. Design and Management of Subsurface Horizontal Drainage to Reduce Salt Loads. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2001, 127, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, E.W.; Ayars, J.E.; Hornbuckle, J.W. Subsurface drainage design and management in irrigated areas of Australia. Irrig. Sci. 2001, 21, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, S.; Hong, D.; Xu, J. Effect of controlled drainage on nitrogen losses from controlled irrigation paddy fields through subsurface drainage and ammonia volatilization after fertilization. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 221, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.Y.F.; Tan, C.S.; Drury, C.F.; Gaynor, J.D. Controlled drainage and subirrigation influences tile nitrate loss and corn yields in a sandy loam soil in Southwestern Ontario. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 90, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesström, I.; Messing, I. Effects of controlled drainage on N and P losses and N dynamics in a loamy sand with spring crops. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 87, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesström, I.; Messing, I.; Linnér, H.; Lindström, J. Controlled drainage—Effects on drain outflow and water quality. Agric. Water Manag. 2001, 47, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Luo, W.; Jia, Z.; Tang, S.; Chen, C. The Pros and Cons of Encouraging Shallow Groundwater Use through Controlled Drainage in a Salt-Impacted Irrigation Area. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 2475–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaggs, R.W.; Fausey, N.R.; Nolte, B.H. Water Management Model Evaluation for North Central Ohio. Agric. Eng. 1981, 24, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.P.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Xu, J.Z.; Yang, S.H.; Hong, D.L. Reducing nitrogen leaching losses from paddy field under water-saving irrigation by water table control. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, N.N.; Huang, J.S.; Xie, H.; Huang, Z.Q. Experimental study of nitrogen leaching pattern in controlled pipe-drainage cotton field. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2010, 26, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunohara, M.D.; Gottschall, N.; Craiovan, E.; Wilkes, G.; Topp, E.; Frey, S.K.; Lapen, D.R. Controlling tile drainage during the growing season in Eastern Canada to reduce nitrogen, phosphorus, and bacteria loading to surface water. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 178, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husk, B.R.; Anderson, B.C.; Whalen, J.K.; Sanchez, J.S. Reducing nitrogen contamination from agricultural subsurface drainage with denitrification bioreactors and controlled drainage. Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 153, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, P.R.; Singh, G.; Nelson, K.A. Nutrient loss from floodplain soil with controlled subsurface drainage under forage production. J. Environ. Qual. 2020, 49, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negm, L.M.; Youssef, M.A.; Jaynes, D.B. Evaluation of DRAINMOD-DSSAT simulated effects of controlled drainage on crop yield, water balance, and water quality for a corn-soybean cropping system in central Iowa. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 187, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, X.; Shao, D.G.; Liu, H.H.; Yuan, J.G. Study on the moving and transforming law of N and P under water-saving irrigation and controlled drainage. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2011, 42, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilundo, M.; Joel, A.; Wesström, I.; Brito, R.; Messing, I. Response of maize root growth to irrigation and nitrogen management strategies in semi-arid loamy sandy soil. Field Crops Res. 2017, 200, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Zhang, F.; Rengel, Z.; Shen, J. Localized fertilization with P plus N elicits an ammonium-dependent enhancement of maize root growth and nutrient uptake—ScienceDirect. Field Crops Res. 2012, 133, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.H.; Al-Kaisi, M.M.; Zhang, Y.S.; Duan, L.S.; Tan, W.M. Tillage practices affect biomass and grain yield through regulating root growth, root-bleeding sap and nutrients uptake in summer maize. Field Crops Res. 2014, 157, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.H.; Chen, F.J.; Wu, Q.P.; Chen, Q.W.; Wang, J.F.; Yuan, L.X.; Mi, G.H. Genetic improvement of root growth increases maize yield via enhanced post-silking nitrogen uptake. Eur. J. Agron. 2015, 63, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.F.; Liu, J.S. Effects of nitrogen management on the growth and yield of mulched and drip-irrigated maize in Northeast Black Soil Regions. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2014, 45, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ale, S.; Bowling, L.C.; Brouder, S.M.; Frankenberger, J.R.; Youssef, M.A. Simulated effect of drainage water management operational strategy on hydrology and crop yield for Drummer soil in the Midwestern United States. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesstrom, I.; Joel, A.; Messing, I. Controlled drainage and subirrigation—A water management option to reduce non-point source pollution from agricultural land. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 198, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.X.; Malone, R.W.; Ma, L.; Jaynes, D.B.; Thorp, K.R.; Green, T.R.; Ahuja, L.R. Modeling the effects of controlled drainage, N rate and weather on nitrate loss to subsurface drainage. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 103, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.M.; Madramootoo, C.A.; Mackenzie, A.F.; Kaluli, J.W.; Smith, D.L. Corn yield and fertilizer N recovery in water-table-controlled corn-rye-grass systems. Eur. J. Agron. 2000, 12, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigg, B.C.; Southwick, L.M.; Fouss, J.L.; Kornecki, T.S. Drainage system impacts on surface runoff, nitrate loss, and crop yield on a southern alluvial soil. Trans. ASAE 2003, 46, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolomio, M.; Borin, M. Controlled drainage and crop production in a long-term experiment in North-Eastern Italy. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 222, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheysari, M.; Sadeghi, S.H.; Loescher, H.W.; Amiri, S.; Zareian, M.J.; Majidi, M.M.; Asgarinia, P.; Payero, J.O. Comparison of deficit irrigation management strategies on root, plant growth and biomass productivity of silage maize. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 182, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Zhang, X.Y.; Liu, X.W.; Zhang, X.Y.; Shao, L.W.; Sun, H.Y.; Chen, S.Y. The effects of nitrogen supply and water regime on instantaneous WUE, time-integrated WUE and carbon isotope discrimination in winter wheat. Field Crop. Res. 2013, 144, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Shi, H.B.; Li, X.Y.; Zhou, H.; Fu, X.J.; Li, Z.Z. Response of maize yield to irrigation and nitrogen rate in different salinization farmlands. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2019, 50, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Hou, Z.N.; Wu, L.S.; Liang, Y.C.; Wei, C.Z. Effects of salinity and nitrogen on cotton growth in arid environment. Plant Soil 2010, 326, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pessarakli, M. Handbook of Plant and Crop Stress, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Soils Layer/cm | Soil Bulk Density (g/cm3) | Soils Type | Saturated Water Capacity/% | Field Moisture Capacity/% | Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity (cm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–20 | 1.426~1.464 | Silt | 0.352~0.354 | 0.219~0.230 | 3.939 × 10−5 |
| 20–40 | 1.468~1.472 | Silty loam | 0.360~0.365 | 0.238~0.242 | 3.798 × 10−5 |
| 40–60 | 1.470~1.476 | Silt | 0.346~0.351 | 0.240~0.246 | 1.238 × 10−5 |
| 60–80 | 1.483~1.488 | Silt | 0.340~0.347 | 0.229~0.234 | 2.073 × 10−5 |
| 80–100 | 1.485~1.490 | Silt | 0.348~0.353 | 0.239~0.241 | 5.176 × 10−5 |
| Soils Layer | Organic Matter (g·kg−1) | Total N (g·kg−1) | Available N (mg·kg−1) | Available P (mg·kg−1) | Available K/(mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plowed layer | 13.54 | 0.85 | 86 | 9.432 | 218 |
| Growth Stages | Seedling Stage | Budding Stage | Flowering Stage | Maturity Stage | Harvest |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | 6/10~7/12 | 7/13~8/4 | 8/5~8/26 | 8/27~9/28 | 9/29 |
| Treatment | CWT1 | CWT2 | FD | OD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drain outflow (mm) | 4.23 | 5.02 | 5.89 | 1.89 |
| NO3--N concentration (mg·L−1) | 5.67 | 5.78 | 5.98 | 9.34 |
| NH4--N concentration (mg·L−1) | 3.55 | 3.59 | 4.57 | 5.88 |
| Treatment | CWT1 | CWT2 | FD | OD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO3--N losses (kg·hm2) | 0.24 ± 0.01 c | 0.29 ± 0.01 b | 0.34 ± 0.02 a | 0.27 ±0.02 bc |
| NH4--N losses (kg·hm2) | 0.15 ± 0.01 b | 0.18 ± 0.02 ab | 0.26 ± 0.01 a | 0.17 ± 0.01 ab |
| Treatment | Germination Rate (%) | Survival Rate (%) | Height (cm) | Stem Diameter (mm) | Yield (kg·hm−2) | ET (mm) | Water-Use Efficiency (kg·hm−2·mm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CWT1 | 90.24 a | 96.62 a | 185.00 a | 27.29 a | 3836.11 a | 258.01 a | 14.87 a |
| CWT2 | 90.14 a | 94.00 b | 177.00 b | 26.00 ab | 3670.33 b | 253.46 b | 14.70 b |
| FD | 90.28 a | 93.71 b | 173.29 c | 25.00 b | 3562.10 c | 250.56 c | 14.22 c |
| OD | 87.60 b | 93.70 b | 162.29 d | 22.57 c | 3451.50 d | 257.19 a | 13.42 d |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dou, X.; Shi, H.; Li, R.; Miao, Q.; Tian, F.; Yu, D.; Zhou, L.; Wang, B. Effects of Controlled Drainage on the Content Change and Migration of Moisture, Nutrients, and Salts in Soil and the Yield of Oilseed Sunflower in the Hetao Irrigation District. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9835. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13179835
Dou X, Shi H, Li R, Miao Q, Tian F, Yu D, Zhou L, Wang B. Effects of Controlled Drainage on the Content Change and Migration of Moisture, Nutrients, and Salts in Soil and the Yield of Oilseed Sunflower in the Hetao Irrigation District. Sustainability. 2021; 13(17):9835. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13179835
Chicago/Turabian StyleDou, Xu, Haibin Shi, Ruiping Li, Qingfeng Miao, Feng Tian, Dandan Yu, Liying Zhou, and Bo Wang. 2021. "Effects of Controlled Drainage on the Content Change and Migration of Moisture, Nutrients, and Salts in Soil and the Yield of Oilseed Sunflower in the Hetao Irrigation District" Sustainability 13, no. 17: 9835. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13179835
APA StyleDou, X., Shi, H., Li, R., Miao, Q., Tian, F., Yu, D., Zhou, L., & Wang, B. (2021). Effects of Controlled Drainage on the Content Change and Migration of Moisture, Nutrients, and Salts in Soil and the Yield of Oilseed Sunflower in the Hetao Irrigation District. Sustainability, 13(17), 9835. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13179835








