Effect of Peatland Siltation on Total and Labile C, N, P and K
Abstract
1. Introduction
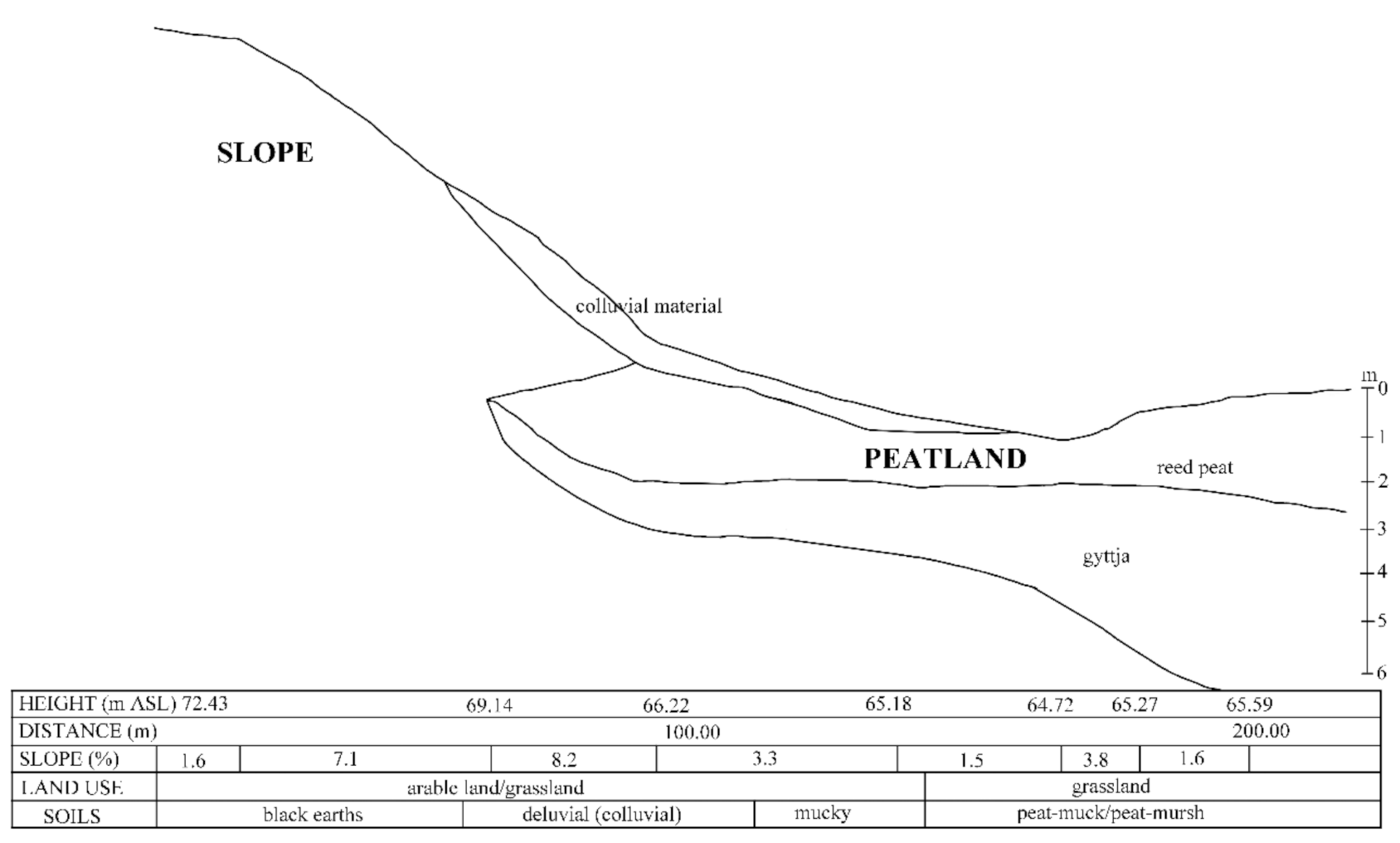
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blazier, M..; Liechty, H. Assessment of Labile Organic Carbon in Soil Using Sequential Fumigation Incubation Procedures. Jove-J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLauchlan, K.K.; Hobbie, S.E. Comparison of labile soil organic matter fractionation techniques. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 1616–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalisz, B.; Lachacz, A.; Glazewski, R. Effects of peat drainage on labile organic carbon and water repellency in NE Poland. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2015, 39, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Nie, X.; Huang, M.; Wang, D.; Xiao, H.; Liu, C.; Peng, H.; Jiang, J.; Zeng, G. The role of dissolved organic matter in soil organic carbon stability under water erosion. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 102, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Jin, M.; Ye, X.; Gao, H.; Chu, W.; Mao, J.; Thompson, M.L. Soil labile organic carbon fractions and soil enzyme activities after 10 years of continuous fertilization and wheat residue incorporation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalbitz, K.; Solinger, S.; Park, J.H.; Michalzik, B.; Matzner, E. Controls on the dynamics of dissolved organic matter in soils: A review. Soil Sci. 2000, 165, 277–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landgraf, D.; Leinweber, P.; Makeschin, F. Cold and hot water-extractable organic matter as indicators of litter decomposition in forest soils. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2006, 169, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, A.; Sarathchandra, U.; Ledgard, S.; Dexter, M.; Lindsey, S. Microbial decomposition of leached or extracted dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen from pasture soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2013, 49, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbitz, K.; Geyer, S. Different effects of peat degradation on dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen. Org. Geochem. 2002, 33, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, W.H.; Zsolnay, A.; Aitkenhead-Peterson, J.A.; Gregorich, E.G.; Jones, D.L.; Joedemann, D.; Kalbitz, K.; Marschner, B.; Schwesig, D. A comparison of methods to determine the biodegradable dissolved organic carbon from different terrestrial sources. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 1933–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, B.; McDowell, R.W.; Condron, L.M.; Cox, N. Can phosphorus fertilizers sparingly soluble in water decrease phosphorus leaching loss from an acid peat soil? Soil Use Manag. 2016, 32, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Song, J.M.; Wang, Q.D.; Li, X.G.; Yuan, H.M.; Li, N.; Duan, L.Q. Characterization of Labile Organic Carbon in Different Coastal Wetland Soils of Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea. Wetlands 2017, 37, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, M.E.; Galantini, J.A.; Martinez, J.M.; Limbozzi, F. Labile soil organic carbon for assessing soil quality: Influence of management practices and edaphic conditions. Catena 2018, 171, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muciaddas, B.; Lewis, T.; Esfandbod, M.; Chen, C.R. Responses of labile soil organic carbon and nitrogen pools to long-term prescribed burning regimes in a wet sclerophyll forest of southeast Queensland, Australia. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norberg, L.; Bergiund, O.; Bergiund, K. Impact of drainage and soil properties on carbon dioxide emissions from intact cores of cultivated peat soils. Mires Peat 2018, 21, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojko, O.; Kabala, C.; Mendyk, L.; Markiewicz, M.; Pagacz-Kostrzewa, M.; Glina, B. Labile and stabile soil organic carbon fractions in surface horizons of mountain soils—Relationships with vegetation and altitude. J. Mt. Sci. 2017, 14, 2391–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, K.; Kalbitz, K. Cycling downwards—Dissolved organic matter in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 52, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.; Holden, J.; Kay, P.; Francis, B.; Foulger, M.; Gledhill, S.; McDonald, A.T.; Walker, A. The impact of peatland drain-blocking on dissolved organic carbon loss and discolouration of water; results from a national survey. J. Hydrol. 2010, 381, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenner, N.; Williams, R.; Toberman, H.; Hughes, S.; Reynolds, B.; Freeman, C. Decomposition ‘hotspots’ in a rewetted peatland: Implications for water quality and carbon cycling. Hydrobiologia 2011, 674, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limpens, J.; Berendse, F.; Blodau, C.; Canadell, J.G.; Freeman, C.; Holden, J.; Roulet, N.; Rydin, H.; Schaepman-Strub, G. Peatlands and the carbon cycle: From local processes to global implications—a synthesis. Biogeosciences 2008, 5, 1475–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, S.E.a.B.A.J. Peatlands and Global Change: Response and Resilience. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2016, 41, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glina, B.; Gajewski, P.; Kaczmarek, Z.; Owczarzak, W.; Rybczynski, P. Current state of peatland soils as an effect of long-term drainage—Preliminary results of peatland ecosystems investigation in the Grojecka Valley (central Poland). Soil Sci. Annu. 2016, 67, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalisz, B.; Lachacz, A.; Glazewski, R. Transformation of some organic matter components in organic soils exposed to drainage. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2010, 34, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachacz, A.; Nitkiewicz, M.; Kalisz, B. Water repellency of post-boggy soils with a various content of organic matter. Biologia 2009, 64, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendyk, L.; Hulisz, P.; Kusza, G.; Switoniak, M.; Gersztyn, L.; Kalisz, B. Sediment origin and pedogenesis in the former mill pond basin of Turznice (north-central Poland) based on magnetic susceptibility measurements. Bull. Geogr. Phys. Geogr. Ser. 2016, 11, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banasik, K.; Hejduk, L.; Krajewski, A.; Wasilewicz, M. The intensity of siltation of a small reservoir in Poland and its relationship to environmental changes. Catena 2021, 204, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerswald, K.; Geist, J. Extent and causes of siltation in a headwater stream bed: Catchment soil erosion is less important than internal stream processes. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, A.S.; Fulop, B.; Honti, M. Detection of hot spots of soil erosion and reservoir siltation in ungauged Mediterranean catchments. Energy Procedia 2012, 18, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Smolczynski, S.; Kalisz, B.; Orzechowski, M. Sequestration of Humus Compounds in Soils of Northeastern Poland. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2011, 20, 755–762. [Google Scholar]
- Smolczynski, S.; Orzechowski, M.; Kalisz, B. Distribution of elements in soil catenas developed in ice-dammed lake and in morainic landscapes in ne poland. J. Elem. 2015, 20, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowinski, P.; Orzechowski, M.; Smolczynski, S.; Kalisz, B. Particle-size distribution in soils in various ground moraine catenas in the masurian lakeland. Pol. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 48, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, O.A.; Musaev, F.A.; Kucher, D.E.; Vinogradov, D.V.; Ushakov, R.N. Sanding of drained peatlands. BIO Web Conf. 2020, 17, 00089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zaidel’man, F.R.; Kozhevin, P.A.; Shvarov, A.P.; Pavlova, E.B.; Gorlenko, M.V. The effect of different sanding methods on the biological activity and gas regime of drained peat soils. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2001, 34, 207–216. [Google Scholar]
- Smólczyński, S.; Orzechowski, M. Soils of ecotone zones of meltwater basins and slopes in a young glacial landscape of the Mazurian Lakeland. Soil Sci. Annu. 2010, 61, 217–226. [Google Scholar]
- Smólczyński, S.; Orzechowski, M. Sorptive properties of upper-silted organic soils in various landscapes of north-eastern Poland. Pol. J. Soil Sci. 2010, 43, 129–140. [Google Scholar]
- Thaysen, E.M.; Reinsch, S.; Larsen, K.S.; Ambus, P. Decrease in heathland soil labile organic carbon under future atmospheric and climatic conditions. Biogeochemistry 2017, 133, 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.J.; Foster, R.A.; McKnight, D.M.; Lisle, J.T.; Littmann, S.; Kuypers, M.M.M.; Foreman, C.M. Microbial formation of labile organic carbon in Antarctic glacial environments. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glina, B.; Bogacz, A.; Wozniczka, P. Nitrogen mineralization in forestry-drained peatland soils in the Stolowe Mountains National Park (Central Sudetes Mts). Soil Sci. Annu. 2016, 67, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Quideau, S.A.; Norris, C.E.; Rees, F.; Dyck, M.; Samadi, N.; Oh, S.W. Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus release from peat and forest floor-based cover soils used during oil sands reclamation. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 97, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.X.; Ta, N.; Li, Z.H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, D.; Zhang, A.; Wang, X.D. Varying pyrolysis temperature impacts application effects of biochar on soil labile organic carbon and humic fractions. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 123, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutter, M.I.; Shand, C.A.; George, T.S.; Blackwell, M.S.A.; Dixon, L.; Bol, R.; MacKay, R.L.; Richardson, A.E.; Condron, L.M.; Haygarth, P.M. Land use and soil factors affecting accumulation of phosphorus species in temperate soils. Geoderma 2015, 257, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orzechowski, M.; Smolczynski, S.; Kalisz, B.; Dlugosz, J.; Sowinski, P. Chemical and mineralogical composition of the holocene soil sediments in north-eastern poland. J. Elem. 2020, 25, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, M.M.; Gupta, V.V.S.R.; Murphy, D.V. Tillage practices altered labile soil organic carbon and microbial function without affecting crop yields. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2010, 48, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolczynski, S.; Orzechowski, M.; Kalisz, B.; Krupinski, K. Selected properties of reclaimed mine soils in the area of a former gravel mine in north-eastern Poland. Soil Sci. Annu. 2020, 71, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalisz, B.; Łachacz, A.; Klasa, A.; Smólczyński, S.; Orzechowski, M.; Sowiński, P. Water permeability of soils amended with sewage sludge on short-rotation plantations in Europe. Pol. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 48, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mueller, L.; Wirth, S.; Schulz, E.; Behrendt, A.; Hoehn, A.; Schindler, U. Implications of soil substrate and land use for properties of fen soils in North-East Germany Part I: Basic soil conditions, chemical and biological properties of topsoils. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2007, 53, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.Z.; Robertson, G.P.; Basso, B.; Hamilton, S.K. Leaching losses of dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen from agricultural soils in the upper US Midwest. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinz, M.; Zak, D. Storage effects on quantity and composition of dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen of lake water, leaf leachate and peat soil water. Water Res. 2018, 130, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wen, Y.C.; Li, X.H.; Li, Y.T.; Yang, X.D.; Lin, Z.; Song, Z.Z.; Cooper, J.M.; Zhao, B.Q. Soil labile organic carbon fractions and soil organic carbon stocks as affected by long-term organic and mineral fertilization regimes in the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 175, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.-J.; Sha, L.-Q.; Schaefer, D.A.; Zhang, Y.-P.; Song, Q.-H.; Tan, Z.-H.; Deng, Y.; Deng, X.-B.; Guan, H.-L. Direct effects of litter decomposition on soil dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen in a tropical rainforest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 81, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, C.; Zeitz, J. Stability of soil organic matter in two northeastern German fen soils: The influence of site and soil development. J. Soils Sediments 2012, 12, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.L.; Silcock, D.J. Impact of NH4NO3 on microbial biomass C and N and extractable DOM in raised bog peat beneath Sphagnum capillifolium and S-recurvum. Biogeochemistry 2000, 49, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

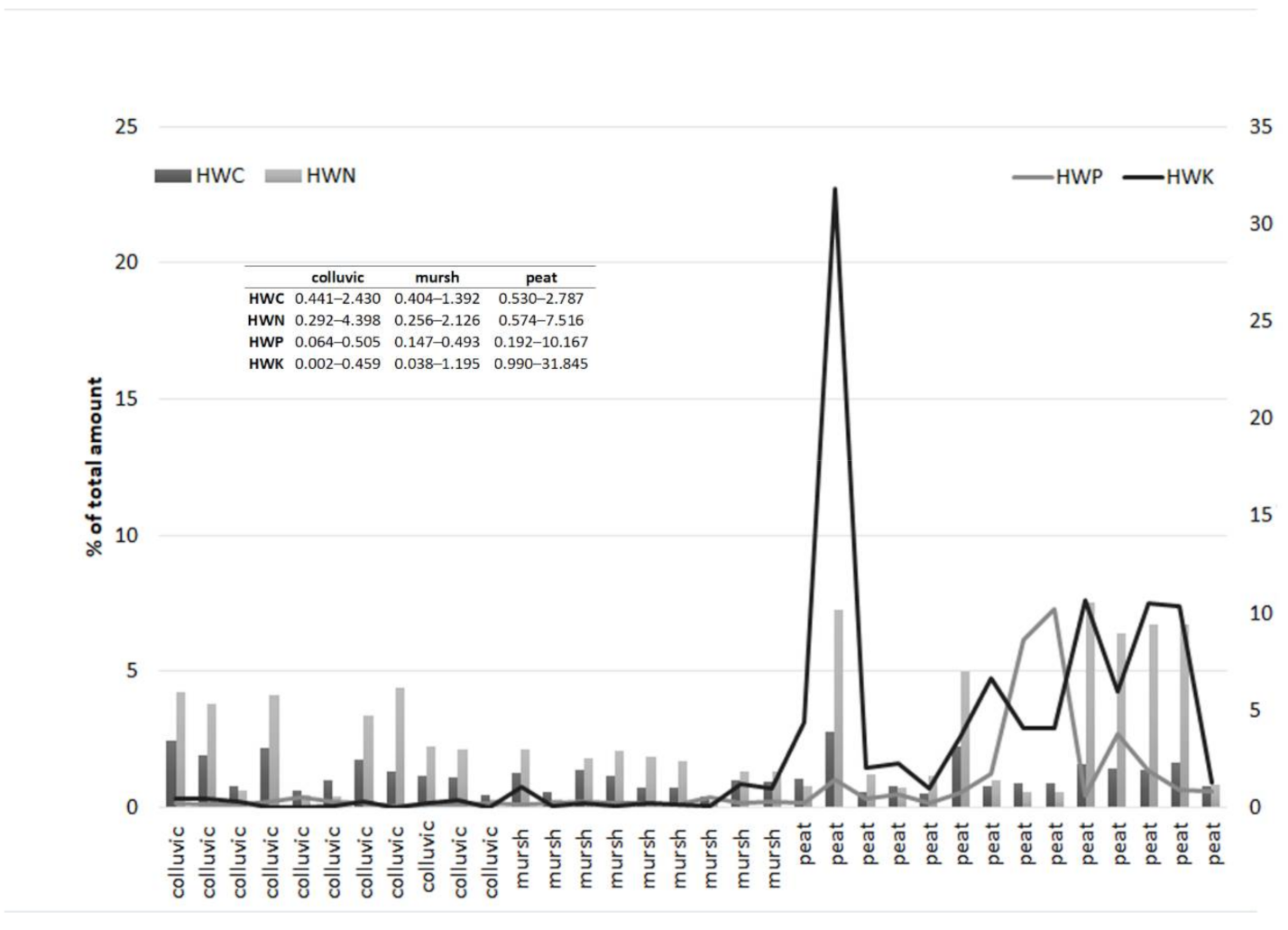
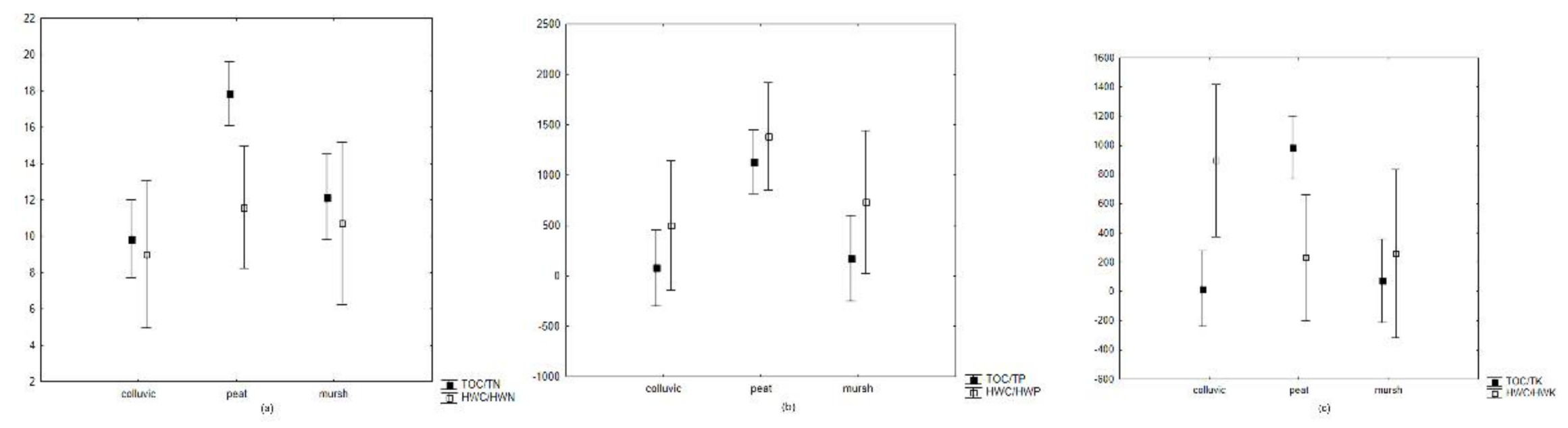
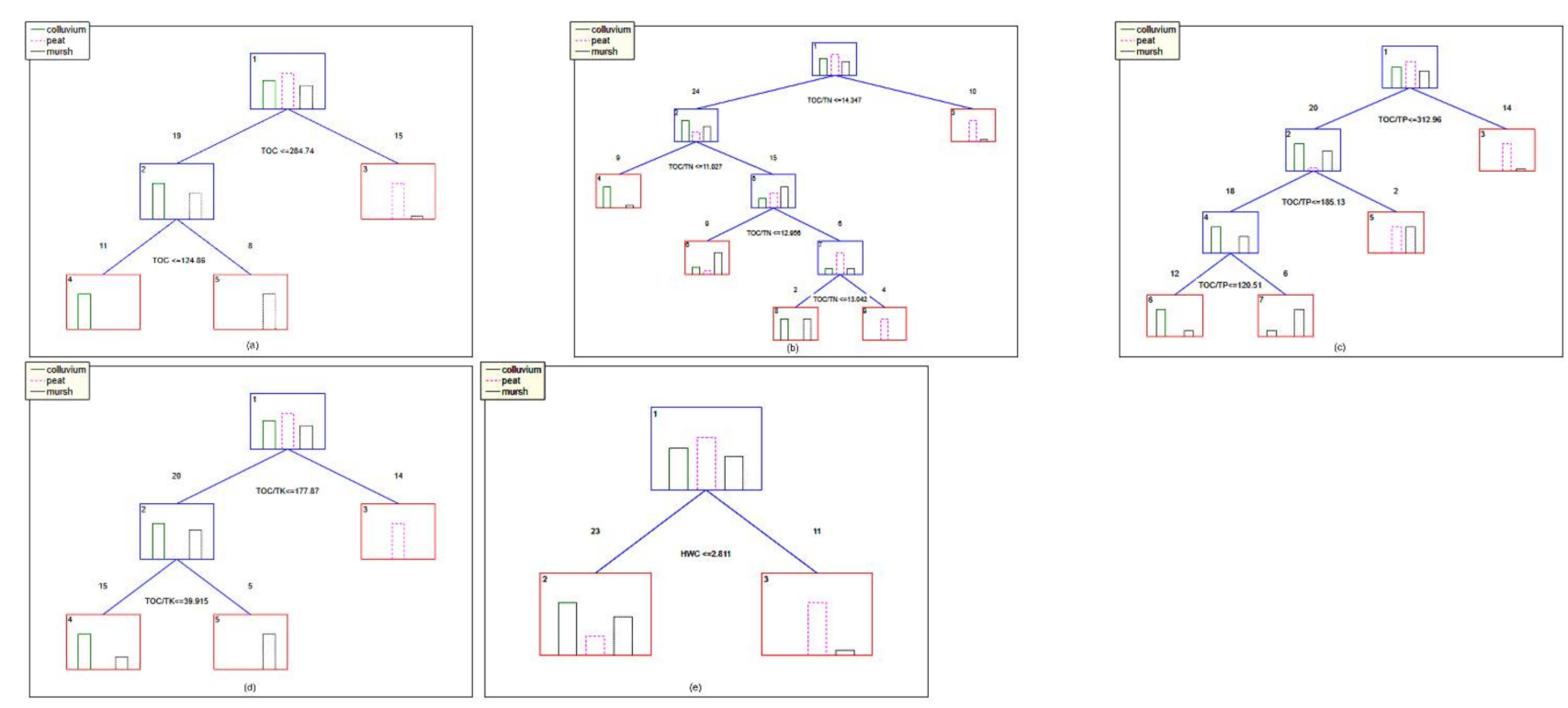
| Soil Sample | OM | TN | TOC | TP | TK | HWC | HWN | HWP | HWK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colluvium | 187.0 (24.4) | 7.9 (30.4) | 77.2 (29.0) | 1.3 (89.9) | 5.1 (60.5) | 0.9 (35.9) | 0.2 (64.0) | 0.002 (65.8) | 0.009 (96.8) |
| Mursh | 405.2 (30.8) | 16.2 (18.0) | 201.4 (31.2) | 1.2 (23.2) | 3.9 (49.9) | 1.8 (43.2) | 0.2 (47.5) | 0.003 (60.3) | 0.010 (68.2) |
| Peat | 760.3 (17.9) | 22.3 (18.7) | 391.9 (13.9) | 0.6 (64.6) | 0.5 (60.0) | 5.1 (62.9) | 0.7 (83.7) | 0.008 (129.5) | 0.024 (79.9) |
| Parameter | TN | TOC | TP | TK | TOC/TN | TOC/TP | TOC/TK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HWC | 0.438 ** | 0.766 * | −0.380 | −0.562 * | 0.772 * | 0.615 * | 0.857 * |
| HWN | 0.246 | 0.627 * | −0.339 | −0.477 ** | 0.816 * | 0.712 * | 0.830 * |
| HWP | 0.571 * | 0.335 | −0.133 | −0.233 | 0.083 | 0.126 | 0.037 |
| HWK | 0.442 ** | 0.574 * | −0.364 | −0.416 | 0.339 | 0.299 | 0.474 ** |
| HWC/HWN | 0.213 | 0.118 | −0.118 | 0.084 | −0.136 | −0.086 | −0.080 |
| HWC/HWP | 0.124 | 0.478 ** | −0.339 | −0.389 | 0.706 * | 0.516 ** | 0.691 * |
| HWC/HWK | −0.351 | −0.299 | 0.668 * | −0.006 | −0.121 | −0.150 | −0.134 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smolczynski, S.; Kalisz, B.; Urbanowicz, P.; Orzechowski, M. Effect of Peatland Siltation on Total and Labile C, N, P and K. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8240. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158240
Smolczynski S, Kalisz B, Urbanowicz P, Orzechowski M. Effect of Peatland Siltation on Total and Labile C, N, P and K. Sustainability. 2021; 13(15):8240. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158240
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmolczynski, Slawomir, Barbara Kalisz, Pawel Urbanowicz, and Miroslaw Orzechowski. 2021. "Effect of Peatland Siltation on Total and Labile C, N, P and K" Sustainability 13, no. 15: 8240. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158240
APA StyleSmolczynski, S., Kalisz, B., Urbanowicz, P., & Orzechowski, M. (2021). Effect of Peatland Siltation on Total and Labile C, N, P and K. Sustainability, 13(15), 8240. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158240






