Abstract
Drawing upon the componential theory of creativity and social information processing theory, this research elucidates how and why the synergy of green HR practices and green strategies stimulate green creativity. It also explores the possible mediation effect of green transformational leadership (TFL) on the relationship between organizational interventions and green creativity. Survey questionnaires were used to collect data from managers working in large manufacturing firms. The structural equation modeling technique was applied to test the hypothesized relationships. Findings of research revealed that green management initiatives and green TFL stimulate green creativity. Moreover, the intervening impact of green TFL on the relationship between the aforementioned relationships was also established. Policymakers should devise green strategies and provide support to green HR practices for the stimulation of green creativity, whereas HR managers must ensure the compatibility of HR functions with corresponding organizational green strategies. Employees involved in green creative behaviors should be rewarded and retained. Training must be provided in order to keep employees abreast of the latest practices for environment conservation. Furthermore, managers should exhibit a green TFL style to advance green management initiatives and fuel green creativity among employees. This study highlights the significance of the synergy between green HR practices and the firm’s green strategies to stimulate employees’ green creativity. Furthermore, green management initiatives were also found to be the contextual precursor of green TFL, which enhances our understanding of the green TFL style. Lastly, the mediation effect of green TFL implies that it can serve as a proximal HR outcome to implement the organizational green agenda.
1. Introduction
Global warming and devastating environmental pollution have increased the need for environmentalism. Therefore, corporations are now dealing with more environmentally concerned stakeholders [1]. Strict environmental regulations, increasing demand for green products, and pressure to comply with international standards are a reflection of stakeholders’ focus on environmental issues [2,3]. To mitigate pressure from various stakeholders, firms have adopted environmental management system, which enhances their corporate image and competitive advantage [4]. In today’s competitive business world, organizations are producing green products to respond to consumers’ environmentalism. To do so, green creativity serves as a competitive weapon to deal with increased competition and customers’ demands [5]. Scholars have argued that the adoption of green creativity leads towards first-mover advantage in resource-efficient production of green products, which ultimately boosts market share [6,7].
Environmental management philosophy originates from the top-level management of any organization. It is now imperative for corporations to adopt environmentally friendly policies to stimulate green creativity [8]. Green creativity was defined as “the development of new ideas about green products, green services, green processes, or green practices that are judged to be original, novel, and useful” [5]. Green creativity transforms the products into sustainable green products that fulfill the organizational green agenda by reducing environmental degradation [9]. For increased understanding, different studies have explored multiple antecedents of green creativity, both at individual and organizational levels. For example, [10] identified that green transformational leadership (TFL) stimulates green creativity in workers, while [11] argued that green human resource management (GHRM) promotes green innovation. These findings corroborate the views presented in various studies that green creative behavior can be nurtured through numerous factors along with leadership [1,6,12]. However, few studies have uncovered the integrative effect of green human resource (HR) practices and organizational strategies (hereafter, green management initiatives) in stimulating green creativity through green TFL.
In pursuit of a green agenda, organizations are actively engaged in the creation of pro-environmental behaviors within employees through practices of green human resource management (GHRM) [13]. According to [14], GHRM is “the HRM aspects of environmental management”. Various scholars [11,15] have stressed the importance of the proper implementation of green HR practices to promote green creativity. On the other hand, green strategies of the firm lead toward better achievement of organizational goals that are related to environmental care [16]. Green strategies reflect the focus of top leadership toward the reduction of carbon footprint. Therefore, this study postulates that both strategic direction and green HR practices can become a foundation for enhancing the green creativity of employees. This is in line with the suggestions proposed by [17], who highlighted the need for an alignment of HR practices and organizational strategies in order to achieve better outcomes. Similarly, the study by [16] also emphasized that the green management initiatives produce a synergetic impact to increase firms’ environmental performance.
Additionally, the implementation of green management initiatives largely depends upon the leadership style exhibited by managers. Nurturing green creativity among employees remains a major concern for organizational managers [18]. The behavior and characteristics of leaders strongly affect the behavior of individuals [19]. Green TFL influences the subordinates to achieve environmental goals and objectives through inspiration, which leads towards performance beyond expectations and resultant green creativity [5]. Therefore, complete support from top management along with HR practices that are focused on the green agenda could lead the managers to exhibit green TFL. The role of green TFL in producing pro-environmental behavior among employees has been widely acknowledged in the literature [10,20,21]. Hence, this research proposes that green management initiatives create an organizational environment, which requires the managers to stimulate green creativity through green TFL.
This research also extends knowledge about organizational initiatives and creativity by exploring the mechanism through which green management initiatives promote green TFL that leads toward employees’ green creativity. Although the direct relationship between green TFL and creativity has been examined in prior research, the role of green management initiatives in promoting green TFL has been considerably overlooked. Therefore, this study aims to identify how green management initiatives may affect green creativity through green TFL. Furthermore, this research explains why green management initiatives are essential in promoting green creativity. This study advances the green TFL literature, in particular, and leadership literature, in general, by proposing green management initiatives as an antecedent to green TFL. Lastly, this investigation also speculates that green TFL may serve as a proximal HR outcome that ensures the implementation of HR strategies.
The remainder of this research paper is organized as follows. Next section details theories and hypotheses development. Section 3 will present the research methodology, while Section 4 details the results obtained after data analysis. Lastly, Section 5 deals with discussion, theoretical implications, managerial implications, and limitations of the research.
2. Theories and Development of Hypotheses
2.1. Componential Theory of Creativity and Social Information Processing Theory
This research draws upon the componential theory of creativity [22] and social information processing theory [23]. Ref. [24] explained that “all humans with normal capacities are able to produce at least moderately creative work in some domain, some of the time- and that the social environment (the work environment) can influence both the level and the frequency of creative behavior”. This theory presents three within-individual components, which are domain-relevant skills (i.e., technical skills, knowledge, and expertise), creativity-relevant processes (i.e., cognitive style, risk-taking, and out-of-the-box thinking), and task motivation (i.e., passion and intrinsic motivation). However, the fourth component is related to the occupational environment in which employees operate. Creativity would be the highest when a person having a high level of knowledge and innovative thinking operates in an exceptionally creative work environment [24]. Therefore, this research posits that green HR practices and green strategies would serve as outside factors that will foster creative behavior through a supportive work environment. On the other hand, green TFL would enhance the motivation, knowledge, and skills of the employees that enables them to implement the creative ideas. Different researchers [6,11,25,26] have also explored outside factors such as GHRM, leadership, management support, and innovative climate that nurture employees’ creativity.
In addition, social information processing theory is used to propose the relationship between green management initiatives and green TFL. This research speculates that green TFL would be developed through green management initiatives. According to the social information processing theory, the actions and attitudes of individuals form according to the social environment in which they operate [23]. Hence, the focus of management towards environmental care coupled with green HR practices may lead the managers towards the exhibition of green TFL style. This is in line with the view of [16], who provided empirical support for the development of green leadership through organizational policies and work environments.
2.2. Green Management Initiatives and Green Creativity
Green creativity is “the development of new ideas about green products, green services, green processes, or green practices that are judged to be original, novel, and useful” [5]. Green strategy, on the other hand, refers to the extent to which green activities are mirrored in organizational strategies for green performance enhancement [27]. The perception of environmental issues in the eyes of top management would directly affect the strategic direction of the organization. Management with environmental focus pays attention to alleviate issues that are related to pollution and environmental degradation; hence, it affects their strategic choice [28]. Similarly, a study conducted by [9] found that the leaders’ interests and motivation for sustainability become the primary reason for achieving organizational green performance through green strategies. Moreover, the green strategy ensures the deployment of necessary resources for the promotion of green culture within firms. Consequently, this culture cultivates green innovation among employees by making them aware of the sensitivity of environmental issues [11].
Even though green strategy acts as a required condition and necessary element to promote sustainable performance, its integration with green HR practices mobilizes human resources so that they may come up with creative techniques for the preservation of the environment [28]. Therefore, the green strategy requires synergy with green HR practices for better implementation of the green agenda [16]. Following the perceptive of [12], the HRM system through green HR practices provides support for the execution of organizational green strategy. Ref. [12] further added that green HRM, coupled with leadership support, promotes employees’ green creativity. Furthermore, green HR practices, which largely accentuate ecological influences and environmental protection of the firm, serve as an apparent link between employees’ innovative behavior and corporate environmental strategy [29,30].
The need to follow fine-grained HR practices rather than standardized HR practices must be emphasized in order to build a diverse pool of capable workers who have a higher level of awareness related to environmental problems [31]. Green HR practices focus on workforce development that acknowledges the significance of exhibiting green behaviors and give value to nature-friendly activities [32]. Furthermore, green HR practices can strengthen the green capability of organizational workers by hiring those who are already mindful of environmental sustainability [33]. Similarly, the training on eco-friendly skills enthuses employees’ knowledge of the green tasks, whereas a green performance management system aids in promoting green behavior among the employees [12]. Green recruitment and selection apply emphasis on employees’ perception, expertise, and knowledge toward environmental protection activities, and it tends to choose the individuals with a higher level of environmentalism. Therefore, the workforce selected through green selection techniques is better prepared to grasp the environmental management priorities of the organizations [14]. Based on the above-presented arguments, this research hypothesizes the following statement:
Hypothesis 1 (H1).
Green management initiatives positively influence green creativity.
2.3. Green Management Initiatives and Green TFL
Green management initiatives serve as a guiding factor for the organizational members in fulfilling the green agenda of the organization. It provides direction, skills, knowledge, and necessary resources for attaining the objective of environmental care. Top management commitment is a significant factor in cultivating a green environment within firms [34]. Environmental care initiatives depend on the thinking of policymakers, whether they understand the importance of green goals or otherwise [35]. Considering the view of [36], effective implementation of green agenda largely depends on the strategies adopted by top management. Similarly, [37] found that the pro-environment policies positively influence the environmental performance of the firms.
Drawing on social information processing theory, this research posits that leaders usually adopt a leadership style that is consistent with the strategies and environment of the company. Green HR policies and the strategic direction of the firm would certainly guide the managers regarding a suitable leadership style for the implementation of the organizational agenda. Following the perspective of [38], organizational strategic focus shapes the behavior of managers and employees. Moreover, the study by [39] argued that the environmentally specific leadership style persuades the employees to adopt green practices for the reduction of hazardous impact on the environment. The HR practices such as recruitment, selection, rewarding, and performance management would mirror the strategic direction of firms through embedded green goals in the whole HR system. Consequently, managers will exhibit a green leadership style when their promotion and performance judgment would depend on the facilitation provided by them to enhance employees’ green knowledge.
Green TFL is considered a vital tool in the organization’s environmental management system [40]. Policies and strategies of the organization are implemented through their managers. Therefore, green HR practices, coupled with green strategic focus, would become the motivating factor for managers to exhibit a green TFL style. The linkage between green HRM and green TFL has been established in previous studies [1,12,41]. Moreover, scholars have argued that the organizational green strategies promote a green culture that is conducive to the applicability of the green TFL style. Based on the above-presented arguments, this study hypothesizes the following statement:
Hypothesis 2 (H2).
Green management initiatives positively influence green TFL.
2.4. Green TFL and Employees’ Green Creativity
Transformational leaders use intellectual stimulation and inspirational motivation, which promote creativity and innovation [42,43]. Transformational leaders act as a champion in fostering innovative thoughts among the employees [44,45]. Leaders who are exhibiting transformational leadership style, stimulate out-of-the-box thinking and enable the workers to consider new ways of looking at an organizational issue [41,45]. Green TFL is a leadership behavior that is characterized by the provision of encouragement, clear vision, motivation, inspiration, and support for developmental needs in order to accomplish the organization’s environmental objectives [1,10].
Green TFL inspires individuals to acquire new skills and techniques [46] and stimulates their green innovation, which enables organizations to market eco-friendly products [47]. Additionally, green TFL persuades the employees to prefer organizational green objectives over their personal agenda and provides them with all the necessary resources required to create novel ideas for the betterment of the environment [6,10]. Thus, employees generate novel ideas when the leaders recognize and encourage their creative thoughts and transform innovative vision [48]. Hence, green TFL is necessary for leading and encouraging its staff to practice green innovation [21,40].
A leader with green values would certainly exert influence on the behavior of followers, which translates into employees’ pro-environmental behavior [49]. By developing good ties with the employees, a green transformational leader will raise the concerns of individuals regarding environmental problems through expressing their green thoughts. The authors of [1] conducted a study on employees working in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and found that the green TFL promotes green innovation. Similarly, another research found that green TFL has a significant impact on the green creativity of individuals who are working in the Chinese IT industry [6]. This research explores the direct effect of green TFL on creativity and also proposes green management initiatives as an antecedent of green TFL. From the above-presented arguments, this study hypothesizes the following statement:
Hypothesis 3 (H3).
Green TFL positively influences green creativity.
2.5. Mediating Effect of Green TFL
The organizational policies and initiatives are implemented through its workforce. Individuals exert efforts according to their specified role in the organizational hierarchy. Therefore, the top leaders play a prominent role in translating, communicating, and implementing green policies. However, in the absence of required resources and leadership capabilities, it is certainly not enough to have green strategies. The study in [50] maintained that transformational leadership implements the organizational initiative of bringing change in the culture.
Transformational leaders significantly influence the behavior of their followers [51,52]. Therefore, green TFL would exert considerable influence on their followers’ green behavior. Leaders usually direct and persuade their subordinates towards the achievement of organizational agendas [53], whereas the HR practices and organizational strategies promote an internal system on a bigger scale, which inspires the employees in a systematic way [54]. Hence, we can infer that both organizational interventions and leadership are required to manage employees, typically from different standpoints. The HR managers would create an atmosphere that is based on the green strategies and environmental focus of the firm. Drawing upon social information processing theory [23], this study posits that green management initiatives provide direction and support to the leaders, who then act according to the strategic direction of the firm. Therefore, operational managers would exhibit green TFL through which they will stimulate green creativity among the employees. On the other hand, the HR managers would perform a supporting role by hiring, promoting, and developing a green workforce in the organization. Besides the HR practices, green strategies would require the operations managers to adopt green measures for the reduction of environmental footprint through the involvement of the green workforce.
Furthermore, scholars have found that the green TFL acts as an intervening variable for stimulating green creativity with the help of innovation-led organizational strategies [55]. Moreover, the environmental care agenda can be advanced through the exhibition of an environmentally specific leadership style [56]. In addition, the authors of [57] argued that the successful implementation of HR practices depends on the proximal HR outcome. Such proximal HR outcome mediates the relationship between HR practices and their intended outcome. Hence, green TFL can become the proximal HR outcome, which translates the green vision of the organization and instills the importance of adopting creative measures for the betterment of the environment. Thus, the following hypothesis is proposed:
Hypothesis 4 (H4).
Green TFL mediates the relationship between green management initiatives and green creativity.
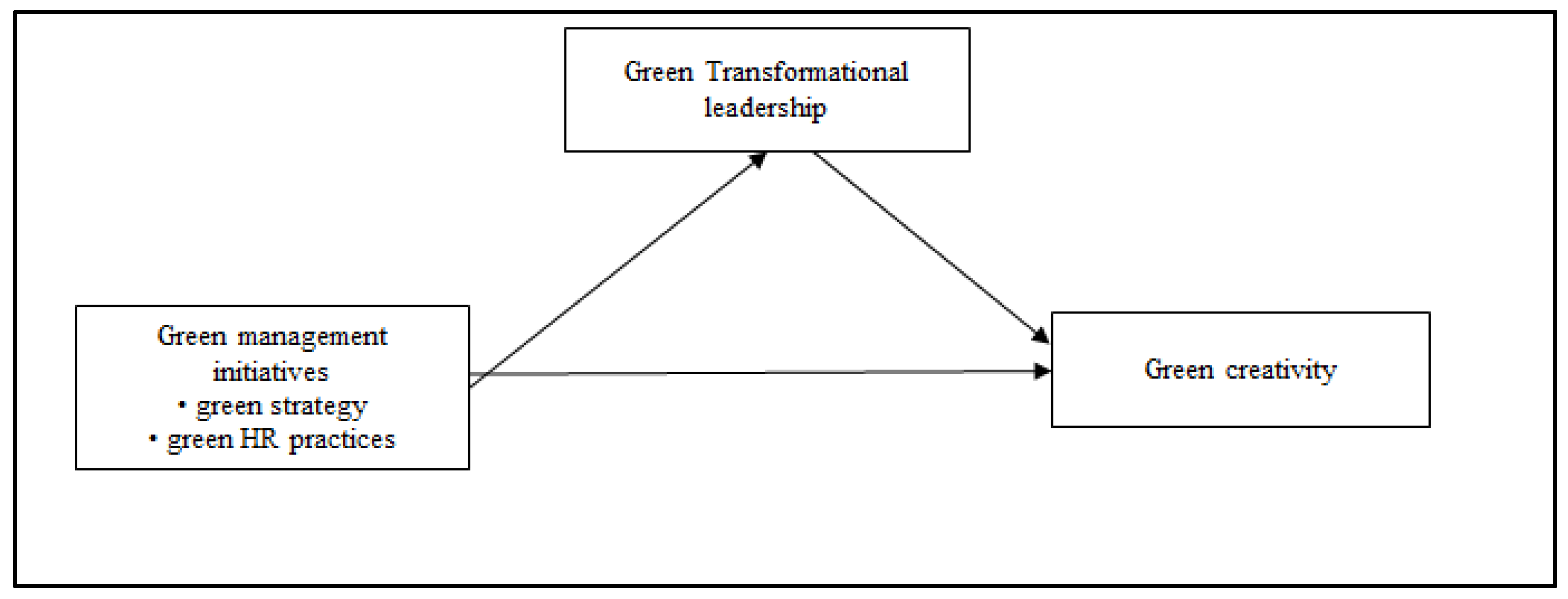
The conceptual model of the current study is depicted in Figure 1.
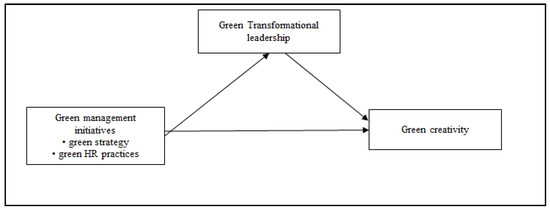
Figure 1.
Conceptual model.
3. Methodology and Measurement
3.1. Sampling and Data Collection
Data were collected from the large manufacturing companies that are operating in the textile, sugar, and cement industries of Pakistan. Large manufacturing firms are now under immense pressure from environmental protection agencies to protect and preserve the environment, resulting in a greater willingness to pursue a green innovation strategy. Moreover, large manufacturing organizations have a well-organized human resource department that can play an effective role in devising and implementing a green strategy. Additionally, the production process of these firms may contaminate water resources, land, and air. Therefore, strict environmental regulations are applied to these firms. Lastly, stakeholders’ demand for the protection of the environment is mounting because the successful implementation of the green agenda largely depends on the operations performed by these manufacturing firms [58].
The criteria for the selection of participating manufacturing firms were based on the number of employees working in those organizations. Firms that had more than one thousand employees were chosen for this research. In addition, the ISO 14001 certified firms were selected for the data collection purpose. To comply with the ISO 14001 standards, organizations tend to ensure that the green management initiatives are implemented across all the functional areas [59]. Hence, it can be assumed that the managers would strictly follow and apply GHRM practices to further the organizational green agenda. Therefore, 250 ISO 14001 certified companies were contacted by sending emails to their HR managers. HR managers were briefed on the purpose of this investigation and made aware of the significance of their response. HR managers were asked to fill in the questionnaire related to green management initiatives, while production managers filled in survey questionnaires on employees’ green creativity and green TFL. The data were collected in two waves for mitigating the potential impact of common method variance (CMV) bias [60]. In the first wave, HR managers responded to green management initiatives and demographics, whereas production managers responded to green TFL. In the second wave, production managers were asked to provide details related to employees’ green creativity, along with managers’ demographic details. Several phone calls and e-mail reminders were used to prompt the managers for the provision of information. The data collection process lasted for three months. From 250 questionnaires, 203 questionnaires contained the required information. Finally, 203 questionnaires were used for the data analysis procedure.
CMV bias was alleviated by applying procedural and statistical measures. In procedural measures, a cover letter outlining the purpose and ensuring the confidentiality of the responses was attached [61]. According to [62], double-barreled and ambiguous questions pose problems in the comprehension stage; therefore, simple and clear wording was used in questions [60]. While applying statistical measures, the collinearity issue was assessed through values of variance inflation factors (VIFs). All values were in the acceptable range of < 3.3 suggested by [63]. Therefore, CMV bias was not a pervasive problem in the data. Table 1 presents the descriptive statistics of 203 responses. Statistics showed that male managers outnumbered female managers, while most of the managers have a master’s degree and above.

Table 1.
Demographic attributes.
3.2. Research Measures
A six-item scale developed by [5] was adopted to measure the perceptions of green TFL. The sample item includes “The leadership in my organization emphasizes the achievement of environmental goals”. This scale was also adopted by various scholars in their studies [1,21]. In this research, the value of Cronbach’s alpha was 0.894.
Green strategy implementation was measured through a seven-item scale developed by [64], which was also adapted by [16]. The sample item includes “Our company has integrated environmental issues into our strategic planning process”.
This study adopted a six-item scale to measure green HR practices, which was developed by [65]. It includes items such as “My company sets green goals for its employees”. Lastly, green creativity was measured through the scale developed by [5], and the value of Cronbach’s alpha was 0.91. This scale contains six items to measure the green creative behavior of employees. The scale was previously adopted by many researchers [6,10]. The sample item includes “This employee would find out creative solutions to environmental problems”.
In addition, prior studies have suggested that age and gender might also influence the employees’ green actions and behaviors [12,66]. Thus, demographic variables (i.e., gender and age) were controlled.
4. Data Analysis and Results
In order to check the hypothesized relationship of variables, this investigation applied the structural equation modeling technique through SmartPLS software. Following the suggestion of [67], SmartPLS was used because of its predictive nature. Moreover, SmartPLS delivers better results despite the small sample size [68]. In addition, SmartPLS also provides enhanced predictive relevance of the model [7].
4.1. Measurement Model
The reliability coefficient of instruments was calculated through Cronbach’s alpha value. All the values of Cronbach’s alpha were in the range of 0.835 to 0.901 (Table 2), which satisfied the criteria of >0.70 value [69]. The constructs used in this investigation had high composite reliability (CR), as the values of CR were in the range of ≥0.795 to 0.884. According to [70], values ranging from 0.7 to 0.9 are considered “good”. Furthermore, convergent validity was established through average variance extracted (AVE) and found values above 0.5 (Table 2). The study in [69] maintained that values ≥ 0.50 represent the convergent validity of constructs. Therefore, all measurement scales had CR and convergent validity.

Table 2.
Composite reliability and convergent validity.
Considering the recommendations of [68], the Heterotraite–Monotrait ratio of correlation (HTMT) was obtained to establish the discriminant validity of constructs used in this study. The values of HTMT were in the range of ≥0.637 to 0.681(Table 3), which satisfied the criteria of <0.85 value suggested by [71]. Hence, the discriminant validity of scales was also established.

Table 3.
The Heterotrait–Monotrait ratio of correlation (HTMT).
4.2. The Structural Model
SmartPLS software version 3.2 was used to run variance-based structural equation modeling. In order to evaluate the structural model, we analyzed the significance of path coefficients, coefficient of determination (R2), the effect size (f2), and predictive relevance of the effect size (Q2). Table 4 presents the results of direct and indirect relationships between variables. It was found that green management initiatives were significantly and positively influencing the green creativity of employees (H1) and green TFL (H2), while green TFL positively and significantly influenced green creativity (H3). Furthermore, the intervening effect of green TFL was empirically established in the green management initiatives–green creativity link (H4). Hence, all the hypotheses of our study were supported.

Table 4.
Testing of hypotheses.
In order to control the demographic variables’ effect, we followed the process outlined by [72]. The results of bootstrapping showed no significant impact of gender and age on the endogenous variable.
Moreover, the value of the R square was also calculated. The R2 indicates the variance in the endogenous construct caused by the predictive variables of the exogenous constructs; this value ranges from zero to one. In the current study, values of R squares are 0.421 for TFL and 0.456 for GC, which means that 42% of the age change in TFL is caused by GMI, and 45.6% of the age change in GC is explained by GMI and TFL together.
Finally, to evaluate the predictive power of the model, we calculated Q2. The Stone–Geisser test was run through the PLS-blindfolding technique. According to [73], the value of Q2 should be greater than zero. The values of Q2 for this study are 0.271 for TFL and 0.286 for, which are well above zero; hence, our model has a predictive relevance.
In order to test the mediation effect, this study has followed the procedure suggested by [74]. As shown in Table 4, this research found a significant indirect effect of green management initiatives on green creativity through green TFL. According to [75] “a significant indirect effect, is the only prerequisite for establishing a mediation effect”. In addition, the direct effect of green management initiatives was also significantly positive with green creativity. Therefore, the partial mediation of green TFL was established [74]. Moreover, both direct and indirect effects were significant and positive (i.e., in the same direction). Therefore, it indicated that green TFL only mediated a portion of the effect of green management initiatives on green creativity, while green management initiatives still explained a portion of green creativity, which is independent of the intervening variable [75]. According to [74], this type of mediation is called complementary partial mediation.
5. Discussion
This research has investigated the relationship between green management initiatives and green creativity through the intervening impact of green TFL. Previously, few studies have explored the synergetic effect of green strategy and green HR practices on green creativity, especially in the context of the Pakistani manufacturing sector. Pakistan is now one of the most greatly affected countries due to climate change and environmental pollution [76]. Thus, the context of this investigation becomes more important for practitioners. This study has explored and found a positive relationship between green management initiatives and green creativity. This result is in line with the previous research findings from various scholars [1,11,12,16,28]. This study also advances and supports previous findings wherein green TFL and green HRM were positively related [1,12] and green TFL positively influenced the employees’ green creativity [6,10,12]. Moreover, empirical evidence of green TFL as an intervening variable advances the current literature of leadership. Different scholars [6,56] have also found that leadership indirectly affects the green creativity of employees.
The results obtained in this investigation are valuable in the context of Asian countries because the manufacturing sector of Pakistan was previously ignored in investigating the impact of organizational green strategy on the green creative behavior of employees. Therefore, this study highlights the need for an effective green HR strategy within organizations of emerging markets. It also provides insights into the organizations operating in Asian countries as to how these firms can promote pro-environmental behaviors among their employees through the adoption of green HR strategies. Few scholars have researched the implementation of green HRM in Chinese firms [33,65], and its effectiveness in Asian organizations was also established. However, the current literature also indicated that several contextual factors such as social conditions, industry characteristics, and national culture might affect the adoption and implementation of green HR strategies. Thus, Asian organizations should initiate those measures that are consistent with their country’s cultural norms and values. Furthermore, the findings of this investigation have several practical and theoretical implications for researchers, HR practitioners, and organizational leaders.
5.1. Theoretical Implications
The results of this study have implications that advance the theories used to underpin the proposed relationships. Drawing upon the componential theory of creativity [22], this research proposed that both the green strategy and green HR practices (green management initiatives) act as outside factors in promoting employees’ green creativity. Results have demonstrated that the organizational strategic focus plays an important role in the stimulation of creativity among individuals. Moreover, green TFL promotes green creative behavior by enhancing technical skills, cognitive skills, and intrinsic motivation (i.e., three inherently individual components proposed in the componential theory of creativity). While applying social information processing theory [23] to the link between green management initiatives and green TFL, it is found that the organizational strategic priorities create a corresponding culture, which requires the leaders to further the organizational agenda through relevant leadership styles. Furthermore, green HR activities, combined with the organizational green agenda, demonstrate strategic environmental concern. Thus, it can be implied that the leaders have a sense of their occupational culture, which influences their attitudes and actions.
This work has combined two important organizational elements (i.e., green strategy and green HR practices) and highlighted its synergetic influence on green creativity through the green TFL. Scholars [12,16,28] have emphasized the need for more empirical studies on the impact of organizational initiatives on green creativity. Therefore, this study has explored the relationship that was relatively overlooked by previous researchers. Additionally, the mediating impact of green TFL advances the leadership literature in a way that the green management initiatives serve as a contextual precursor of green TFL. Hence, it implies that the leaders advance the organizational vision and policies and ensure its successful implementation by exhibiting a relevant leadership style.
HRM and leadership have crucial roles to play in wreaking the creative potential of employees [77,78]. Previous studies [12,79,80] have explored the interaction impact of HR practices and leadership styles, while this work has uncovered that leadership can become a central element in the execution of HR policies. Therefore, it is suggested that the organizations should promote a green TFL style for the stimulation of employees’ green creativity. For doing so, organizations must demonstrate their environmental care through the creation of green strategies and motivate their managers to exhibit a green TFL style. Managers will then serve as catalysts to stimulate green creativity among workers.
5.2. Practical Implications
This study provides a range of key insights to policymakers and managers regarding how they can stimulate green creativity for the achievement of better outcomes. First, the green strategic focus of the firm would enhance its corporate image in the eyes of various stakeholders who have an increasing focus on environmental protection. Therefore, top managers must realize the importance of having green strategies in place to mitigate the stakeholders’ pressures. Likewise, a better corporate image will also meet the needs of customers who are more environmentally conscious. Moreover, initiatives for environmental care should not be treated as a financial burden; rather, it should be realized that green creativity may provide a competitive advantage to the firm. Resultantly, new green markets can also be served by targeting environmentally focused people.
The findings of this study suggest that the combination of green HR practices and green strategy influences green creativity. Hence, organizational policymakers should recognize the value of combined efforts required to further the green agenda. HR managers must ensure the compatibility of HR functions with the corresponding organizational green strategy. Furthermore, employees who are involved in green creative behaviors should be rewarded and retained. Training must be provided in order to make employees abreast of the latest practices for environmental conservation. Job descriptions of employees and managers should include critical success factors related to the exhibition of green behavior. The selection process should incorporate measurements through which pro-environmental behavior and environmental awareness of applicants can be gauged. In a nutshell, organizations are supposed to have a conducive green HR system that facilitates, encourages, and stimulates employees’ green creativity.
This study proposes that the managers should exhibit a green TFL style to develop green management initiatives and stimulate employees’ green creativity. Transformational leaders can better leverage pro-environmental behaviors when they receive full support from organizational strategy and the HR department. Hence, the development of green TFL relies heavily on the existence of green management initiatives. This provides valuable insight to top management that it requires a good green strategy to promote a green TFL style within the organization. Consequently, green TFL would help to achieve organizational green agenda through creative employees. Leaders may stimulate employees’ green creativity through multiple interventions such as rewarding green behavior, provision of autonomy to implement creative ideas, knowledge enhancement through training, and green team building.
5.3. Limitations and Directions for Future Research
This research has some limitations that will become suggestions for future research. First, this investigation was conducted in the manufacturing sector; therefore, it limits the generalizability of findings to other sectors. Hence, future research should extend this conceptual model in other sectors such as the information technology sector and the automobile sector, as both industries are experiencing green radical innovation to reduce carbon footprint. Second, this research has not explored the possible moderating effect of employees’ pro-environmental behavior; hence, future research may advance the findings of this study by incorporating employees’ level construct. Moreover, future studies should also incorporate employees’ perceptions of leadership style. Third, this study was based on the perception of organizational members only; therefore, future research should also obtain the perspective of external stakeholders such as customers and suppliers. Lastly, this research has identified the impact of only one leadership style, i.e., green TFL. Thus, future studies should also consider using other leadership styles, such as servant leadership and inclusive leadership.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.M. and M.F.; data curation, A.M.; formal analysis, M.F. and J.-K.L.; methodology, M.F. and J.-K.L.; writing—original draft preparation, A.M. and S.J.; writing—review and editing, A.M. and S.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially funded by the Ilma University, Karachi, Pakistan under the Ilma Research Grant Program.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Singh, S.K.; Del Giudice, M.; Chierici, R.; Graziano, D. Green innovation and environmental performance: The role of green transformational leadership and green human resource management. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2020, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada, G.C.; Klenke, T.; Mejía-Ortíz, L.M. Regulatory Challenges in Realizing Integrated Coastal Management—Lessons from Germany, Costa Rica, Mexico and South Africa. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, W.; Ramanathan, R.; Nath, P. Environmental pressures and performance: An analysis of the roles of environmental innovation strategy and marketing capability. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2017, 117, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Tang, G.; Jackson, S.E. Green human resource management research in emergence: A review and future directions. Asia Pac. J. Manag. 2018, 35, 769–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-S.; Chang, C.-H. The Determinants of Green Product Development Performance: Green Dynamic Capabilities, Green Transformational Leadership, and Green Creativity. J. Bus. Ethics 2013, 116, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Bhutto, T.A.; Xuhui, W.; Maitlo, Q.; Zafar, A.U.; Ahmed Bhutto, N. Unlocking employees’ green creativity: The effects of green transformational leadership, green intrinsic, and extrinsic motivation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.Y.; Yusliza, M.Y.; Ramayah, T.; Fawehinmi, O. Nexus between green intellectual capital and green human resource management. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Guo, S. Selecting Green Supplier of Thermal Power Equipment by Using a Hybrid MCDM Method for Sustainability. Sustainability 2014, 6, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eide, A.E.; Saether, E.A.; Aspelund, A. An investigation of leaders’ motivation, intellectual leadership, and sustainability strategy in relation to Norwegian manufacturers’ performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 120053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Dhar, R.L. Effect of green transformational leadership on green creativity: A study of tourist hotels. Tour. Manag. 2016, 57, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Yu, H.; Xu, H. Effects of green human resource management and managerial environmental concern on green innovation. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Liu, H.; Chin, T.; Hu, D. The Continuous Mediating Effects of GHRM on Employees’ Green Passion via Transformational Leadership and Green Creativity. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guerci, M.; Longoni, A.; Luzzini, D. Translating stakeholder pressures into environmental performance—The mediating role of green HRM practices. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2016, 27, 262–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renwick, D.W.S.; Redman, T.; Maguire, S. Green Human Resource Management: A Review and Research Agenda. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2013, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pham, N.T.; Vo Thanh, T.; Tučková, Z.; Thuy, V.T.N. The role of green human resource management in driving hotel’s environmental performance: Interaction and mediation analysis. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2019, 102392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, T.T. Integrating green strategy and green human resource practices to trigger individual and organizational green performance: The role of environmentally-specific servant leadership. J. Sustain. Tour. 2020, 28, 1193–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostroff, C.; Bowen, D.E. Reflections on the 2014 Decade Award: Is There Strength in the Construct of HR System Strength? Acad. Manag. Rev. 2016, 41, 196–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Cordeiro, J.; Sarkis, J. Institutional pressures, dynamic capabilities and environmental management systems: Investigating the ISO 9000—Environmental management system implementation linkage. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 114, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, B.M. Leadership and Performance beyond Expectations; Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985; ISBN 9780029018101. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, J.L.; Carleton, E. Uncovering How and When Environmental Leadership Affects Employees’ Voluntary Pro-environmental Behavior. J. Leadersh. Organ. Stud. 2018, 25, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, K.; Liu, W. Value Congruence: A Study of Green Transformational Leadership and Employee Green Behavior. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amabile, T. A model of creativity and innovation in organizations. Res. Organ. Behav. 1988, 10, 123–167. [Google Scholar]
- Salancik, G.R.; Pfeffer, J. A Social Information Processing Approach to Job Attitudes and Task Design. Adm. Sci. Q. 1978, 23, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amabile, T. Motivating Creativity in Organizations: On Doing What You Love and Loving What You Do. Calif. Manag. Rev. 1997, 40, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, N.K.; Dhar, R.L. Transformational leadership, innovation climate, creative self-efficacy and employee creativity: A multilevel study. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2015, 51, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, F.-C. Does transformational, ambidextrous, transactional leadership promote employee creativity? Mediating effects of empowerment and promotion focus. Int. J. Manpow. 2016, 37, 1250–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, L.; Wu, Y. Green strategy for gaining competitive advantage in housing development: A China study. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, W.; Li, X.; Zheng, M.; Liu, Y.; Yan, J. Commitment to Human Resource Management of the Top Management Team for Green Creativity. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Renwick, D.W.S.; Jabbour, C.J.C.; Muller-Camen, M.; Redman, T.; Wilkinson, A. Contemporary developments in Green (environmental) HRM scholarship. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2016, 27, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bos-Nehles, A.; Renkema, M.; Janssen, M. HRM and innovative work behaviour: A systematic literature review. Pers. Rev. 2017, 46, 1228–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Konrad, A.M. Causality Between High-Performance Work Systems and Organizational Performance. J. Manag. 2017, 43, 973–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, N.; Nik Mahmood, N.H.; Yusliza, M.Y.; Ramayah, T.; Noor Faezah, J.; Khalid, W. Green Human Resource Management for organisational citizenship behaviour towards the environment and environmental performance on a university campus. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Paillé, P.; Jia, J. Green human resource management practices: Scale development and validity. Asia Pac. J. Hum. Resour. 2018, 56, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, B.F.; Huang, S. Achieving sustainability through attention to human resource factors in environmental management. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2001, 21, 1539–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrini, A.; dos Lins, L.S. Integration between environmental management and strategic planning in the oil and gas sector. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 4869–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moraes, S.S.; Chiappetta-Jabbour, C.J.; Battistelle, R.A.G.; Rodrigues, J.M.; Renwick, D.S.W.; Foropon, C.; Roubaud, D. When knowledge management matters: Interplay between green human resources and eco-efficiency in the financial service industry. J. Knowl. Manag. 2019, 23, 1691–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Obeidat, S.M.; Al Bakri, A.A.; Elbanna, S. Leveraging “Green” Human Resource Practices to Enable Environmental and Organizational Performance: Evidence from the Qatari Oil and Gas Industry. J. Bus. Ethics 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, N.; Higgs, M. How Strategic Focus Relates to the Delivery of Leadership Training and Development. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2016, 55, 541–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, T.T. Effects of environmentally-specific servant leadership on green performance via green climate and green crafting. Asia Pac. J. Manag. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhang, D.; Lyu, C.; Zhang, H. Does Seeing “Mind Acts Upon Mind” Affect Green Psychological Climate and Green Product Development Performance? The Role of Matching between Green Transformational Leadership and Individual Green Values. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.-S.; Chang, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-H. Green Transformational Leadership and Green Performance: The Mediation Effects of Green Mindfulness and Green Self-Efficacy. Sustainability 2014, 6, 6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elkins, T.; Keller, R.T. Leadership in research and development organizations: A literature review and conceptual framework. Leadersh. Q. 2003, 14, 587–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, B.M. Does the transactional—Transformational leadership paradigm transcend organizational and national boundaries? Am. Psychol. 1997, 52, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.I.; Chow, C.; Wu, A. The role of transformational leadership in enhancing organizational innovation: Hypotheses and some preliminary findings. Leadersh. Q. 2003, 14, 525–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldman, D.A.; Bass, B.M. Transformational leadership at different phases of the innovation process. J. High Technol. Manag. Res. 1991, 2, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, P.B.; Lei, H. The mediating role of trust in stimulating the relationship between transformational leadership and knowledge sharing processes. J. Knowl. Manag. 2018, 22, 521–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriopoulos, C.; Lewis, M.W. Managing Innovation Paradoxes: Ambidexterity Lessons from Leading Product Design Companies. Long Range Plann. 2010, 43, 104–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amabile, T.; Pillemer, J. Perspectives on the Social Psychology of Creativity. J. Creat. Behav. 2012, 46, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.L.; Barling, J. Greening organizations through leaders’ influence on employees’ pro-environmental behaviors. J. Organ. Behav. 2013, 34, 176–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Liao, H.; Taylor, M.S.; Kim, S. Effects of high-performance work systems on transformational leadership and team performance: Investigating the moderating roles of organizational orientations. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2018, 57, 1065–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.P. Improving Organizational Effectiveness through Transformational Leadership; Bass, B.M., Avolio, B.J., Eds.; (Hardcover); Sage Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1996; Volume 22, ISBN 0-8039-5235-X. [Google Scholar]
- Avolio, B.J.; Bass, B.M. Transformational leadership, charisma, and beyond. In Emerging Leadership Vistas; International Leadership Symposia Series; Lexington Books: Lanham, MD, USA; D. C. Heath and Com: Lexington, MA, USA, 1988; pp. 29–49. ISBN 0-669-15331-1. [Google Scholar]
- Northouse, P.G. Leadership: Theory and Practice; SAGE: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2013; ISBN 9781452203409. [Google Scholar]
- Lievens, F. Human Resource Management; Lannoo Campus: Leuven, Belgium, 2015; ISBN 9789401426404. [Google Scholar]
- Do, H.; Budhwar, P.S.; Patel, C. Relationship between innovation-led HR policy, strategy, and firm performance: A serial mediation investigation. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2018, 57, 1271–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, T.T. Environmentally-specific servant leadership and green creativity among tourism employees: Dual mediation paths. J. Sustain. Tour. 2020, 28, 86–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Takeuchi, R.; Lepak, D.P. Where do We Go From Here? New Perspectives on the Black Box in Strategic Human Resource Management Research. J. Manag. Stud. 2013, 50, 1448–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Lai, K.; Liu, C.; Wei, F.; Ma, M.; Jia, S.; Jiang, Z.; Lv, L. Promoting sustainability of manufacturing industry through the lean energy-saving and emission-reduction strategy. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ghazali, B.M.; Afsar, B. Green human resource management and employees’ green creativity: The roles of green behavioral intention and individual green values. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2020, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Podsakoff, N.P. Sources of Method Bias in Social Science Research and Recommendations on How to Control It. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2011, 63, 539–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Lee, J.Y.; Podsakoff, N.P. Common Method Biases in Behavioral Research: A Critical Review of the Literature and Recommended Remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 2003, 88, 879–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourangeau, R.; Rips, L.J.; Rasinski, K. The Psychology of Survey Response; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; ISBN 9780521576291. [Google Scholar]
- Kock, N. Common Method Bias: A Full Collinearity Assessment Method for PLS-SEM. In Partial Least Squares Path Modeling; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 245–257. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, S.B.; Iyer, E.S.; Kashyap, R.K. Corporate Environmentalism: Antecedents and Influence of Industry Type. J. Mark. 2003, 67, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, J.; Shen, J.; Deng, X. Effects of Green HRM Practices on Employee Workplace Green Behavior: The Role of Psychological Green Climate and Employee Green Values. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2017, 56, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Kim, Y.; Han, K.; Jackson, S.E.; Ployhart, R.E. Multilevel Influences on Voluntary Workplace Green Behavior: Individual Differences, Leader Behavior, and Coworker Advocacy. J. Manag. 2017, 43, 1335–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M.; Gudergan, S.P. Advanced Issues in Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling; SAGE Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 9781483377391. [Google Scholar]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2015, 43, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Risher, J.J.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M. When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2019, 31, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling, 4th ed.; Methodology in the Social Sciences; Guilford Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 9781462523351. [Google Scholar]
- Kock, N. Using WarpPLS in e-collaboration studies: Mediating effects, control and second order variables, and algorithm choices. Int. J. e-Collab. 2011, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M.; Smith, D.; Reams, R.; Hair, J.F. Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM): A useful tool for family business researchers. J. Fam. Bus. Strateg. 2014, 5, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitzl, C.; Roldan, J.L.; Cepeda, G. Mediation analysis in partial least squares path modeling. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2016, 116, 1849–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrión, G.C.; Nitzl, C.; Roldán, J.L. Mediation Analyses in Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling: Guidelines and Empirical Examples. In Partial Least Squares Path Modeling; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 173–195. [Google Scholar]
- Mumtaz, M. Climate Change Impacts and Adaptation in Agricultural Sector: The Case of Local Responses in Punjab, Pakistan; de Oliveira, J.A.P., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2019; Chapter 5; ISBN 978-1-78985-668-2. [Google Scholar]
- Leroy, H.; Segers, J.; van Dierendonck, D.; den Hartog, D. Managing people in organizations: Integrating the study of HRM and leadership. Hum. Resour. Manag. Rev. 2018, 28, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, A.; Farrukh, M.; Wu, Y.; Abdul Wahab, S. Does inclusive leadership incite innovative work behavior? Hum. Syst. Manag. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, E.P.; Gardner, W.L.; Gullifor, D.P.; Tribble, L.L.; Li, M. Authentic Leadership and High-Performance Human Resource Practices: Implications for Work Engagement. Res. Pers. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2017, 35, 103–153. [Google Scholar]
- Neves, P.; Almeida, P.; Velez, M.J. Reducing intentions to resist future change: Combined effects of commitment-based HR practices and ethical leadership. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2018, 57, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).