Removal of Estradiol, Diclofenac, and Triclosan by Naturally Occurring Microalgal Consortium Obtained from Wastewater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Algal Consortium, Culture Medium, and Growth Conditions
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Experimental Setup
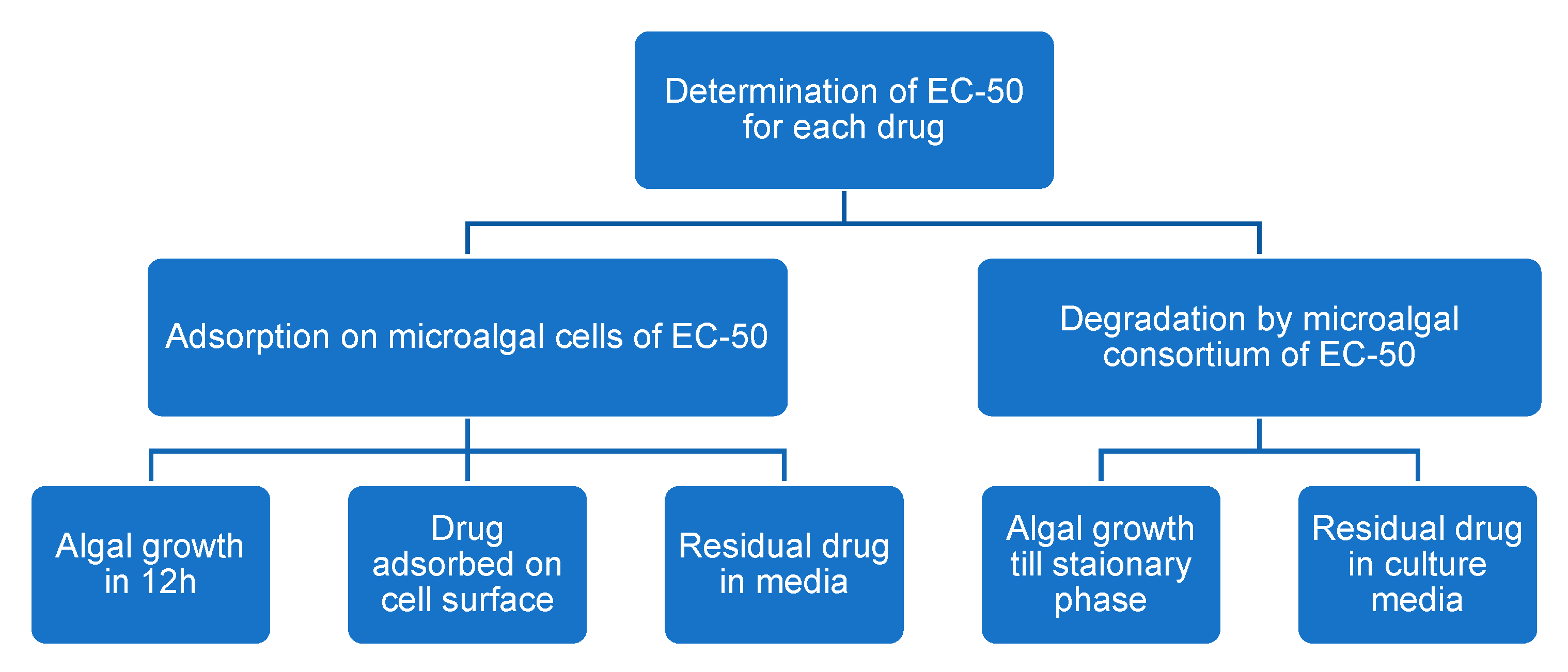
2.3.1. Growth Inhibitory Concentrations for EST, DCF, and TCS
2.3.2. Drug Adsorption on the Microalgal Surface
2.3.3. Drug Degradation by Microalgae
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.4.1. Algal Density and Chlorophyll Analysis
2.4.2. HPLC Analysis of the Drugs
Analysis of Drug Adsorbed on Microalgal Surface
Analysis of Residual Drug in Culture Media
2.4.3. Specific Removal of Drugs
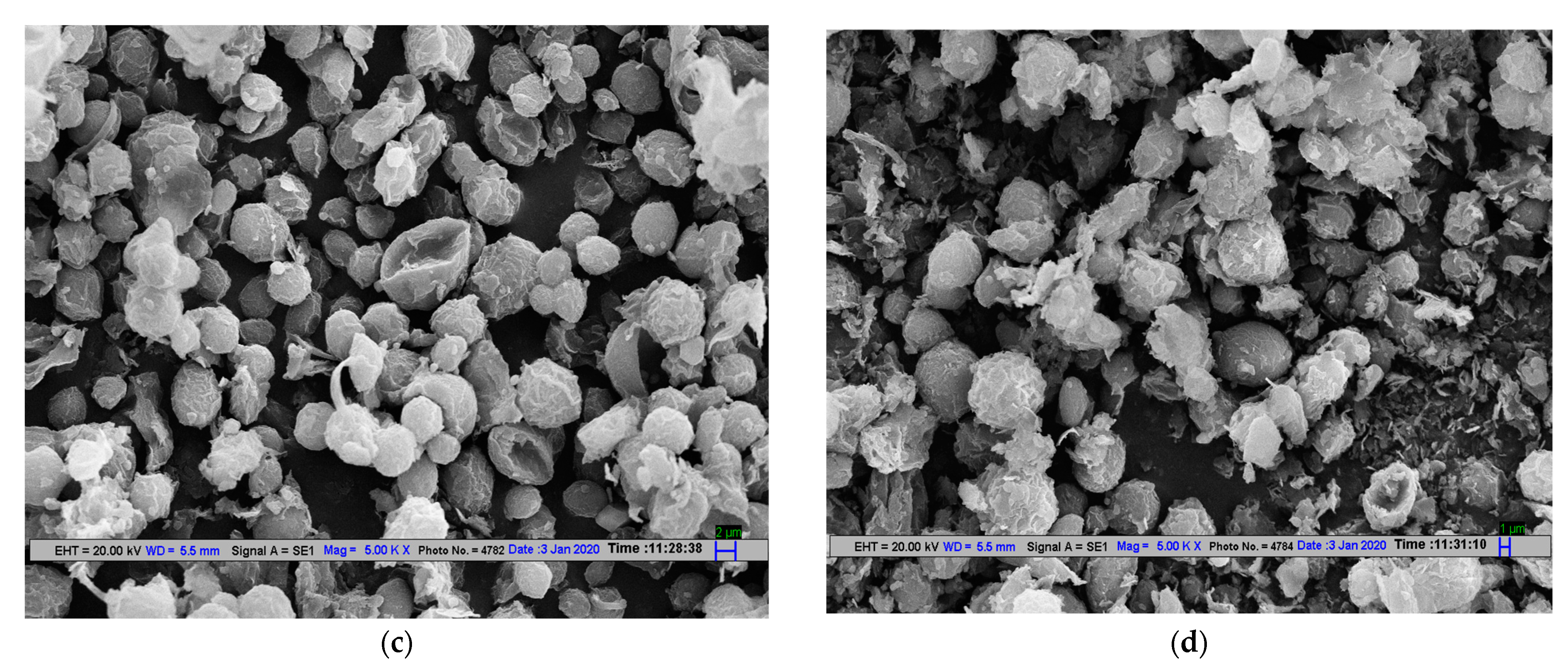
2.4.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy of Microalgal Cells
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
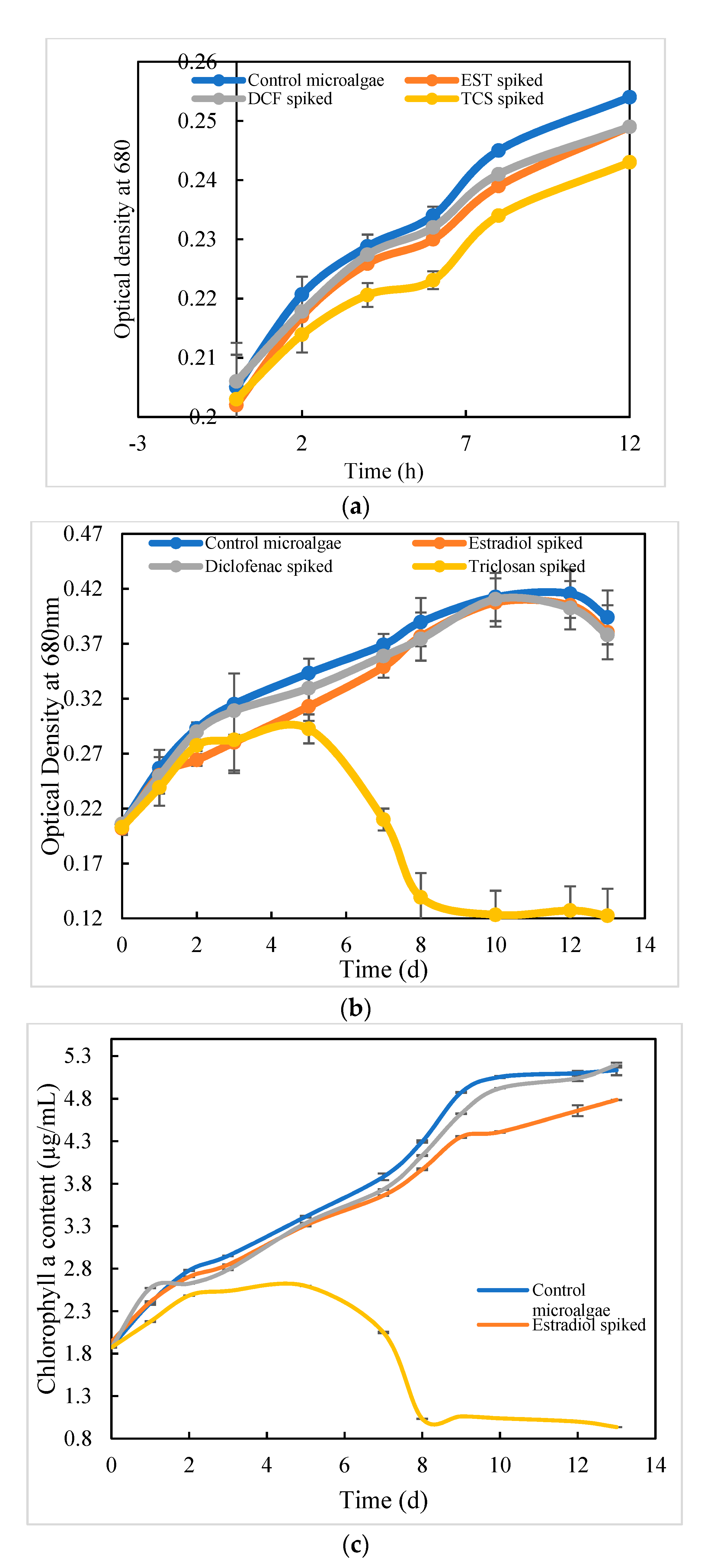
3.1. Growth Inhibitory Concentrations for EST, DCF, and TCS
3.2. Drug Adsorption on the Microalgal Surface
3.2.1. Algal Density and Chlorophyll Analysis
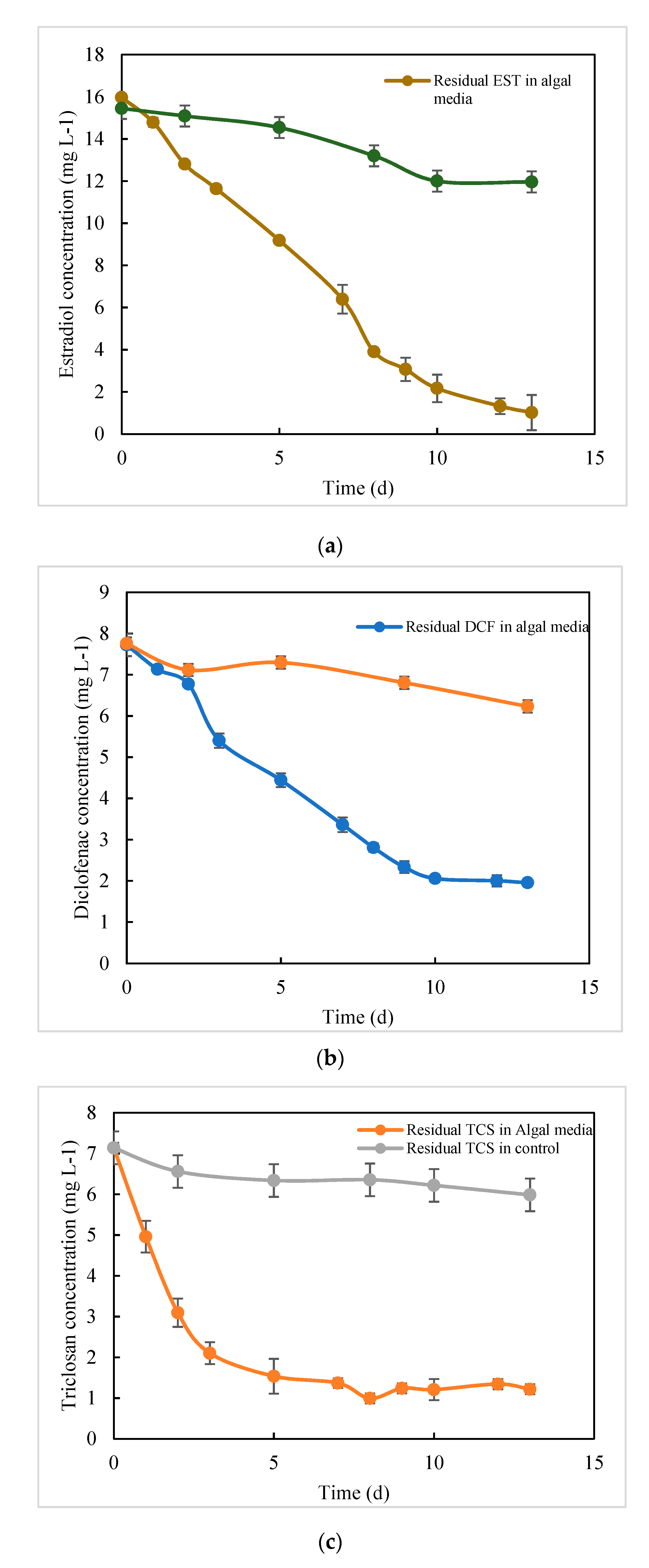
3.2.2. Analysis of the Drug Adsorbed on Microalgal Cells
3.3. Analysis of Residual Drug in Culture Media after Degradation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Noguera-Oviedo, K.; Aga, D.S. Lessons learned from more than two decades of research on emerging contaminants in the environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 316, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, N.H.; Reinhard, M.; Gin, K.Y.-H. Occurrence and fate of emerging contaminants in municipal wastewater treatment plants from different geographical regions-a review. Water Res. 2018, 133, 182–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.; Kumar, R.; Kishor, K.; Mlsna, T.; Pittman, C.U., Jr.; Mohan, D. Pharmaceuticals of emerging concern in aquatic systems: Chemistry, occurrence, effects, and removal methods. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 3510–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frederic, O.; Yves, P. Pharmaceuticals in hospital wastewater: Their ecotoxicity and contribution to the environmental hazard of the effluent. Chemosphere 2014, 115, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Poi, C.; Costil, K.; Bouchart, V.; Halm-Lemeille, M.P. Toxicity assessment of five emerging pollutants, alone and in binary or ternary mixtures, towards three aquatic organisms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 6122–6134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daughton, C.G.; Ternes, T.A. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment: Agents of subtle change? Environ. Health Perspect. 1999, 107 (Suppl. 6), 907–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S.; Aydin, M.E.; Ulvi, A.; Kilic, H. Antibiotics in hospital effluents: Occurrence, contribution to urban wastewater, removal in a wastewater treatment plant, and environmental risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 544–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verlicchi, P.; Galletti, A.; Petrovic, M.; Barceló, D. Hospital effluents as a source of emerging pollutants: An overview of micropollutants and sustainable treatment options. J. Hydrol. 2010, 389, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orias, F.; Perrodin, Y. Characterisation of the ecotoxicity of hospital effluents: A review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2013, 454–455, 250–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joss, A.; Keller, E.; Alder, A.C.; Göbel, A.; McArdell, C.S.; Ternes, T.; Siegrist, H. Removal of pharmaceuticals and fragrances in biological wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3139–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hai, F.I.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.C. A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci. Total. Environ. 2014, 473–474, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, T.T.; Blanch, E.W.; Jones, O.A. Predicted environmental concentration and fate of the top 10 most dis-pensed Australian prescription pharmaceuticals. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 10966–10976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, D.G.J. Pollution from drug manufacturing: Review and perspectives. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kristiansson, E.; Fick, J.; Janzon, A.; Grabic, R.; Rutgersson, C.; Weijdegerd, B.; Larsson, D.J. Pyrosequencing of antibiotic-contaminated river sediments reveals high levels of resistance and gene transfer elements. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubbert, C.; Baars, C.; Dayakar, A.; Lippmann, N.; Rodloff, A.C.; Kinzig, M.; Sörgel, F. Environmental pollu-tion with antimicrobial agents from bulk drug manufacturing industries in Hyderabad, South India, is associated with dissemination of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase and carbapenemase-producing pathogens. Infection 2017, 45, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Yang, M.; Hu, J.; Ren, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K. Determination and fate of oxytetracycline and related com-pounds in oxytetracycline production wastewater and the receiving river. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 2008, 27, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, G.A.; Berglund, B.; Khan, K.M.; Lindgren, P.-E.; Fick, J. Occurrence and Abundance of Antibiotics and Resistance Genes in Rivers, Canal and near Drug Formulation Facilities—A Study in Pakistan. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, C.W.; Ji, S.L.; Ren, H.Y. Determination of steroid estrogens in wastewater treatment plant of a controceptives producing factory. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 121, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, W.J.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, E.S.; Shin, S.K.; Hwang, S.R.; Oh, J.E. Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceu-ticals in wastewater from households, livestock farms, hospitals and pharmaceutical manufactures. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, P.; Prajapati, S.K.; Malik, A. Screening native microalgal consortium for biomass production and nutrient removal from rural wastewaters for bioenergy applications. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 91, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.-Q.; Ying, G.-G.; Yang, B.; Liu, S.; Lai, H.-J.; Liu, Y.-S.; Chen, Z.-F.; Zhou, G.-J. Biotransformation of progesterone and norgestrel by two freshwater microalgae (Scenedesmus obliquus and Chlorella pyrenoidosa): Transformation kinetics and products identification. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Qiu, C.B.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, Z.P.; Yang, H. Bioaccumulation and degradation of pesticide fluroxypyr are associated with toxic tolerance in green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osundeko, O.; Dean, A.P.; Davies, H.; Pittman, J.K. Acclimation of microalgae to wastewater environments in-volves increased oxidative stress tolerance activity. Plant Cell Physiol. 2014, 55, 1848–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aderemi, A.O.; Novais, S.C.; Lemos, M.F.; Alves, L.M.; Hunter, C.; Pahl, O. Oxidative stress responses and cellular energy allocation changes in microalgae following exposure to widely used human antibiotics. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 203, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Field, J.A.; Thurman, E.M. Glutathione Conjugation and Contaminant Transformation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, N.M.; Anderson, K.E. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Diclofenac. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1997, 33, 184–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandborgh-Englund, G.; Adolfsson-Erici, M.; Odham, G.; Ekstrand, J. Pharmacokinetics of Triclosan Following Oral Ingestion in Humans. J. Toxicol. Environ. Heal. Part A 2006, 69, 1861–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Prajapati, S.K.; Malik, A.; Vijay, V.K. Cultivation of native algal consortium in semi-continuous pi-lot scale raceway pond for greywater treatment coupled with potential methane production. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 5581–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulations.gov, EPA. Algal Toxicity [EPA 712-C-006]. 2012. Available online: www.regulations.gov/document?D=EPA-HQ-OPPT-2009-0154-0003 (accessed on 31 May 2017).
- Chinnasamy, S.; Bhatnagar, A.; Claxton, R.; Das, K.C. Biomass and bioenergy production potential of microalgae consortium in open and closed bioreactors using untreated carpet industry effluent as growth medium. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 6751–6760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wilt, A.; Butkovskyi, A.; Tuantet, K.; Leal, L.H.; Fernandes, T.V.; Langenhoff, A.; Zeeman, G. Micropollutant removal in an algal treatment system fed with source separated wastewater streams. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 304, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Peng, D.-D.; Shi, C.-H.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Y.-T.; Lu, B. Selective determination of trace 17β-estradiol in dairy and meat samples by molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction and HPLC. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 1916–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escapa, C.; Coimbra, R.N.; Paniagua, S.; Garcia, A.I.; Otero, M. Comparative assessment of diclofenac removal from water by different microalgae strains. Algal Res. 2016, 18, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricart, M.; Guasch, H.; Alberch, M.; Barcel, D.; Bonnineau, C.; Geiszinger, A.; Proia, L. Triclosan persistence through wastewater treatment plants and its potential toxic effects on river biofilms. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 100, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prajapati, S.K.; Bhattacharya, A.; Malik, A.; Vijay, V.K. Pretreatment of algal biomass using fungal crude enzymes. Algal Res. 2015, 8, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wong, Y.S.; Tam, N.F.Y. Green microalgae in removal and biotransformation of estradiol and ethinylestradiol. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, Q.; He, N.; Sun, K.; Sun, D.; Wu, X.; Duan, S. Removal and Biodegradation of 17β-Estradiol and Diethylstilbestrol by the Freshwater Microalgae Raphidocelis subcapitata. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fent, K.; Weston, A.A.; Caminada, D. Ecotoxicology of human pharmaceuticals. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 76, 122–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleuvers, M. Aquatic ecotoxicity of pharmaceuticals including the assessment of combination effects. Toxicol. Lett. 2003, 142, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, T.; Weiss, S.; Schymanski, E.; von der Ohe, P.C.; Schmitt-Jansen, M.; Altenburger, R.; Streck, G.; Brack, W. Identification of a phytotoxic photo-transformation product of diclofenac using effect-directed analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1461–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt-Jansen, M.; Bartels, P.; Adler, N.; Altenburger, R. Phytotoxicity assessment of diclofenac and its photo-transformation products. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarazako, N.; Ishibashi, H.; Teshima, K.; Kishi, K.; Arizono, K. Effects of triclosan on various aquatic organ-isms. Environ. Sci. 2004, 11, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Franz, S.; Altenburger, R.; Heilmeier, H.; Schmitt-Jansen, M. What contributes to the sensitivity of microalgae to triclosan? Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 90, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Poon, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Cai, Z. Removal and reductive dechlorination of triclosan by Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 1498–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taştan, B.E.; Tekinay, T.; Çelik, H.S.; Özdemir, C.; Cakir, D.N. Toxicity assessment of pesticide triclosan by aquatic organisms and degradation studies. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 91, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.Q.; Kurade, M.B.; Jeon, B.H. Biodegradation of levofloxacin by an acclimated freshwater microalga, Chlorella vulgaris. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norvill, Z.; Shilton, A.; Guieysse, B. Emerging contaminant degradation and removal in algal wastewater treatment ponds: Identifying the research gaps. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 313, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matamoros, V.; Gutiérrez, R.; Ferrer, I.; García, J.; Bayona, J.M. Capability of microalgae-based wastewater treatment systems to remove emerging organic contaminants: A pilot-scale study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 288, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, G.J.; Ying, G.G.; Liu, S.; Zhou, L.J.; Chen, Z.F.; Peng, F.Q. Simultaneous removal of inorganic and or-ganic compounds in wastewater by freshwater green microalgae. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 2018–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, A.-P.; Hu, Z.-L.; Wong, Y.-S.; Tam, N.F.-Y. Removal of fluoranthene and pyrene by different microalgal species. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.M.; Scrimshaw, M.D.; Lester, J.N. Biotransformation and Bioconcentration of Steroid Estrogens by Chlorella vulgaris. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Habteselassie, M.Y.; Resurreccion, E.P.; Mantripragada, V.; Peng, S.; Bauer, S.; Colosi, L.M. Evaluating removal of steroid estrogens by a model alga as a possible sustainability benefit of hypothetical integrated algae cultivation and wastewater treatment systems. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2544–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlade, E.; Hom-Diaz, A.; Blanquez, P.; Martinez-Alonso, M.; Vicent, T.; Gaju, N. Effect of cultivation condi-tions on 17b-estradiol removal in laboratory and pilot-plant photobioreactors by an algal-bacterial consortium treating urban wastewater. Water Res. 2018, 137, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruksrithong, C.; Phattarapattamawong, S. Removals of estrone and 17β-estradiol by microalgae cultivation: Kinetics and removal mechanisms. Environ. Technol. 2017, 40, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guan, Y.; Gao, B.; Yue, Q. Antioxidant responses and degradation of two antibiotic contaminants in Microcystis aeruginosa. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 86, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hom-Diaz, A.; Llorca, M.; Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Vicent, T.; Barcelo, D.; Blanquez, P. Microalgae cultivation on wastewater digestate: (B-estradiol and 17a-ethynylestradiol degradation and transformation products identification. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 155, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Poon, K.; Cai, Z. Removal and metabolism of triclosan by three different microalgal species in aquatic environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 342, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Acharya, K. Removal of trimethoprim, sulfamethoxazole, and triclosan by the green alga Nannochloris sp. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 315, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.G.; Zhao, F.; Rezenom, Y.H.; Russell, D.H.; Chu, K.-H. Biodegradation of triclosan by a wastewater microorganism. Water Res. 2012, 46, 4226–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veetil, P.G.P.; Nadaraja, A.V.; Bhasi, A.; Khan, S.; Bhaskaran, K. Degradation of Triclosan under Aerobic, Anoxic, and Anaerobic Conditions. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 167, 1603–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-M.; Murugesan, K.; Schmidt, S.; Bokare, V.; Jeon, J.-R.; Kim, E.-J.; Chang, Y.-S. Triclosan susceptibility and co-metabolism—A comparison for three aerobic pollutant-degrading bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 2206–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.-H.; Church, J.; Lee, S.-J.; Park, J.; Lee, W.H. Use of microalgae for advanced wastewater treatment and sustainable bioenergy generation. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2016, 33, 882–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zangar, R.C.; Davydov, D.R.; Verma, S. Mechanisms that regulate production of reactive oxygen species by cytochrome P450. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 199, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, N.; Teramoto, T.; Kasai, F.; Sano, T.; Tamaoki, M.; Aono, M.; Kubo, A.; Kamada, H.; Azumi, Y.; Saji, H. Glycosylation of bisphenol A by freshwater microalgae. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroutsos, D.; Katapodis, P.; Samiotaki, M.; Panayotou, G.; Kekos, D. Detoxification of 2,4-dichlorophenol by the marine microalga Tetraselmis marina. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, M.A.; Barros, M.P.; Campos, S.C.G.; Pinto, E.; Rajamani, S.; Sayre, R.T.; Colepicolo, P. Biochemical biomarkers in algae and marine pollution: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2008, 71, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.; Lee, C.H.; Ko, K.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, K.N.; Kim, M.K.; Chung, Y.H.; Kim, D.; Yeo, I.K.; Oda, T. Use of phenol-induced oxidative stress acclimation to stimulate cell growth and biodiesel production by the oceanic microalga Dunaliella salina. Algal Res. 2016, 17, 61e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zheng, F.; Guo, R. Algal feedback and removal efficiency in a sequencing batch reactor algae process (SBAR) to treat the antibiotic cefradine. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bano, F.; Malik, A.; Ahammad, S.Z. Removal of Estradiol, Diclofenac, and Triclosan by Naturally Occurring Microalgal Consortium Obtained from Wastewater. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7690. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13147690
Bano F, Malik A, Ahammad SZ. Removal of Estradiol, Diclofenac, and Triclosan by Naturally Occurring Microalgal Consortium Obtained from Wastewater. Sustainability. 2021; 13(14):7690. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13147690
Chicago/Turabian StyleBano, Farhat, Anushree Malik, and Shaikh Z. Ahammad. 2021. "Removal of Estradiol, Diclofenac, and Triclosan by Naturally Occurring Microalgal Consortium Obtained from Wastewater" Sustainability 13, no. 14: 7690. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13147690
APA StyleBano, F., Malik, A., & Ahammad, S. Z. (2021). Removal of Estradiol, Diclofenac, and Triclosan by Naturally Occurring Microalgal Consortium Obtained from Wastewater. Sustainability, 13(14), 7690. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13147690




