Assessing the Impact of the National Sustainable Development Planning of Resource-Based Cities Policy on Pollution Emission Intensity: Evidence from 270 Prefecture-Level Cities in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Analysis and Research Hypotheses
3. Methods and Variable Selection
3.1. Econometric STRATEGIES
3.2. Variable Selection
3.2.1. Dependent Variable
3.2.2. Core Explanatory Variables
3.2.3. Control Variables
3.2.4. Mediation Variables
3.2.5. Data Resources
4. Results
4.1. Parallel Trend Test
4.2. Benchmark Regression Results
4.3. Analysis of the Influence Mechanism
4.4. Heterogeneity Tests
4.4.1. Analysis of City-Size Heterogeneity
4.4.2. Analysis of City-Type Heterogeneity
4.5. Endogenous Test
4.6. Robustness Test
4.6.1. Counterfactual Test
4.6.2. Placebo Test
4.6.3. Removing the Interference of Other Related Policies
4.6.4. Replacing the Dependent Variable
5. Discussion
5.1. Discussion of the Benchmark Regression Results
5.2. Discussion of the Influencing Mechanism Results
5.3. Discussion of Heterogeneity Test Results
5.3.1. Discussion of City-Size Heterogeneity Results
5.3.2. Discussion of City-Type Heterogeneity Results
6. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, T. Ecological economics in China: Origins, dilemmas and prospects. Ecol. Econ. 2002, 41, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Long, R.; Chen, H. Economic transition policies in Chinese resource-based cities: An overview of government efforts. Energy Policy 2013, 55, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Wang, J.; Jing, Z. Tempo-spatial changes of ecological vulnerability in resource-based urban based on genetic projection pursuit model. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatsuka, H.; Zeng, D.Z.; Zhao, L. Resource-Based Regions, the Dutch Disease and City Development. 2012. Available online: https://www.rieti.go.jp/jp/publications/dp/13e001.pdf (accessed on 29 June 2021).
- Yang, X.; Wu, H.; Ren, S.; Ran, Q.; Zhang, J. Does the development of the internet contribute to air pollution control in China? Mechanism discussion and empirical test. Struct. Chang. Econ. Dyn. 2021, 56, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windsperger, J. Resource-based view of competitive advantage of cities. J. Econ. Bus. 2006, 2, 20–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Dong, J. Evaluation of green growth efficiency of oil and gas resource-based cities in China. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, L.; Ding, L.; Deng, F.; Luo, X.B.; Luo, S.L. Principles for the application of nanomaterials in environmental pollution control and resource reutilization. In Nanomaterials for the Removal of Pollutants and Resource Reutilization; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- He, G.; Bao, K.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Li, S.; Jin, L. Assessment of ecological vulnerability of resource-based cities based on entropy-set pair analysis. Environ. Technol. 2021, 42, 1874–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Lo, K.; Qiu, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, H. Regional economic resilience of resource—Based cities and influential factors during economic crises in China. Growth Chang. 2020, 51, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Ye, X.; Lee, J.; Lu, X.; Zheng, L.; Wu, K. Effects of urbanization on ecosystem service values in a mineral resource-based city. Habitat Int. 2015, 46, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.Y.; Lee, J.; Zhou, T.; Wu, D. Shrinking cities and resource-based economy: The economic restructuring in China’s mining cities. Cities 2017, 60, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Tan, F.; Lu, Z. Resource-based cities (RBC): A road to sustainability. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2014, 21, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lei, Y.; Pan, D.; Si, C. Research on sustainable development of resource-based cities based on the DEA approach: A case study of Jiaozuo, China. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 2016, 5024837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, G. Research on Residents’ Willingness to Pay for Promoting the Green Development of Resource-Based Cities: A Case Study in Chifeng. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhai, G.; Zhang, Y. Ecological vulnerability assessment and spatial pattern optimization of resource-based cities: A case study of Huaibei City, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2020, 27, 606–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Wang, J. Sustainable development evaluation of the society–economy–environment in a resource-based city of China: A complex network approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murshed, S.M.; Serino, L.A. The pattern of specialization and economic growth: The resource curse hypothesis revisited. Struct. Chang. Econ. Dyn. 2011, 22, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yi, P.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y. Assessment of coordinated development between social economy and ecological environment: Case study of resource-based cities in Northeastern China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 59, 102208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Yan, T.; Xia, S.; Chen, F. Innovation or introduction? The impact of technological progress sources on industrial green transformation of resource-based cities in China. Front. Energy Res. 2020, 8, 598141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Y. Evaluation of economic transformation and upgrading of resource-based cities in Shaanxi province based on an improved TOPSIS method. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 37, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.J.; Guo, P.; Huang, G.H.; Shen, N. Optimization of the industrial structure facing sustainable development in resource-based city subjected to water resources under uncertainty. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2013, 27, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Wang, T.; Li, D.; Zhou, X. How energy technology innovation affects transition of coal resource-based economy in China. Energy Policy 2016, 92, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Ren, S.; Ran, Q.; Hao, Y. Does local government competition aggravate haze pollution? A new perspective of factor market distortion. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2020, 100959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Chen, S. Resource curse, environmental regulation and transformation of coal-mining cities in China. Resour. Policy 2019, 101447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, T.; Stevens, T. Do user fees exclude low-income people from resource-based recreation? J. Leis. Res. 2000, 32, 341–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaels, G. The long term consequences of resource—Based specialisation. Econ. J. 2011, 121, 31–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Lou, Y.; Lu, J.; Yin, L.; Yu, X. Simulation analysis of resource-based city development based on system dynamics: A case study of Panzhihua. Appl. Math. Nonlinear Sci. 2018, 3, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, X.M.; Kong, F.Z.; Zhan, C.S. Assessment of water resources carrying capacity in Tianjin City of China. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 857–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, H. Urban resilience and urban sustainability: What we know and what do not know? Cities 2018, 72, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Kong, Y.; Ren, X.; Shi, Y.; Chiang, S. The determinants of urban sustainability in Chinese resource-based cities: A panel quantile regression approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Shi, Y.; Wan, K. Integrated evaluation of the carrying capacities of mineral resource-based cities considering synergy between subsystems. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 108, 105701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, F.; Yan, L.; Wang, D. Policy effects on the sustainable development of resource-based cities in China: A case study of Yichun City. Resour. Policy 2021, 72, 102145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, F.; Yan, L.; Wang, D. The complexity for the resource-based cities in China on creating sustainable development. Cities 2020, 97, 102571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, H.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Gu, M.; Ke, X. Regional analysis of the green development level differences in Chinese mineral resource-based cities. Resour. Policy 2019, 61, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, S.; Yang, M.; Xu, F. The effects of China’s sustainable development policy for resource-based cities on local industrial transformation. Resour. Policy 2021, 71, 101940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.Z. How do special economic zones and industrial clusters drive China’s rapid development. In Policy Research Working Papers; The World Bank: Washington, WA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Fang, Y.P.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Assessment of urban resilience based on the transformation of resource-based cities: A case study of Panzhihua, China. Ecol. Soc. 2021, 26, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, N. Does smart city policy improve energy efficiency? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Kamruzzaman, M. Planning, development and management of sustainable cities. Sustainability 2015, 7, 14677–14688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiping, R. Circular economy action programs and countermeasures for small and medium-sized resource-based cities of China-case study of Zibo city of Shandong province. Energy Procedia 2011, 5, 2183–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, M.M.; Alam, K. Clean energy, population density, urbanization and environmental pollution nexus: Evidence from Bangladesh. Renewable Energy. 2021, 172, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attour, A.; Burger-Helmchen, T.; Zhong, J.; Nieminen, M. Resource-based co-innovation through platform ecosystem: Experiences of mobile payment innovation in China. J. Strategy Manag. 2015, 8, 283–298. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Hao, Y.; Ren, S.; Yang, X.; Xie, G. Does internet development improve green total factor energy efficiency? Evidence from China. Energy Policy 2021, 153, 112247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Luo, F. Comparative Study on the Optimization Path of Industrial Value Chain in China’s Resource-Based Cities. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Millar, C.C.; Choi, C.J. Development and knowledge resources: A conceptual analysis. J. Knowl. Manag. 2010, 14, 759–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayadi, O.F.; Saffu, K.; Apori, S.O.; Elijah-Mensah, A.; Ahumatah, J. The contribution of human capital and resource-based view to small- and medium-sized tourism venture performance in Ghana. Int. J. Emerg. Mark. 2008, 3, 268–284. [Google Scholar]
- Oduse, S.; Zewotir, T.; North, D. The impact of antenatal care on under-five mortality in Ethiopia: A difference-in-differences analysis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2021, 21, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, R.; Shao, S.; Yang, L. High-speed rail and CO2 emissions in urban China: A spatial difference-in-differences approach. Energy Econ. 2021, 99, 105271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.A.; Seshadri, U.; Kumar, P.; Aqdas, R.; Patwary, A.K.; Riaz, M. Nexus between green finance and climate change mitigation in N-11 and BRICS countries: Empirical estimation through difference in differences (DID) approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 6504–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, R.M.; Kenny, D.A. The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Ye, B.; Gao, M.; Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; Xiao, Z.; Wu, H. How does ecology of finance affect financial constraints? Empirical evidence from Chinese listed energy-and pollution-intensive companies. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 246, 119061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Jing, J.; Yan, Z.; Sun, C. Does government information transparency contribute to pollution abatement? Evidence from 264 Chinese cities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Hao, Y.; Ren, S. How do environmental regulation and environmental decentralization affect green total factor energy efficiency: Evidence from China. Energy Econ. 2020, 91, 104880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimian, H.; Li, Q.; Chen, H.F. Assessing urban sustainable development in Isfahan. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 253, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinatizadeh, S.; Azmi, A.; Monavari, S.M.; Sobhanardakani, S. Evaluation and prediction of sustainability of urban areas: A case study for Kermanshah city, Iran. Cities 2017, 66, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Ren, S.; Ran, Q. Can the new energy demonstration city policy reduce environmental pollution? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 287, 125015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, A.; Ozturk, I.; Hassan, A.; Zafar, S.M.; Ullah, S. The effect of ICT on energy consumption and economic growth in South Asian economies: An empirical analysis. Telemat. Inform. 2021, 58, 101537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Li, M.; Pu, C.; Xu, H. Study on the industrial structure optimization under constraint of energy intensity. Energy Environ. 2021, 32, 134–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Ding, Y. Assessing the influence of urban transportation infrastructure construction on haze pollution in China: A case study of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2021, 87, 106547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rjoub, H.; Odugbesan, J.A.; Adebayo, T.S.; Wong, W.K. Sustainability of the moderating role of financial development in the determinants of environmental degradation: Evidence from Turkey. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, N.; Haščič, I.; Kalamova, M. Environmental policy design characteristics and technological innovation: Evidence from patent data. OECD Environ. Work. Pap. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, B.; Apergis, N. The impact of internet use on air pollution: Evidence from emerging countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 4174–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Ali, S.; Dong, K.; Li, R.Y.M. How does fiscal decentralization affect CO2 emissions? The roles of institutions and human capital. Energy Econ. 2021, 94, 105060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi-ying, R.; Jin-ning, Z.; Xiao-dong, Y. Does High-Speed Railway Improve the Efficiency of Urban Green Development—An Empirical Test Based on Difference in Difference Model. J. Guizhou Univ. Financ. Econ. 2020, 38, 100–110. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Qu, M. Impact of Environmental Regulation on Scientific and Technological Competitiveness of Resource-Based Cities in China—Based on Panel Data of 33 Resource-Based Cities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Deng, Q.H.; Liu, W.W.; Huang, B.L.; Shi, L.Z. Characteristics of ventilation coefficient and its impact on urban air pollution. J. Cent. South Univ. 2012, 19, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, D.; Qiu, Y. Urban carbon emission intensity under emission trading system in a developing economy: Evidence from 273 Chinese cities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 5168–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Law, S.H.; Samad, A.R.B.A.; Mohamad, W.N.B.W.; Wang, J.; Yang, X. Impact of financial development and technological innovation on the volatility of green growth—evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; de Jong, M.; Cheng, B. Getting depleted resource-based cities back on their feet again—the example of Yichun in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 134 Pt A, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, D.-Z.; Zhao, L. Pollution havens and industrial agglomeration. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2009, 58, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
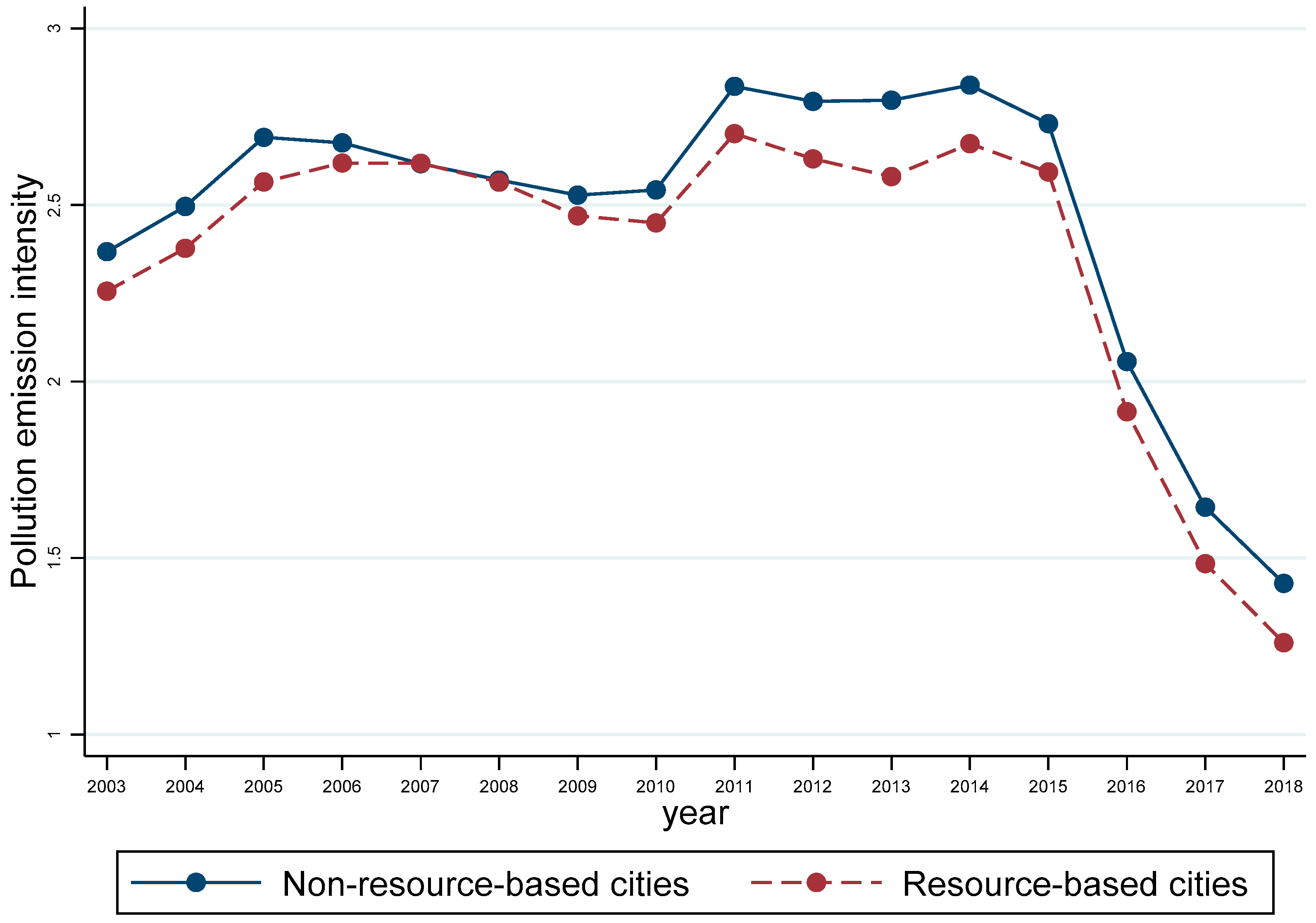
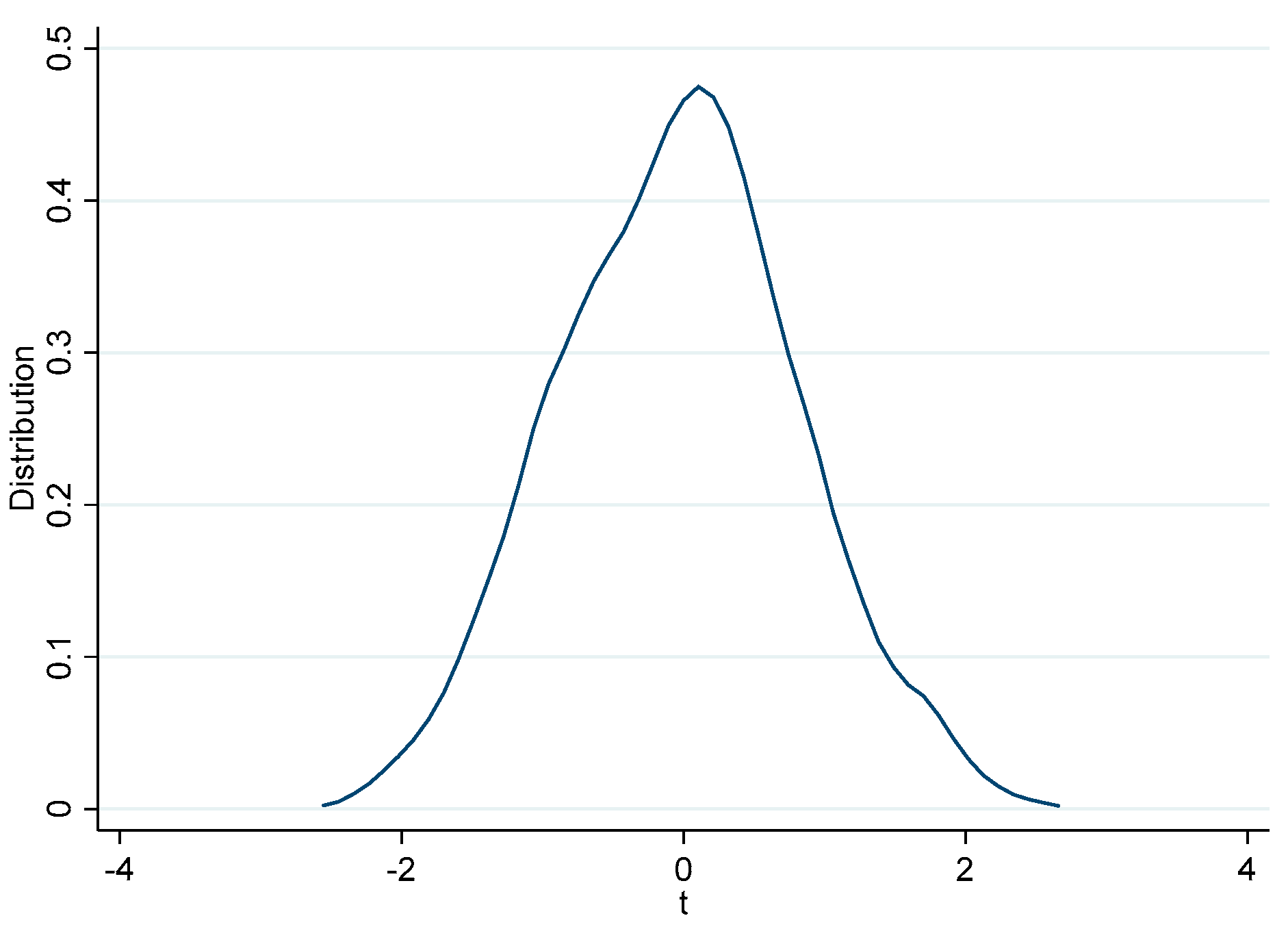
| Variables | Variable Symbols | N | Mean | Sd |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pollution emission intensity | EQ | 4320 | 2.4064 | 1.2583 |
| Economic development | RGDP | 4320 | 10.2102 | 0.8322 |
| Population density | POPL | 4320 | 5.7638 | 0.9043 |
| Advanced industrial structure | IND | 4320 | 0.86329 | 0.4530 |
| Infrastructure construction | JCSS | 4320 | 10.9536 | 7.9239 |
| Financial development | FD | 4320 | 16.0316 | 1.3518 |
| Technological innovation | TI | 4320 | 6.3233 | 1.8254 |
| Digital transformation | DT | 4320 | 3.4172 | 1.2552 |
| Human capital | HUM | 4320 | 1.115 | 1.4011 |
| Variables | Pollution Emission Intensity | |
|---|---|---|
| Average Treatment Effects | Dynamic Effects | |
| TREAT × TIME | −0.1705 ** | |
| (0.0594) | ||
| TREAT × YEAR2013 | −0.0180 | |
| (0.0416) | ||
| TREAT × YEAR2014 | 0.0507 | |
| (0.0439) | ||
| TREAT × YEAR2015 | −0.0429 | |
| (0.0476) | ||
| TREAT × YEAR2016 | −0.7238 *** | |
| (0.0579) | ||
| TREAT × YEAR2017 | −1.1804 *** | |
| (0.0788) | ||
| TREAT × YEAR2018 | −1.3440 *** | |
| (0.0896) | ||
| Cons | 4.8728 *** | 2.7961 * |
| (0.6207) | (0.0753) | |
| Control variables | Yes | Yes |
| Individual effect | Yes | Yes |
| Year effect | Yes | Yes |
| R2 | 0.1576 | 0.3688 |
| N | 4320 | 4320 |
| Variables | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EQ | TI | EQ | DT | EQ | HUM | EQ | |
| TREAT × TIME | −3.2114 *** | 3.2396 *** | 3.4609 *** | 0.1797 *** | −3.2668 *** | 0.5389 *** | −4.1818 ** |
| (0.5535) | (0.2992) | (0.5969) | (0.0224) | (0.5574) | (0.0432) | (0.5386) | |
| MID | −0.2284 *** | −0.8045 ** | −3.7661 *** | ||||
| (0.0299) | (0.3756) | (0.1866) | |||||
| Cons | −15.3389 *** | −54.514 *** | −2.4964 *** | −10.6969 *** | −33.1306 *** | −9.4400 *** | −11.0271 *** |
| (3.1753) | (1.4891) | (3.3559) | (0.1127) | (4.8853) | (0.2169) | (3.1882) | |
| Control variables | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Individual effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Sobel test | −0.7398 (z = −6.23, p = 0.000) | −0.1445 (z = −2.069, p = 0.039) | −2.0296 (z = −10.61, p = 0.000) | ||||
| Bootstrap test(direct effect) | −2.4609 (z = −4.32, p = 0.000) | −3.0668 (z = −5.94, p = 0.000) | −1.1818 (z = −2.27, p = 0.023) | ||||
| Bootstrap test (indirect effect) | −0.7398 (z = −4.31, p = 0.000) | −0.1445 (z = −1.94, p = 0.052) | −2.0296 (z = −9.97, p = 0.000) | ||||
| Indirect effect (%) | 23.11% | 4.49% | 63.20% | ||||
| N | 4314 | 4320 | 4320 | 4314 | 4314 | 4314 | 4314 |
| R2 | 0.2220 | 0.3518 | 0.1097 | 0.8397 | 0.2165 | 0.5237 | 0.2835 |
| Variables | Megacities | Large Cities | Small and Medium-Sized Cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| TREAT×TIME | −0.2462 *** | −0.1845 *** | 0.4745 ** |
| (0.0748) | (0.0616) | (0.1951) | |
| Cons | 0.7553 * | 0.7415 * | −0.4911 * |
| (0.5406) | (0.4831) | (1.7708) | |
| Control variables | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Individual effect | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year effect | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 1499 | 2661 | 160 |
| R2 | 0.1138 | 0.1166 | 0.6721 |
| Variables | Full Samples | Mature Resource-Based Cities | Growing Resource Cities | Declining Resource-Based Cities | Regenerative Resource-Based Cities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TREAT × TIME | −0.1321 *** | −0.1309 ** | 0.4904 ** | −0.2758 * | −0.1580 |
| (0.0503) | (0.0555) | (0.1941) | (0.1808) | (0.1287) | |
| Cons | 1.6367 *** | 3.3817 *** | 5.6391 *** | 2.7967 ** | 0.0573 ** |
| (0.2812) | (0.3699) | (1.2846) | (1.1097) | (0.8049) | |
| Control variables | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Individual effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 2652 | 1966 | 206 | 240 | 240 |
| R2 | 0.2094 | 0.2359 | 0.3306 | 0.2163 | 0.3141 |
| Variables | First Stage | Second Stage |
|---|---|---|
| TREAT × TIME | EQ | |
| IV | 0.2340 *** | |
| (0.0727) | ||
| TREAT×TIME | −2.2128 ** | |
| (0.9827) | ||
| Cons | 1.5457 *** | 7.3296 *** |
| (0.3997) | (1.8817) | |
| Control variables | Yes | Yes |
| Individual effect | Yes | Yes |
| Year effect | Yes | Yes |
| N | 4320 | 4320 |
| R2 | 0.4115 | 0.1007 |
| F-value | 130.74 |
| Variables | YEAR-2010 | YEAR-2011 |
|---|---|---|
| TREAT × TIME | 1.1803 | 1.1521 |
| (0.7718) | (0.7763) | |
| Cons | (0.7718) | (0.77630) |
| 4320 | 4320 | |
| Control variables | Yes | Yes |
| Individual effect | Yes | Yes |
| Year effect | Yes | Yes |
| N | 4320 | 4320 |
| R2 | 0.1603 | 0.1626 |
| Variables | EQ |
|---|---|
| TREAT × TIME | −9.9771 *** |
| (0.9277) | |
| Cons | 18.0690 *** |
| (5.93) | |
| Control variables | Yes |
| Individual effect | Yes |
| Year effect | Yes |
| N | 2969 |
| R2 | 0.2915 |
| Variables | Pollution Emission Intensity | |
|---|---|---|
| Average Treatment Effects | Dynamic Effects | |
| TREAT × TIME | −0.3234 *** | |
| (0.0773) | ||
| TREAT × YEAR2013 | −0.6279 *** | |
| (0.1058) | ||
| TREAT × YEAR2014 | 0.5726 *** | |
| (0.1135) | ||
| TREAT × YEAR2015 | −0.6582 *** | |
| (0.1168) | ||
| TREAT × YEAR2016 | −1.3425 *** | |
| (0.1300) | ||
| TREAT × YEAR2017 | −1.9344 *** | |
| (0.1540) | ||
| TREAT × YEAR2018 | −1.9861 *** | |
| (0.1358) | ||
| Cons | −5.7586 *** | −8.4452 *** |
| (0.3824) | (0.0753) | |
| Control variables | Yes | Yes |
| Individual effect | Yes | Yes |
| Year effect | Yes | Yes |
| R2 | 0.2395 | 0.3955 |
| N | 4320 | 4320 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Ran, Q.; Yang, X.; Shen, J. Assessing the Impact of the National Sustainable Development Planning of Resource-Based Cities Policy on Pollution Emission Intensity: Evidence from 270 Prefecture-Level Cities in China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7293. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137293
Meng Y, Liu L, Wang J, Ran Q, Yang X, Shen J. Assessing the Impact of the National Sustainable Development Planning of Resource-Based Cities Policy on Pollution Emission Intensity: Evidence from 270 Prefecture-Level Cities in China. Sustainability. 2021; 13(13):7293. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137293
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Yuxin, Lu Liu, Jianlong Wang, Qiying Ran, Xiaodong Yang, and Jianliang Shen. 2021. "Assessing the Impact of the National Sustainable Development Planning of Resource-Based Cities Policy on Pollution Emission Intensity: Evidence from 270 Prefecture-Level Cities in China" Sustainability 13, no. 13: 7293. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137293
APA StyleMeng, Y., Liu, L., Wang, J., Ran, Q., Yang, X., & Shen, J. (2021). Assessing the Impact of the National Sustainable Development Planning of Resource-Based Cities Policy on Pollution Emission Intensity: Evidence from 270 Prefecture-Level Cities in China. Sustainability, 13(13), 7293. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137293







