A New Rural-Urban Fish Food System Was Established in Kenya–Learning from Best Practices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. A Transitioning Rural-Urban Food System Approach and Methodology
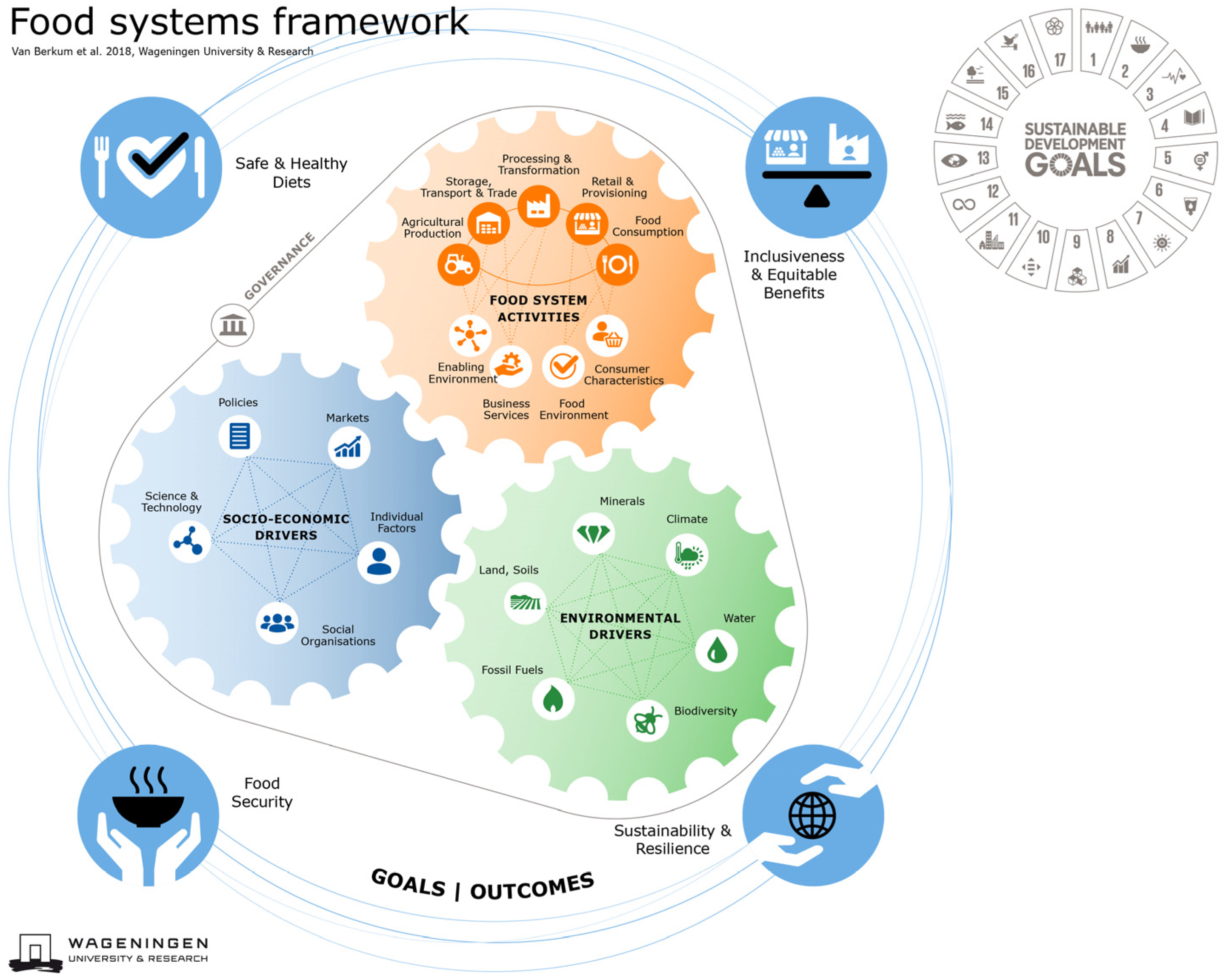
2.1. The Rural-Urban Food System Framework
2.2. Nyeri-Kibera
2.3. The Methodological Approach
3. Implementation of New Innovative Fish Food System Solutions for Kibera
4. Discussing Institutional Contexts in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA)
5. Concluding Remarks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UN-Habitat. Slum Almanac 2015/2016: Tracking Improvement in the Lives of Slum Dwellers; United Nations Centre for Human Settlements: Nairobi, Kenya, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Talukdar, D. Cost of being a slum dweller in Nairobi: Living under dismal conditions but still paying a housing rent premium. World Dev. 2018, 109, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Von Braun, J. Rural-Urban Linkages for Growth, Employment and Poverty Reduction. Available online: https://www.ifpri.org/publication/rural-urban-linkages-growth-employment-and-poverty-reduction-0 (accessed on 4 September 2020).
- Serraj, R.; Pingali, P. Agriculture & Food Systems to 2050: Global Trends, Challenges and Opportunities; World Scientific Series in Grand Public Policy Challenges of the 21st Century; World Scientific: Singapore, 2018; Volume 2, p. 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battersby, J.; Watson, W. (Eds.) Urban Food Systems Governance and Poverty in African Cities; Routledge: Oxford, UK, 2019; p. 290. [Google Scholar]
- Van Berkum, S.; Broeze, J.; Herens, M.; de Rooij, B.; Soma, K.; Roosendaal, L. Urbanisation, Migration and Food System Transformations: Concepts and Methodologies for a Better Understanding of the Dynamics of Urban Food Systems and Migration Settlements; REPORT 2020-046; Wageningen University and Research, Wageningen Economic Research: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2020; p. 34. [Google Scholar]
- Achungo, B.C. The Social Transformation of the People Living in Kibera Slum in Nairobi County Following the Kenya Slum Upgrading Programme. Master’s Thesis, Institute of Anthropology, Gender and African Studies University of Nairobi, Nairobi, Kenya, 11 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kinyanyi, H. Migration Decision Making: A Case Study of Kibera, Nairobi. Master’s Thesis, University of Nairobi, Nairobi, Kenya, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- DePuma, S. The Political Narrative Behind Infrastructural Inadequacies in Kibera. 2015. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/22398505/The_Political_Narrative_Behind_Infrastructural_Inadequacies_in_Kibera (accessed on 4 September 2020).
- Mohamed, S.F.; Mberu, B.U.; Amendah, D.D.; Kiman Murage, E.W.; Ettarh, R.; Schfield, L.; Egondi, T.; Wekesah, F.; Kyobutungi, C. Poverty and Uneven Food Security in Urban Slums. In Rapid Urbanisation, Urban Food Deserts and Food Security in Africa; Crush, J., Battersby, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chege, P.; Kuria, E.; Kimiye, J. A comparative study on dietary practices, morbidity patterns and nutrition status of HIV/AIDS infected and non-infected pre-school children in Kibera slum, Kenya. J. Appl. Biosci. 2010, 32, 2008–2014. [Google Scholar]
- Olack, B.; Feikin, D.R.; Cosmas, L.O.; Odero, K.O.; Okoth, G.O.; Montgomery, J.M.; Breiman, R.F. Mortality Trends observed in population-based surveillance of an urban slum settlement, Kibera, Kenya, 2007–2010. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongosi, A.N.; Gericke, G.; Mbuthia, E.; Oelofse, A. Food variety, dietary diversity and perceived hunger among lactating women (0-6months postpartum) in a low socio-economic area in Nairobi Kenya. Afr. J. Food Agric. Nutr. Dev. 2014, 14, 8663–8675. [Google Scholar]
- Obwanga, B.; Soma, K.; Ayuya, O.I.; Rurangwa, E.; van Wonderen, D.; Beekman, G.; Kilelu, C. Exploring Enabling Factors for Commercializing the Aquaculture Sector in Kenya; 3R Research Report/Centre for Development Innovation 3R Research Report 011; Wageningen Centre for Development Innovation: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2020; p. 54. [Google Scholar]
- Obwanga, B.; Mbauni, C.; Mwangi, G.F.; Soma, K. Food System Value-Chain Adaptability-Can New Opportunities Increase Food Security and Food Safety in Kibera? In Proceedings of the Linking Aquaculture to Urban FOOD systems: Workshop Report Discussing New Opportunities with the Aquaculture Value-Chains between Nyeri—Kibera, Nairobi, Kenya, 29 May 2020; p. 14. Available online: https://library.wur.nl/WebQuery/wurpubs/fulltext/528591 (accessed on 10 December 2020).
- UN. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development Resolution Adopted by the General Assembly on 25 September 2015. Available online: https://www.un.org/ga/search/view_doc.asp?symbol=A/RES/70/1&Lang=E (accessed on 4 September 2020).
- Van Berkum, S.; Dengerink, J.; Ruben, R. The Food Systems Approach: Sustainable Solutions for a Sufficient Supply of Healthy Food; Memorandum 2018-064; Wageningen Economic Research: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2018; p. 34. [Google Scholar]
- Fresco, L.O.; Ruben, R.; Herens, M. Challenges and perspectives for supporting sustainable and inclusive food systems. GREAT Insights Mag. 2017, 6, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- HLPE. Food Losses and Waste in the Context of Sustainable Food Systems; CFS Committee on World Food Security HLPE: Rome, Italy, 2014; p. 117. [Google Scholar]
- Béné, C.; Mehta, L.; McGranahan, G.; Cannon, T.; Gupte, J.; Tanner, T. Resilience as a policy narrative: Potentials and limits in the context of urban planning. Clim. Dev. 2018, 10, 116–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. Food Systems and Natural Resources. In A Report of the Working Group on Food Systems of the International Resource Panel; Westhoek, H., Ingram, J., van Berkum, S., Özay, L., Hajer, M., Eds.; United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP): Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; p. 34. [Google Scholar]
- GLOPAN. Food Systems and Diets: Facing the Challenges of the 21st Century; Global Panel on Agriculture and Food Systems for Nutrition: London, UK, 2016; p. 133. [Google Scholar]
- De Rooij, B.; Tabeau, E.; Soma, K.; van Scheltinga, C.T.; Kuiper, M.; Verma, M.; Stuiver, M. The ‘Water, Food, Energy and Ecosystem Nexus’ and Migration: An Explorative Study of Key Drivers of Migration Flows and Their Impacts; Wageningen Environmental Research 2981: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2019; p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Crush, J. Linking Food Security, Migration and Development. Int. Migr. 2013, 51, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ostrom, E. Understanding Institutional Diversity; Princeton University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009; p. 357. [Google Scholar]
- Rauschmayer, F.; Bauler, T.; Schäpke, N. Towards a thick understanding of sustainability transitions—Linking transition management, capabilities and social practices. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 109, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soma, K.; Dijkshoorn-Dekker, M.W.C.; Polman, N.B.P. Incentives to Contribute to Flood Adaptation in Cities: Stakeholder Analyses in Belgium, the UK and the Netherlands. 2018. Available online: https://library.wur.nl/WebQuery/wurpubs/fulltext/438335 (accessed on 5 September 2020).
- Soma, K.; Dijkshoorn-Dekker, M.W.C.; Polman, N.B.P. Stakeholder contributions through transitions towards urban sustainability. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 37, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soma, K.; van den Burg, S.W.K.; Hoefnagel, E.W.J.; Stuiver, M. Social innovation—A future pathway for Blue growth? Marine Policy 2018, 87, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soma, K.; van den Burg, S.W.K.; Selnes, T.; van der Heide, C.M. Assessing social innovation across offshore sectors in the Dutch North Sea. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2019, 167, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klerkx, L.; Aarts, N.; Leeuwis, C. Adaptive management in agricultural innovation systems: The interactions between innovation networks and their environment. Agric. Syst. 2010, 10, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klerkx, L.; Leeuwis, C. Matching demand and supply in the agricultural knowledge infrastructure: Experiences with innovation intermediaries. Food Policy 2008, 33, 260–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klerkx, L.; Leeuwis, C. Establishment and embedding of innovation brokers at different innovation system levels: Insights from the Dutch agricultural sector. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2009, 76, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanja, J.M.; Nganga, E. Sanitation and hygiene in Kibera Slums. In Women Concerns and Nurses Promotional Tools; Helsinki Metropolia University of Applied Sciences: Helsinki, Finland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Farm Africa. Market Study of the Aquaculture market in Kenya: Kenya Market-Led Aquaculture Programme (KMAP); Farm Africa: Nairobi, Kenya, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Awuor, F.J.; Obiero, K.; Munguti, J.; Oginga, J.O.; Kyule, D.; Opiyo, M.A.; Oduor-Odote, P.; Yongo, E.; Owiti, H.; Ochiewo, J. Market linkages and distribution channels of cultured, capture and imported fish in Kenya. Aquac. Stud. 2019, 19, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obwanga, B.; Rurangwa, E.; Soma, K.; Kilelu, C. A Comparative Study of Aquaculture Sector Development in Egypt, Ghana and Nigeria: Insights for Kenya’s Sustainable Domestic Sector Development; Research Report 006; Wageningen University & Research: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2018; p. 27. [Google Scholar]
- Etzioni, A. The Moral Dimension: Towards a New Economics; The Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 1988; p. 300. [Google Scholar]
- Hausman, D.M. The Inexact and Separate Science of Economics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992; p. 373. [Google Scholar]
- Fehr, E.; Schmidt, K.M. Fairness, incentives, and contractual choices. Eur. Econ. Rev. 2000, 44, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ostrom, E. A Behavioral Approach to the Rational Choice Theory of Collective Action: Presidential Address, American Political Science Association, 1997. Am. Political Sci. Rev. 1998, 82, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, S.; Gintis, H. Persistent parochialism: Trust and exclusion in ethnic networks. J. Econ. Behavour Organ. 2004, 40, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gintis, H. Towards the Unity of the Human Behavioral Sciences. Politics Philos. Econ. 2004, 3, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rommetvedt, H. The multiple logics of decision-making. Eur. Political Sci. 2006, 5, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehr, E.; Gächter, S. Reciprocity and economics: The economic implications of Homo Reciprocans. Eur. Econ. Rev. 1998, 42, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, T.; Termeer, E.; Motovska, N.; Kunz, M.; Ayuya, O.I.; Soma, K. Social Capital and Food Security in Kibera; Wageningen University and Research: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vatn, A. Rationality, institutions and environmental policy. Ecol. Econ. 2005, 55, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, A. Rationality and Social Choice. Am. Econ. Rev. 1995, 85, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Birhane, A. Algorithmic Colonization of Africa. Scripted 2020, 17, 389–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, G.; Frankema, E.; Jerven, M. Patterns of manufacturing growth in Sub-Saharan Africa: From colonization to the present. In The Spread of Modern Industry to the Periphery Since 1871; O’Rourke, K., Williamson, J., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 345–373. [Google Scholar]
- Frankema, E.; van Waijenburg, M. Africa rising? A historial perspective. Afric. Aff. 2018, 117, 543–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bryceson, I. Coastal Aquaculture Developments in Tanzania: Sustainable and Non-sustainable Experiences. West. Indian Ocean. J. Mar. Sci. 2002, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Bryceson, I.; Massinga, A. Coastal Resources and Management Systems Influenced by Conflict and Migration: Mecúfi, Mozambique. Ambio 2002, 31, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatn, A. An institutional analysis of methods for environmental appraisal. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 2207–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soma, K.; Vatn, A. Representing the common goods–stakeholders vs. citizens. Land Use Policy 2014, 41, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkingham, J.; Chepngeno-Langat, G.; Evandrou, M. Outward migration from large cities: Are older migrants in Nairobi Returning. Popul. Space Place 2012, 18, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyne, C.J. Doing Bad by Doing Good: Why Humanitarian Action Fails; Standford University Press: Standford, CA, USA, 2013; p. 257. [Google Scholar]
- Buss, T.F. Haiti in the Balance: Why Foreign Aid Has Failed and What We Can Do About It; A Brookings Institution Press and the National Academy of Public Administration Publication: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; p. 231. [Google Scholar]
- Geels, F.W. The multi-level perspective on sustainability transitions: Responses to seven criticisms. Environ. Innov. Soc. Transit. 2011, 1, 24–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. A Strategy for Smart, Sustainable and Inclusive Growth; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2010; p. 35. [Google Scholar]
- Ayuya, O.I.; Soma, K.; Obwanga, B. Socio-Economic Drivers of Fish Species Consumption Preferences in Kenya’s Urban Informal Food System. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Challenges | Local Solutions |
|---|---|
| Demand meets supply challenges | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Kibera quality assurance challenges | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Nyeri fish farm cooperative quality assurance challenges | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soma, K.; Obwanga, B.; Kanyuguto, C.M. A New Rural-Urban Fish Food System Was Established in Kenya–Learning from Best Practices. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7254. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137254
Soma K, Obwanga B, Kanyuguto CM. A New Rural-Urban Fish Food System Was Established in Kenya–Learning from Best Practices. Sustainability. 2021; 13(13):7254. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137254
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoma, Katrine, Benson Obwanga, and Charles Mbauni Kanyuguto. 2021. "A New Rural-Urban Fish Food System Was Established in Kenya–Learning from Best Practices" Sustainability 13, no. 13: 7254. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137254
APA StyleSoma, K., Obwanga, B., & Kanyuguto, C. M. (2021). A New Rural-Urban Fish Food System Was Established in Kenya–Learning from Best Practices. Sustainability, 13(13), 7254. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137254





