An Overview on Railway Impacts on Coastal Environment and Beach Tourism in Sicily (Italy)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Italian Railway Framework
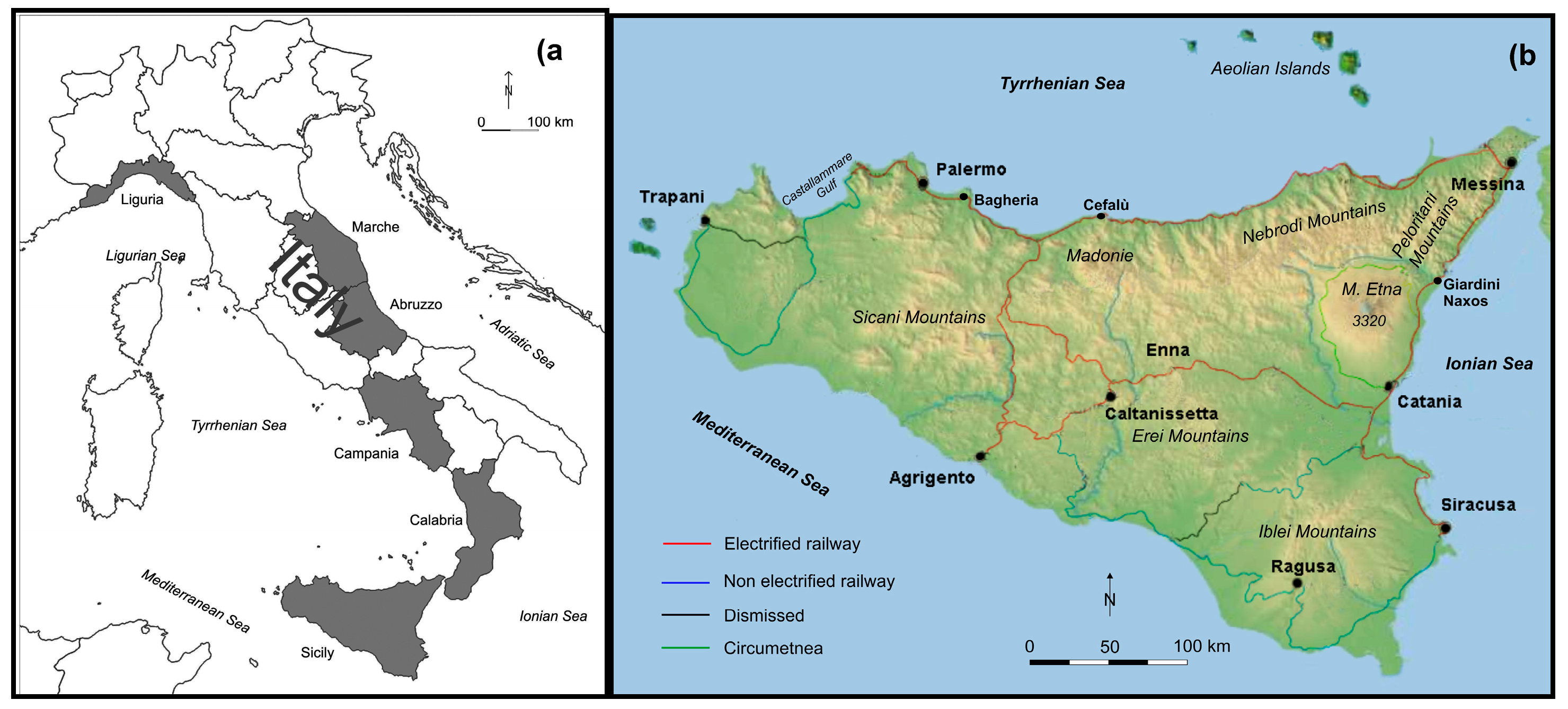
3. Study Area: Morphology and Railway Setting
4. Methodology
5. Results: Distribution of Railway Segments
6. Discussion
6.1. Railway Line and Coastal Squeeze
6.2. Railway Impact on Coastal Tourism
7. Conclusions
- (i)
- Railway distance from the shoreline. When the railway is directly emplaced on (or it is very close to) the coastal environment, greatly affects it by damaging/destroying ecosystems and affecting tourist activities and impeding coastal landward migration;
- (ii)
- Railway position in respect to the settlements. If it is located between the houses and the beach, it has a higher landscape impact and limits beach access;
- (iii)
- Coastal typology. In general, sandy sectors (i.e., beaches and dunes systems), with respect to rocky sectors (rock shore platforms and cliffs), present greater ecological value (if large and well-vegetated dune ridges exist) and tourist interest. Further, sandy sectors are very sensitive to sea-level rise and storms impact that, under determinate conditions, can favor the landward migration of the whole coastal system, which is limited by the presence of the railway. Such problems are further enhanced when coastal protection structures (groins, breakwaters, rip-rap revetments, etc.) are constructed to protect the coast.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corbin, A. El Territorio del Vacío Occidente y la Invención de la Playa; Editorial Mondadori: Barcelona, Spain, 1993; pp. 1750–1840. [Google Scholar]
- Rubio, D. Gestión Integral de Playas, Agencia Valenciana de Turismo; Editorial Sintesis: Madrid, Spain, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Houston, J.R. The economic value of beaches—A 2013 update. Shore Beach 2013, 81, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Duck, R. On the Edge: Coastlines of Britain; Edinburgh University Press: Edinburgh, UK, 2015; p. 222. [Google Scholar]
- Aoki, E. Japanese railway history. JPN Railw. Transp. Rev. 1994, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Fierro, G.; Berriolo, G.; Ferrari, M. Le Spiagge Della Liguria Occidentale. Analisi Evolutiva; Regione Liguria: Genova, Italy, 2010; p. 174. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, D.; O’Callaghan, M. Coastal Morphology: An Introduction to the Study of the Bray-Killiney Coastline. Unpubl. B.Sc. Dissertation, Civ. Eng. Univ. Coll, Duvblin. In Artificial Structures and Shorelines; Carter, R.W.G., Orford, J.D., Eds.; Ireland Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1979; pp. 155–163. [Google Scholar]
- Vsevelod, P.Z.; Maurice, L.S. Protecting the Black Sea- Georgian S.S.R. Gravel Coast. J. Coast. Res. 1987, 3, 201–209. [Google Scholar]
- Ashpiz, E.S.; Egorov, A.O.; Ushakov, A.E. Application of composite materials for the protection of sea shores and engineering structures against the impact of waves. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2010, 130, 231–239. [Google Scholar]
- Stuff. Available online: https://www.stuff.co.nz/timaru-herald/news/69698416/weather-erodes-railway-line-near-timaru (accessed on 19 March 2021).
- Atkinson, N. ‘Call of the beaches’ Rail travel and the democratisation of holidays in interwar New Zealand. J. Transp. Hist. 2012, 33, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, H.J.; Finkl, C.W. Beach nourishment: Case studies. In Engineered Coasts; Chen, J., Eisma, D., Hotta, K., Walker, H.J., Eds.; Kluver Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 23–59. [Google Scholar]
- The Guardian. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2014/feb/05/uk-storms-live-updates (accessed on 5 February 2014).
- BBC News. Available online: https://www.bbc.com/news/magazine-31113368 (accessed on 4 February 2015).
- Garland Consultancy. Available online: http://www.garlandconsultancy.com/our-projects/infrastructure/coastal-protection-works.html (accessed on 10 March 2017).
- Smith, A.M.; Guastella, L.A.; Bundy, S.C.; Mather, A.A. Combined marine storm and Saros spring high tide erosion events along the KwaZulu-Natal coast in March 2007. J. Sci. 2007, 103, 274–276. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, D.; Shaw, J.; Gehrels, W.R. Sea-level rise impacts on transport infrastructure: The notorious case of the coastal railway line at Dawlish, England. J. Transp. Geogr. 2016, 51, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snoussi, M.; Ouchani, T.; Kuakhi, A.; Niang-Diop, I. Impacts of sea-level rise on the Moroccan coastal zone: Quantifying coastal erosion and flooding in the Tangier Bay. Geomorphology 2006, 107, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Stafford Smith, M.; McAllister, R.R.J.; Leitch, A.; McFallan, S.; Meharg, S. Coastal Inundation under Climate Change: A Case Study in South East Queensland. CSIRO Climate Adaptation Flagship Working Paper No. 6; National Library of Australia: Canberra, Australia, 2010; p. 28. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, P.R.; Nair, R.; Kapshe, M.; Garg, A.; Balasubramaniam, S.; Menon, D.; Sharma, K.K. Development and Climate: An Assessment for India; Indian Institute of Management: Ahmedabad, India, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Nillesen, E.E.M.; Van Ierland, E.C. Climate Adaptation in the Netherlands. The Netherlands Programme Scientific Assessment and Policy Analysis Climate Change; Wageningen University: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Doody, J.P. ‘Coastal squeeze’-An historical perspective. J. Coast. Conserv. 2004, 10, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithgow, D.; Martínez, M.L.; Gallego-Fernández, J.B.; Silva, R.; Ramírez-Vargas, D.L. Exploring the cooccurrence between coastal squeeze and coastal tourism in a changing climate and its consequences. Tour. Manag. 2019, 74, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anfuso, G.; Williams, A.T.; Martínez, G.C.; Botero, C.M.; Hernández, J.A.C.; Pranzini, E. Evaluation of the scenic value of 100 beaches in Cuba: Implications for coastal tourism management. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2017, 142, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botero, C.; Pereira, C.; Tosic, M.; Manjarrez, G. Design of an index for monitoring the environmental quality of tourist beaches from a holistic approach. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2015, 108, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.; Micallef, A. Beach Management: Principles and Practice; Routledge: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dodds, R.; Kelman, I. How Climate Change is Considered in Sustainable Tourism Policies: A Case of The Mediterranean Islands of Malta and Mallorca. Tour. Rev. Int. 2008, 12, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrovie Siciliane. Available online: https://www.ferroviesiciliane.it (accessed on 5 February 2016).
- Mancinelli, A.; Lorenzoni, C. Le opera di protezione dei litorali marchigiani. In La Difesa dei Litorali in Italia; Aminti, P., Pranzini, E., Eds.; Edizioni delle Autonomie: Roma, Italy, 1993; pp. 309–326. [Google Scholar]
- Pranzini, E. Italy. In Coastal Erosion and Protection in Europe; Pranzini, E., Williams, A., Eds.; Routledge: Abington, UK, 2013; pp. 294–323. [Google Scholar]
- Foresta, S. The Railway. Dynamics and Processes of Territorial Transformation in Calabria. ArcHistoR 2018, 4, 123–135. [Google Scholar]
- Guiducci, F.; Lo Presti, F.; Scalzo, M. Intervento di ripascimento tra Paola e S. Lucido (CS). In La Difesa dei Litorali in Italia; Aminti, P., Pranzini, E., Eds.; Edizioni delle Autonomie: Roma, Italy, 1993; pp. 195–214. [Google Scholar]
- Lanza, S.; Randazzo, G. Tourist-beach protection in north-eastern Sicily (Italy). J. Coast. Conserv. 2013, 17, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, R.; Franchino, A.; Merlini, S.; Sulli, A. Central western Sicily structural setting interpreted from seismic reflection profiles. Mem. Soc. Geol. Ital. 2000, 55, 5–16. [Google Scholar]
- Avellone, G.; Barchi, M.R.; Catalano, R.; Morticelli, M.G.; Sulli, A. Interference between shallow and deep-seated structures in the Sicilian fold and thrust belt, Italy. J. Geol. Soc. 2010, 167, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Privitera, S.L. La Geografia Della Costa Siciliana tra Minacce e Opportunità. Casi di Studio; Edizioni Lussografica: Caltanissetta, Italy, 2017; p. 175. [Google Scholar]
- Antonioli, F.; Kershaw, S.; Renda, P.; Rust, D.; Belluomini, G.; Cerasoli, M.; Radtke, U.; Silenzi, S. Elevation of the last interglacial highstand in Sicily (Italy): A benchmark of coastal tectonics. Quat. Int. 2006, 145–146, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, F.; Ferranti, L.; Lambeck, K.; Kershaw, S.; Verrubbi, V.; Dai Pra, G. Late Pleistocene to Holocene record of changing uplift-rates in southern Calabria and northeastern Sicily (southern Italy, Central Mediterranean Sea). Tectonophysics 2006, 422, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, M.; Lickorish, W.H.; Diliberto, S.E.; Geremia, F.; Maniscalco, R.; Maugeri, S.; Pappalardo, G.; Rapisarda, F.; Scamarda, G. Geological Map of the Licata Fold-Belt (South-Central Sicily). 1:50.000 Scale; SELCA, Ed.; Dipartimento di Scienze della Terra, Università di Catania: Florence, Italy, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Doody, J.P. Coastal squeeze and managed realignment in southeast England, does it tell us anything about the future? Ocean Coast. Manag. 2013, 79, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English Nature. Coastal Squeeze, Saltmarsh Loss and Special Protection Areas; English Nature Research Report No. 710; Royal Haskoning for English Nature: Peterborough, UK, 2006; p. 55. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, M.L.; Mendoza-Gonzalez, G.; Silva, R.; Mendoza, E. Land use changes and sea level rise may induce a “coastal squeeze” on the coasts of Veracruz, Mexico. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2014, 29, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M.; Dennison, W.C.; Orth, R.J.W.; Carruthers, T.J.B. The charisma of coastal ecosystems: Addressing the imbalance. Estuaries Coasts 2008, 31, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pontee, N. Defining coastal squeeze: A discussion. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2013, 84, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bella, S. L’abusivismo edilizio e il fenomeno della seconda casa lungo la costa meridionale della provincia di Catania. Esempio di errato intervento sul territorio. In Proceedings of the Atti XXIII Congresso Geografico Italiano, Catania, Italy, 9–13 May 1983; pp. 173–187. [Google Scholar]
- Randazzo, G.; Scrofani, L. Economic development and coastal environment in Sicily (Italy) in an Integrated Coastal Management policy. In Proceedings of the Atti XXIII Congresso Internazionale: Mediterranean & Black Sea ICZM 96, Sarigerme, Turkey, 2–5 November 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Nordstrom, K.F.; Lampe, R.; Vandremark, L.M. Reestablishing naturally functioning dunes on developed coasts. Environ. Manag. 2000, 25, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithgow, D.; Martínez, M.L.; Gallego-Fernández, J.B.; Hesp, P.A.; Flores, P.; Gachuz, S.; Rodríguez-Revelo, N.; Jiménez-Orocio, O.; Mendoza-González, G.; Álvarez- Molina, L.L. Linking restoration ecology with coastal dune restoration. Geomorphology 2013, 199, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, E.; Novelli, C.; Barbato, F.; Menegoni, P.; Iannetta, M.; Nascetti, G. Coastal dune systems and disturbance factors: Monitoring and analysis in central Italy. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 183, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallego-Fernández, J.B.; Sánchez, I.A.; Ley, C. Restoration of isolated and small coastal sand dunes on the rocky coast of northern Spain. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Mantia, T. Storia dell’eucalitticoltura in Sicilia. Nat. Sicil. 2013, 37, 587–628. [Google Scholar]
- Scatena, C. La Difesa dal Mare delle Linee Ferroviarie; Azienda Autonoma Ferrovie dello Stato: Roma, Italy, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Amore, C.; Giuffrida, E. L’influenza dell’interramento dei bacini artificiali del Simeto sul litorale del Golfo di Catania. Boll. Soc. Geol. Ital. 1984, 103, 731–753. [Google Scholar]
- Basco, D.R. Seawall impact on adjacent beaches: Separating fact from fiction. J. Coast. Res. 2004, 39, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Amore, C.; Giuffrida, E.; Privitera, S. Morphodynamic-sedimentological effects of the artificial barriers along the Tyrrhenian and Mediterranean Sicily coastlines. (poster). In Proceedings of the MEDCOAST 2003—The Sixth International Conference on the Mediterranean Coastal Environment, Ravenna, Italy, 7–11 October 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Molina, R.; Anfuso, G.; Manno, G.; Gracia, F.J. The Mediterranean Coast of Andalusia (Spain): Medium-Term Evolution and Impacts of Coastal Structures. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griggs, G.B. The impacts of coastal armoring. Shore Beach 2005, 73, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Doody, J.P. Sand Dune Inventory of Europe, 2nd ed.; National Coastal Consultants/EUCC, the Coastal Union, in collaboration with the IGU Coastal Commission. Published on CDROM; Liverpool Hope University: Liverpool, UK, 2008; p. 126. [Google Scholar]
- Statistica. Available online: https://www.statistica.com (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- Papale, D. Taormina Segreta-La Belle Epoque 1876–1914; P&M; 1995; P&M is the editorial. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, M.; Liu, S. Non market values of ecosystem services provided by coastal and nearshore and marine systems. In Ecological Economics of the Oceans and Coasts; Patterson, M., Glavovicic, B., Eds.; Edward Elgar Publishing Limited: Cheltenham, UK, 2008; pp. 119–139. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, A.T. Definitions and typologies of coastal tourism beach destinations. In Disappearing Destinations: Climate Change and Future Challenges for Coastal Tourism; Jones, A., Phillips, M.R., Eds.; CABI International: Wallingford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, R.C.; Alder, J. Coastal Planning and Management; E & FN Spon: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ergin, A.; Karaesmen, E.; Micallef, A.; Williams, A.T. A new methodology for evaluating coastal scenery: Fuzzy logic systems. Area 2004, 36, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manno, G.; Anfuso, G.; Messina, E.; Williams, A.T.; Suffo, M.; Liguori, V. Decadal evolution of coastline armouring along the Mediterranean Andalusia littoral (South of Spain). Ocean Coast. Manag. 2016, 124, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeoshenkova, V.; Newton, A. Overview of erosion and beach quality issues in three Southern European countries: Portugal, Spain and Italy. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2015, 118, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gual, M.M.; Pons, G.X.; Prieto, J.A.M.; Perea, A.R. A critical view of the Blue Flag beaches in Spain using environmental variables. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2015, 105, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brower, D.J.; Dreyfoos, W. Public access to ocean beaches: If you find a parkingspace, how do you get to the beach? Coast. Zone Manag. 1979, 5, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micallef, A.; Williams, A.T. Application of a novel approach to beach classification in the Maltese Islands. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2004, 47, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmer, P. Martin’s Beach Litigation and Eroding Public Access Rights to the California Coast Annual Review of Environmental and Natural Resource Law: In the Briefs. Ecol. Law Q. 2018, 45, 427–438. [Google Scholar]
- Cartlidge, N. Whose Beach is it anyway? In Towards Liveable Cities and Better Communities Smart Vision International; Taplin, J., Ed.; Smart Vision International: Perth, Australia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, C.-O.; Dixon, A.W.; Mjelde, J.W.; Draper, J. Valuing visitors’ economic benefits of public beach access points. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2008, 51, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Espresso. Available online: http://temi.repubblica.it/espresso-il68/1966/09/10/hanno-messo-il-mare-in-gabbia/ (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Benson, E.D.; Hansen, J.L.; Schwartz, A.L.; Smersh, G.T. Pricing Residential Amenities: The Value of a View. J. Real Estate Financ. Econ. 1998, 16, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischer, A. A room with a view—A valuation of the Mediterranean Sea view. Tour. Manag. 2012, 33, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendoza-González, G.; Martínez, M.L.; Guevara, R.; Pérez-Maqueo, O.; Garza-Lagler, M.C.; Howard, D.A. Towards a Sustainable Sun, Sea, and Sand Tourism: The Value of Ocean View and Proximity to the Coast. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strand, J.; Vågnes, M. The relationship between property values and railroad proximity: A study based on hedonic prices and real estate brokers’ appraisals. Transportation 2001, 28, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Distance from the Shoreline (m) | Length of Railway Segments Located between the Shoreline and Settlements | Length of the Segments Defended by Artificial Structures | Percentage of the Railway Length Defended by Artificial Structures in Each Coastal Strip |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0–50 | 29.2 km | 8.0 km | 27.3% |
| 50–100 | 17.2 km | 1.7 km | 9.7% |
| 0–100 | 46.4 km | 9.6 km | 20.8% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cinelli, I.; Anfuso, G.; Privitera, S.; Pranzini, E. An Overview on Railway Impacts on Coastal Environment and Beach Tourism in Sicily (Italy). Sustainability 2021, 13, 7068. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137068
Cinelli I, Anfuso G, Privitera S, Pranzini E. An Overview on Railway Impacts on Coastal Environment and Beach Tourism in Sicily (Italy). Sustainability. 2021; 13(13):7068. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137068
Chicago/Turabian StyleCinelli, Irene, Giorgio Anfuso, Sandro Privitera, and Enzo Pranzini. 2021. "An Overview on Railway Impacts on Coastal Environment and Beach Tourism in Sicily (Italy)" Sustainability 13, no. 13: 7068. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137068
APA StyleCinelli, I., Anfuso, G., Privitera, S., & Pranzini, E. (2021). An Overview on Railway Impacts on Coastal Environment and Beach Tourism in Sicily (Italy). Sustainability, 13(13), 7068. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137068








