Metadata Analysis to Evaluate Environmental Impacts of Wheat Residues Burning on Soil Quality in Developing and Developed Countries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Data Collection and Analysis Method
2.3. Statistical Analysis
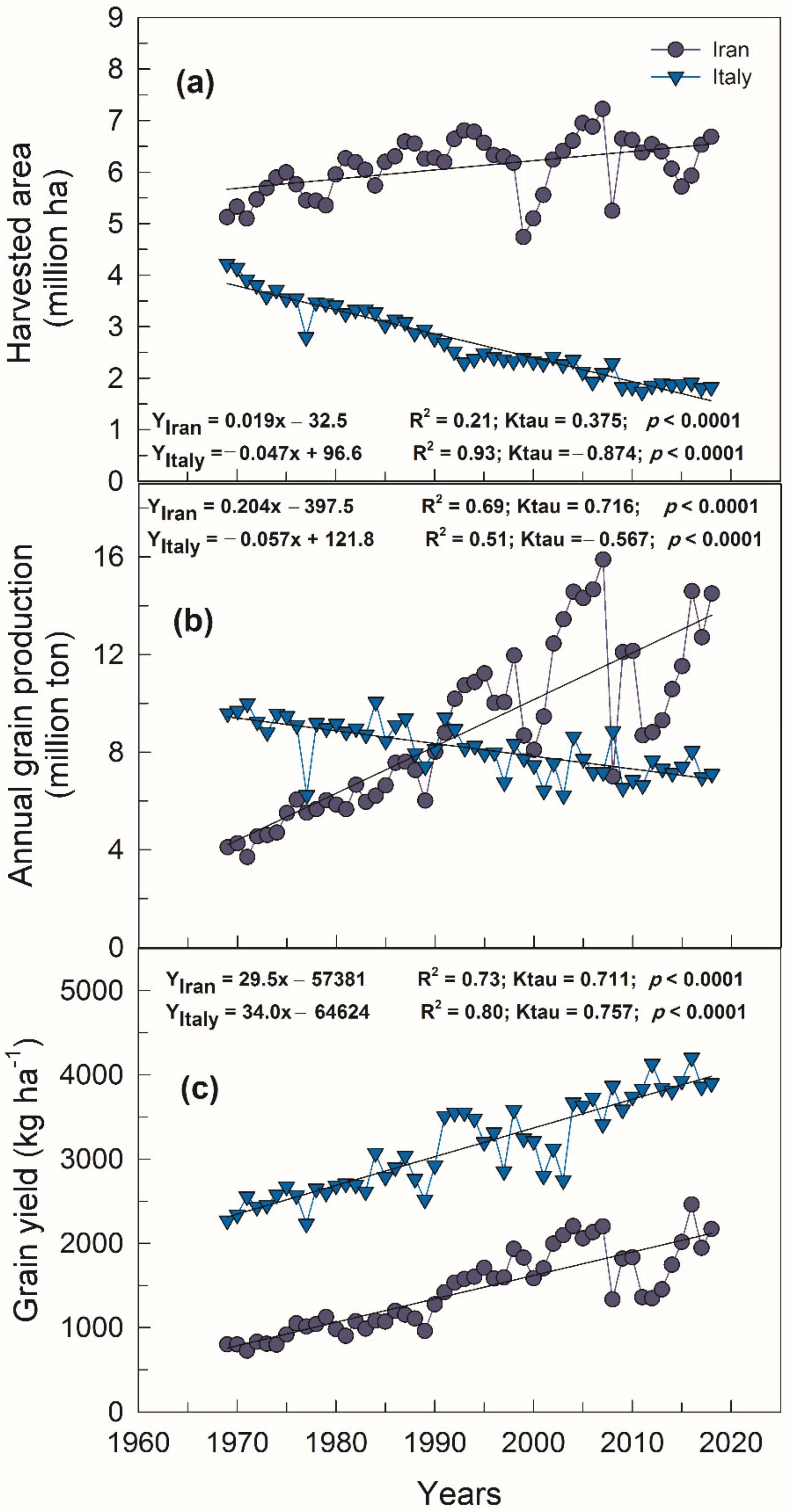
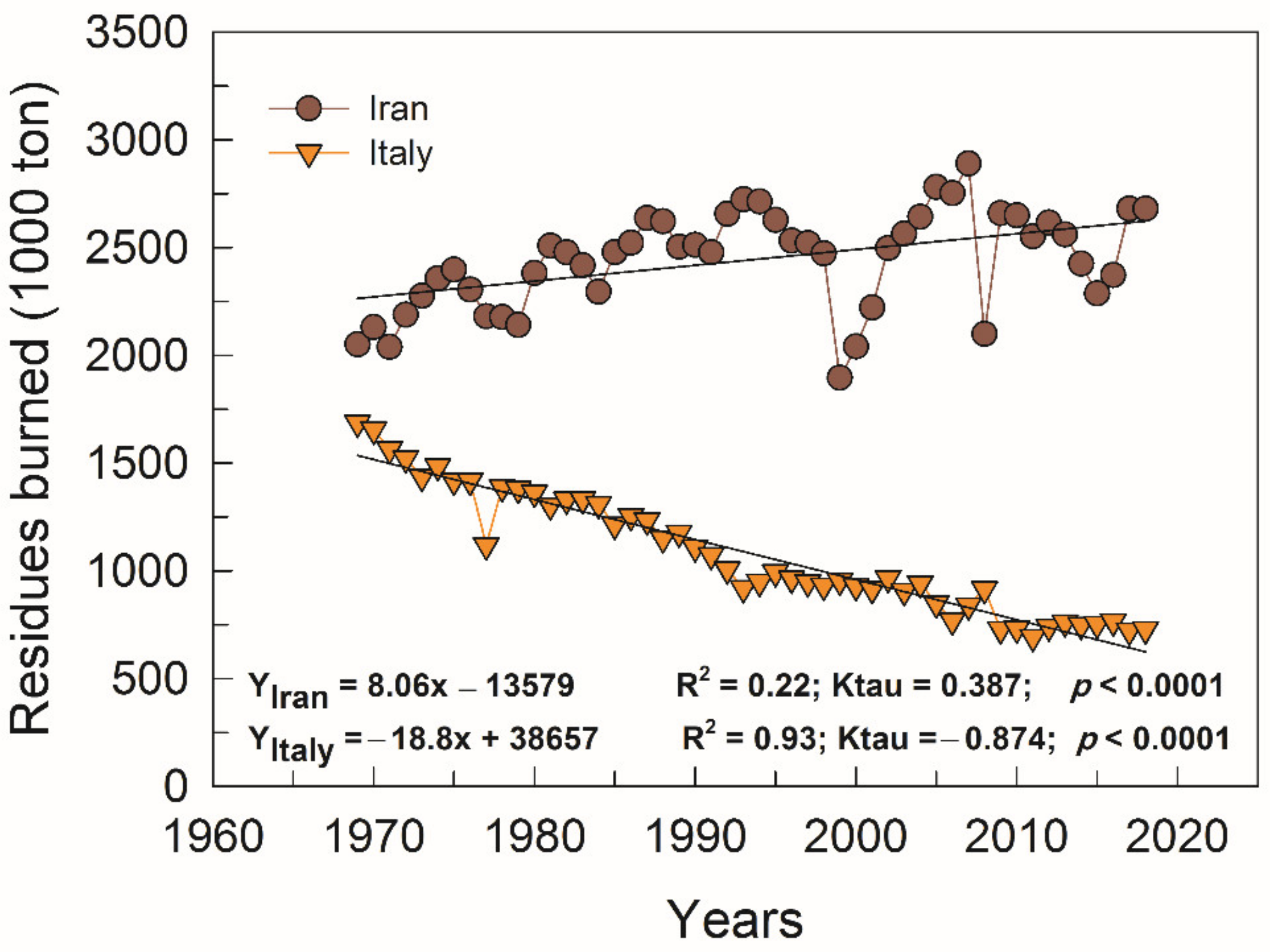
3. Results and Discussion
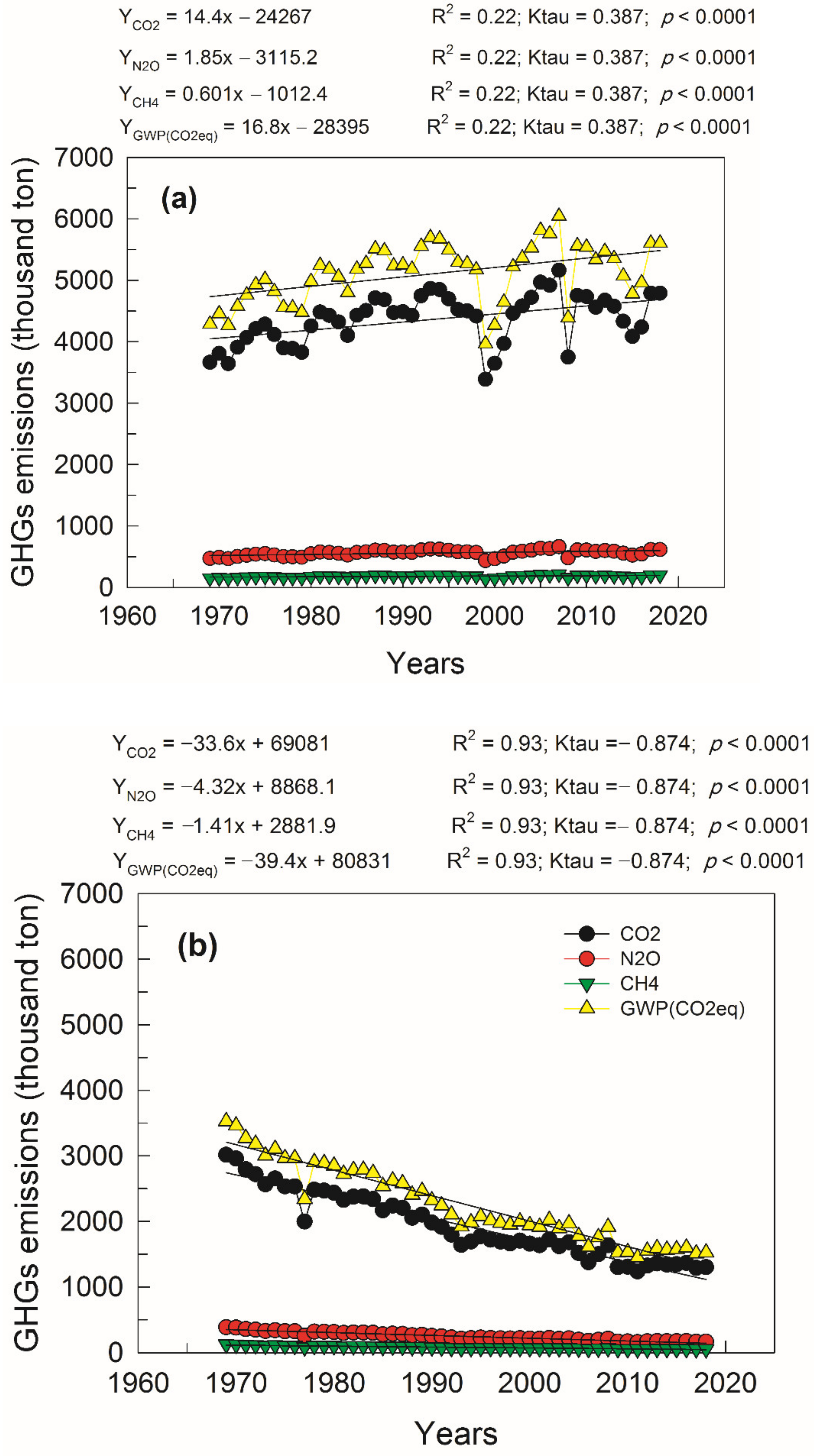
3.1. GHG Emission
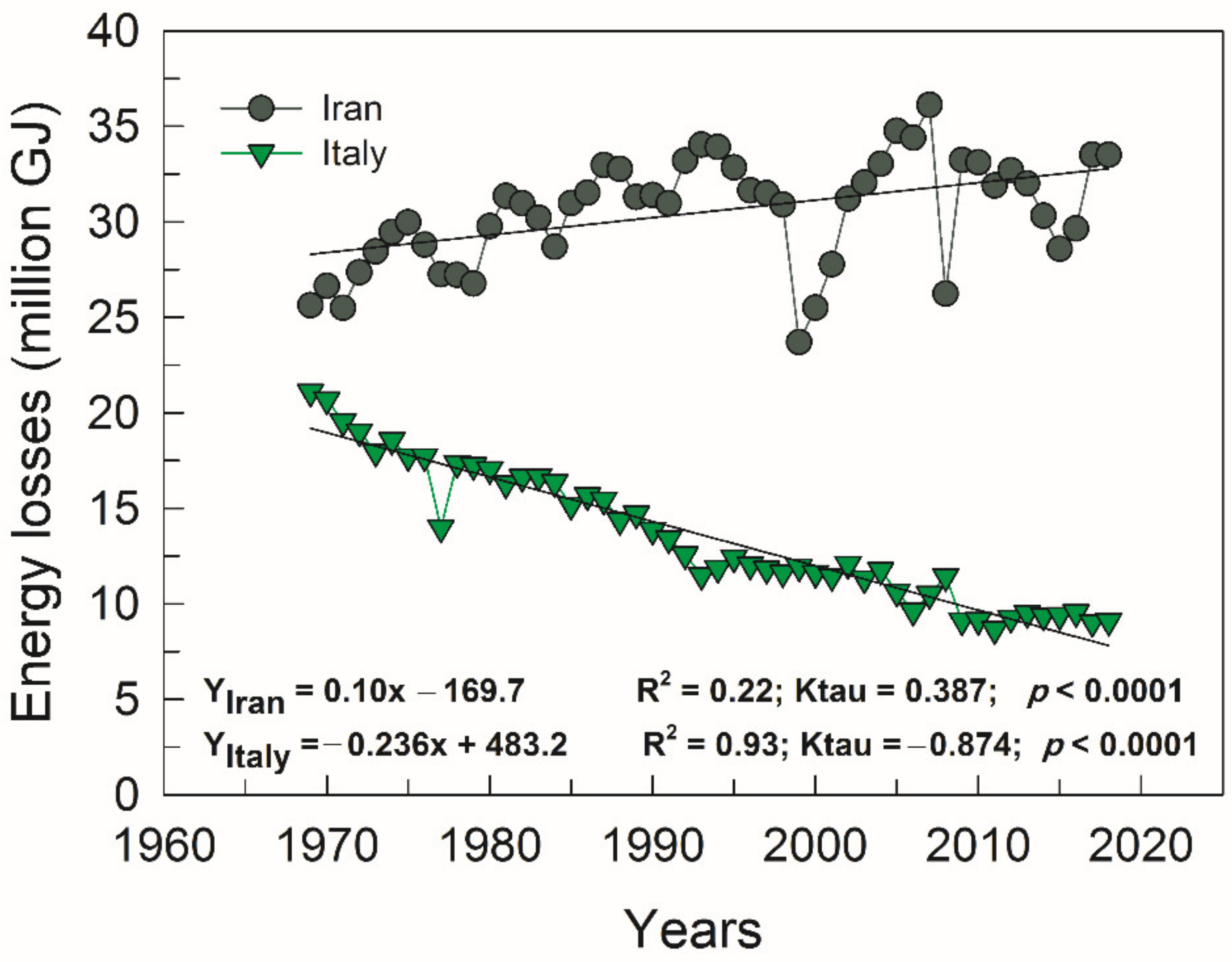
3.2. Energy Losses
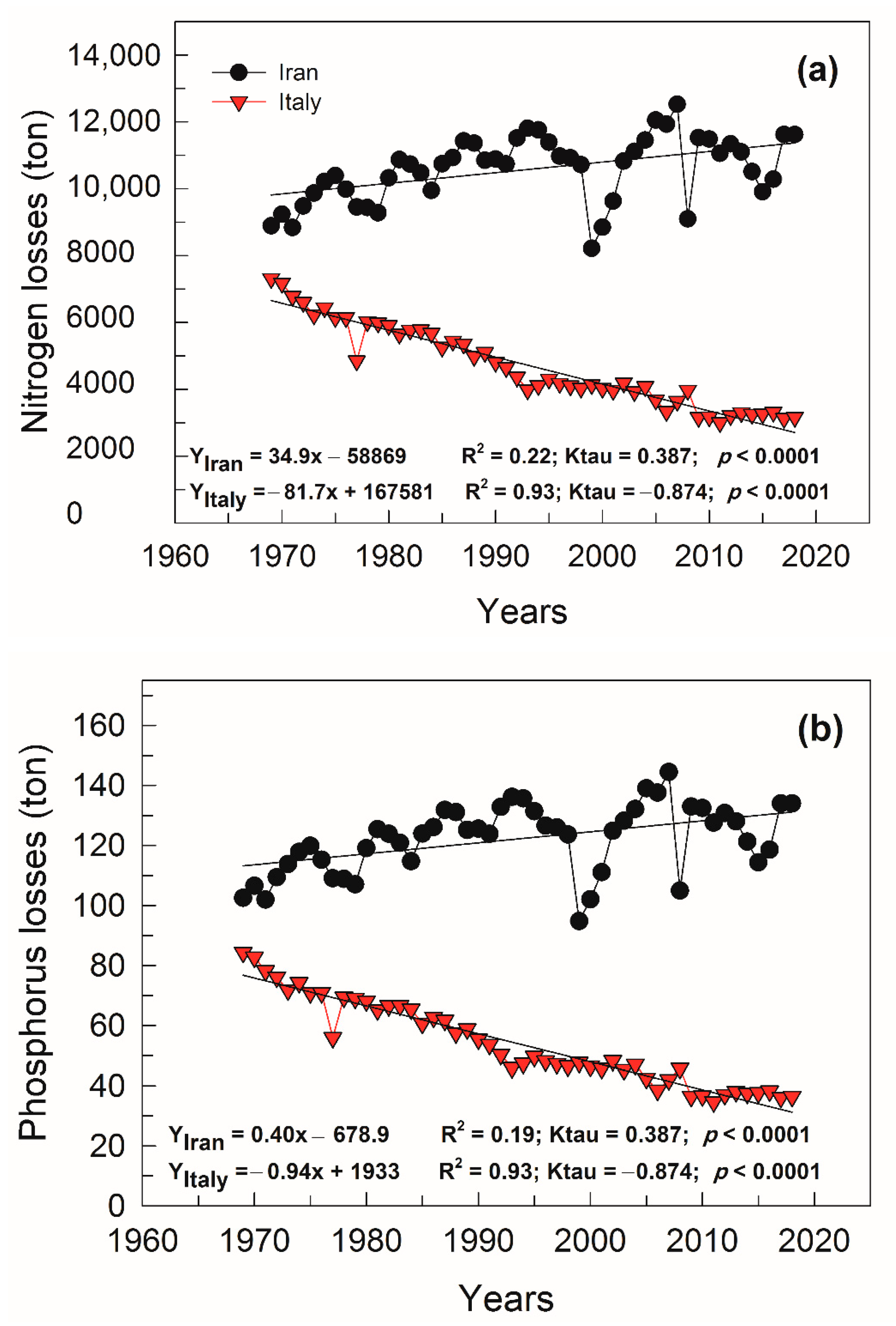
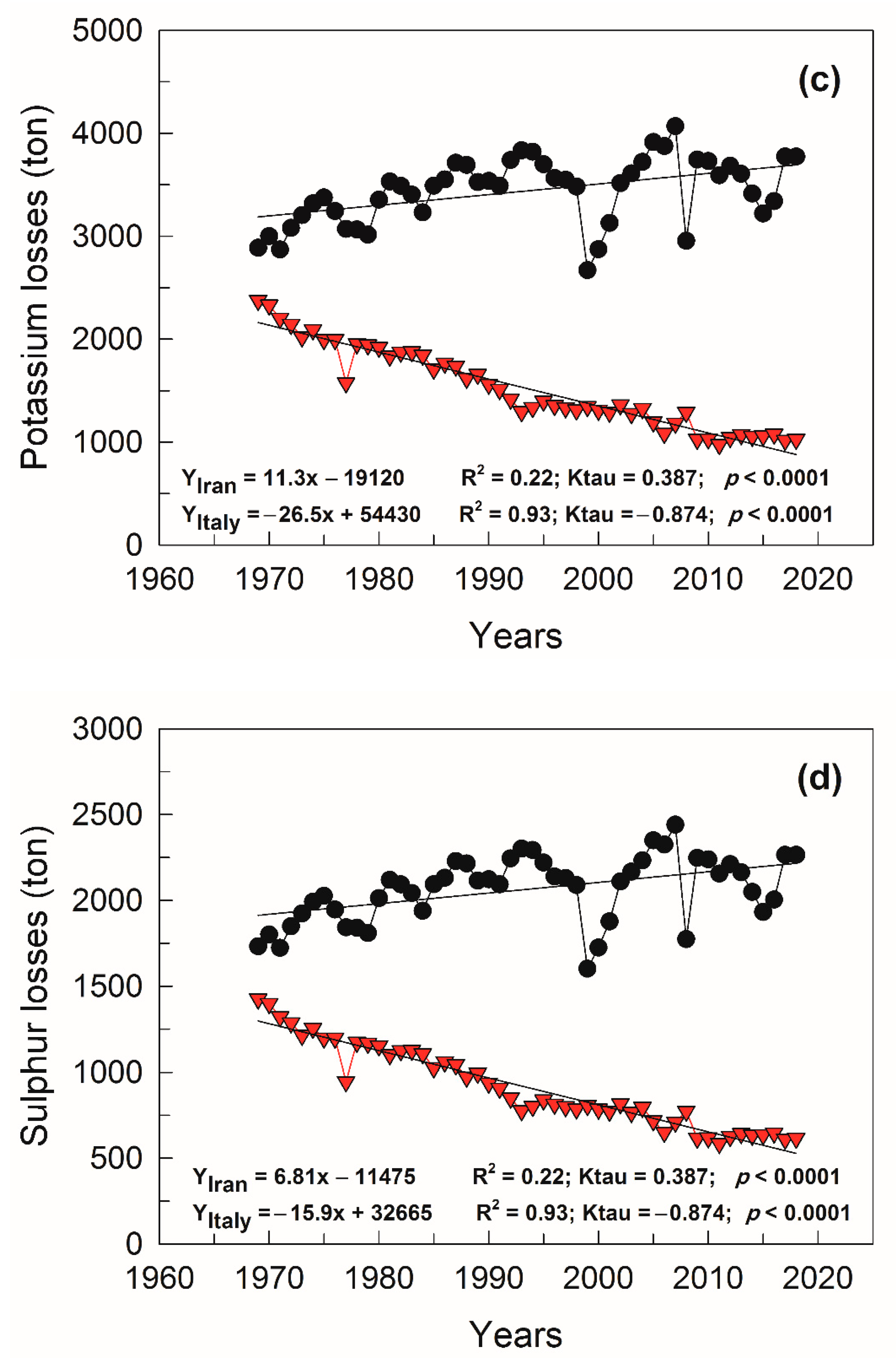
3.3. Nutrients’ Losses
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brankatschk, G.; Finkbeiner, M. Crop rotations and crop residues are relevant parameters for agricultural carbon footprints. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 37, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiertz, J. Nitrogen, sustainable agriculture and food security: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cutforth, H.; Chai, Q.; Gan, Y. Farming tactics to reduce the carbon footprint of crop cultivation in semiarid areas. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacinthe, P.-A.; Lal, R.; Kimble, J. Carbon budget and seasonal carbon dioxide emission from a central Ohio Luvisol as influenced by wheat residue amendment. Soil Tillage Res. 2002, 67, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, P.V.F.; Farrell, R.E.; Bell, G.; Taveira, C.J.; Congreves, K.A.; Voroney, R.P.; Wagner-Riddle, C. Crop residues contribute minimally to spring-thaw nitrous oxide emissions under contrasting tillage and crop rotations. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 152, 108057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil quality impacts of residue removal for bioethanol production. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 102, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordán, A.; Zavala, L.M.; Gil, J. Effects of mulching on soil physical properties and runoff under semi-arid conditions in southern Spain. Catena 2010, 81, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranaivoson, L.; Naudin, K.; Ripoche, A.; Affholder, F.; Rabeharisoa, L.; Corbeels, M. Agro-ecological functions of crop residues under conservation agriculture. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 37, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Adhya, T.; Pathak, H.; Raghuram, N.; Sharma, C. Issues and Policies for Reactive Nitrogen Management in the Indian Region. Indian Nitrogen Assess. 2017, 491–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, P.; Barman, D. Crop residue management and greenhouse gases emissions in tropical rice lands. In Soil Management and Climate Change; Academic Press: London, UK, 2018; pp. 323–335. [Google Scholar]
- Lehtinen, T.; Schlatter, N.; Baumgarten, A.; Bechini, L.; Krüger, J.; Grignani, C.; Spiegel, H. Effect of crop residue incorporation on soil organic carbon and greenhouse gas emissions in European agricultural soils. Soil Use Manag. 2014, 30, 524–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R.P.; Montes-Molina, J.A.; Govaerts, B.; Six, J.; van Kessel, C.; Fonte, S.J. Crop residue retention enhances soil properties and nitrogen cycling in smallholder maize systems of Chiapas, Mexico. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 103, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lu, M.; Cui, J.; Li, B.; Fang, C. Effects of straw carbon input on carbon dynamics in agricultural soils: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 1366–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Härri, A.; Levänen, J.; Koistinen, K. Marginalized Small-Scale Farmers as Actors in Just Circular-Economy Transitions: Exploring Opportunities to Circulate Crop Residue as Raw Material in India. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erenstein, O. Crop residue mulching in tropical and semi-tropical countries: An evaluation of residue availability and other technological implications. Soil Tillage Res. 2002, 67, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heard, J.; Cavers, C.; Adrian, G. Up in smoke-nutrient loss with straw burning. Better Crops 2006, 90, 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Jat, H.; Jat, R.; Nanwal, R.; Lohan, S.K.; Yadav, A.; Poonia, T.; Jat, M. Energy use efficiency of crop residue management for sustainable energy and agriculture conservation in NW India. Renew. Energy 2020, 155, 1372–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrani, M.; Raufat, M.; Ghadiri, H. Influence of wheat residue management on irrigated corn grain production in a reduced tillage system. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 94, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolo, P.; Kihara, J.; Mucheru-Muna, M.; Njeru, E.M.; Kinyua, M.; Sommer, R. Application of residue, inorganic fertilizer and lime affect phosphorus solubilizing microorganisms and microbial biomass under different tillage and cropping systems in a Ferralsol. Geoderma 2021, 390, 114962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.K.; Sahai, S.; Singh, N.; Dixit, C.; Singh, D.; Sharma, C.; Garg, S. Residue burning in rice–wheat cropping system: Causes and implications. Curr. Sci. 2004, 87, 1713–1717. [Google Scholar]
- Kaushal, L.A.; Prashar, A. Agricultural crop residue burning and its environmental impacts and potential causes–case of northwest India. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2021, 64, 464–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhi, S.; Kutcher, H. Small grains stubble burning and tillage effects on soil organic C and N, and aggregation in northeastern Saskatchewan. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 94, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, T.; Bhagat, R. Impact of rice straw management practices on yield, nitrogen uptake and soil properties in a wheat-rice rotation in northern India. Fertil. Res. 1992, 33, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Sharma, G.K.; Kumar, P.; Singh, S.; Singh, R. Effect of Crop Residues Management on Soil Properties and Crop Productivity of Rice-wheat System in Inceptisols of Seemanchal Region of Bihar. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2019, 37, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mandal, K.G.; Misra, A.K.; Hati, K.M.; Bandyopadhyay, K.K.; Ghosh, P.K.; Mohanty, M. Rice residue-management options and effects on soil properties and crop productivity. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2004, 2, 224–231. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sobky, E.-S.E. Effect of burned rice straw, phosphorus and nitrogen fertilization on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Ann. Agric. Sci. 2017, 62, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junpen, A.; Pansuk, J.; Kamnoet, O.; Cheewaphongphan, P.; Garivait, S. Emission of air pollutants from rice residue open burning in Thailand, 2018. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, K.; Singh, T.; Mor, S.; Singh, V.; Mandal, T.K.; Bhatti, M.S.; Beig, G. Real-time monitoring of air pollutants in seven cities of North India during crop residue burning and their relationship with meteorology and transboundary movement of air. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasko, K.; Vadrevu, K. Improved rice residue burning emissions estimates: Accounting for practice-specific emission factors in air pollution assessments of Vietnam. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadrevu, K.; Lasko, K. Fire regimes and potential bioenergy loss from agricultural lands in the Indo-Gangetic Plains. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 148, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Wang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Tani, H.; Zhong, G.; Sun, Z. Study on spatial distribution of crop residue burning and PM2.5 change in China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 204–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Guo, M.; Miura, M.; Xiao, Y. Influence of biomass burning on local air pollution in mainland Southeast Asia from 2001 to 2016. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. FAOSTAT/Productionstat/Crops. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Revised on 2 December 2020. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data (accessed on 22 December 2020).
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, Update 2015 International soil classification system for naming soils and creating legends for soil maps. In World Soil Resources Reports No. 106; FAO: Roma, Italy, 2015; p. 192. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, P.R.; Skea, J.; Calvo Buendia, E.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Pörtner, H.-O.; Roberts, D.C.; Zhai, P.; Slade, R.; Connors, S.; van Diemen, R.; et al. Climate Change and Land: An IPCC Special Report on Climate Change, Desertification, Land Degradation, Sustainable Land Management, Food Security, and Greenhouse Gas Fluxes in Terrestrial Ecosystems; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/srccl/ (accessed on 8 August 2019).
- Jamali, M.; Soufizadeh, S.; Yeganeh, B.; Emam, Y. A comparative study of irrigation techniques for energy flow and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in wheat agroecosystems under contrasting environments in south of Iran. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 139, 110704. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, B.; Eberbach, P.; Evans, J.; Wade, L. Stubble Retention in Cropping Systems in Southern Australia: Benefits and Challenges; Clayton, E.H., Burns, H.M., Eds.; Industry & Investment: Orange, Australia, 2010; Available online: http://www.csu.edu.au/research/grahamcentre/ (accessed on 12 August 2010).
- Schultz, J.; French, R. Mineral content of herbage and grain of Halberd wheat in South Australia. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 1976, 16, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, R.; Byerlee, D.; Edmeades, G. Crop Yields and Global Food Security; ACIAR: Canberra, Australia, 2014; pp. 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; He, H.; Lu, S.; Chen, D.; Zhu, J. Quantification of crop residue burning in the field and its influence on ambient air quality in Suqian, China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1961–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, S.; Sharma, C.; Singh, S.; Gupta, P.K. Assessment of trace gases, carbon and nitrogen emissions from field burning of agricultural residues in India. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2011, 89, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, C.; Habib, G.; Kadamba, D.; Shrivastava, M.; Leon, J.F.; Crouzille, B.; Streets, D. Emissions from open biomass burning in India: Integrating the inventory approach with high-resolution Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) active-fire and land cover data. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2006, 20, GB2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Peng, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Wei, M.; Li, W.; Mellouki, A. An estimation of CO2 emission via agricultural crop residue open field burning in China from 1996 to 2013. J. Clean Prod. 2016, 112, 2625–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, K.; Singh, T.; Mor, S. Emissions of air pollutants from primary crop residue burning in India and their mitigation strategies for cleaner emissions. J. Clean Prod. 2019, 208, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wu, Q.; Wang, F. Regional optimization of new straw power plants with greenhouse gas emissions reduction goals: A comparison of different logistics modes. J. Clean Prod. 2017, 161, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Bhave, P.V.; Puppala, S.P.; Shakya, K.; Maharjan, B.; Byanju, R.M. A model-ready emission inventory for crop residue open burning in the context of Nepal. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks-Bielska, R.; Bielski, S.; Novikova, A.; Romaneckas, K. Straw stocks as a source of renewable energy. A case study of a district in Poland. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, A.; Kumar, A. Optimal siting and size of bioenergy facilities using geographic information system. Appl. Energy 2012, 94, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, H.; Cohen, W.B.; Lopes, D.; Aranha, J. Assessment of forest biomass for use as energy. GIS-based analysis of geographical availability and locations of wood-fired power plants in Portugal. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 2551–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xie, G.; Li, S.; Ge, L.; He, T. The productive potentials of sweet sorghum ethanol in China. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 2360–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Havrysh, V.; Klymchuk, O.; Nitsenko, V.; Balezentis, T.; Streimikiene, D. Utilization of crop residue for power generation: The case of Ukraine. Sustainability 2019, 11, 7004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Zhuang, D.; Fu, J.; Huang, Y.; Wen, K. Bioenergy potential from crop residues in China: Availability and distribution. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiloidhari, M.; Das, D.; Baruah, D. Bioenergy potential from crop residue biomass in India. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 32, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, N. Role of plant nutrients in plant growth and physiology. In Plant Nutrients and Abiotic Stress Tolerance; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 51–93. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Kumar, S.; Joshi, L. Socioeconomic and Environmental Implications of Agricultural Residue Burning: A Case Study of Punjab, India; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.P.; Dhaliwal, H.S.; Sidhu, H.S.; Manpreet-Singh, Y.S.; Blackwell, J. Economic assessment of the Happy Seeder for rice-wheat systems in Punjab, India. In Proceedings of the Event 52nd Annual Conference of the Australian Agricultural and Resource Economics Society, Canberra, Australia, 6–8 February 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Giardina, C.P.; Sanford, R.L.; Døckersmith, I.C.; Jaramillo, V.J. The effects of slash burning on ecosystem nutrients during the land preparation phase of shifting cultivation. Plant Soil 2000, 220, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jamali, M.; Bakhshandeh, E.; Yaghoubi Khanghahi, M.; Crecchio, C. Metadata Analysis to Evaluate Environmental Impacts of Wheat Residues Burning on Soil Quality in Developing and Developed Countries. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6356. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13116356
Jamali M, Bakhshandeh E, Yaghoubi Khanghahi M, Crecchio C. Metadata Analysis to Evaluate Environmental Impacts of Wheat Residues Burning on Soil Quality in Developing and Developed Countries. Sustainability. 2021; 13(11):6356. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13116356
Chicago/Turabian StyleJamali, Mohsen, Esmaeil Bakhshandeh, Mohammad Yaghoubi Khanghahi, and Carmine Crecchio. 2021. "Metadata Analysis to Evaluate Environmental Impacts of Wheat Residues Burning on Soil Quality in Developing and Developed Countries" Sustainability 13, no. 11: 6356. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13116356
APA StyleJamali, M., Bakhshandeh, E., Yaghoubi Khanghahi, M., & Crecchio, C. (2021). Metadata Analysis to Evaluate Environmental Impacts of Wheat Residues Burning on Soil Quality in Developing and Developed Countries. Sustainability, 13(11), 6356. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13116356





