A Systematic Review of Enterprise Innovation Ecosystems
Abstract
1. Introduction
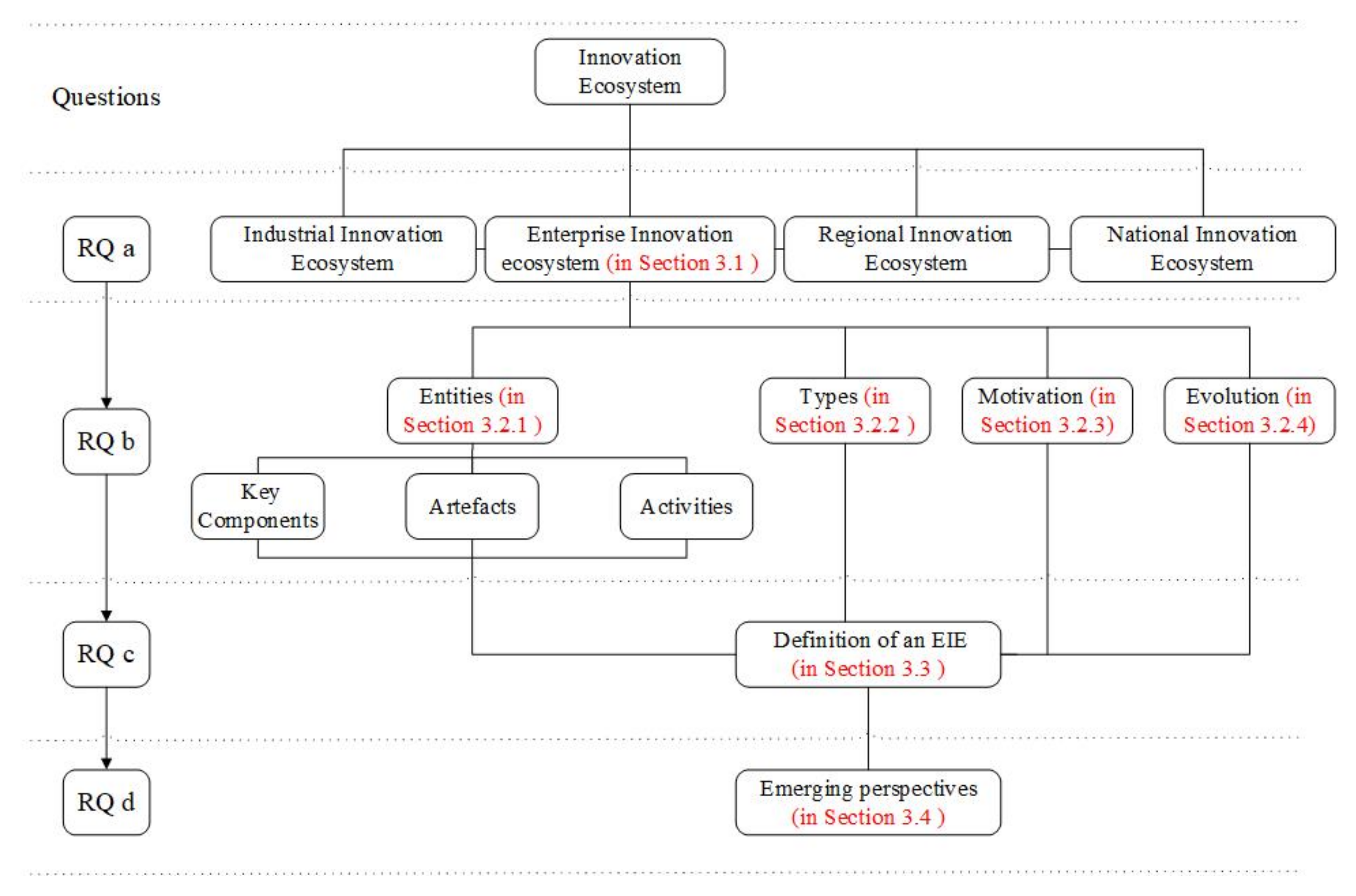
- RQa.
- How can the position of an EIE be clarified in the overall innovation ecosystems?
- RQb.
- What is an EIE, including its entity, type, evolution mechanism, and motivation mechanism?
- RQc.
- How is an EIE defined?
- RQd.
- What is the latest research progress and future trends of EIEs?
2. Methodology
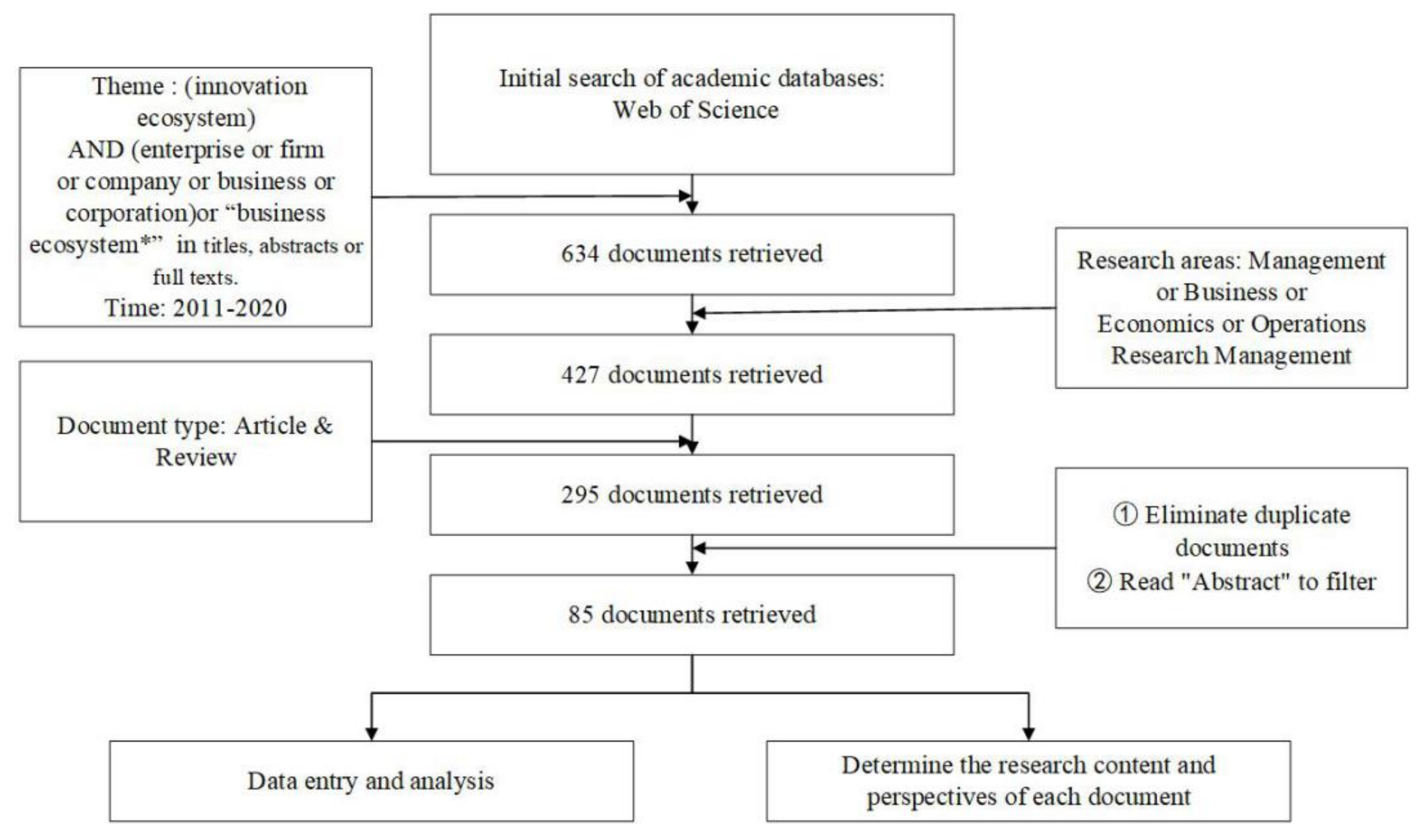
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Analysis
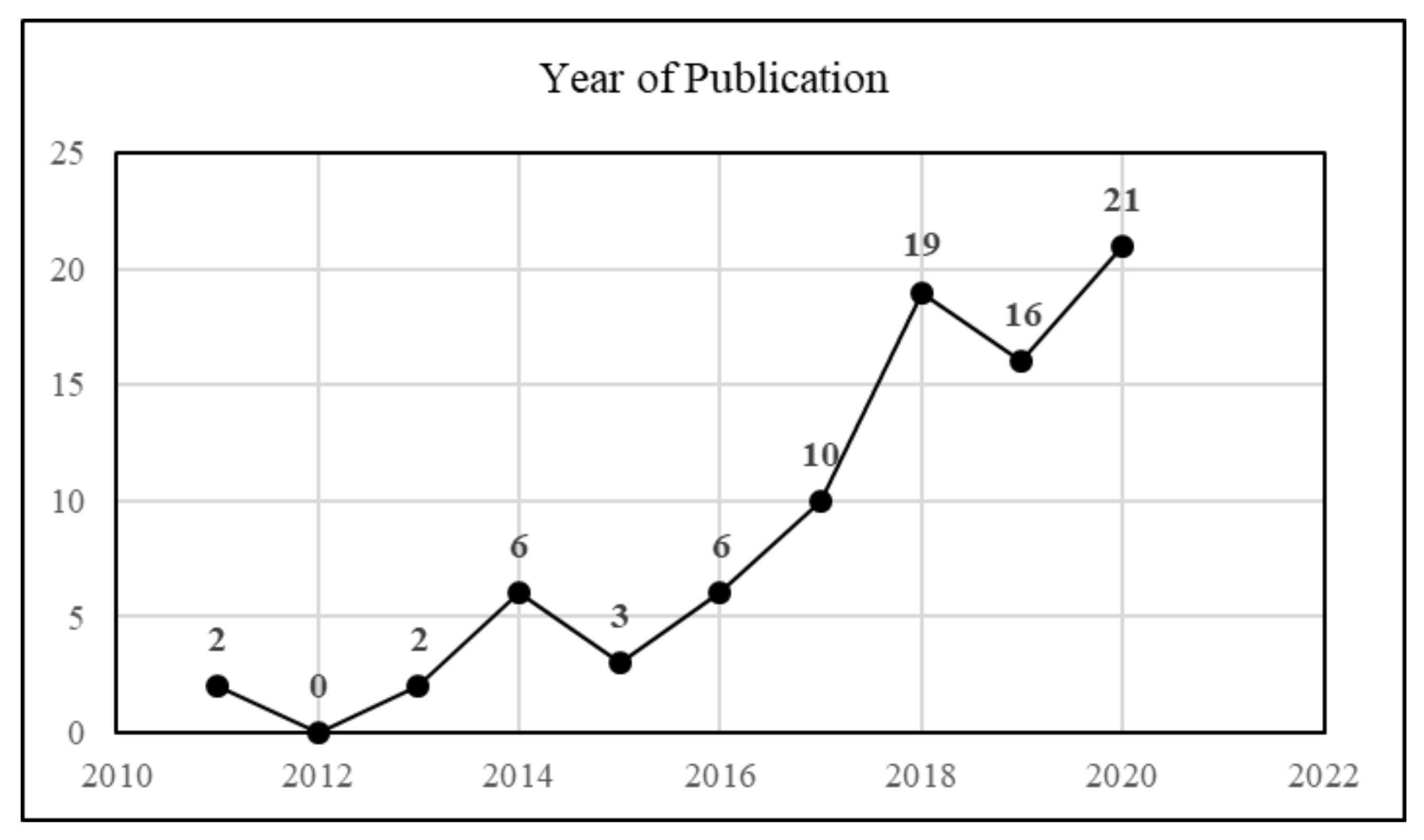
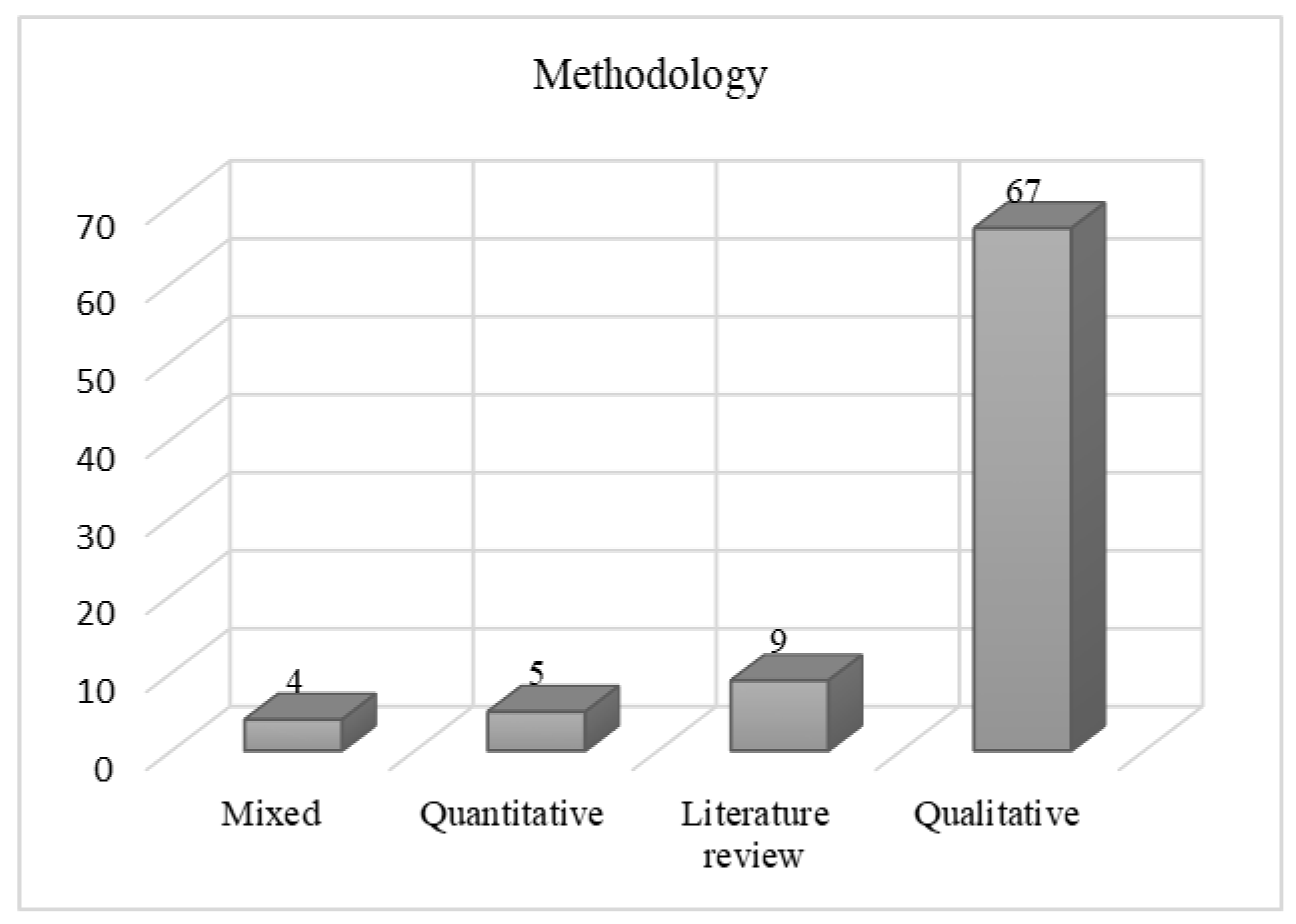
2.2.1. Descriptive Analysis
- (1)
- Time distribution analysis of the research literature
- (2)
- Analysis of Journal Distribution of the Research Literature
- (3)
- Method used in selected articles
- (4)
- Highly cited literature analysis
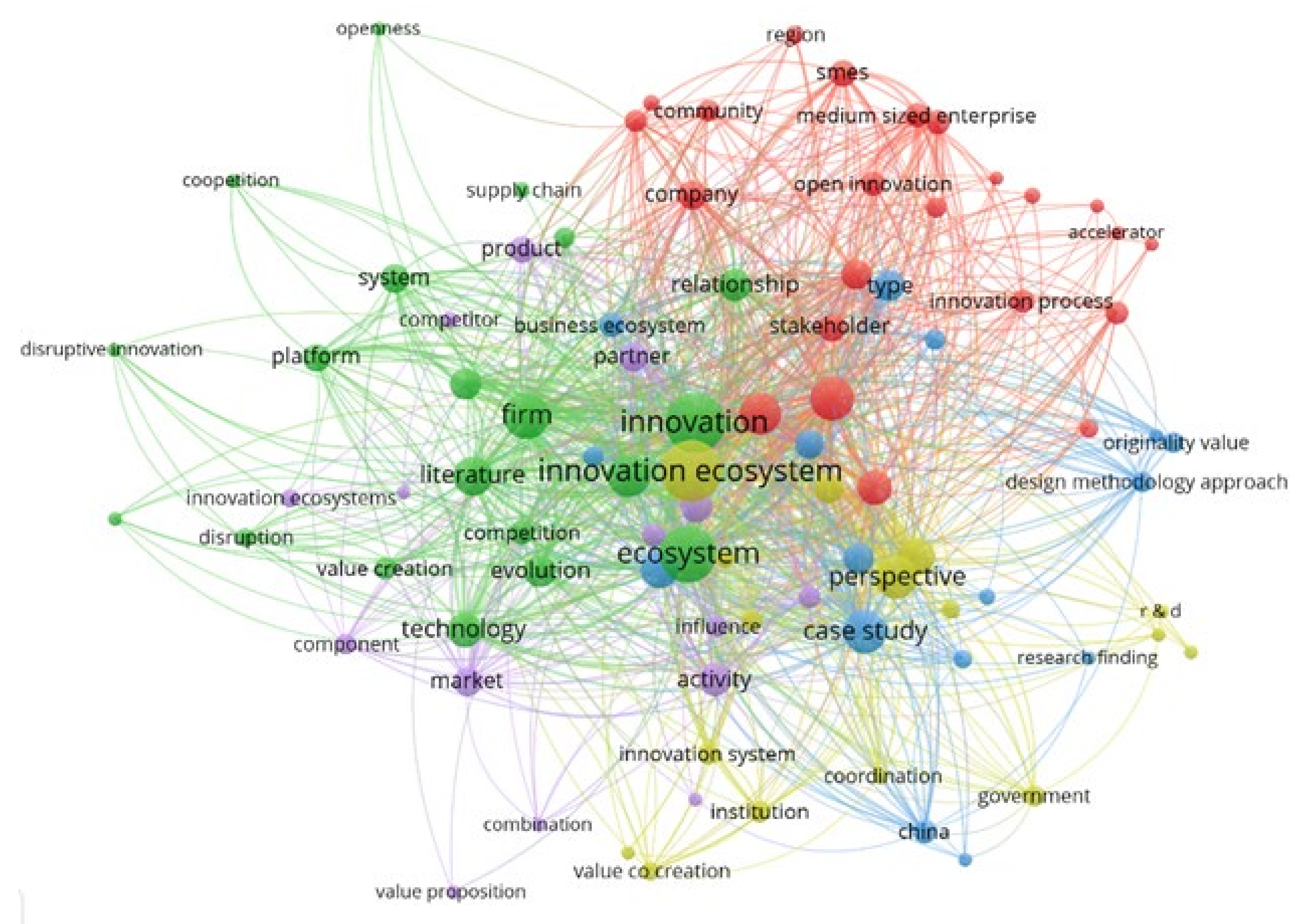
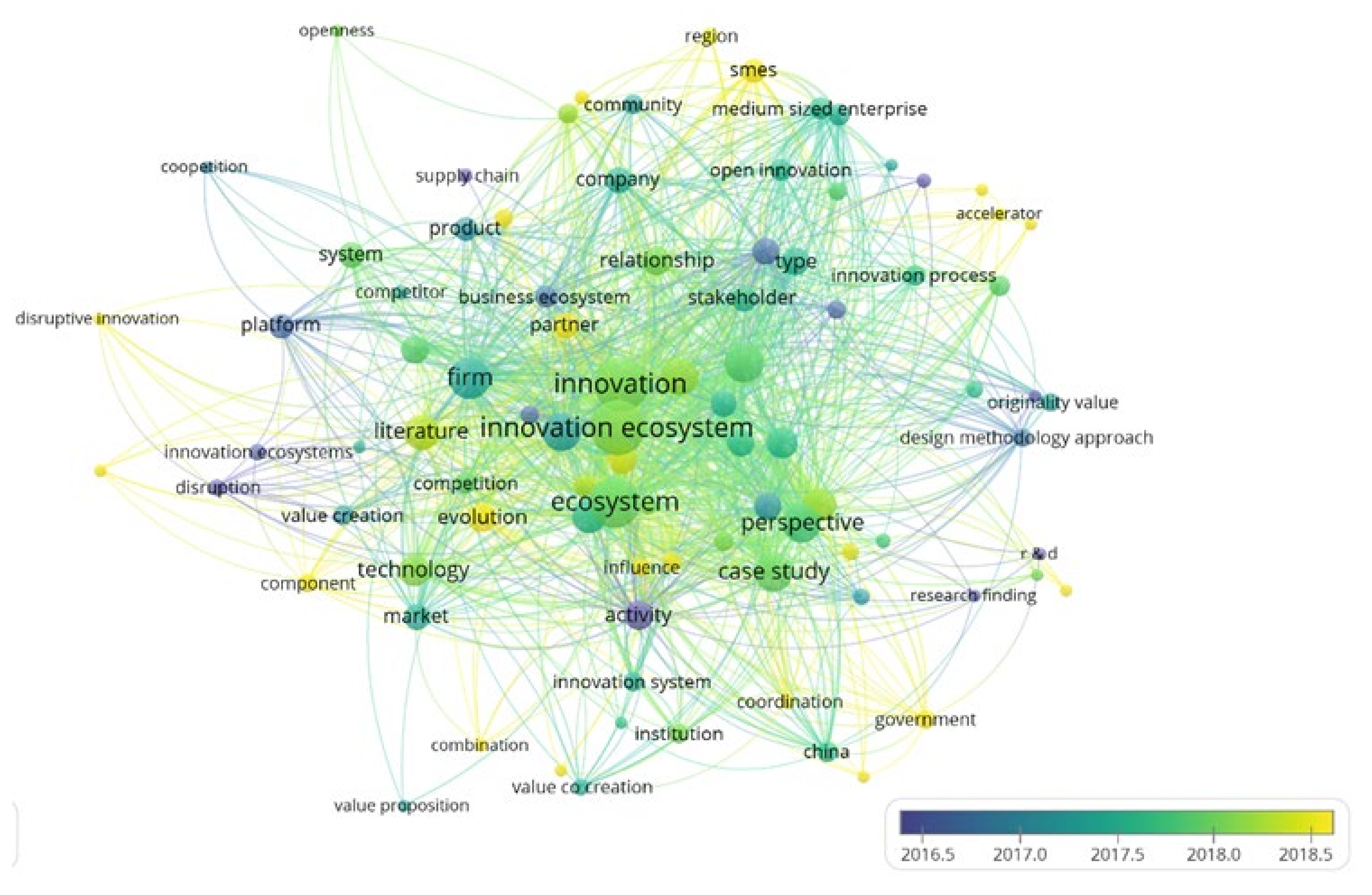
2.2.2. Keyword Cluster Analysis
- RQ a.
- How can the EIE position be clarified in the overall innovation ecosystem?
- RQ b.
- What is an EIE, including its entity, type, motivation mechanism, and evolution mechanism?
- 1.
- (no)-entities:
- (1)
- component-key components: actor/key actor-key actors, supply chain-innovation chain, network-innovation network, and platform-innovation platform.
- (2)
- (no)-artifacts: technology-technology, knowledge-knowledge, and resource-resources.
- (3)
- relationship-relations: cooperation/coopetition/collaboration/combination-collaborative, complementarity-complementary, and competition-competitive.
- 2.
- type–types: SMEs-SMEs, (no)-core enterprise.
- 3.
- (no) motivation: driver-driving factors and barrier-hindering factors.
- 4.
- evolution-evolution.
- RQ c.
- How is an EIE defined?
- RQ d.
- What are the avenues for future research?
2.3. Data Synthesis
3. Enterprise Innovation Ecosystem Analysis
3.1. Clarification of Innovation Ecosystems
3.2. Detailed and Comprehensive Analysis of EIEs
3.2.1. Entities of EIEs
- (1)
- Key components
- (2)
- Artifacts
- (3)
- Relations
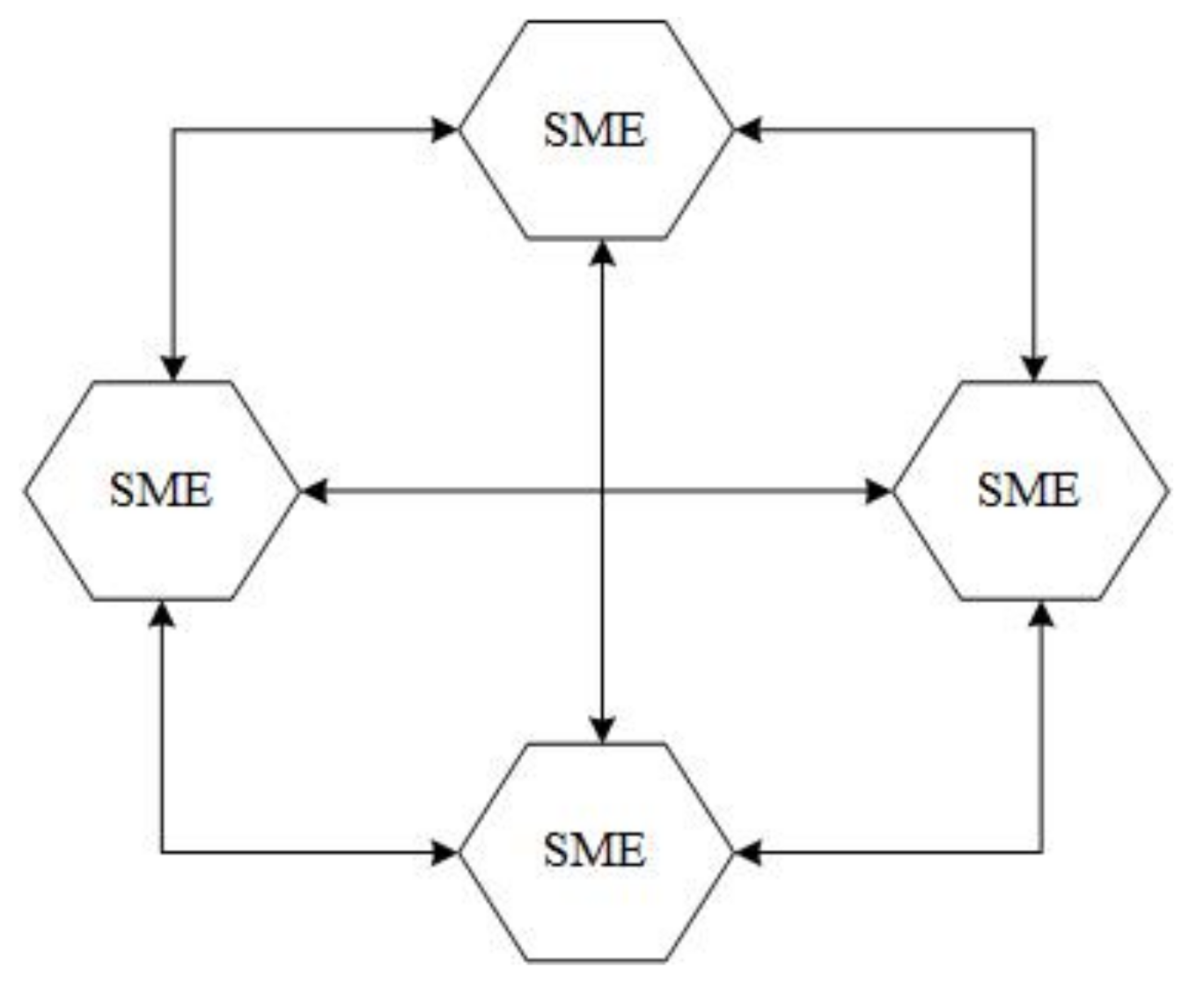
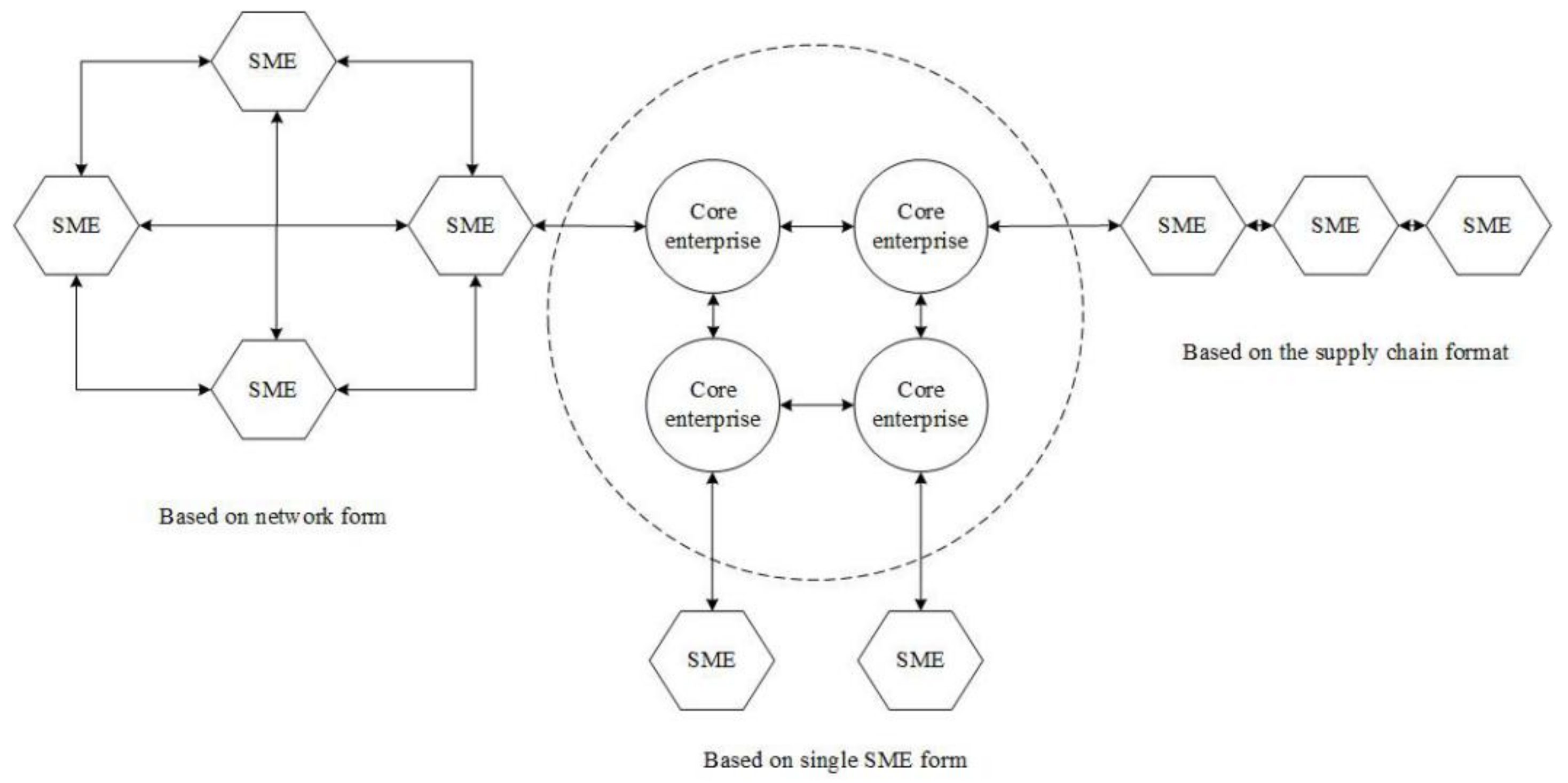
3.2.2. Types of EIEs
- (a)
- EIEs without a core enterprise(s)
- (b)
- EIEs with a core enterprise(s)
3.2.3. The Motivating Mechanism of EIEs
- (1)
- Driving forces:
- (2)
- Hindering forces:
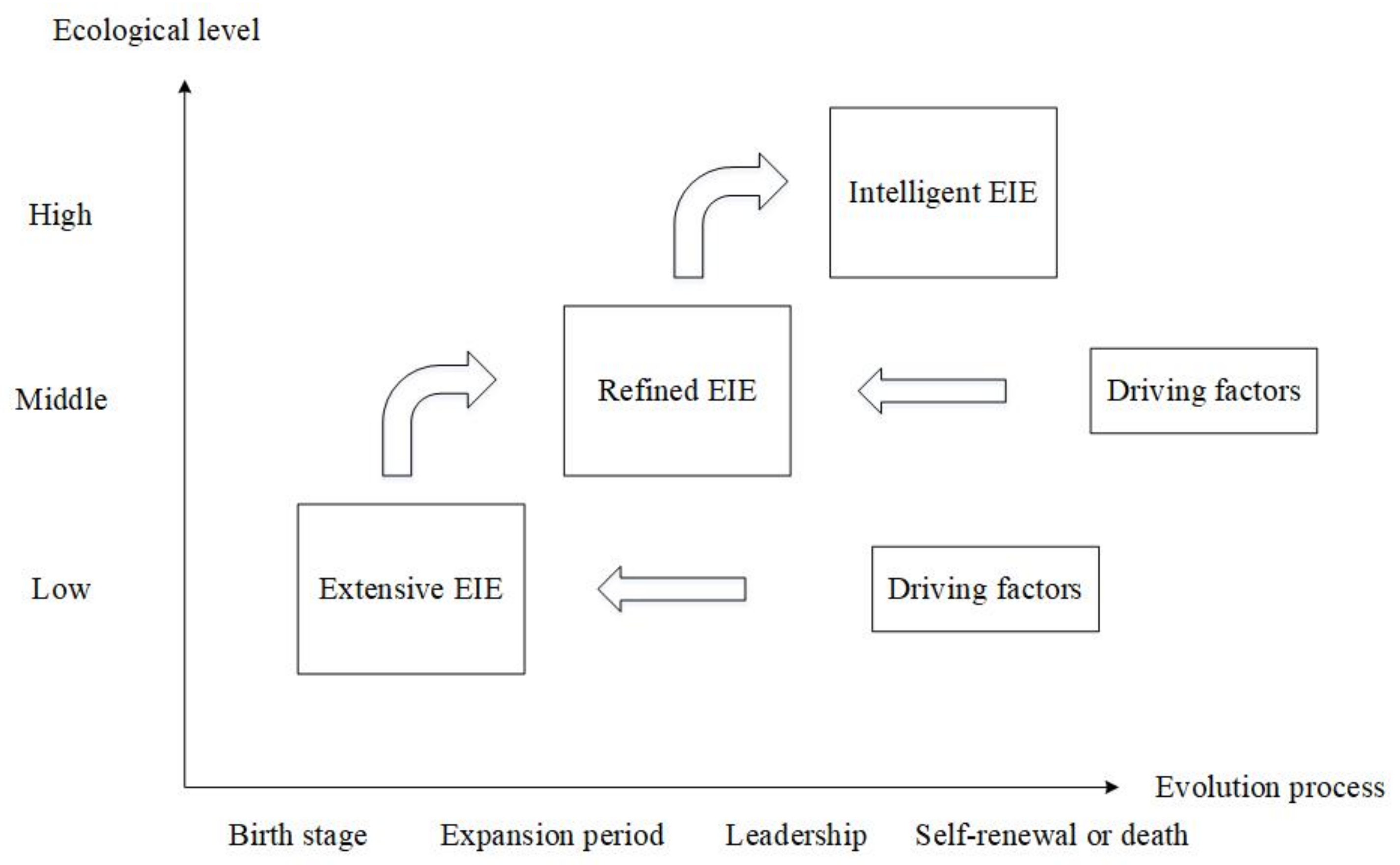
3.2.4. The Evolution of EIEs
3.3. Definition of EIEs
3.4. Emerging Research Directions
- a.
- Ecosystem perspective
- b.
- Triple/Quadruple/Quintuple helix
- c.
- Entrepreneurship
- d.
- Destructive innovation
- e.
- Open innovation
- f.
- Sustainable innovation
- g.
- Value creation and value capture
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Implications
- a.
- Theoretical implications
- b.
- Practical implications
- c.
- Policy recommendations
5.3. Research Limitations and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Serial Number | Title of Top Cited Articles | Purpose of the Study | Research Design | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Connecting local entrepreneurial ecosystems to global innovation networks: open innovation, double networks and knowledge integration | The research explores whether R&D strategies such as open innovation, knowledge integration, and double networks will be affected by the innovation ecology. | Qualitative Research Design | This study suggests a simultaneous need for local and global, as well as internal and external, knowledge integration. |
| 2 | Entrepreneurship in Innovation Ecosystems: Entrepreneurs’ Self-Regulatory Processes and Their Implications for New Venture Success | The research focuses on the self-regulating processes of ecosystem entrepreneurs and the potential role of these processes in entrepreneurs’ efforts to balance the requirements set by ecosystem leaders with their own corporate goals. | Qualitative Research Design: the focus is on the hub-based innovation ecosystem, which involves a single company in which a company assumes the leadership of the ecosystem | Promote the understanding of the innovation ecosystem by arousing attention to the potential role of all aspects of the entrepreneur’s self-regulation process on the success of the innovation ecosystem. |
| 3 | Industry Platforms and Ecosystem Innovation | The research brings together the latest literature on “industry platforms” and shows how it relates to managing innovations inside and outside the company, how to deal with technological and market interference, and changes over time. | Qualitative Research Design: literature analysis and case comparison analysis | First, analyze the examples of different industries and divide the platform into internal platforms and external platforms; secondly, summarize the general propositions about platform design, economics, and strategic management; finally, review Intel’s case and other examples to illustrate the technical, strategic and business challenges faced by platform leaders and their competitors. |
| 4 | Innovation through Institutionalization: A Service Ecosystems Perspective | This article explores the role of institutions in innovation from a service-ecosystems perspective, which helps to unify diverging views on innovation and extend the research regarding innovation systems. | Drawing on institutional theories, this approach broadens the scope of innovation beyond the firm. | Market innovation is driven by the combinatorial evolution of value propositions and the emergence and institutionalization of new solutions. |
| 5 | Innovation Ecosystems: A Critical Examination | This paper is a critical review of the “innovation ecosystem” idea. | Literature review, logical argumentation, and examination of national projects | This study describes the gaps in the innovation ecosystem, points out the direction to close the gaps, and provides recommendations for the careful use of the term “ecosystem”. |
| 6 | Ecosystem as Structure: An Actionable Construct for Strategy | Develop a feasible strategic framework for the structure of the ecosystem | This article presents a structuralist approach to conceptualizing the ecosystem construct. | The study presents a clear definition of the ecosystem construct, a grammar for characterizing ecosystem structure, and a characterization of the distinctive aspects of ecosystem strategy. |
| 7 | Unpacking the innovation ecosystem construct: Evolution, gaps, and trends | This research is to clarify the concept of the innovation ecosystem, identify trends and research opportunities | The study conducts a systematic literature review from 1993 to 2016, with a hybrid methodology including bibliometric and content analysis. | “Business ecosystem” relates mainly to value capture, while “innovation ecosystem” relates mainly to value creation. |
| 8 | Managing Ecosystems for Service Innovation: A Dynamic Capability View | Adopting an ecosystem and dynamic capability perspective, this study examines ecosystem-related capabilities for developing service innovation in product-centric firms. | The study uses a mixed-methods approach focusing on the energy utility sector. | (1) Firms with high service-in-novation intensity possess significantly stronger ecosystem-related capabilities than firms with lower service-innovation intensity. (2) Successful service innovators consider not only value-adding partnerships, such as suppliers and customers, to be relevant for service innovation, but also relationships with non-direct value-adding ecosystem stakeholders (e.g., local governments, communities, legislators). |
| 9 | Innovation Ecosystems: A Conceptual Review and a New Definition | The purpose of the study is to review received definitions of innovation ecosystems and related concepts and to propose a synthesized definition of an innovation ecosystem. | Conceptual history studies and literature on methodology for conceptual analysis. | An innovation ecosystem is the evolving set of actors, activities, and artifacts, and the institutions and relations, including complementary and substitute relations, that are important for the innovative performance of an actor or a population of actors. |
References
- Ghazinoory, S.; Sarkissian, A.; Farhanchi, M.; Saghafi, F. Renewing a dysfunctional innovation ecosystem: The case of the Lalejin ceramics and pottery. Technovation 2020, 96–97, 102122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z. Core firm based view on the mechanism of constructing an enterprise innovation ecosystem: A case study of haier group. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ouyang, T.; Wei, W.X.; Cai, J. How do manufacturing enterprises construct e-commerce platforms for sustainable development? a case study of resource orchestration. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakala, H.; O’Shea, G.; Farny, S.; Luoto, S. Re-storying the business, innovation and entrepreneurial ecosystem concepts: The model-narrative review method. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2019, 22, 10–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Ming, X.; Zhang, X. Sustainable and smart product innovation ecosystem: An integrative status review and future perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 274, 12300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granstranda, O.; Holgerssonb, M. Innovation ecosystems: A conceptual review and a new definition. Technovation 2020, 90–91, 102098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheli, P. Doing design thinking: Conceptual review, synthesis and research agenda. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2019, 36, 124–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, L.A.D.V.; Facin, A.L.F.; Salerno, M.S.; Ikenami, R.K. Unpacking the innovation ecosystem construct: Evolution, gaps and trends. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 136, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatraman, A.G.A.N. Contingency perspectives of organizational strategy: A critical review of the empirical research. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1985, 10, 421–434. [Google Scholar]
- Dedehayir, O.; Mäkinen, S.J.; Ortt, J.R. Roles during innovation ecosystem genesis: A literature review. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 136, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lütjen, H.; Schultz, C.; Tietze, F.; Urmetzer, F. Managing ecosystems for service innovation: A dynamic capability view. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 104, 506–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Hu, W.; Qiao, Y.; Zhou, Y. Mapping an innovation ecosystem using network clustering and community identification: A multi-layered framework. Scientometrics 2020, 124, 2057–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzucato, M.; Robinson, D.K.R. Co-creating and directing innovation ecosystems? NASA’s changing approach to public-private partnerships in low-earth orbit. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 136, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Liu, Y.; Luo, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, C. Does a cute artificial intelligence assistant soften the blow? The impact of cuteness on customer tolerance of assistant service failure. Ann. Tour. Res. 2021, 87, 103114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, S.; Li, Q. Welcoming host, cozy house? The impact of service attitude on sensory experience. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2021, 95, 102949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargo, S.L.; Wieland, H.; Akaka, M.A. Innovation through institutionalization: A service ecosystems perspective. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2015, 44, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenal, A.; Armuña, C.; Feijoo, C.; Ramos, S.; Xu, Z.; Moreno, A. Innovation ecosystems theory revisited: The case of artificial intelligence in China. Telecommun. Policy 2020, 44, 101960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawer, A. Bridging differing perspectives on technological platforms: Toward an integrative framework. Res. Policy 2014, 43, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, K.; Liu, Z.; Shi, Y. Reshaping the business ecosystem in China: Case studies and implications. J. Sci. Technol. Policy China 2011, 2, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambisan, S.; Baron, R.A. Entrepreneurship in innovation ecosystems: Entrepreneurs’ self-regulatory processes and their implications for new venture success. Entrep. Theory Pract. 2012, 37, 1071–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawer, A.; Cusumano, M.A. Industry platforms and ecosystem innovation. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2013, 31, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.P. The group dynamics of interorganizational relationships. Adm. Sci. Q. 2016, 61, 621–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Wu, A. The role of extraordinary sensory experiences in shaping destination brand love: An empirical study. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2021, 38, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lv, X. Feeling dark, seeing dark: Mind–body in dark tourism. Ann. Tour. Res. 2021, 86, 103087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, J.; Yu, F.; Zhu, Z. Establishing the enterprises’ innovation ecosystem based on dynamics core competence—the case of China’s high-speed railway. Emerg. Mark. Financ. Trade 2018, 55, 843–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, G.B.; Ayala, N.F.; Frank, A.G. Industry 4.0 innovation ecosystems: An evolutionary perspective on value cocreation. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 228, 107735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Qi, Y.; Tian, C. The construction and evolution of technological innovation ecosystem of Chinese firms: A case study of LCD technology of CEC Panda. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.; Abreu, A.; Dias, A.; Calado, J.M.F.; Anes, V.; Soares, J. A framework for risk assessment in collaborative networks to promote sustainable systems in innovation ecosystems. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Attour, A.; Burger-Helmchen, T.; Nieminen, M. Resource-based co-innovation through platform ecosystem: Experiences of mobile payment innovation in China. J. Strategy Manag. 2015, 8, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, D.; Kumar, V.; Garza-Reyes, J.A.; Godsell, J. Towards a more circular economy: Exploring the awareness, practices, and barriers from a focal firm perspective. Prod. Plan. Control. 2018, 29, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubreziova, I.; Diacikova, A.; Sokil, O.; Apostol, S. Innovation ecosystems for the moldovan small and medium-sized enterprises. Mark. Manag. Innov. 2020, 2, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahle, J.H.; Marcon, É.; Ghezzi, A.; Frank, A.G. Smart products value creation in SMEs innovation ecosystems. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2020, 156, 120024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, E.B.; Uygun, Y. Strengthening advanced manufacturing innovation ecosystems: The case of Massachusetts. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 136, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, A.M.; Wang, W.H.; Wan, S. A survey on blocking technology of entity resolution. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2020, 35, 769–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, C.; Pan, Q. Convergent multiagent formation control with collision avoidance. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2020, 36, 1805–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brem, A.; Radziwon, A. Efficient triple helix collaboration fostering local niche innovation projects—A case from Denmark. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2017, 123, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, M.; Zhao, C.; Pan, Q.; Du, C. Formation control and collision avoidance for multi-UAV systems based on Voronoi partition. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2020, 63, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhao, C.; Xu, Z.; Pan, Q. Object traversing by monocular UAV in outdoor environment. Asian J. Control 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ye, R.; Ding, L.; Lu, C.; Euwema, M. From “transplant with the soil” toward the establishment of the innovation ecosystem: A case study of a leading high-tech company in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 136, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, K.; Kim, W.; Park, K. Complementary multiplatforms in the growing innovation ecosystem: Evidence from 3D printing technology. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 136, 192–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adner, R.; Kapoor, R. Value creation in innovation ecosystems: How the structure of technological interdependence affects firm performance in new technology generations. Strateg. Manag. J. 2010, 31, 306–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritala, P.; Agouridas, V.; Assimakopoulos, D.; Gies, O. Value creation and capture mechanisms in innovation ecosystems: A comparative case study. Int. J. Technol. Manag. 2013, 63, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarikka-Stenroos, L.; Ritala, P. Network management in the era of ecosystems: Systematic review and management framework. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2017, 67, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dattée, B.; Alexy, O.; Autio, E. Maneuvering in poor visibility: How firms play the ecosystem game when uncertainty is high. Acad. Manag. J. 2018, 61, 466–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Fernández, S.; Kubus, R.; Mascareñas Pérez-Iñigo, J. Innovation ecosystems in the EU: Policy evolution and horizon Europe proposal case study (the actors’ perspective). Sustainability 2019, 11, 4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pique, J.M.; Berbegal-Mirabent, J.; Etzkowitz, H. Triple Helix and the evolution of ecosystems of innovation: The case of Silicon Valley. Triple Helix 2018, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, X. How do firms meet the challenge of technological change by redesigning innovation ecosystem? A case study of IBM. Technol. Manag. 2019, 80, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Liu, Z.; Feng, L. Identifying opportunities for sustainable business models in manufacturing: Application of patent analysis and generative topographic mapping. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 27, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.; Matias, J.C.O. Open innovation 4.0 as an enhancer of sustainable innovation ecosystems. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surie, G. Creating the innovation ecosystem for renewable energy via social entrepreneurship: Insights from India. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2017, 121, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltagui, A.; Rosli, A.; Candi, M. Exaptation in a digital innovation ecosystem: The disruptive impacts of 3D printing. Res. Policy 2020, 49, 103833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmié, M.; Wincent, J.; Parida, V.; Caglar, U. The evolution of the financial technology ecosystem: An introduction and agenda for future research on disruptive innovations in ecosystems. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2020, 151, 119779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walrave, B.; Talmar, M.; Podoynitsyna, K.S.; Romme, A.G.L.; Verbong, G.P.J. A multi-level perspective on innovation ecosystems for path-breaking innovation. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 136, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.S.; Garud, R.; Kumaraswamy, A. The disruptor’s dilemma: TiVo and the U.S. television ecosystem. Strat. Manag. J. 2016, 37, 1829–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radziwon, A.; Bogers, M. Open innovation in SMEs: Exploring inter-organizational relationships in an ecosystem. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 146, 573–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesbrough, H.; Kim, S.; Agogino, A. Chez panisse: Building an open innovation ecosystem. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2014, 56, 144–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Liu, B.; Liu, Z. Manufacturer’s business strategy: Interaction of sharing economy and product rollover. Complexity 2020, 2020, 2328602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Q. Pricing decisions and innovation strategies choice in supply chain with competing manufacturers and common supplier. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Feng, J. Manufacturer’s sharing servitization transformation and product pricing strategy. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1503. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L. Changing port governance model: Port spatial structure and trade efficiency. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 95, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klewitz, J.; Hansen, E.G. Sustainability-oriented innovation of SMEs: A systematic review. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucci, T.; Runfola, A.; Guercini, S.; Zanni, L. The role of actors in interactions between “innovation ecosystems”: Drivers and implications. IMP J. 2018, 12, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J. Idea generation and new direction for exploitation technologies of coal-seam gas through recombinative innovation and patent analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Niu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K. Discovering technology opportunity by keyword-based patent analysis: A hybrid approach of morphology analysis and USIT. Sustainability 2020, 12, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Feng, J.; Wang, J. Resource-constrained innovation method for sustainability: Application of morphological analysis and TRIZ inventive principles. Sustainability 2020, 12, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Xiong, L.; Cheng, J.; Xie, X. New results on stabilization analysis for fuzzy semi-Markov jump chaotic systems with state quantized sampled-data controller. Inform. Sci. 2020, 521, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lv, X.; Tang, Z. The impact of mortality salience on quantified self behavior during the COVID-19 pandemic. Pers. Indiv. Differ. 2021, 180, 110972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Hao, J. A dissipative structure theory-based investigation of a construction and demolition waste minimization system in China. J. Environ. Plann. Man. 2021, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkokari, K.; Ketonen-Oksi, S. Innovation ecosystems as structures for value co-creation. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2019, 9, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani, A.; Ruiz-Aliseda, F. Equilibrium innovation ecosystems: The dark side of collaborating with complementors. Manag. Sci. 2016, 62, 534–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.S.; Phillips, F.; Park, S.; Lee, E. Innovation ecosystems: A critical examination. Technovation 2016, 54, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Xu, Y. Research on the coordination mechanism of value cocreation of innovation ecosystems: Evidence from a chinese artificial intelligence enterprise. Complexity 2021, 2021, 7629168. [Google Scholar]
- Nylund, P.A.; Brem, A.; Agarwal, N. Innovation ecosystems for meeting sustainable development goals: The evolving roles of multinational enterprises. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 281, 125329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, Z.; Haijun, W. Structure and evolution mechanism of the enterprise innovation ecosystem in terms of modularity: A longitudinal case study on Haier Group from 2005 to 2019. Sci. Res. Manag. 2021, 42, 33–46. [Google Scholar]

| Journals | Number |
|---|---|
| Technological Forecasting & Social Change | 18 |
| Sustainability | 7 |
| Technovation | 5 |
| Journal of Cleaner Production | 4 |
| Industrial Marketing Management | 2 |
| International Journal of Technology Management | 2 |
| Research Policy | 2 |
| Strategic Management Journal | 2 |
| Serial Number | Title of Top Cited Articles | Year | Number of Citations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Connecting local entrepreneurial ecosystems to global innovation networks: open innovation, double networks and knowledge integration | 2011 | 51 |
| 2 | Entrepreneurship in Innovation Ecosystems: Entrepreneurs’ Self-Regulatory Processes and Their Implications for New Venture Success | 2013 | 355 |
| 3 | Industry Platforms and Ecosystem Innovation | 2014 | 434 |
| 4 | Innovation through institutionalization: A service ecosystems perspective | 2015 | 226 |
| 5 | Innovation ecosystems: A critical examination | 2016 | 147 |
| 6 | Ecosystem as Structure: An Actionable Construct for Strategy | 2017 | 287 |
| 7 | Unpacking the innovation ecosystem construct: Evolution, gaps and trends | 2018 | 68 |
| 8 | Managing ecosystems for service innovation: A dynamic capability view | 2019 | 55 |
| 9 | Innovation ecosystems: A conceptual review and a new definition | 2020 | 22 |
| System | NIEs | RIEs | IIEs | EIEs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classification standard | spatial geography | spatial geography | attribute similarity | attribute similarity |
| Level | meso | medium | medium | micro |
| Perspective | country | region | industry | enterprise |
| Aim | serve national goals | develop regional economy | development area | develop technology and obtain resources |
| Innovation focus | national economy | regional economy | industrial development | business growth |
| Key Actors | Description | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Focal firm | Ecosystem orchestrator and provider of products and services, who plays a leadership role in an innovation ecosystem | Leader |
| Government | Improve policies and regulations and cultivate financing systems | Organizer |
| Suppliers | Provide resources, technology, knowledge and services, etc. | Orchestrator |
| Manufacturers | Product manufacturer | Participant |
| Service providers | Product service provider | Participant |
| Startups | Small innovative company, providing key technology | Participant |
| SMEs | Small and medium-sized enterprises | Participant |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, L.; Lu, J.; Wang, J. A Systematic Review of Enterprise Innovation Ecosystems. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5742. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105742
Feng L, Lu J, Wang J. A Systematic Review of Enterprise Innovation Ecosystems. Sustainability. 2021; 13(10):5742. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105742
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Lijie, Jiarui Lu, and Jinfeng Wang. 2021. "A Systematic Review of Enterprise Innovation Ecosystems" Sustainability 13, no. 10: 5742. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105742
APA StyleFeng, L., Lu, J., & Wang, J. (2021). A Systematic Review of Enterprise Innovation Ecosystems. Sustainability, 13(10), 5742. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105742






