Twitter Social Network in University Teaching. Digital Innovation Strategy for Social Responsibility
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Design
2.1. Objectives
- SO1
- To increase and enrich the interaction between university students, teachers and society, through microblogging services, and more specifically through Twitter.
- SO2
- To promote the degree of involvement of students with the subjects, promoting an active methodology.
- SO3
- To deepen exploration into the contents worked on in the face-to-face classes; activities that propitiate their reflection.
2.2. Context Features and Sample
2.3. Methodology
- “Didactics in Social Education” #innovUPO #didactica
- “Evaluation, quality and educational innovation for social cohesion” #innovUPO #evalcal
- “Educational intervention for the social integration of people at risk of exclusion” #innovUPO #intervencion
- “Management and organization of Social Education centres and institutions” #innovUPO #diror
- “New Technologies and Information Management” #innovUPO #TICL1
3. Results Regarding the Use of Twitter
3.1. Subject 1: Didactics in Social Education (DSE)
3.2. Subject 2: “Evaluation, Quality and Educational Innovation for Social Cohesion” (EVAL)
3.3. Subject 3: “Educational Intervention for the Social Integration of People at Risk of Exclusion” (INT)
3.4. Subject 4: “Management and Organization of Social Education Centres and Institutions” (DIOR)
3.5. Subject 5: “New Technologies and Information Management” (NNTT)
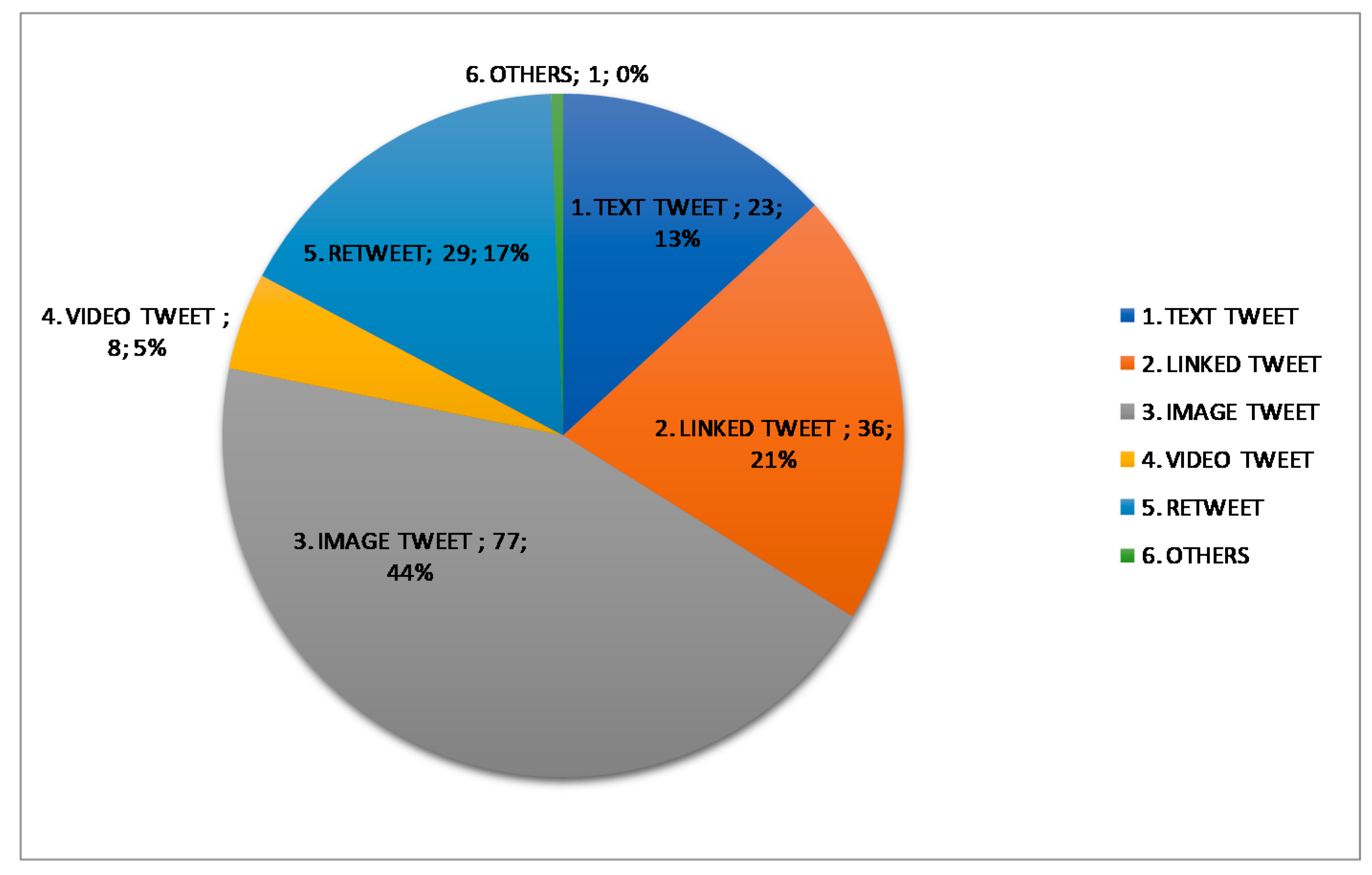
3.6. Overall Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aguiar, B.O.; Velázquez, R.M.; Aguiar, J.L. Innovación docente y empleo de las TIC en la Educación Superior. Rev. Espac. 2019, 40, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- González-Martínez, J.; Esteve-Mon, F.M.; Rada, V.L.; Vidal, C.E.; Cervera, M.G. INCOTIC 2.Una nueva herramienta para la autoevaluación de la competencia digital del alumnado universitario. Profr. Rev. De Currículum Y Form. Del Profr. 2018, 22, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombillo-Rivero, I.; Nambalo-Mulay-Dua, J.; Torres-Alonso, A.; Pérez-Hernández, B. La innovación educativa en el uso de los medios de enseñanza: Una propuesta de solución que incluye las TIC/Educational Innovation in the Use of Teaching Materials–A Proposed Solution Including Information and Communication Technologies. Rev. Cuba. De Educ. Super. 2019, 3, 195–212. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, M.S.P.; Sepúlveda, G.C.T.; Ramírez-Montoya, M.-S. Educational innovation and digital competencies: The case of OER in a private Venezuelan university. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2016, 13, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Neira, E.; Salinas-Ibáñez, J.; de Benito-Crosseti, B. La observación reflexiva y su papel en la incorporación de Tecnologías Emergentes en el aula. Areté: Rev. Digit. Del Dr. En Educ. De La Univ. Cent. De Venez. 2018, 4, 79–98. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; McGrath, I. Innovation in higher education in China: Are teachers ready to integrate ICT in English language teaching? Technol. Pedagog. Educ. 2011, 20, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zempoalteca, B.; González, J.; Barragán, J.; Guzmán, T. Factores que influyen en la incorporación de las Tecnologías de la Información y la Comunicación en universidades públicas: Una aproximación desde la autopercepción docente. Rev. De La Educ. Super. 2018, 47, 51–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounenou, K.; Roussos, P.; Yotsidi, V.; Tountopoulou, M. Trainee Teachers’ Intention to Incorporating ICT Use into Teaching Practice in Relation to their Psychological Characteristics: The Case of Group-based Intervention. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 190, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Flores, J.; Santero, J.R.; Torres-Gordillo, J.-J. Factors that explain the use of ICT in secondary-education classrooms: The role of teacher characteristics and school infrastructure. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 68, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAB Spain. Estudio Anual Redes Sociales. Available online: https://iabspain.es/wp-content/uploads/estudio-redes-sociales-2018_vreducida.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2019).
- López-Zapico, M.A.; Tascón-Fernández, J. El uso de Twitter como herramienta para la enseñanza universitaria en el ámbito de las ciencias sociales. Un estudio de caso desde la historia económica. Rev. Teoría De La Educ. Educ. Y Cult. En La Soc. De La Inf. 2013, 14, 316. Available online: http://campus.usal.es/~revistas_trabajo/index.php/revistatesi/article/view/10233/10667 (accessed on 9 May 2019).
- Gómez-Aguilar, M.; Roses-Campos, S.; Batlle, P.F.; Roses, S.; Gómez, M. The Academic Use of Social Networks among University Students. Comunicar Media Educ. Res. J. 2012, 19, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, E.G.; Taboada, M.D.L.M.; Rodríguez-Carmona, L.M. Análisis del valor comunicativo de las redes sociales en el ámbito universitario: Estudio de los usos de Twitter en el aula. Estud. Sobre El Mensaje Periodístico 2012, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apple, M.W. Education and Godly Technology: Gender, Culture, and the Work of Home Schooling. Soc. Anal. 2006, 50, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Agut, M.P.; Aznar-Minguet, P.; Ull-Solis, A.; Piñero-Guilamany, A. Promoción de la sostenibilidad en los curricula de la enseñanza superior desde el punto de vista del profesorado: Un modelo de formación por competencias. Educ. Siglo XXI 2007, 25, 187–208. [Google Scholar]
- Agirreazkuenaga, L. Embedding Sustainable Development Goals in Education. Teachers’ Perspective about Education for Sustainability in the Basque Autonomous Community. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decuypere, M.; Hoet, H.; Vandenabeele, J. Learning to Navigate (in) the Anthropocene. Sustainability 2019, 11, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemens, G. Connectivism: A Learning Theory for the Digital Age. Int. J. Instr. Technol. Distance Learn. 2005, 2, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Aznavwrian-Salas, L. Conectivismo: Una Teoría Del Aprendizaje En La Era Digital; Editorial Académica Española (EAE): Alemania, Germany, 2017; Available online: https://www.comenius.cl/recursos/virtual/minsal_v2/Modulo_1/Recursos/Lectura/conectivismo_Siemens.pdf (accessed on 18 April 2020).
- Schwarz, B.B.; Asterhan, C.S. E-Moderation of Synchronous Discussions in Educational Settings: A Nascent Practice. J. Learn. Sci. 2011, 20, 395–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabero-Almenara, J. Reflexiones educativas sobre las tecnologías de la información y la comunicación (TIC). Tecnol. Cienc. Y Educ. 2015, 1, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- León, R.C.; Gámez, A.N.; Barroso-Osuna, J. Las Competencias Del Profesorado Universitario Desde El Modelo Tpack (Conocimiento Tecnológico Y Pedagógico Del Contenido). Pixel-Bit Rev. De Medios Y Educ. 2016, 49, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Haro-Ollé, J.J. Redes Sociales Para la Educación; Ediciones Anaya Multimedia: Madrid, Spain, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- López-García, J.C. Uso de Twitter en educación. Available online: http://www.eduteka.org/TwitterEducacion.php (accessed on 16 June 2019).
- Cabero-Almenara, J.; Díaz, V.M. Educational Possibilities of Social Networks and Group Work. University Students’ Perceptions. Comunicar 2014, 21, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abella-García, V.; Delgado-Benito, V. Aprender a usar Twitter y usar Twitter para aprender. Profesorado. Rev. De Curric. Y Form. Del Profr. 2015, 19, 364–378. [Google Scholar]
- Prieto, R.R. Una experiencia de interacción crítica y reflexiva a propósito de una campaña sobre Twitter en la asignatura de Teoría del Derecho. IJERI: Int. J. Educ. Res. Innov. 2017, 7, 186–201. [Google Scholar]
- Bonwell, C.; Eison, J. Active learning: Creating excitement in the classroom. In ASHE-ERIC Higher Education Report, no. 1; The George Washington University: Washington, DC, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez, L. Conectivismo como teoría de aprendizaje: Conceptos, ideas y posibles limitaciones. Rev. Educ. Y Tecnol. 2012, 1, 111–122. [Google Scholar]
- Weisburd, D. Justifying the use of non-experimental methods and disqualifying the use of randomized controlled trials: Challenging folklore in evaluation research in crime and justice. J. Exp. Criminol. 2010, 6, 209–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo, G.; Aigneren, M.; Ruiz, J. Experimental y no-experimental. La Sociol. En sus Escen. 2008, 18, 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, J.H. Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1963, 58, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domizi, D.P. Microblogging To Foster Connections And Community in a Weekly Graduate Seminar Course. TechTrends 2013, 57, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlap, J.C.; Lowenthal, P.R. Tweeting the night away: Using Twitter to enhance social presence. J. Inf. Syst. Educ. 2009, 20, 129. [Google Scholar]
- Ebner, M. Interactive Lecturing by Integrating Mobile Devices and Microblogging in Higher Education. J. Comput. Inf. Technol. 2009, 17, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-C.; Ching, Y.-H. Mobile microblogging: Using Twitter and mobile devices in an online course to promote learning in authentic contexts. Int. Rev. Res. Open Distrib. Learn. 2012, 13, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Shah, S.J.; Cromptom, H. Using Twitter to Support Reflective Learning in an Asynchronous Online Course. Australas. J. Educ. Technol. 2019, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perifanou, M.A. Language Micro-gaming: Fun and Informal Microblogging Activities for Language Learning. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2009, 49, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Giridharan, B. Use of social media applications in classroom: Analysis from education perspective. Iop Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 495, 012108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacković, N.; Kerry, R.; Lowe, R.; Lowe, T. Being knowledge, power and profession subordinates: Students’ perceptions of Twitter for learning. Internet High. Educ. 2017, 33, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
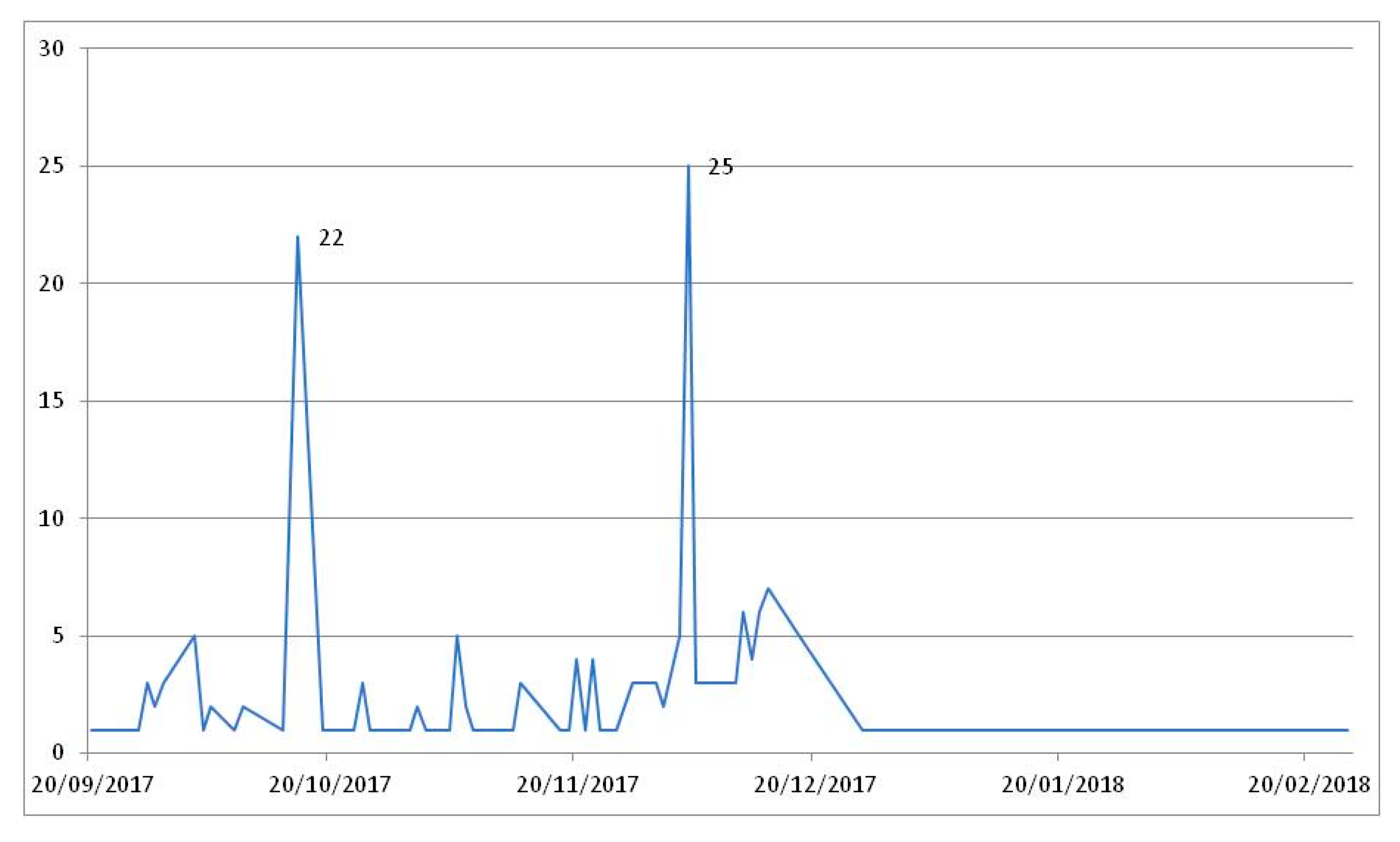
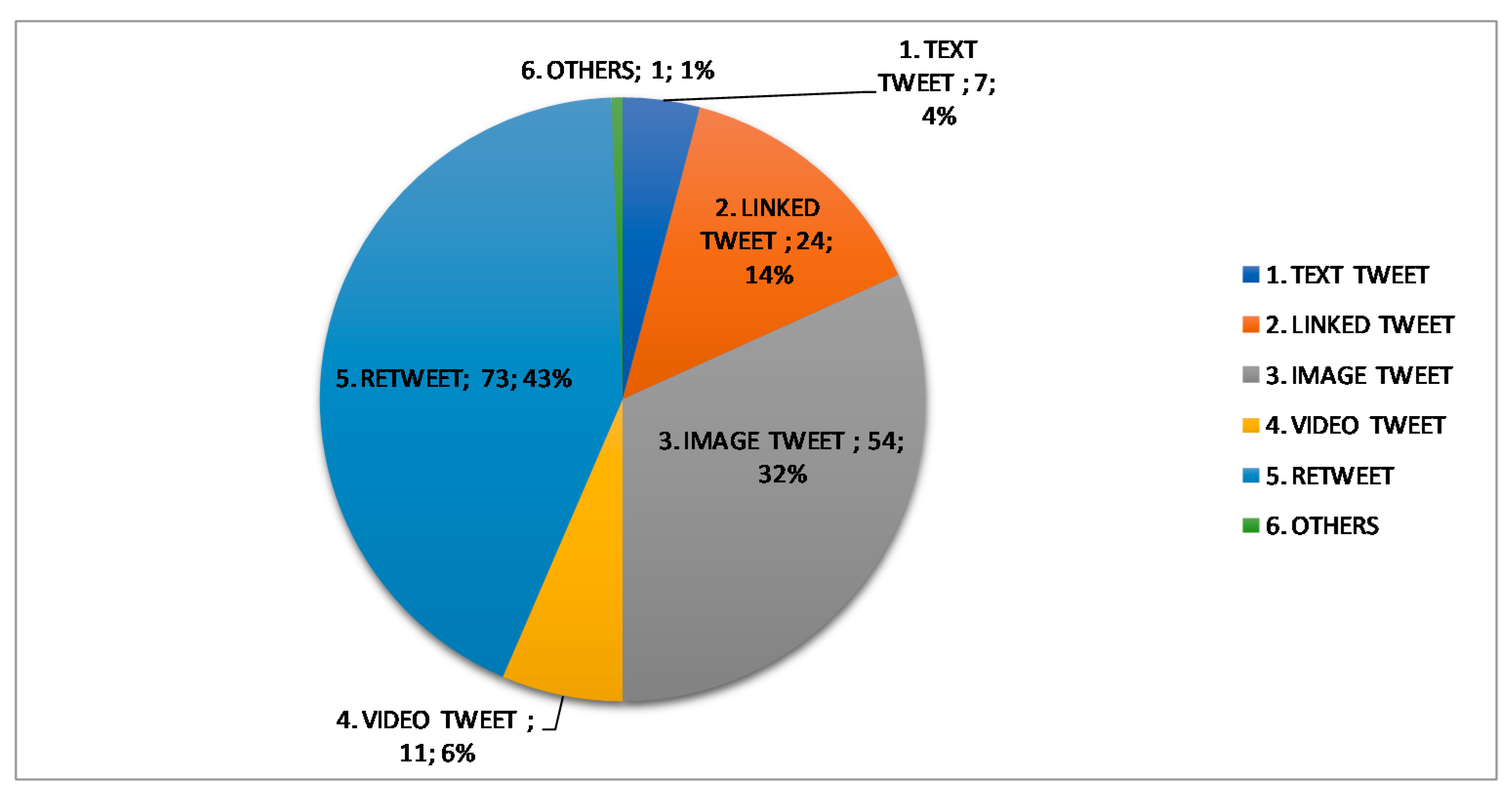
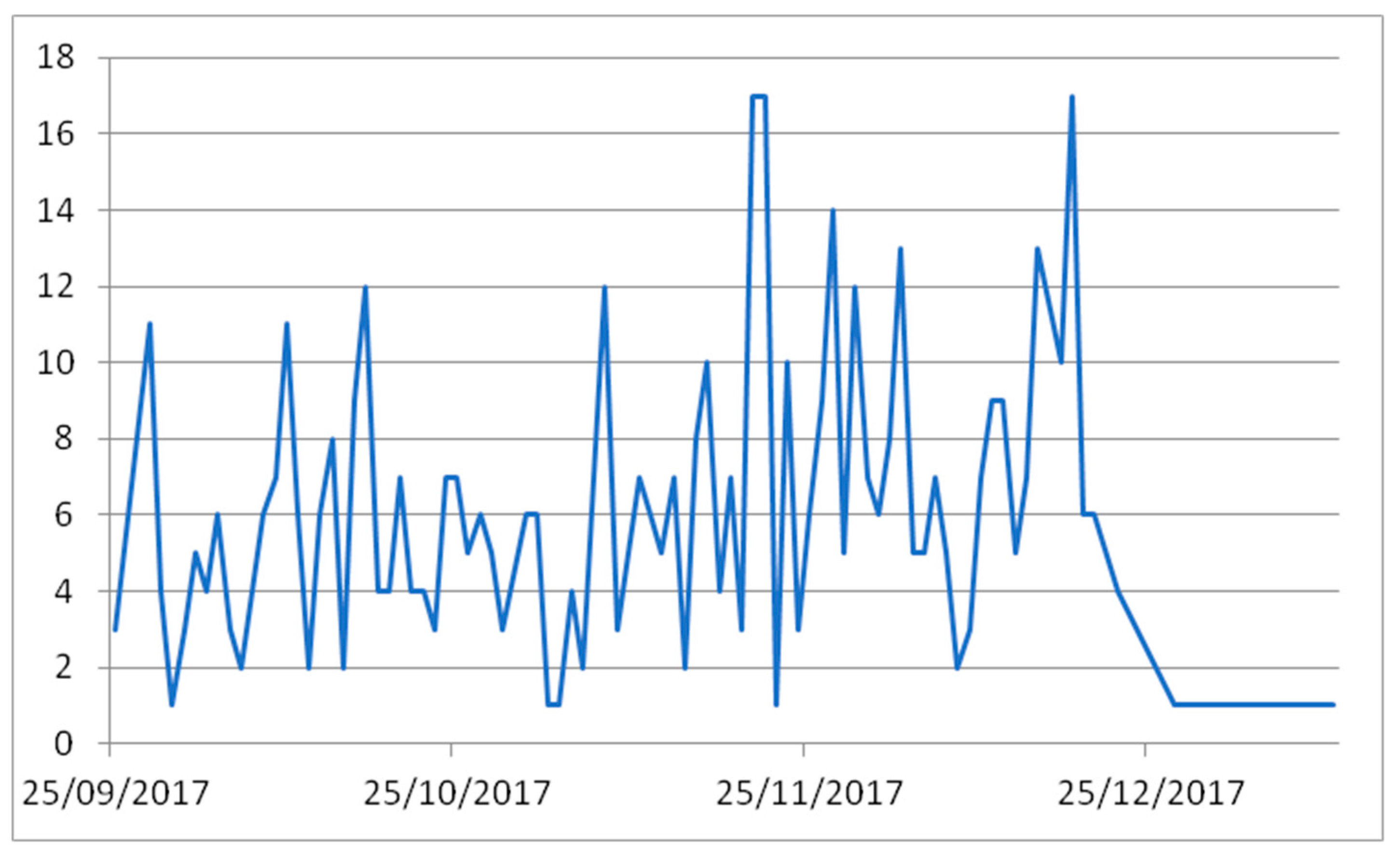
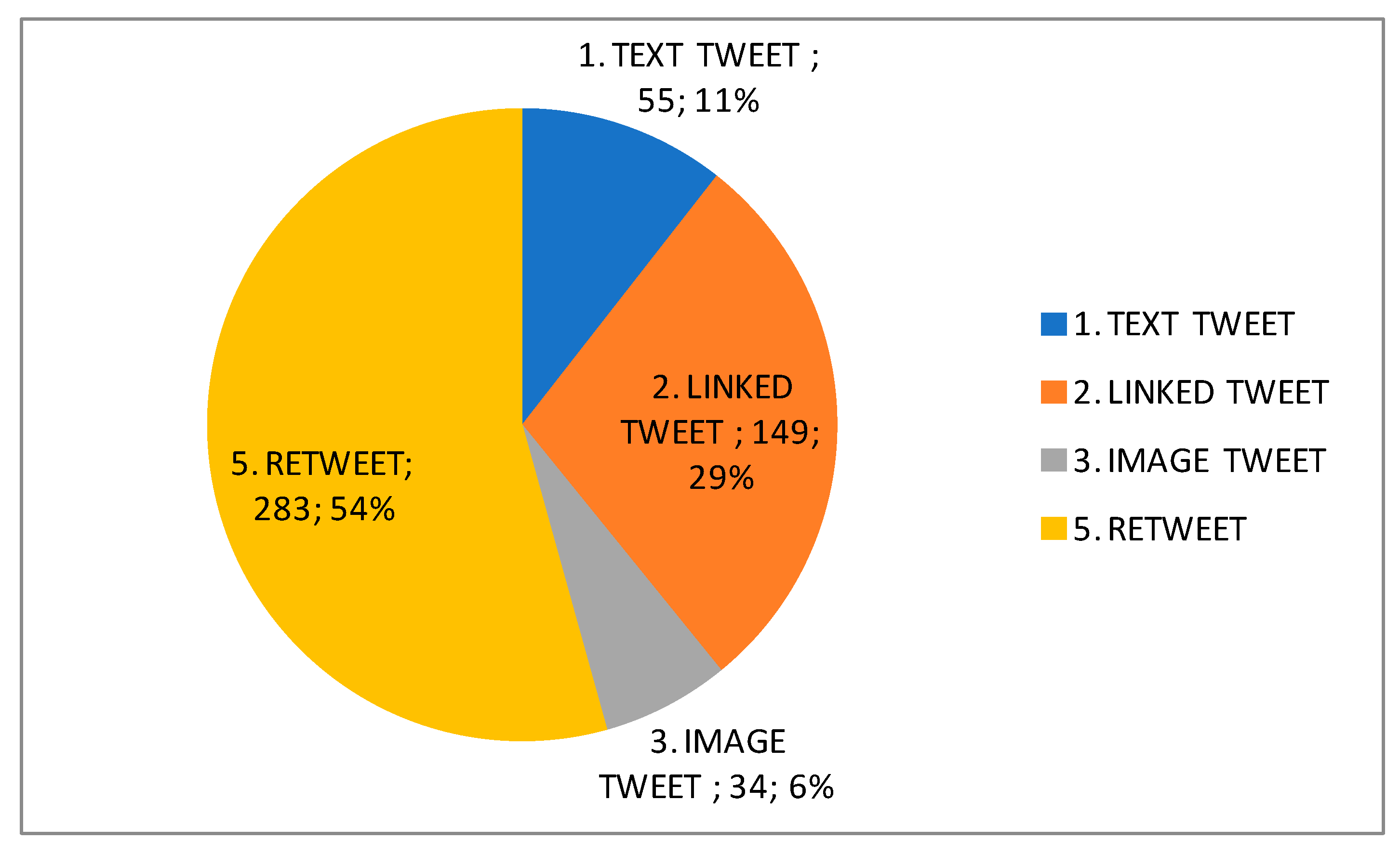

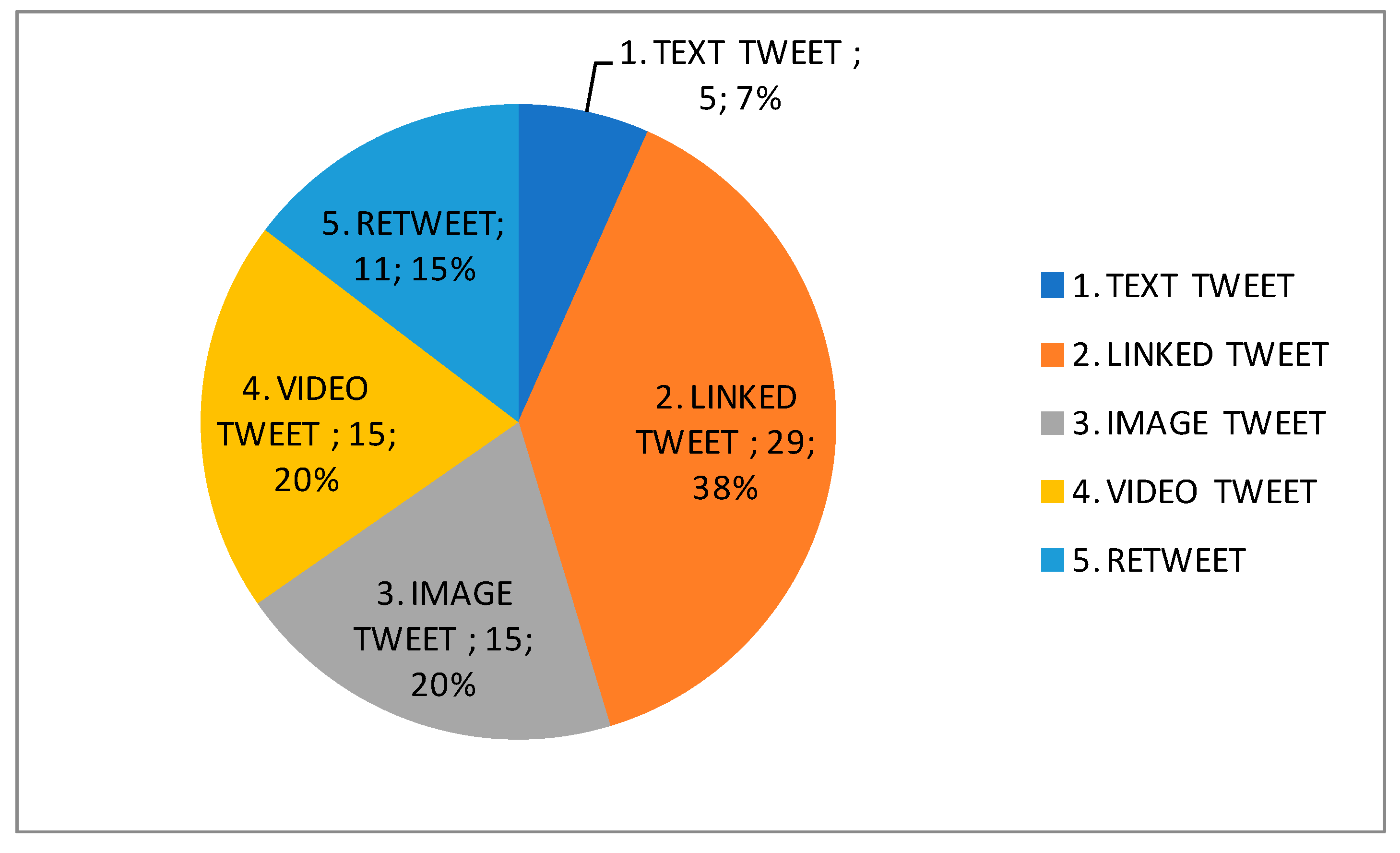
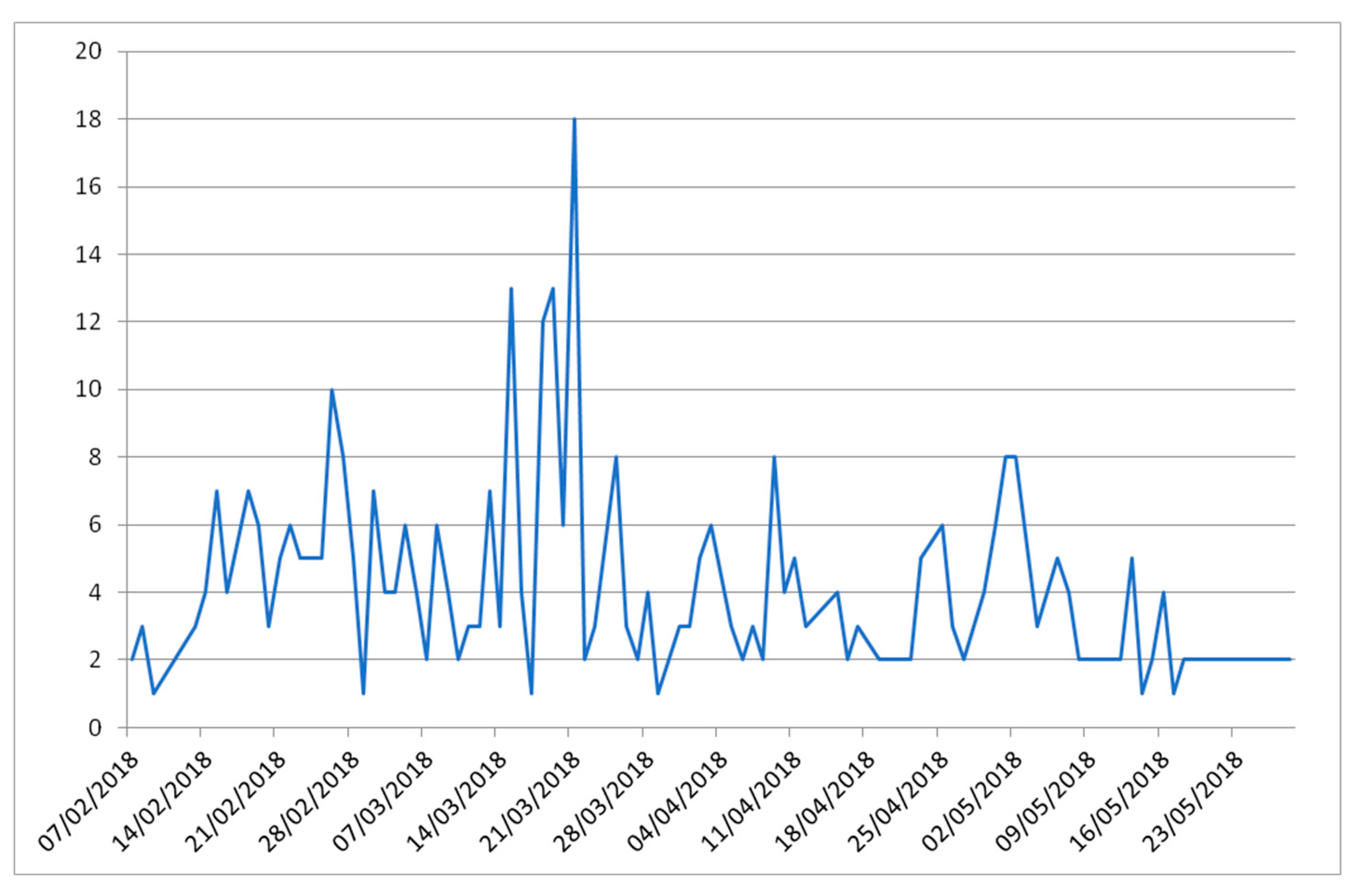
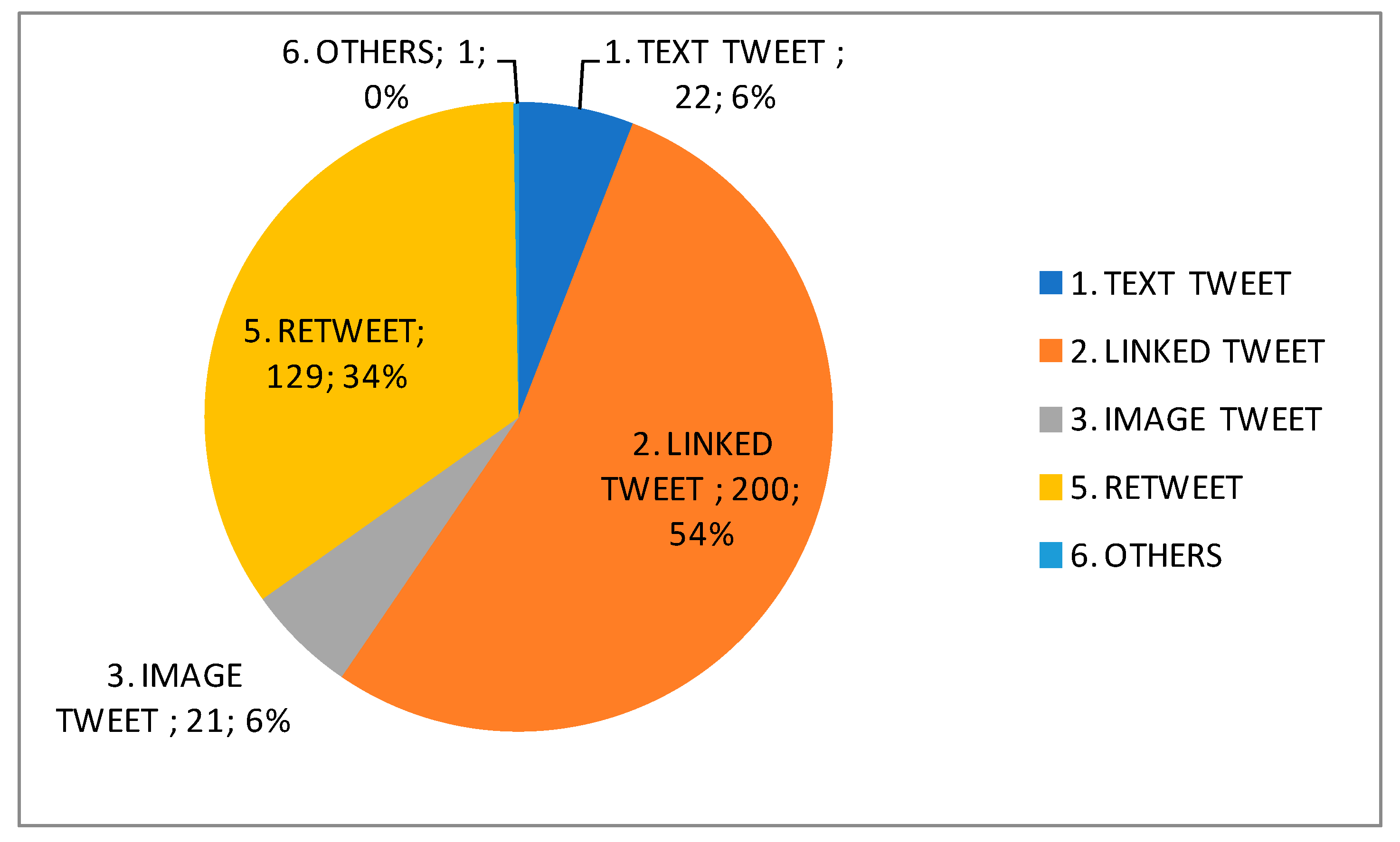
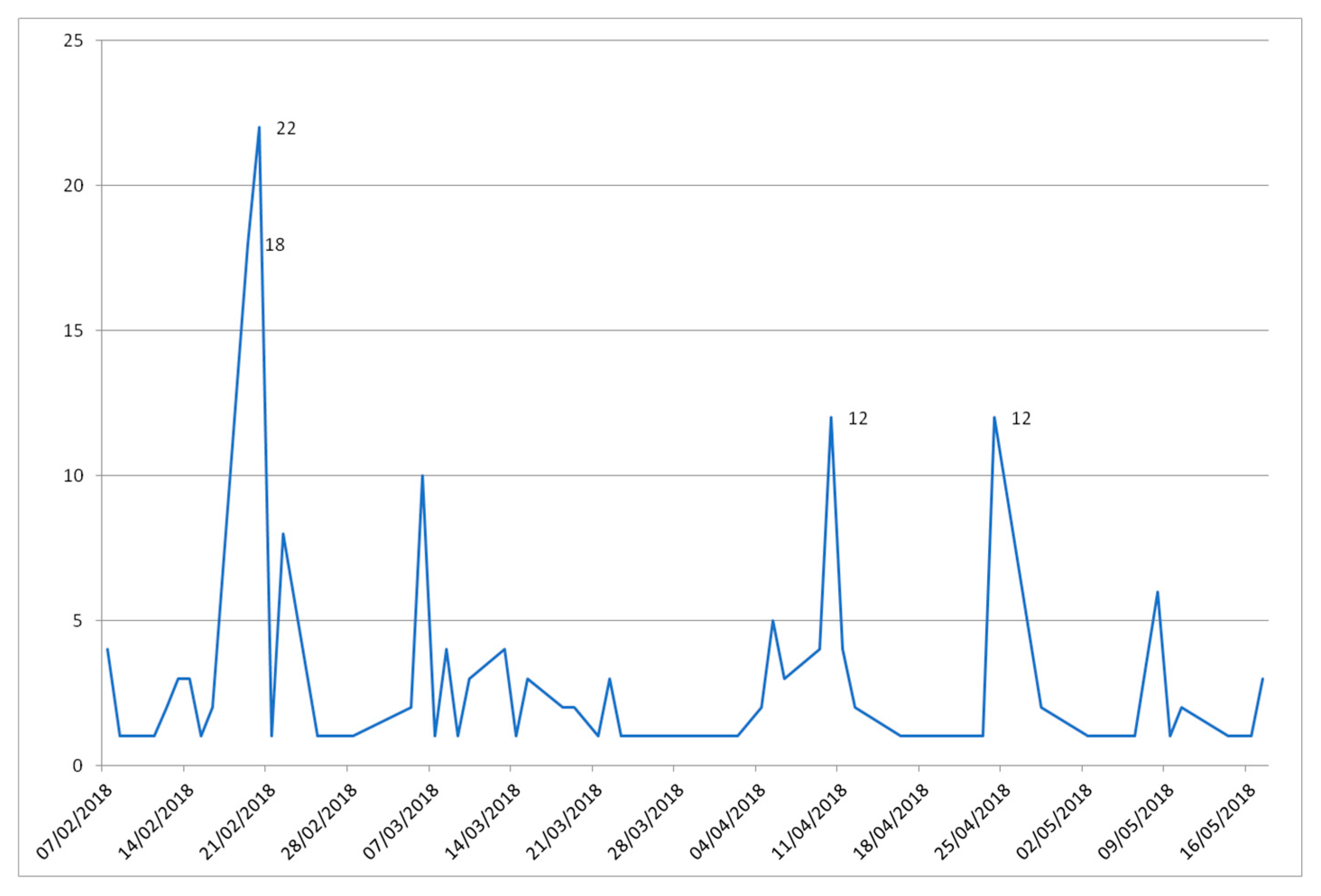
| Subjects | Course/Degree | Enrolled Students | Participants | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Twitter Users | Not Twitter Users | ||||||
| M | W | M | W | M | W | ||
| 1. Didactics in Social Education (DSE) | First of double degree in SE & SW | 5 | 55 | 3 | 39 | 0 | 9 |
| 2. Evaluation, quality and educational innovation for social cohesion (EVAL) | Fourth of degree in SE | 7 | 43 | 1 | 13 | 0 | 1 |
| 3. Evaluation, quality and educational innovation for social cohesion (EVAL) | Fifth of double degree in SE & SW | 3 | 48 | 1 | 15 | 0 | 2 |
| 4. Educational intervention for the social integration of people at risk of exclusion (INT) | Second of degree in SE | 10 | 49 | 7 | 27 | 0 | 3 |
| 5. Management and organization of Social Education centres and institutions (DIOR) | Fourth of degree in SE | 6 | 42 | 1 | 12 | 0 | 1 |
| 6. New Technologies and Information Management (NNTT) | First of degree in SW (L1) | 8 | 54 | 4 | 36 | 1 | 5 |
| TOTAL | 39 | 291 | 17 | 142 | 1 | 21 | |
| 330 | 159 | 22 | |||||
| Subjects | Total Participants | % |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Didactics in Social Education (DSE) | 35 | 58.3% |
| 2. Evaluation, quality and educational innovation for social cohesion (EVAL) | 23 | 22.8% |
| 3. Educational intervention for the social integration of people at risk of exclusion (INT) | 9 | 15.25% |
| 4. Management and organization of Social Education centres and institutions (DIOR) | 11 | 22.9% |
| 5. New Technologies and Information Management (NNTT) | 30 | 48.38% |
| Total | 108 | 32.7% |
| Subjects | Hashtags | Links to All Posts |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Didactics in Social Education (DSE) | #innovUPO #didáctica | https://twitter.com/search?f=tweets&vertical=default&q=%23innovUPO%20%23did%C3%A1ctica&src=savs |
| 2. Evaluation, quality and educational innovation for social cohesion (EVAL) | #innovUPO #evalcal | https://twitter.com/search?f=tweets&vertical=default&q=%23innovUPO%20%20%23evalcal&src=savs |
| 3. Educational intervention for the social integration of people at risk of exclusion (INT) | #innovUPO #intervencion | https://twitter.com/search?f=tweets&vertical=default&q=%23innovUPO%20%20%23intervencion&src=savs |
| 4. Management and organization of Social Education centres and institutions (DIOR) | #innovUPO #diror | https://twitter.com/search?f=tweets&vertical=default&q=%23innovUPO%20%23diror&src=savs |
| 5. New Technologies and Information Management (NNTT) | #innovUPO #TICL1 | https://twitter.com/search?f=tweets&vertical=default&q=%23innovUPO%20%23TICL1&src=savs |
| Subjects | Total Posts | Reactions to the Tweets | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Answers | Retweets | Likes | ||
| 1. Didactics in Social Education. | 170 | 9 | 318 | 407 |
| 2. Evaluation, quality and educational innovation for social cohesion. | 521 | 30 | 209 | 900 |
| 3. Educational intervention for the social integration of people at risk of exclusion. | 75 | 1 | 55 | 171 |
| 4. Management and organization of Social Education centres and institutions. | 373 | 8 | 162 | 621 |
| 5. New Technologies and Information Management | 174 | 14 | 256 | 419 |
| TOTAL | 1313 | 62 | 1000 | 2518 |
| POSTS | ANSWERS | RETWEETS | LIKES | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | 262.6 | 12.4 | 200 | 503.6 |
| Variance | 32,644.3 | 118.3 | 9902.5 | 74,506.8 |
| SD | 180.7 | 10.9 | 99.5 | 273.0 |
| CV | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Median | 174 | 9 | 209 | 419 |
| Quartile 1 | 170 | 8 | 162 | 407 |
| Quartile 2 | 174 | 9 | 209 | 419 |
| Quartile 3 | 373 | 14 | 256 | 621 |
| Xmin | 75 | 1 | 55 | 171 |
| Xmax | 521 | 30 | 318 | 900 |
| Range | 446 | 29 | 263 | 729 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torres-Barzabal, L.M.; Martínez-Gimeno, A.; Hermosilla-Rodríguez, J.M. Twitter Social Network in University Teaching. Digital Innovation Strategy for Social Responsibility. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3350. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083350
Torres-Barzabal LM, Martínez-Gimeno A, Hermosilla-Rodríguez JM. Twitter Social Network in University Teaching. Digital Innovation Strategy for Social Responsibility. Sustainability. 2020; 12(8):3350. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083350
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorres-Barzabal, Luisa María, Almudena Martínez-Gimeno, and José Manuel Hermosilla-Rodríguez. 2020. "Twitter Social Network in University Teaching. Digital Innovation Strategy for Social Responsibility" Sustainability 12, no. 8: 3350. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083350
APA StyleTorres-Barzabal, L. M., Martínez-Gimeno, A., & Hermosilla-Rodríguez, J. M. (2020). Twitter Social Network in University Teaching. Digital Innovation Strategy for Social Responsibility. Sustainability, 12(8), 3350. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083350





