CSR Remanufacturing Supply Chains under WTP Differentiation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Remanufacturing Supply Chain with Recycling Approaches
2.2. Corporate Social Responsibility in Supply Chains
2.3. WTP Differentiation
3. Model Description and Analysis
3.1. Notation and Assumption
| Unit retail price of the product | |
| Unit wholesale price of the product | |
| Unit cost of a product | |
| Recovery scale parameter | |
| Consumers’ willingness to pay for both new and remanufactured products, | |
| Capacity of the market | |
| Unit of the manufacturer paid to customers for a returned unit | |
| The fraction of CSR, | |
| The consumer surplus | |
| Return rate of used products from the consumers | |
| The profit function of in model | |
| Total profit function of in model | |
| , , , , denotes new and remanufacturing product; , , , denotes retailer, manufacturer, the supply; , , denotes centralized and decentralized model | |
3.2.1. Decentralized Remanufacturing Supply Chain with CSR
3.2.2. The Centralized Case
3.2.3. Comparison and Analysis
4. Numerical Analysis
4.1. Numerical Simulation and Discussion
4.2. Revenue-Sharing Contract
5. Conclusions and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nunen, J.; Euiwijk, R.A. E-enabled closed-loop supply chains. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2004, 46, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, A.; Sundaresan, S.; Zhang, B. Retail-Online competition under value uncertainty. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2014, 23, 1129–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.-M.; Li, Y.; Xu, L. Channel leadership, performance and coordination in closed loop supply chains. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2013, 146, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, W.; Kevin, C.D.; Hess, J.D. Direct marketing indirect profits: A strategic analysis of dual channel supply chain design. Manag. Sci. 2003, 49, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debo, L.G.; Tokay, L.B.; Van Wassenhove, L.N. Market segmentation and product technology selection for remanufacturable products. Manag. Sci. 2005, 51, 1193–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Huang, D.; Tian, Y. Optimization for production/remanufacturing system with return rate dependent on price and quality under uncertainty. In International Workshop on Computer Science for Environmental Engineering and EcoInformatics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 158, pp. 166–172. [Google Scholar]
- Őstlin, J.; Sundin, E.; Björkman, M. Importance of closed-loop supply chain relationships for product remanufacturing. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2008, 115, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savaskan, R.; Canan, B.S.; Van Wassenhove, L.N. Closed-loop supply chain models with product remanufacturing. Manag. Sci. 2004, 50, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Webster, S. Competition in remanufacturing and the effects of government subsides. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2008, 111, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swan, P.L. Optimal durability, second-hand markets, and planned obsolescence. J. Polit. Econ. 1972, 80, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.X.; Webster, S.; Suresh, N.C. Would a Risk-Averse newsvendor order less at a higher selling price. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2009, 196, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zikopoulos, C.; Tagaras, G. Reverse supply chains: Effects of collection network and returns classification on profitability. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 264, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrick, A. Gap offers unusual look at factory conditions. Wall Str. J. 2004, 243, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Auger, P.; Burke, P.; Devinney, T.M.; Louviere, J.J. What will consumers pay for social products features? J. Bus. Ethics 2003, 42, 281–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Survey of Corporate Social Responsibility Reporting; KPMG: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008.
- Amaeshi, K.M.; Osuji, O.K.; Nnodim, P. Corporate social responsibility in supply chains of global brands: A boundaryless responsibility? Clarifications, exceptions and implications. J. Bus. Ethics 2008, 81, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, C.R.; Jennings, M.M. Social responsibility and supply chain relationships. Transp. Res. Part E 2002, 38, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.; Seyyed, M.; Nourim, H.M.; Choi Tsan, M.; Ebrahimi, S. Supply chain systems optimization with dual channel and demand disruptions: Sustainability, CSR investment and pricing coordination. Inf. Sci. 2019, 503, 606–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, C.F. Improving corporate social responsibility in a supply chain through a new revenue sharing contract. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2014, 151, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modak, N.M.; Kazemi, N.; Cárdenas-Barrón, L.E. Investigating structure of a two-echelon closed-loop supply chain using social work donation as a Corporate Social Responsibility practice. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 207, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, D.; Li, K.W. A game-theoretic analysis of social responsibility conduct in two-echelon supply chains. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2012, 138, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; Panda Nikunja, M.; Cárdenas-Barrón, L.E. Coordinating a socially responsible closed-loop supply chain with product recycling. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 188, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, T.; Xu, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, S.; Lai, K.K. Remanufacturing Decisions with WTP Discrepancy and Uncertain Quality of Product Returns. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Nie, J.; Qu, T. Choosing reverse channels under collection responsibility sharing in a closed-loop supply chain with re-manfacturing. J. Intell. Manuf. 2015, 26, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guide, V.; Daniel, R., Jr.; Li, J.Y. The potential for cannibalization of new products sales by remanufactured products. Decis. Sci. 2010, 41, 547–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaker, D.A.; Keller, K.L. Consumer evaluations of brand extensions. J. Mark. 1990, 54, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorasayan, J.; Ryan, S.M. Optimal price and quantity of refurbished products. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2006, 15, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, G.; Swaminathan, J.M. Managing new and re-manfactured products. Manag. Sci. 2006, 52, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, G.; Swaminathan, J.M. Managing new and differentiated remanufactured products. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 203, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachon, G.P.; Lariviere, M.A. Supply chain coordination with revenue sharing contract: Strengths and limitations. Manag. Sci. 2005, 51, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Shah, J. Supply chain analysis under green sensitive consumer demand and cost sharing contract. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 164, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, K.; Popiuc, M.N. Reverse supply chain coordination by revenue sharing contract: A case for the personal computers industry. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2014, 233, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.A. Supply chain coordination under a revenue-sharing contract with corporate social responsibility and partial demand information. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2018, 205, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, N.; Jia, T.; Chen, H. Reverse revenue sharing contract versus two-part tariff contract under a closed-loop supply chain system. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 2016, 5464570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, G.W.; Rutstrolm, E.E. Experimental evidence on the existence of hypothetical bias in value elicitation methods. In Handbook of Experimental Economics Results; Plott, C., Smith, V.L., Eds.; Elsevier Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 752–770. [Google Scholar]
- Guide, V.; Daniel, R., Jr.; Teunter, R.H.; Van Wassenhove, L.N. Matching demand and supply to maximize profits from remanufacturing. Manag. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2003, 5, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Song, M.; Lee, L.H.; Ching, W.K. Analysis for strategy of closed-loop supply chain with dual recycling channel. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2013, 144, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, P.; Huang, M.; Guo, L.; Shi, T. Dual recycling channel decision in retailer oriented closed-loop supply chain for construction machinery remanufacturing. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadis, P. An integrated System Dynamics model for strategic capacity planning in closed-loop recycling networks: A dynamic analysis for the paper industry. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2013, 32, 116–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modak, N.M.; Modak, N.; Panda, S.; Sana, S.S. Analyzing structure of two-echelon closed-loop supply chain for pricing, quality and recycling management. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 512–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Li, C.; Zeng, Q.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J. A green closed-loop supply chain coordination mechanism based on third-party recycling. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, C.; Cheng, X.; Chen, W. Decision and coordination of closed-loop supply chain considering recycling channel competition. Ind. Eng. Manag. 2018, 23, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, P.R.; Poist, R.F. Socially responsible logistics: An exploratory study. Transp. J. 2002, 41, 23–35. [Google Scholar]
- Maloni, M.J.; Brown, M.E. Corporate social responsibility in the supply chain: An application in the food industry. J. Bus. Ethics 2006, 68, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S. Coordination of a socially responsible supply chain using revenue sharing contract. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2014, 67, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stekelorum, R.; Laguir, I.; Elbaz, J. Transmission of CSR requirements in supply chains: Investigating the multiple mediating effects of CSR activities in SMEs. Appl. Econ. 2019, 51, 4642–4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stekelorum, R. The roles of SMEs in implementing CSR in supply chains: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2019, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; Modak, N.M.; Pradhan, D. Corporate social responsibility, channel coordination and profit division in a two-echelon supply chain. Int. J. Manag. Sci. Eng. Manag. 2016, 11, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devavrat, P. Exploring the relationship between the markets for new and used durable goods: The case of automobiles. Mark. Sci. 1992, 11, 54–167. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Yang, X. Study of profit coordination of remanufacturing closed-loop supply chain based on WTP differentiation. Appl. Res. Comput. 2014, 31, 388–391. [Google Scholar]
- Long, X.; Ge, J.; Shu, T.; Liu, Y. Analysis for recycling and remanufacturing strategies in a supply chain considering consumers’ heterogeneous WTP. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 148, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.P.; Liang, L.; Liu, L.; Ieromonachou, P. Coordination contracts of dual-channel with cooperation advertising in closed-loop supply chains. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 183, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, T.; Liu, Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, S.; Lai, K.K. Pricing decisions of CSR closed-loop supply chain with carbon emission constraints. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
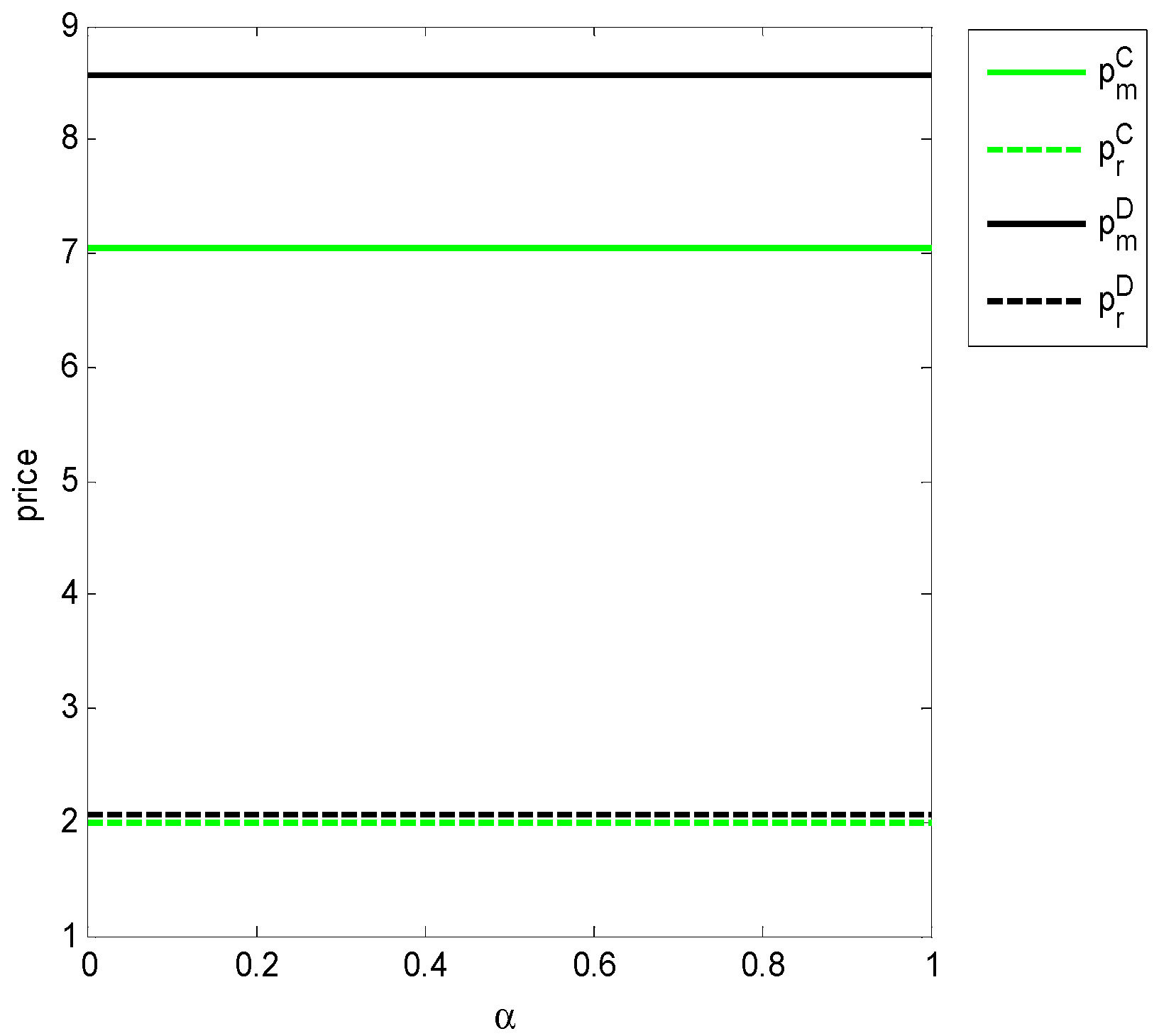
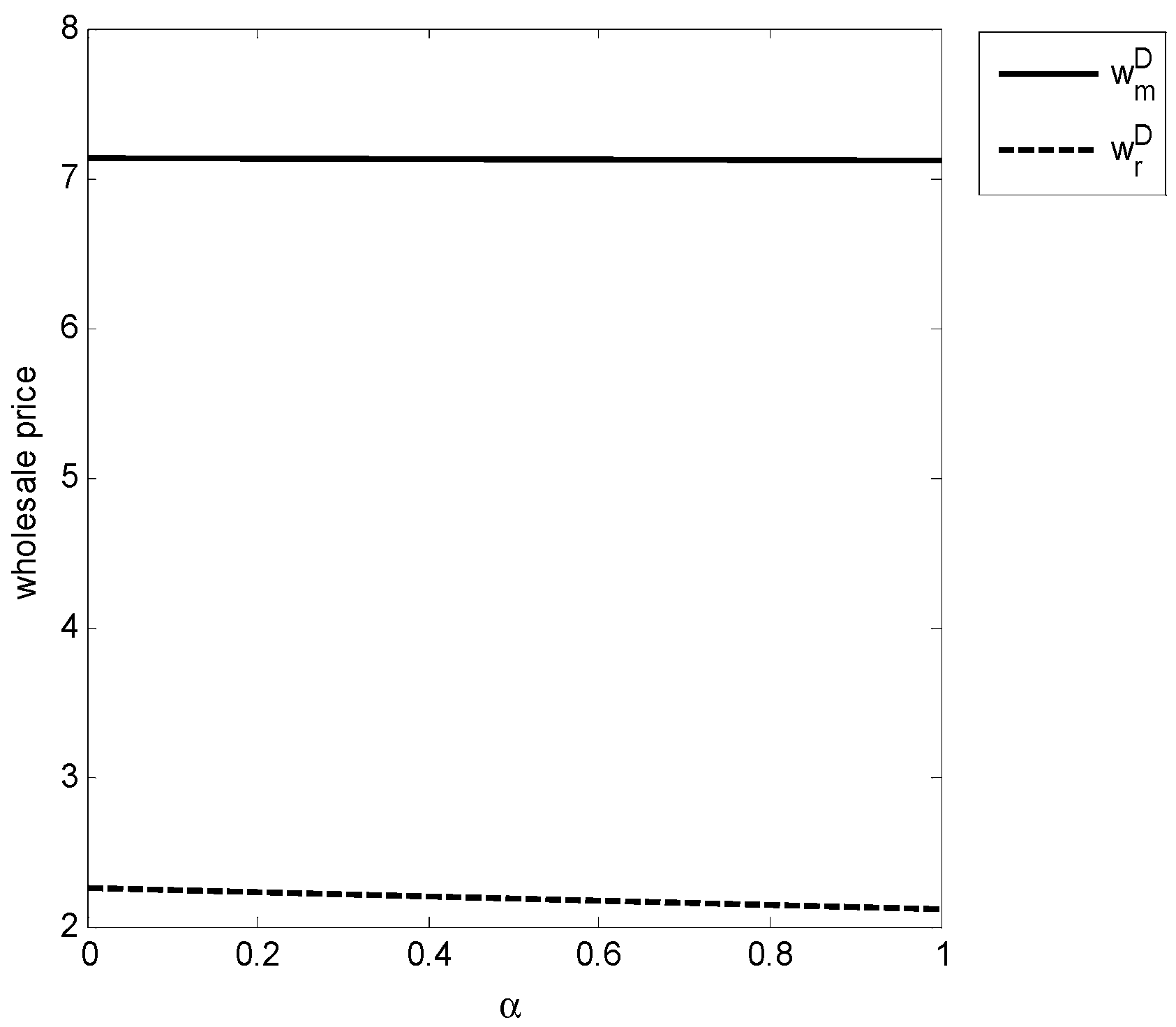
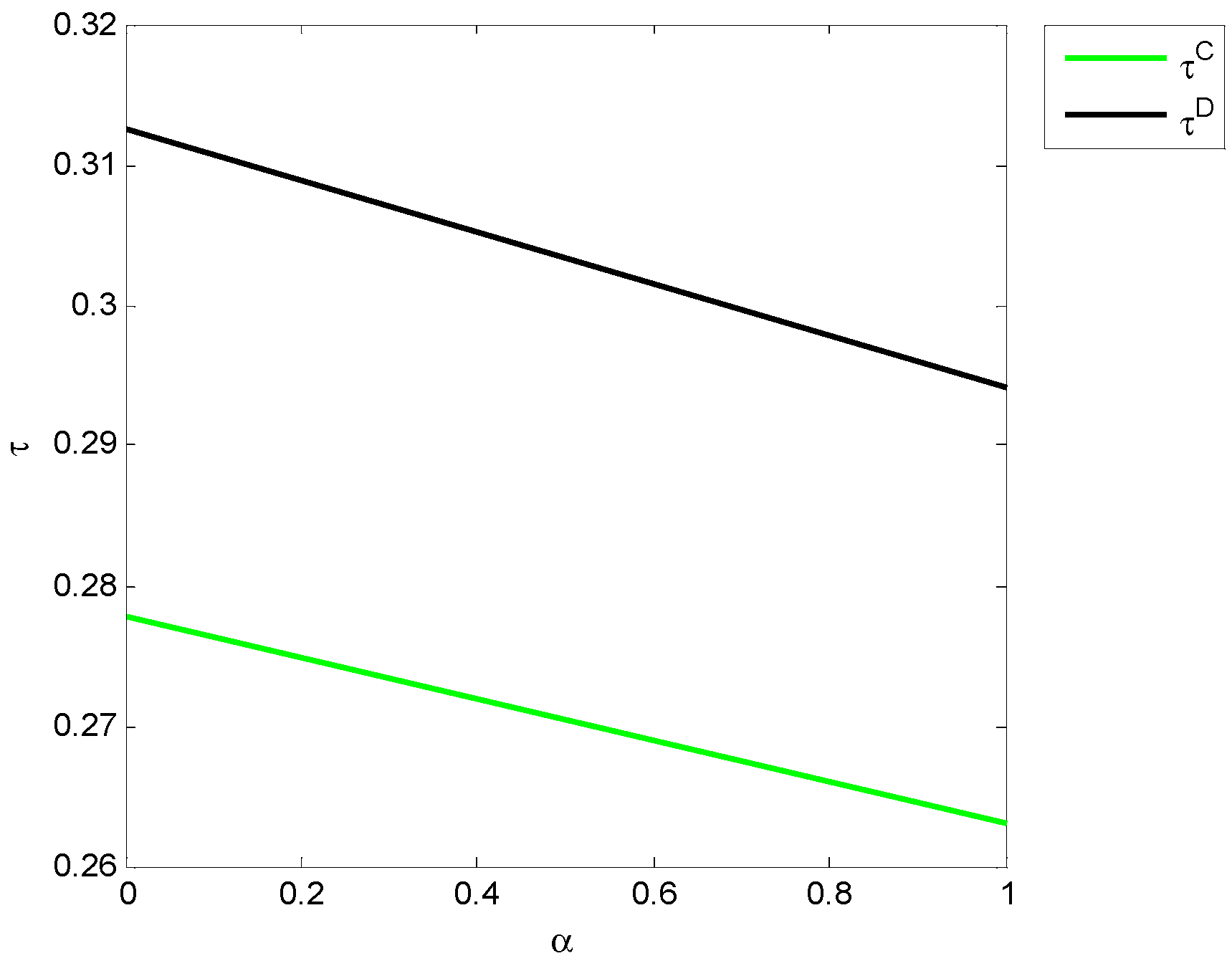
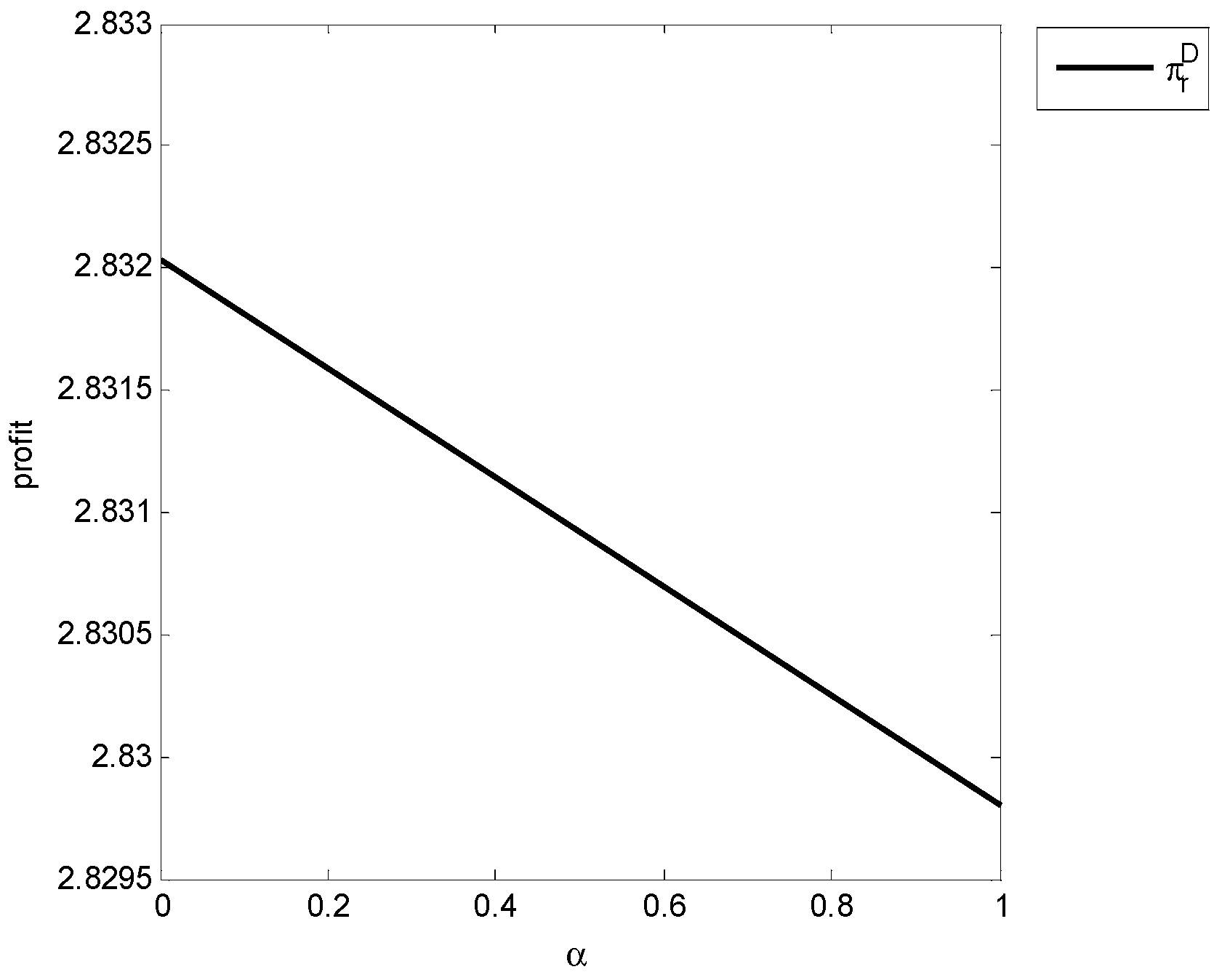
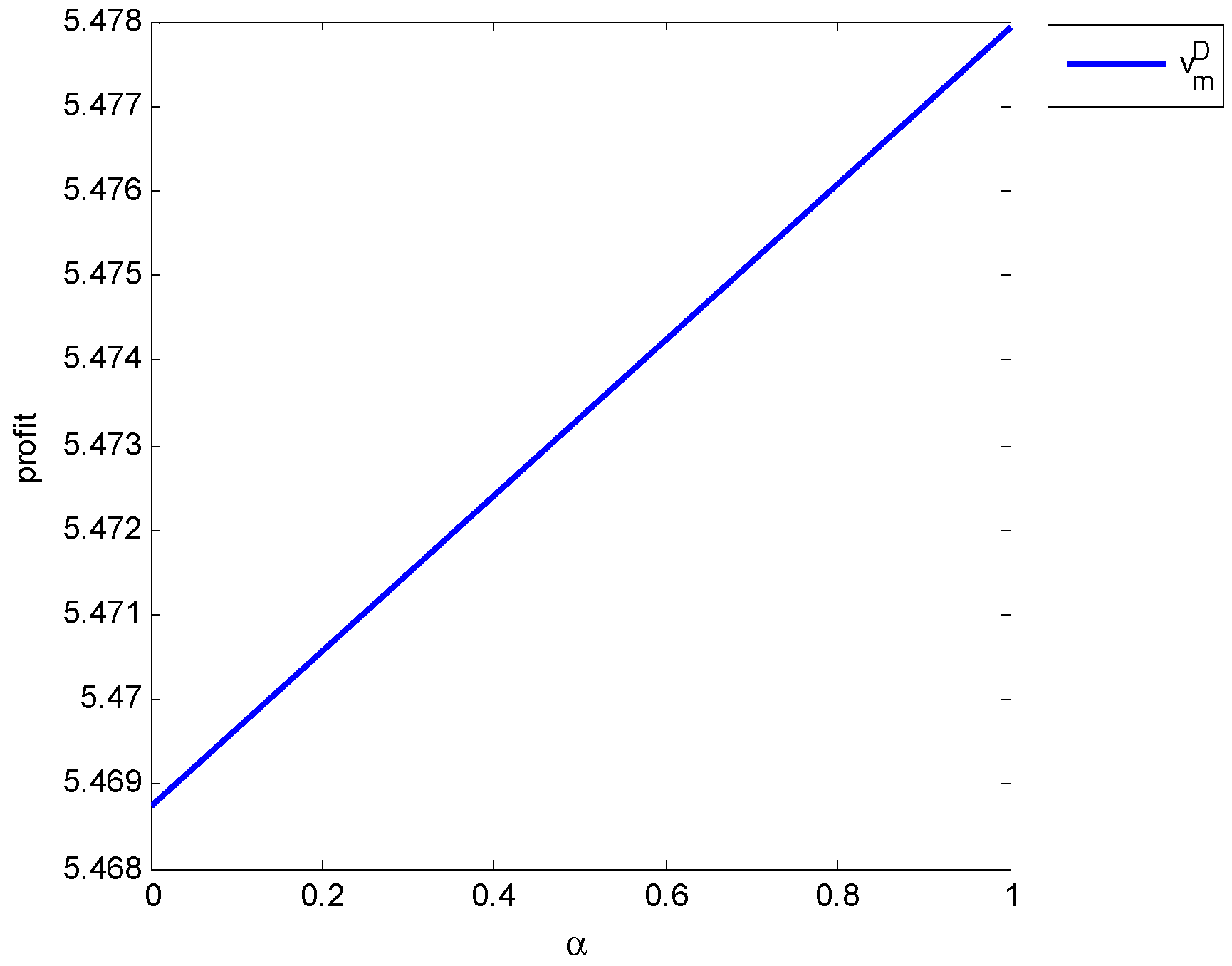
| Optimal Decision | ||
|---|---|---|
| /Profits | Model C | Model D |
| Nil | ||
| Nil | ||
| Nil | ||
| Decision or Profits | Trend | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1 | ||
| 0.2762 | 0.2747 | 0.2732 | 0.2717 | 0.2703 | 0.2688 | 0.2674 | 0.266 | 0.2646 | 0.2632 | ||
| 0.3106 | 0.3086 | 0.3067 | 0.3049 | 0.303 | 0.3012 | 0.2294 | 0.2976 | 0.2959 | 0.2941 | ||
| 2.8318 | 2.8316 | 2.8313 | 2.8311 | 2.8309 | 2.8306 | 2.8304 | 2.8302 | 2.83 | 2.8298 | ||
| 5.4688 | 5.4688 | 5.4688 | 5.4688 | 5.4689 | 5.469 | 5.469 | 5.4691 | 5.4692 | 5.4693 | ||
| 5.4697 | 5.4706 | 5.4716 | 5.4724 | 5.4733 | 5.4741 | 5,475 | 5.4757 | 5.4765 | 5.4779 | ||
| 11.1111 | 11.1111 | 11.1111 | 11.1112 | 11.1112 | 11.1113 | 11.1113 | 11.1114 | 11.1114 | 11.1115 | ||
| 11.1119 | 11.1126 | 11.1134 | 11.1141 | 11.1149 | 11.1156 | 11.1163 | 11.117 | 11.1177 | 11.1184 | ||
| 8.3015 | 8.3024 | 8.3029 | 8.3035 | 8.3042 | 8.3047 | 8.3054 | 8.3059 | 8.3065 | 8.3077 | ||
| 0.7471 | 0.7471 | 0.7471 | 0.7471 | 0.7471 | 0.7471 | 0.7471 | 0.7471 | 0.7471 | 0.7472 | ||
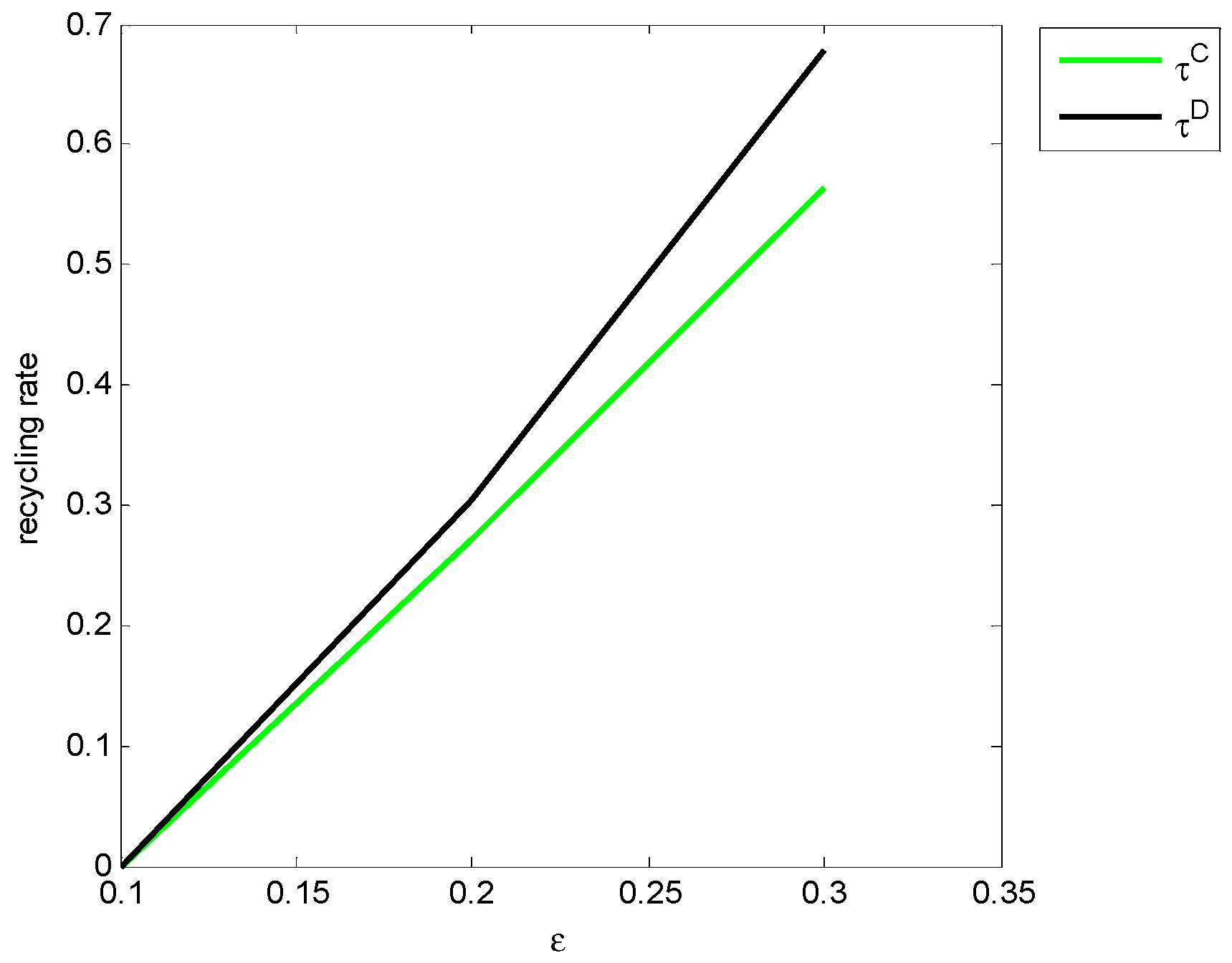
| 0.0008 | 0.0015 | 0.0023 | 0.0029 | 0.0037 | 0.0043 | 0.005 | 0.0056 | 0.0053 | 0.0069 | ||
| 0.0009 | 0.0018 | 0.0028 | 0.0036 | 0.0044 | 0.0051 | 0.006 | 0.0066 | 0.0073 | 0.0086 | ||
| Decision or Profits | Trend | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1 | ||
| 0.5831 | 0.578 | 0.5731 | 0.5682 | 0.5634 | 0.5587 | 0.554 | 0.5495 | 0.545 | 0.5405 | ||
| 0.7067 | 0.6993 | 0.692 | 0.6849 | 0.678 | 0.6711 | 0.6645 | 0.6579 | 0.6515 | 0.6452 | ||
| 2.382 | 2.3788 | 2.3758 | 2.3729 | 2.37 | 2.3673 | 2.3646 | 2.362 | 2.3595 | 2.357 | ||
| 3.7501 | 3.7503 | 3.7507 | 3.7512 | 3.7518 | 3.7526 | 3.7535 | 3.7545 | 3.7555 | 3.7567 | ||
| 3.7576 | 3.765 | 3.7722 | 3.7794 | 3.7863 | 3.7931 | 3.7998 | 3.8064 | 3.8128 | 3.8191 | ||
| 8.3404 | 8.3405 | 8.3407 | 8.341 | 8.3414 | 8.3418 | 8.3423 | 8.3429 | 8.3435 | 8.3442 | ||
| 8.3455 | 8.3505 | 8.3555 | 8.3604 | 8.3652 | 8.3699 | 8.3746 | 8.3791 | 8.3836 | 8.388 | ||
| 6.1396 | 6.1438 | 6.148 | 6.1523 | 6.1563 | 6.1604 | 6.1644 | 6.1684 | 6.1723 | 6.1761 | ||
| 0.7357 | 0.7357 | 0.7358 | 0.7359 | 0.7359 | 0.736 | 0.7361 | 0.7361 | 0.7362 | 0.7363 | ||
| 0.0051 | 0.01 | 0.0148 | 0.0194 | 0.0238 | 0.0281 | 0.0323 | 0.0362 | 0.0401 | 0.0438 | ||
| 0.0075 | 0.0147 | 0.0215 | 0.0282 | 0.0345 | 0.0405 | 0.0463 | 0.0519 | 0.0573 | 0.0624 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, L.; Shu, T.; Chen, S.; Wang, S.; Lai, K.K. CSR Remanufacturing Supply Chains under WTP Differentiation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12062197
Dai L, Shu T, Chen S, Wang S, Lai KK. CSR Remanufacturing Supply Chains under WTP Differentiation. Sustainability. 2020; 12(6):2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12062197
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Lili, Tong Shu, Shou Chen, Shouyang Wang, and Kin Keung Lai. 2020. "CSR Remanufacturing Supply Chains under WTP Differentiation" Sustainability 12, no. 6: 2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12062197
APA StyleDai, L., Shu, T., Chen, S., Wang, S., & Lai, K. K. (2020). CSR Remanufacturing Supply Chains under WTP Differentiation. Sustainability, 12(6), 2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12062197







