Sustainable Management of Digital Transformation in Higher Education: Global Research Trends
Abstract
1. Introduction
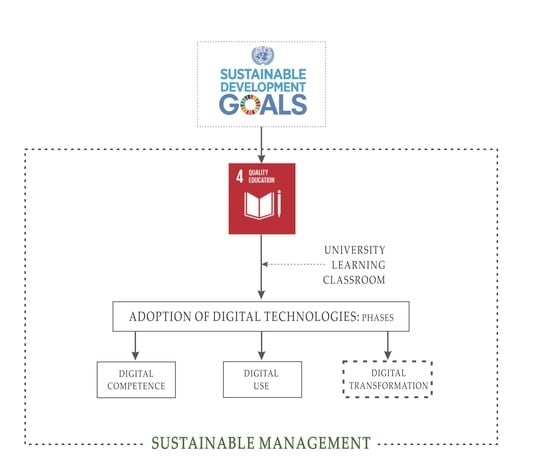
2. Literature Review and Conceptual Framework
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results and Discussion
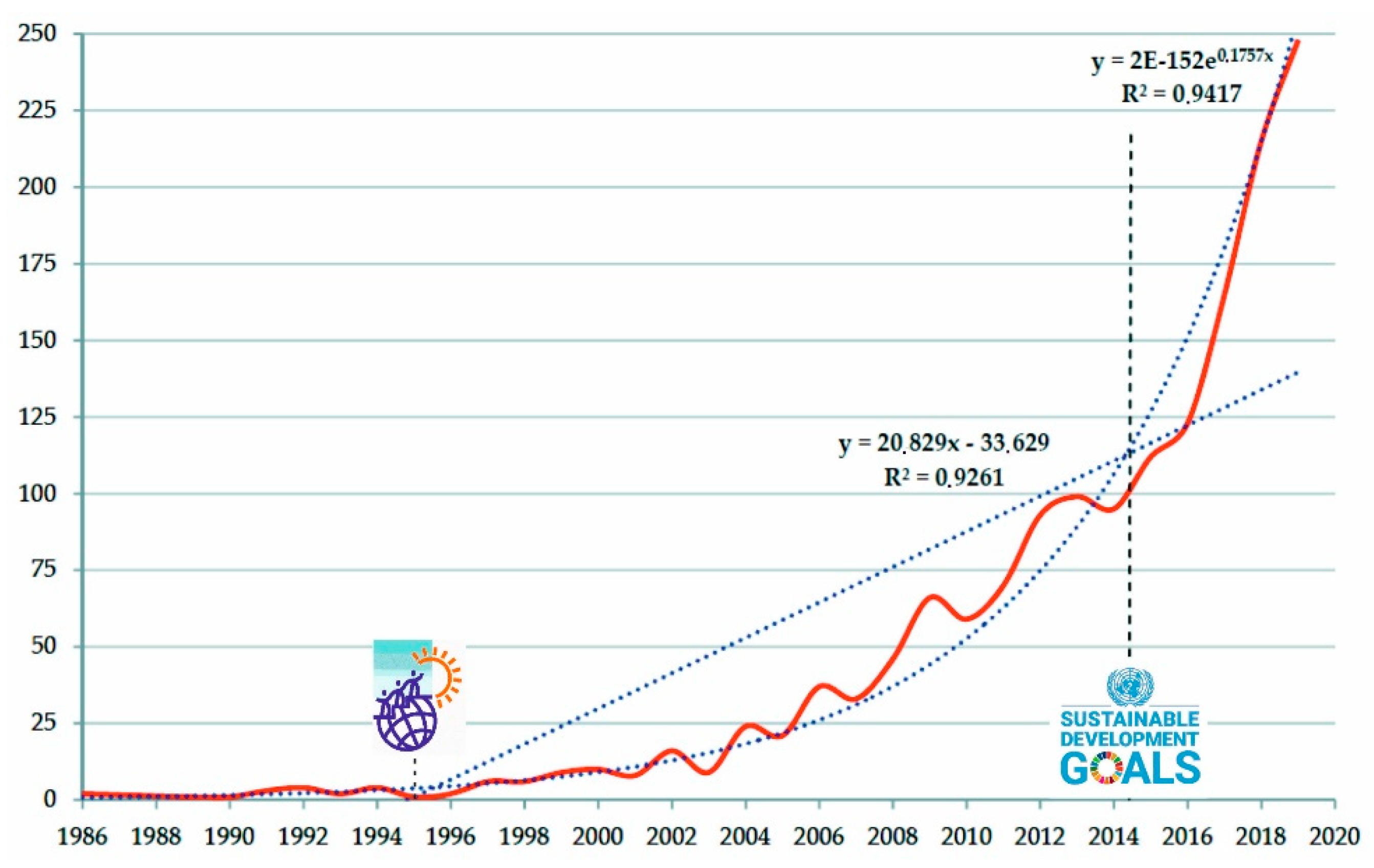
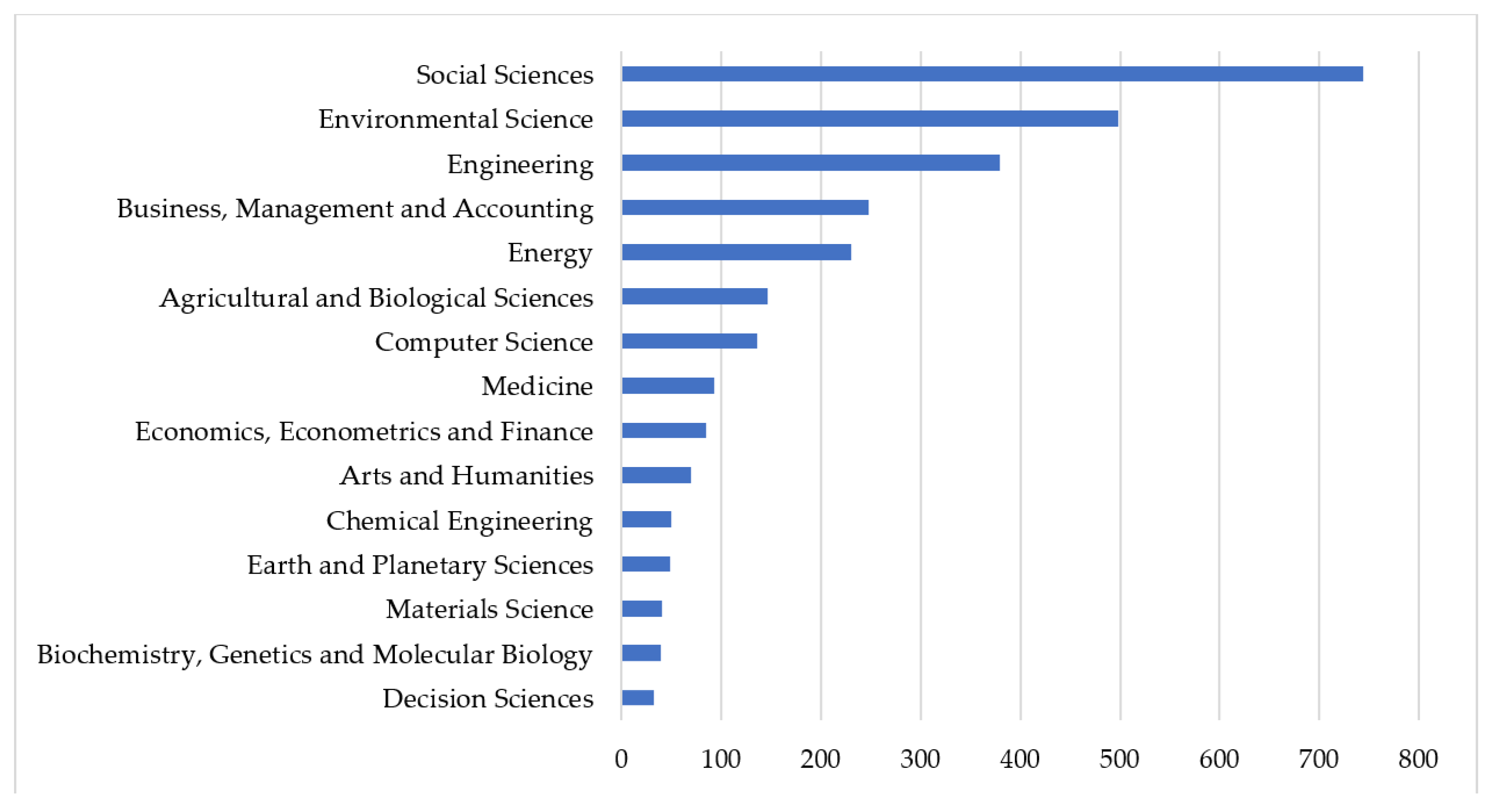
4.1. Scientific Production and Subject Area
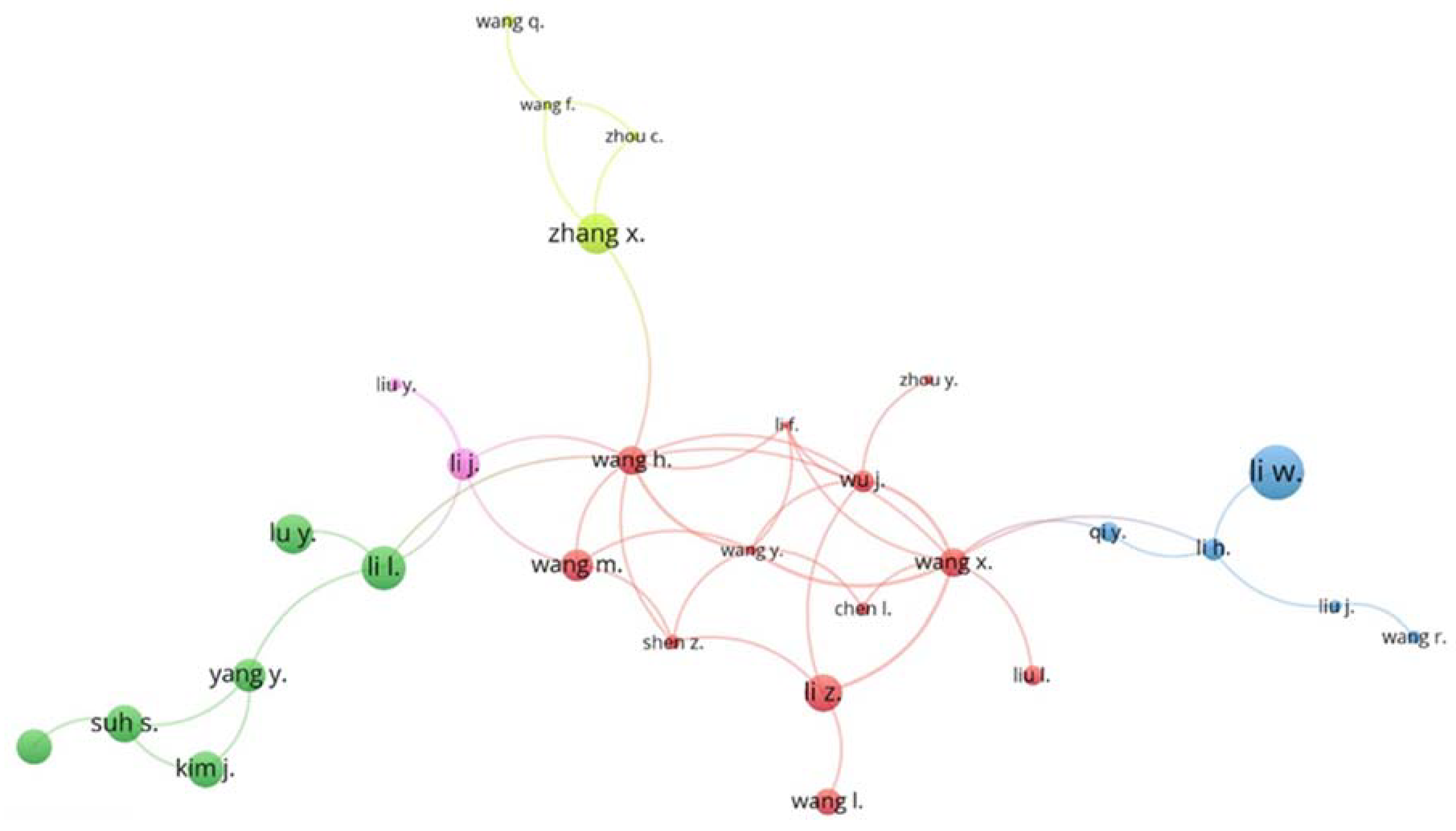
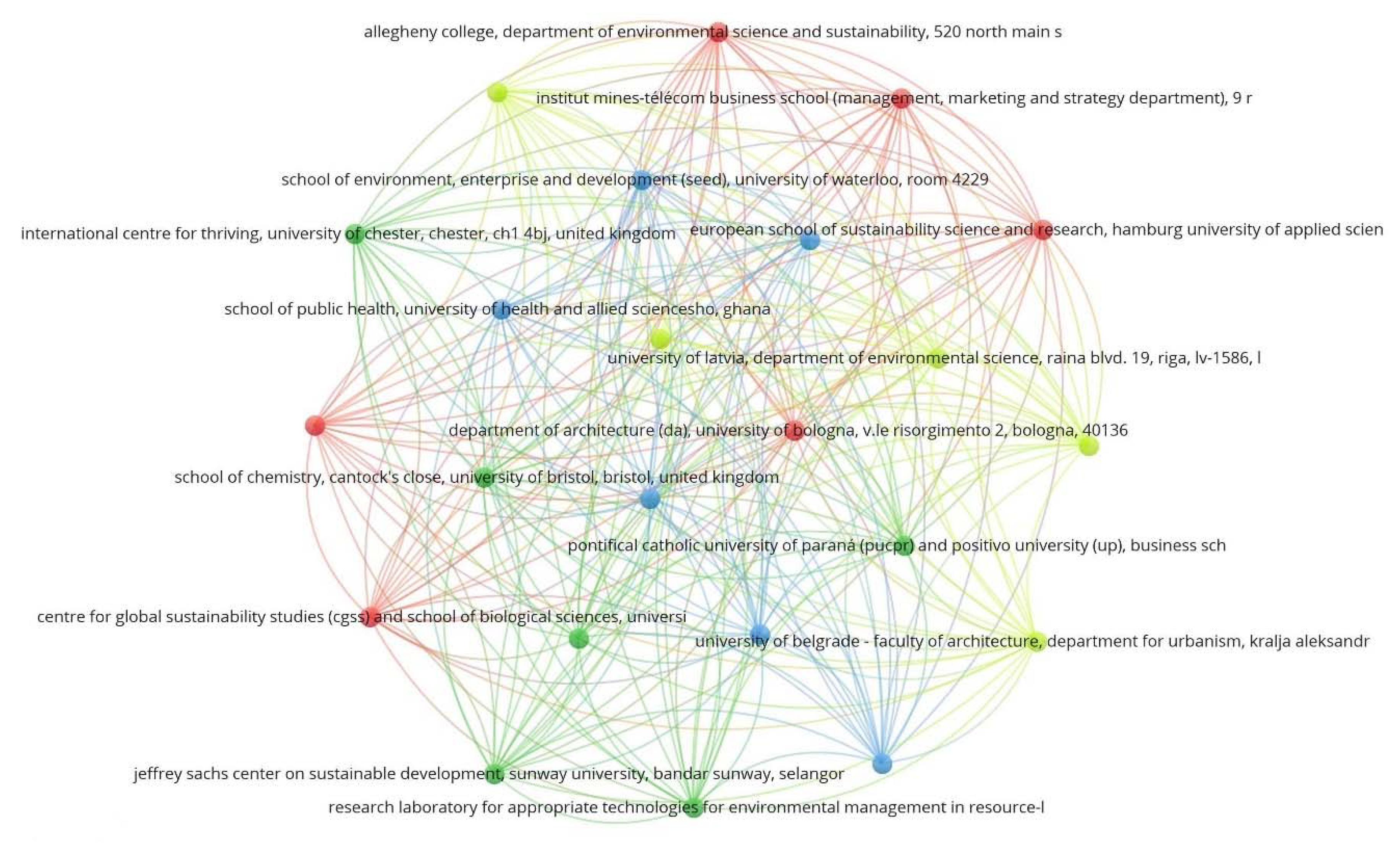
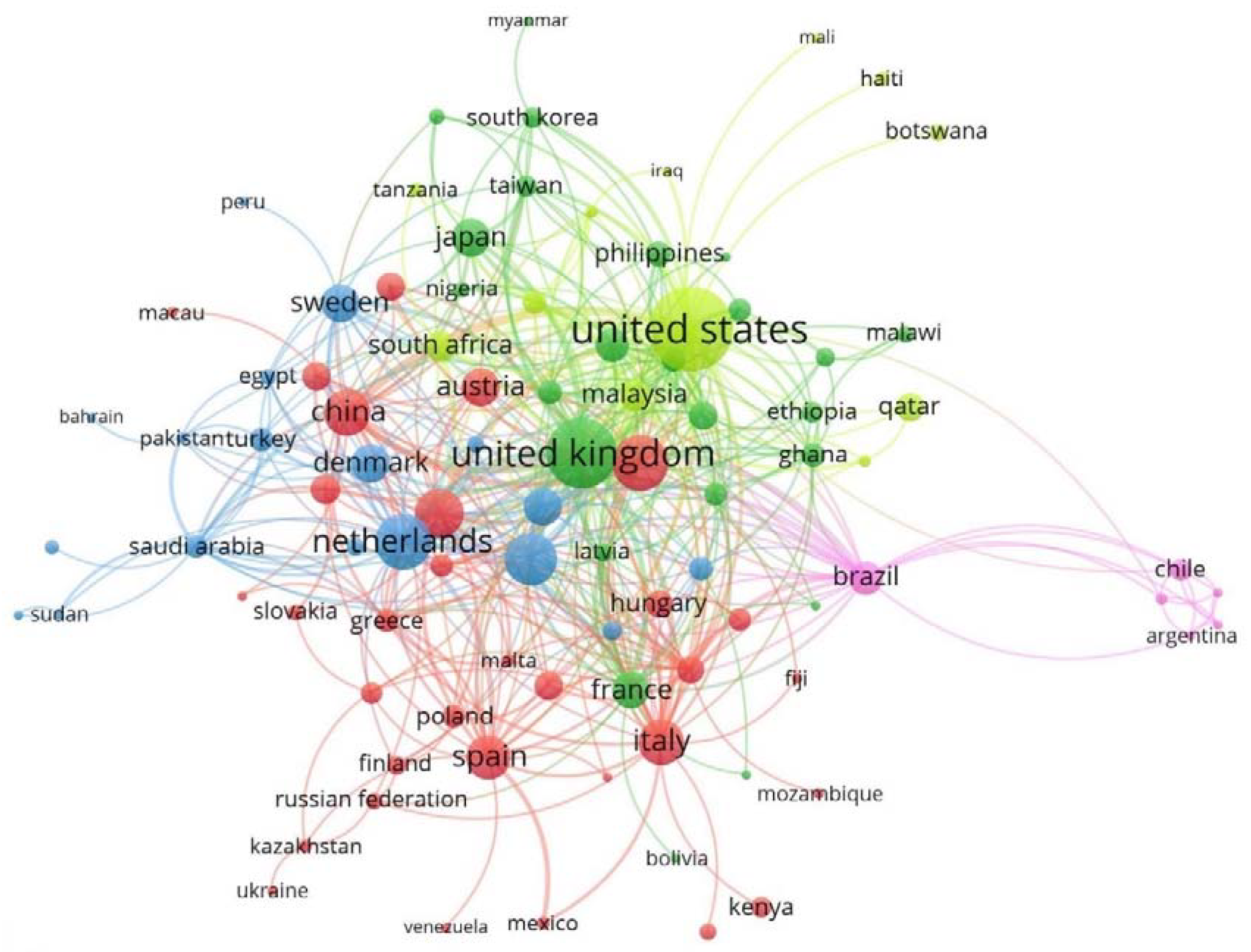
4.2. Publications by Author, Institution, and Country
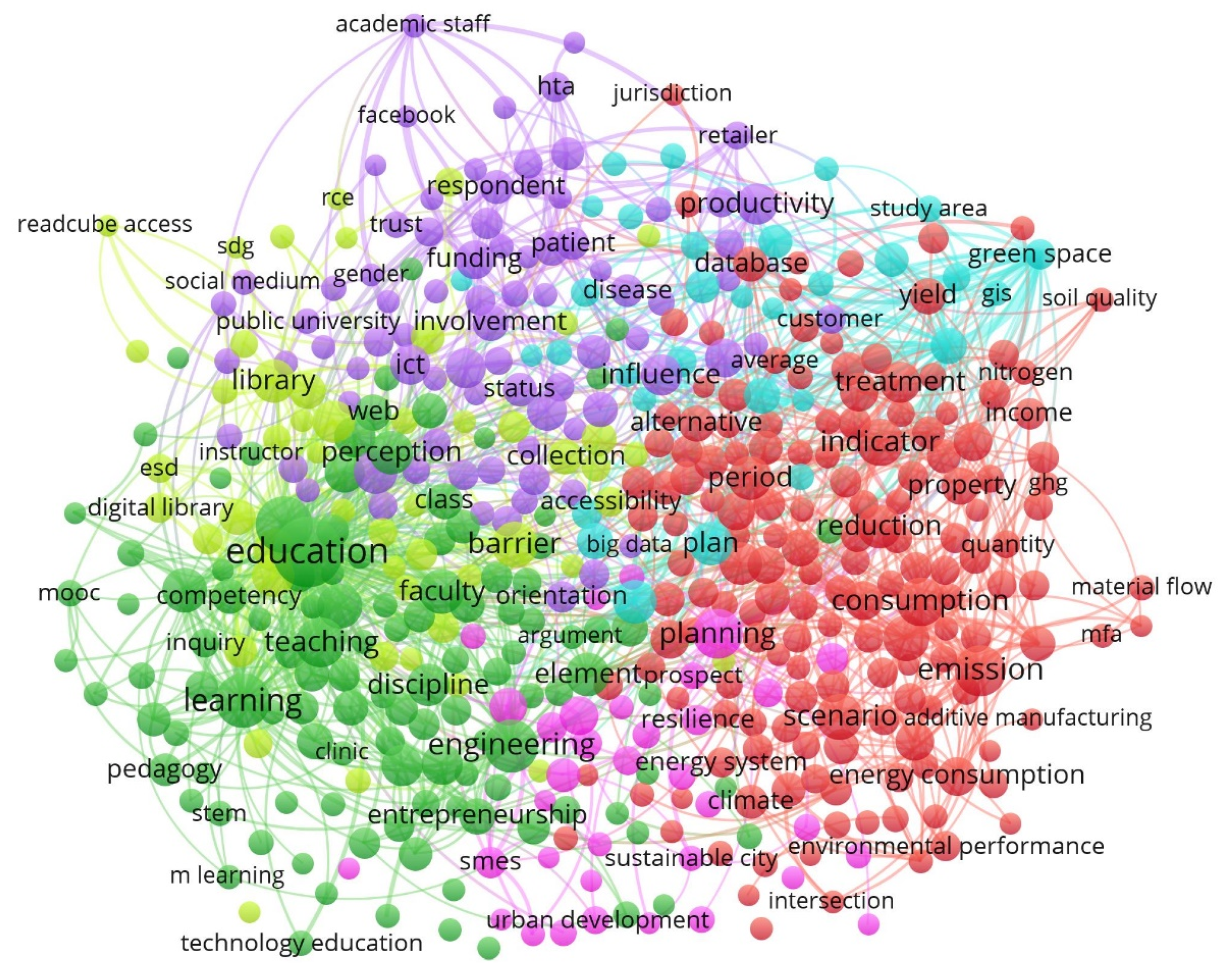
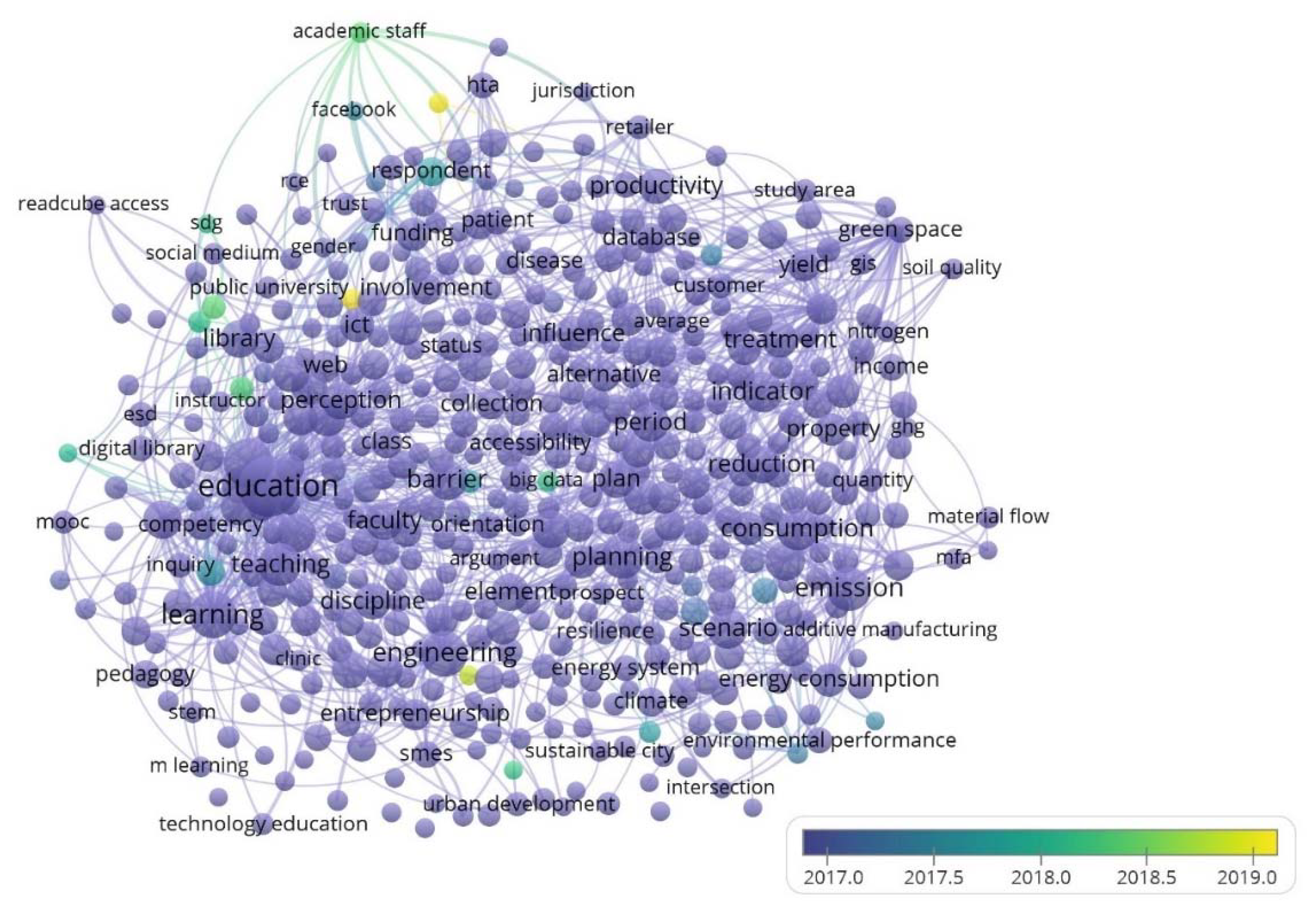
4.3. Keyword Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Testov, V.A. On some methodological problems of digital transformation of education. Inform. Educ. 2019, 10, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcum, D. The Digital Transformation of Information, Education, and Scholarship. Int. J. Humanit. Arts Comput. 2014, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syam, N.; Sharma, A. Waiting for a sales renaissance in the fourth industrial revolution: Machine learning and artificial intelligence in sales research and practice. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2018, 69, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlow, C.; Hediger, A. Digital Transformation in Higher Education—Buzzword or Opportunity? ELearn 2019, 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D. University Education and Contents in The Fourth Industrial Revolution. Humanit. Contens 2016, 42, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, B.; Rutledge, D. Digital learners and the overlapping of their personal and educational digital engagement. Comput. Educ. 2014, 77, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, A. Using connectivism theory and technology for knowledge creation in cross-cultural communication. Res. Learn. Technol. 2018, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formánková, S.; Kučerová, R.; Hrdličková, A. International standards of social responsibility and their suitability for high educational institutions. World Rev. Entrep. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 14, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babbitt, C.W. Communicating science for clean technology. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2018, 20, 1735–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, K. Defining Digital Sustainability. Libr. Trends 2007, 56, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slawsky, D. Teaching digital asset management in a higher education setting. J. Digit. Asset Manag. 2010, 6, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sita Nirmala Kumaraswamy, K.; Chitale, C.M. Collaborative knowledge sharing strategy to enhance organizational learning. J. Manag. Dev. 2012, 31, 308–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trencher, G.; Yarime, M.; McCormick, K.B.; Doll, C.N.H.; Kraines, S.B. Beyond the third mission: Exploring the emerging university function of co-creation for sustainability. Sci. Public Policy 2013, 41, 151–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.A. Conceptualizing digital literacies and digital ethics for sustainability education. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2014, 15, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, T.J.; Klobas, J.E.; Renzi, S. Critical success factors for the continuation of e-learning initiatives. Internet High. Educ. 2014, 22, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, R. Innovation in Higher Education. J. Digit. Learn. Teach. Educ. 2015, 31, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milicevic, M. Contemporary Education and Digital Technologies. Int. J. Soc. Sci. Humanit. 2015, 5, 656–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrish, M. Toward transformation: Digital tools for online dance pedagogy. Arts Educ. Policy Rev. 2016, 117, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghemawat, P. Strategies for Higher Education in the Digital Age. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2017, 59, 56–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Toit, J.; Verhoef, A.H. Embodied digital technology and transformation in higher education. Transform. High. Educ. 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosn-Chelala, M. Exploring sustainable learning and practice of digital citizenship: Education and place-based challenges. Educ. Citizsh. Soc. Justice 2018, 14, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. ICT and the UN’s Sustainable Development Goal for Education: Using ICT to Boost the Math Performance of Immigrant Youths in the US. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Hong, A.; Song, H.-D. The Relationships of Family, Perceived Digital Competence and Attitude, and Learning Agility in Sustainable Student Engagement in Higher Education. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybach, I. Institutional aspects of educational quality management in higher educational establishments. Econ. Dev. 2019, 18, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussbaum, M.; Diaz, A. Classroom logistics: Integrating digital and non-digital resources. Comput. Educ. 2013, 69, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldie, J.G.S. Connectivism: A knowledge learning theory for the digital age? Med. Teach. 2016, 38, 1064–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conradie, P.W. Supporting Self-Directed Learning by Connectivism and Personal Learning Environments. Int. J. Inf. Educ. Technol. 2014, 4, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, W. Connectivism learning and teaching: A new learning theory or an evolution in blended theory and pedagogy? Asian Int. J. Soc. Sci. 2014, 14, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa’adi, S. Introduction to Views of Connectivism Theory of Learning. Regist. J. 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, M.E. A Theory for Knowing in the Network Society. Int. J. Inf. Commun. Technol. Hum. Dev. 2014, 6, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Saykili, A. Higher Education in The Digital Age: The Impact of Digital Connective Technologies. J. Educ. Technol. Online Learn. 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kop, R.; Hill, A. Connectivism: Learning theory of the future or vestige of the past? Int. Rev. Res. Open Distrib. Learn. 2008, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Transue, B.M. Connectivism and Information Literacy: Moving from Learning Theory to Pedagogical Practice. Public Serv. Q. 2013, 9, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androutsos, A.; Brinia, V. Developing and Piloting a Pedagogy for Teaching Innovation, Collaboration, and Co-Creation in Secondary Education Based on Design Thinking, Digital Transformation, and Entrepreneurship. Educ. Sci. 2019, 9, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McTavish, M.; Filipenko, M. Reimagining Understandings of Literacy in Teacher Preparation Programs Using Digital Literacy Autobiographies. J. Digit. Learn. Teach. Educ. 2016, 32, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B. Tasks of Administrative Service Innovation in the Fourth Industrial Revolution Era. J. Policy Dev. 2018, 18, 159–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berawi, M.A. The Fourth Industrial Revolution: Managing Technology Development for Competitiveness. Int. J. Technol. 2018, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, A.W.; Karnouskos, S.; Kaynak, O.; Shi, Y.; Yin, S. Industrial Cyberphysical Systems: A Backbone of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Ieee Ind. Electron. Mag. 2017, 11, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uvarov, A.Y. From computer literacy to digital transformation of education. Inform. Educ. 2019, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-A. Are We Ready for the Fourth Industrial Revolution? Yearb. Med Inform. 2016, 25, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M. Education as Transformation – Education for transformation. Development 2010, 53, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, B. The hidden architecture of higher education: Building a big data infrastructure for the “smarter university”. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2018, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, M.J. Artificial intelligence and higher education. Enroll. Manag. Rep. 2018, 22, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q. Digital Transformation of Education Publishing in China. Publ. Res. Q. 2015, 31, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkeli, S.; Schophuizen, M. Decomposing the Complexity of Value: Integration of Digital Transformation of Education with Circular Economy Transition. Soc. Sci. 2019, 8, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnke, I.; Kumar, S. Digital Didactical Designs: Teachers’ Integration of iPads for Learning-Centered Processes. J. Digit. Learn. Teach. Educ. 2014, 30, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newhouse, C.P.; Cooper, M.; Pagram, J. Bring Your Own Digital Device in Teacher Education. J. Digit. Learn. Teach. Educ. 2015, 31, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, E. What constitutes a proper education? Digit. Investig. 2014, 11, 79–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borthwick, A.C.; Hansen, R. Digital Literacy in Teacher Education: Are Teacher Educators Competent? J. Digit. Learn. Teach. Educ. 2017, 33, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Crawford, D.; Thompson, A.D.; Lindstrom, D. Leveling Up: Modeling Digital Badging for Preservice Teachers. J. Digit. Learn. Teach. Educ. 2014, 30, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgstock, R. Educating for digital futures: What the learning strategies of digital media professionals can teach higher education. Innov. Educ. Teach. Int. 2014, 53, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamburg, I. Inclusive Education and Digital Social innovation. Adv. Soc. Sci. Res. J. 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, J. Digital culture clash: “massive” education in the E-learning and Digital Cultures MOOC. Distance Educ. 2014, 35, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Declaration on Higher Education for the Twenty-first Century: Vision and Action and Framework for Priority Action for Change and Development in Higher Education adopted by the World Conference on Higher Education Higher Education in the Twenty-First Century: Vision and Action. Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000141952 (accessed on 3 March 2020).
- Elfert, M. Lifelong learning in Sustainable Development Goal 4: What does it mean for UNESCO’s rights-based approach to adult learning and education? Int. Rev. Educ. 2019, 65, 537–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeren, E. Understanding Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 4 on “quality education” from micro, meso and macro perspectives. Int. Rev. Educ. 2019, 65, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, S. Education Diplomacy at the Intersection of Gender Equality and Quality Education. Child. Educ. 2019, 95, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guijarro, F.; Poyatos, J. Designing a Sustainable Development Goal Index through a Goal Programming Model: The Case of EU-28 Countries. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanemann, U. Examining the application of the lifelong learning principle to the literacy target in the fourth Sustainable Development Goal (SDG 4). Int. Rev. Educ. 2019, 65, 251–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, T. Research on educational leadership and management. Educ. Manag. Adm. Leadersh. 2018, 46, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K. The human side of management. Int. J. Educ. Manag. 2019, 33, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkovich, I.; Eyal, O. Ethics education in leadership development. Educ. Manag. Adm. Leadersh. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristina, S.T.; Popescu, D.M.; Stoica, E.; Erculescu, L.M. Managing the Influence of Resources on Educational Performance. Int. J. Sustain. Econ. Manag. 2018, 7, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Lawton, W. Universities, the digital divide and global inequality. J. High. Educ. Policy Manag. 2018, 40, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, E.H. Internationalization in higher education and global access in a digital age. Libr. Manag. 2009, 30, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanaugh, J.M.; Giapponi, C.C.; Golden, T.D. Digital Technology and Student Cognitive Development. J. Manag. Educ. 2015, 40, 374–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Monteiro, S. Creating Social Change: The Ultimate Goal of Education for Sustainability. Int. J. Soc. Sci. Humanit. 2016, 6, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachý, J. Scientometrics—What to do? Scientometrics 1994, 30, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, W.E. The unit of analysis (objects of study) in bibliometrics and scientometrics. Scientometrics 1996, 35, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granovsky, Y.V. Scientometrics, theory of experiment and optimization of research. Scientometrics 1989, 15, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, R.; Hu, X. Under-cited influential work by Eugene Garfield. Scientometrics 2017, 114, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakus, M.; Ersozlu, A.; Clark, A. Augmented Reality Research in Education: A Bibliometric Study. Eurasia J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2019, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Lv, T. A Bibliometric Analysis on Land Degradation: Current Status, Development, and Future Directions. Land 2020, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nunen, K.; Li, J.; Reniers, G.; Ponnet, K. Bibliometric analysis of safety culture research. Saf. Sci. 2018, 108, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, G.T.; Lim Yap, K. Bibliometric analysis and curriculum mapping of travel medicine research. J. Travel Med. 2017, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abad-Segura, E.; Cortés-García, F.J.; Belmonte-Ureña, L.J. The sustainable approach to corporate social responsibility: A global analysis and future trends. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweileh, W.M. Research trends on human trafficking: A bibliometric analysis using Scopus database. Glob. Health 2018, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Zamar, M.D.; Ortiz Jiménez, L.; Sánchez Ayala, A.; Abad-Segura, E. The Impact of the University Classroom on Managing the Socio-Educational Well-being: A Global Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, R.; Mahajan, P. Relationship amongst ResearchGate altmetric indicators and Scopus bibliometric indicators. New Libr. World 2015, 116, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad-Segura, E.; González-Zamar, M.D. Effects of Financial Education and Financial Literacy on Creative Entrepreneurship: A Worldwide Research. Educ. Sci. 2019, 9, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md Khudzari, J.; Kurian, J.; Tartakovsky, B.; Raghavan, G.S.V. Bibliometric analysis of global research trends on microbial fuel cells using Scopus database. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 136, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooding, S.; Wilcox-Jay, K.; Lewison, G.; Grant, J. Co-author inclusion: A novel recursive algorithmic method for dealingwith homonyms in bibliometric analysis. Scientometrics 2006, 66, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellnhofer, K. Visualised bibliometric mapping on smart specialisation: A co-citation analysis. Int. J. Knowl. Based Dev. 2018, 9, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, G.; Wang, M.; Feng, J. Clustering ensemble method based on co-occurrence similarity. J. Comput. Appl. 2011, 31, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durda, K.; Buchanan, L.; Caron, R. Grounding co-occurrence: Identifying features in a lexical co-occurrence model of semantic memory. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1210–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, A. Can Competition Be Detected Using Species Co-Occurrence Data? Ecology 1987, 68, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.A.; Somers, K.M.; Harvey, H.H. Similarity Coefficients: Measures of Co-Occurrence and Association or Simply Measures of Occurrence? Am. Nat. 1989, 133, 436–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Tang, Z.; Zou, X. Mapping the Knowledge Domain of Smart-City Research: A Bibliometric and Scientometric Analysis. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Raan, A.F.J.; Van der Velde, J.G.M. Bibliometric mapping and early warning for emerging topics: Exploring developments in materials science. Res. Eval. 1991, 1, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2009, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarillo, F. Language in Social Science Databases: English Versus Non-English Articles in JSTOR and Scopus. Behav. Soc. Sci. Libr. 2014, 33, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.N. World Summit for Social Development: Copenhagen, Denmark, March 6–12. Foreign Policy Bull. 1995, 5, 39–41. [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.H. Build Capacity for International Health Agenda on the “Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. ” Health Policy Manag. 2015, 25, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verniory, P. “Social Sciences” or “Disciplines of the Subject”? Human & Social Studies. Res. Pract. 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, R. E-Sciences as research technologies: Reconfiguring disciplines, globalizing knowledge. Soc. Sci. Inf. 2008, 47, 131–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinings, B.; Gegenhuber, T.; Greenwood, R. Digital innovation and transformation: An institutional perspective. Inf. Organ. 2018, 28, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, T. Researching Culture through Big Data: Computational Engineering and the Human and Social Sciences. Soc. Sci. 2018, 7, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-K. Social Sciences and Sustainability. Soc. Sci. 2011, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad-Segura, E.; González-Zamar, M.D. Análisis de las competencias en la educación superior a través de flipped classroom. Rev. Iberoam. De Educ. 2019, 80, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Zamar, M.D.; Abad-Segura, E. El aula invertida: Un desafío para la enseñanza universitaria. VirtualidadEduc. Y Cienc. 2020, 11, 75–91. Available online: https://revistas.unc.edu.ar/index.php/vesc/article/view/27449 (accessed on 9 March 2020).
- Crittenden, V.; Peterson, R.A. Digital Disruption: The Transdisciplinary Future of Marketing Education. J. Mark. Educ. 2019, 41, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateer, J.; Haillay, S. Digital disruption and its implications in generating “impact” through film and television Practice-as-Research. Media Pract. Educ. 2019, 20, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerron-Quintana, P.A. Money demand heterogeneity and the great moderation. J. Monet. Econ. 2009, 56, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullard, J.; Singh, A. Learning and The Great Moderation*. Int. Econ. Rev. 2012, 53, 375–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armesto, M.T.; Piger, J.M. International Perspectives on the “Great Moderation”. Econ. Synop. 2005, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Wang, Y. China Digital Governance Development Review Over the Past Two Decades. Int. J. Public Adm. Digit. Age 2018, 5, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H. Digital or Trade? The Contrasting Approaches of China and US to Digital Trade. J. Int. Econ. Law 2018, 21, 297–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Seta, G. Networking China: The digital transformation of the Chinese economy, written by Yu Hong. Asiascape: Digit. Asia 2018, 5, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane, M.; Chen, Y. Digital China. Asiascape Digit. Asia 2017, 4, 52–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengston, D.N. Futures Research Methods and Applications in Natural Resources. Soc. Nat. Resour. 2019, 32, 1099–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayum, A. Natural Resource Mapping Using Landsat and Lidar towards Identifying Digital Elevation, Digital Surface and Canopy Height Models. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Nat. Resour. 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Ding, C.; Yang, L.; Lei, Z.; Zheng, C. Study of decoupled charge blasting based on high-speed digital image correlation method. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 83, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K. Digital Orthogonal-Filters Enhanced Spatial Modulation for High-Speed Indoor Optical Wireless Communications. J. Lightwave Technol. 2019, 37, 5988–5995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asi, Y.M.; Williams, C. The role of digital health in making progress toward Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 3 in conflict-affected populations. Int. J. Med Inform. 2018, 114, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skues, J.; Alexander, S.-L.; Wise, L. Examining the impact of goal attainment and training goal on overall training satisfaction among vocational education and training completers. Educ. Train. 2019, 61, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.; Chapleau, A.; Schell, M.; Vaughan, V.; Colzin, C. Leveraging technology in field education for digital natives: Using goal attainment scaling. Soc. Work Educ. 2019, 39, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirkony, C. Students learning science: Representation construction in a digital environment. Environ. Educ. Res. 2019, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakunina, G.E. Research of digital communications models within organizations and at the state level in the countries-leaders in the use of digital communication technologies. E Manag. 2020, 2, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midiyanti, R.; Yao, M.H. The Dynamic Relationship between Globalization and Economic Growth: Its Implication on Business Policy. Int. J. Appl. Bus. Res. 2019, 1, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yanitsky, O.N. Education in the Context of Current Globalization. Int. Res. High. Educ. 2019, 4, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digital Education Action Plan. Education and Training. European Commision. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/education/education-in-the-eu/digital-education-action-plan_en (accessed on 12 February 2020).
- Khrushch, S.; Ostrovska, V. Methods of Exposure Informatively Psychological Influences in Social Networks. Digit. Platf. Inf. Technol. Sociocult. Sphere 2019, 2, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachenko, O.; Danilenko, A. Confidentiality of Users’ Data in Modern Messengers. Digit. Platf. Inf. Technol. Sociocult. Sphere 2019, 2, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R. A bibliometric study: Journal of management research and analysis. J. Manag. Res. Anal. 2019, 6, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wu, Y. Global Research Trends of Intuitionistic Fuzzy Set: A Bibliometric Analysis. J. Intell. Syst. 2019, 28, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treglia, E.; Magnanini, A.; Caione, G.; Lungu, M.A. Assistive Technologies, Digital Literacy and Didactic for Inclusion. Int. J. Digit. Lit. Digit. Competence 2019, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldabas, R. Barriers and facilitators of using augmentative and alternative communication with students with multiple disabilities in inclusive education: Special education teachers’ perspectives. Int. J. Incl. Educ. 2019, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooten, J.J. Integrating discussion and digital media to increase classroom interaction. Int. Rev. Econ. Educ. 2020, 33, 100174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Dahshan, G. The development of digital intelligence DQ our children one of the requirements of life in the digital age. Int. J. Res. Educ. Sci. 2019, 2, 49–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koufou, A. Supporting cultural education using digital concept mapping. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Stud. 2016, 5, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Achi, D.M.; Halabi, N.R.; Kaafarani, B. Transformative Education: Students in the Spotlight—A Holistic Pedagogical Approach. Sci. J. Educ. 2019, 7, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegener, C.; Aakjær, M. Upcycling—A new perspective on waste in social innovation. J. Comp. Soc. Work 2016, 11, 242–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, J.; Rauch, C.; Wierzbicki, A. Teaching Upcycling to Impact Environmental Attitudes. J. Technol. Educ. 2019, 30, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, K.; Cooper, T.; Kettley, S. Developing Interventions for Scaling Up UK Upcycling. Energies 2019, 12, 2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, K.; Cooper, T.; Kettley, S. Factors Influencing Upcycling for UK Makers. Sustainability 2019, 11, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, P.; Wright, A.M. Upcycling a Schol Comm Unit: Building Bridges with Creativity, Reallocations, and Limited Resources. Ser. Libr. 2020, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, I. Digital economy and related risks in social protection of community. Citise 2019, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donohoe, S. Netnography: Doing Ethnographic Research Online. Int. J. Advert. 2010, 29, 328–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, R.; Mansor, M. The Relationship between Knowledge Management and Organizational Learning with Academic Staff Readiness for Education 4.0. Eurasian J. Educ. Res. 2020, 20, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED). Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/International_Standard_Classification_of_Education_(ISCED) (accessed on 16 February 2020).
- Dombrowski, M.; Dombrowski, Z.; Sachenko, A.; Sachenko, O. Method of decision-making the proactive project management of organizational development. Math. Modeling Comput. 2019, 6, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirgensons, M.; Kapenieks, J. Blockchain and the Future of Digital Learning Credential Assessment and Management. J. Teach. Educ. Sustain. 2018, 20, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugsbakken, H.; Langseth, I. The Blockchain Challenge for Higher Education Institutions. Eur. J. Educ. 2019, 2, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Meneses, E. El Fenómeno MOOC y el Futuro de la Universidad. Front. De La Cienc. 2017, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez Cano, E.; López Meneses, E. Virtual Tutoring and Counseling in Schools. ISRN Educ. 2012, 2012, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Article Title [Reference] | Author(s) | Year | Journal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Defining Digital Sustainability [10] | Bradley, K. | 2007 | Library Trends |
| Teaching digital asset management in a higher education setting [11] | Slawsky, D. | 2010 | Journal of Digital Asset Management |
| Collaborative knowledge sharing strategy to enhance organizational learning [12] | Sita Nirmala Kumaraswamy, K.; Chitale, C.M. | 2012 | Journal of Management Development |
| Beyond the third mission: Exploring the emerging university function of co-creation for sustainability [13] | Trencher, G.; Yarime, M.; McCormick, K.B.; Doll, C.N.H.; Kraines, S.B. | 2013 | Science and Public Policy |
| Conceptualizing digital literacies and digital ethics for sustainability education [14] | Brown, S.A. | 2014 | International Journal of Sustainability in Higher Education |
| Critical success factors for the continuation of e-learning initiatives [15] | McGill, T.J.; Klobas, J.E.; Renzi, S. | 2014 | The Internet and Higher Education |
| Innovation in Higher Education [16] | Hansen, R. | 2015 | Journal of Digital Learning in Teacher Education |
| Contemporary Education and Digital Technologies [17] | Milicevic, M. | 2015 | International Journal of Social Science and Humanity |
| Toward transformation: Digital tools for online dance pedagogy [18] | Parrish, M. | 2016 | Arts Education Policy Review |
| Strategies for Higher Education in the Digital Age [19] | Ghemawat, P. | 2017 | California Management Review |
| Embodied digital technology and transformation in higher education [20] | Du Toit, J.; Verhoef, A.H. | 2018 | Transformation in Higher Education |
| Exploring sustainable learning and practice of digital citizenship: Education and place-based challenges [21] | Ghosn-Chelala, M. | 2018 | Education, Citizenship and Social Justice |
| ICT and the UN’s Sustainable Development Goal for Education: Using ICT to Boost the Math Performance of Immigrant Youths in the US [22] | Kim, S. | 2018 | Sustainability |
| The Relationships of Family, Perceived Digital Competence and Attitude, and Learning Agility in Sustainable Student Engagement in Higher Education [23] | Kim, H.; Hong, A.; Song, H.-D. | 2018 | Sustainability |
| Institutional aspects of educational quality management in higher educational establishments [24] | Dybach, I. | 2019 | Economics of Development |
| Author | Affiliation | City, Country | First Article * | Last Article * | Main Keywords |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mulder, K.F. | The Hague University of Applied Sciences | The Hague, The Netherlands | 2004 | 2012 | Sustainable Development, Sustainability, Active Learning |
| Cappellaro, F. | ENEA Centro Ricerche Casaccia | Rome, Italy | 2014 | 2019 | Active Citizenship, Appropriate Technologies, Co-design |
| Schandl, H. | Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization | Canberra, Australia | 2006 | 2018 | Industrial Ecology, Developing Countries, Material Flow |
| Yarime, M. | University of Tokyo | Tokyo, Japan | 2013 | 2017 | Sustainability, Co-creation, Transformation |
| Asif, M. | King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals | Dhahran, Saudi Arabia | 2017 | 2019 | Sustainability, Solar Energy, Alternative Energy |
| Brandli, L.L. | Universidade de Passo Fundo | Passo Fundo, Brazil | 2019 | 2019 | Sustainable Development, Higher Education, Barriers to Innovation and Sustainability in Universities |
| Cotana, F. | Università degli Studi di Perugia | Perugia, Italy | 2013 | 2016 | Sustainable Development, Acoustic Performance, Bioconversion |
| Cumo, F. | Università degli Studi di Roma La Sapienza | Rome, Italy | 2010 | 2016 | Sustainable Development, Advanced Technology, Digital Storage |
| Eisenmenger, N. | Universität für Bodenkultur Wien | Wien, Austria | 2006 | 2015 | Industrial Ecology, Materials Flow Analysis (MFA) Sustainability |
| Ferrer-Balas, D. | Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya | Barcelona, Spain | 2008 | 2012 | Pedagogy, Sustainable Development, Engineering Education |
| Institution | City, Country | Main Keywords |
|---|---|---|
| Delft University of Technology | Zuid-Holland, the Netherlands | Sustainable Development, Sustainability, Engineering Education |
| Arizona State University | Arizona, USA | Sustainable Development, Education, Digital Storytelling |
| Purdue University | Indiana, USA | Education, Sustainability, Technology |
| University of Technology Sydney | New South Wales, Australia | Higher Education, Sustainable Development, Sustainability |
| Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya | Barcelona, Spain | Sustainability, Sustainable Development, Education |
| ETH Zürich | Zurich, Switzerland | Sustainability, Sustainable Development, Environmental Impact |
| Open University | Milton Keynes, UK | Education, Higher Education, E-learning |
| Massachusetts Institute of Technology | Cambridge, USA | Sustainability, Sustainable Development, Carbon Emission |
| University of California | Berkeley, USA | Sustainability, Climate Change, Life Cycle Analysis |
| Tsinghua University | Beijing, China | Sustainable Development, Industrial Ecology, Environmental Technology |
| Cluster Number * | Color | Cluster Name ** | % | Main Countries |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Red | Australia | 34.44 | China, Spain, Italy, Germany, Norway, Poland, Russia, Finland |
| 2 | Green | UK | 26.67 | France, Japan, Taiwan, Serbia, Ghana, Latvia, South Korea |
| 3 | Blue | The Netherlands | 18.89 | Canada, Switzerland, Sweden, Denmark, Turkey, Israel |
| 4 | Yellow | USA | 13.33 | Malaysia, Ireland, Qatar, South Africa, Bangladesh |
| 5 | Rose | Brazil | 6.67 | Argentina, Chile, Costa Rica, Guatemala, Panama |
| CNu | C | CNa | % | Main Keywords |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Red | Environmental impact | 33.89 | Circular economy, Life cycle assessment, Recycling, Technology development, Social impact |
| 2 | Green | Education | 24.21 | Higher education, App, Distance Learning, Sustainability education, Massive open online course (MOOC) |
| 3 | Violet | ICT | 17.26 | Bioinformatics, Digital technology, Sustainability science, Facebook, Data analysis |
| 4 | Yellow | Library | 10.74 | Digital library, Accessibility, Computing, Creativity, Higher education institution |
| 5 | Rose | Computer | 7.37 | Simulation, Energy performance, Competitive advantage, Sustainable city, Smart city |
| 6 | Blue | Green space | 6.53 | Information system, Global change, Future development, Competitiveness, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abad-Segura, E.; González-Zamar, M.-D.; Infante-Moro, J.C.; Ruipérez García, G. Sustainable Management of Digital Transformation in Higher Education: Global Research Trends. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2107. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12052107
Abad-Segura E, González-Zamar M-D, Infante-Moro JC, Ruipérez García G. Sustainable Management of Digital Transformation in Higher Education: Global Research Trends. Sustainability. 2020; 12(5):2107. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12052107
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbad-Segura, Emilio, Mariana-Daniela González-Zamar, Juan C. Infante-Moro, and Germán Ruipérez García. 2020. "Sustainable Management of Digital Transformation in Higher Education: Global Research Trends" Sustainability 12, no. 5: 2107. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12052107
APA StyleAbad-Segura, E., González-Zamar, M.-D., Infante-Moro, J. C., & Ruipérez García, G. (2020). Sustainable Management of Digital Transformation in Higher Education: Global Research Trends. Sustainability, 12(5), 2107. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12052107