Aging, Living Environment, and Sustainability: What Should be Taken into Account?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Aging and Living Environment
2.1. Features and Needs of the Elderly Population
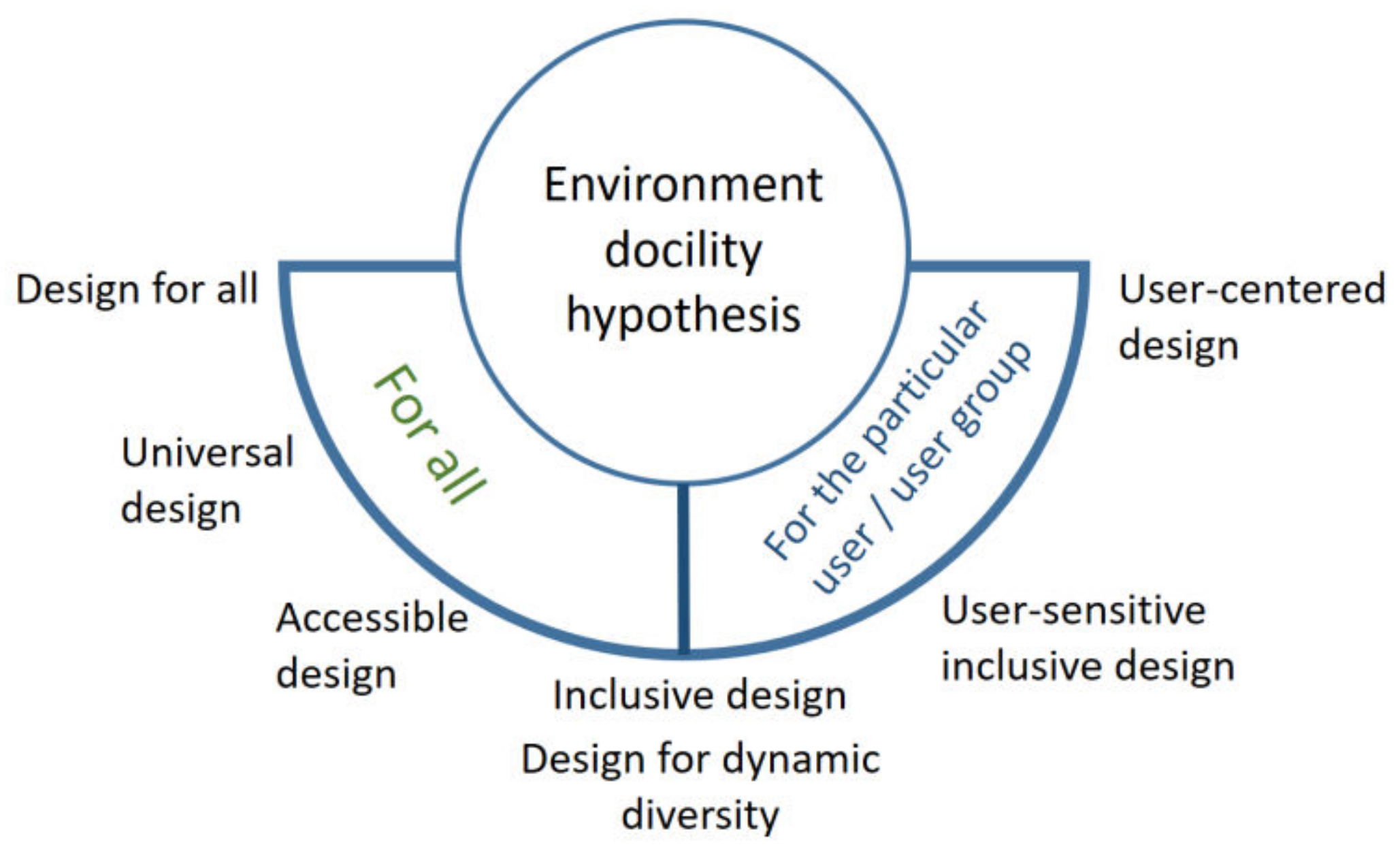
2.2. Design for Elderly Population
3. Sustainable Aging and Sustainable Living Environment
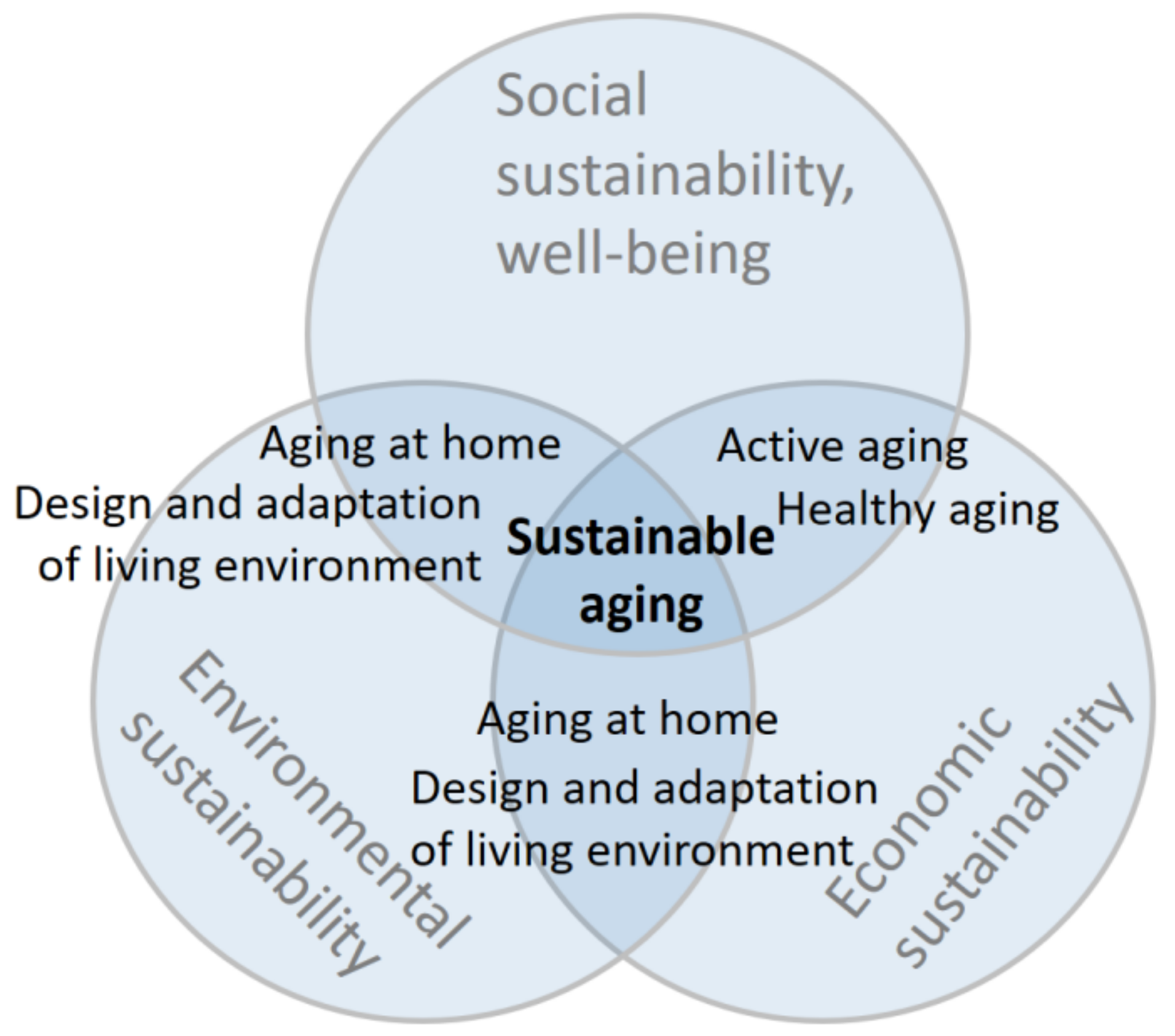
3.1. The Aspects of Sustainable Aging
3.2. Biophilic Design as a Part of Sustainable Ageing
- -
- Nature in the space, meaning the presence and diversity of natural elements and features within the human environment, including vegetation, water bodies, animal species;
- -
- Natural analogs, meaning objects, materials, colors, shapes, patterns, and algorithms that are analogous to natural ones and evoke similar human responses;
- -
- Nature of the space, meaning different solutions of organization of spaces that evoke physiological responses, including prospect, refuge, mystery, risk/peril, characteristic to the experience of the natural environment.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crews, D.E.; Zavotka, S. Aging, disability, and frailty: Implications for universal design. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 2006, 25, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ageing Report 2018. Underlying Assumptions and Projection Methodologies. European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/sites/info/files/economy-finance/ip065_en.pdf (accessed on 2 January 2020).
- Jayantha, W.M.; Qianb, Q.K.; Yia, C.O. Applicability of ‘aging in place’ in redeveloped public rental housing estates in Hong Kong. Cities 2018, 83, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afacan, Y.; Erbug, C. An interdisciplinary heuristic evaluation method for universal building design. Appl. Ergon. 2009, 40, 731–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, D.L.; Goldfarb, A.I. Psychological needs of aged patients at home. Am. J. Public Health 1996, 10, 1716–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.E. Architecture for the silver generation: Exploring the meaning of appropriate space for ageing in a Swedish municipality. Health Place 2011, 17, 572–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Jiménez, A.; Barrios-Padura, A.; Molina-Huelva, M. Sustainable building renovation for an ageing population: Decision support system through an integral assessment method of architectural interventions. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 39, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severinsen, C.; Breheny, M.; Stephens, C. Ageing in unsuitable places. Hous. Stud. 2016, 31, 714–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, F.; Thomson, C. Housing an ageing population: Implications for managing the social housing stock. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual ARCOM Conference, Reading, UK, 2–4 September 2013; Smith, S.D., Ahiaga-Dagbui, D.D., Eds.; Association of Researchers in Construction Management: Reading, UK, 2013; pp. 1185–1195. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, E.J.; Mitchell, L.; Stride, C.B. Good places for ageing in place: Development of objective built environment measures for investigating links with older people’s well-being. BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, A.F.; Gregor, P. Design for older and disabled people—Where do we go from here? Univers. Access Inf. Soc. 2002, 2, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, K.; Weir, P.L.; Azar, D.; Azar, N.R. Universal Design: A Step toward Successful Aging. J. Aging Res. 2013, 3, 324624. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3570931/ (accessed on 2 January 2020). [CrossRef]
- De Souza, S.C.; de Oliveira Post, A.P.D. Universal Design: An urgent need. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2016, 216, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mustaquim, M.M. A study of universal design in everyday life of elderly adults. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 67, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Kaushik, I. Design for sustainable aging: Improving design communication through building information modelling and game engine integration. Procedia Eng. 2015, 118, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iecovich, E. Aging in place: From theory to practice. Anthropological Notebooks 2014, 20, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Thoma-Lürken, T.; Bleijlevens, M.H.C.; Lexis, M.A.S.; de Witte, L.P.; Hamers, J.P.H. Facilitating aging in place: A qualitative study of practical problems preventing people with dementia from living at home. Geriatr. Nurs. 2018, 39, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sixsmith, J.; Sixsmith, A.; Malmgren Fänge, A.; Naumann, D.; Kucsera, C.; Tomsone, S.; Haak, M.; Dahlin-Ivanoff, S.; Woolrych, R. Healthy ageing and home: The perspectives of very old people in five European countries. Soc. Sci. Med. 2014, 106, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceros, J.C.; Pols, J.; Domènech, M. Where is grandma? Home telecare, good aging and the domestication of later life. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2015, 93, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senior Living Sustainability Guide. With Seniors in Mind. 2011. Available online: https://www.withseniorsinmind.org (accessed on 13 July 2019).
- Day, K.; Carreon, D.; Stump, C. The therapeutic design of environments for people with dementia: A review of the empirical research. Gerontol. 2000, 40, 397–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elderly People in Lithuania. Statistics Lithuania. 2014. Available online: https://osp.stat.gov.lt/services-portlet/pub-edition-file?id=3030 (accessed on 10 June 2019).
- Shabalin, V. Psychology and psychopathology of the elderly. Int. J. Cult. Ment. Health 2018, 11, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, H.; Åhman, H.; Yngling, A.A.; Gulliksen, J. Universal design, inclusive design, accessible design, design for all: Different concepts—One goal? On the concept of accessibility—Historical, methodological and philosophical aspects. Univers. Access Inf. Soc. 2015, 14, 505–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, M.P. The Impact of the environment on aging and behavior. In Handbook of the Psychology of Aging; Warner Schaie, K., Ed.; Van Nostrand Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1977; pp. 276–301. [Google Scholar]
- Iwarsson, S.; Stahl, A. Accessibility, usability and universal design—Positioning and definition of concepts describing person-environment relationships. Disabil. Rehabil. 2003, 25, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannuscio, C.; Block, J. Social capital and successful aging: The role of senior housing. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 139, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeGroff, H.; McCall, W. Biophilic Design. An Alternative Perspective for Sustainable Design in Senior Living. Perkins Eastman. 2016. Available online: https://www.perkinseastman.com (accessed on 2 January 2020).
- Gillis, K.; Gatersleben, B. A review of psychological literature on the health and well-being benefits of biophilic design. Buildings 2015, 5, 948–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, E.O. Biophilia, the Human Bond with Other Species; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, E.O. Biphilia and conservation ethics. In The Biophilia Hypothesis; Kellert, S., Wilson, E.O., Eds.; Shearwater Books: Washington, DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Kellert, S.; Calabrese, E. The Practice of Biophilic Design. 2015. Available online: https://www.biophilic-design.com (accessed on 2 January 2020).
- Andrews, M. Biophilia: The Secret to Happiness and Well-Being in the City. 2017. Available online: https://marthaaandrews.wixsite.com/design/dissertation (accessed on 2 January 2020).
- Beatley, T. Biophilic Cities: Integrating Nature into Urban Design and Planning; Island Press: Washington, DC, US, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Browning, W.; Ryan, C.; Clancy, J. 14 Patterns of Biophilic Design; Terrapin Bright Green, LLC: New York, NY, US, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, C.O.; Browning, W.D.; Clancy, J.O.; Andrews, S.L.; Kallianpurkar, N.B. Biophilic design patterns. Emerging nature-based parameters for health and well-being in the built environment. Int. J. Archit. Res. Archnet-Ijar 2014, 8, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerwagen, J. Biophilia, health, and well-being. In Restorative Commons: Creating Health and Well-being through Urban Landscapes; Campbell, L., Wiesen, A., Eds.; Gen. Tech Rep. NRS-P-39; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Northern Research Station: Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, 2009; pp. 38–57. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, E.A. Biophilic urbanism: Making cities sustainable through ecological design. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Civil, Architecture and Sustainable Development (CASD-2016), London, UK, 1–2 December 2016; pp. 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifi, M.; Sabernejad, J. Investigation of biophilic architecture patterns and prioritizing them in design performance in order to realize sustainable development goals. Eur. Online J. Nat. Soc. Sciences. Spec. Issue Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2016, 5, 335–337. [Google Scholar]
- Biophilic Design—Connecting with Nature to Improve Health and Well-Being. 2019. Available online: https://www.oliverheath.com/biophilic-design-connecting-nature-improve-health-well/ (accessed on 13 July 2019).
- Lupton, E.; Lipps, A. The Senses: Design Beyond Vision; Cooper Hewitt, Smithsonian Design Museum and Princeton Architectural Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]


| Principles [4,14] | Solutions [12] |
|---|---|
| Equitable Use, meaning the design that can be used by people with different abilities | Automatically opening door |
| No threshold, zero-step entrances | |
| No threshold walk-in shower | |
| Wider than standard doorways and corridors | |
| Counter tops with varying levels that can be used by standing and seated users, and people of different heights | |
| Flexibility in Use, meaning the design that can meet a wide array of individual preferences and abilities without special adaptations | Open floor plan |
| Various household equipment with the larger buttons far enough apart that can be pressed accurately | |
| Simple, Intuitive Use, meaning the design that is easily understandable and intuitively usable | Various instructions presented in a series of clear illustrations instead of the use of text |
| Perceptible Information, meaning the design that effectively communicates the necessary information to the user | Information provided in contrasting colors, large letters, audible feedback of appliances |
| Tolerance for Error, defining the design that minimizes hazards and the adverse consequences of accidental or unintended actions | The layout of hallways and corridors allowing the user to return to common areas |
| Low Physical Effort, meaning the design that can be used efficiently and comfortably and with a minimum of fatigue | Automatically opening door |
| Counter tops with varying levels that can be used by standing and seated users, and people of different heights | |
| Installation of a downstairs bathroom | |
| Planning promoting compactness and walkability, creating short drives and walking distances in communities | |
| Size and Space for Approach and Use, meaning the design that provides appropriate size and space for approach, reach, manipulation, and use | Items and appliances mounted on walls that are clearly visible, easily reachable, and easy for all hand sizes to use |
| Staircases with consistent treads that are straight and provide a stopping place in the middle between levels |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grazuleviciute-Vileniske, I.; Seduikyte, L.; Teixeira-Gomes, A.; Mendes, A.; Borodinecs, A.; Buzinskaite, D. Aging, Living Environment, and Sustainability: What Should be Taken into Account? Sustainability 2020, 12, 1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051853
Grazuleviciute-Vileniske I, Seduikyte L, Teixeira-Gomes A, Mendes A, Borodinecs A, Buzinskaite D. Aging, Living Environment, and Sustainability: What Should be Taken into Account? Sustainability. 2020; 12(5):1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051853
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrazuleviciute-Vileniske, Indre, Lina Seduikyte, Armanda Teixeira-Gomes, Ana Mendes, Anatolijs Borodinecs, and Deimante Buzinskaite. 2020. "Aging, Living Environment, and Sustainability: What Should be Taken into Account?" Sustainability 12, no. 5: 1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051853
APA StyleGrazuleviciute-Vileniske, I., Seduikyte, L., Teixeira-Gomes, A., Mendes, A., Borodinecs, A., & Buzinskaite, D. (2020). Aging, Living Environment, and Sustainability: What Should be Taken into Account? Sustainability, 12(5), 1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051853







