Abstract
This study investigates the monitoring effectiveness of the largest institutional blockholder in Korea, the Korean National Pension Service (KNPS), on firms’ engagement in corporate social responsibility (CSR). We use a large, unique sample from Korea, where the financial market is primarily characterized by chaebols. We show that lagged KNPS blockholdings do not significantly influence investee firms’ concurrent CSR indexes. This result indicates that even the largest institutional blockholder in Korea does not actively engage in firms’ CSR initiatives to enhance their long-term performance and prosperity. Overall, our results suggest that institutional investors should more actively serve as an effective corporate governance mechanism in emerging Asian markets, where companies aim to be profitable and long-term corporate governance is very important.
1. Introduction
The role of the institutional investors has gradually expanded in worldwide financial markets. Institutions’ ownership of firms has grown substantially in recent decades (for example, the Conference Board reported that institutional ownership in the 1000 largest U.S. firms rose from 46% in 1987 to 73% by the end of 2009; in addition, the Korea Exchange showed that the market capitalization of institutional investors in Korea was approximately 45% as of 2012), and they are increasingly involved in firms’ major management decisions. Thus, the institutions’ ownership directly influences a firm’s prospects. Many studies show that institutional investors affect governance structures that, in turn, influence firm value and crucial corporate decisions. For example, Smith [1], Carleton, Nelson, and Weisbach [2], Del Guercio and Hawkins [3], and Gillan and Starks [4] note that institutional investors actively offer supervision for corporate decisions and policies at annual meetings by presenting shareholder proposals and negotiating with management. Additionally, institutional investors affect corporate decisions on multiple fronts, such as research and development (R&D) [5], earnings management [6], executive compensation [7,8], payout policies [9], mergers and acquisitions [10,11], and fundamental financial health [12] (the literature also provides evidence of ineffective and inactive institutional monitoring [1,3,13,14,15]; in a recent work, Chung et al. [12] argue that the mixed findings on institutional monitoring can be attributed to the heterogeneity of institutional investors: only long-term institutional investors and those with substantial firm ownership can monitor effectively).
As part of their incentive to monitor, institutional investors (particularly dedicated institutional investors—Bushee [16] and Bushee and Goodman [17] define dedicated institutional investors as those who normally have large shareholdings, maintain long-run perspectives, and support long-term management decisions that enhance firms’ sustainability and long-term performance; such investors are known to oppose myopic, short-term, profit-seeking management decisions, which are often supported by minority shareholders, who are mostly domestic individual investors) may be significantly interested in maintaining a firm’s long-term reputation and survival [10,12,16,18]. In particular, they are likely to be motivated by corporate social responsibility (CSR) preferences. These preferences may prompt corporate investments, which influence not only the sustainability and performance of firms, but also the wealth and shareholders’ rights. For example, El Ghoul et al. [19] report a tendency of firms with greater CSR engagement to have lower costs of equity. Wu and Lin [20] also find positive effects of CSR activities on financial capability of firms. Janney and Gove [21] indicate that CSR is beneficial to a firm because it helps protect the firm’s reputation even if scandals or major crises occur. Furthermore, Freeman [22] demonstrates that if firms seek opportunities for strategic competitive advantages, they must adapt to their stakeholders. For instance, Turban and Greening [23] find that CSR provides strategic advantages by helping firms attract and retain talented employees. Besides, effective monitoring of institutional investors and their motivations plays an important role in determining the directions and objectives of CSR because CEO overconfidence is negatively associated with CSR activities [24].
Previous studies find that CSR activities increase market value of firms, and that, in Asian countries, market participants evaluate firms’ CSR investments [25]. However, relatively few studies have been conducted on the Korean market, and meaningful outcomes for investors and CSR researchers in Asia are limited in number. The rapid economic growth of Korea and the prosperity of Korean firms have been disproportionately attributed to market participants. Thus, stakeholders are increasingly asking firms to fulfil social responsibilities and to protect their rights [26]. In response, Korean firms are increasing their investments in CSR [27], and managers’ awareness about their social duties is rising [28]. Shareholders and government authorities have increased the pressure on Korean firms to undertake CSR activities since the 1997 Asian financial crisis. For instance, they compelled firms to invest in projects related to CSR [29]. To build their social reputation, firms may also volunteer to highlight CSR activities [30].
However, as most institutional investors are corporate outsiders, we cannot overlook the possibility that institutional investors (particularly transient institutional investors) are affected by short-termism. Furthermore, such investors may negatively view CSR activities as requiring substantial investment and costs but providing uncertain future profits [31]. Long-term investors usually trade less frequently than short-term investors do. Therefore, short-term investors can threaten a firm’s management by liquidating their shares. Such actions may send a negative signal to other investors and create downward price pressure, forcing managers to chase short-term goals, which can harm long-term firm value. For instance, Bushee [16] shows that corporate managers make myopic investment decisions when institutional investors in firms exhibit momentum trading and high turnover. Gaspar, Massa, and Matos [32] find that if firms are owned by short-term investors, they fare worse in takeovers regardless of whether they are acquirers or targets. Yan and Zhang [33] report that short-term institutions often have good information and tend to trade actively by exploiting their informational advantage. Burns, Kedia, and Lipson [34] note that ownership by short-term institutions is positively related to the likelihood and severity of financial misreporting.
The empirical evidence on the association between firms’ CSR levels and their institutional ownership is mixed. For example, Johnson and Greening [35] find a significant positive relationship between CSR and institutional ownership. However, Graves and Waddock [36] find no relationship between the two. More recent evidence is also ambiguous. Cox, Brammer, and Millington [37] and Neubaum and Zahra [38] report a positive relationship between CSR and institutional investors whose investment horizons are long-term. Moreover, Cox and Wicks [39] and Oh, Chang, and Martynov [40] document a positive relationship between long-term ownership by pension funds and CSR. In contrast, Barnea and Rubin [41] and Dam and Scholtens [42] find no significant association between institutional investors and CSR.
We conjectured that the inconsistency in previous findings originated from the coarse classification of institutional investors. If dedicated institutional investors, who take a long-term perspective, play a dominant role in determining a firm’s management decisions, the increased institutional ownership alleviates CSR investments. However, if transient institutional investors have a greater influence on firms’ investment decisions, then institutional ownership negatively affects CSR levels. To understand these contrasting roles, we considered institutional blockholders (i.e., institutional investors with large shareholdings) that hold at least a 5% share in an investee firm and explore their effect on firms’ CSR activities.
We focused specifically on the largest institutional blockholder in Korea, the Korean National Pension Service (KNPS). In addition to CSR trade-offs, institutional monitoring demands time, resources, and expertise, all of which are costly. Thus, investors with significant shareholdings are most likely to engage in monitoring because they can reap sufficient benefits from CSR. Chen, Harford, and Li [10] demonstrate that not all institutions with a long-term horizon have the incentives and methods to monitor firm’s management. They show that the extent to which institutional investors hold shares is an important factor affecting their influence on firms’ activities, because institutional investors with large shareholdings cannot readily liquidate their positions even when they are not satisfied with corporate decisions. Thus, following Chen, Harford, and Li [10], we defined institutional ownership with a large shareholding as ownership, held by an institution, that accounts for at least 5% of a firm’s shares outstanding at the end of the year.
We focused on firms’ CSR activities in Korea, a leading emerging market in which the importance of CSR is increasing. This provided us with a unique data set developed by the Citizens’ Coalition for Economic Justice (CCEJ). We employed the proprietary Korea Economic Justice Institute (KEJI)-CSR index as a proxy for a CSR activity of a firm (the KEJI was formerly known as the CCEJ. For more information, see http://www.ccej.or.kr/index.php?mid=page_org_7). The unregulated economic dominance of chaebols and their affiliates has hindered efficient corporate governance for a long time in Korea. Even large institutional investors are under the influence of chaebols. Naturally, it is difficult to dissolve such complicated bonds, which are a combination of the various groups’ interests. Nonetheless, the government’s efforts, such as chaebol reforms, deserve mention because they have successfully connected corporate investment with CSR. Therefore, we focused on the institutional blockholders’ role of intensifying the pressure on CSR by examining the long-term advantages and possible disadvantages of CSR investments for managers and stakeholders.
We continued to provide evidence on the effectiveness of CSR monitoring within the framework of a trade-off between control and liquidity. Next, we discussed the moderating effects of R&D on the relationship between CSR and institutional blockholdings from a long-term perspective. Furthermore, specific aspects of the CSR index were examined, which we related to institutional blockholdings to comprehend concerns and interests of institutional investors linked to CSR.
Our study makes several contributions to the literature. First, it shows the weak role of institutional investors in CSR activities and adds to the body of research on institutional monitoring in emerging markets. Second, it examines subdimensions of CSR. Finally, our robust findings suggest that Korea’s largest institutional investors do not play an important role in promoting CSR activities in emerging markets. In those markets, commitment of firms to CSR is essential for their long-term prosperity.
2. Institutional Monitoring and CSR in the Korean Market
Oh, Chang, and Martynov [40] report a positive association between CSR and institutional ownership in the Korean market. Thus, they suggest that institutional monitoring positively influences firms’ CSR activities. However, their sample spans only a year, and, therefore, their empirical evidence is highly biased. Additionally, their imprecise classification of institutional investor intensity is another problem. For instance, they regard public pension funds as stronger monitoring institutions than insurance companies, securities firms, and investment banks.
The related literature divides institutional investors into two groups: pressure-sensitive and pressure-insensitive. Some institutions, including banks or insurance companies, are very sensitive to pressure and tend to string along (or collude) with firms’ boards to maintain existing or potential business relationships. Conversely, some institutions, including mutual funds and independent investment advisors, are insensitive to pressure; tend to have weaker business relationships with firms. Therefore, it is more probable that they exert monitoring efforts. Brickley, Lease, and Smith [43] demonstate that pressure-sensitive institutions have limited investment and business relationships with their investee firms. Hartzell and Starks [7] find that institutional investor activism is more noticeable in pressure-insensitive institutions. Moreover, investment banks and securities firms are not readily differentiable in the Korean market because their activities largely overlap. Thus, our study considers a large data sample of firms over a decade, thereby providing robust empirical results, and focuses on institutional blockholders that cannot be misclassified.
The Korean market provides a unique environment in which to investigate the relationship between institutional blockholdings and CSR. In particular, many Korean firms have been influenced by chaebols (i.e., family-controlled business conglomerates) for long. The Korea Fair Trade Commission announced that, as of 2015, chaebols (e.g., the Samsung, Hyundai, Doosan, GS, and LG groups) consisted of 61 business conglomerates and 1696 subsidiaries. The total market value of chaebols exceeds KRW 2258 trillion, and they constitute a considerable portion of the firms listed on the Korea Exchange (KRX). Most chaebol-affiliated firms are run by owner-managers. Therefore, the board of directors is usually made up of companions of the chaebol families and insiders, as a result, corporate decision-making is not very transparent [44]. This weak internal governance structure in chaebol-affiliated firms enables managers to prioritize their interests at the expense of those of stakeholders. Hence, institutional monitoring could significantly affect corporate decision-making as an external governance mechanism in the Korean market, especially when institutions own significant percentages of stock.
3. Sample Data
We obtained financial data on the sample firms from DataGuidePro, a product of FnGuide, which provides data on the South Korean financial market. DataGuidePro includes comprehensive information on KRX-listed firms and is equivalent to the U.S. Compustat database. FnOwnership, also managed by FnGuide, provides ownership data for each blockholder in each company. Since 2004, Korean legislation has mandated that any blockholder owning 5% or more shares of an investee firm in the stock market must report details of its all equity positions to the Financial Supervisory Service, which is equivalent to the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. FnGuide compiles these mandatory filings and gathers ownership data on shareholders who own at least 5% of an investee firm’s shares outstanding. Thus, our sample includes only those firms for which KNPS holds 5% or more of the shares outstanding. The final sample consists of 554 Korean firm-year observations for the period from 2009 to 2017.
Following Chen, Harford, and Li [10], we defined the variable KNPS_BIO as KNPS blockholdings that include at least 5% of a firm’s shares outstanding. In addition to the disclosure requirements for shares above this level, blockholders’ sizable stakes incentivize them to bear the costs of monitoring managerial behavior, as their large shareholdings (5% or more) and low liquidities render them long-term investors. Within the passive institutional monitoring frameworks proposed by Edmans [45] and Admati and Pfleiderer [46], stock trading and the threat of selling off shares are the key mechanisms used to motivate or discipline managers. We obtained data for KNPS_BIO at the end of the latest quarter before the period for which the three accounting earnings attributes are estimated. For example, the proxies for the accounting earnings attributes estimated over the fiscal period from May 2009 to April 2010 are linked to blockholders’ ownership at the end of March 2009.
We employed the KEJI-CSR index (K_CSR) as a proxy for the firms’ CSR activities. This CSR index is highly credible and is used for empirical analysis and the annual Good Corporation Awards (due to the lack of access to Korean CSR data, little research has been conducted in this market. Our study analyzes the longest period available in the CCEJ’s data sets). It evaluates firms using six categories: fairness, financial soundness, consumer protection, social charity/aid, employee satisfaction, and environmental commitment. The maximum sum of the scores of the individual components is 100.
Because our study examines the effect of institutional monitoring on CSR activities of firms, we must control for other factors, which may influence such activities and are related to institutional ownership. For this purpose, we constructed characteristic variables of firms. We also used cash flows from operating activities (CASHF), R&D expenses (RNDS), leverage (LEV), the book-to-market ratio (BM), firm size (SIZE), the return on assets (ROA), Tobin’s Q (Q), the Herfindahl–Hirschman Index (HHI), and the standard deviation of daily stock returns (SD) as controls.
Previous studies document that performance, risk, liquidity, and firm size are related to institutional ownership. Waddock and Graves [47] report that size predicts institutional ownership and that larger firms are more likely to be subject to external pressures. Hong, Kubik, and Scheinkman [48] suggest that financial slack affects CSR activities of a firm, and that leverage and asset tangibility (estimated by R&D expenses) can measure the credit constraints of a firm. Moreover, McWilliams and Siegel [49] show that R&D expenses are crucial factors that can affect CSR adoption. Gompers and Metrick [50] demonstrate that the return on assets and Tobin’s Q, as measures of firm performance, are linked to institutional ownership. We also considered the book-to-market ratio because it is related to CSR [19]. Surroca and Tribó [51] find that the operational cash flow of a firm can explain its CSR activities. Campbell [52] develops the return volatility index as an indicator of a stock’s liquidity. In addition, the Herfindahl–Hirschman Index, as a measure of market competitiveness, influences CSR.
Table 1 presents descriptive statistics for the sample. Specifically, we report the mean, standard deviation, 25th percentile, median, 75th percentile, and minimum and maximum values of the key variables during the sample period. We found that when the KNPS owns more than 5% of a firm’s shares, it owns approximately 8% (with a maximum of approximately 15%) of the total shares outstanding of the firm on average. The standard deviation of KNPS_BIO is approximately 2.4%, suggesting that it has sufficient variation in the sample. Moreover, the CSR indexes based on a scale of 100 are centered on a mean of approximately 64 (with a maximum of around 76 and minimum of around 52). This finding suggests that CSR adoption by Korean firms is not well established. In addition, the sample contains relatively large firms that are better able to engage in relevant activities, offering further scope for CSR development, as in other emerging markets.

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics.
Figure 1 presents the yearly cross-sectional averages of KNPS_BIO and K_CSR for the sample period. The purple dotted line represents KNPS_BIO. As shown, KNPS blockholdings have increased consistently in recent years, suggesting that their influence on firms is becoming increasingly important. Our analyses focused on the relationship between future CSR activities and KNPS blockholdings to incorporate the time it takes for institutional monitoring to influence managerial decisions and for engagement in CSR to materialize. Figure 1 does not clearly indicate that CSR activity tends to comove with KNPS_BIO, but shows the relationship at the aggregate level only. Thus, the causal relationship at the firm level also needs to be investigated.
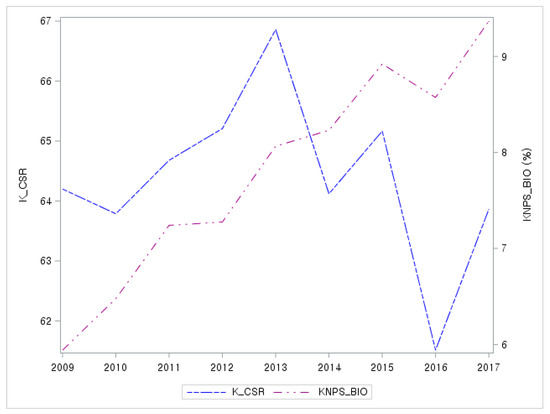
Figure 1.
Annual cross-sectional averages of KNPS blockholdings that include at least 5% of a firm’s shares outstanding (KNPS_BIO) and KEJI-CSR index (K_CSR) from 2009 to 2017.
4. Empirical Analysis
We started our study by determining the correlations between the key variables. We examined the relationship between KNPS_BIO and K_CSR, and Table 2 shows the Pearson’s (contemporaneous) correlation coefficients between these variables. The results show that KNPS_BIO is not significantly positively correlated with K_CSR. Thus, firms with KNPS blockholdings do not necessarily allocate more resources to CSR activities, providing new insights into the previously documented relationship between institutional ownership with large shareholdings and CSR activities of firms. However, because the correlations are contemporaneous, we could not establish a causal relationship between the two variables. Thus, we employed lagged KNPS_BIO to ease this concern in our regression analyses. Multivariate analyses are required considering the significant associations between the other variables.

Table 2.
Correlation analysis.
In Table 3, we explore the association between lagged institutional ownership and concurrent CSR activities through univariate analysis. By taking into account lagged KNPS blockholdings, we allowed sufficient time for the KNPS to undertake monitoring and for their efforts to result in CSR activities. Thus, if the KNPS promotes CSR activities of firms, we should find a positive association between K_CSR and lagged KNPS_BIO. Specifically, firms are grouped into quartiles considering the average lagged KNPS_BIO, which is measured prior to the end of the year for which K_CSR is captured. K_CSR does not monotonically increase as KNPS_BIO increases. Furthermore, the difference between K_CSR of the two extreme quintiles is not statistically significant. This finding does not provide evidence to support our conjecture that institutional influence, measured by KNPS blockholdings, significantly impacts firms’ CSR adoption. Overall, the findings suggest that the KNPS is not willing to incur the monitoring costs of engaging with firms in which it has large shares to address potential CSR risks.

Table 3.
Portfolio sorting approach.
To incorporate all the information provided by CSR activities, we used panel regressions with K_CSR as the dependent variable. Furthermore, we controlled for other firm characteristics that may affect CSR activities. We included a market dummy (MARKET_D) because CSR activities can be different by the market where stocks of firms are listed. Here, MARKET_D takes a value of one if a firm’s stock is listed on the Korea Composite Stock Price Index 200 (KOSPI 200) and a value of zero otherwise. KOSPI 200 firms are typically large. Specifically, we used the following model to investigate the association between lagged institutional ownership (D_IO/F_IO) and K_CSR:
K_CSRi,t = α + β1·KNPS_BIOi,t−1 + β2·SIZEi,t−1 + β3·LEVi,t−1 + β4·Qi,t−1 + β5·RNDSi,t−1 + β6·BMi,t−1 + β7·CASHFi,t−1 + β8·SDi,t−1 + β9·HHIi,t−1 + β10·MARKET_Di,t−1 + εi,t.
Following Petersen [53], we evaluated panel regression models to reflect cross-sectional and time-series correlations. We calculated the t-statistics depending on two-way clustered standard errors. Table 4 shows the estimation results. The first column reveals that the coefficient of lagged KNPS_BIO is not statistically significant. This result does not support the previous finding that institutional blockholders are actively involved in CSR activities in developed markets. Additionally, it is not consistent with recent study that institutional investors may engage in modifying CSR policies of firms using voting and CSR shareholder proposals [54] and through personal commitment to CSR issues [55]. However, the relationship between serial CSR activities may weaken this finding if CSR adoption of firms is not significantly different over time. To handle this potential issue, lagged K_CSR was included in the models to control for the serial correlation between K_CSR values over time. However, even after controlling for lagged K_CSR, the coefficient of lagged KNPS_BIO in the second column is not statistically significant. Overall, the findings in the first two columns do not support the institutional blockholder monitoring hypothesis.

Table 4.
Influence of Korean National Pension Service (KNPS) blockholdings on corporate social responsibility (CSR) activities.
In the third and fourth columns of Table 4, we specifically examine the effect of lagged KNPS blockholdings on CSR activities for chaebols. Chaebols’ weak internal governance may engender information asymmetry between managers and outside shareholders. Thus, we included a dummy variable that indicates whether a firm is a chaebol affiliate (Chaebol_Dummy) as well as the interactions between lagged KNPS blockholdings and the chaebol dummy. We used the annual classifications of the Korea Fair Trade Commission to define firms as chaebol affiliates or non-chaebol affiliates. We found that only chaebol affiliates show a negative and significant association with K_CSR (at the 5% level). This result is understandable because chaebols and their affiliates favor profit-seeking behavior in the short term, whereas CSR engagement requires a long-term view. Notably, we discovered that the coefficient of the interaction between Chaebol_Dummy and KNPS_BIO is not statistically significant. This outcome substantiates the passive monitoring stance taken by the KNPS with respect to CSR engagement in chaebols. Furthermore, the results still hold when we included lagged K_CSR.
Next, we investigated whether the KNPS is interested in the components of CSR activities for its large blockholdings. In particular, we estimated the panel regression models in Equation (1) with the individual components of K_CSR as dependent variables. Table 5 shows the empirical results based on the six dimensions of K_CSR. We report that lagged KNPS_BIO is not significantly linked to any of the six dimensions of K_CSR: financial soundness (C1), fairness (C2), social charity/aid (C3), consumer protection (C4), environmental commitment (C5), and employee satisfaction (C6). This result implies that the KNPS is not necessarily more concerned about specific facets of CSR.

Table 5.
Influence of KNPS blockholdings on components of CSR activities.
To further explore the role of institutional blockholders in the CSR activities of Korean firms, we conducted additional empirical analyses. First, we examined the circumstances where institutional blockholders more actively monitor managers. Next, we focused on monitoring incentives based on the trade-off between control and liquidity. Because institutional blockholders have large investment positions, they inherently face liquidity issues when they obtain adverse information about investee firms, increasing the likelihood that these investors will intervene to correct managerial failures [13,14]. Thus, the KNPS should be more (or less) willing to wield monitoring pressure on low- (or high-) liquidity firms in which it is a large blockholder. To better comprehend this relationship, we measured the yearly average of the daily illiquidity ratio [56], relying on volume and daily stock return data from the KRX. Then, we used that ratio as a proxy for the investee firm’s level of liquidity:
Following Amihud [56], is the return of stock i on day d, is the number of trading days in a year, and is the trading volume of stock i (in USD) on day d. Using this measure, we split the firms into two groups (i.e., low- and high-liquidity firms) and showed the results after repeating the baseline regression in the first and second columns of Table 6. We found that the monitoring of institutional blockholders on CSR activities is effective only in relatively illiquid surroundings. The coefficient of KNPS_BIO is not statistically significant, as shown in the first column in the table. In addition, the relationship between KNPS_BIO and K_CSR has no explanatory power for liquid firms. Panel B considers the effects of various interactions between the key variables. Overall, these results show that the KNPS is not likely to monitor CSR activities when firms confront high liquidity costs. Finally, we examined the effect of institutional blockholders on CSR activities in firms with different investment opportunities. Greater investment opportunities are reflected by higher R&D expenses (RNDS) and are often accompanied by higher agency costs [57,58] due to increased information asymmetry. However, R&D-intensive firms are concerned with long-term growth, and R&D can produce unique products and services, both of which contribute to firms’ profitability. As is already known, institutional blockholders have a mostly long-term investment horizon and can punish myopic corporate decisions. Thus, we supposed that their investment objectives were in line with those of R&D-intensive firms. Considering the long-term advantages of CSR for both shareholder and stakeholder welfare and in alleviating agency conflicts [49], we expected that institutional blockholders will wield more (or less) pressure on firms that invest more (or less) in R&D. Following Ayers, Ramalingegowda, and Yeung [57], we employed RNDS as an indicator for disparate levels of investment opportunities and expected greater (lower) monitoring effectiveness in firms with high (low) RNDS ratios.

Table 6.
Moderating effect of liquidity and R&D on the influence of KNPS blockholdings on CSR activities.
Table 6 show the results of this subsample in the third and fourth columns. Observing the estimation results for each subsample, we do not find a stronger monitoring effect on CSR activities for firms with high RNDS. This result corroborates our previous findings that KNPS blockholdings have no significant impact on corporate decisions (e.g., CSR activities), especially in the presence of adverse information. Overall, our results show that the KNPS does not seem to actively promote CSR to yield long-term benefits in its large blockholdings.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we examine whether institutional investors influence CSR. We find that institutional investors do not necessarily affect CSR activities of firms in the Korean financial market, even when these investors are large blockholders. This study contributes to the literature on institutional investors and CSR, most of which focuses on U.S. firms. In particular, we show that lagged KNPS blockholdings are not significantly correlated with firms’ CSR activities. Furthermore, the KNPS does not significantly impact any dimension of CSR activities. Our findings are robust even after considering past CSR activities.
Overall, the findings are inconsistent with large institutional blockholders playing an active role and suggest that they do not necessarily use their ownership to promote firms’ commitment to CSR. Regarding a reason for this finding, it is possible that institutional blockholders, as outside shareholders, do not effectively curb the managerial bias of CEOs whose overconfidence is negatively associated with CSR activities [24]. (However, one may argue that this could be attributed to the culture effect of the CEOs’ overconfidence toward CSR activities (see, for example, Tang et al. [58] and McCarthy et al. [59]).) This leads to a managerial implication that the exercise of stewardship can promote active CSR even in the presence of erratic CEOs.
This study adds to the recent literature examining firm performance and CSR activities. Loh, Thomas, and Wang [60] demonstrate that sustainability reporting practices are positively correlated with firm value for Singapore-listed companies. This positive relationship also holds for firms in Hong Kong and China [61]. Recently, Hategan and Curea-Pitorac [62] corroborated the positive effect of CSR activities on firm value. Notably, Kim, Park, and Lee [63] document that the ownership structure in firms largely affects the CSR–firm value nexus in Korea. Also, this work contributes to the large body of literature in institutional monitoring role [64,65,66,67].
Moreover, the Korean market draws researchers’ interests to study CSR because chaebols dominate the market. Chaebols are typically controlled by family members, who have substantial power over corporate decision-making, and, therefore, are liable to myopic behavior and self-interest at the cost of outside shareholders and other stakeholders. This unique market environment allows us to fill an important gap in the literature on CSR and firm value.
However, this study did not discuss some agendas, and, thus, can be extended beyond this research. First, as financially unconstrained firms with overconfident CEOs can engage in extravagant CSR spending [24], further investigations regarding corporate governance are warranted that focus on the roles of broader stakeholders, including institutional investors and creditors. Second, the implications provided for the Korean market can be tested for the U.S. and other major markets, for example, via the MSCI KLD 400 Social Index. We leave these tasks for future studies.
Author Contributions
C.Y.C. designed and performed the research, and analyzed the data. C.Y.C. wrote the paper. D.C., P.M.S.C. and J.H.C. revised the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the research program of Kookmin University in Korea.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Smith, M.P. Shareholder activism by institutional investors: Evidence from CalPERS. J. Financ. 1996, 51, 227–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carleton, W.T.; Nelson, J.A.; Weisbach, M.S. The influence of institutions on corporate governance through private negotiations: Evidence from TIAA-CREF. J. Financ. 1998, 53, 1335–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Guercio, D.; Hawkins, J. The motivation and impact of pension fund activism. J. Financ. Econ. 1999, 52, 293–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillan, S.L.; Starks, L.T. Corporate governance proposals and shareholder activism: The role of institutional investors. J. Financ. Econ. 2000, 57, 275–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Barr, W.M.; Conley, J.M.; Brancato, C.K. Fortune and Folly: The Wealth and Power of Institutional Investing; Irwin Professional Pub: Chicago, IL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, R.; Firth, M.; Kim, J. Institutional monitoring and opportunistic earnings management. J. Corp. Financ. 2002, 8, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartzell, J.C.; Starks, L.T. Institutional investors and executive compensation. J. Financ. 2003, 58, 2351–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janakiraman, S.; Radhakrishnan, S.; Tsang, A. Institutional investors, managerial ownership, and executive compensation. J. Account. Audit. Financ. 2010, 25, 673–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinstein, Y.; Michaely, R. Institutional holdings and payout policy. J. Financ. 2005, 60, 1389–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Harford, J.; Li, K. Monitoring: Which institutions matter? J. Financ. Econ. 2007, 86, 279–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.A.; Massa, M.; Matos, P. Shareholders at the gate? Institutional investors and cross-border mergers and acquisitions. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2010, 23, 601–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, K.; Zykaj, B.B. Institutional monitoring: Evidence from the F-score. J. Bus. Financ. Account. 2015, 42, 885–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffee, J.C. Liquidity versus control: The institutional investor as corporate monitor. Columbia Law Rev. 1991, 91, 1277–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhide, A. The hidden costs of stock market liquidity. J. Financ. Econ. 1993, 34, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrino, R.; Sias, R.W.; Starks, L.T. Voting with their feet: Institutional ownership changes around forced CEO turnover. J. Financ. Econ. 2003, 68, 3–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushee, B.J. The influence of institutional investors on myopic R&D investment behavior. Account. Rev. 1998, 73, 305–333. [Google Scholar]
- Bushee, B.J.; Goodman, T.H. Which institutional investors trade based on private information about earnings and returns? J. Account. Res. 2007, 45, 289–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushee, B. Do institutional investors prefer near-term earnings over long-run value? Contemp. Account. Res. 2001, 18, 207–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ghoul, S.; Guedhami, O.; Kwok, C.C.; Mishra, D.R. Does corporate social responsibility affect the cost of capital? J. Bank. Financ. 2011, 35, 2388–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.I.; Lin, H.F. The correlation of CSR and consumer behavior: A study of convenience store. Int. J. Mark. Stud. 2014, 6, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janney, J.J.; Gove, S. Reputation and corporate social responsibility aberrations, trends, and hypocrisy: Reactions to firm choices in the stock option backdating scandal. J. Manag. Stud. 2011, 48, 1562–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R.E. Strategic Management: A Stakeholder Approach; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Turban, D.B.; Greening, D.W. Corporate social performance and organizational attractiveness to prospective employees. Acad. Manag. J. 1997, 40, 658–672. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.-H.; Byun, J.; Choi, P.M.S. Managerial overconfidence, corporate social responsibility, and financial constraints. Sustainability 2020, 12, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, Y.L.; Tan, W.; Ahn, H.J.; Zhang, Z. Does corporate social responsibility matter in Asian emerging markets? J. Bus. Ethics. 2010, 92, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y.S.; Jun, H. The shaping of corporate social responsibility in Korea’s economic development. Glob. J. Bus. Manag. Account. 2011, 1, 10–20. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, B. Contextualising CSR in Asia: Corporate Social Responsibility in Asian Economies; Lien Centre for Social Innovation: Singapore, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, E.; Chun, S.; Choi, D. International diversification, corporate social responsibility, and corporate governance: Evidence from Korea. J. Appl. Bus. Res. 2015, 31, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Aguilera, R.V. CSR dynamics in South Korea and Japan: A comparative analysis. In Corporate Social Responsibility: A Case Study Approach; Mallin, C., Ed.; Edward Elgar Publishing Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 123–147. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, B.B.; Lee, D.; Park, Y. Corporate social responsibility, corporate governance and earnings quality: Evidence from Korea. Corp. Gov. Int. Rev. 2013, 21, 447–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Park, K.; Ryu, D. Corporate environmental responsibility: A legal origins perspective. J. Bus. Ethics 2017, 140, 381–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, J.M.; Massa, M.; Matos, P. Shareholder investment horizons and the market for corporate control. J. Financ. Econ. 2005, 76, 135–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.S.; Zhang, Z. Institutional investors and equity returns: Are short-term institutions better informed? Rev. Financ. Stud. 2009, 22, 893–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, N.; Kedia, S.; Lipson, M. Institutional ownership and monitoring: Evidence from financial misreporting. J. Corp. Financ. 2010, 16, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.A.; Greening, D.W. The effects of corporate governance and institutional ownership types on corporate social performance. Acad. Manag. J. 1999, 42, 564–576. [Google Scholar]
- Graves, S.B.; Waddock, S.A. Institutional owners and corporate social performance. Acad. Manag. J. 1994, 37, 1034–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, P.; Brammer, S.; Millington, A. An empirical examination of institutional investor preferences for corporate social performance. J. Bus. Ethics 2004, 52, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubaum, D.O.; Zahra, S.A. Institutional ownership and corporate social performance: The moderating effects of investment horizon, activism, and coordination. J. Manag. 2006, 32, 108–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, P.; Wicks, P.G. Institutional interest in corporate responsibility: Portfolio evidence and ethical explanation. J. Bus. Ethics 2011, 103, 143–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, W.Y.; Chang, Y.K.; Martynov, A. The effect of ownership structure on corporate social responsibility: Empirical evidence from Korea. J. Bus. Ethics 2011, 104, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnea, A.; Rubin, A. Corporate social responsibility as a conflict between shareholders. J. Bus. Ethics 2010, 97, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, L.; Scholtens, B. Does ownership type matter for corporate social responsibility? Corp. Gov. 2012, 20, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brickley, J.A.; Lease, R.C.; Smith, C.W. Ownership structure and voting on antitakeover amendments. J. Financ. Econ. 1988, 20, 267–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.J. Ownership structure, expropriation, and performance of group-affiliated companies in Korea. Acad. Manag. J. 2003, 46, 238–253. [Google Scholar]
- Edmans, A. Does the stock market fully value intangibles? Employee satisfaction and equity prices. J. Financ. Econ. 2011, 101, 621–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Admati, A.R.; Pfleiderer, P. The “Wall Street Walk” and shareholder activism: Exit as a form of voice. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2009, 22, 2645–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddock, S.A.; Graves, S.B. The corporate social performance–financial performance link. Strat. Manag. J. 1997, 18, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Kubik, J.D.; Scheinkman, J.A. Financial Constraints on Corporate Goodness; Working paper No. w18476; National Bureau of Economic Research: Boston, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- McWilliams, A.; Siegel, D. Profit maximizing corporate social responsibility. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2001, 26, 504–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gompers, P.A.; Metrick, A. Institutional investors and equity prices. Q. J. Econ. 2001, 116, 229–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surroca, J.; Tribó, J.A. Managerial entrenchment and corporate social performance. J. Bus. Financ. Account. 2008, 35, 748–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.L. Why would corporations behave in socially responsible ways? An institutional theory of corporate social responsibility. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2007, 32, 946–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.A. Estimating standard errors in finance panel data sets: Comparing approaches. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2009, 22, 435–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Guercio, D.; Tran, H. Institutional investor activism. In Socially Responsible Finance and Investing; Baker, H.K., Nofsinger, J.R., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Newark, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 359–380. [Google Scholar]
- Dimson, E.; Karakaş, O.; Li, X. Active ownership. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2015, 28, 3225–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amihud, Y. Illiquidity and stock returns: Cross-section and time-series effects. J. Financ. Mark. 2002, 5, 31–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, B.C.; Ramalingegowda, S.; Yeung, P.E. Hometown advantage: The effects of monitoring institution location on financial reporting discretion. J. Account. Econ. 2011, 52, 41–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Qian, C.; Chen, G.; Shen, R. How CEO hubris affects corporate social (ir) responsibility. Strateg. Manag. J. 2015, 36, 1338–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, S.; Oliver, B.; Song, S. Corporate social responsibility and CEO confidence. J. Bank. Financ. 2017, 75, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, L.; Thomas, T.; Wang, Y. Sustainability reporting and firm value: Evidence from Singapore-listed companies. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.J.; Sethuraman, K.; Lam, J.Y. Impact of corporate social responsibility dimensions on firm value: Some evidence from Hong Kong and China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hategan, C.-D.; Curea-Pitorac, R.-I. Testing the correlations between corporate giving, performance and company value. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.S.; Park, K.; Lee, S.H. Corporate social responsibility, ownership structure, and firm value: Evidence from Korea. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chung, C.Y.; Sul, H.K.; Wang, K. Does hometown advantage matter? The case of institutional blockholder monitoring on earnings management in Korea. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2018, 49, 196–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, P.M.S.; Chung, C.Y.; Hwang, J.H.; Liu, C. Heads I Win, Tails You Lose: Institutional Monitoring Of Executive Pay Rigidity. J. Financ. Res. 2019, 42, 789–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, P.M.S.; Chung, C.Y.; Liu, C. Self-attribution of overconfident CEOs and asymmetric investment-cash flow sensitivity. N. Am. J. Econ. Financ. 2018, 46, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.Y.; Hur, S.K.; Liu, C. Institutional investors and cost stickiness: Theory and evidence. N. Am. J. Econ. Financ. 2019, 47, 336–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).