Intelligence in Tourist Destinations Management: Improved Attention-based Gated Recurrent Unit Model for Accurate Tourist Flow Forecasting
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Traditional Methods in Tourist Flow Forecasting
1.2. Improved Attention-based Gated Recurrent Unit Model in Tourist Flow Forecasting
1.3. Web Search Index and Climate Comfort in Tourist Flow Forecasting
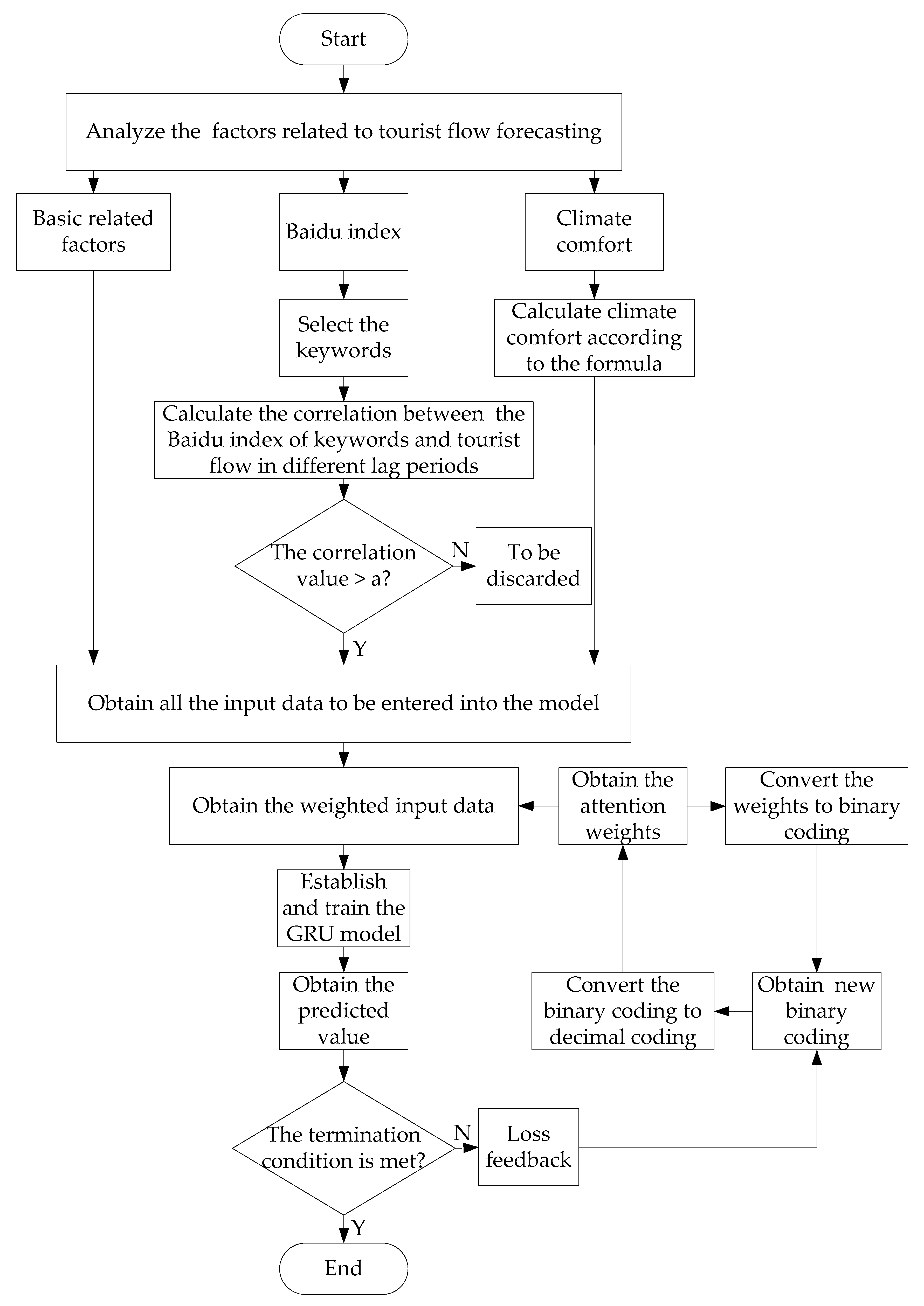
2. Methods
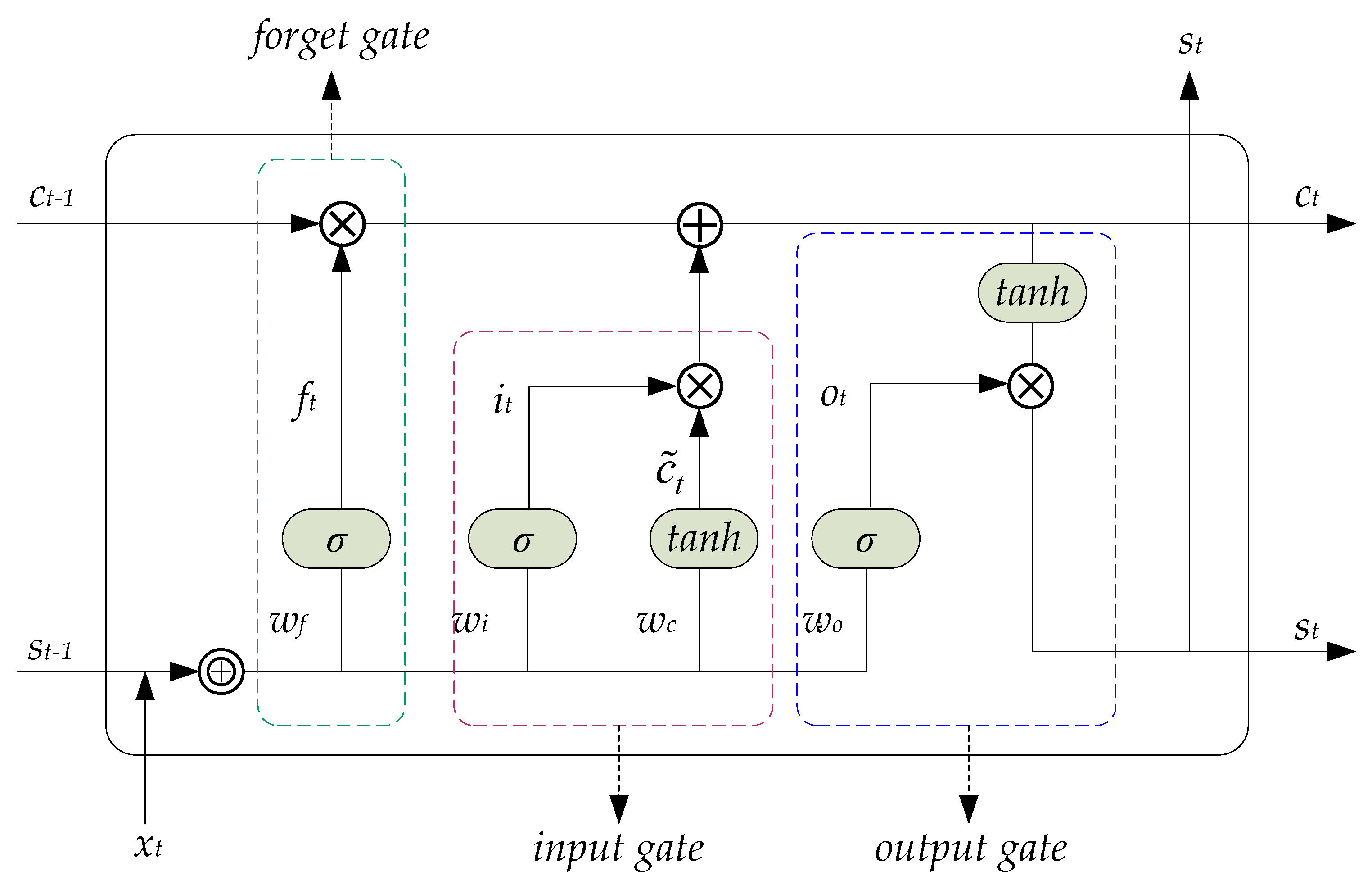
2.1. LSTM (GRU’s Precursor)
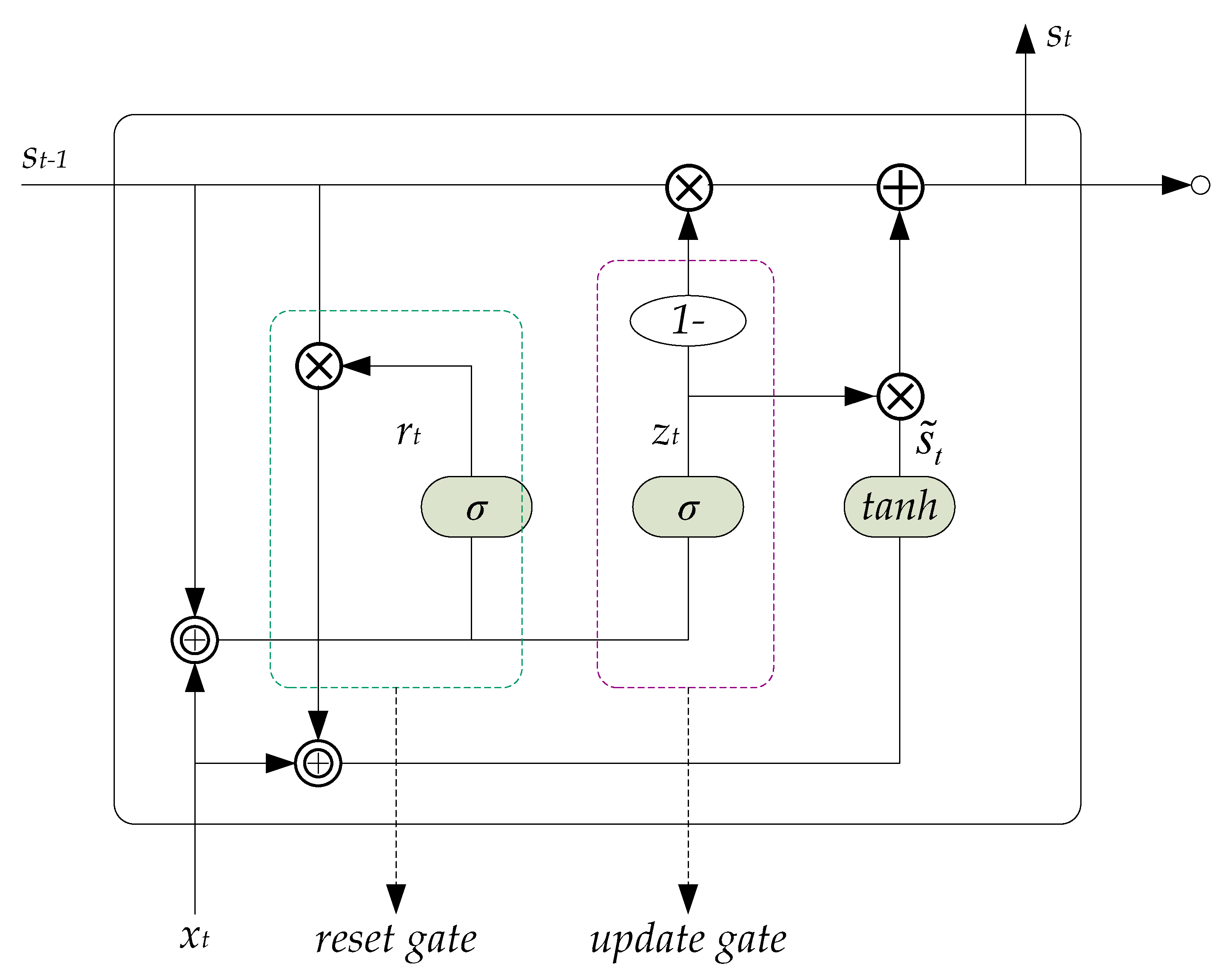
2.2. GRU
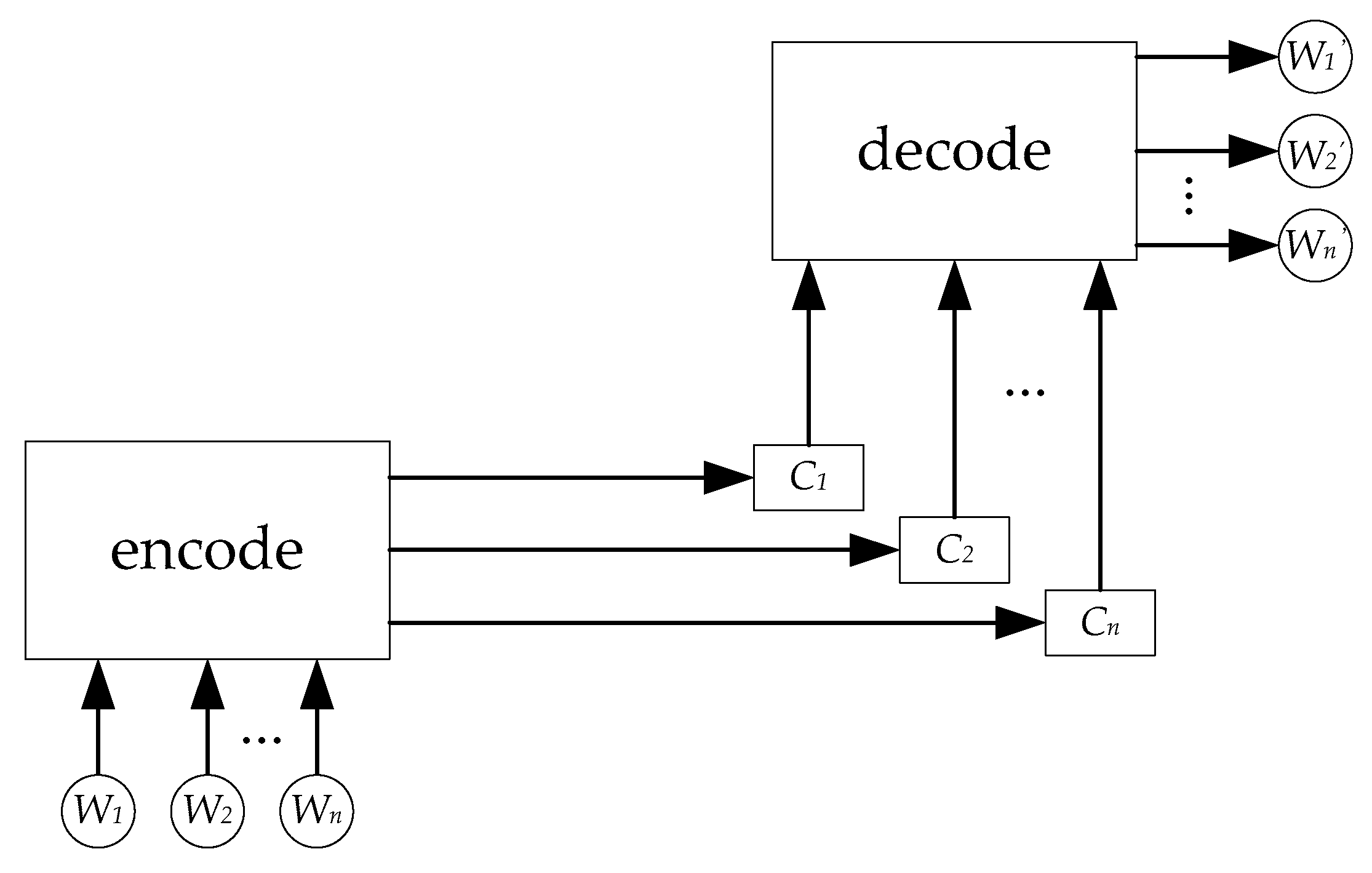
2.3. Attention Mechanism
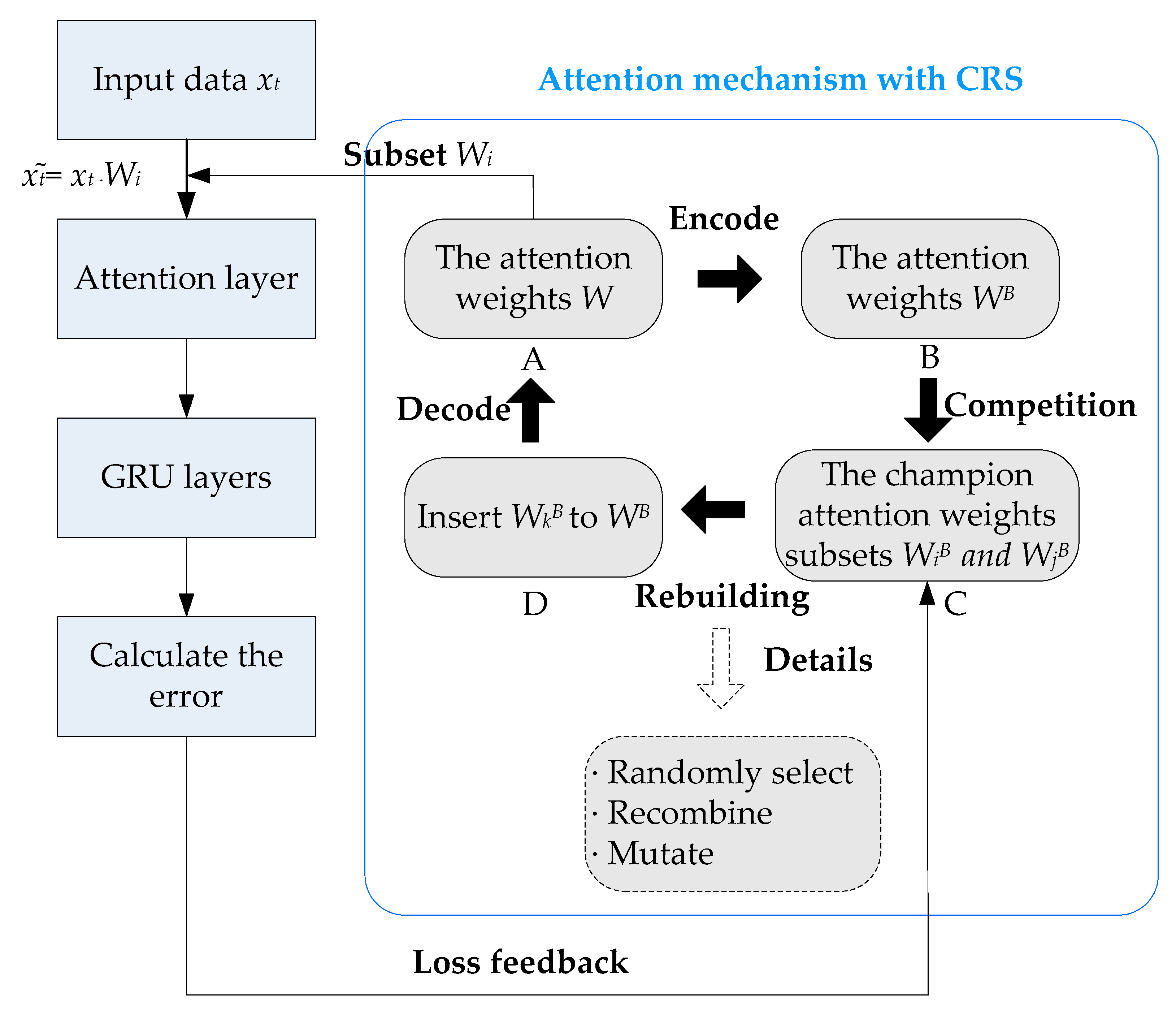
2.4. IA-GRU Model
3. Data Preparation
3.1. Basic Data
3.2. Baidu Index of Keywords
3.3. Climate Comfort
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Building IA-GRU Model
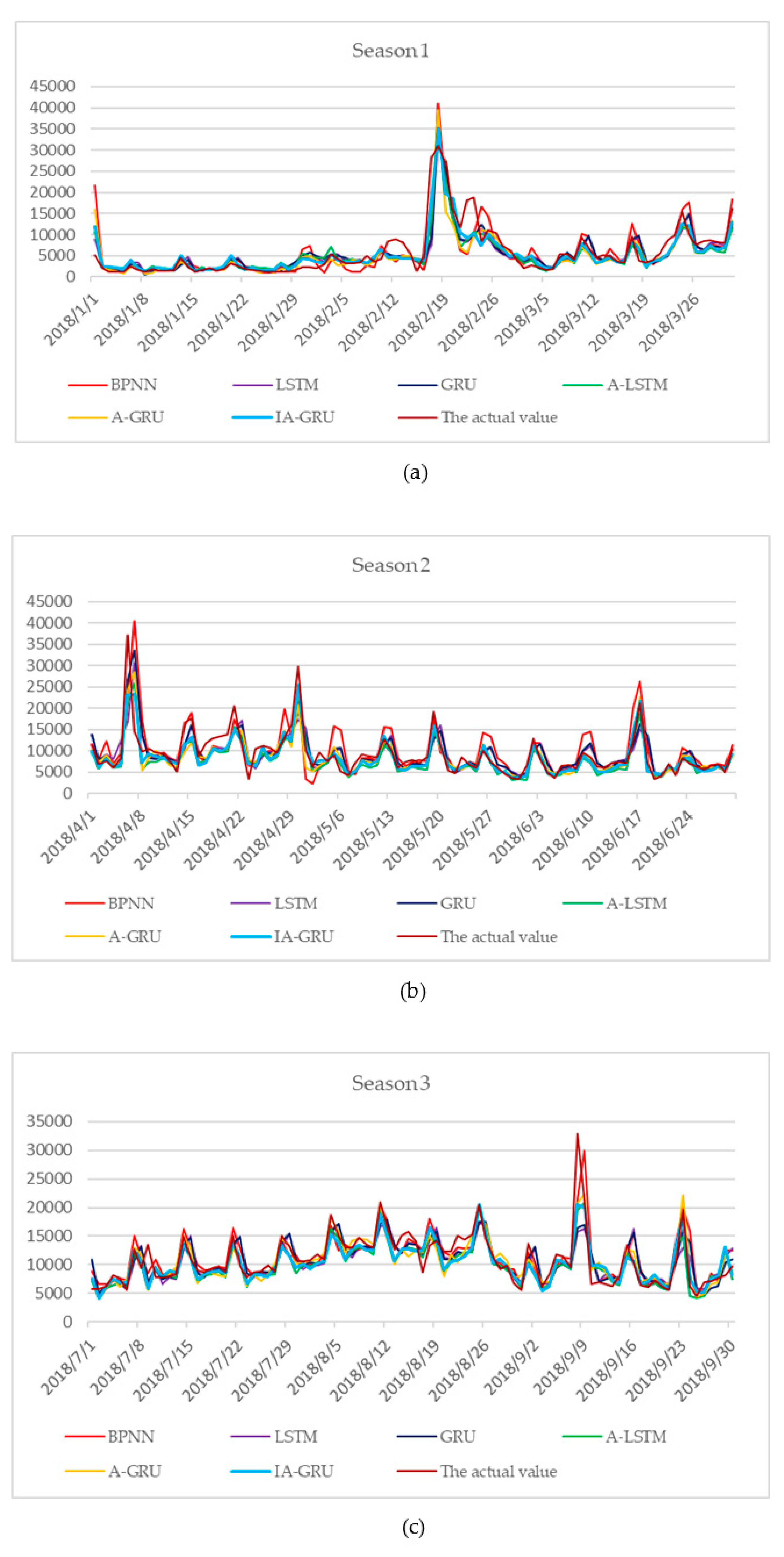
4.2. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J. Anhui Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Song, H.; Witt, S.F. Recent developments in econometric modeling and forecasting. J. Travel Res. 2005, 44, 82–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, C.; Dohnal, M.; Kathrada, M.; Law, R. A practitioners guide to time-series methods for tourism demand forecasting—A case study of Durban, South Africa. Tour. Manag. 2001, 22, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croes, R.R.; Vanegas, M., Sr. An econometric study of tourist arrivals in Aruba and its implications. Tour. Manag. 2005, 26, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, A.C.M.; Ramos, F.F. Modelling inbound international tourism demand to Portugal. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2002, 4, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, S.F.; Song, H.; Wanhill, S. Forecasting tourism-generated employment: The case of denmark. Tour. Econ. 2004, 10, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, F.-L. Forecasting tourism demand with ARMA-based methods. Tour. Manag. 2009, 30, 740–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Alana, L. Modelling international monthly arrivals using seasonal univariate long-memory processes. Tour. Manag. 2005, 26, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-F.; Chang, Y.-H.; Chang, Y.-W. Seasonal ARIMA forecasting of inbound air travel arrivals to Taiwan. Transportmetrica 2009, 5, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-Y.; Wang, C.-H. Support vector regression with genetic algorithms in forecasting tourism demand. Tour. Manag. 2007, 28, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.-C.; Dong, Y.; Chen, L.-Y.; Wei, S.-Y. SVR with hybrid chaotic genetic algorithms for tourism demand forecasting. Appl. Soft Comput. 2011, 11, 1881–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benardos, P.; Vosniakos, G.-C. Optimizing feedforward artificial neural network architecture. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2007, 20, 365–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, R.; Au, N. A neural network model to forecast Japanese demand for travel to Hong Kong. Tour. Manag. 1999, 20, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, R. Back-propagation learning in improving the accuracy of neural network-based tourism demand forecasting. Tour. Manag. 2000, 21, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.; Van Merriënboer, B.; Bahdanau, D.; Bengio, Y. On the properties of neural machine translation: Encoder-decoder approaches. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1259. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.; Van Merriënboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1078.1406. [Google Scholar]
- Soltau, H.; Liao, H.; Sak, H. Neural speech recognizer: Acoustic-to-word LSTM model for large vocabulary speech recognition. arXiv 2016, arXiv:09975.1610. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Yuan, J.; Chen, L. Short-term load forecasting using EMD-LSTM neural networks with a Xgboost algorithm for feature importance evaluation. Energies 2017, 10, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujeeb, S.; Javaid, N.; Ilahi, M.; Wadud, Z.; Ishmanov, F.; Afzal, M.K. Deep long short-term memory: A new price and load forecasting scheme for big data in smart cities. Sustainability 2019, 11, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cao, H. Prediction for tourism flow based on LSTM neural network. Proced. Comput. Sci. 2018, 129, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahdanau, D.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. arXiv 2014, arXiv:0473.1409. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Describing multimedia content using attention-based encoder-decoder networks. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2015, 17, 1875–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Song, D.; Chen, H.; Cheng, W.; Jiang, G.; Cottrell, G. A dual-stage attention-based recurrent neural network for time series prediction. arXiv 2017, arXiv:02971.1704. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Ke, S.; Zhang, J.; Yi, X.; Zheng, Y. GeoMAN: Multi-level Attention Networks for Geo-sensory Time Series Prediction. In Proceedings of the IJCAI, Stockholm, Sweden, 13–19 July 2018; pp. 3428–3434. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Hori, T.; Watanabe, S. Joint CTC-Attention Based End-to-End Speech Recognition Using Multi-Task Learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017; pp. 4835–4839. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, Q.; Yan, K.; Du, Y. Short-term photovoltaic power forecasting based on long short term memory neural network and attention mechanism. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 78063–78074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, D. Bi-directional long short-term memory method based on attention mechanism and rolling update for short-term load forecasting. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2019, 109, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.; Shan, Z.; Fang, Y.; Lin, C. An LSTM-based method with attention mechanism for travel time prediction. Sensors 2019, 19, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Kong, D.; Han, H.; Zhao, Y. EA-LSTM: Evolutionary attention-based LSTM for time series prediction. Knowl. Based Syst. 2019, 181, 104785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Benfu, L. A review of researches on the correlation between internet search and economic behavior. Manag. Rev. 2011, 23, 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.; Varian, H. Predicting the present with Google trends. Econ. Record 2012, 88, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangwayo-Skeete, P.F.; Skeete, R.W. Can Google data improve the forecasting performance of tourist arrivals? Mixed-data sampling approach. Tour. Manag. 2015, 46, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önder, I.; Gunter, U. Forecasting tourism demand with google trends for a major European city destination. Tour. Anal. 2016, 21, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Goh, C.; Hung, K.; Chen, J.L. Relative climate index and its effect on seasonal tourism demand. J. Travel Res. 2018, 57, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Liang, C.-Y.; Hong, W.-C.; Gu, D.-X. Forecasting holiday daily tourist flow based on seasonal support vector regression with adaptive genetic algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 26, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Pan, B.; Evans, J.A.; Lv, B. Forecasting Chinese tourist volume with search engine data. Tour. Manag. 2015, 46, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathopoulos, T.; Wu, H.; Zacharias, J. Outdoor human comfort in an urban climate. Build. Environ. 2004, 39, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Bi, W. Seasonal Variation Analysis and SVR Forecast of Tourist Flows During the Year: A Case Study of Huangshan Mountain. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Big Data Analysis (ICBDA), Beijing, China, 10–12 March 2017; pp. 921–927. [Google Scholar]

| Lag Period | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | … |
| Correlation | 1.000 | 0.718 | 0.443 | 0.324 | 0.243 | 0.197 | 0.256 | 0.341 | … |
| Lag Period | 365 | 366 | 367 | 368 | 369 | 370 | 371 | 372 | … |
| Correlation | 0.522 | 0.350 | 0.280 | 0.212 | 0.147 | 0.187 | 0.267 | 0.201 | … |
| lag Period | Huangshan | Huangshan Weather | Huangshan Tourism Guide | Huangshan Tourism | Huangshan Scenic Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.510 | 0.107 | 0.523 | 0.107 | 0.330 |
| 1 | 0.552 | 0.180 | 0.597 | 0.206 | 0.367 |
| 2 | 0.556 | 0.236 | 0.614 | 0.281 | 0.356 |
| 3 | 0.491 | 0.221 | 0.569 | 0.278 | 0.299 |
| 4 | 0.432 | 0.198 | 0.510 | 0.262 | 0.242 |
| 5 | 0.393 | 0.178 | 0.462 | 0.241 | 0.202 |
| 6 | 0.330 | 0.146 | 0.411 | 0.160 | 0.172 |
| 7 | 0.280 | 0.125 | 0.374 | 0.115 | 0.150 |
| … | … | … | … | … | … |
| 365 | 0.322 | 0.099 | 0.350 | 0.170 | 0.156 |
| 366 | 0.363 | 0.118 | 0.396 | 0.236 | 0.183 |
| 367 | 0.376 | 0.123 | 0.413 | 0.259 | 0.185 |
| 368 | 0.362 | 0.118 | 0.404 | 0.259 | 0.165 |
| 369 | 0.346 | 0.115 | 0.385 | 0.246 | 0.144 |
| 370 | 0.292 | 0.098 | 0.337 | 0.171 | 0.115 |
| 371 | 0.244 | 0.089 | 0.298 | 0.124 | 0.086 |
| 372 | 0.253 | 0.106 | 0.293 | 0.170 | 0.085 |
| lag Period | Huangshan Tickets | Huangshan First-Line Sky | Anhui Huangshan | Huangshan Weather Forecast | Huangshan Guide |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.232 | 0.209 | 0.372 | 0.188 | 0.354 |
| 1 | 0.281 | 0.198 | 0.462 | 0.324 | 0.463 |
| 2 | 0.275 | 0.184 | 0.542 | 0.420 | 0.500 |
| 3 | 0.243 | 0.166 | 0.527 | 0.397 | 0.473 |
| 4 | 0.217 | 0.147 | 0.489 | 0.354 | 0.426 |
| 5 | 0.209 | 0.135 | 0.455 | 0.329 | 0.383 |
| 6 | 0.195 | 0.128 | 0.376 | 0.272 | 0.301 |
| 7 | 0.153 | 0.118 | 0.312 | 0.239 | 0.237 |
| … | … | … | … | … | … |
| 365 | 0.206 | 0.114 | 0.260 | 0.199 | 0.158 |
| 366 | 0.208 | 0.114 | 0.322 | 0.261 | 0.241 |
| 367 | 0.194 | 0.112 | 0.355 | 0.280 | 0.258 |
| 368 | 0.184 | 0.106 | 0.362 | 0.264 | 0.255 |
| 369 | 0.182 | 0.102 | 0.356 | 0.260 | 0.244 |
| 370 | 0.168 | 0.097 | 0.301 | 0.212 | 0.190 |
| 371 | 0.152 | 0.089 | 0.253 | 0.178 | 0.146 |
| 372 | 0.135 | 0.081 | 0.273 | 0.218 | 0.167 |
| Models | MAPE(%) | R |
|---|---|---|
| IA-GRU | 20.81 | 0.9761 |
| A-GRU | 21.71 | 0.9674 |
| A-LSTM | 22.87 | 0.9711 |
| GRU | 25.43 | 0.9547 |
| LSTM | 25.57 | 0.9480 |
| BPNN | 28.58 | 0.9462 |
| Models | MAPE(%) | R |
|---|---|---|
| IA-GRU | 22.43 | 0.9736 |
| A-GRU | 24.55 | 0.9696 |
| A-LSTM | 25.46 | 0.9660 |
| GRU | 27.36 | 0.9494 |
| LSTM | 27.91 | 0.9659 |
| BPNN | 30.17 | 0.9460 |
| Models | MAPE(%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| One Keyword | Two Keywords | Three Keywords | Four Keywords | |
| IA-GRU | 22.34 | 22.04 | 22.40 | 21.33 |
| A-GRU | 23.74 | 23.68 | 23.19 | 23.54 |
| A-LSTM | 24.59 | 24.38 | 24.09 | 23.89 |
| GRU | 27.16 | 25.86 | 24.99 | 25.54 |
| LSTM | 27.43 | 27.40 | 27.66 | 26.78 |
| BPNN | 29.81 | 29.87 | 29.24 | 28.78 |
| Models | R | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| One Keyword | Two Keywords | Three Keywords | Four Keywords | |
| IA-GRU | 0.9677 | 0.9707 | 0.9720 | 0.9761 |
| A-GRU | 0.9644 | 0.9673 | 0.9713 | 0.9678 |
| A-LSTM | 0.9678 | 0.9740 | 0.9662 | 0.9736 |
| GRU | 0.9533 | 0.9563 | 0.9517 | 0.9532 |
| LSTM | 0.9688 | 0.9485 | 0.9724 | 0.9725 |
| BPNN | 0.9464 | 0.9397 | 0.9445 | 0.9528 |
| Models | MAPE(%) | R |
|---|---|---|
| IA-GRU | 21.48 | 0.9688 |
| A-GRU | 22.67 | 0.9663 |
| A-LSTM | 23.89 | 0.9766 |
| GRU | 25.62 | 0.9538 |
| LSTM | 26.89 | 0.9504 |
| BPNN | 28.86 | 0.9542 |
| Models | MAPE(%) | R |
|---|---|---|
| IA-GRU | 20.81 | 0.9761 |
| A-GRU | 21.71 | 0.9674 |
| A-LSTM | 22.87 | 0.9711 |
| GRU | 25.43 | 0.9547 |
| LSTM | 25.57 | 0.9480 |
| BPNN | 28.58 | 0.9462 |
| Months | MAPE(%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IA-GRU | A-GRU | A-LSTM | GRU | LSTM | BPNN | |
| 1 | 40.86 | 32.38 | 48.92 | 41.85 | 40.28 | 51.30 |
| 2 | 30.73 | 35.58 | 38.16 | 37.47 | 35.41 | 46.67 |
| 3 | 25.82 | 27.82 | 23.95 | 29.35 | 29.18 | 32.32 |
| 4 | 23.26 | 26.88 | 26.95 | 27.97 | 30.16 | 29.25 |
| 5 | 13.72 | 17.56 | 17.67 | 21.45 | 23.44 | 33.58 |
| 6 | 14.25 | 14.27 | 15.84 | 18.7 | 18.34 | 24.52 |
| 7 | 12.53 | 14.51 | 13.27 | 14.86 | 16.96 | 13.55 |
| 8 | 13.38 | 13.36 | 11.94 | 11.71 | 11.74 | 11.16 |
| 9 | 18.51 | 17.03 | 18.25 | 23.60 | 24.48 | 26.94 |
| 10 | 18.27 | 17.62 | 23.14 | 29.84 | 30.13 | 28.15 |
| 11 | 14.17 | 16.26 | 16.68 | 18.11 | 21.62 | 21.22 |
| 12 | 24.82 | 28.24 | 20.74 | 30.93 | 25.79 | 25.63 |
| Average | 20.81 | 21.71 | 22.87 | 25.43 | 25.57 | 28.58 |
| Months | R | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IA-GRU | A-GRU | A-LSTM | GRU | LSTM | BPNN | |
| 1 | 0.9538 | 0.8650 | 0.9502 | 0.9132 | 0.9506 | 0.8226 |
| 2 | 0.9546 | 0.9219 | 0.9443 | 0.9270 | 0.9226 | 0.8804 |
| 3 | 0.9779 | 0.9751 | 0.9803 | 0.9554 | 0.9498 | 0.9585 |
| 4 | 0.9673 | 0.9447 | 0.9557 | 0.9309 | 0.9070 | 0.9054 |
| 5 | 0.9880 | 0.9808 | 0.9823 | 0.9648 | 0.9581 | 0.9348 |
| 6 | 0.9915 | 0.9895 | 0.9917 | 0.9698 | 0.9682 | 0.9788 |
| 7 | 0.9845 | 0.9810 | 0.9852 | 0.9764 | 0.9723 | 0.9878 |
| 8 | 0.9912 | 0.9890 | 0.9938 | 0.9913 | 0.9912 | 0.9918 |
| 9 | 0.9685 | 0.9709 | 0.9675 | 0.9390 | 0.9319 | 0.9496 |
| 10 | 0.9860 | 0.9875 | 0.9750 | 0.9718 | 0.9580 | 0.9725 |
| 11 | 0.9842 | 0.9802 | 0.9806 | 0.9714 | 0.9609 | 0.9685 |
| 12 | 0.9549 | 0.9582 | 0.9663 | 0.9402 | 0.9459 | 0.9529 |
| Average | 0.9761 | 0.9674 | 0.9711 | 0.9547 | 0.9480 | 0.9462 |
| Huangshan | Huangshan Travel Guide | Anhui Huangshan | Huangshan Guide | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training set | 0.295 | 0.445 | 0.225 | 0.275 |
| Test set | 0.478 | 0.656 | 0.061 | 0.321 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, W.; Jin, J.; Wang, B.; Li, K.; Liang, C.; Dong, J.; Zhao, S. Intelligence in Tourist Destinations Management: Improved Attention-based Gated Recurrent Unit Model for Accurate Tourist Flow Forecasting. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041390
Lu W, Jin J, Wang B, Li K, Liang C, Dong J, Zhao S. Intelligence in Tourist Destinations Management: Improved Attention-based Gated Recurrent Unit Model for Accurate Tourist Flow Forecasting. Sustainability. 2020; 12(4):1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041390
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Wenxing, Jieyu Jin, Binyou Wang, Keqing Li, Changyong Liang, Junfeng Dong, and Shuping Zhao. 2020. "Intelligence in Tourist Destinations Management: Improved Attention-based Gated Recurrent Unit Model for Accurate Tourist Flow Forecasting" Sustainability 12, no. 4: 1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041390
APA StyleLu, W., Jin, J., Wang, B., Li, K., Liang, C., Dong, J., & Zhao, S. (2020). Intelligence in Tourist Destinations Management: Improved Attention-based Gated Recurrent Unit Model for Accurate Tourist Flow Forecasting. Sustainability, 12(4), 1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041390





