Managing Sustainable Urban Tourism Development: The Case of Ljubljana
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Sustainable Urban Development
2.2. Sustainable Tourism
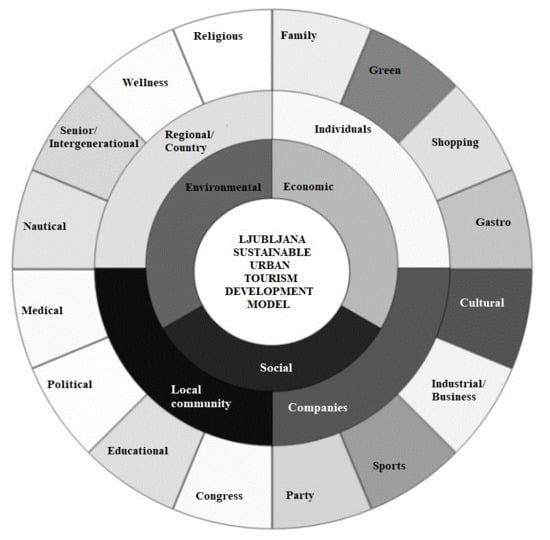
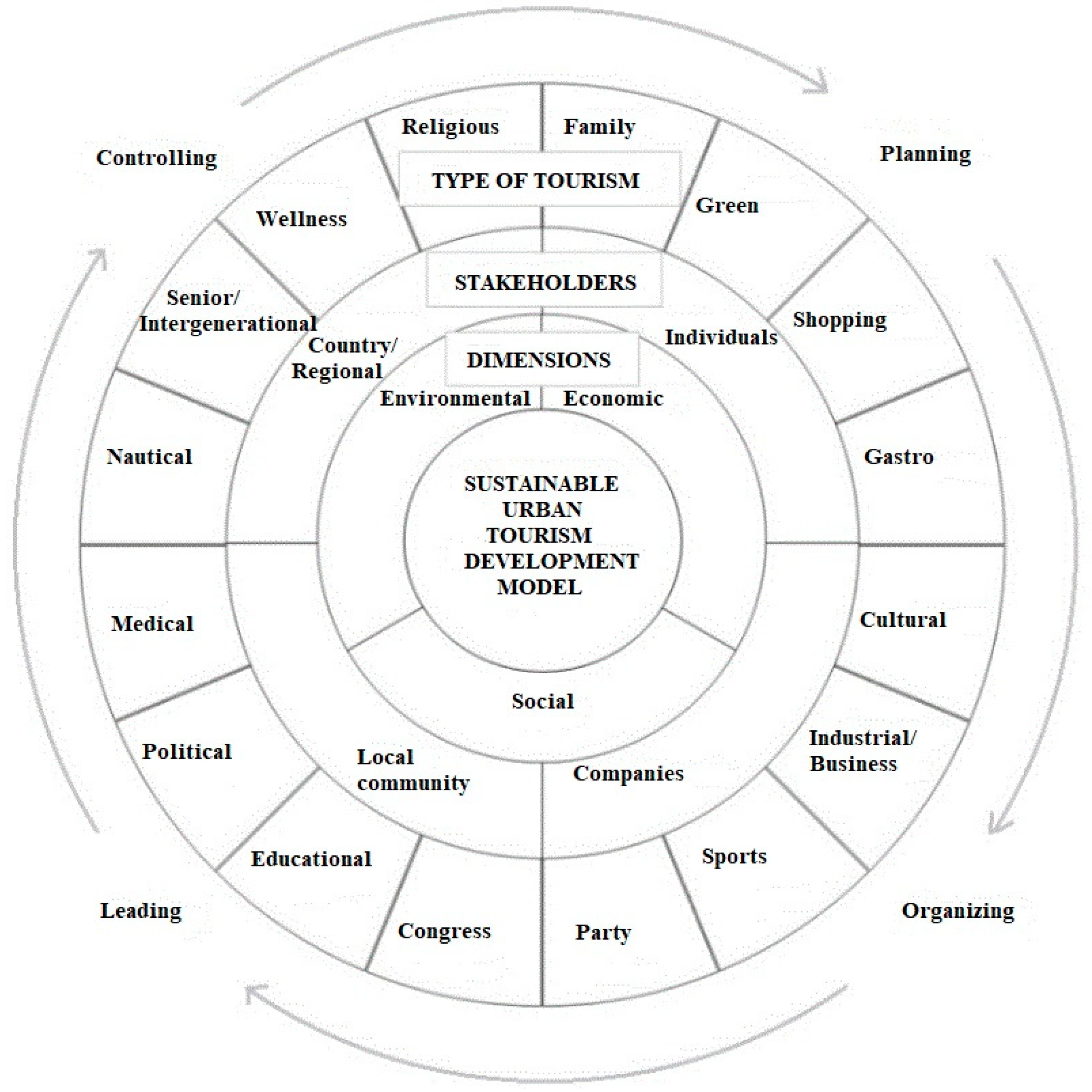
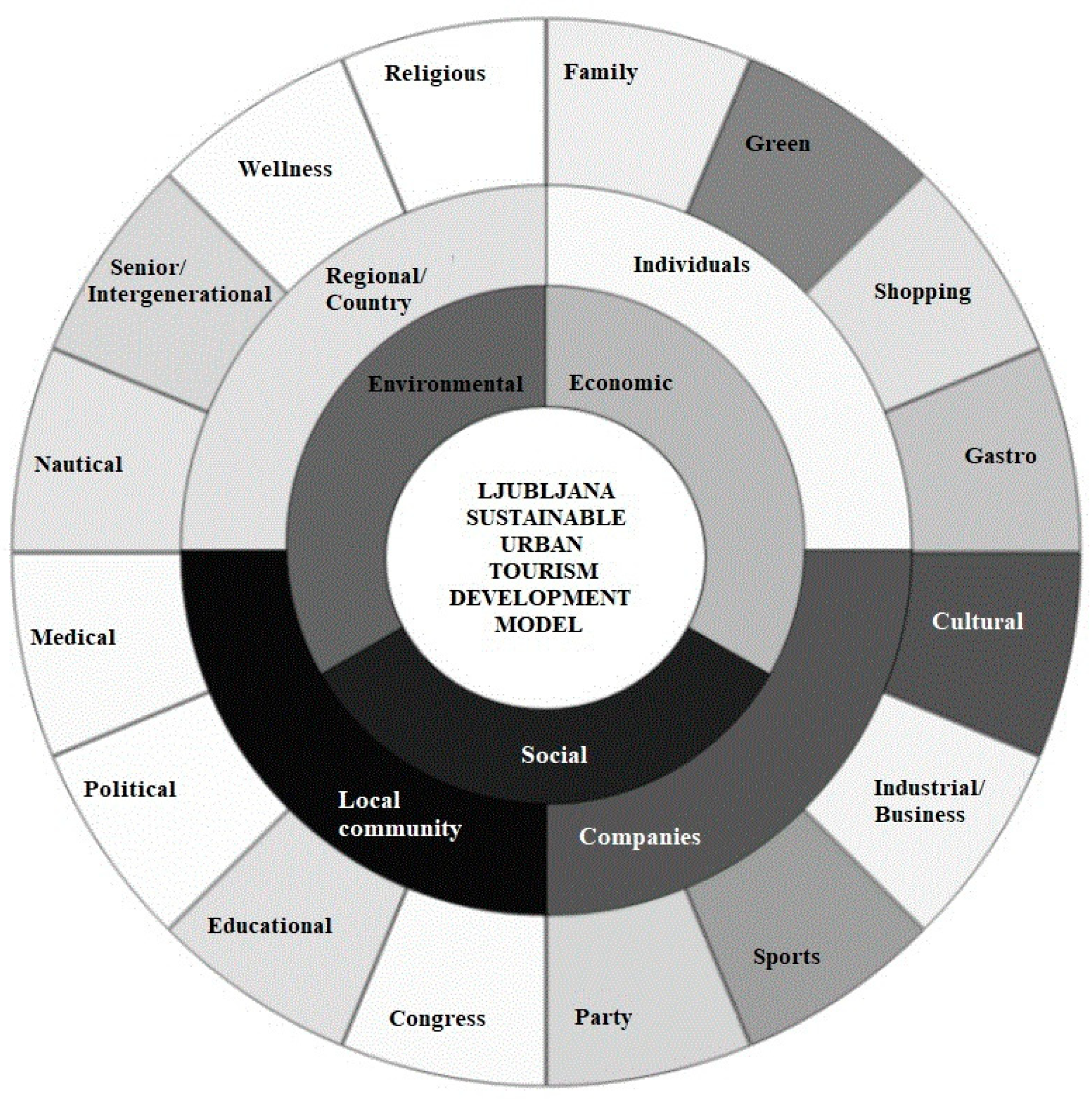
3. Conceptual Model Development
- dimensions of sustainability (environmental, economic, and social) [68];
- different stakeholders: individuals, companies, local community, and country/regional level;
- relevant types of tourism that can be developed in selected urban environments based on resources available; as, for example, family, green, shopping, gastro, cultural, business/industrial, sports, party, congress, educational, political, medical, nautical, intergenerational, wellness, or religious.
4. Method
4.1. Context of the Conceptual Model Application: The Case of Ljubljana
4.2. The Case of Ljubljana—Data Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grosseck, G.; Țîru, L.G.; Bran, R.A. Education for Sustainable Development: Evolution and Perspectives: A Bibliometric Review of Research, 1992–2018. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, N.; Cooper, C. Innovation for sustainable urban tourism: Some thoughts on best practice. Revista de Administracao Publica (RAP) 2010, 44, 1171–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, R.; Joppe, M. The application of ecotourism to urban areas. Tourism 2003, 51, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations, Sustainable Development Goals. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/?menu=1300 (accessed on 17 January 2020).
- Simon, D.; Arfidsson, H.; Anand, G.; Bazaz, A.; Fenna, G.; Foster, K.; Jain, G.; Hansson, S.; Evans Marix, L.; Moodley, N.; et al. Developing and testing the Urban Sustainable Development Goal’s targets and indicators—A five-city study. Environ. Urban. 2016, 28, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reckien, D.; Creutzig, F.; Fernandez, B.; Lwasa, S.; Tovar-Restrepo, M.; Mcevoy, D.; Satterthwaite, D. Climate change, equity and the Sustainable development Goals: An urban perspective. Environ. Urban. 2017, 29, 159–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.J.; Hanson, M.E.; Liverman, D.M.; Merideth, R.W. Global sustainability: Toward definition. Environ. Manag. 1987, 11, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roseland, M. Dimensions of the eco-city. Cities 1997, 14, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Commission on Environment and Development. Our Common Future; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Camagni, R. Sustainable urban development: Definition and reasons for a research programme. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 1998, 10, 6–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieżel, M.; Piotrowski, P.; Wiechoczek, J. The Research on Sustainable Tourism in the Light of Its Paradigms. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sustainable Development. Available online: https://www.unwto.org/sustainable-development (accessed on 25 August 2019).
- Timur, S.; Getz, D. Sustainable tourism development: How do destination stakeholders perceive sustainable urban tourism? Sustain. Dev. 2009, 17, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamfir, A.; Corbos, R.A. Towards sustainable tourism development in urban areas: Case study on Bucharest as tourist destination. Sustainability 2015, 7, 12709–12722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Önder, I.; Wöber, K.; Zekan, B. Towards a sustainable urban tourism development in Europe: The role of benchmarking and tourism management information systems—A partial model of destination competitiveness. Tourism Econ. 2017, 23, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiati, M.P.; Lestari, N.S.; Wiastuti, R.D. Public parks as urban tourism in Jakarta. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018. Available online: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1755-1315/126/1/012063 (accessed on 17 January 2020).
- Schmithüsen, F.J. Three hundred years of applied sustainability in forestry—Working papers. For. Policy For. Econ. Dep. For. Sci. Int. Ser. 2013, 64, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wilderer, P.A. Sustainable water resource management: The science behind the scene. Sustain. Sci. 2007, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiersum, K.F. 200 Years of Sustainability in Forestry: Lessons from History. Environ. Manag. 1995, 19, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterlin, J.; Dimovski, V.; Tvaronavičiene, M.; Grah, B.; Kaklauskas, A. The strategic process of developing social aspects of sustainability through the vision reflection in business education. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2018, 24, 1718–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grah, B.; Dimovski, V.; Peterlin, J. A Shift in Perceiving Organisational Metaphors among Business Administration Students in an EU Country: A Window into the Current Thinking of Future Employees. Drus. Istraz. 2018, 27, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yung, E.H.K.; Chan, E.H.W. Implementation challenges to the adaptive reuse of heritage buildings: Towards the goals of sustainable, low carbon cities. Habitat Int. 2012, 36, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, S. Determining a sustainable city model. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2006, 21, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Web of Science—Sustainable Urban Development. Available online: https://wcs.webofknowledge.com/RA/analyze.do?product=WOS&SID=D11cdgs6ilzObNM6gIl&field=PY_PublicationYear_PublicationYear_en&yearSort=true (accessed on 25 October 2019).
- Shepherd, A.; Ortolano, L. Strategic environmental assessment for sustainable urban development. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 1996, 16, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tweed, C.; Sutherland, M. Built cultural heritage and sustainable urban development. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 83, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haughton, G. Developing sustainable urban development models. Cities 1997, 14, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markusen, A. Urban development and the politics of a creative class: Evidence from a study of artists. Environ. Plan. 2006, 38, 1921–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaklauskas, A.; Kazimieras Zavadskas, E.; Šaparauskas, J. Conceptual modelling of sustainable Vilnius development. Ukio Technologinis ir Ekonominis Vystymas 2009, 15, 154–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzelecka, M.; Bynum Boley, B.; Strzelecka, C. Empowerment and resident support for tourism in rural Central and Eastern Europe (CEE): The case of Pomerania, Poland. J. Sustain. Tour. 2017, 25, 554–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronau, W. Encouraging behavioural change towards sustainable tourism: A German approach to free public transport for tourists. J. Sustain. Tour. 2017, 25, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wan, Y.K.P. Residents’ support for festivals: Integration of emotional solidarity. J. Sustain. Tour. 2017, 25, 517–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higham, J.; Lűck, M. Urban Ecotourism: A Contradiction in Terms? J. Ecotour. 2002, 1, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doods, R. Sustainable tourism and policy implementation: Lessons from the case of Calvia, Spain. Curr. Issues Tour. 2007, 10, 296–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eligh, J.; Welford, R.; Ytterhus, B. The production of sustainable tourism: Concepts and examples from Norway. Sust. Dev. 2002, 10, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Web of Science —Sustainable Tourism. Available online: https://wcs.webofknowledge.com/RA/analyze.do?product=WOS&SID=D11cdgs6ilzObNM6gIl&field=PY_PublicationYear_PublicationYear_en&yearSort=true (accessed on 25 October 2019).
- Girard, L.F.; Nocca, F. From linear to circular tourism. Aestimum 2017, 70, 51–74. [Google Scholar]
- Vandermey, A. Assessing the importance of urban tourism: Conceptual and measurement issues. Tour. Manag. 1984, 5, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, D.G. An Integrative Framework for Urban Tourism Research. Ann. Tour. Res. 2001, 28, 926–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogerson, C.M. Urban tourism, economic regeneration and inclusion: Evidence from South Africa. Local Econ. 2012, 28, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, G.; Page, S.J. Urban tourism research: Recent progress and current paradoxes. Tour. Manag. 2011, 32, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’loughlin, J. Spatial inequalities in Western cities: A comparison of North American and German urban areas. Soc. Indic. Res. 1983, 13, 185–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D.; Griffin, T.; Hayllar, B. Urban Tourism Research: Developing an Agenda. Ann. Tour. Res. 2008, 35, 1032–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postma, A.; Schmuecker, D. Understanding and overcoming negative impacts of tourism in city destinations: Conceptual model and strategic framework. J. Tour. Futures 2017, 3, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muler Gonzalez, V.; Coromina, L.; Gali, N. Overtourism: Resident’s perceptions of tourism impact as an indicator of resident social carrying capacity-case study of a Spanish heritage town. Tour. Rev. 2018, 73, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M. Sharing economy: A review and agenda for future research. Int. J. Hosp. Manage. 2016, 57, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boes, K.; Buhalis, D.; Inversini, A. Smart tourism destinations: Ecosystems for tourism destination competitiveness. Int. J. Tour. Cities 2016, 2, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Towards investment and financing for sustainable tourism. In OECD Tourism Trends and Policies 2018; OECD: Paris, France, 2018; pp. 93–117. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Robin, C.; Celemín-Pedroche, M.S.; Santander-Astorga, P.; Alonso-Almeida, M.M. Green Practices in Hospitality: A Contingency Approach. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estêvão, R.S.G.; Ferreira, F.A.F.; Rosa, A.A.; Govindan, K.; Meidutė-Kavaliauskienė, I. A socio-technical approach to the assessment of sustainable tourism: Adding value with a comprehensive process-oriented framework. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, J.E.; Filimonau, V.; Hibbert, J.F.; Cherrett, T.; Davies, N.; Norgate, S.; Speed, C.; Winstanley, C. Tourism communities and social ties: The role of online and offline tourist social networks in building social capital and sustainable practice. J. Sustain. Tour. 2017, 25, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richins, H. Influences on Tourism Development Decision Making: Coastal Local Government Areas in Eastern Australia. J. Sustain. Tour. 2000, 8, 207–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, Y.; Nawijn, J.; Peeters, P.M. Happiness and limits to sustainable tourism mobility: A new conceptual model. J. Sustain. Tour. 2013, 21, 1017–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardoin, N.M.; Wheaton, M.; Bowers, A.W.; Hunt, A.C.; Durham, W.H. Nature-based tourism’s impact on environmental knowledge, attitudes, and behavior: A review and analysis of the literature and potential future research. J. Sustain. Tour. 2015, 23, 838–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeldner, C.R.; Ritchie, J.R.B.; McIntosh, R.W. Tourism, Principles, Practices, philosophies; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Masnavi, M.R.; Gharai, F.; Hajibandeh, M. Exploring urban resilience thinking for its application in urban planning: A review of literature. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrato, B.F.; Ballesteros Pelegrin, G.A.; Sanchez Sanchez, M.A. Analysis of the activities of environmental protection and tourist management in the Regional Park of Calblanque, Monte de las Cenizas and Pena del Aguila (Murcia, SE Spain). Cuad. de Tur. 2019, 43, 123–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talent, M. Smarter Cities: Cleaning Electricity, gas and water Metered Consumption Data for Social and Urban Research. J. Sustain. Dev. Energy Water Environ. Syst. 2019, 7, 466–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambiri, D.; Biagi, B.; Royuela, V. Quality of Life in the Economic and Urban Economic Literature. Soc. Indic. Res. 2007, 84, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rius-Ulldemolins, J.; Posso Jimenez, L. Culture, urban transformation and citizen empowerment against gentrification. Comparison between the case of Getsemani (Cartagena de Indias) and Raval (Barcelona). Eure-revista Latinoam. de Estud. urbano Reg. 2016, 42, 97–122. [Google Scholar]
- Turok, I.; Scheba, A. “Right to the city” and the New Urban Agenda: Learning from the right to housing. Territ. Politic. Gov. 2019, 7, 494–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez Aviles, J.I. Between the right to the city and identity: Indigenous population in contexts of high urban segregation. Rev. Incl. 2020, 7, 17–41. [Google Scholar]
- Erdmenger, E. Community Resilience in Urban Tourist Destinations. Z. Tour. 2019, 11, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Xiao, X.; Xu, Y.; Xie, H. The impact of water quality changes on tourism capacity at Golden Lake, China. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2013, 11, 1069–1072. [Google Scholar]
- O’Reilly, A.M. Tourism carrying capacity: Concept and issues. Tour. Manag. 1986, 7, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlya, B.; Das, A.K. New Urban Agenda in Asia-Pacific: Governance for Sustainable and Inclusive Cities; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 3–36. [Google Scholar]
- Ahern, J. Urban landscape sustainability and resilience: The promise and challenges of integrating ecology with urban planning and design. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padin, C. A sustainable tourism planning model: Components and relationships. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2012, 24, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daft, R.L.; Marcic, D. Understanding Management; Cengage Learning: Stamford, CT, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, R.K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods; SAGE: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, R.K. Qualitative Research from Start to Finish; The Guliford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, R.K. Applications of Case Study Research, 3rd ed.; SAGE Publications Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Penger, S. Učeča se organizacija in oblikovanje pozitivne organizacijske identitete: Študija primera slovenskega podjetja [Learning organization and design of positive organizational identity: Case study of Slovene company]. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Economics, University of Ljubljana, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 11 December 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Langley, A. Doing and Publishing Qualitative Research; EGOS: Helsinki, Finnland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- City of Ljubljana. Ljubljana Again Makes the List of the World’s Most Sustainable Destinations. Available online: https://www.ljubljana.si/en/news/ljubljana-again-makes-the-list-of-the-worlds-most-sustainable-destinations/ (accessed on 25 October 2019).
- Crnek, D. Ljubljana as the welcoming city. In Proceedings of the 1st Southeast Europe Smart Society Conference, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 20 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vissit Ljubljana. Ljubljana, a Sustainability-MINDED destination. Available online: https://www.visitljubljana.com/en/meetings/why-ljubljana/ljubljana-a-sustainability-minded-destination/ (accessed on 25 October 2019).
- European Comission. 2016—Ljubljana. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/environment/europeangreencapital/winning-cities/2016-ljubljana/ (accessed on 25 October 2019).
- Tigu, G.; Iorgulescu, M.C.; Ravar, A.S. The impact of creativity and innovation in the hospitality industry on customers. J. Tour. Chall. Trends 2013, 6, 9–33. [Google Scholar]
- Knowles, N.L.B. Targeting sustainable outcomes with adventure tourism: A political ecology approach. Ann. Tour. Res. 2019, 79, 102809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gössling, S.; Peeters, P.; Hall, C.M.; Ceron, J.P.; Dubois, G.; Scott, D. Tourism and water use: Supply, demand, and security. An international review. Tour. Manag. 2012, 33, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, B. What is rural tourism? J. Sustain. Tour. 1994, 2, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurigová, Z.; Lencsésová, Z. Monitoring system of sustainable development in cultural and mountain tourism destinations. J. Compet. 2015, 7, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moja Ljubljanica. Available online: http://mojaljubljanica.si/ (accessed on 25 October 2019).
- Espiner, S.; Orchiston, C.; Higham, J. Resilience and sustainability: A complementary relationship? Towards a practical conceptual model for the sustainability-resilience nexus in tourism. J. Sustain. Tour. 2017, 25, 1385–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellen MacCarthur Foundation. Available online: https://www.ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/ (accessed on 25 October 2019).
- GSTC. Strategic Plan. Available online: https://www.gstcouncil.org/ (accessed on 25 October 2019).
- Tavernor, R. Visual and cultural sustainability: The impact of tall buildings on London. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 83, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ţigu, G.; Andreeva, M.; Nica, A.M. Education and training needs in the field of visitors receiving structures and tourism services in the Lower Danube region. Amfiteatru Econ. J. 2010, 12, 735–760. [Google Scholar]
- Ţigu, G.; Popescu, D.; Hornoiu, R.I. Corporate Social Responsibility—An European Approach through the Tourism SME’s Perspectives. Amfiteatru Econ. J. 2016, 18, 742–756. [Google Scholar]
- Cabezas, H.; Pawlowski, C.W.; Mayer, A.L.; Hoagland, N.T. Sustainability: Ecological, social, economic, technological, and systems perspectives. In Technological Choices for Sustainability; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 37–64. [Google Scholar]
- Roblek, V.; Meško, M.; Dimovski, V.; Peterlin, J. Smart technologies as social innovation and complex social issues of the Z generation. Kybernetes 2019, 48, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, Y.; Björk, P.; Weidenfeld, A. Authenticity and place attachment of major visitor attractions. Tour. Manag. 2016, 52, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, C.M.; Baird, T.; Michael James, M.; Ram, Y. Climate change and cultural heritage: Conservation and heritage tourism in the Anthropocene. J. Herit. Tour. 2016, 11, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seixas, J.; Simoes, S.G.; Gouveia, J.P.; Dias, L. The Smart City of Evora. In Smart City Emergence: Cases from around the World; Anthopoulos, L., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 21–50. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Dynamics. World Urbanization prospects: The 2014 Revision. Available online: https://population.un.org/wup/Publications/Files/WUP2014-Report.pdf (accessed on 17 January 2020).
- Roblek, V. The Smart City of Vienna. In Smart City Emergence: Cases from around the World; Anthopoulos, L., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 105–129. [Google Scholar]
- Delmastro, C.; De Miglio, R.; Chidi, A.; Gargiulo, M.; Pisano, P. The Smart City of Torino. In Smart City Emergence: Cases from around the World; Anthopoulos, L., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 51–83. [Google Scholar]
| Gender | Ljubljana Residency | Number of Respondents | Sustainability Dimension (in %) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Economic | Social | Environmental | |||
| Male | Yes | 68 | 4.66 | 16.77 | 13.35 |
| No | 76 | 5.59 | 20.19 | 13.35 | |
| Female | Yes | 78 | 8.39 | 21.43 | 17.08 |
| No | 100 | 9.01 | 27.64 | 17.08 | |
| Total | 322 | 27.64 | 86.02 | 60.87 | |
| Gender | Ljubljana Residency | Stakeholders (in %) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Individual | Company | Local Community | Country/Regional | ||
| Male | Yes | 0.93 | 13.35 | 20.19 | 2.17 |
| No | 0.31 | 16.77 | 21.43 | 2.17 | |
| Female | Yes | 0.31 | 14.60 | 23.60 | 3.73 |
| No | 0.93 | 21.74 | 29.81 | 4.04 | |
| Total | 2.48 | 66.46 | 95.03 | 12.11 | |
| Gender | Ljubljana Residency | Stakeholders (in %) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family | Green | Shopping | Gastro | Cultural | Business/ Industrial | Sports | Party | Congress | Educational | Political | Medical | Nautical | Senior/ Intergenerational | Wellness | Religious | ||
| Male | Yes | 1.24 | 9.94 | 2.48 | 3.42 | 12.42 | 1.55 | 8.39 | 2.80 | 0.00 | 1.55 | 0.31 | 0.00 | 3.42 | 4.04 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| No | 0.62 | 9.32 | 1.55 | 5.59 | 13.35 | 1.24 | 9.32 | 4.35 | 0.00 | 4.66 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2.17 | 3.42 | 0.31 | 0.00 | |
| Female | Yes | 3.42 | 14.29 | 3.11 | 5.59 | 18.01 | 1.55 | 9.94 | 4.04 | 0.93 | 2.48 | 0.00 | 0.93 | 2.48 | 4.04 | 0.31 | 0.00 |
| No | 1.86 | 14.91 | 4.97 | 8.70 | 23.29 | 0.31 | 10.25 | 5.28 | 0.62 | 3.73 | 0.00 | 0.62 | 2.80 | 4.35 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Total | 7.14 | 48.45 | 12.11 | 23.29 | 67.08 | 4.66 | 37.89 | 16.46 | 1.55 | 12.42 | 0.31 | 1.55 | 10.87 | 15.84 | 0.62 | 0.00 | |
| Quotation No. | Respondent | Quotation |
|---|---|---|
| Quotation 1 | Respondent 14 | “… a meeting point or a base of cultural activities, more resources and attention would be given to non-governmental organizations. I believe that the overproduction of cultural activities took place in Ljubljana due to too large supply per inhabitant. An individual could take a tour around Ljubljana so a tourist could see Ljubljana through the eyes of a resident. Also, the stories about the city are needed.” |
| Quotation 2 | Respondent 16 | “… more dance events to engage the older adults in an environment where they are connected with the young, more active involvement of schools and school premises in the immediate areas by conducting more free-time activities in the afternoons, and to organize interactive tourist guidance of the Roman Emona [part of Ljubljana].” |
| Quotation 3 | Respondent 19 | “…due to the disconnection of people, Ljubljana remains closed, Ljubljana lacks variegation and diversity, we are not sufficiently aware of our culture and cultural heritage. People need to be addressed with stories, we must emphasize our identity, crafts, history, and culture, it looks like we overemphasize sport and underemphasize culture. We have good projects, but we need to advertise them more […] For example, Ljubljana could gain and earn a lot from foreign guides, as for example, if you are a local guide, you have to have a license to guide around the city, meanwhile foreign guides can walk around the city worry-free, without licenses, and that should be changed, we could earn extra money here.” |
| Quotation 4 | Respondent 24 | “…inaccessibility of the parts of the city for disabled, we need more drinking water fountains, more public toilets accessible also for disabled people, we need to emphasize and promote local food, open a restaurant with local food and drinks at Čopova street.” |
| Quotation 5 | Respondent 36 | “…more sports events for all generations, introduce the Gladiator event in Ljubljana, to revive the Koseško pond, to be able to rent pedal boats for a ride at Zbilje lake, to organize more outdoor cinemas (in Tivoli, at the Congress square, etc.), better promotion of Ljubljana, greater connection of the residents by for example exchanging items or garage sales.” |
| Quotation 6 | Respondent 38 | “… adapt Ljubljana for short city breaks, by offering more shopping centers, more active experiences in Ljubljana and more romantic experiences in Ljubljana. The need to emphasize architecture with the focus on Plečnik, more fun events, more experiences of Ljubljana by night.” |
| Quotation 7 | Respondent 41 | “…Improved marketing with the emphasis on the analysis of tourists’ expectations, more youth benefits in terms of additional offers and guides around Slovenia divided by their age to have a peer as a guide.” |
| Quotation 8 | Respondent 123 | “…more green areas, elimination of traffic jams, better traffic connections with Ljubljana, more information on events in Ljubljana, a place where I will feel a sense of belonging to Ljubljana.” |
| Quotation 9 | Respondent 127 | “…higher number of festivals, a product through which a person could experience Ljubljana from the past, more parking spots near the center.” |
| Quotation 10 | Respondent 178 | “…higher number of concerts in the center, better signage of the sights, the route of Roman Ljubljana, some great attraction” |
| Quotation 11 | Respondent | “…increased supply of vegan food in a trendy restaurant increased supply of local fruits and vegetables at a more affordable price, more fruit trees, not only ornamental ones but also the edible ones. Multiple urban installations by the principle of Prostorož or Light Guerrilla. I want a playground with endless trampolines.” |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grah, B.; Dimovski, V.; Peterlin, J. Managing Sustainable Urban Tourism Development: The Case of Ljubljana. Sustainability 2020, 12, 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12030792
Grah B, Dimovski V, Peterlin J. Managing Sustainable Urban Tourism Development: The Case of Ljubljana. Sustainability. 2020; 12(3):792. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12030792
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrah, Barbara, Vlado Dimovski, and Judita Peterlin. 2020. "Managing Sustainable Urban Tourism Development: The Case of Ljubljana" Sustainability 12, no. 3: 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12030792
APA StyleGrah, B., Dimovski, V., & Peterlin, J. (2020). Managing Sustainable Urban Tourism Development: The Case of Ljubljana. Sustainability, 12(3), 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12030792