An Alternative Statistical Model for Predicting Salinity Variations in Estuaries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Source
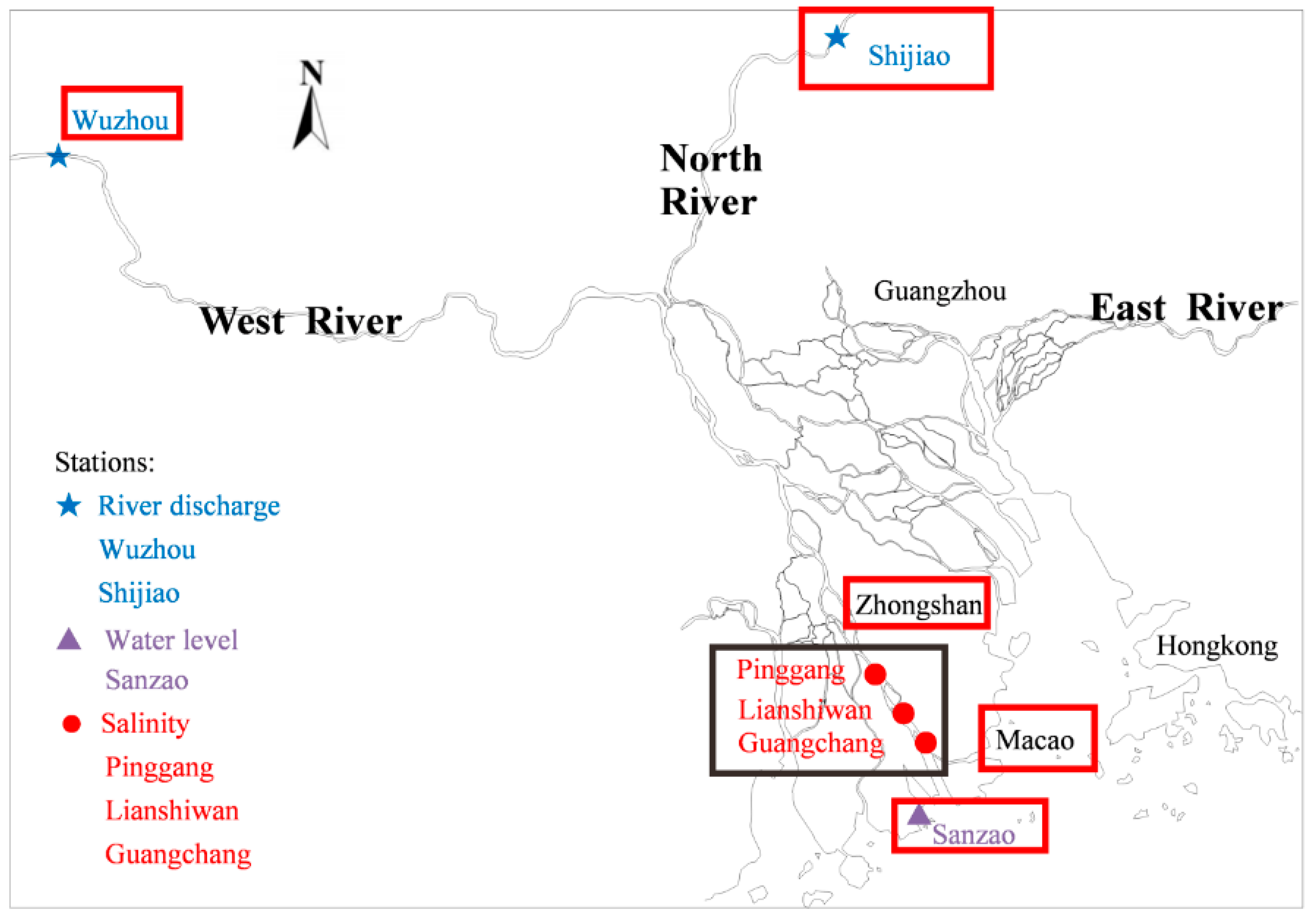
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source
3. Model Development
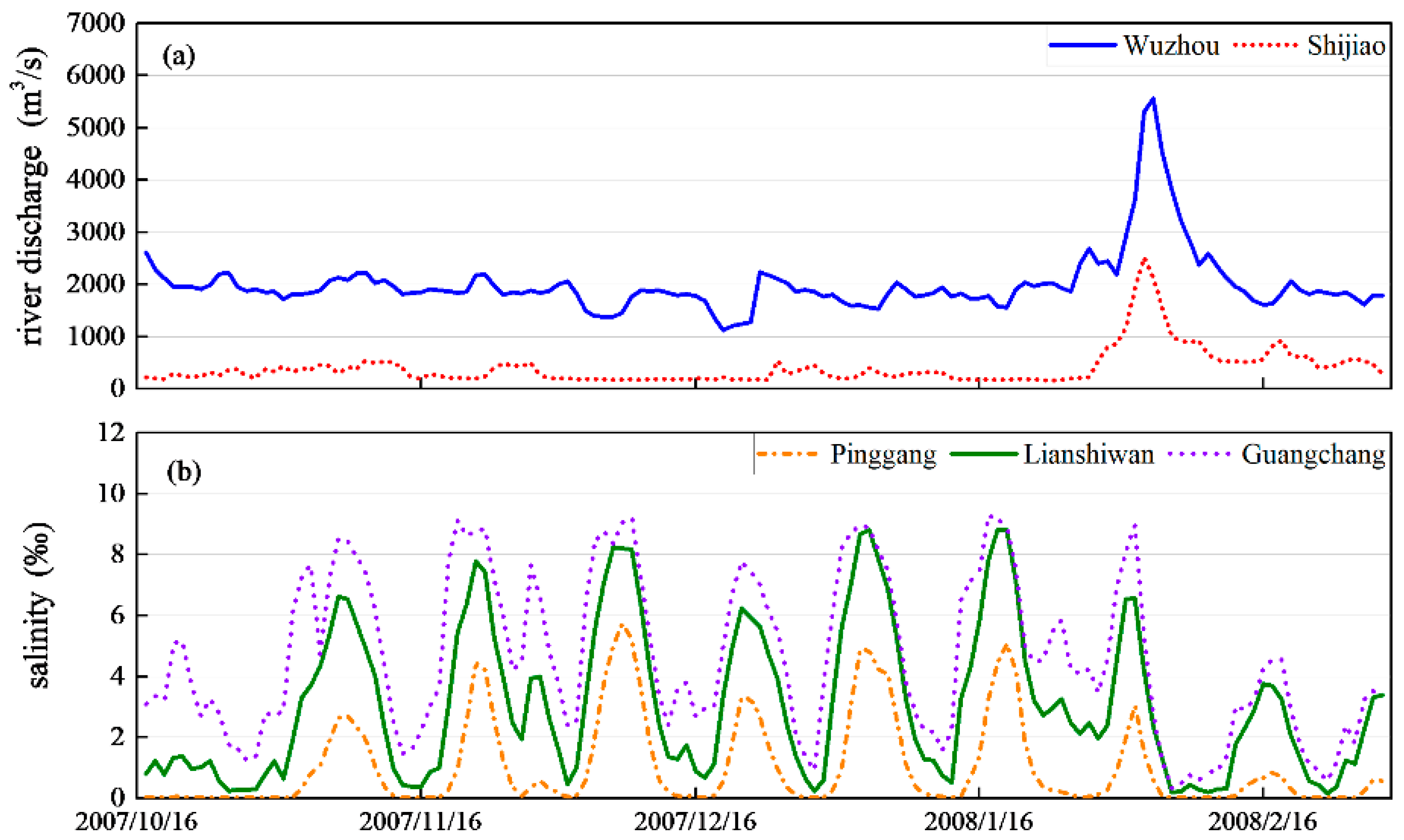
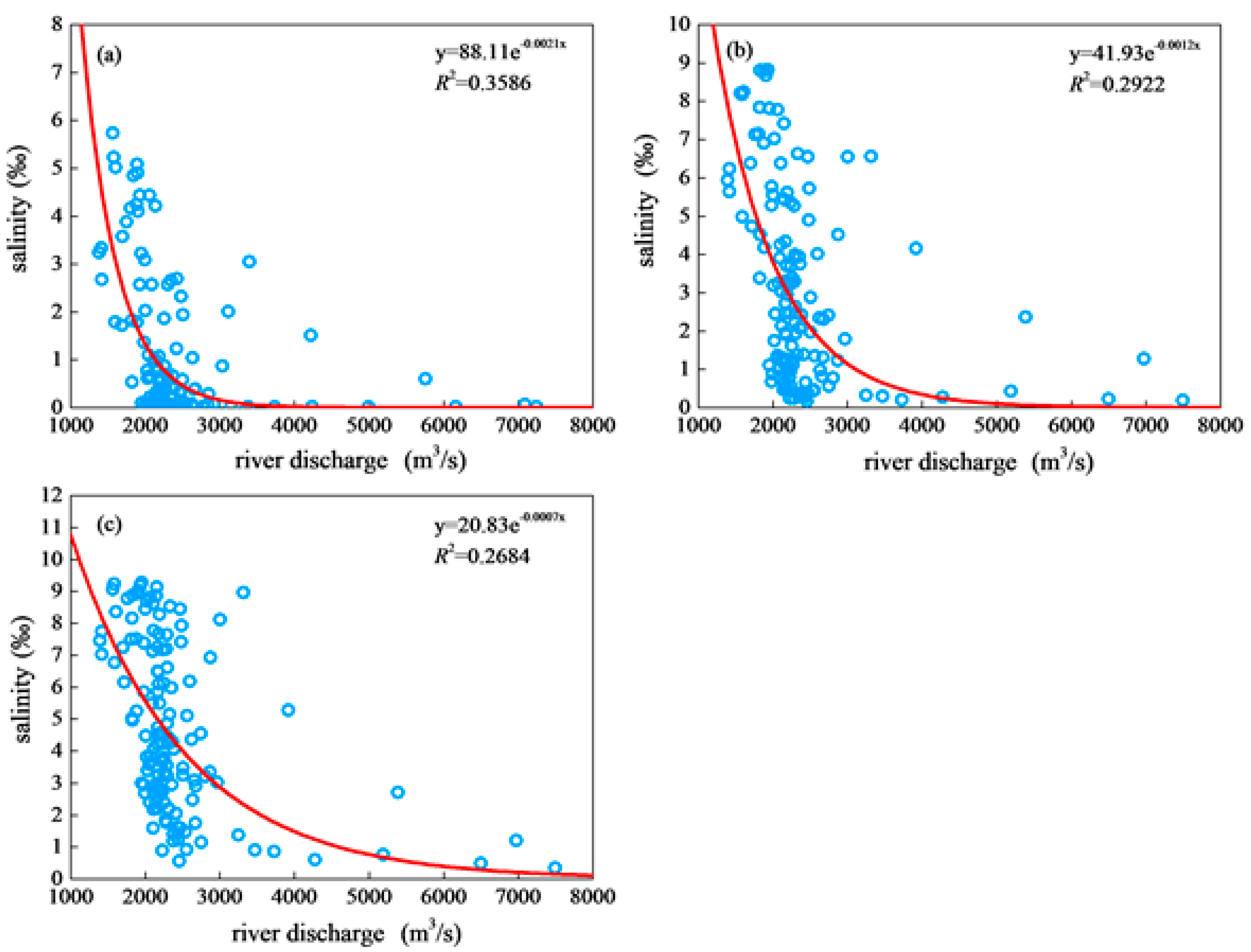
3.1. Relationship between Salinity and River Discharge
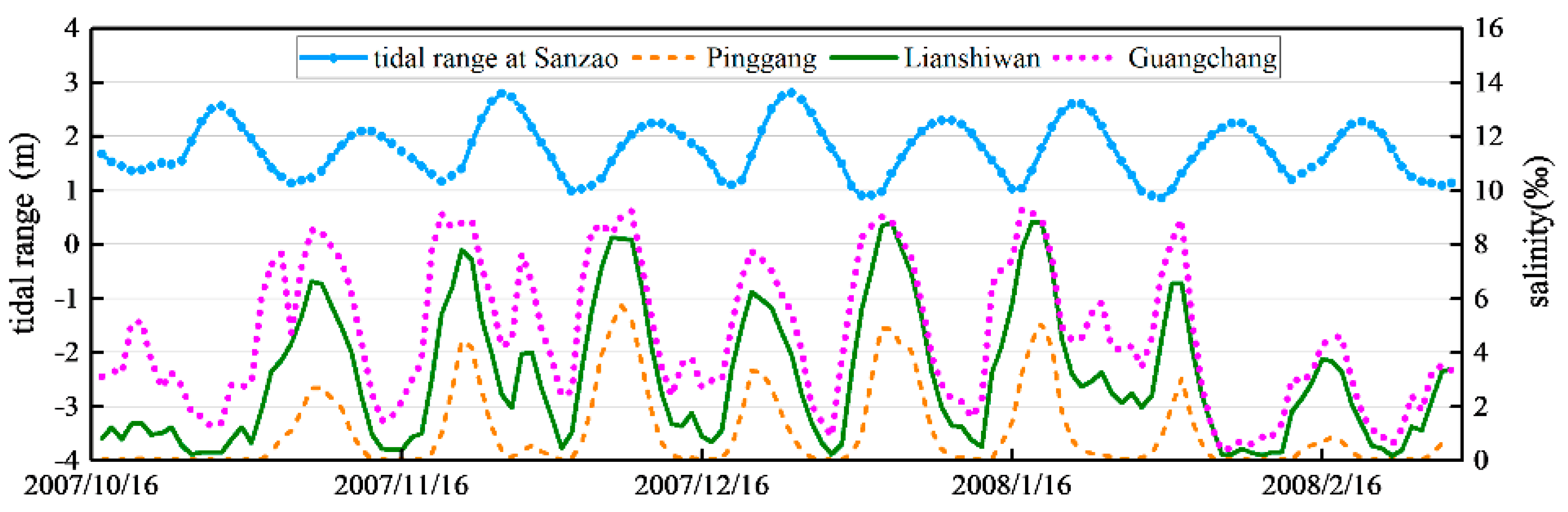
3.2. Relationship between Salinity and Tidal Range
3.3. Model Formulation
4. Model Calibration, Application and Further Tests
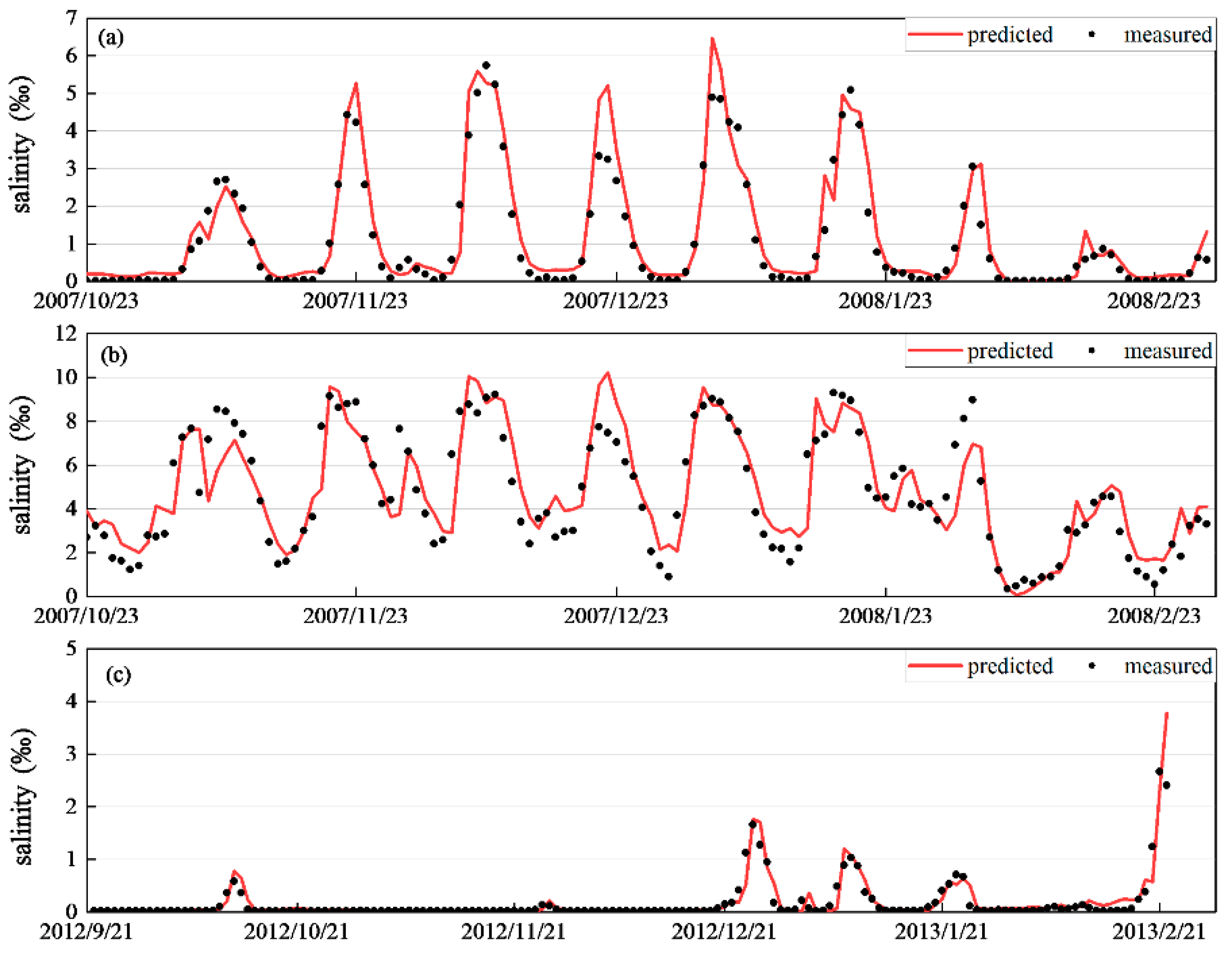
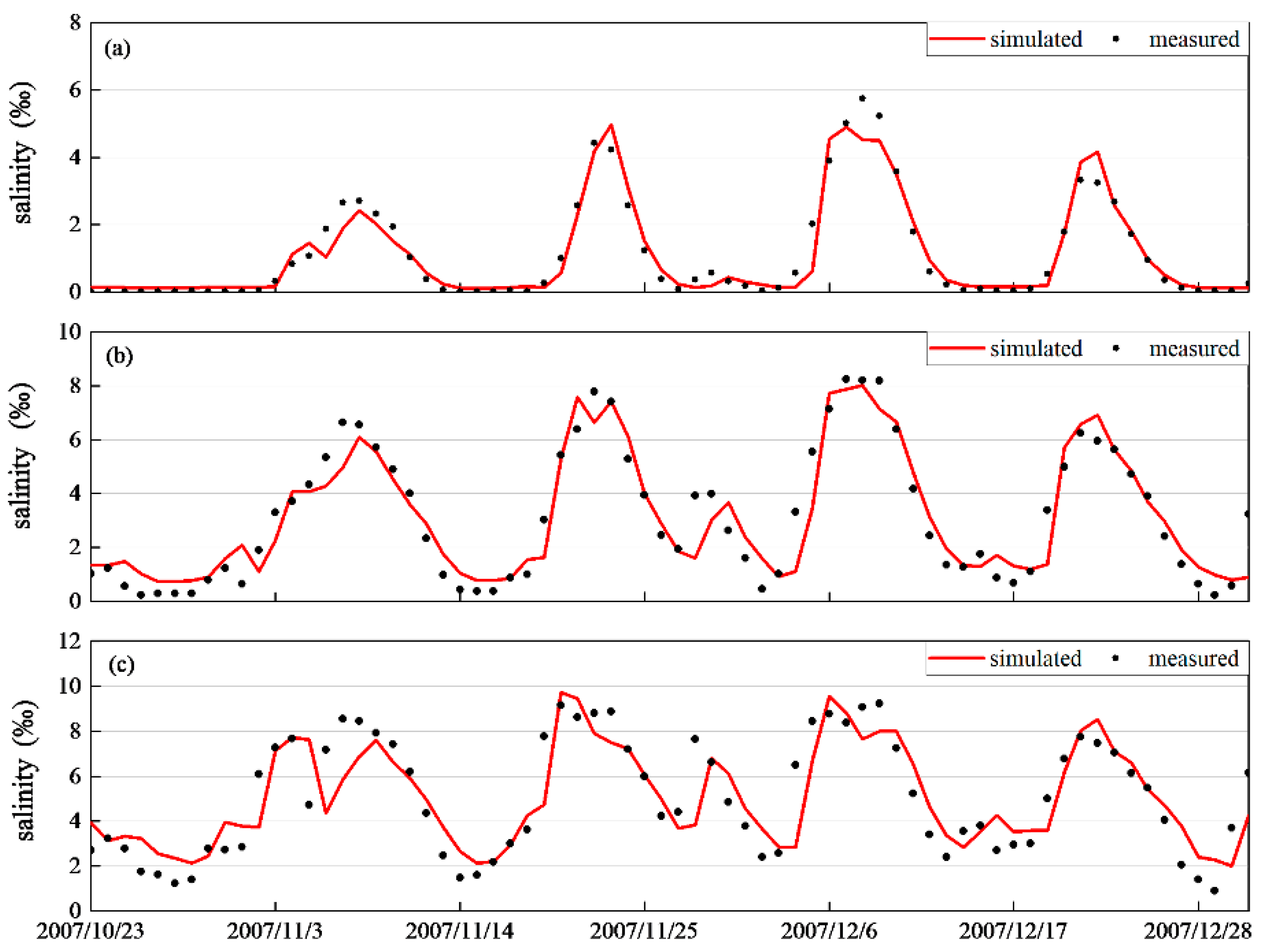
4.1. Model Calibration
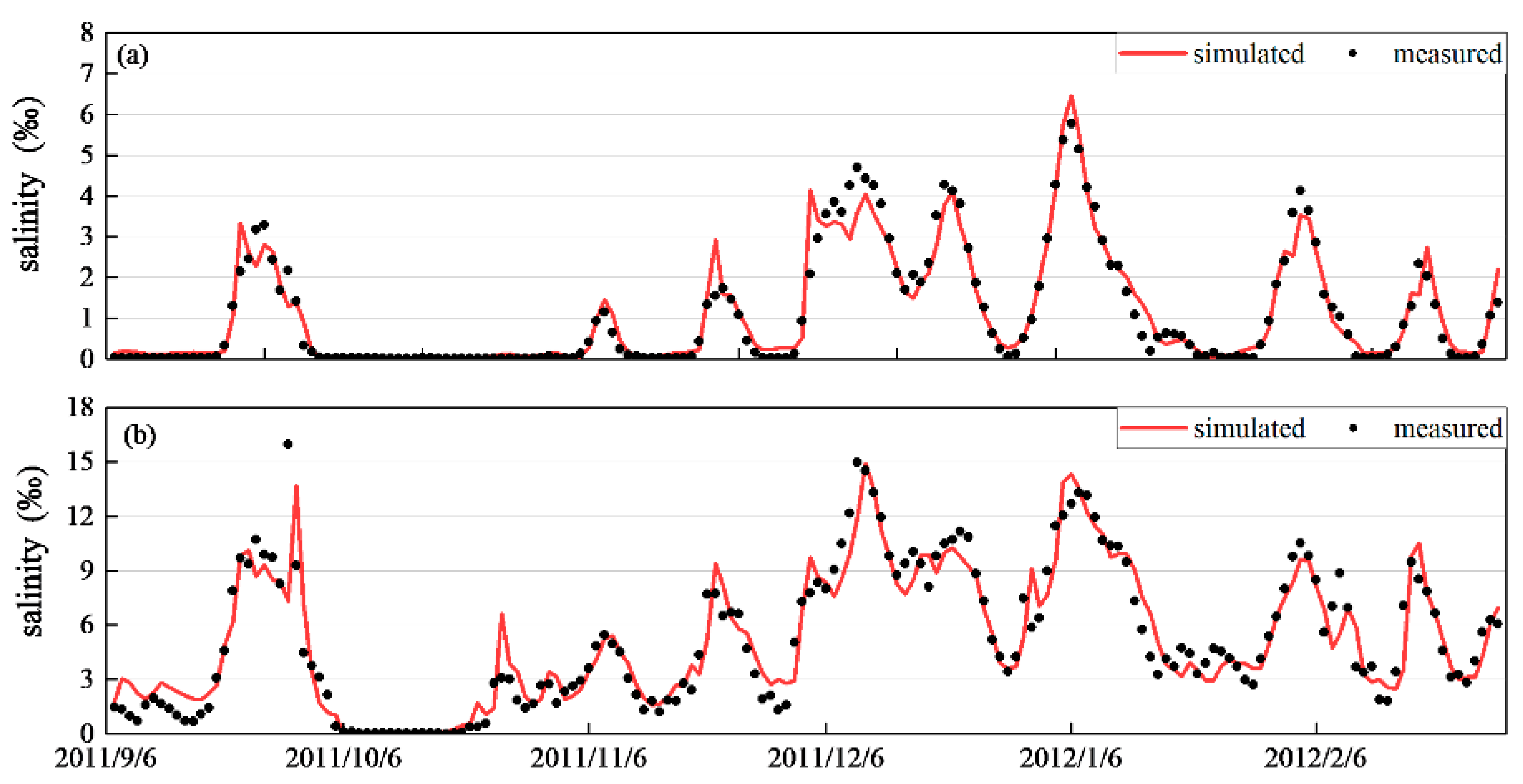
4.2. Model Application
4.3. Further Tests
4.3.1. Sensitivity Analysis of River Discharge
4.3.2. Cross-Validation
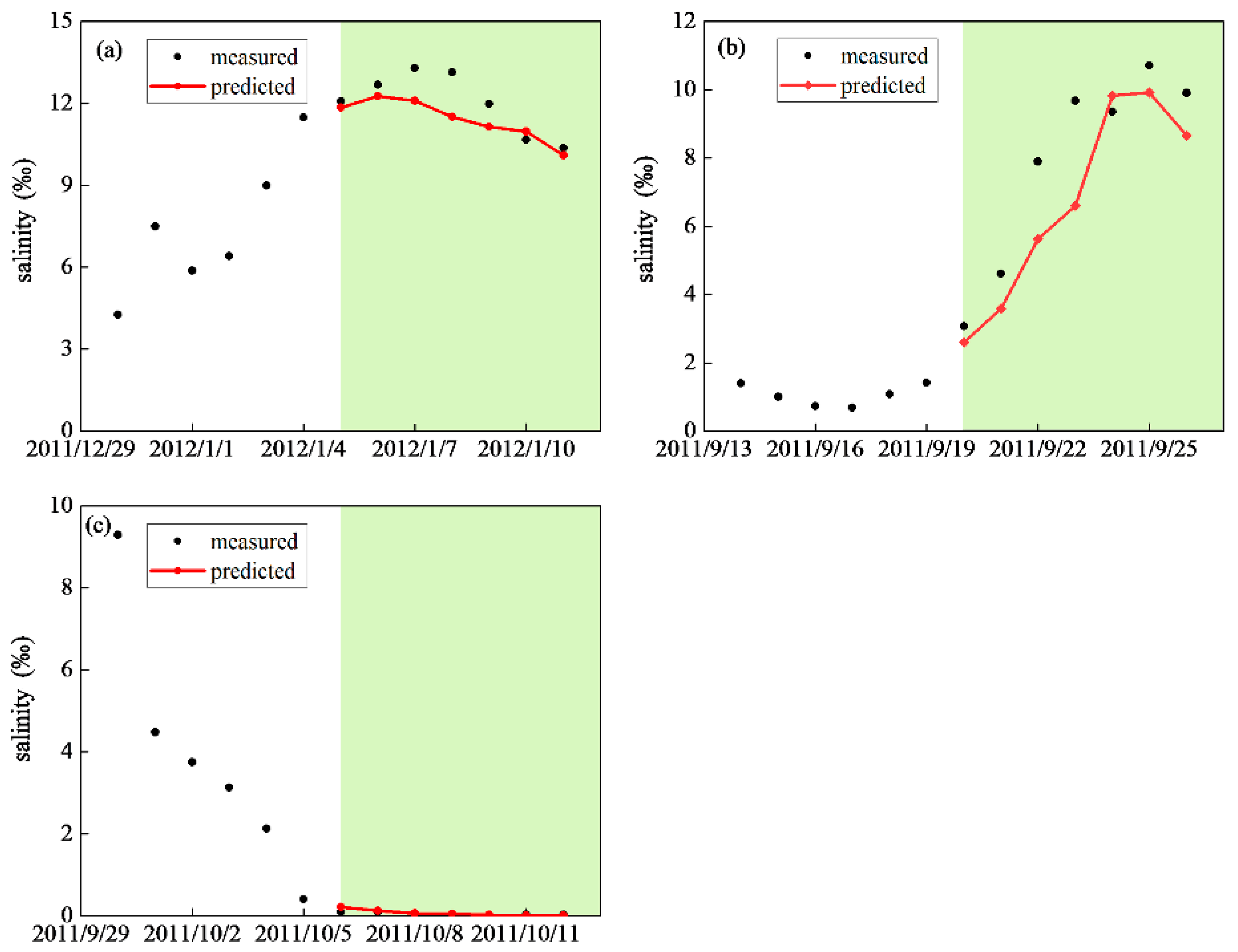
4.3.3. Analysis of Weekly Prediction
4.3.4. Analysis of Short-Term Time-Series
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, W.; Shen, J. The response of salt intrusion to changes in river discharge and tidal mixing during the dry season in the Modaomen Estuary, China. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, 769–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostaschuk, R.A.; Atwood, L.A. River discharge and tidal controls on salt-wedge position and implicat. Can. J. Civil Eng. 2011, 17, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, S.C.; Craft, C.B. Global change and tidal freshwater wetlands: Scenarios and impacts. In Tidal Freshwater Wetlands; Margraf Publishers: Weikersheim, Germany, 2009; pp. 253–266. [Google Scholar]
- Turrell, W.; Brown, J.; Simpson, J. Salt Intrusion and Secondary Flow in a Shallow, Well-mixed Estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1996, 42, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, D.K.; Geyer, W.R.; Lerczak, J.A. Structure, variability, and salt flux in a strongly forced salt wedge estuary. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Chen, C.; Ding, P.; Beardsley, R.C.; Lin, H.; Ge, J.; Kong, Y. Saltwater intrusion into the Changjiang River: A model-guided mechanism study. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xu, Y.J. Development and application of a remote sensing-based salinity prediction model for a large estuarine lake in the US Gulf of Mexico coast. J. Hydrol. 2008, 360, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerczak, J.A.; Geyer, W.R.; Ralston, D.K. The Temporal Response of the Length of a Partially Stratified Estuary to Changes in River Flow and Tidal Amplitude. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2009, 39, 915–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burchard, H. Combined Effects of Wind, Tide, and Horizontal Density Gradients on Stratification in Estuaries and Coastal Seas. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2009, 39, 2117–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, M. Effects of winds on stratification and circulation in a partially mixed estuary. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, M. Wind-driven lateral circulation in a stratified estuary and its effects on the along-channel flow. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2012, 117, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purkiani, K.; Becherer, J.; Klingbeil, K.; Burchard, H. Wind-induced variability of estuarine circulation in a tidally energetic inlet with curvature. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2016, 121, 3261–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, A.F.; Goodrich, D.E. Modeling of Wind-Induced Destratification in Chesapeake Bay. Estuaries 1990, 13, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrich, D.M.; Boicourt, W.C.; Hamilton, P.; Pritchard, D.W. Wind-Induced Destratification in Chesapeake Bay. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1987, 17, 2232–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, M.E.; Friedrichs, C.T.; Brubaker, J. Control of estuarine stratification and mixing by wind-induced straining of the estuarine density field. Estuaries 2005, 28, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, T.W.; Najjar, R.G.; Zhong, L.; Li, M. Is there a signal of sea-level rise in Chesapeake Bay salinity? J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigg, N.J.; Ivey, G.N. A laboratory investigation into shear-generated mixing in a salt wedge estuary. Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn. 1997, 85, 65–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Yuan, L.; Gao, S.; Chen, R.; Su, B. Experimental study on the relationship between tide strength and salt intrusion length. Adv. Water Sci. 2013, 24, 251–257. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, A.D.; Gisen, J.I.A.; Van Der Zaag, P.; Savenije, H.H.G.; Karim, U.F.A.; Masih, I.; Popescu, I. Predicting the salt water intrusion in the Shatt al-Arab estuary using an analytical approach. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 4031–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Savenije, H.H.; Zuo, S.; Jiang, C.; Chua, V.P. A predictive model for salt intrusion in estuaries applied to the Yangtze estuary. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 1336–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisen, J.I.A.; Savenije, H.H.G.; Nijzink, R.C. Revised predictive equations for salt intrusion modelling in estuaries. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 2791–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaha, D.C.; Cho, Y.-K.; Kim, T.-W. Effects of River Discharge and Tide Driven Sea Level Variation on Saltwater Intrusion in Sumjin River Estuary: An Application of Finite-Volume Coastal Ocean Model. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 287, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchepetkin, A.F.; McWilliams, J.C. The regional oceanic modeling system (ROMS): A split-explicit, free-surface, topography-following-coordinate oceanic model. Ocean Model. 2005, 9, 347–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Baptista, A.M. SELFE: A semi-implicit Eulerian–Lagrangian finite-element model for cross-scale ocean circulation. Ocean Model. 2008, 21, 71–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Ye, F.; Stanev, E.V.; Grashorn, S. Seamless cross-scale modeling with SCHISM. Ocean Model. 2016, 102, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, G.J.; Maier, H.R.; Dandy, G.C. Input determination for neural network models in water resources applications. Part 2. Case study: Forecasting salinity in a river. J. Hydrol. 2005, 301, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, J.S.; Hutton, P.H.; Chen, L.; Roy, S.B. A hybrid empirical-Bayesian artificial neural network model of salinity in the San Francisco Bay-Delta estuary. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 93, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohmer, J.; Brisset, N. Short-term forecasting of saltwater occurrence at La Comté River (French Guiana) using a kernel-based support vector machine. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, D.; Brett, H. The relationship between CDOM and salinity in estuaries: An analytical and graphical solution. J. Mar. Syst. 2008, 73, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Wan, Y. Time series modeling and prediction of salinity in the Caloosahatchee River Estuary. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 5804–5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Xin, Y.; Xie, C.; Qi, L.I. An empirical predictive model for saltwater intrusion in the South Branch influenced by tidal flow from the North Branch in the Yangtze River Estuary. Adv. Water Sci. 2017, 28, 213–222. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, N.; Westrich, B.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Y. A coupling simulation based on a hydrodynamics and water quality model of the Pearl River Delta, China. J. Hydrol. 2011, 396, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, P.; Wang, S.S.J.; Robinson, C.E.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.-G.; Barry, D.A. Memory of past random wave conditions in submarine groundwater discharge. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 2401–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, P.; Wang, S.S.J.; Shen, C.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, C.; Li, L. Predictability and Quantification of Complex Groundwater Table Dynamics Driven by Irregular Surface Water Fluctuations. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 2436–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Xin, P.; Lu, C.; Robinson, C.E.; Li, L.; Barry, D. Effects of episodic rainfall on a subterranean estuary. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 5774–5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.H.; Song, Z.Y.; Zhang, C.M.; He, Y.; Yu, S.C.; Kong, J.; Li, L. Analytical Model for Surface Saltwater Intrusion in Estuaries. J. Coast. Res. 2017, 33, 712–719. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Sun, Z.L.; Zhu, L.L.; Huang, S.H. Numerical simulation of salinity in Qiantang river estuary. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2013, 44, 829–836. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, B.; Bao, Y.; Huang, Y. Salt wedge with vertical structure of discontinuous and continuous distribution in modaomen waterway. Sci. Sin. Phys. Mech. Astron. 2011, 41, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Liu, J.; Ren, J.; Xu, W.; Qi, Z. Research of Law and Dynamic Mechanism for Strong Saline Water Intrusion in Modaomen Waterway. Sci. Sin. Phys. Mech. Astron. 2009, 39, 1527–2534. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, P.; Chen, X.H.; Liu, B. Analysis of tidal saltwater intrusion and its variation in Modaomen channel. J. China Hydrol. 2007, 27, 65–67. [Google Scholar]
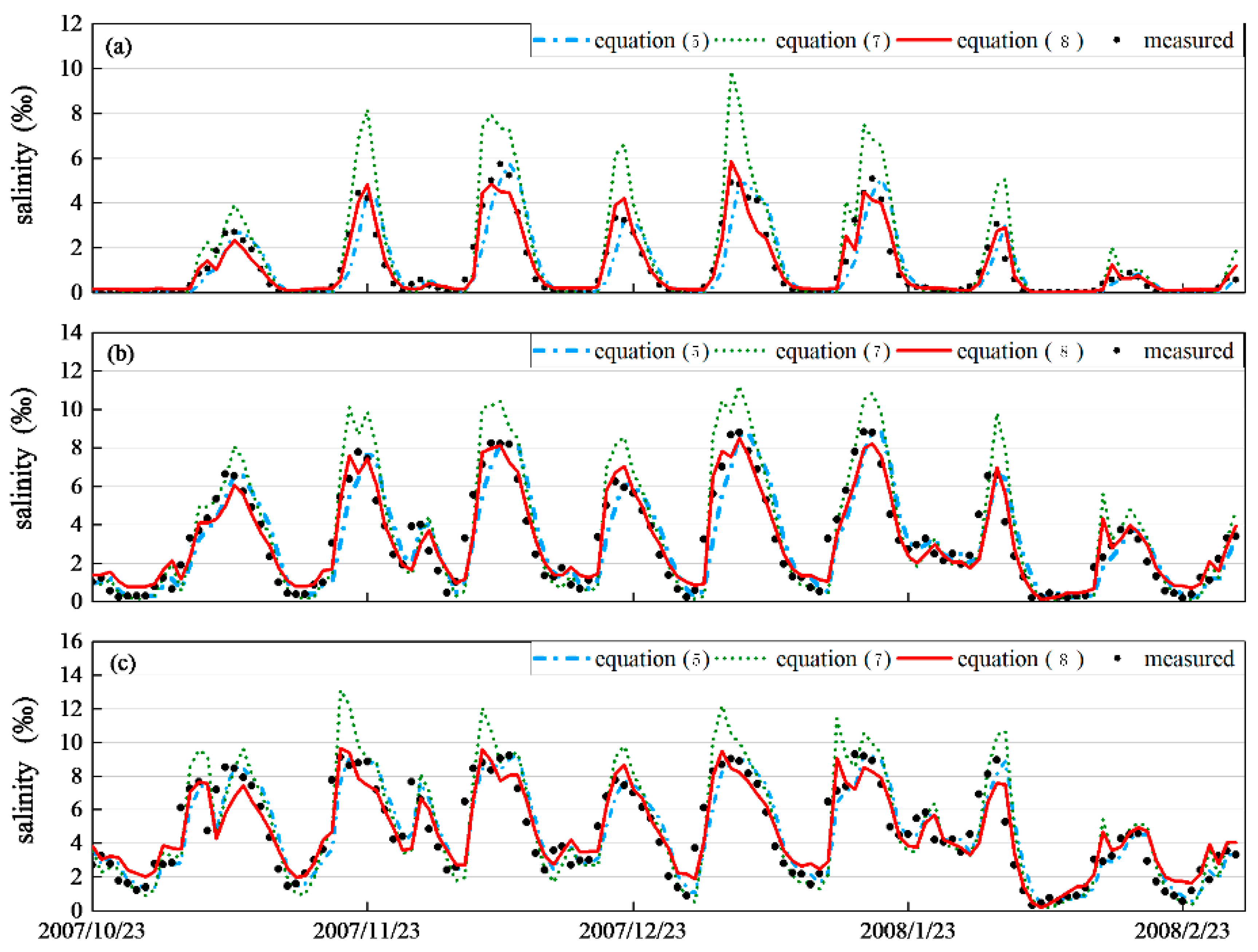
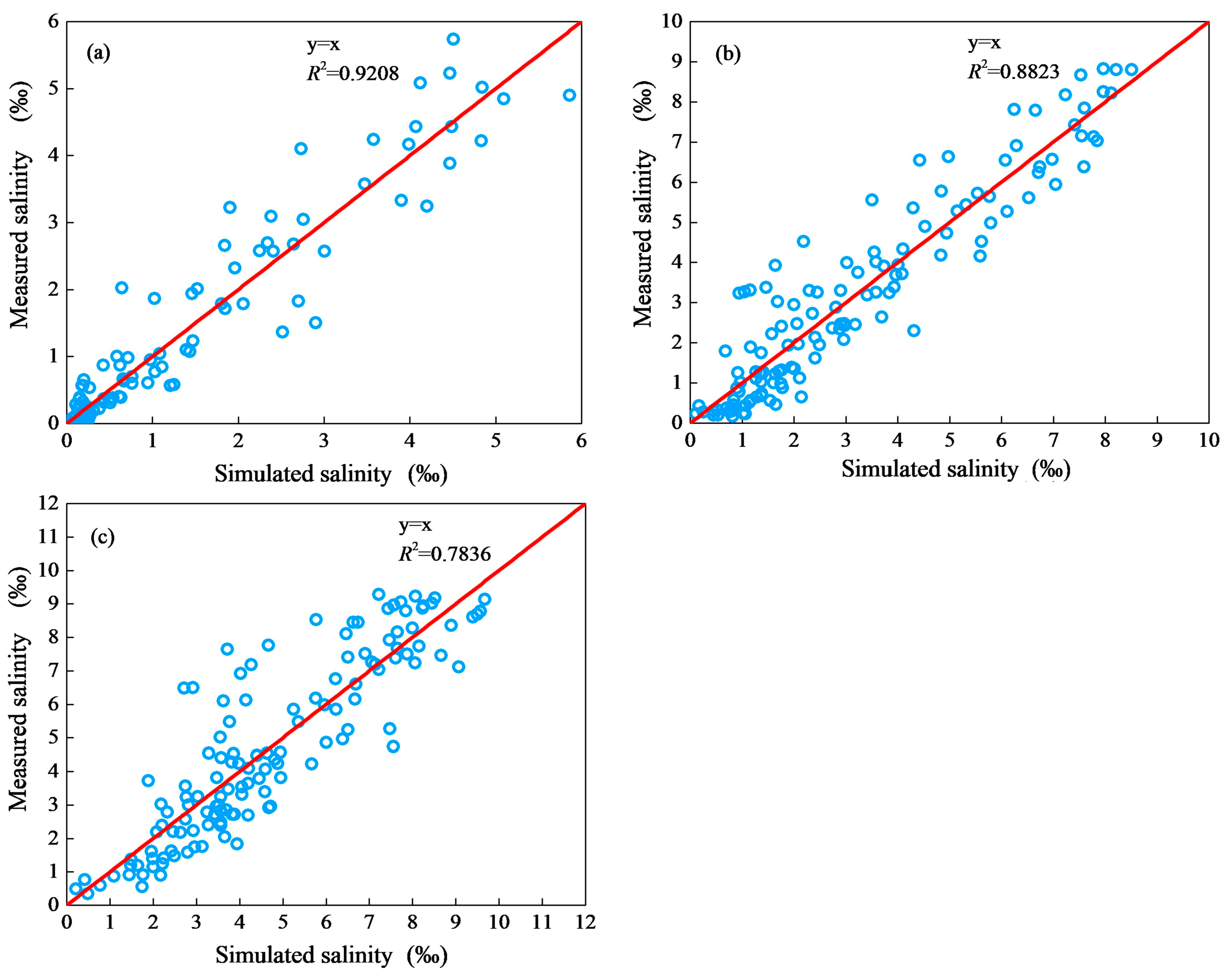
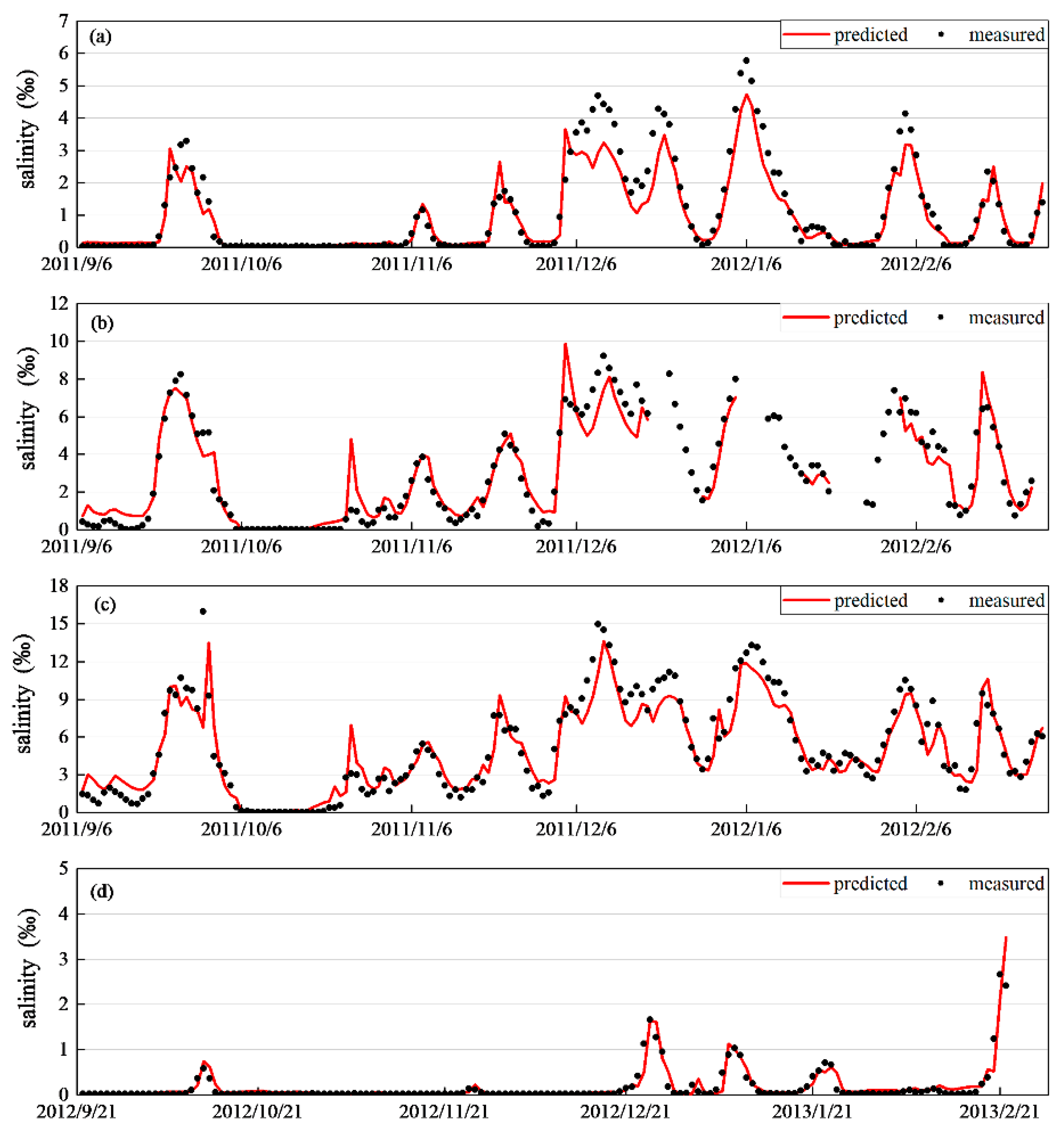
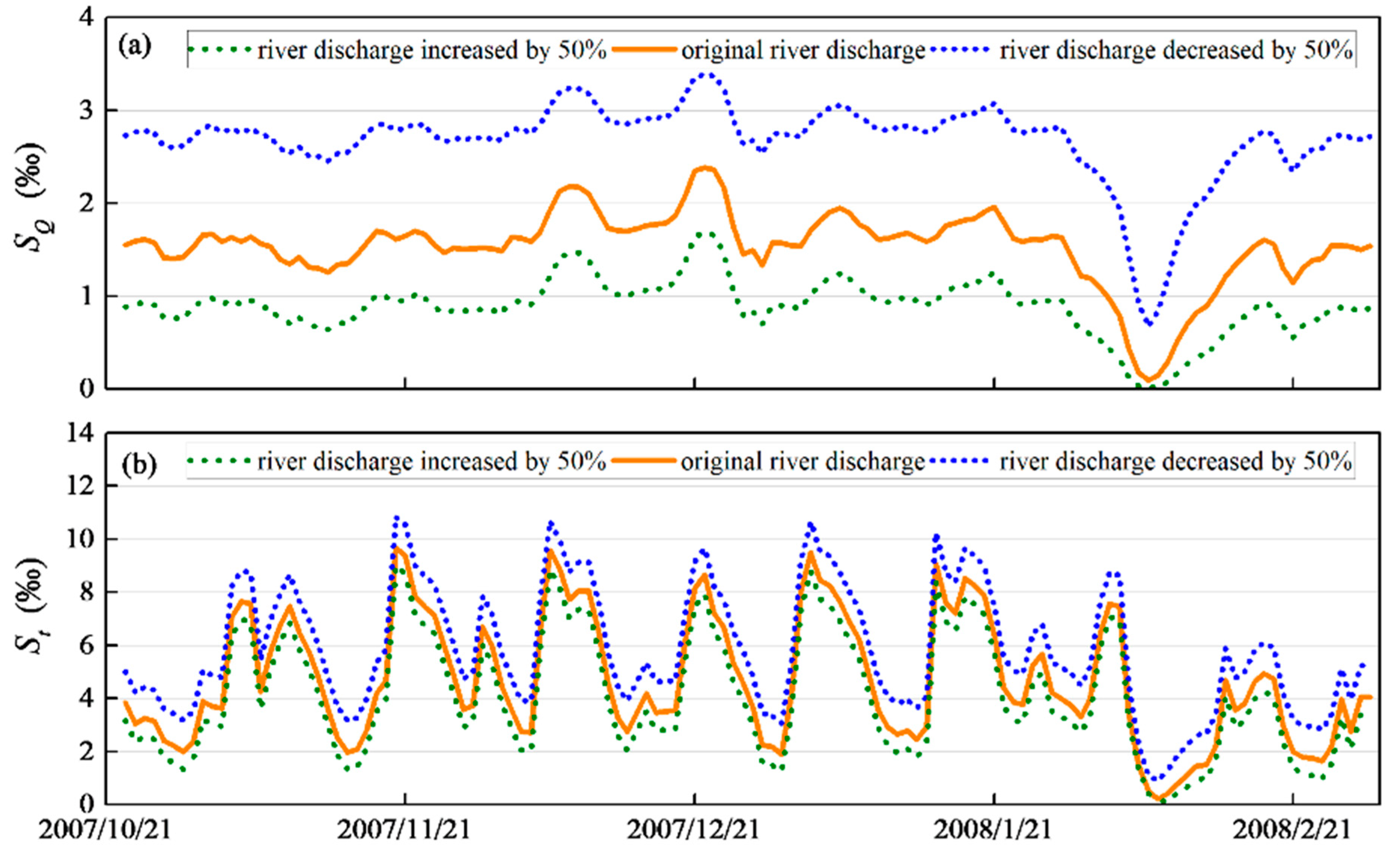

| Location | A | B | C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pinggang | 2.4429 | −0.0013 | 0.5711 |
| Lianshiwan | 3.1579 | −0.0006 | 0.6701 |
| Guangchang | 4.8074 | −0.0005 | 0.6349 |
| Location | n | (‰) | Omin (‰) | Omax (‰) | R2 | RMSE (‰) | NSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pinggang | |||||||
| Calibration (2007–2008) | 130 | 1.0847 | 0.0146 | 5.7379 | 0.9208 | 0.4201 | 0.9207 |
| Application (2011–2012) | 176 | 1.1040 | 0.0212 | 5.7767 | 0.9195 | 0.5066 | 0.8750 |
| Application (2012–2013) | 154 | 0.1622 | 0.0158 | 2.6646 | 0.8560 | 0.1551 | 0.8377 |
| Lianshiwan | |||||||
| Calibration (2007–2008) | 130 | 3.1935 | 0.1633 | 8.8179 | 0.8823 | 0.8553 | 0.8822 |
| Application (2011–2012) | 142 | 2.8297 | 0.0053 | 9.2096 | 0.8904 | 0.8946 | 0.8882 |
| Guangchang | |||||||
| Calibration (2007–2008) | 130 | 4.7043 | 0.3429 | 9.2829 | 0.7836 | 1.2363 | 0.7876 |
| Application (2011–2012) | 176 | 5.2052 | 0.0173 | 15.9654 | 0.8617 | 1.4963 | 0.8503 |
| Location | n | (‰) | Omin (‰) | Omax (‰) | R2 | RMSE (‰) | NSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pinggang | |||||||
| Calibration (23 October 2007 to 31 December 2007) | 70 | 1.1142 | 0.0200 | 5.7379 | 0.9361 | 0.3763 | 0.9361 |
| Application (1 January 2008 to 29 February 2008) | 60 | 1.0502 | 0.0146 | 5.0863 | 0.9025 | 0.4702 | 0.9012 |
| Lianshiwan | |||||||
| Calibration (23 October 2007 to 31 December 2007) | 70 | 3.1534 | 0.2342 | 8.2496 | 0.8694 | 0.8761 | 0.8694 |
| Application (1 January 2008 to 29 February 2008) | 60 | 3.2403 | 0.1633 | 8.8179 | 0.8593 | 0.8946 | 0.8339 |
| Guangchang | |||||||
| Calibration (1 January 2008 to 29 February 2008) | 70 | 5.0674 | 0.8933 | 9.2304 | 0.7235 | 1.3283 | 0.7235 |
| Application (1 January 2008 to 29 February 2008) | 60 | 4.2807 | 0.3429 | 9.2829 | 0.8359 | 1.1329 | 0.8294 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, R.; Kong, J.; Shen, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W. An Alternative Statistical Model for Predicting Salinity Variations in Estuaries. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10677. https://doi.org/10.3390/su122410677
Ye R, Kong J, Shen C, Zhang J, Zhang W. An Alternative Statistical Model for Predicting Salinity Variations in Estuaries. Sustainability. 2020; 12(24):10677. https://doi.org/10.3390/su122410677
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Ronghui, Jun Kong, Chengji Shen, Jinming Zhang, and Weisheng Zhang. 2020. "An Alternative Statistical Model for Predicting Salinity Variations in Estuaries" Sustainability 12, no. 24: 10677. https://doi.org/10.3390/su122410677
APA StyleYe, R., Kong, J., Shen, C., Zhang, J., & Zhang, W. (2020). An Alternative Statistical Model for Predicting Salinity Variations in Estuaries. Sustainability, 12(24), 10677. https://doi.org/10.3390/su122410677




