Ecotoxicity Responses of the Macrophyte Algae Nitellopsis obtusa and Freshwater Crustacean Thamnocephalus platyurus to 12 Rare Earth Elements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Charophyte Algae Cell Lethality Testing
2.3. Shrimp Lethality Testing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rigault, S.; Piguet, C. Predictions and assignments of NMR spectra for strongly paramagnetic supramolecular lanthanide complexes: The effect of the “gadolinium break”. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 9304–9305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, D.P.; Jiang, J. Distinction between light and heavy lanthanide(III) ions based on the 1H NMR spectra of heteroleptic triple-decker phthalocyaninato sandwich complexes. J. Phys. Chem. 2001, 105, 7525–7533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, G. Rare earth elements in soil and plant systems—A review. Plant Soil 2004, 267, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, E.; Sherman, A.M.; Wallington, T.J.; Everson, M.P.; Field, F.R.; Roth, R.; Kirchain, R.E. Evaluating rare earth element availability: A case with revolutionary demand from clean technologies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3406–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, V.; Vignati, D.A.L.; Leyval, C.; Giamberini, L. Environmental fate and ecotoxicity of lanthanides: Are they a uniform group beyond chemistry? Environ. Int. 2014, 71, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T.; Blanpain, B.; Van Gerven, T.; Yang, Y.; Walton, A.; Buchert, M. Recycling of rare earths: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 51, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaram, V. Rare Earth Elements: A review of applications, occurrence, exploration, analysis, recycling, and environmental impact. Geosci. Front. 2019, 10, 1285–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansel, B. From electronic consumer products to e-wastes: Global outlook, waste quantities, recycling challenges. Environ. Int. 2016, 98, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwenzi, W.; Mangori, L.; Danha, C.; Chaukura, N.; Dunjana, N.; Sanganyado, E. Sources, behaviour, and environmental and human health risks of high-technology rare earth elements as emerging contaminants. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Henriques, B.; Pinto, J.; Fabre, E.; Dias, M.; Soares, J.; Carvalho, L.; Vale, C.; Pinheiro-Torres, J.; Pereira, E. Influence of toxic elements on the simultaneous uptake of rare earth elements from contaminated waters by estuarine macroalgae. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulaksiz, S.; Bau, M. Anthropogenic dissolved and colloid/nanoparticle-bound samarium, lanthanum and gadolinium in the Rhine River and the impending destruction of the natural rare earth element distribution in rivers. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 362, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneller, F.E.C.; Kalf, D.F.; Weltje, L.; Van Wezel, A.P. Maximum Permissible Concentrations and Negligible Concentrations for Rare Earth Elements (REE); RIVM Report No. 601501011; National Institute of Public Health and the Environment: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kulaksiz, S.; Bau, M. Rare earth elements in the Rhine River, Germany: First case of anthropogenic lanthanum as a dissolved microcontaminant in the hydrosphere. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Freire, A.; Minguez, L.; Pelletier, M.; Cayer, A.; Caillet, C.; Devin, S.; Gross, E.M.; Guérold, F.; Pain-Devin, S.; Vignati, D.A.L.; et al. Assessment of baseline ecotoxicity of sediments from a prospective mining area enriched in light rare earth elements. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, P.; Paces, T.; Dulski, P.; Moteani, G. Anthropogenic Gd in surface water, drainage system, and the water supply of the city of Prague, Czech Republic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2387–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogowska, J.; Olkowska, E.; Ratajczyk, W.; Wolska, L. Gadolinium as a new emerging contaminant of aquatic environment. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 1523–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brünjes, R.; Hofmann, T. Anthropogenic gadolinium in freshwater and drinking water systems. Water Res. 2020, 182, 115966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atinkpahoun, C.N.H.; Pons, M.-N.; Louis, P.; Leclerc, J.-P.; Henri, H.; Soclo, H.H. Rare earth elements (REE) in the urban wastewater of Cotonou (Benin, West Africa). Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M.; Knappe, A.; Dulski, P. Anthropogenic gadolinium as a micropollutant in river waters in Pennsylvania, and in Lake Erie, northeastern United States. Chem. Erde 2006, 66, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurvet, I.; Juganson, K.; Vija, H.; Sihtmäe, M.; Blinova, I.; Syvertsen-Wiig, G.; Kahru, A. Toxicity of nine (doped) rare earth metal oxides and respective individual metals to aquatic microorganisms Vibrio fischeri and Tetrahymena thermophila. Materials 2017, 10, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinova, I.; Lukjanova, A.; Muna, M.; Vija, H.; Kahru, A. Evaluation of the potential hazard of lanthanides to freshwater microcrustaceans. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgmann, U.; Couillard, Y.; Doyle, P.; Dixon, G. Toxicity of sixty-three metals and metalloids to Hyalella azteca at two levels of water hardness. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, P.; Zhao, Q.; Su, D.; Li, P.; Stagnitti, F. Biological toxicity of lanthanide elements on algae. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaise, C.; Gagné, F.; Harwood, M.; Quinn, B.; Hanana, H. Ecotoxicity responses of the freshwater cnidarian Hydra attenuata to 11 rare earth elements. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 163, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannier, N.; Bado-Nilles, A.; Delalain, P.; Aguerre-Chariol, O.; Pandard, P. Ecotoxicity of non-aged and aged CeO2 nanomaterials towards freshwater microalgae. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 180, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, V.; Vignati, D.A.L.; Pons, M.-N.; Montarges-Pelletier, E.; Bojic, C.; Giamberini, L. Lanthanide ecotoxicity: First attempt to measure environmental risk for aquatic organism. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 199, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joonas, E.; Aruoja, V.; Olli, K.; Syvertsen-Wiig, G.; Vija, H.; Kahru, A. Potency of (doped) rare earth oxide particles and their constituent metals to inhibit algal growth and induce direct toxic effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 593–594, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Freire, J.E.; Muna, M.; Cossu-Leguille, C.; Vignati, D.A.L.; Giamberini, L. Assessment of the toxic effects of mixtures of three lanthanides (Ce, Gd, Lu) to aquatic biota. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 661, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergsten-Torralba, L.R.; Magalhães, D.P.; Giese, E.C.; Nascimento, C.R.S.; Pinho, J.V.A.; Buss, D.F. Toxicity of three rare earth elements, and their combinations to algae, microcrustaceans, and fungi. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 201, 110795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röhder, L.A.; Brandta, T.; Sigg, L.; Behra, R. Influence of agglomeration of cerium oxide nanoparticles and speciation of cerium(III) on short term effects to the green algae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 152, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Akl, P.; Smith, S.; Wilkinson, K.J. Linking the chemical speciation of cerium to its bioavailability in water for a freshwater alga. Environ. Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 34, 1711–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.-G.; Yang, G.; Wilkinson, K.J. Biotic ligand model explains the effects of competition but not complexation for Sm biouptake by Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Řezanka, T.; Kaineder, K.; Mezricky, D.; Řezanka, M.; Bišová, K.; Zachleder, V.; Vítová, M. The effect of lanthanides on photosynthesis, growth, and chlorophyll profile of the green alga Desmodesmus quadricauda. Photosynth. Res. 2016, 130, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kawakami, H.; Aoki, M.; Tuzuki, M. Evaluation of metal toxicity in Chlorella kessleri from the perspective of the periodic table. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2008, 81, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vítová, M.; Čížková, M.; Zachleder, V. Lanthanides and Algae. In Lanthanides; Awwad, N.S., Mubarak, A.T., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, M.S.; Scheffer, M.; Coops, H.; Simons, J. The role of characean algae in the management of eutrophic shallow lakes. J. Phycol. 1998, 34, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manusadžianas, L.; Maksimov, G.; Darginavičienė, J.; Jurkonienė, S.; Sadauskas, K.; Vitkus, R. Response of charophyte Nitellopsis obtusa to heavy metals at the cellular, cell membrane and enzyme levels. Environ. Toxicol. 2002, 17, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigutytė, R.; Nimptsch, J.; Manusadžianas, L.; Pflugmacher, S. Response of oxidative stress enzymes in charophyte Nitellopsis obtusa exposed to allochthonous leaf extracts from beech Fagus sylvatica. Biologija 2009, 55, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gylytė, B.; Manusadžianas, L.; Sadauskas, K.; Vitkus, R.; Jurkonienė, S.; Karitonas, R.; Petrošius, R.; Skridlaitė, G.; Vaičiūnienė, J. Latent cell mortality after short-term exposure of Nitellopsis obtusa cells to copper oxide nanoparticles. Botanica 2015, 21, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Manusadžianas, L.; Caillet, C.; Fachetti, L.; Gylytė, B.; Grigutytė, R.; Jurkonienė, S.; Karitonas, R.; Sadauskas, K.; Thomas, F.; Vitkus, R.; et al. Toxicity of copper oxide nanoparticle suspensions to aquatic biota. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manusadžianas, L.; Gylytė, B.; Grigutytė, R.; Karitonas, R.; Sadauskas, K.; Vitkus, R.; Šiliauskas, L.; Vaičiūnienė, J. Accumulation of copper in the cell compartments of charophyte Nitellopsis obtusa after its exposure to copper oxide nanoparticle suspension. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 27653–27661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurkonienė, S.; Maksimov, G.; Darginavičienė, J.; Sadauskas, K.; Vitkus, R.; Manusadžianas, L. Leachate toxicity assessment by responses of algae Nitellopsis obtusa membrane ATPase and cell resting potential, and with Daphtoxkit F™ magna test. Environ. Toxicol. 2004, 19, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumińsky, C. Solubility and the periodic table of elements. Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostkevičienė, J.; Sinkevičienė, Z. A preliminary checklist of Lithuanian macroalgae. Bot. Lith. 2008, 14, 11–27. [Google Scholar]
- SOP (Standard Operating Procedure). Thamnotoxkit FTM. In Crustacean Toxicity Screening Test for Freshwater; Microbiotests: Gent, Belgium, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Environment Canada. Guidance Document on Statistical Methods for Environmental Toxicity Tests; Report EPS 1/RM/46; Environment Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Emsley, J. The Elements; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Verweij, W. CHEAQS: A Program for Calculating Chemical Equilibria in Aquatic Systems (CHEAQS Pro, succeeded by CHEAQS Next), version 2020.2, dated July 2020. Available online: https://www.cheaqs.eu (accessed on 17 August 2020).
- CEC (Commission of the European Communities). Technical Guidance Document in Support of Commission Directive 93/67/EEC on Risk Assessment for New Notified Substances. Part. II, Environmental Risk Assessment; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Barry, M.; Meehan, B.J. The acute and chronic toxicity of lanthanum to Daphnia carinata. Chemosphere 2000, 41, 1669–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltje, L.; Verhoof, L.R.C.W.; Verweij, W.; Hamers, T. Lutetium speciation and toxicity in microbial bioassay: Testing the free-ion model for lanthanides. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 6597–6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Peng, C.; Ding, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, P.; Li, N.; Lan, T.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Toxicity of cerium and thorium on Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 134, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltje, L.; Brouwer, A.H.; Verburg, T.G.; Wolterbeek, H.T.; de Goeij, J.J.M. Accumulation and elimination of lanthanum by duckweed (Lemna minor L.) as influenced by organism growth and lanthanum sorption to glass. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2002, 21, 1483–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltje, L.; Heidenreich, H.; Zhu, W.; Wolterbeek, H.T.; Korhammer, S.; de Goeij, J.J.M.; Markert, B. Lanthanide concentrations in freshwater plants and molluscs, related to those in surface water, pore water and sediment. A case study in The Netherlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 286, 191–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Rare Earth Element | Atomic Number | Crystalline Ionic Radius *, pm | Nitellopsis obtusa | Thamnocephalus Platyurus | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC50 (95% CI), mg Metal/L | Ratio of LC50s | 24-h LC50 (95% CI), mg Metal/L | ||||||||
| 8 Days | 12 Days | 16 Days | 20 Days | 24 Days | 8 Days/24 Days | Based on Nominal Concentrations | Based on Free Ion [Ln3+] ** | |||
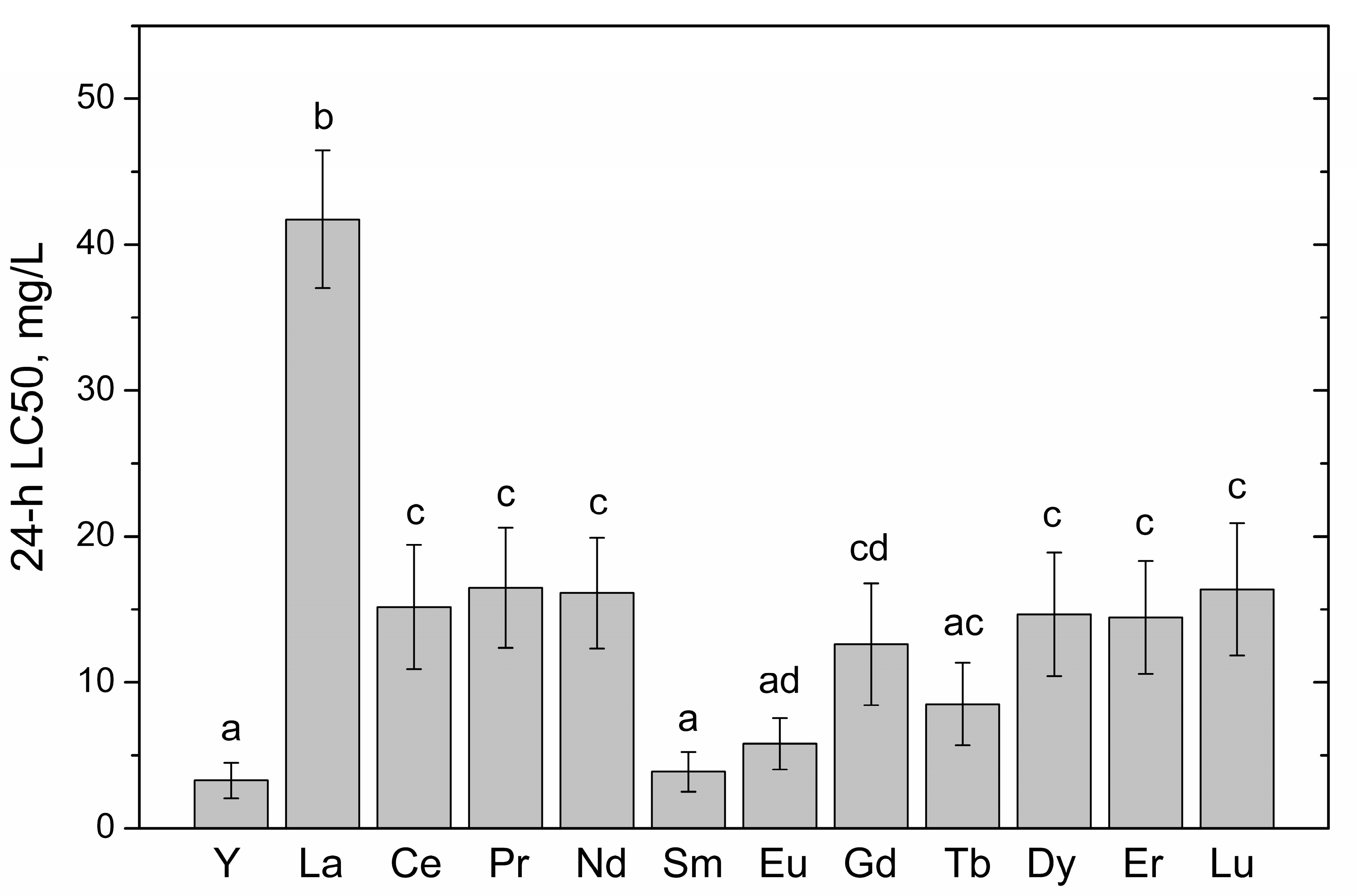
| Yttrium (Y) | 39 | 106 | 138 (95.1–202) | 28.3 (20.3–39.5) | 6.12 (5.32–7.03) | 5.17 (4.66–5.73) | 4.38 (4.16–4.62) | 32 | 3.22 (2.47–4.20) | 0.22 (0.17–0.29) |
| Lanthanum (La) | 57 | 122 | 101 (77.5–132) | 43.3 (37.1–50.5) | 30.7 (25.2–37.3) | 27.3 (21.6–34.6) | 21.5 (15.7–29.5) | 4.7 | 45.2 (39.3–51.9) | 10.6 (9.03–12.4) |
| Cerium (Ce) | 58 | 107 | 121 (104–141) | 73.1 (65.9–80.9) | 51.1 (46.0–56.7) | 45.8 (14.3–50.9) | 26.0 (19.9–33.9) | 4.7 | 15.1 (11.6–19.8) | 2.23 (1.68–2.97) |
| Praseodymium (Pr) | 59 | 106 | 51.4 (42.3–62.6) | 35.4 (28.1–44.6) | 24.1 (17.7–32.8) | 11.2 (7.36–17.0) | 3.17 (2.20–4.58) | 16 | 16.1 (12.1–21.4) | 1.98 (1.45–2.69) |
| Neodymium (Nd) | 60 | 104 | 51.4 (47.9–55.3) | 28.0 (23.8–32.8) | 19.2 (16.4–22.4) | 14.2 (12.4–16.4) | 14.4 (11.3–18.4) | 3.6 | 15.2 (11.2–20.5) | 1.52 (1.10–2.09) |
| Samarium (Sm) | 62 | 100 | 71.9 (–) | 35.3 (21.0–41.6) | 22.9 (20.0–26.2) | 16.6 (13.6–20.1) | 13.1 (10.9–15.6) | 5.5 | 3.88 (2.78–5.42) | 0.26 (0.19–0.35) |
| Europium (Eu) | 63 | 98 | 44.7 (37.3–53.4) | 33.3 (31.0–35.7) | 26.2 (22.7–30.3) | 16.7 (13.5–20.8) | 12.2 (9.80–15.3) | 3.7 | 5.20 (3.87–6.98) | 0.35 (0.25–0.47) |
| Gadolinium (Gd) | 64 | 97 | 32.0 (25.5–40.2) | 22.2 (18.7–26.4) | 17.1 (13.8–21.1) | 3.30 (2.33–4.68) | 0.39 (0.23–0.66) | 83 | 11.8 (7.96–17.5) | 0.90 (0.59–1.37) |
| Terbium (Tb) | 65 | 93 | 128 (81.6–201) | 31.9 (25.8–39.6) | 23.1 (18.3–29.1) | 16.8 (12.9–21.9) | 8.67 (7.02–10.7) | 15 | 8.11 (5.60–11.8) | 0.51 (0.34–0.77) |
| Dysprosium (Dy) | 66 | 91 | 167 (82.2–339) | 40.6 (31.8–52.0) | 33.5 (26.3–42.6) | 25.0 (17.8–35.1) | 8.01 (3.29–19.5) | 21 | 15.7 (12.6–19.5) | 0.84 (0.66–1.08) |
| Erbium (Er) | 68 | 89 | 286 (117–700) | 70.7 (55.3–90.3) | 37.6 (30.3–46.6) | 19.1 (15.9–23.1) | 2.79 (1.47–5.29) | 103 | 14.6 (11.7–18.4) | 0.66 (0.52–0.85) |
| Lutetium (Lu) | 71 | 85 | 260 (165–412) | 127 (83.1–195) | 48.2 (34.9–66.7) | 15.0 (8.40–26.7) | 1.82 (0.59–5.63) | 143 | 15.7 (12.2–20.3) | 0.51 (0.38–0.69) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manusadžianas, L.; Vitkus, R.; Gylytė, B.; Cimmperman, R.; Džiugelis, M.; Karitonas, R.; Sadauskas, K. Ecotoxicity Responses of the Macrophyte Algae Nitellopsis obtusa and Freshwater Crustacean Thamnocephalus platyurus to 12 Rare Earth Elements. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7130. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177130
Manusadžianas L, Vitkus R, Gylytė B, Cimmperman R, Džiugelis M, Karitonas R, Sadauskas K. Ecotoxicity Responses of the Macrophyte Algae Nitellopsis obtusa and Freshwater Crustacean Thamnocephalus platyurus to 12 Rare Earth Elements. Sustainability. 2020; 12(17):7130. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177130
Chicago/Turabian StyleManusadžianas, Levonas, Rimantas Vitkus, Brigita Gylytė, Reda Cimmperman, Mindaugas Džiugelis, Rolandas Karitonas, and Kazys Sadauskas. 2020. "Ecotoxicity Responses of the Macrophyte Algae Nitellopsis obtusa and Freshwater Crustacean Thamnocephalus platyurus to 12 Rare Earth Elements" Sustainability 12, no. 17: 7130. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177130
APA StyleManusadžianas, L., Vitkus, R., Gylytė, B., Cimmperman, R., Džiugelis, M., Karitonas, R., & Sadauskas, K. (2020). Ecotoxicity Responses of the Macrophyte Algae Nitellopsis obtusa and Freshwater Crustacean Thamnocephalus platyurus to 12 Rare Earth Elements. Sustainability, 12(17), 7130. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177130




