Regional Green Eco-Efficiency in China: Considering Energy Saving, Pollution Treatment, and External Environmental Heterogeneity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Hypotheses
2.1. Overview of Eco-Efficiency
2.2. Hypotheses
- Hypothesis 1 on Government Support and Resource Utilization
- Hypothesis 2 on Urbanization Level and Resource Utilization
- Hypothesis 3 on Industrial Structure and Resource Utilization
- Hypothesis 4 on Energy Consumption Structure and Resource Utilization
- Hypothesis 5 on Technological Progress and Resource Utilization
- Hypothesis 6 on Environmental Regulation and Resource Utilization
- Hypothesis 7 on Economic Development and Resource Utilization
3. Methodology
3.1. Phase One: Initial Eco-Efficiency Evaluation Using a Two-Stage Production Structure DEA Model
3.2. Phase Two: External Environment and Statistical Noise Elimination by Applying SFA
3.3. Phase Three: Eco-Efficiency Evaluation by Using Formulas (1)–(3) with the Adjusted Inputs
4. Variables and Data
4.1. Input and Output Variables and Data Description
4.2. Influence Factors Indexes and Data Description
5. Empirical Results Analysis
5.1. Effect of External Environment on Energy Saving Efficiency
5.2. Effect of the External Environment on Pollution Treatment Efficiency
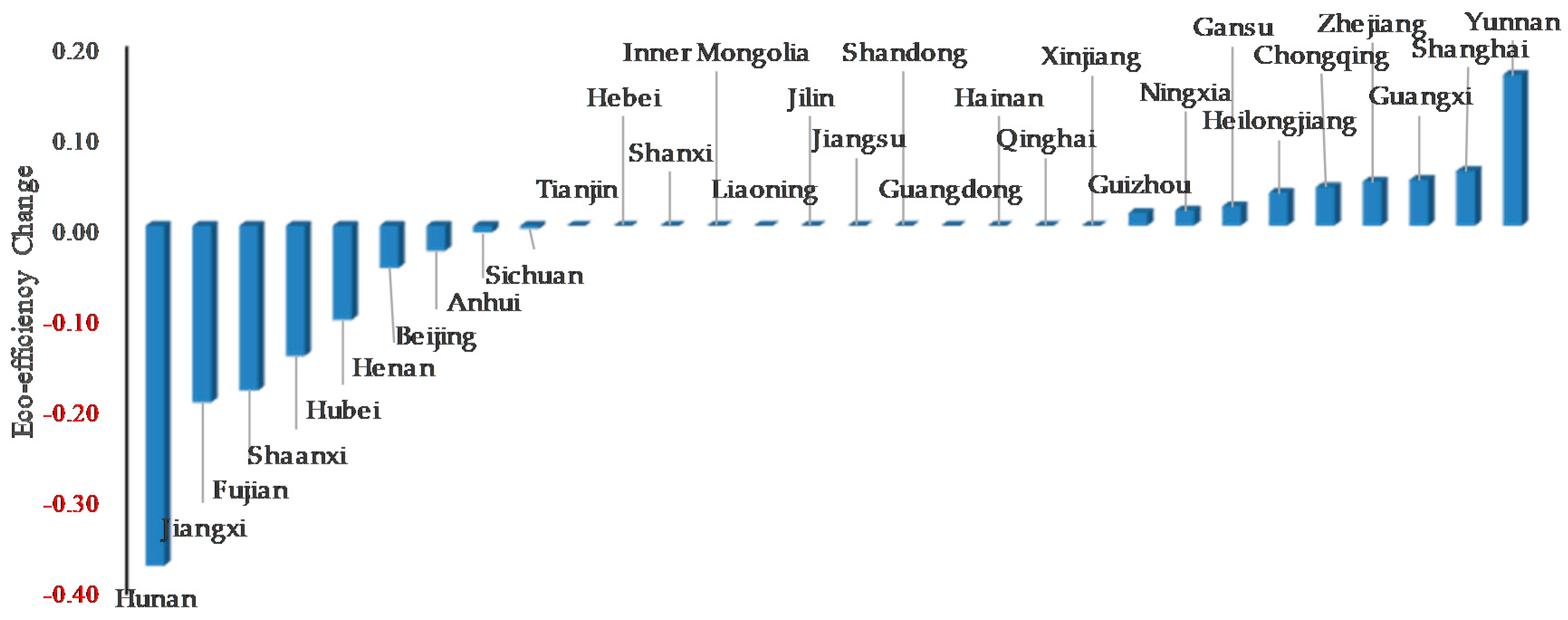
5.3. The Analysis of Initial and Adjusted Eco-Efficiency
5.4. Implications and Suggestions
6. Discussion and Conclusions
6.1. Discussion
6.2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, M.; Cao, S.; Wang, S. The impact of knowledge trade on sustainable development and environment-biased technical progress. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 144, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics. National Data. Available online: http://data.stats.gov.cn/easyquery.htm?cn=C01 (accessed on 15 August 2020).
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, X.; Valdmanis, V.; Baležentis, T. Evaluating economic and environmental performance of the Chinese industry sector. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Energy Division of National Bureau of Statistics. China Statistical Yearbook on Environment (2011–2018); China Statistical Press: Beijing, China, 2012–2019.
- Ouyang, X.; Wei, X.; Sun, C.; Du, G. Impact of factor price distortions on energy efficiency: Evidence from provincial-level panel data in China. Energy Policy 2018, 118, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Huang, D.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, Q. The regional green growth and sustainable development of China in the presence of sustainable resources recovered from pollutions. Ann. Oper. Res. 2019, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, L. Industrial eco-efficiency in China: A provincial quantification using three-stage data envelopment analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, W.; Tang, Z.; Gao, X.; Wan, Z.; Zhang, X. The impact of government role on high-quality innovation development in mainland China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Zhu, J. Impact of energy saving and emission reduction policy on urban sustainable development: Empirical evidence from china. Appl. Energy 2019, 239, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincer, I.; Rosen, M.A. A worldwide perspective on energy, environment and sustainable development. Int. J. Energy Res. 1998, 22, 1305–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Z.; Zeng, R.; Han, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Fu, H. Energy efficiency evaluation and energy saving based on dea integrated affinity propagation clustering: Case study of complex petrochemical industries. Energy 2019, 179, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Peng, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J. Environmental efficiency and economic growth of China: A Ray slack-based model analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 269, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaltegger, S.; Sturm, A. Ecological rationality: Approaches to design of ecology-oriented management instruments. Die Unt. 1990, 4, 273–290. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Total-factor ecological efficiency and productivity in Yangtze River Economic Belt, China: A non-parametric distance function approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 200, 844–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charmondusit, K.; Phatarachaisakul, S.; Prasertpong, P. The quantitative ecoefficiency measurement for small and medium enterprise: A case study of wooden toy industry. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2014, 16, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Guo, X.; Wu, H.; Yu, J. Evaluating air quality in China based on daily data: Application of integer data envelopment analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 198, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinos-Senante, M.; Gémar, G.; Gómez, T.; Caballero, R.; Sala-Garrido, R. Eco-efficiency assessment of wastewater treatment plants using a weighted Russell directional distance model. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 1066–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Xu, L.; Tang, L.; Xiang, X. Eco-efficiency of the Western Taiwan Straits Economic Zone: An evaluation based on a novel eco-efficiency model and empirical analysis of influencing factors. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 234, 638–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskela, M.; Vehmas, J. Defining eco-efficiency: A case study on the Finnish forest industry. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2012, 21, 546–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Fisher, R.; Wang, J.L.; Cui, L.B. Environmental performance evaluation with big data: Theories and methods. Ann. Oper. Res. 2018, 270, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Li, X.; Yuan, B.; Li, D.; Chen, X. The effects of three types of environmental regulation on eco-efficiency: A cross-region analysis in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 173, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Bi, J.; Fan, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Ge, J. Eco-efficiency analysis of industrial system in China: A data envelopment analysis approach. Ecol. Econ. 2008, 68, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Business Council for Sustainable Development. Eco-Efficient Leadership for Improved Economicand Environmental Performance; World Business Council for Sustainable Development: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, S.F. Research on ecological efficiency in Fujian province. J. Minjiang Univ. 2009, 30, 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.S.; Lu, Z.W.; Yang, Z.F. Preliminary study on the basic characteristics of environmental management. Environ. Sustain. Dev. 2004, 4, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.C. Environmental efficiency—One of the paths for developing circular economy. Environ. Sustain. Dev. 2005, 1, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlström, K.; Ekins, P. Eco-efficiency trends in the UK steel and aluminum industries: Differences between resource ef fi ciency and resource productivity. J. Ind. Ecol. 2005, 9, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.; Chang, Y.; Cheng, B. The eco-efficiency of pulp and paper industry in China: An assessment based on slacks-based measure and Malmquiste Luenberger index. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 127, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickwitz, P.; Melanen, M.; Rosenström, U.; Seppälä, J. Regional eco-efficiency indicators—A participatory approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2006, 14, 1603–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tsai, H.; Wu, J. Regional hotel performance and benchmarking in the Pearl River Delta: An input and output efficiency analysis. Int. J. Contempor. Hosp. Manag. 2018, 30, 855–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.; Rhodes, E. Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1978, 2, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhou, Z.; Ma, C.; Liu, D.; Shen, W. Two-stage DEA models with undesirable input-intermediate-outputs. Omega 2015, 56, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. Dealing with Undesirable Outputs in DEA: A Slacks-Based Measure (SBM) Approach. 2003. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284047010_Dealing_with_undesirable_outputs_in_DEA_a_Slacks-Based_Measure_SBM_approach (accessed on 18 August 2020).
- An, Q.; Chen, H.; Wu, J.; Liang, L. Measuring slacks-based efficiency for commercial banks in China by using a two-stage DEA model with undesirable output. Ann. Oper. Res. 2015, 235, 13–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Q.; Majeed, S. Fujian’s industrial eco-efficiency: Evaluation based on SBM and the empirical analysis of lnfluencing factors. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Zhao, X.; Cheng, F. The comparison analysis of total factor productivity and eco-efficiency in China’s cement manufactures. Energy Policy 2015, 81, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhu, T. Research on regional industrial eco-efficiency in china based on data envelopment analysis theory. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 4, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.L.; Zhang, C.Y. The heterogeneity of industrial eco-efficiency in China from the perspective of environmental pressure. Sci. Technol. Manag. Res. 2016, 10, 243–248. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.M.; Fang, M.Q. Evaluation of urban eco-economy efficiency: Taking Hunan province as an example. Urban Issues 2015, 3, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Chu, J. Environmental efficiency of land transportation in China: A parallel slack-based measure for regional and temporal analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Meng, F.; Ang, S. A new approach for fair efficiency decomposition in two-stage structure system. Oper. Res. 2018, 18, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.; Hwang, S.N. Efficiency decomposition in two-stage data envelopment analysis: An application to non-life insurance companies in Taiwan. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2008, 185, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Wang, S.; Liu, W. A two-stage DEA approach for environmental efficiency measurement. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 3041–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lu, L.; Lu, W.; Lin, B. A survey of DEA applications. Omega 2013, 41, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z. Measuring Eco-Efficiency of Agriculture in China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, K. Eco-Efficiency Assessment of Intensive Rice Production in Japan: Joint Application of Life Cycle Assessment and Data Envelopment Analysis. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, L.; Hall, M.J.; Simper, R. The impact of macroeconomic and regulatory factors on bank efficiency: A non-parametric analysis of Hong Kong’s banking system. J. Bank Financ. 2006, 30, 1443–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, H.; Lovell, C.; Schmidt, S.; Yaisawarng, S. Accounting for environmental effects and statistical noise in data envelopment analysis. J. Prod. Anal. 2002, 17, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Luo, R.; Yao, L.; Cao, S.; Wang, S.; Lev, B. Assessing integrated water use and wastewater treatment systems in China: A mixed network structure two-stage SBM DEA model. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 185, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhu, Q.; Chu, J.; Liang, L. Two-stage network structures with undesirable intermediate outputs reused: A DEA based approach. Comput. Econ. 2015, 46, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lin, B. Impact of energy conservation policies on the green productivity in China’s manufacturing sector: Evidence from a three-stage DEA model. Appl. Energy 2016, 168, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Liang, N.; Xu, H. Efficiency evaluation of Chinese regional industrial systems with undesirable factors using a two-stage slacks-based measure approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 87, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Li, Y. The evaluation of transportation energy efficiency: An application of three-stage virtual frontier DEA. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2014, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Golley, J. ‘Green’ productivity growth in China’s industrial economy. Energy Econ. 2014, 44, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, F.; Hsueh, C. Measuring relative efficiency of government-sponsored R&D projects: A three-stage approach. Eval. Program Plan. 2009, 32, 178–186. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, B.; Duan, N.; Wang, Y. Environmental efficiency and abatement cost of China’s industrial sectors based on a three-stage data envelopment analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 153, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, L.; Ma, T.; Liu, Q. Research on three-stage DEA model. Syst. Eng. 2014, 32, 144–149. [Google Scholar]
- Simar, L.; Wilson, P.W. Estimation and inference in two-stage, semi-parametric models of production processes. J. Econom. 2007, 136, 31–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Wu, C.; Zhang, M. Research on the evaluating method of non-renewable energy efficiency based on China’s provincial data: Green growth perspective. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 733, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, S. Innovation efficiency evaluation of hi-tech development zones based on the three stage model. Manag. Rev. 2016, 28, 42–52. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.T.; Lee, D.J.; Park, S.J.; Zhang, Y.; Sultanov, A. Measuring the efficiency of the investment for renewable energy in Korea using data envelopment analysis. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2015, 47, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speak, A.; Rothwell, J.; Lindley, S.; Smith, C. Urban particulate pollution reduction by four species of green roof vegetation in a UK city. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 61, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Deng, X.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z. Exploring the relationship between urbanization and urban eco-efficiency: Evidence from prefecture-level cities in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 1487–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.Y.; Lo, K.; Tong, L.J. Eco-efficiency analysis of industrial systems in the Songhua River Basin: A decomposition model approach. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menanteau, P.; Finon, D.; Lamy, M.L. Prices versus quantities: Choosing policies for promoting the development of renewable energy. Energy Policy 2003, 31, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Palmer, K.; Woerman, M. Analysis of the Bingaman clean energy standard proposal. Resour. Energy Econ. 2014, 36, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, R.Z.; Deng, Z.Q.; Hu, J.L. Clean energy use and total-factor efficiencies: An international comparison. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 1158–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Song, M. Influences of reverse outsourcing on green technological progress from the perspective of a global supply chain. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development. Towards Green Growth: Monitoring Progress; OECD: Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.Y. Research on Green Innovation Incentive of Environmental Regulation; Graduate School of Chinese Academy Of Social Sciences: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.G.; Wang, Y.J. Environment Kuznets curve or regulation results? Financ. Econ. Rev. 2010, 152, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.J. Research on the Interactive Relationship between Environmental Quality and Economic Development Based on Trend Analysis. J. Dongbei Univ. Financ. Econ. 2012, 1, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.B.; Ren, S.G.; Cai, C.Y. Evaluation of industrial eco-efficiency of urban agglomeration in the Yangtze River Delta. Bus. Res. 2017, 6, 163–169. [Google Scholar]
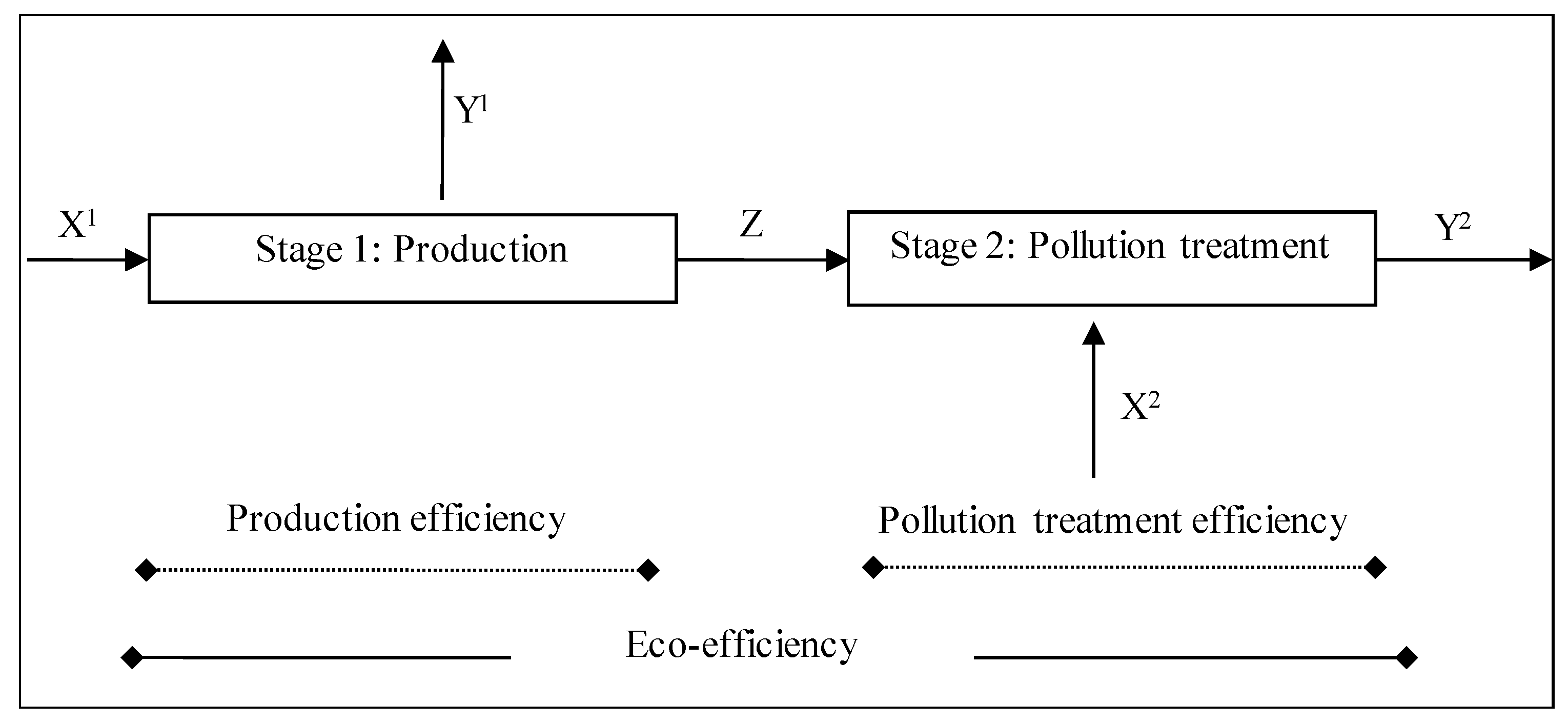

| Stage | Type | Variable | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Production stage | Nondiscretionary input | Labor | Million person |
| Total fixed assets investment | 100 Billion Yuan | ||
| Discretionary input | Energy consumption | 100 Million Ton Coal | |
| Industrial water consumption | 100 Million m3 | ||
| Total electricity consumption | 100 Million KWH | ||
| Desirable output | GDP | 100 Million Yuan | |
| Industrial added value | 100 Million Yuan | ||
| Undesirable output | Industrial wastewater | 100 Million Ton | |
| Industrial solid waste | 10 Million Ton | ||
| Industrial SO2 emissions | 10,000 Ton | ||
| Pollution treatment stage | Discretionary input | Investment in industrial pollution control | 100 Million Yuan |
| Desirable output | Comprehensive utilization of industrial waste | 10 Million Ton | |
| Centralized waste gas treatment facilities | Set | ||
| Industrial wastewater treatment capacity | 100 Million Ton |
| Index | Government Support | Urbanization Level | Industrial Structure | Energy Consumption Structure | Technological Progress | Environmental Regulation | Economic Development |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | 2.4181 | 1.5210 | 1.1669 | 1.9750 | 4.1732 | 4.3877 | 1.0718 |
| Min | 0.5051 | 0.7293 | 0.4563 | 0.2678 | 0.1877 | 0.4183 | 0.9407 |
| Median | 0.9320 | 0.9577 | 1.0565 | 0.9164 | 0.8342 | 0.8220 | 0.9873 |
| S.D. | 0.4098 | 0.2068 | 0.1801 | 0.4316 | 0.7694 | 0.7493 | 0.0365 |
| Production Stage (Energy Saving) | Pollution Treatment Stage | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Variables | Labor | Total Fixed Assets Investment | Industrial Water Consumption | Total Electricity Consumption | Energy Consumption | Investment in Industrial Pollution Control | Environmental Variables |
| Government support | −79.2744 *** | −1.9543 | −7.0664 * | 0.2197 ** | 0.0009 | 1.8228 ** | Technological progress |
| Urbanization level | −146.7464 *** | −2.7983 | 0.8336 | 0.7448 *** | −0.0177 | −0.3763 | Environmental regulation |
| Industrial structure | 40.2790 *** | 0.2363 | 17.8169 *** | −0.0117 | −0.0106 | −29.0912 *** | Economic development |
| Energy consumption structure | −94.7909 *** | −0.7805 | −6.3638 ** | 0.2342 ** | 0.0041 | 1.9325 * | Energy consumption structure |
| σ2 | 39323.3680 | 7.9743 | 901.2093 | 0.2459 | 0.4915 | 284.4505 | σ2 |
| γ | 0.9958 | 0.9998 | 0.9999 | 0.9983 | 0.9999 | 0.9998 | γ |
| Log of likelihood function | −176.17 | −56.61 | −120.26 | −73.21 | −108.41 | −100.37 | Log of likelihood function |
| Provinces | Energy Saving Efficiency | Pollution Treatment Efficiency | Eco-Efficiency | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Adjusted | Initial | Adjusted | Initial | Adjusted | |
| Beijing | 0.9997 | 1 | 1.1486 | 1.1868 | 0.8704 | 0.8426 |
| Tianjin | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Hebei | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Shanxi | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Inner Mongolia | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Liaoning | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Jilin | 1 | 1 | 2.2699 | 2.2699 | 0.4405 | 0.4405 |
| Heilongjiang | 0.7745 | 0.8208 | 1.3389 | 1.3349 | 0.5785 | 0.6149 |
| Shanghai | 0.6999 | 0.9024 | 1.8731 | 2.0812 | 0.3736 | 0.4336 |
| Jiangsu | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Zhejiang | 0.9677 | 1 | 1.4531 | 1.3993 | 0.6660 | 0.7146 |
| Anhui | 0.7307 | 0.8715 | 1.0404 | 1.2546 | 0.7023 | 0.6947 |
| Fujian | 0.752 | 0.8944 | 1.2882 | 2.2227 | 0.5837 | 0.4024 |
| Jiangxi | 0.7572 | 0.8770 | 1.0587 | 1.6836 | 0.7152 | 0.5209 |
| Shandong | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Henan | 0.8626 | 0.8354 | 1.4357 | 1.5075 | 0.6008 | 0.5542 |
| Hubei | 0.8930 | 0.9157 | 2.0307 | 2.7253 | 0.4397 | 0.3360 |
| Hunan | 1 | 0.8208 | 1 | 1.3100 | 1 | 0.6266 |
| Guangdong | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Guangxi | 0.8445 | 0.8957 | 1.1194 | 1.1131 | 0.7544 | 0.8047 |
| Hainan | 1 | 1.0000 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Chongqing | 0.7202 | 0.7748 | 1.2854 | 1.2854 | 0.5603 | 0.6028 |
| Sichuan | 0.9518 | 0.9501 | 1.1018 | 1.1042 | 0.8638 | 0.8604 |
| Guizhou | 0.9666 | 0.9722 | 1.0859 | 1.0753 | 0.8901 | 0.9042 |
| Yunnan | 1 | 1 | 1.1987 | 1 | 0.8343 | 1 |
| Shaanxi | 1 | 1 | 1.4163 | 1.7770 | 0.7061 | 0.5628 |
| Gansu | 0.7181 | 0.7840 | 3.0789 | 3.0789 | 0.2332 | 0.2546 |
| Qinghai | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Ningxia | 0.9180 | 0.9483 | 1.8091 | 1.8091 | 0.5074 | 0.5242 |
| Xinjiang | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Average | 0.9186 | 0.9421 | 1.3011 | 1.4073 | 0.7773 | 0.7565 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Yang, R.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, D. Regional Green Eco-Efficiency in China: Considering Energy Saving, Pollution Treatment, and External Environmental Heterogeneity. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7059. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177059
Liu H, Yang R, Zhou Z, Huang D. Regional Green Eco-Efficiency in China: Considering Energy Saving, Pollution Treatment, and External Environmental Heterogeneity. Sustainability. 2020; 12(17):7059. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177059
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hongwei, Ronglu Yang, Zhixiang Zhou, and Dacheng Huang. 2020. "Regional Green Eco-Efficiency in China: Considering Energy Saving, Pollution Treatment, and External Environmental Heterogeneity" Sustainability 12, no. 17: 7059. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177059
APA StyleLiu, H., Yang, R., Zhou, Z., & Huang, D. (2020). Regional Green Eco-Efficiency in China: Considering Energy Saving, Pollution Treatment, and External Environmental Heterogeneity. Sustainability, 12(17), 7059. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177059





