Intelligent System for the Predictive Analysis of an Industrial Wastewater Treatment Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Related Works Description
2.2. Variable Prediction
2.3. Fault Detection
- -
- The system’s ability to operate under some given circumstances.
- -
- The time range in which equipment needs no maintenance and logistic support [17].
2.4. Big Data Tools
2.5. Computational Techniques
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Model Design
- Flow
- COD of influent water
- Suspended solids in influent water (SS)
- Mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSS)
- Mixed liquor volatile suspended solids (MLVSS)
- Nitrogen (N)
- pH
- Mixed liquor dissolved oxygen (DO)
- Food to microorganism (F/M)
- EQ = Equalizer
- BIO = Bioreactor
- BT_N = Bioreactor Pit N
- BT_C = Bioreactor Pit C
- Clari = Clarifier
- OxT = Oxidation Tank
- D = Discharge Pit
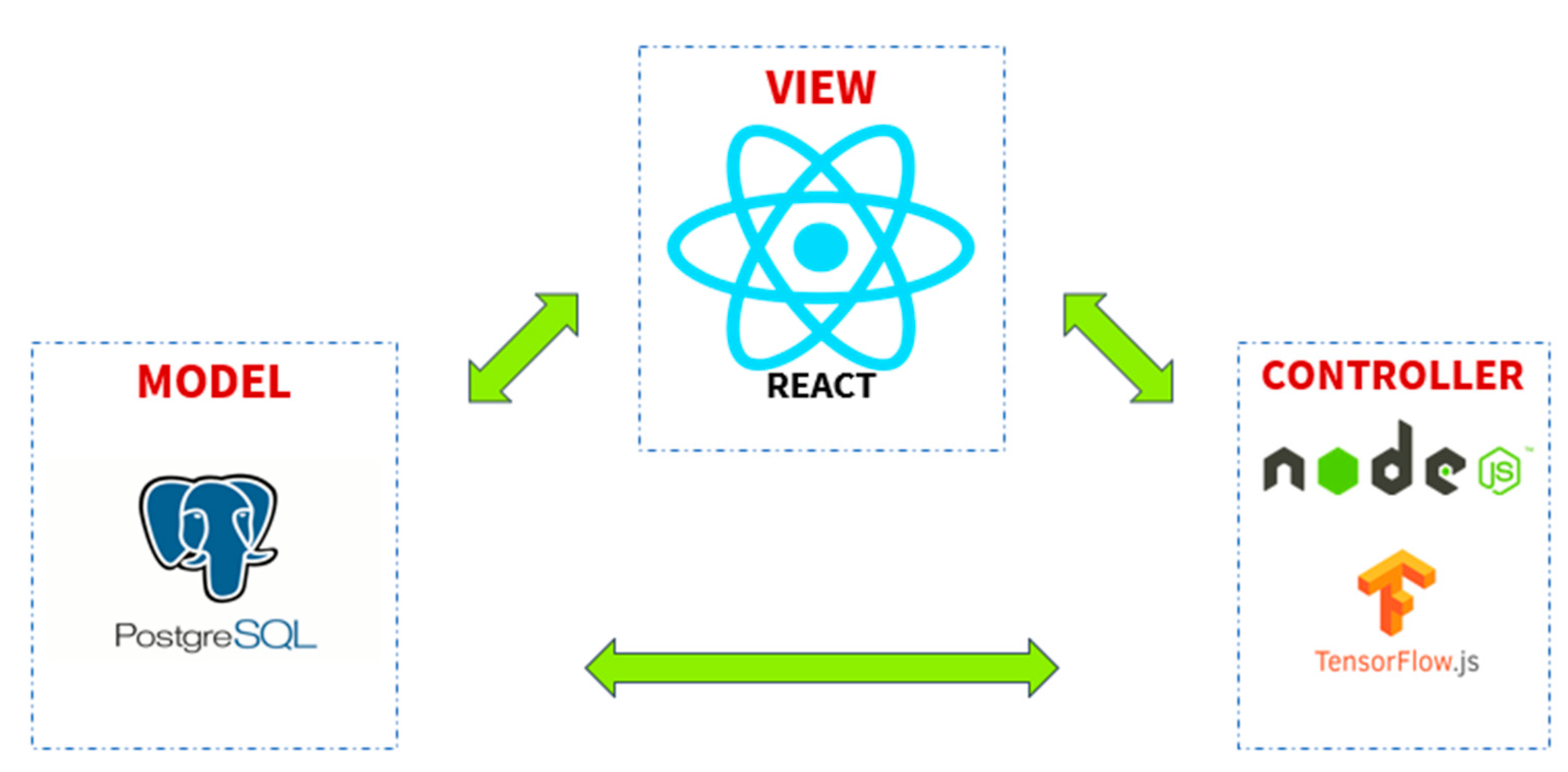
3.2. Platform Design
4. Results
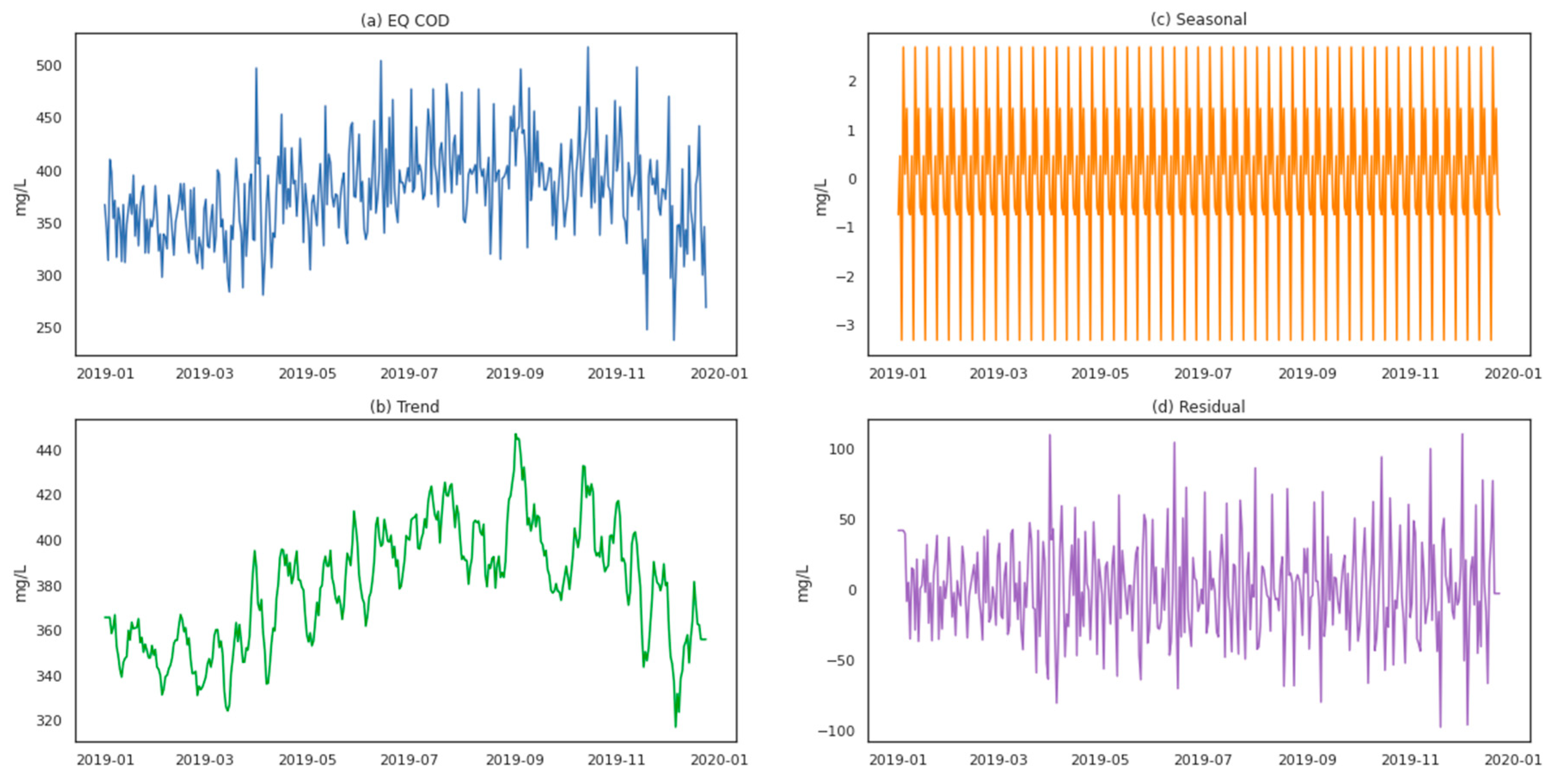
4.1. Time-Series Decomposition
4.2. Autocorrelation Study
4.3. Correlation Study
- BT_C_MLVSS
- D_SS
- BT_C_N
- EQ_N
- Clari_DO
- F/M
4.4. Artificial Neural Network
4.5. Web Platform.
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Definition |
| ANFIS | Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system |
| ANN | Artificial neural network |
| BN | Bayesian network |
| BP | Backpropagation network |
| COD | Chemical oxygen demand |
| DC | Determination coefficient |
| DT | Decision tree |
| drel | Relative efficiency criteria |
| ELM | Extreme learning machine |
| F/M | Food to microorganism |
| FFNN | Feedforward neural network |
| FL | Fuzzy logic |
| FNN | Fuzzy neural network |
| GA | Genetic algorithm |
| GND | Gaussian naive Bayes |
| GRI | Global Reporting Initiative |
| HRT | Hydraulic retention time |
| ICS | Improved cuckoo search |
| IPW | Iterative predictor weighting |
| KNN | K-nearest neighbors |
| MAPE | Mean absolute percentage error |
| MLPANN | Multilayer perceptron ANN |
| MLR | Multilinear regression |
| MSE | Mean square error |
| MLSS | Mixed liquor suspended solids |
| MLVSS | Mixed liquor volatile suspended solids |
| NARX | Multivariate nonlinear autoregressive exogenous |
| NFC | Neuro-fuzzy controller |
| NH4-N | Ammonium |
| NSE | Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency |
| O&G | Oil and grease |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| PCC | Pearson correlation coefficient |
| PLS | Partial least squares |
| QL | Q-learning |
| R | Correlation coefficient |
| R2 | Coefficient of determination |
| RBFANN | Radial basis function ANN |
| RF | Random forest |
| RMSE | Root mean square error |
| RMSEP | Root mean squared error of prediction |
| SCFL | Supervised committee FL |
| SOM | Self-organizing maps |
| SRM | Structural risk minimization |
| SVI | Sludge volume index |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| TP | Total phosphorus |
| TSS | Total suspended solids |
| UVE | Uninformative variable elimination |
| WWTP | Wastewater treatment plant |
References
- UNWWA Programme. The United Nations World Water Development Report 3: Water in a Changing World; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sener, E.S.S.; Devraz, A. Evaluation of water quality using water quality index (WQI) method and GIS in Aksu River (SW-Turkey). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newhart, K.B.; Holloway, R.W.; Hering, A.S.; Cath, T.Y. Data-driven performance analyses of wastewater treatment plants: A review. Water Res. 2019, 157, 498–513. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anjun, M.; Al-Makishah, N.H.; Barakat, M.A. Wastewater sludge stabilization using pre-treatment methods. Proc. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 102, 615–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchobanoglous, G.; Schroeder, E.E. Water Quality: Characteristics, Modeling, Modification; Addison-Wesley Publishing Company: Boston, MA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Lake, B.M.; Ullman, T.D.; Tenebaum, J.B.; Gershman, S.J. Building machines that learn and think like people. Behav. Brain Sci. 2017, 40, e253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V´ıtez, J.S.T.; Oppeltov´a, P. Evaluation of the efficiency of selected wastewater treatment plant. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2012, 60, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.M.P.; Hallet, S.H.; Jude, S. Leveraging big data tools and technologies: Addressing the challenges of the water quality sector. Sustainability 2017, 9, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Sbroiavacca, A.; Sbroiavacca, F. Industry 4.0: The Exploitation of Big Data and Forthcoming Perspectives, Economic and Social Development. In Book of Proceedings, Proceedings of the 35thInternational Scientific Conference on Economic and Social Development–Sustainability from an Economic and Social Perspective, Lisbon, Portugal, 15–16 November 2018; ESD Publishing: Varazdin, Croatia, 2018; pp. 742–745. [Google Scholar]
- Nourani, V.; Elkiran, G.; Abba, S.I. Wastewater treatment plant performance analysis using artificial intelligence—An ensemble approach. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 2064–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Yang, S.; He, L.; Chen, Y.; Ren, N. Intelligent control/operational strategies in WWTPs through an integrated Q-learning algorithm with ASM2d-guided reward. Water 2019, 11, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yang, H.Z.; Liang, X.F. Prediction analysis of a wastewater treatment system using a Bayesian network. Environ. Model.Softw. 2013, 40, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggege, J.; Benrejeb, M.; Borne, P. On the design of a neuro-fuzzy controller—Application to the control of a bioreactor. J. Syst. Sci. Syst. Eng. 2005, 14, 417–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadiri, A.A.; Shokri, S.; Tsai, F.T.; Asghari Moghaddam, A. Prediction of effluent quality parameters of a wastewater treatment plant using a supervised committee fuzzy logic model. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Zhu, S.; Qiao, J.; Guo, M. Data-driven intelligent monitoring system for key variables in wastewater treatment process. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 26, 2093–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Jeong, K.; Lim, J.; Jo, J.; Kim, Y.M.; Park, J.-P.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, K.H. Prediction of effluent concentration in a wastewater treatment plant using machine learning models. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 32, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsina, E.F.; Chica, M.; Trawiński, K.; Regattieri, A. On the use of machine learning methods to predict component reliability from data-driven industrial case studies. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 5, 2419–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dairi, A.; Cheng, T.; Harrou, F.; Sun, Y.; Leiknes, T. Deep learning approach for sustainable WWTP operation: A case study on data-driven influent conditions monitoring. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, M.; Mirbagheri, S.A.; Bagheri, Z.; Kamarkhani, A.M. Modeling and optimization of activated sludge bulking for a real wastewater treatment plant using hybrid artificial neural networks-genetic algorithm approach. Proc. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2015, 95, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ráduly, B.; Gernaey, K.V.; Capodaglio, A.; Mikkelsen, P.S.; Henze, M. Artificial neural networks for rapid WWTP performance evaluation: Methodology and case study. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liukkonen, M.; Laakso, I.; Hiltunen, Y. Advanced monitoring platform for industrial wastewater treatment: Multivariable approach using the self-organizing map. Environ. Model. Softw. 2013, 48, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, J.; Latrille, E.; Harmand, J.; Robles, Á.; Ferrer, J.; Gaida, D.; Wolf, C.; Mairet, F.; Bernard, O.; Alcaraz-González, V.; et al. Instrumentation and control of anaerobic digestion processes: A review and some research challenges. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 615–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, M.; Gins, G. Industrial Process Monitoring in the Big Data/Industry 4.0 Era: From Detection, to Diagnosis, to Prognosis. Process 2017, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zounemat-Kermani, M.; Stephan, D.; Hinkelmann, R. Multivariate NARX neural network in prediction gaseous emissions within the influent chamber of wastewater treatment plants. Atmospheric Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1812–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Cao, J.; Jegatheesan, V.; Du, X. A Real-time BOD Estimation Method in Wastewater Treatment Process Based on an Optimized Extreme Learning Machine. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhong, N.; Tu, X.; Jia, J.; Wang, J. Tackling environmental challenges in pollution controls using artificial intelligence: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Del-Olmo, F.; Gaudioso, E.; Duro, N.; Dormido, R. Machine Learning Weather Soft-Sensor for Advanced Control of Wastewater Treatment Plants. Sensors 2019, 19, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangüesa, R.; Burrell, P. Application of Bayesian Network Learning Methods to Waste Water Treatment Plants. Appl. Intell. 2000, 13, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Gao, F.; Chen, G. Wastewater quality monitoring system using sensor fusion and machine learning techniques. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellana, S.; West, D. Predictive modeling for wastewater applications: Linear and nonlinear approaches. Environ. Model. Softw. 2009, 24, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsina, E.F.; Cabri, G.; Regattieri, A. A neural network approach to find the cumulative failure distribution: Modeling and experimental evidence. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 2016, 32, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, T.; Al Kadri, M. Big data analytics on the cloud. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Comput. Appl. Sci. (IJETCAS) 2015, 24, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, T.; Al Kadri, M.; Khan, N.A. Review of programming languages and tools for big data analytics. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Sci. 2017, 8, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar]
- Valentín-Vargas, A.; Toro-Labrador, G.; Massol-Deyá, A.A. Bacterial community dynamics in full-scale activated sludge bioreactors: Operational and ecological factors driving community assembly and performance. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryer, J.D.; Chan, K.-S. Time Series Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dagum, E. Time series modelling and decomposition. Statistica 2013, 70, 5. [Google Scholar]















| Area | Amazon | Microsoft | |
| Big data storage | S3 | Azure | Google Cloud services |
| Big data analytics | Elastic MapReduce (Hadoop) | Hadoop on Azure | BigQuery |
| Relational database | MySQL or Oracle | SQL Azure | Cloud SQL |
| NoSQL database | DynamoDB | Table storage | App Engine Datastore |
| MapReduce | Elastic MapReduce (Hadoop) | Hadoop on Azure | App Engine |
| Streaming processing | Nothing prepackaged | StreamInsight | Search API |
| Machine learning | Hadoop + Mahout | Hadoop + Mahout | Prediction API |
| Data sources | Public datasets | Windows Azure marketplace | A few sample datasets |
| Availability | Public production | Some services in private beta | Some services in private beta |
| Ref | Year | Method | Prediction | Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [10] | 2018 | FFNN, ANFIS, SVM, MLR | BOD, COD, TN | DC, RMSE |
| [11] | 2019 | Q-learning | - | - |
| [12] | 2012 | Bayesian network | COD, TP, TN | - |
| [13] | 2005 | NFC | Dilution rate | - |
| [14] | 2018 | FL, SCFL, ANN | BOD, COD, TSS | MAPE |
| [15] | 2018 | FNN, PCA | BOD, COD, TSS, TP, NH4-N | - |
| [16] | 2015 | ANN, SVM | TP, TSS, COD | R2, NSE, drel |
| [19] | 2015 | MLPANN–GA, RBFANN–GA | SVI | - |
| [20] | 2006 | ANN | BOD, COD, TSS, TN | R2 |
| [21] | 2013 | SOM | - | - |
| [24] | 2019 | NARX | H2S emission | MAPE, RMSE, GRI |
| [25] | 2019 | ICS–ELM, BP | BOD | - |
| [29] | 2012 | PLS, IPW–PLS, Boosting-IPW–PLS | COD, TSS, NTU | MinE, RMSEP, MaxE, R |
| [34] | 2012 | - | BOD, TSS, HRT, F/M | - |
| Algorithm | % | Algorithm | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| ANN | 64.71 | KNN | 5.88 |
| SVM | 23.53 | PCA | 5.88 |
| Fuzzy | 17.65 | PLS | 5.88 |
| BN | 11.76 | QL | 5.88 |
| RF | 11.76 | GND | 5.88 |
| DT | 5.88 | ICS | 5.88 |
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Flow_to_EQ | 0.067 |
| Flow_efl | 0.048 |
| BT_C_MLSS | 0.50 |
| BT_C_MLVSS | 0.51 |
| BT_N_MLSS | 0.51 |
| BT_N_MLVSS | 0.51 |
| D_SS | 0.52 |
| EQ_N | 0.51 |
| BT_C_N | 0.34 |
| BT_N_N | 0.21 |
| D_N | 0.18 |
| OxT_pH Morning | 0.28 |
| OxT_pH Afternoon | 0.28 |
| EQ_pH | 0.12 |
| BT_N_pH | 0.051 |
| D_pH | 0.024 |
| BT_N_DO | 0.31 |
| BT_C_DO | 0.11 |
| Clari_DO | 0.41 |
| F/M | 0.40 |
| D_COD_ON | 0.0078 |
| EQ_COD (t) | 0.61 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arismendy, L.; Cárdenas, C.; Gómez, D.; Maturana, A.; Mejía, R.; Quintero M., C.G. Intelligent System for the Predictive Analysis of an Industrial Wastewater Treatment Process. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6348. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12166348
Arismendy L, Cárdenas C, Gómez D, Maturana A, Mejía R, Quintero M. CG. Intelligent System for the Predictive Analysis of an Industrial Wastewater Treatment Process. Sustainability. 2020; 12(16):6348. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12166348
Chicago/Turabian StyleArismendy, Luis, Carlos Cárdenas, Diego Gómez, Aymer Maturana, Ricardo Mejía, and Christian G. Quintero M. 2020. "Intelligent System for the Predictive Analysis of an Industrial Wastewater Treatment Process" Sustainability 12, no. 16: 6348. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12166348
APA StyleArismendy, L., Cárdenas, C., Gómez, D., Maturana, A., Mejía, R., & Quintero M., C. G. (2020). Intelligent System for the Predictive Analysis of an Industrial Wastewater Treatment Process. Sustainability, 12(16), 6348. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12166348





