Globalization, Country Risks, and Trade in Tourism Services: Evidence from China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology
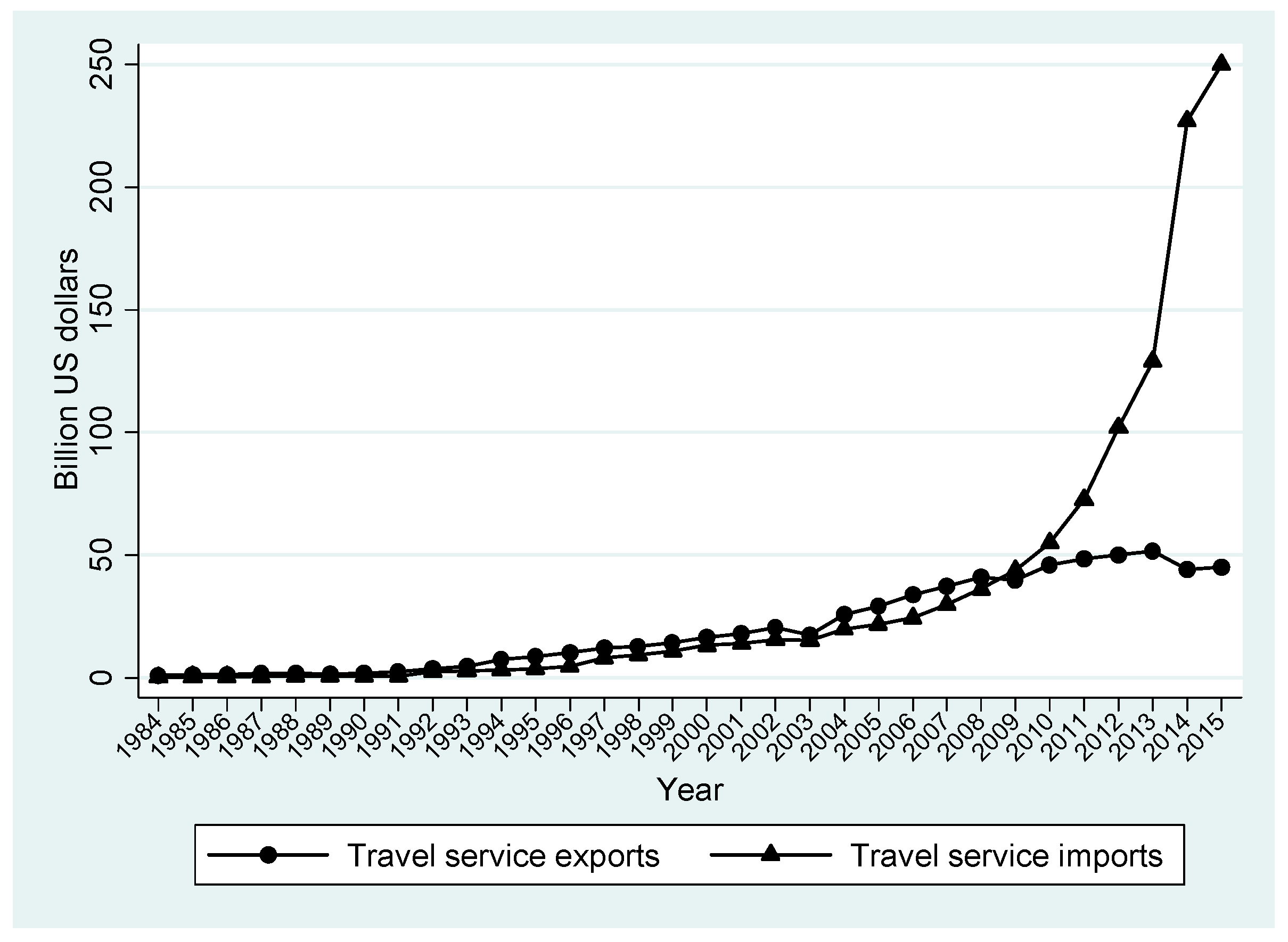
4. Data Specification
5. Empirical Results
5.1. Unit Root Test and ARDL Bounds Tests
5.2. Estimation of the ARDL Models
5.3. The CUSUM and CUSUMSQ Tests of Stability
6. Discussion and Implication
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hidayati, F. Tourism and economic growth: The role of globalization. J. Public Adm. Stud. 2018, 2, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, V.S.; Yang, Y.; Li, G. Where can tourism-led growth and economy-driven tourism growth occur. J. Travel Res. 2019, 58, 760–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, P.K.; Narayan, S.; Prasad, A.; Prasad, B.C. Tourism and economic growth: A panel data analysis for Pacific Island countries. Tour. Econ. 2010, 16, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.F.; Tan, E.C. Does tourism effectively stimulate Malaysia’s economic growth. Tour. Manag. 2015, 46, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayed, H.; Fletcher, J. Report: Globalization of economic activity: Issues for tourism. Tour. Econ. 2002, 8, 207–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Prashar, S.; Jana, R.K. Does international tourism spur international trade and output. Evidence from wavelet analysis. Tour. Econ. 2019, 25, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Difficulties and Countermeasures to Improving of Inbound Tourism in China. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Education Reform and Modern Management, Phuket, Thailand, 6–7 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Liao, C. Research on the Deficit of China’s Tourism Service Trade and Countermeasures. Am. J. Ind. Bus. Manag. 2017, 7, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dreher, A. Does globalization affect growth. Evidence from a new index of globalization. Appl. Econ. 2006, 38, 1091–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, S.H.; Webster, C. Tourism’s impact on growth: The role of globalisation. Ann. Tour. Res. 2013, 41, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Li, G.; Cao, Z. Tourism and Economic Globalization: An emerging research agenda. J. Travel Res. 2018, 57, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.-B.; Zhang, W.; Ding, K. Does globalization influence inbound tourism. Evidence from a dynamic panel threshold analysis. J. Travel Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hociung, I.G.; Frâncu, L.G. Globalization-tourism-communication, competitiveness triangle on the market affected by the economic crisis. Theor. Appl. Econ. 2012, 19, 133–146. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, M.H. Tourism and globalization in the Arab world. Int. J. Bus. Soc. Sci. 2010, 1, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer, L. Globalization of tourism: Drivers and outcomes. Tour. Recreat Res. 2015, 40, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Qu, M.; Bao, J. Impact of crisis events on Chinese outbound tourist flow: A framework for post-events growth. Tour. Manag. 2019, 74, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmasrene, T.; Lee, J.W. Assessing the dynamic impact of tourism, industrialization, urbanization, and globalization on growth and environment in Southeast Asia. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2017, 24, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint Akadiri, S.; Lasisi, T.T.; Uzuner, G.; Akadiri, A.C. Examining the impact of globalization in the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: The case of tourist destination states. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 12605–12615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulczyk-Dynowska, A.; Bal-Domańska, B. The National parks in the context of tourist function development in territorially linked municipalities in poland. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, M.F.; Pennington-Gray, L. Profiling risk perceptions of tourists. Ann. Tour. Res. 2004, 31, 1051–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu-Lastres, B.; Ritchie, B.W.; Pan, D.Z. Risk reduction and adventure tourism safety: An extension of the risk perception attitude framework (RPAF). Tour. Manag. 2019, 74, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakos, K.; Kutan, A.M. Regional Effects of Terrorism on Tourism in Three Mediterranean Countries. J. Confl. Resolut. 2003, 47, 621–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javid, E.; Katircioglu, S. The globalization indicators-tourism development nexus: A dynamic panel-data analysis. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2017, 22, 1194–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, N.A.; Rosbi, S. Effect of Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) to tourism industry. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. Sci. 2020, 7, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.L.; McAleer, M.; Ramos, V. A charter for sustainable tourism after COVID-19. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Tourism Organization. Impact Assessment of the COVID-19 Outbreak on International Tourism; World Tourism Organization: Madrid, Spain, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, M. APAC: COVID-19 Impact on Tourist Arrivals by Country or Region; Statista: Hamburg, Germany, 2020; Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1103147/apac-covid-19-impact-on-tourist-arrivals-by-country/ (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Cheer, J.M. Human flourishing, tourism transformation and COVID-19: A conceptual touchstone. Tour. Geogr. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gössling, S.; Scott, D.; Hall, C.M. Pandemics, tourism and global change: A rapid assessment of COVID-19. J. Sustain. Tour. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.M.; Scott, D.; Gössling, S. Pandemics, transformations and tourism: Be careful what you wish for. Tour. Geogr. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjalager, A.M. Stages in the economic globalization of tourism. Ann. Tour. Res. 2007, 34, 437–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prideaux, B. Factors affecting bilateral tourism flows. Ann. Tour. Res. 2005, 32, 780–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vietze, C. Cultural effects on inbound tourism into the USA: A gravity approach. Tour. Econ. 2012, 18, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S.; Prideaux, B.; Timothy, D. Factors affecting bilateral Chinese and Japanese travel. Ann. Tour. Res. 2016, 61, 80–95. [Google Scholar]
- Harb, G.; Bassil, C. Gravity analysis of tourism flows and the ‘multilateral resistance to tourism’. Curr. Issues Tour. 2020, 23, 666–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, B.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, L.; Ma, Y. China’s outbound tourism–Stages, policies and choices. Tour. Manag. 2017, 58, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, R. The implications of increasing globalization and regionalism for the economic growth of small island states. World Dev. 2004, 32, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyaupane, G.P.; Timothy, D.J. Power, regionalism and tourism policy in Bhutan. Ann. Tour. Res. 2010, 37, 969–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J.C. Regionlisation and tourism: The Indonesia-Malaysia-Singapore growth triangle. Curr. Issues Tour. 2001, 4, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dredge, D.; Jenkins, J. Destination place identity and regional tourism policy. Tour. Geogr. 2003, 5, 383–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.; Vanetti, M. Locational strategies of international hotel chains. Ann. Tour. Res. 2005, 32, 1077–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogerson, J.M. Unpacking the growth of hotel chains in Africa: Enterprises and patterns. Mediterr. J. Soc. Sci. 2014, 5, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Clancy, M. Global commodity chains and tourism: Past research and future directions. In Political Economy of Tourism: A Critical Perspective; Routledge: London, UK, 2010; pp. 99–116. [Google Scholar]
- Rey, B.; Myro, R.L.; Galera, A. Effect of low-cost airlines on tourism in Spain. A dynamic panel data model. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2011, 17, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyarto, G.; Blake, A.; Sinclair, M.T. Tourism and globalization: Economic impact in Indonesia. Ann. Tour. Res. 2003, 30, 683–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stezhko, N.; Oliinyk, Y.; Polishchuk, L.; Tyshchuk, I.; Parfinenko, A.; Markhonos, S. International Tourism in the System of Modern Globalization Processes. Int. J. Manag. 2020, 11, 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Sequeira, T.; Nunes, P.M. Does tourism influence economic growth. A dynamic panel data approach. Econ. Rec. 2008, 84, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheyvens, R. The challenge of sustainable tourism development in the Maldives: Understanding the social and political dimensions of sustainability. Asia Pac. Viewp. 2011, 52, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilat, Y.; Einav, L. Determinants of international tourism: A three-dimensional panel data analysis. Appl. Econ. 2004, 36, 1315–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, G.; Saha, S. Do political instability, terrorism, and corruption have deterring effects on tourism development even in the presence of UNESCO heritage. A cross-country panel estimate. Tour. Anal. 2013, 18, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, O.; Poudyal, N.C.; Larson, L.R. The influence of sociopolitical, natural, and cultural factors on international tourism growth: A cross-country panel analysis. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2017, 19, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Su, J.-J.; Campbell, N. Does Political and Economic Freedom Matter for Inbound Tourism? A Cross-National Panel Data Estimation. J. Travel Res. 2017, 56, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musavengane, R.; Siakwah, P.; Leonard, L. The nexus between tourism and urban risk: Towards inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable outdoor tourism in African cities. J. Outdoor Recreat. Tour. 2020, 29, 100254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, D.; McGrew, A.; Goldblatt, D.; Perraton, J. Global Transformations: Politics, Economics and Culture; Stanford University Press: Stanford, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, S.H.; Ivanova, M.G. Do hotel chains improve destination’s competitiveness. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2016, 19, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alola, U.V.; Cop, S.; Alola, A.A. The spillover effects of tourism receipts, political risk, real exchange rate, and trade indicators in Turkey. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2019, 21, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaran, M.H.; Shin, Y.; Smith, R. Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. Appl. Econom. 2001, 16, 289–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreher, A.; Gaston, N.; Martens, P. Measuring Globalization-Gauging Its Consequences; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dickey, D.A.; Fuller, W.A. Distribution of the estimation for autoregressive time series with a unit root. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1979, 74, 427–431. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, P.C.B.; Perron, P. Testing for a Unit root in Time Series Regression. Biometrika 1988, 75, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, S.; Juselius, K. Maximum likelihood estimation and inference on cointegration with applications to the demand for money. Oxf. Bull. Econ. Stat. 1990, 52, 161–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrittella, M.; Bigano, A.; Roson, R.; Tol, R.S. A general equilibrium analysis of climate change impacts on tourism. Tour. Manag. 2006, 27, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massidda, C.; Mattana, P. A SVECM analysis of the relationship between international tourism arrivals, GDP and trade in Italy. J. Travel Res. 2013, 52, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dritsakis, N. Tourism as a long-run economic growth factor: An empirical investigation for Greece using causality analysis. Tour. Econ. 2004, 10, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunst, I. The role of the government in promoting tourism investment in selected Mediterranean countries-implications for the Republic of Croatia. Tour. Hosp. Manag. 2011, 17, 115–130. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, A. China’s Current Account: External Rebalancing or Capital Flight. Int. Financ. Discuss. Pap. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwack, S.Y.; Ahn, C.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Yang, D.Y. Consistent estimates of world trade elasticities and an application to the effects of Chinese Yuan (RMB) appreciation. J. Asian Econ. 2007, 18, 314–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogru, T.; Isik, C.; Sirakaya-Turk, E. The balance of trade and exchange rates: Theory and contemporary evidence from tourism. Tour. Manag. 2019, 74, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Magnini, V.P.; Fesenmaier, D.R. Information technology and consumer behavior in travel and tourism: Insights from travel planning using the internet. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2015, 22, 244–249. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X. From digitization to the age of acceleration: On information technology and tourism. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2018, 25, 147–150. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.J. Analysis on the causes and countermeasures of China’s tourism trade deficit. Chongqing Soc. Sci. 2016, 4, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
| Variable | Obs | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LnTSEX | 32 | 3.40 | 0.28 | 2.98 | 3.90 |
| LnTSIM | 32 | 3.15 | 0.51 | 1.66 | 4.05 |
| LnTSTB | 32 | 0.25 | 0.70 | −1.02 | 1.83 |
| LnOG | 32 | 3.84 | 0.32 | 3.20 | 4.13 |
| LnEG | 32 | 3.77 | 0.18 | 3.33 | 3.99 |
| LnSG | 32 | 3.45 | 0.65 | 2.18 | 4.01 |
| LnPG | 32 | 4.20 | 0.26 | 3.70 | 4.44 |
| LnCR | 32 | 4.28 | 0.09 | 4.05 | 4.39 |
| LnPR | 32 | 4.17 | 0.07 | 4.03 | 4.32 |
| LnGDP | 32 | 7.48 | 0.80 | 6.18 | 8.78 |
| LnREER | 32 | 4.28 | 0.09 | 4.05 | 4.39 |
| LnTSEX | LnTSIM | LnTSTB | LnOG | LnEG | LnSG | LnPG | LnGDP | LnREER | LnCR | LnPR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LnTSEX | 1.000 | ||||||||||
| LnTSIM | −0.533 *** (0.002) | 1.000 | |||||||||
| LnTSTB | 0.784 *** (0.000) | −0.943 *** (0.000) | 1.000 | ||||||||
| LnOG | −0.408 ** (0.021) | 0.828 *** (0.000) | −0.767 *** (0.000) | 1.000 | |||||||
| LnEG | −0.342 * (0.056) | 0.832 *** (0.0000) | −0.744 *** (0.000) | 0.975 *** (0.000) | 1.0000 | ||||||
| LnSG | −0.450 *** (0.0097) | 0.822 *** (0.000) | −0.780 *** (0.000) | 0.996 *** (0.000) | 0.961 *** (0.000) | 1.000 | |||||
| LnPG | −0.343 * (0.055) | 0.796 *** (0.000) | −0.719 *** (0.000) | 0.986 *** (0.000) | 0.950 *** (0.000) | 0.975 *** (0.000) | 1.000 | ||||
| LnGDP | −0.405 ** (0.021) | 0.809 *** (0.000) | −0.753 *** (0.000) | 0.912 *** (0.000) | 0.882 *** (0.000) | 0.900 *** (0.000) | 0.891 *** (0.000) | 1.000 | |||
| LnREER | −0.210 (0.248) | −0.334 * (0.061) | 0.163 (0.373) | −0.484 *** (0.005) | −0.542 *** (0.001) | −0.466 *** (0.007) | −0.521 *** (0.002) | −0.191 (0.294) | 1.000 | ||
| LnCR | −0.197 (0.280) | 0.607 *** (0.000) | −0.522 *** (0.002) | 0.747 *** (0.000) | 0.696 *** (0.000) | 0.735 *** (0.000) | 0.758 *** (0.000) | 0.657 *** (0.000) | −0.328 * (0.067) | 1.000 | |
| LnPR | 0.425 ** (0.015) | −0.152 (0.406) | 0.278 (0.123) | −0.020 (0.915) | −0.028 (0.881) | −0.040 (0.829) | 0.029 (0.877) | −0.189 (0.302) | −0.322 * (0.072) | 0.550 *** (0.001) | 1.000 |
| Variables | ADF Test | PP Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model with Constant | Model with Constant and Trend | Model with Constant | Model with Constant and Trend | |
| Variables in level | ||||
| LnTSEX | −2.11 (0) | −2.47 (0) | −2.21 | −2.47 |
| LnTSIM | −0.95 (3) | −1.92 (3) | −2.75 * | −3.90 ** |
| LnTSTB | −1.87 (0) | −2.48 (1) | −2.00 | −2.70 |
| LnOG | −2.47 (0) | −0.89 (0) | −3.26 ** | −0.44 |
| LnEG | −3.62 ** (3) | −1.79 (3) | −5.66 *** | −2.76 |
| LnSG | −2.07 (0) | −1.03 (0) | −2.49 | −0.77 |
| LnPG | −1.88 (0) | −1.25 (0) | −2.07 | −1.23 |
| LnCR | −1.82 (0) | −2.50 (0) | −1.76 | −2.56 |
| LnPR | −2.22 (0) | −2.25 (0) | −2.29 | −2.31 |
| LnGDP | 0.38 (4) | −4.69 *** (3) | −0.05 | −1.63 |
| LnREER | −3.46 ** (0) | −2.86 (0) | −3.41 ** | −3.98 ** |
| Variables in difference | ||||
| DLnTSEX | −5.46 *** (0) | −5.40 *** (0) | −5.48 *** | −5.41 *** |
| DLnTSIM | −5.10 *** (2) | −4.96 *** (2) | −9.72 *** | −8.90 *** |
| DLnTSTB | −5.07 *** (0) | −4.97 *** (0) | −5.34 *** | −5.23 *** |
| DLnOG | −4.92 *** (0) | −6.20 *** (4) | −4.92 *** | −9.12 *** |
| DLnEG | −4.57 *** (1) | −5.36 *** (2) | −4.74 *** | −6.76 *** |
| DLnSG | −5.26 *** (0) | −4.72 *** (4) | −5.26 *** | −7.64 *** |
| DLnPG | −4.83 *** (0) | −5.55 *** (4) | −4.82 *** | −5.92 *** |
| DLnCR | −4.12 *** (2) | −4.14 ** (2) | −8.10 *** | −9.00 *** |
| DLnPR | −5.74 *** (0) | −4.14 ** (2) | −6.47 *** | −7.22 *** |
| DLnGDP | −3.58 ** (1) | −3.45 * (1) | −2.92 * | −2.88 |
| DLnREER | −4.30 *** (0) | −5.04 *** (0) | −4.22 *** | −7.90 *** |
| Estimated Model | F-Statistic | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OG | EG | SG | PG | ||
| LnTSEXt = f (LnGLOBt, LnCRt, LnGDPt, LnREERt) | 4.80 *** | 7.96 *** | 3.97 ** | 7.52 *** | |
| LnTSEXt = f (LnGLOBt, LnPRt, LnGDPt, LnREERt) | 6.37 *** | 7.68 *** | 3.78 ** | 4.66 *** | |
| LnTSIMt = f (LnGLOBt, LnCRt, LnGDPt, LnREERt) | 12.69 *** | 12.98 *** | 6.46 *** | 4.35 ** | |
| LnTSIMt = f (LnGLOBt, LnPRt, LnGDPt, LnREERt,) | 5.63 *** | 16.23 *** | 10.08 *** | 7.12 *** | |
| LnTSTBt = f (LnGLOBt, LnCRt, LnGDPt, LnREERt) | 3.81 ** | 4.49 *** | 3.88 ** | 6.89 *** | |
| LnTSTBt = f (LnGLOBt, LnPRt, LnGDPt, LnREERt,) | 4.58 *** | 7.69 *** | 3.69 ** | 4.49 *** | |
| LnTSEXt = f (LnGLOB, LnGLOBt*LnCRt, LnGDPt, LnREERt) | 3.90 ** | 9.17 *** | 23.36 *** | 3.68 ** | |
| LnTSEXt = f (LnGLOB, LnGLOBt*LnPRt, LnGDPt, LnREERt) | 5.02 *** | 3.35 ** | 4.77 *** | 4.55 *** | |
| LnTSIMt = f (LnGLOBt, LnGLOBt*LnCRt, LnGDPt, LnREERt) | 12.82 *** | 13.41 *** | 8.19 *** | 5.25 *** | |
| LnTSIMt = f (LnGLOBt, LnGLOBt*LnPRt, LnGDPt, LnREERt) | 15.69 *** | 4.01 ** | 11.81 *** | 7.59 *** | |
| LnTSTBt = f (LnGLOBt, LnGLOBt*LnCRt, LnGDPt, LnREERt) | 4.16 ** | 6.67 *** | 4.04 ** | 7.67 *** | |
| LnTSTBt = f (LnGLOBt, LnGLOBt*LnPRt, LnGDPt, LnREERt) | 3.39 * | 7.19 *** | 3.64 ** | 6.29 *** | |
| Critical value | |||||
| 10% | 5% | 1% | |||
| I(0) | I(1) | I(0) | I(1) | I(0) | I(1) |
| 2.20 | 3.09 | 2.56 | 3.49 | 3.29 | 4.37 |
| Globalization Variables | Overall Globalization | Economic Globalization | Social Globalization | Political Globalization | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panel A: Consider composite risk in the models | ||||||||
| LnGLOB | −1.95 *** (0.58) | −8.04 ** (2.29) | −0.95 (0.93) | 2.97 ** (1.32) | −0.89 *** (0.26) | −5.90 *** (0.78) | −2.60 ** (0.96) | −5.15 * (2.14) |
| LnCR | −0.23 (0.97) | −3.29 *** (0.95) | −0.25 (1.20) | −3.10 *** (0.87) | ||||
| LnGLOB*LnCR | 0.92 * (0.37) | −0.89 *** (0.20) | 1.04 *** (0.16) | 0.06 (0.31) | ||||
| LnGDP | 0.58 *** (0.16) | 0.98 *** (0.18) | 0.13 (0.14) | 0.10 (0.12) | 0.56 *** (0.13) | 0.63 *** (0.04) | 0.91 *** (0.29) | 1.32 ** (0.29) |
| LnREER | −1.40 ** (0.49) | −1.82 ** (0.50) | −0.83 * (0.46) | −0.72 * (0.34) | −2.13 *** (0.40) | −1.05 *** (0.16) | −2.73 *** (0.87) | −3.81 ** (0.89) |
| Constant | 13.37 *** (3.53) | 20.13 *** (3.70) | 22.71 *** (3.61) | 7.91 ** (3.12) | 13.08 ** (5.52) | 8.33 *** (0.76) | 32.72 *** (6.01) | 31.55 *** (6.40) |
| Panel B: Consider political risk in the models | ||||||||
| LnGLOB | −2.41 *** (0.31) | −5.23 *** (1.10) | −3.76 *** (1.02) | 0.36 (1.21) | −1.01 (0.55) | −4.75 ** (1.31) | −4.82 *** (0.86) | −5.12 *** (1.24) |
| LnPR | 0.69 (0.61) | 2.25 (1.51) | 3.04 (2.17) | −1.86 (1.23) | ||||
| LnGLOB*LnPR | 0.54 ** (0.21) | −0.61 ** (0.25) | 0.82 ** (0.28) | 0.29 (0.22) | ||||
| LnGDP | 0.74 *** (0.11) | 0.86 *** (0.13) | 0.44 (0.25) | 0.09 (0.16) | 0.28 (0.50) | 0.68 *** (0.13) | 1.29 *** (0.27) | 1.09 *** (0.27) |
| LnREER | −1.64 *** (0.34) | −1.25 ** (0.45) | −0.29 (0.50) | −1.25 ** (0.53) | 0.77 (1.89) | −1.06 ** (0.38) | −4.34 *** (0.89) | −2.62 *** (0.66) |
| Constant | 11.36 *** (3.22) | 13.95 *** (2.48) | 5.72 (4.70) | 15.68 *** (4.05) | −11.58 (10.13) | 7.97 *** (1.61) | 41.28 *** (8.80) | 23.61 *** (4.46) |
| Variables | Overall Globalization | Economic Globalization | Social Globalization | Political Globalization | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARDL (3,2,3,3,2) | ARDL (3,3,4,4,4) | ARDL (3,3,3,3,2) | ARDL (3,1,3,3,2) | ARDL (1,0,3,0,3) | ARDL (5,3,3,3,3) | ARDL (1,0,2,3,0) | ARDL (4,4,3,4,4) | |
| D(LnGLOB)t | −0.46 (0.65) | −11.64 *** (1.91) | −0.26 (0.53) | 2.32 ** (0.77) | −3.88 *** (0.54) | −5.78 ** (1.35) | ||
| D(LnGLOB)t−1 | 2.95 *** (0.89) | 8.86 *** (1.93) | 0.567 (0.51) | 3.34 *** (0.57) | 8.70 ** (2.18) | |||
| D(LnGLOB)t−2 | 7.79 *** (1.51) | −2.40 *** (0.52) | 4.67 *** (0.43) | 2.95 * (1.24) | ||||
| D(LnGLOB)t−3 | 8.58 *** (1.49) | |||||||
| D(LnCR)t | 0.50 (0.69) | −2.26 *** (0.60) | −1.09 * (0.59) | −0.45 (0.59) | ||||
| D(LnCR)t−1 | 1.38 * (0.74) | 0.57 (0.57) | 0.52 (0.58) | 3.88 *** (0.76) | ||||
| D(LnCR)t−2 | −1.67 ** (0.70) | −2.17 *** (0.58) | −2.13 *** (0.65) | |||||
| D(LnGLOB*LnCR)t | 1.49 *** (0.31) | −0.60 *** (0.09) | 0.60 *** (0.12) | 0.46 (0.27) | ||||
| D(LnGLOB*LnCR)t−1 | −0.26 (0.21) | 0.10 (0.09) | −0.35 ** (0.11) | −0.67 * (0.29) | ||||
| D(LnGLOB*LnCR)t−2 | −1.35 *** (0.23) | −0.60 *** (0.09) | −0.98 *** (0.08) | 0.44 (0.29) | ||||
| D(LnGLOB*LnCR)t−3 | 0.37 ** (0.10) | |||||||
| ECT(−1) | −1.97 *** (0.30) | −2.92 *** (0.43) | −1.45 *** (0.17) | −1.41 *** (0.16) | −1.00 *** (0.180) | −2.68 *** (0.16) | −0.97 *** (0.13) | −2.37 *** (0.34) |
| Variables | Overall Globalization | Economic Globalization | Social Globalization | Political Globalization | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARDL (3,2,3,3,2) | ARDL (3,3,4,4,4) | ARDL (3,4,3,4,1) | ARDL (3,0,3,3,2) | ARDL (3,4,4,1,4) | ARDL (3,3,3,4,4) | ARDL (1,3,2,3,2) | ARDL (1,1,2,0,0) | |
| D(LnGLOB)t | −0.85 (0.56) | −4.80 *** (0.83) | −3.09 *** (0.64) | −1.68 *** (0.25) | −1.93 ** (0.72) | −3.23 *** (0.64) | −2.13 *** (0.62) | |
| D(LnGLOB)t−1 | 4.19 *** (0.84) | 4.50 ** (1.14) | 4.91 *** (0.75) | 2.52 ** (0.93) | 1.79 ** (0.63) | |||
| D(LnGLOB)t−2 | 4.07 *** (0.85) | −2.52 *** (0.52) | 1.80 ** (0.83) | |||||
| D(LnGLOB)t−3 | 2.80 *** (0.64) | |||||||
| D(LnPR)t | 0.76 (0.49) | 1.12 ** (0.48) | −0.12 (0.56) | −2.17 ** (0.93) | ||||
| D(LnPR)t−1 | 0.42 (0.50) | −2.45 *** (0.60) | 1.66 ** (0.51) | 2.44 *** (0.58) | ||||
| D(LnPR)t−2 | −2.19 *** (0.63) | −1.67 *** (0.49) | −1.73 ** (0.56) | |||||
| D(LnPR)t−3 | 1.88 *** (0.44) | |||||||
| D(LnGLOB*LnPR)t | 0.33 (0.17) | −0.32 * (0.15) | −0.05 (0.16) | 0.17 (0.11) | ||||
| D(LnGLOB*LnPR)t−1 | −0.02 (0.12) | 0.16 (0.12) | −0.44 * (0.19) | 0.27 *** (0.08) | ||||
| D(LnGLOB*LnPR)t−2 | −0.68 *** (0.14) | −0.47 *** (0.13) | −1.17 *** (0.20) | |||||
| D(LnGLOB*LnPR)t−3 | 0.30 ** (0.09) | |||||||
| ECT(−1) | −2.30 *** (0.31) | −2.32 *** (0.39) | −1.45 *** (0.17) | −1.25 *** (0.24) | −1.01 *** (0.16) | −2.25 *** (0.31) | −1.24 *** (0.20) | −0.75 *** (0.13) |
| Globalization Variables | Overall Globalization | Economic Globalization | Social Globalization | Political Globalization | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panel A: Consider composite risk in the models | ||||||||
| LnGLOB | 4.46 ** (0.97) | 9.24 ** (2.02) | 5.47 *** (0.93) | 11.05 ** (1.94) | −2.02 (1.59) | 5.29 * (2.33) | 4.17 *** (0.85) | 6.33 *** (1.10) |
| LnCR | −5.70 ** (1.48) | −5.29 ** (1.36) | 12.10 * (6.72) | −1.78 * (0.80) | ||||
| LnGLOB*LnCR | −1.27 ** (0.30) | −1.35 ** (0.31) | −0.97 (0.46) | −0.44 ** (0.16) | ||||
| LnGDP | −0.60 * (0.23) | −0.47 * (0.20) | −0.01 (0.14) | 0.02 (0.13) | 1.04 (0.78) | −0.09 (0.19) | −0.71 ** (0.24) | −0.80 *** (0.18) |
| LnREER | 0.98 (0.51) | 0.80 (0.46) | −0.33 (0.59) | −0.46 (0.52) | 0.61 (1.55) | 0.28 (0.55) | 1.92 ** (0.70) | 2.22 *** (0.55) |
| Constant | 10.62 * (3.71) | −11.21 * (3.92) | 7.81 (4.83) | −13.58 ** (4.01) | −49.06 * (24.34) | −0.80 (3.03) | −9.75 * (4.62) | −19.25 *** (3.85) |
| Panel B: Consider political risk in the models | ||||||||
| LnGLOB | 3.38 ** (1.24) | 4.52 ** (1.19) | 2.21 * (0.91) | −2.93 (2.67) | 0.66 *** (0.15) | 3.38 ** (0.90) | 3.76 *** (0.37) | 5.82 *** (0.59) |
| LnPR | −3.30 (2.27) | −0.81 (2.45) | −2.21 * (0.92) | −2.22 *** (0.54) | ||||
| LnGLOB*LnPR | −0.63 ** (0.20) | 0.45 (0.45) | −0.65 ** (0.19) | −0.51 *** (0.12) | ||||
| LnGDP | −0.10 (0.43) | −0.19 (0.18) | 0.002 (0.184) | 0.71 * (0.34) | 0.04 (0.11) | 0.003 (0.14) | −0.80 *** (0.11) | −0.79 *** (0.11) |
| LnREER | 1.40 (1.48) | −0.14 (0.28) | 0.55 (1.14) | −1.01 (1.05) | −0.47 (0.27) | −0.54 * (0.23) | 1.81 *** (0.38) | 1.79 *** (0.37) |
| Constant | −2.63 (12.09) | −1.59 (1.80) | −3.82 (13.23) | 7.67 (8.83) | 12.46 ** (3.57) | 3.77 ** (1.16) | −5.34 (3.77) | −14.38 *** (2.45) |
| Variables | Overall Globalization | Economic Globalization | Social Globalization | Political Globalization | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARDL (4,4,4,4,4) | ARDL (4,4,4,4,4) | ARDL (4,4,4,4,4) | ARDL (4,4,4,4,4) | ARDL (1,0,3,2,0) | ARDL (4,4,4,4,3) | ARDL (3,3,3,3,3) | ARDL (2,3,3,3,3) | |
| D(LnGLOB)t | 2.02 ** (0.29) | 2.80 ** (0.64) | 0.38 (0.26) | 2.83 ** (0.73) | −1.29 (0.76) | 0.52 (0.57) | −5.91 *** (1.29) | |
| D(LnGLOB)t−1 | −4.58 *** (0.35) | −12.92 *** (0.84) | −6.81 *** (0.55) | −13.29 *** (0.90) | −9.53 *** (0.88) | −6.68 *** (1.28) | −4.26 ** (1.41) | |
| D(LnGLOB)t−2 | −2.32 *** (0.34) | −9.90 *** (0.73) | −3.97 *** (0.38) | −11.47 *** (0.68) | −8.13 *** (0.79) | −3.17 ** (1.14) | ||
| D(LnGLOB)t−3 | −2.15 *** (0.32) | −5.18 *** (0.58) | −3.13 *** (0.30) | −8.65 *** (0.75) | −3.58 *** (0.63) | |||
| D(LnCR)t | −0.66 (0.41) | −1.38 * (0.47) | 4.15 *** (0.63) | −1.05 (1.15) | ||||
| D(LnCR)t−1 | 7.92 *** (0.52) | 5.45 *** (0.38) | 1.09 ** (0.41) | −0.87 (0.72) | ||||
| D(LnCR)t−2 | 7.38 *** (0.47) | 6.69 *** (0.46) | 1.70 *** (0.46) | 1.30 * (0.64) | ||||
| D(LnCR)t−3 | 2.71 *** (0.33) | 4.61 *** (0.44) | ||||||
| D(LnGLOB*LnCR)t | −0.27 * (0.11) | −0.53 ** (0.13) | 0.30 (0.16) | −0.38 (0.26) | ||||
| D(LnGLOB*LnCR)t−1 | 1.90 *** (0.13) | 1.38 *** (0.10) | 1.87 *** (0.18) | −0.31 * (0.16) | ||||
| D(LnGLOB*LnCR)t−2 | 1.79 *** (0.12) | 1.72 *** (0.12) | 1.77 *** (0.17) | 0.29 * (0.14) | ||||
| D(LnGLOB*LnCR)t−3 | 0.74 *** (0.09) | 1.27 *** (0.12) | 0.77 *** (0.14) | |||||
| ECT(−1) | −1.63 *** (0.11) | −1.84 *** (0.13) | −1.38 *** (0.10) | −1.54 *** (0.11) | −0.28 *** (0.04) | −1.57 *** (0.15) | −1.76 *** (0.28) | −1.80 *** (0.26) |
| Variables | Overall Globalization | Economic Globalization | Social Globalization | Political Globalization | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARDL (3,3,4,4,4) | ARDL (4,4,4,4,3) | ARDL (4,4,4,4,3) | ARDL (3,0,2,2,2) | ARDL (4,3,4,4,3) | ARDL (4,4,4,4,3) | ARDL (1,3,3,3,2) | ARDL (1,3,3,3,2) | |
| D(LnGLOB)t | 2.82 *** (0.51) | 1.64 ** (0.44) | 0.68 ** (0.23) | 0.36 ** (0.12) | 0.27 (0.48) | −0.42 (0.43) | 2.29 *** (0.65) | |
| D(LnGLOB)t−1 | 2.04 *** (0.42) | −7.18 *** (0.49) | 0.32 (0.25) | −0.36 ** (0.11) | −6.02 *** (0.52) | −7.60 *** (1.11) | −7.44 *** (1.12) | |
| D(LnGLOB)t−2 | 2.19 *** (0.50) | −5.54 *** (0.53) | −1.93 *** (0.27) | 0.28* (0.11) | −5.94 *** (0.57) | −1.80 ** (0.74) | −3.44 *** (1.02) | |
| D(LnGLOB)t−3 | −3.64 *** (0.39) | −1.16 ** (0.26) | ||||||
| D(LnPR)t | 3.01 *** (0.64) | 3.95 *** (0.30) | 0.63 (0.38) | −2.87 *** (0.54) | ||||
| D(LnPR)t−1 | 5.34 *** (0.60) | 5.35 *** (0.37) | 4.33 *** (0.41) | 0.03 (0.38) | ||||
| D(LnPR)t−2 | 3.94 *** (0.49) | 4.45 *** (0.35) | 5.11 *** (0.51) | 1.88 *** (0.51) | ||||
| D(LnPR)t−3 | 1.13 ** (0.36) | 1.28 *** (0.20) | 2.51 *** (0.34) | |||||
| D(LnGLOB*LnPR)t | −0.08 (0.09) | 0.50 *** (0.12) | 0.01 (0.10) | −0.66 *** (0.20) | ||||
| D(LnGLOB*LnPR)t−1 | 1.28 *** (0.10) | 0.19 * (0.10) | 1.27 *** (0.11) | 0.001 (0.09) | ||||
| D(LnGLOB*LnPR)t−2 | 1.32 *** (0.10) | 1.44 *** (0.13) | 0.41 *** (0.11) | |||||
| D(LnGLOB*LnPR)t−3 | 0.59 *** (0.07) | 0.73 *** (0.09) | ||||||
| ECT(−1) | −0.62 *** (0.08) | −1.97 *** (0.14) | −1.40 *** (0.09) | −0.59 *** (0.10) | −1.63 *** (0.15) | −1.99 *** (0.16) | −1.88 *** (0.24) | −1.85 *** (0.23) |
| Globalization Variables | Overall Globalization | Economic Globalization | Social Globalization | Political Globalization | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panel A: Consider composite risk in the models | ||||||||
| LnGLOB | −0.01 (2.04) | −26.25 *** (5.93) | 8.16 (5.08) | 19.07 ** (8.04) | 2.93 (2.11) | −13.76 * (5.74) | −8.05 *** (1.75) | −6.54 ** (2.25) |
| LnCR | −3.23 (3.59) | −14.09 *** (4.43) | −16.75 ** (7.77) | −1.33 (1.82) | ||||
| LnGLOB*LnCR | 3.50 ** (0.90) | −2.96 ** (1.01) | 2.50 * (1.14) | −0.15 (0.30) | ||||
| LnGDP | −0.39 (0.57) | 1.98 ** (0.47) | −1.08 (0.69) | −1.72 ** (0.79) | −1.50 (1.10) | 0.68 (0.42) | 1.78 ** (0.47) | 1.62 *** (0.42) |
| LnREER | 0.77 (1.93) | −2.59 ** (0.99) | 0.36 (2.03) | 2.70 (1.78) | 1.88 (2.76) | −1.02 (1.30) | −5.63 ** (1.44) | −4.98 *** (1.31) |
| Constant | 11.30 (14.94) | 41.22 *** (9.19) | 32.87 * (16.13) | −27.26 (17.38) | 58.98 ** (23.39) | 10.14 (6.77) | 51.21 *** (8.82) | 40.05 *** (8.91) |
| Panel B: Consider political risk in the models | ||||||||
| LnGLOB | −5.15 *** (1.01) | −11.07 ** (2.22) | −2.73 * (1.19) | 4.92 *** (1.37) | −1.92 ** (0.59) | −0.39 (2.27) | −8.62 ** (2.02) | −8.69 *** (1.50) |
| LnPR | 5.04 ** (1.96) | −3.05 (1.97) | 6.18 * (3.17) | −1.20 (2.36) | ||||
| LnGLOB*LnPR | 1.36 ** (0.39) | −1.45 *** (0.22) | −0.09 (0.47) | 0.06 (0.30) | ||||
| LnGDP | 0.80 * (0.36) | 1.26 ** (0.32) | −0.49 (0.28) | −0.89 *** (0.18) | 0.39 (0.44) | 0.08 (0.41) | 1.71 * (0.64) | 2.04 *** (0.29) |
| LnREER | −0.12 (1.04) | −0.98 (0.62) | −0.14 (0.72) | 0.21 (0.43) | 1.16 (1.21) | 0.58 (1.14) | −5.35 * (1.98) | −6.14 *** (0.96) |
| Constant | −7.05 (8.86) | 15.45 ** (3.36) | 25.40 *** (7.23) | 7.60 ** (2.98) | −27.72 * (13.84) | −2.29 (5.00) | 52.04 ** (17.37) | 47.88 *** (6.33) |
| Variables | Overall Globalization | Economic Globalization | Social Globalization | Political Globalization | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARDL (4,0,3,3,2) | ARDL (3,3,4,4,4) | ARDL (1,3,3,3,3) | ARDL (1,1,3,4,0) | ARDL (1,1,3,3,1) | ARDL (3,3,3,4,4) | ARDL (3,4,4,3,4) | ARDL (3,3,3,3,3) | |
| D(LnGLOB)t | −21.23 *** (3.38) | 1.81* (0.94) | 5.11 *** (1.20) | 0.42 (0.42) | −4.41 * (1.83) | −4.99 *** (0.91) | −1.41 (1.50) | |
| D(LnGLOB)t−1 | 18.43 *** (2.80) | −3.89 *** (0.90) | 6.66 ** (1.84) | 5.49 *** (1.14) | 2.74 * (1.49) | |||
| D(LnGLOB)t−2 | 15.59 *** (2.31) | −2.98 ** (0.99) | 12.35 *** (1.89) | 6.04 *** (1.20) | 7.53 *** (1.92) | |||
| D(LnGLOB)t−3 | 1.53 (0.98) | |||||||
| D(LnCR)t | −2.10 * (1.09) | −5.62 *** (1.05) | −3.82 *** (1.10) | −4.31 ** (1.34) | ||||
| D(LnCR)t−1 | 1.74 (1.21) | 1.29 (1.08) | 2.20 * (1.14) | 2.70 * (1.21) | ||||
| D(LnCR)t−2 | −2.67 ** (1.11) | −2.91 ** (0.98) | −2.71 *** (0.81) | −3.11 ** (1.04) | ||||
| D(LnCR)t−3 | −2.01 * (0.89) | |||||||
| D(LnGLOB*LnCR)t | 2.04 *** (0.44) | −1.18 *** (0.23) | 0.37 (0.35) | −0.61 * (0.33) | ||||
| D(LnGLOB*LnCR)t−1 | −1.52 *** (0.28) | −0.51 *** (0.14) | −0.99 ** (0.35) | 0.75 ** (0.23) | ||||
| D(LnGLOB*LnCR)t−2 | −2.50 *** (0.32) | −1.18 *** (0.16) | −2.70 *** (0.40) | −0.74 *** (0.22) | ||||
| D(LnGLOB*LnCR)t−3 | 0.96 *** (0.16) | |||||||
| ECT(−1) | −0.86 *** (0.15) | −1.88 *** (0.27) | −0.56 *** (0.09) | −0.47 *** (0.06) | −0.46 *** (0.08) | −1.42 *** (0.21) | −1.65 *** (0.18) | −1.42 *** (0.17) |
| Variables | Overall Globalization | Economic Globalization | Social Globalization | Political Globalization | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARDL (3,2,3,4,4) | ARDL (4,4,4,4,4) | ARDL (4,3,4,4,0) | ARDL (4,0,4,4,0) | ARDL (3,2,3,4,4) | ARDL (3,0,2,3,1) | ARDL (4,4,4,3,4) | ARDL (1,3,3,3,2) | |
| D(LnGLOB)t | −5.73 *** (0.98) | −9.25 *** (1.51) | −1.25 (0.88) | −2.19 *** (0.48) | −6.78 *** (1.22) | −2.48 ** (1.10) | ||
| D(LnGLOB)t−1 | 3.45 ** (1.06) | 16.38 *** (2.50) | 0.04 (0.74) | 1.01 ** (0.43) | 4.61 ** (1.35) | 4.96 *** (1.40) | ||
| D(LnGLOB)t−2 | 15.90 *** (2.55) | −4.50 *** (0.86) | 4.11 ** (1.39) | 4.02 ** (1.45) | ||||
| D(LnGLOB)t−3 | 7.52 ** (1.75) | 2.80 * (1.04) | ||||||
| D(LnPR)t | −0.46 (0.97) | −5.35 *** (0.95) | −0.30 (1.06) | −2.59 * (1.08) | ||||
| D(LnPR)t−1 | −1.67 * (0.82) | −3.54 *** (0.87) | −2.01 * (0.96) | 2.24 * (1.02) | ||||
| D(LnPR)t−2 | −6.05 *** (1.00) | −5.54 *** (0.89) | −6.02 *** (1.17) | −2.50 * (1.03) | ||||
| D(LnPR)t−3 | −1.41 ** (0.58) | −1.43 (0.90) | ||||||
| D(LnGLOB*LnPR)t | 0.48 (0.26) | −1.77 *** (0.23) | 0.20 * (0.11) | −0.12 (0.21) | ||||
| D(LnGLOB*LnPR)t−1 | −1.38 ** (0.30) | −0.59 *** (0.14) | 0.50 *** (0.11) | 0.57 *** (0.16) | ||||
| D(LnGLOB*LnPR)t−2 | −1.85 *** (0.25) | −1.35 *** (0.18) | −0.36 * (0.18) | |||||
| D(LnGLOB*LnPR)t−3 | −0.58 * (0.22) | −0.34 ** (0.13) | ||||||
| ECT(−1) | −1.39 *** (0.20) | −2.97 *** (0.40) | −1.46 *** (0.17) | −1.47 *** (0.19) | −1.20 *** (0.20) | −0.99 *** (0.18) | −1.51 *** (0.19) | −1.36 *** (0.19) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Chiu, Y.-B. Globalization, Country Risks, and Trade in Tourism Services: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5869. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145869
Zhang W, Chiu Y-B. Globalization, Country Risks, and Trade in Tourism Services: Evidence from China. Sustainability. 2020; 12(14):5869. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145869
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wenwen, and Yi-Bin Chiu. 2020. "Globalization, Country Risks, and Trade in Tourism Services: Evidence from China" Sustainability 12, no. 14: 5869. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145869
APA StyleZhang, W., & Chiu, Y.-B. (2020). Globalization, Country Risks, and Trade in Tourism Services: Evidence from China. Sustainability, 12(14), 5869. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145869





