Value Creation through Corporate Sustainability in the Port Sector: A Structured Literature Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sustainability and Corporate Social Responsibility
2.1. Definition of Sustainability
2.2. Perception of Sustainability
2.3. Gains from Implementing Corporate Social Responsibility
2.4. Challenges of Introducing Corporate Social Responsibility in the Maritime Sector
3. Methodology
3.1. Comparison with Past Literature Reviews
3.2. Literature Analysis Description
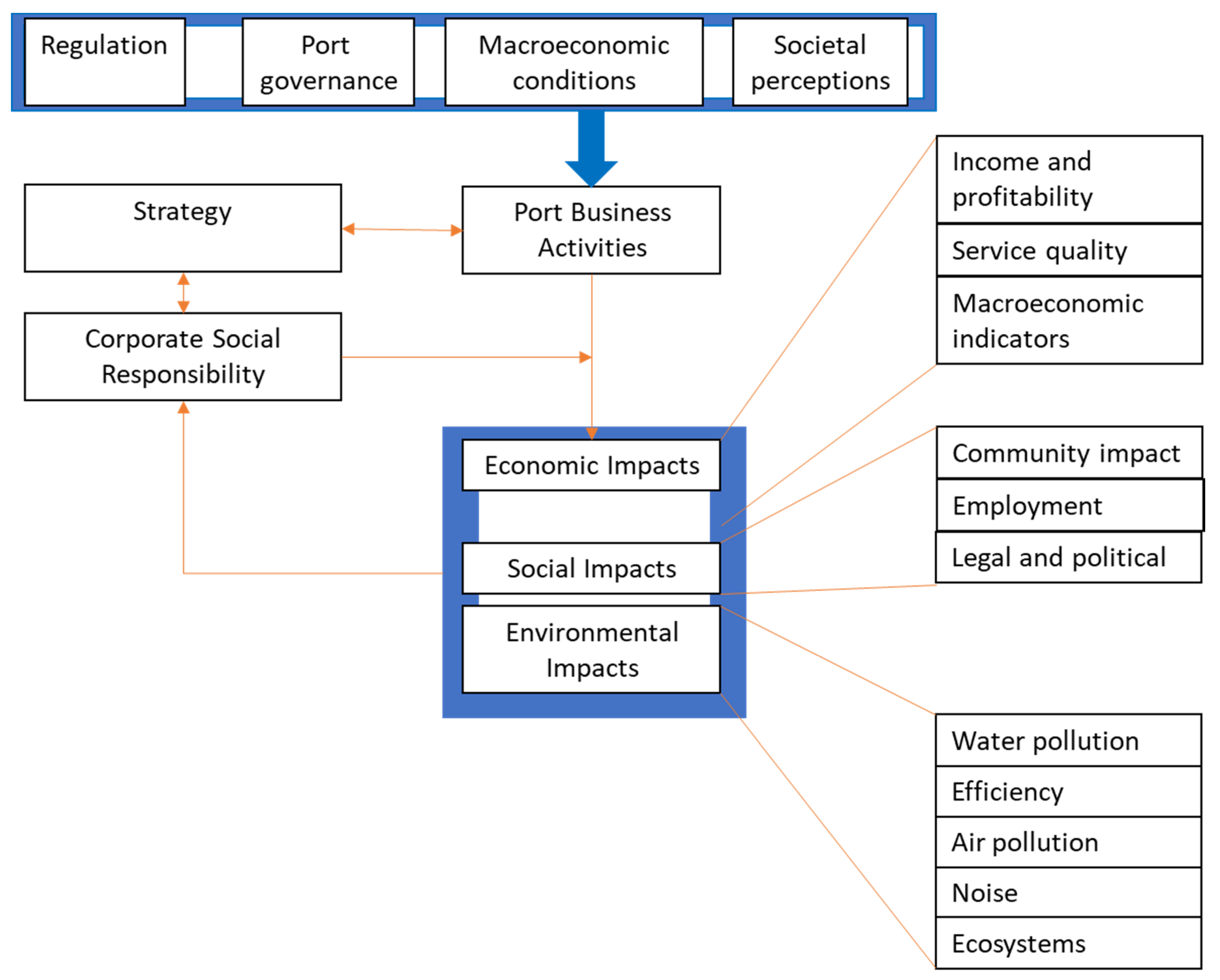
4. Framework Analysis
5. Conclusions
- Test and refine the proposed framework;
- Enhance the framework on the basis of similar studies in other domains;
- Determine adequate metrics to measure value and impacts;
- Develop an economic model to evaluate the relationship between port business activities and CSR;
- Test the framework by quantifying the value of CSR activities to specific port cases and then across ports.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, C.S.; Lai, P.L.; Chiang, Y.P. Container Terminal Employees’ Perceptions of the Effects of Sustainable Supply Chain Management on Sustainability Performance. Marit. Policy Manag. 2016, 43, 597–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.S.L.; Notteboom, T. The Greening of Ports: A Comparison of Port Management Tools Used by Leading Ports in Asia and Europe. Transp. Rev. 2014, 34, 169–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acciaro, M. Corporate Responsibility and Value Creation in the Port Sector. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2015, 18, 291–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.H.; Lun, Y.H.V.; Wong, C.W.Y.; Cheng, T.C.E. Measures for Evaluating Green Shipping Practices Implementation. Int. J. Shipp. Transp. Logist. 2013, 5, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.S.L.; Lim, J.M. Incorporating Corporate Social Responsibility in Strategic Planning: Case of Ship-Operating Companies. Int. J. Shipp. Transp. Logist. 2016, 8, 273–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Thai, V.V. A Study of the Influence of Sustainable Management Activities on Customer Satisfaction and Long-Term Orientation in the Shipping Industry: Evidence from Users of Korean Flagged Shipping Service. Int. J. Shipp. Transp. Logist. 2016, 8, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yliskylä-Peuralahti, J.; Gritsenko, D. Binding Rules or Voluntary Actions? A Conceptual Framework for CSR in Shipping. WMU J. Marit. Aff. 2014, 13, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parviainen, T.; Lehikoinen, A.; Kuikka, S.; Haapasaari, P. How Can Stakeholders Promote Environmental and Social Responsibility in the Shipping Industry? WMU J. Marit. Aff. 2018, 17, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, R.T.; Ponte, S.; Lister, J. Buyer-Driven Greening? Cargo-Owners and Environmental Upgrading In Maritime Shipping. Geoforum 2016, 68, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinwoodie, J.; Truck, S.; Knowles, H.; Benhin, J.; Sansom, M. Sustainable Development of Maritime Operations in Port. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2012, 21, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandermeulen, J.H. Environmental Trends of Ports and Harbors: Implications for Planning and Management. Marit. Policy Manag. 1996, 23, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooms, M.; Verbeke, A.; Haezendonck, E. Stakeholder Management and Path Dependence in Large-Scale Transport Infrastructure Development: The Port of Antwerp Case (1960–2010). J. Transp. Geogr. 2013, 27, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, S.; Thai, V.V.; Wong, Y.D. Towards Sustainable Asean Port Development: Challenges and Opportunities for Vietnamese Ports. Asian J. Shipp. Logist. 2016, 32, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, D.W.; Warford, J.J. The Concepts of Sustainable Development: World without End: Economics, Environment, and Sustainable Development; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Elkington, J. Towards the Sustainable Corporation: Win-Win-Win Business Strategies for Sustainable Development. Calif. Manag. Rev. 1994, 36, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.S.; Shang, K.C.; Lin, C.C. Examining Sustainability Performance at Ports: Port Managers’ Perspectives on Developing Sustainable Supply Chains. Marit. Policy Manag. 2016, 43, 909–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejvar, M.; Lai, K.H.; Lo, C.K.; Fürst, E.W. Strategic Responses to Institutional Forces Pressuring Sustainability Practice Adoption: Case-Based Evidence from Inland Port Operations. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 61, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, K.X.; Xiao, Y. Measuring Marine Environmental Efficiency of a Cruise Shipping Company Considering Corporate Social Responsibility. Mar. Policy 2019, 99, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acciaro, M.; Vanelslander, T.; Sys, C.; Ferrari, C.; Roumboutsos, A.; Giulliano, G.; Lam, J.S.L.; Kapros, S. Environmental Sustainability In Seaports: A Framework for Successful Innovation. Marit. Policy Manag. 2014, 41, 480–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, J.F.; Brynolf, S.; Wilewska-Bien, M.; Andersson, K. (Eds.) Shipping and the Environment: Improving Environmental Performance in Marine Transportation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yliskylä-Peuralahti, J.; Gritsenko, D.; Viertola, J. Corporate Social Responsibility and Quality Governance in Shipping. Ocean Yearb. 2015, 29, 417–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, K.F.; Thai, V.V. Corporate Social Responsibility and Service Quality Provision in Shipping Firms: Financial Synergies or Trade-Offs? Marit. Policy Manag. 2017, 44, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, E.G. Port Planning and Development; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Puig, M.; Wooldridge, C.; Michail, A.; Darbra, R.M. Current Status and Trends of the Environmental Performance in European Ports. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 48, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai, V.V.; Balasubramanyam, L.; Yeoh, K.K.L.; Norsofiana, S. Revisiting the Seafarer Shortage Problem: The Case of Singapore. Marit. Policy Manag. 2013, 40, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Österman, C.; Rose, L. Assessing Financial Impact of Maritime Ergonomics on Company Level: A Case Study. Marit. Policy Manag. 2015, 42, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobetz, W.; Merikas, A.; Mrika, A.; Tsionas, M.G. Corporate Social Responsibility Disclosure: The Case of International Shipping. Transp. Res. Part E 2014, 71, 18–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.; Van Der Linde, C. Toward A New Conception of the Environment-Competitiveness Relationship. J. Econ. Perspect. 1995, 9, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, S.; Maltz, A.; Dooley, K. The Link Between Economic and Environmental Performance of The Top 10 Us Ports. Marit. Policy Manag. 2017, 44, 227–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargett, T.R.; Williams, M.F. Wilh. Wilhelmsen Shipping Company: Moving from CSR Tradition to CSR Leadership. Corp. Gov. 2009, 9, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, J.; Poulsen, R.T.; Ponte, S. Orchestrating Environmental Governance in Maritime Shipping. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2015, 34, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Tsai, Y.L. Factors Influencing Shippers to Use Multiple Country Consolidation Services in International Distribution Centers. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2009, 122, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, S.; Song, D.W.; Park, S. Does more competition result in better port performance? Marit. Econ. Logist. 2018, 20, 433–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranfield, D.; Denyer, D.; Smart, P. Towards A Methodology for Developing Evidence-Informed Management Knowledge by Means of Systematic Review. Br. J. Manag. 2003, 14, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sislian, L.; Jaegler, A.; Cariou, P. A Literature Review on Port Sustainability and Ocean’s Carrier Network Problem. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2016, 19, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachizawa, M.E.; Yew Wong, C. Towards A Theory of Multi-Tier Sustainable Supply Chains: A Systematic Literature Review. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2014, 19, 643–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centobelli, P.; Cerchione, R.; Esposito, E. Environmental Sustainability in the Service Industry of Transportation and Logistics Service Providers: Systematic Literature Review and Research Directions. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 53, 454–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelista, P.; Santoro, L.; Thomas, A. Environmental Sustainability in Third-Party Logistics Service Providers: A Systematic Literature Review From 2000–2016. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Pettit, S.; Abouarghoub, W.; Beresford, A. Port Sustainability and Performance: A Systematic Literature Review. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2019, 72, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denyer, D.; Tranfield, D. Producing a Systematic Review. In The Sage Handbook of Organizational Research Methods; Sage Publications Ltd.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 671–689. [Google Scholar]
- Davarzani, H.; Fahimnia, B.; Bell, M.; Sarkis, J. Greening Ports and Maritime Logistics: A Review. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2016, 48, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeev, A.; Pati, R.K.; Padhi, S.S.; Govindan, K. Evolution of Sustainability in Supply Chain Management: A Literature Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 162, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguinis, H.; Glavas, A. What We Know and Don’t Know About Corporate Social Responsibility: A Review and Research Agenda. J. Manag. 2012, 38, 932–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerkan, K.Y.; Seter, H. Reviewing Tools and Technologies for Sustainable Ports: Does Research Enable Decision Making In Ports? Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2019, 72, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakam, M.H.; Solvang, W.D. Container Ports Sustainability-A Literature Review. In IEEE 4th International Conference on Cognitive Infocommunications (Coginfocom); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 803–810. [Google Scholar]
- Shields, P.; Rangarajan, N. A Playbook for Research Methods: Integrating Conceptual Frameworks and Project Management; New Forums Press: Stillwater, OK, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Miles, M.B.; Hubermann, A.M. Qualitative Data Analysis: A Sourcebook of New Methods; Sage: Beverly Hills, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Ashrafi, M.; Acciaro, M.; Walker, T.R.; Magnan, G.M.; Adams, M. Corporate sustainability in Canadian and US maritime ports. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, T.; Adams, M.; Walker, T.R. Sustainability initiatives in Canadian ports. Mar. Policy 2019, 6, 103519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lam, J.S.L. Sustainability and interactivity between cities and ports: A two-stage data envelopment analysis (DEA) approach. Marit. Policy Manag. 2018, 45, 944–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aregall, M.G.; Bergqvist, R.; Monios, J. A global review of the hinterland dimension of green port strategies. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 59, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notteboom, T.; Lam, J. The greening of terminal concessions in seaports. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmer, S.; Nguyen, H.O.; Bandara, Y.M.; Yeni, K. Non-price competition in the port sector: A case study of ports in Turkey. Asian J. Shipp. Logist. 2016, 32, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, R.T.; Ponte, S.; Sornn-Friese, H. Environmental upgrading in global value chains: The potential and limitations of ports in the greening of maritime transport. Geoforum 2018, 89, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.S.L.; Yap, W.Y. A stakeholder perspective of port city sustainable development. Sustainability 2019, 11, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Lam, J.S.L. A systems framework for the sustainable development of a Port City: A case study of Singapore’s policies. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2017, 22, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Zhang, D.; Yan, X.; Yang, Z. A novel model for the quantitative evaluation of green port development–A case study of major ports in China. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 61, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Pak, M. A Delphi analysis on green performance evaluation indices for ports in China. Marit. Policy Manag. 2017, 44, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teerawattana, R.; Yang, Y.C. Environmental performance indicators for green port policy evaluation: Case study of Laem Chabang port. Asian J. Shipp. Logist. 2019, 35, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vaio, A.; Varriale, L.; Alvino, F. Key performance indicators for developing environmentally sustainable and energy efficient ports: Evidence from Italy. Energy Policy 2018, 122, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipper, C.A.; Vreugdenhil, H.; De Jong, M.P.C. A sustainability assessment of ports and port-city plans: Comparing ambitions with achievements. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 57, 84–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antão, P.; Calderón, M.; Puig, M.; Michail, A.; Wooldridge, C.; Darbra, R.M. Identification of occupational health, safety, security (OHSS) and environmental performance indicators in port areas. Saf. Sci. 2016, 85, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotrikla, A.M.; Lilas, T.; Nikitakos, N. Abatement of air pollution at an Aegean island port utilizing shore side electricity and renewable energy. Mar. Policy 2017, 75, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boile, M.; Theofanis, S.; Sdoukopoulos, E.; Plytas, N. Developing a Port Energy Management Plan: Issues, Challenges, and Prospects. Transp. Res. Rec. 2016, 2549, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiau, T.A.; Chuen-Yu, J.K. Developing an indicator system for measuring the social sustainability of offshore wind power farms. Sustainability 2016, 8, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerts, M.; Dooms, M. Sustainability Reporting for Inland Port Managing Bodies: A Stakeholder-Based View on Materiality. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notteboom, T.; Lugt, L.V.D.; Saase, N.V.; Sel, S.; Neyens, K. The Role of Seaports in Green Supply Chain Management: Initiatives, Attitudes, and Perspectives in Rotterdam, Antwerp, North Sea Port, and Zeebrugge. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.S.L.; Li, K.X. Green port marketing for sustainable growth and development. Transp. Policy 2019, 84, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguí, X.; Puig, M.; Quintieri, E.; Wooldridge, C.; Darbra, R.M. New environmental performance baseline for inland ports: A benchmark for the European inland port sector. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 58, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, M.; Pla, A.; Seguí, X.; Darbra, R.M. Tool for the identification and implementation of Environmental Indicators in Ports (TEIP). Ocean Coast. Manag. 2017, 140, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, E.C.; Neto, F.J.K. Tools for evaluating environmental performance at Brazilian public ports: Analysis and proposal. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iris, C.; Lam, J.S.L. A review of energy efficiency in ports: Operational strategies, technologies and energy management systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 112, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturini, G.; Iris, Ç.; Kontovas, C.A.; Larsen, A. The multi-port berth allocation problem with speed optimization and emission considerations. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 54, 142–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Chen, Q.; Quan, X.; Long, L.; Fung, R.Y. Berth allocation considering fuel consumption and vessel emissions. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2011, 47, 1021–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, M.; Hu, H. Berth allocation and quay crane-yard truck assignment considering carbon emissions in port area. Int. J. Shipp. Transp. Logist. 2019, 11, 216–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, K.; Li, X.; Tian, Q. The Impact of the allocation of facilities on reducing carbon emissions from a green container terminal perspective. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Ge, Y.E. Modeling assignment of quay cranes using queueing theory for minimizing CO2 emission at a container terminal. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 61, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
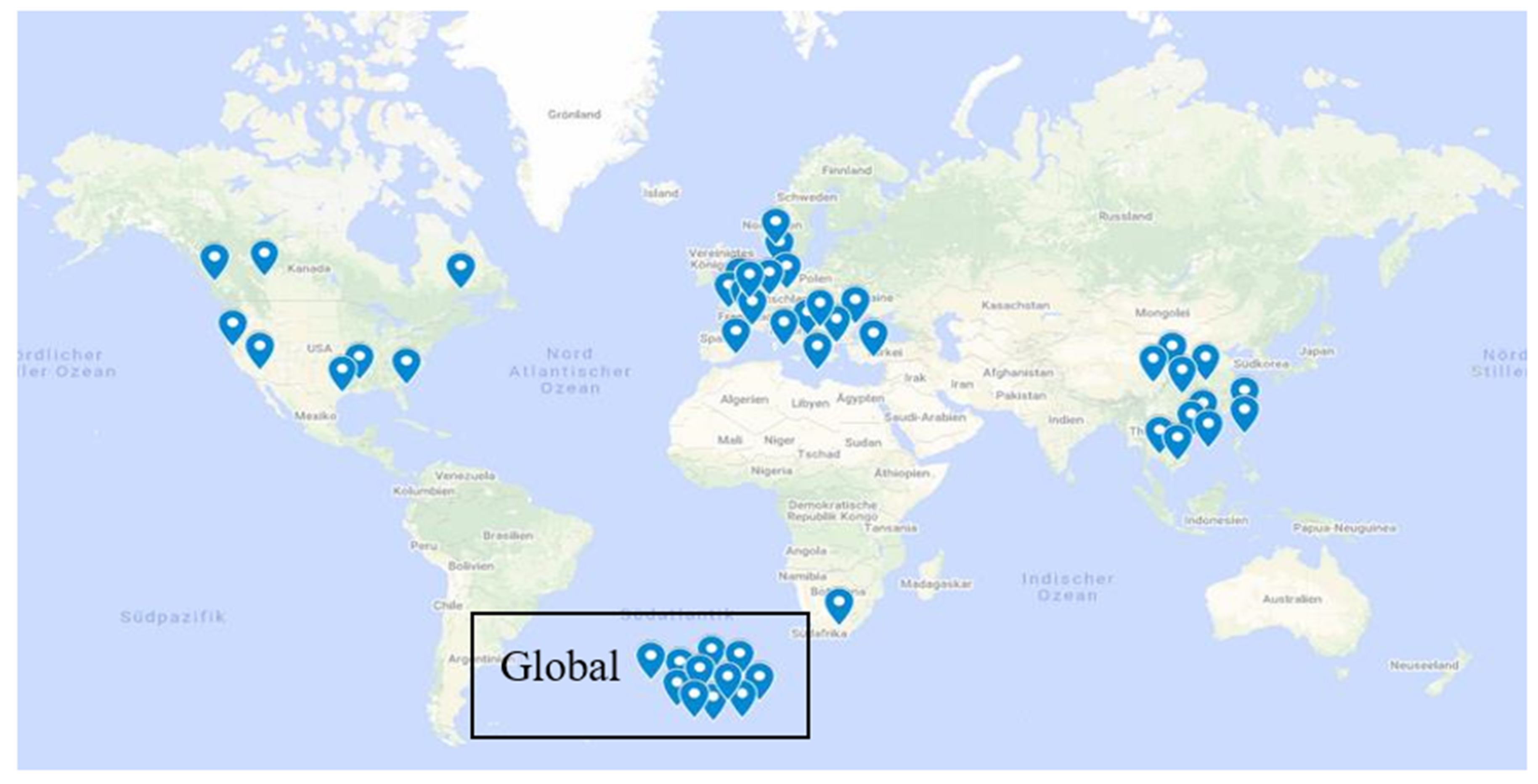
| Publisher | Year | Scope | Timeframe | Sample | Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maritime sustainability literature reviews | |||||
| [35] Sislian et al. | 2016 | 198 | 1987–2013 | 49 | 0.247 |
| [39] Lim et al. | 2019 | 704 | 1990–2017 | 21 | 0.030 |
| [41] Davarzani et al. | 2016 | 2180 | 1975–2014 | 338 | 0.155 |
| [42] Bjerkan and Seter | 2019 | 148 | 2010–2018 | 70 | 0.473 |
| [43] Hakam and Solvang | 2013 | 334 | 1985–2012 | N.A. | N.A. |
| This study | 2020 | 104 | 2016–2020 | 72 | 0.692 |
| Other supply-chain sustainability literature reviews | |||||
| [36] Tachizawa and Wong | 2014 | 681 | 1976–2014 | 39 | 0.057 |
| [37] Centobelli et al. | 2017 | 415 | 1960–2014 | 46 | 0.111 |
| [38] Evangelista et al. | 2018 | 582 | 2000–2016 | 88 | 0.151 |
| [44] Rajeev et al. | 2017 | 1068 | 2000–2015 | 59 | 0.055 |
| [45] Aguinis and Glavas | 2012 | 588 | 1970–2011 | 181 | 0.308 |
| Year of Publication | Number of Contributions |
|---|---|
| 2016 | 20 |
| 2017 | 17 |
| 2018 | 22 |
| 2019 | 10 |
| 2020 (till June) | 3 |
| Sum | 72 |
| CSR | ||||
| OR | Port | AND NOT | Airport | |
| Corporate Social Responsibility | AND | OR | ||
| OR | Shipping | |||
| green | AND | OR | ||
| OR | Harbor | |||
| sustainable | AND | OR | ||
| OR | Maritime | |||
| sustainability | ||||
| OR | ||||
| environmental | ||||
| OR | ||||
| green | ||||
| OR | Port pricing | AND NOT | Airport | |
| sustainable | AND | OR | ||
| OR | Port incentives | AND NOT | Airport | |
| environmental |
| Journal | Contributions |
|---|---|
| Transportation Research Part D | 16 |
| Maritime Policy & Management | 10 |
| Sustainability | 7 |
| The Asian Journal of Shipping and Logistics | 5 |
| Marine Policy | 4 |
| Journal of Cleaner Production | 3 |
| Energy Policy | 3 |
| Maritime Economics & Logistics | 2 |
| Journal of Business Ethics | 2 |
| International Journal on Shipping and Transport Logistics | 2 |
| Environmental Science and Policy | 2 |
| WMU Journal on Maritime Affairs | 2 |
| Transport Policy | 2 |
| Geoforum | 2 |
| Research in transportation business & management | 2 |
| Marine Pollution Bulletin | 1 |
| Sustainable Development | 1 |
| Journal of Marine Science and Engineering | 1 |
| Safety Science | 1 |
| Ocean and Coastal Management | 1 |
| Transportation Research Record | 1 |
| Journal of Transport Geography | 1 |
| International Journal of Logistics Management | 1 |
| Total | 72 |
| Cluster | Usable Framework | Contributions |
|---|---|---|
| Underlying theories | Corporate social responsibility (CSR)-affecting theories | [33] |
| CSR customer satisfaction theories | [22] | |
| CSR theories | [29,38] | |
| CSR policy and decisions | Policy initiatives and practices | [9,19,48] |
| Port examples on environmental strategies | [17] | |
| Power/fuel topics | [42] | |
| Top 10 environmental priorities in EU ports mentioned | [49] | |
| Policy initiatives and practices | [50] | |
| Owner alliances | [8] | |
| Ship rating schemes | [8] | |
| Green hinterland strategy matrix | [51] | |
| Instruments available to port authorities | [52] | |
| Affecting factors | Port competition | [53] |
| Management’s perception/concerns about CSR | [5,6] | |
| Implementation complexity | [54] | |
| Stakeholders | [55] | |
| Measurements | Sustainability performance measurements | [1,16,56,57,58,59] |
| Environmental Performance Indicators | [60] | |
| [61] | ||
| [62] | ||
| Particular Matter 10 comparison of ship/shore energy sources | [63] | |
| Generic energy mapping and consumption | [64] | |
| Social sustainability indicators | [65] |
| Cluster | Aspect | Measurement | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Income and profitability | Amount of cargo handled | annual cargo volume | [56] |
| Productivity/throughput/growth | cargo volume per vessel | [56,57,61] | |
| Corporate and property taxes | tax income | [56] | |
| Input cost | costs | [56] | |
| Investment and market share | investment amount, market share | [6,61] | |
| Management efficiency | [56] | ||
| Service quality | Hinterland connection | meters of transport ways, amounts of connections | [61,66] |
| Quality of handling | numbers of accidents, environmental impact per handling | [6,53,61] | |
| Port operations | qualitative questionnaires | [53,56] | |
| Port charges | costs | [56] | |
| Input cost | costs | [56] | |
| Macro-value | GDP generation | GDP income | [56,57,66] |
| Tax generation | tax income | [56] | |
| Trade facilitation | trade amounts | [56] | |
| Cruise tourism | passenger numbers | [61] | |
| Traffic | transhipments, cargo handling | [53,61] |
| Cluster | Aspect | Measurement | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Community impact | Employment | number of jobs created | [6,56,61,66] |
| Safety | number of safety incidents | [56,62] | |
| Security | number of security incidents | [62] | |
| Resilience | recovery time | [57,61] | |
| Heritage and cultural impact | existing Yes/No | [56,61] | |
| Employment quality | CSR communication/education | quality of training | [1,5,16,58,60] |
| CSR decision involvement | existing Yes/No | [16] | |
| Corporate culture | existing Yes/No | [16,58,67] | |
| Legal and political benefits | CSR policy | existing Yes/No | [1,5,6,16,58,60] |
| CSR information publication | number of reports | [5,16,58,68] | |
| CSR efforts beyond compliance | existing Yes/No | [1,58] | |
| Establishment of evaluation indicators | existing Yes/No | [1,58] | |
| Green port development plan | plan existing | [1,5,54,60] |
| Cluster | Aspect | Measurement | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water pollution management | Fuel spill contingency plan | existing Yes/No | [58] |
| Ballast water pollutant control | existing Yes/No | [6,58,61] | |
| Cargo spill control prevention | existing Yes/No | [58] | |
| Sewage/wastewater treatment | existing Yes/No | [56,57,58,60,66] | |
| Eco-efficiency | Hazard waste management | existing Yes/No | [56,58,62,69,70] |
| Solid waste dumping management | existing Yes/No | [56,57,58,60] | |
| Energy consumption | in KW/h | [16,58,60,61,62,66,70,71,72] | |
| Water consumption | in liters | [60,62,69,70] | |
| Waste generation | in tons | [60,66,70,71] | |
| Green materials/designs for construction | existing Yes/No | [1,16,58] | |
| Heat generation | [58] | ||
| Energy quality | renewable source Yes/No | [16,54,58,63,64,68,72] | |
| Air pollution management | Speed/combustion reduction | existing Yes/No | [1,58,60] |
| Regulations on the emissions of toxic gas | existing Yes/No | [16,54,57,58,62,69,70,71] | |
| Cold ironing | existing Yes/No | [1,58,72] | |
| Encouraging the use of low-sulphur fuel | existing Yes/No | [1,54,58,72] | |
| Encouraging public transport mode development | existing Yes/No | [58] | |
| Light emissions | sustainable source Yes/No | [58,60] | |
| Dust control | existing Yes/No | [16,58] | |
| Emission reduction due to berth allocation | in tons | [73,74,75,76,77] | |
| Noise control | Noise reduction | in decibels | [58] |
| Regulations on noise control | existing Yes/No | [57,58,66,70] | |
| Avoiding disturbance to the community during infrastructure construction and expansion | [58] | ||
| Marine ecological protection and biology system preservation | Wetland and marine habitat preservation | existing Yes/No | [56,58,61] |
| Reducing infrastructure disturbance to marine biology density | [56,58,61,70] | ||
| Port entrance sediment and coastal erosion control | existing Yes/No | [58,61] | |
| Soil and sediment quality | [62,69,70] | ||
| Biotope creation | existing Yes/No | [61,66] | |
| Tree planting in port area | existing Yes/No | [16,58] | |
| Dredging sediment disposal | existing Yes/No | [58,61,66] | |
| Ballast water pollutant control | existing Yes/No | [58,61] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stein, M.; Acciaro, M. Value Creation through Corporate Sustainability in the Port Sector: A Structured Literature Analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5504. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145504
Stein M, Acciaro M. Value Creation through Corporate Sustainability in the Port Sector: A Structured Literature Analysis. Sustainability. 2020; 12(14):5504. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145504
Chicago/Turabian StyleStein, Michael, and Michele Acciaro. 2020. "Value Creation through Corporate Sustainability in the Port Sector: A Structured Literature Analysis" Sustainability 12, no. 14: 5504. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145504
APA StyleStein, M., & Acciaro, M. (2020). Value Creation through Corporate Sustainability in the Port Sector: A Structured Literature Analysis. Sustainability, 12(14), 5504. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145504






