The Effect of Tuition Fee Constraints on Financial Management: Evidence from Korean Private Universities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Theoretical Background
3.1. University Accounting System in Korea
3.2. Korean University Tuition Policy, Government Subsidy Mechanism
3.3. Conceptual Framework
4. Research Design
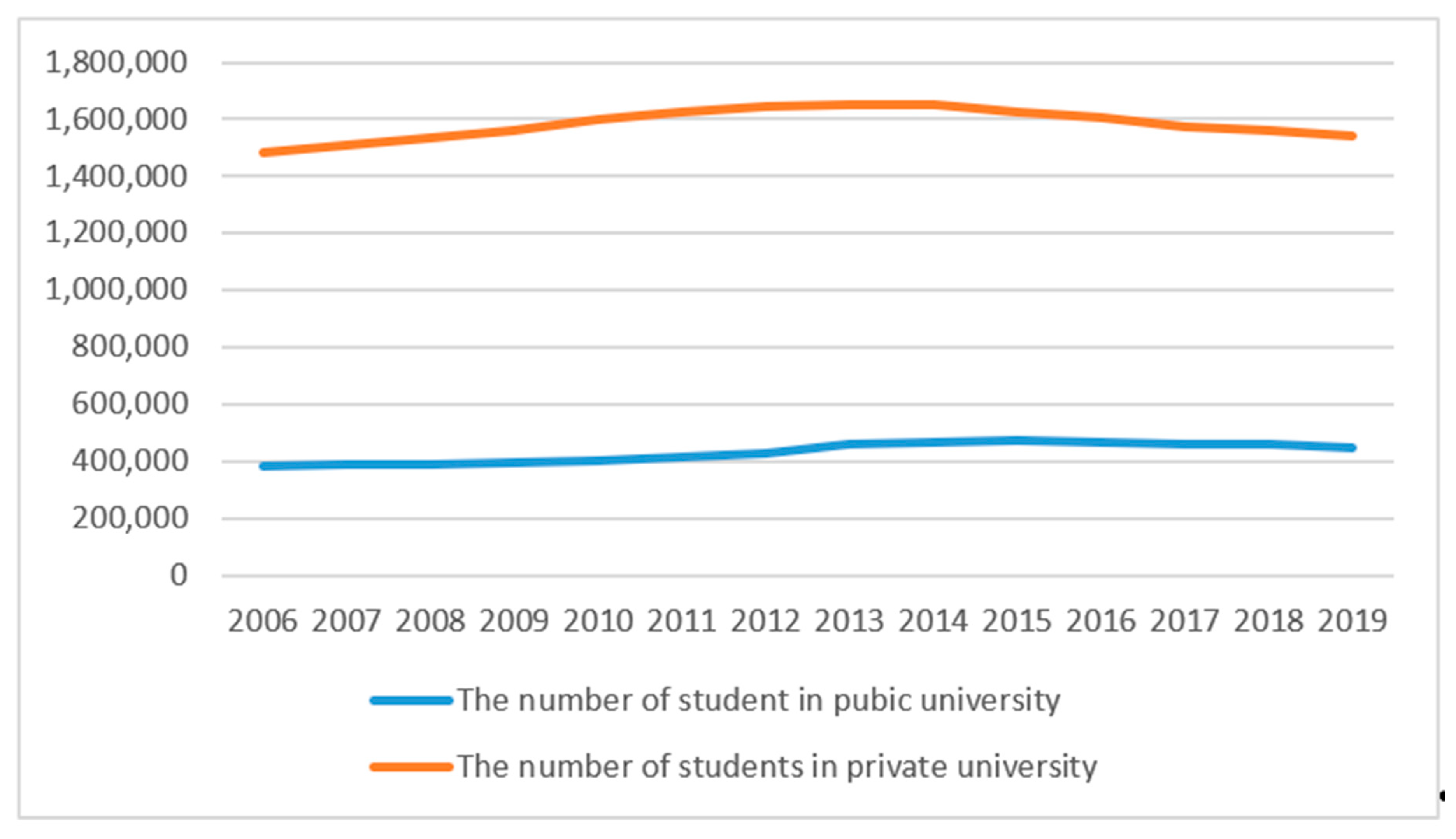
4.1. Data
4.2. Method of Analysis
5. Results
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boehner, J.A.; McKeon, H.P. The College Cost Crisis: A Congressional Analysis of College Costs and Implications for America’s Higher Education System. 2003. Available online: http://www2.bgsu.edu/downloads/finance/file17013.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- Kim, M.M.; Ko, J. The impacts of state control policies on college tuition increase. Educ. Policy 2015, 29, 815–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumper, M. State efforts to keep public colleges affordability in the face of fiscal stress. In The Finance of Higher Education: Theory, Research, Policy & Practice; Paulsen, M.B., Smart, J.C., Eds.; Agathon Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 321–354. [Google Scholar]
- Haptman, A.M. The College Tuition Spiral: An Examination of Why Charges Are Increasing; Macmillan and the American Council on Education and The College Board: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Okunade, A.A. What factors influence state appropriations for public higher education in the United States? J. Educ. Financ. 2004, 30, 123–138. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, D.; Rubenson, K.; Jones, G.; Shanahan, T. The political economy of post-secondary education: A comparison of British Columbia, Ontario and Québec. High. Educ. 2009, 57, 549–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deering, D.; Sa, C.M. Financial management of Canadian universities: Adaptive strategies to fiscal constraints. Tert. Educ. Manag. 2014, 20, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumport, P. Academic restructuring: Organizational change and institutional imperatives. Higher Educ. 2000, 39, 67–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, M.B. The economics of human capital and investment in higher education. In The Finance of Higher Education: Theory, Research, Policy and Practice; Paulsen, M.B., Smart, J.C., Eds.; Agathon Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 55–94. [Google Scholar]
- Dearden, L.; Fitzsimons, E.; Wyness, G. The Impact of Tuition Fees and Support on University Participation in the UK; Centre for the Economics of Education: London, UK, 2011; p. 126. [Google Scholar]
- Kivistö, J.A. Agency Theory as a Framework for the Government-University Relationship; Higher Education Group/Tampere University Press: Tampere, Finland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Caruana, J.; Brusca, I.; Caperchione, E.; Cohen, S.; Manes Rossi, F. (Eds.) Financial Sustainability of Public Sector Entities: The Relevance of Accounting Frameworks; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Di Carlo, F.; Modugno, G.; Agasisti, T.; Catalano, G. Changing the Accounting System to Foster Universities’ Financial Sustainability: First Evidence from Italy. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, T.J.; Orszag, P.R. Funding Restrictions at Public Universities: Effects and Policy Implications; Working Paper, Brookings Institution: Washington, DC, USA, September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Burgess, B. Evaluating the polices that lead to substantial tuition variation at public land-grant universities. Plan. High. Educ. 2011, 39, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Boatman, A.; L’Orange, H. State Tuition, Fees, and Financial Assistance Policies for Public Colleges and Universities; 2005–06; State Higher Education Executive Officers: Denver, CO, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Crowford, C.; Dearden, L. The Impact of the 2006–2007 HE Finance Reforms on HE Participation; BIS Research Paper, no.13; Department for Business, Innovation and Skills: London, UK, 2010.
- Görgen, K.; Schienle, M. Evaluating Effects of Tuition Fees: Lasso for the Case of Germany. 2019. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1909.08299.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2019).
- Bahrs, M.; Siedler, T. University Tuition Fees and High School Students’ Educational Intentions; Discussion Paper Series, No. 12053; IZA Institute of Labor Economics: Bonn, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gawellek, B.; Süssmuth, B.; Singh, D. Tuition fees and instructional quality. Econ. Bull. 2016, 36, 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J.S. Influence of Half-Tuition Policy and Political Economy; Korea Economic Research Institute: Seoul, Korea, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- McLendon, M.K.; Hearn, J.C.; Mokher, C.G. Partisans, professionals, and power: The role of political factors in state higher education funding. J. High. Educ. 2009, 80, 686–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, L.L.; Rhoades, G. Rising administrative costs: Seeking explanations. J. High. Educ. 1995, 66, 187–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheslock, J.J.; Gianneschi, M. Replacing state appropriations with alternative revenue sources: The case of voluntary support. J. High. Educ. 2008, 79, 208–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearn, J.C.; Lewis, D.R.; Kallsen, L.; Holdsworth, J.A.; Jones, L.M. “Incentives for managed growth”: A case study of incentives-based planning and budgeting in a large public research university. J. High. Educ. 2006, 77, 286–316. [Google Scholar]
- Gros Louis, K.R.R.; Thompson, M. Responsibility center budgeting and management at Indiana University. In Incentive-Based Budgeting Systems in Public Universities; Priest, D.M., Becker, W.E., Hossler, D., John, E.P.S., Eds.; E. Elgar: Cheltenham, UK; Northhampton, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 93–108. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, E.M. Rationality in the Academy Why Responsibility Center Budgeting Is a Wrong Step Down the Wrong Road. Chang. Mag. High. Learn. 1997, 29, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B. Can academic values mesh with fiscal responsibility? Business-like budgeting clashes with team spirit, some psychologists say. Monit. Psychol. 2000, 31, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Jaquette, O.; Kramer, D.A.; Curs, B.R. Growing the Pie? The Effect of Responsibility Center Management on Tuition Revenue. J. High. Educ. 2018, 89, 637–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liefner, I. Funding, resource allocation and performance in higher education system. High. Educ. 2003, 46, 469–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandberg, D.A.; Fowles, J.T.; McLendon, M.K. The governor and the state higher education executive officer: How the relationship shapes state financial support for higher education. J. High. Educ. 2017, 88, 110–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gornitzka, Å.; Stensaker, B.; Smeby, J.-C.; de Boer, H. Contract arrangements in the Nordic countries. Solving the efficiency/effectiveness dilemma? High. Educ. Eur. 2004, 29, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.H.; Ban, S.J. Study on the reform of a tuition setting method in higher education. J. Educ. Adm. 1999, 17, 283–326. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.M.; Lee, S.D. An analysis on issues and logics on New National Student Aid Program. J. Educ. Adm. 2012, 30, 79–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, S.A. The economic theory of agency: The principal’s problem. Am. Econ. Rev. 1973, 63, 134–139. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, M.C.; Meckling, W.H. Theory of the firm: Managerial behavior, agency costs and ownership structure. J. Financ. Econ. 1976, 3, 305–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, J.W.; Zeckhauser, R.J. Principals and Agents: The Structure of Business; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Arrow, K. The economics of agency. In Principals and Agents: The Structure of Business; Pratt, J., Zeckhauser, R., Eds.; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1985; pp. 37–51. [Google Scholar]
- Lowry, R. Governmental structure, trustee selection, and public university prices and spending. Am. J. Political Sci. 2001, 45, 845–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldridge, J.V. Power and Conflict in the University: Research in the Sociology of Complex Organizations; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Enders, J.; Fulton, O. Higher Education in a Globalising World: International Trends and Mutual Observations A festschrift in honour of Ulrich Teichler; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Winston, G.C. Subsidies, hierarchy and peers: The awkward economics of higher education. J. Econ. Perspect. 1999, 13, 13–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, H.R. The costs of Higher Education: How much Do Colleges and Universities Spend per Student and How Much Should They Spend? Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Garvin, D.A. The Economics of University Behavior; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Salancik, G.; Pfeffer, J. The bases and use of power in organizational decision making. Adm. Sci. Q. 1974, 19, 453–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.; Lin, C.F.; Chu, J. Unit Root Tests in Panel Data: Asymptotic and Finite Sample Properties. J. Econometrics. 2002, 98, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millett, J.D. Academic Community: An Essay on Organization; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, B.R. The organizational saga in higher education. Adm. Sci. Q. 1972, 17, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroup, H. Bureaucracy in Higher Education; The Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.R.; Farley, A.; Naidoo, M. Analysis of government-university relationship from the perspective of agency theory. J. Educ. Pract. 2012, 3, 12–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, J.E.; Kivisto, J.A. Interest, information and incentives in higher education: Principal-agent theory and is potential application to the study of higher education governance. In Higher Education: Handbook of Theory and Research; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.H.; Kim, H.K. Financial support and university performance in Korea universities: A panel data approach. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, D. Performance-based university research funding systems. Res. Policy 2016, 41, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, J.R.; Laws, A.L.; Strauss, J.C. Responsibility Center Management: A Guide to Balancing Academic Entrepreneurship with Fiscal Responsibility; National Association of College and University Business Officers: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]

| Category | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tuition fee income | 11,042,157 | 11,740,739 | 12,670,596 | 13,160,818 | 13,735,532 |
| Government transfer and endowment income | 1,696,934 | 1,872,182 | 2,001,802 | 2,531,757 | 2,619,801 |
| Education-related administrative fee income | 423,100 | 479,569 | 536,024 | 625,224 | 718,247 |
| Non-education income | 637,659 | 756,620 | 832,873 | 878,081 | 806,131 |
| Income from investments and other assets | 773,985 | 993,405 | 744,290 | 895,250 | 980,278 |
| Income from sale of fixed assets | 94,701 | 89,610 | 41,390 | 28,896 | 36,678 |
| Receipts for current liabilities | 2057 | 2090 | 3043 | 644 | 2644 |
| Receipts for fixed liabilities | 102,857 | 98,865 | 186,425 | 150,581 | 203,458 |
| Unused balance carried forward from the previous term | 1,256,314 | 1,241,322 | 1,450,637 | 1,744,106 | 1,864,169 |
| Category | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 |
| Tuition fee income | 13,724,007 | 13,781,492 | 13,725,653 | 13,395,827 | 13,657,620 |
| Transfer and endowment income | 2,704,543 | 3,994,669 | 4,686,934 | 5,168,779 | 5,712,058 |
| Education-related administrative fee income | 766,296 | 924,573 | 990,304 | 1,004,594 | 1,079,303 |
| Non-education income | 803,171 | 739,496 | 578,832 | 547,841 | 425,648 |
| Income from investments and other assets | 1,629,779 | 1,230,731 | 1,082,146 | 1,348,758 | 1,404,353 |
| Income from sale of fixed assets | 25,073 | 65,699 | 59,364 | 156,265 | 155,745 |
| Receipts for current liabilities | 635,149 | 345,378 | 2865 | 1466 | 1538 |
| Receipts for fixed liabilities | 239,273 | 137,209 | 220,868 | 180,160 | 169,693 |
| Unused balance carried forward from the previous term | 1,852,146 | 2,144,458 | 1,950,733 | 1,448,032 | 1,335,294 |
| Category | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Remuneration | 6,078,237 | 6,326,260 | 6,818,692 | 7,273,686 | 7,735,373 |
| Management and operating expenses | 1,683,451 | 1,830,510 | 1,998,206 | 2,131,326 | 2,304,174 |
| Expenditure on research and students | 2,846,651 | 3,141,699 | 3,476,399 | 4,017,846 | 4,270,347 |
| Non-education expenses | 147,816 | 152,705 | 169,697 | 205,459 | 176,330 |
| Transfer expenses | 23,793 | 17,436 | 14,682 | 31,671 | 29,612 |
| Expenditure from investments and other assets | 1,464,843 | 1,755,249 | 1,770,188 | 1,895,335 | 1,761,906 |
| Fixed asset purchase expenses | 2,345,657 | 2,465,258 | 2,458,940 | 2,483,390 | 2,603,733 |
| Repayments for current liabilities | 11,512 | 10,968 | 14,302 | 12,282 | 17,301 |
| Repayments for fixed liabilities | 101,982 | 133,637 | 118,034 | 114,185 | 112,007 |
| Unused balance carried forward to the following term | 1,325,820 | 1,440,680 | 1,627,939 | 1,850,177 | 1,974,108 |
| Category | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 |
| Remuneration | 7,966,689 | 8,590,134 | 8,895,711 | 8,865,079 | 9,299,141 |
| Management and operating expenses | 2,420,198 | 2,536,298 | 2,531,540 | 2,477,145 | 2,532,611 |
| Expenditure for research and students | 4,570,886 | 5,851,675 | 6,607,738 | 7,039,274 | 7,527,429 |
| Non-education expenses | 160,657 | 125,146 | 111,182 | 100,329 | 93,943 |
| Transfer expenses | 16,061 | 4413 | 5188 | 6001 | 6485 |
| Expenditure from investments and other assets | 1,884,229 | 1,294,934 | 1,224,080 | 1,354,988 | 1,417,681 |
| Fixed asset purchase expenses | 2,568,536 | 2,528,381 | 2,208,582 | 2,097,255 | 1,799,602 |
| Repayments for current liabilities | 8244 | 8570 | 10,091 | 14,829 | 23,231 |
| Repayments for fixed liabilities | 168,805 | 150,449 | 142,292 | 227,812 | 144,819 |
| Unused balance carried forward to the following term | 1,997,045 | 1,950,127 | 1,562,814 | 1,272,696 | 1,119,711 |
| Category | Variable | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Control variables | Fiscal year: 2006–2015 | |
| Size: Fewer than 5000 students = 1, 5000 to fewer than 10,000 students = 2, 10,000 students and more = 3 | ||
| Finance size: Fewer than 10 billion KRW = 1, 10 billion KRW to fewer than 50 billion KRW = 2, 50 billion to 100 billion KRW = 3, 100 billion KRW to 200 billion KRW = 4, 200 billion KRW and more = 5 | ||
| University establishment year | ||
| Independent variables | Tuition fee | |
| Government subsidies | ||
| Dependent variables | Operating expenses | shirking |
| Expenditure from investments and other assets | shirking | |
| Fixed asset purchase expenses | shirking | |
| Unused balance carried forward to the following term | budget maximization | |
| Labor costs | cross-subsidization | |
| Research expenses | cross-subsidization | |
| Laboratory fees | cross-subsidization | |
| Student support fees | cross-subsidization |
| Mean | Min. | Max. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tuition fees | 93,513,167 | 7,366,817 | 383,330,038 |
| Government subsidies | 9,853,121 | 1 | 66,359,084 |
| Labor costs | 60,953,790 | 4,532,384 | 482,828,806 |
| Operating expenses | 16,242,164 | 1,443,113 | 123,557,121 |
| Research expenses | 4,221,199 | 1 | 79,950,857 |
| Laboratory fees | 1,801,100 | 56,887 | 9,283,436 |
| Student support fees | 2,658,183 | 5029 | 22,782,981 |
| Expenditure from investments and other assets | 12,704,207 | 1 | 180,521,886 |
| Fixed asset purchase expenses | 17,184,608 | 220,055 | 142,486,789 |
| Unused balance carried forward to the following term | 8,764,900 | 1 | 120,581,735 |
| Variable | LLC | Fisher | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Label variables | Tuition fees | −5.0838 *** | 4.5162 *** |
| Government subsidies | 5.5706 | 7.8925 *** | |
| Labor costs | −1.4675 * | 0.2549 *** | |
| Operating expenses | −4.0846 *** | 1.7872 ** | |
| Research expenses | −10.3454 *** | 3.9814 *** | |
| Laboratory fees | −5.2519 *** | 6.2017 | |
| Student support fees | −2.5769 ** | 2.5867 ** | |
| Expenditure from investments and other assets | −23.0822 *** | 6.4828 *** | |
| Fixed asset purchase expenses | −9.0398 *** | 9.3314 *** | |
| Unused balance carried forward to the following term | −8.3428 *** | 2.9690 ** | |
| Log-trans variables | Tuition fee | −5.8952 *** | 8.9989 *** |
| Government subsidies | −26.1368 *** | 14.2754 *** | |
| Labor costs | −3.6059 *** | 3.4120 *** | |
| Operating expenses | −9.0974 *** | 1.8012 ** | |
| Research expenses | −5.3402 *** | 2.0106 *** | |
| Laboratory fees | −6.4330 *** | 8.4936 *** | |
| Student support fees | −5.2303 *** | 1.3841 ** | |
| Expenditure from investments and other assets | −12.3069 *** | 10.6963 *** | |
| Fixed asset purchase expenses | −9.8209 *** | 8.6506 *** | |
| Unused balance carried forward to the following term | −16.2357 *** | 7.5542 ** |
| Labor Costs | Operating Expenses | Research Expenses | Laboratory Fees | Student Support Fees | Expenditure from Investments and Other Assets | Fixed Asset Purchase Expenses | Unused Balance Carried Forward to the Following Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 0.18 | 0.28 | 5.18 * | 4.16 | 0.72 | 6.37 * | 1.27 |
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | Average | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tuition fee | 9.092 | 7.794 | 1.304 | 3.883 | 3.386 | −2.284 | −0.135 | 0.890 | −0.995 | 2.548 |
| Government subsidies | 8.570 | 36.428 | 100.466 | 19.575 | 7.403 | 107.680 | 39.059 | 20.077 | 8.675 | 38.659 |
| Labor costs | 6.505 | 8.107 | 4.458 | 6.322 | 5.941 | 4.715 | 3.357 | 2.310 | 2.461 | 4.908 |
| Operating expenses | 11.252 | 9.158 | 3.802 | 7.533 | 6.180 | 1.036 | 0.628 | 2.441 | −0.980 | 4561 |
| Research expenses | 14.125 | −5.551 | 1.927 | 1.509 | 2.516 | −1.755 | −3.494 | −6.026 | −4.796 | −0.172 |
| Laboratory fees | 4.033 | 6.036 | 8.768 | 6.212 | 8.435 | −3.512 | 0.278 | −1.520 | −3.624 | 2.790 |
| Student support fees | 13.043 | 13.765 | 19.309 | 15.078 | 12.918 | 11.496 | −0.341 | −0.655 | 1.671 | 9.587 |
| Expenditure from investments and other assets | 30.744 | −4.078 | 5.594 | −4.745 | 11.735 | −32.190 | −2.244 | 5.537 | −2.232 | 0.902 |
| Fixed asset purchase expenses | 8.164 | −4.974 | −5.409 | 9.149 | 0.230 | −5.029 | −9.313 | −4.372 | −9640 | −2.355 |
| Unused balance carried forward to the following term | 9.675 | 18.619 | 11.833 | 7.212 | 10.941 | −7.980 | −22.097 | −13.076 | −8.729 | 0.711 |
| Labor Costs | Operating Expenses | Research Expenses | Laboratory Fees | Student Support Fees | Expenditure from Investments and Other Assets | Fixed Asset Purchase Expenses | Unused Balance Carried forward to the Following Term | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Estimate | Estimate | Estimate | Estimate | Estimate | Estimate | Estimate | Estimate |
| (Std. Error) | (Std. Error) | (Std. Error) | (Std. Error) | (Std. Error) | (Std. Error) | (Std. Error) | (Std. Error) | |
| 2007 | −0.01476 | 0.02942 | −0.29437 | −0.03216 | 0.07339 | 0.19713 | −0.0895 | 0.06827 |
| (0.02828) | (0.03829) | (0.21530) | (0.05692) | (0.08135) | (0.27129) | (0.10077) | (0.33895) | |
| 2008 | −0.00123 | 0.05373 | −0.37764 | −0.04957 | 0.08899 | 0.26373 | −0.03832 | 0.32757 |
| (0.02891) | (0.03914) | (0.22010) | (0.05819) | (0.08316) | (0.27734) | (0.10302) | (0.34651) | |
| 2009 | 0.02181 | 0.06809 | −0.19920 | −0.00080 | 0.17710 | 0.22303 | −0.05294 | 0.78988 * |
| (0.03016) | (0.04084) | (0.22962) | (0.06070) | (0.08676) | (0.28933) | (0.10747) | (0.36149) | |
| 2010 | 0.04474 | 0.10817 * | −0.34752 | 0.02670 | 0.25682 * | 0.45069 | −0.06073 | 1.04254 ** |
| (0.03096) | (0.04192) | (0.23570) | (0.06231) | (0.08905) | (0.29699) | (0.11032) | (0.37107) | |
| 2011 | 0.08719 ** | 0.16186 *** | −0.13834 | 0.09393 | 0.33886 *** | 0.29161 | −0.06897 | 1.18069 ** |
| (0.03137) | (0.04247) | (0.23882) | (0.06314) | (0.09023) | (0.30092) | (0.11178) | (0.37598) | |
| 2012 | 0.14862 *** | 0.17923 *** | −0.23124 | 0.03539 | 0.34256 *** | 0.01490 | −0.10851 | 1.10039 ** |
| (0.03314) | (0.04487) | (0.25233) | (0.06671) | (0.09534) | (0.31794) | (0.11810) | (0.39724) | |
| 2013 | 0.17934 *** | 0.16132 *** | −0.36277 | 0.02197 | 0.31807 ** | −0.22887 | −0.29921 * | 0.74546 * |
| (0.03404) | (0.04609) | (0.25916) | (0.06851) | (0.09792) | (0.32655) | (0.12130) | (0.40800) | |
| 2014 | 0.19776 *** | 0.16181 *** | −0.33982 | 0.01604 | 0.29624 ** | −0.19081 | −0.37022 ** | 0.57306 |
| (0.03460) | (0.04685) | (0.26341) | (0.06964) | (0.09953) | (0.33191) | (0.12329) | (0.41470) | |
| 2015 | 0.22787 *** | 0.15175 *** | −0.40713 | 0.00869 | 0.30619 ** | 0.19899 | −0.55517 *** | 0.40590 |
| (0.03478) | (0.04709) | (0.26478) | (0.07000) | (0.10004) | (0.33363) | (0.12393) | (0.41684) | |
| Size 2 | 0.00568 | −0.16353 *** | 1.07321 *** | −0.39731 *** | 0.12522 | 0.02251 | −0.30039 * | 0.49460 |
| (0.03377) | (0.04573) | (0.25712) | (0.06797) | (0.09715) | (0.32399) | (0.12035) | (0.40480) | |
| Size 3 | 0.20578 *** | −0.19757 ** | 0.84919 * | −0.46930 *** | 0.16738 | −0.57829 | −0.24054 | 1.27007 * |
| (0.04993) | (0.06761) | (0.38016) | (0.10050) | (0.14364) | (0.47902) | (0.17794) | (0.59850) | |
| Finance size 2 | −0.08645 | −0.04505 | −1.26558 * | −0.12601 | 0.25969 | −1.34524 * | −0.89541 *** | −3.43467 *** |
| (0.07106) | (0.09622) | (0.54104) | (0.14303) | (0.20442) | (0.68173) | (0.25324) | (0.85177) | |
| Finance size 3 | 0.11619 * | 0.24477 ** | −0.50636 | 0.48793 *** | 0.54865 ** | −0.34339 | −0.08124 | −1.35397 * |
| (0.06669) | (0.09031) | (0.50778) | (0.13424) | (0.19186) | (0.63983) | (0.23767) | (0.79941) | |
| Finance size 4 | 0.56976 *** | 0.37265 *** | −0.14532 | 0.64218 *** | 0.60163 ** | 0.52592 | −0.06373 | −2.31693 * |
| (0.07855) | (0.10636) | (0.59806) | (0.15811) | (0.22597) | (0.75359) | (0.27993) | (0.94155) | |
| Finance size 5 | 0.62062 *** | 0.82258 *** | −0.41478 | 0.51976 *** | 0.83239 *** | 0.47565 | 0.63097 * | 0.31588 |
| (0.07778) | (0.10531) | (0.59218) | (0.15655) | (0.22374) | (0.74617) | (0.27717) | (0.93228) | |
| Year | −0.00084 * | 0.00003 | −0.0065 * | −0.00450 *** | 0.00235 | −0.01328 *** | −0.00436** | −0.0033 |
| (0.00042) | (0.00057) | (0.00322) | (0.00085) | *(0.00122) | (0.00406) | (0.00151) | (0.00507) | |
| tuition fee | 0.71858 *** | 0.739 *** | 1.31021 *** | 0.91076 *** | 0.72633 *** | 1.57892 *** | 0.65774 *** | −0.32858 |
| (0.02958) | (0.04006) | (0.22523) | (0.05954) | (0.08510) | (0.28380) | (0.10542) | (0.35459) | |
| government subsidies | 0.01338 *** | 0.02026 *** | 0.01060 | 0.02347 * | 0.07606 *** | −0.07408 | 0.00344 | −0.02347 |
| (0.00506) | (0.00685) | (0.03851) | (0.01018) | (0.01455) | (0.04852) | (0.01802) | (0.06062) |
| Labor Costs | Operating Expenses | Research Expenses | Laboratory Fees | Student Support Fees | Expenditure from Investments and Other Assets | Fixed Asset Purchase Expenses | Unused Balance Carried Forward to the Following Term | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | Estimate | Estimate | Estimate | Estimate | Estimate | Estimate | Estimate | |
| (Std. Error) | (Std. Error) | (Std. Error) | (Std. Error) | (Std. Error) | (Std. Error) | (Std. Error) | (Std. Error) | |
| Size 2 | 0.10932 ** | −0.0755 | 0.90783 ** | −0.36045 *** | 0.35643 ** | −0.33384 | −0.31036 ** | −0.18047 |
| (−0.03547) | (−0.04949) | (−0.28127) | (−0.07475) | (−0.10414) | (−0.35398) | (−0.1323) | (−0.44232) | |
| Size 3 | 0.28677 *** | −0.12888 * | 0.74141 * | −0.44008 *** | 0.34773 ** | −0.82654 * | −0.24356 | 0.76844 |
| (−0.04893) | (−0.06826) | (−0.38799) | (−0.10311) | (−0.14366) | (−0.4883) | (−0.1825) | (−0.61015) | |
| Finance size 2 | −0.02854 | 0.00312 | −1.11739 ** | −0.10065 | 0.38524 * | −1.20538 * | −0.84749 ** | −3.52164 *** |
| (−0.06824) | (−0.09521) | (−0.54119) | (−0.14382) | (−0.20038) | (−0.6811) | (−0.25456) | (−0.85106) | |
| Finance size 3 | 0.15811 ** | 0.28038 ** | −0.57538 | 0.50281 ** | 0.6422 ** | −0.49051 | −0.08574 | −1.62956 ** |
| (−0.06394) | (−0.08922) | (−0.50708) | (−0.13475) | (−0.18776) | (−0.63818) | (−0.23852) | (−0.79744) | |
| Finance size 4 | 0.55514 *** | 0.35987 ** | −0.03909 | 0.63863 *** | 0.56775 ** | 0.69299 | −0.0439 | −2.12168 ** |
| (−0.07513) | (−0.10482) | (−0.59578) | (−0.15833) | (−0.2206) | (−0.74981) | (−0.28024) | (−0.93692) | |
| Finance size 5 | 0.52856 *** | 0.7445 *** | −0.29402 | 0.4865 ** | 0.62742 ** | 0.75534 | 0.63401 ** | 0.88397 |
| (−0.07529) | (−0.10504) | (−0.59706) | (−0.15866) | (−0.22107) | (−0.75142) | (−0.28083) | (−0.93893) | |
| Year | −0.00055 | 0.00029 | −0.00848 ** | −0.00442 *** | 0.00305 ** | −0.01638 *** | −0.00472 ** | −0.00705 |
| (−0.00041) | (−0.00058) | (−0.00328) | (−0.00087) | (−0.00121) | (−0.00413) | (−0.00154) | (−0.00516) | |
| tuition fee | −2.79458 *** | −2.26815 ** | 12.46893 ** | −0.2286 | −7.1948 ** | 21.48103 ** | 2.23008 | 29.25179 ** |
| (−0.6576) | (−0.91749) | (−5.21486) | (−1.38582) | (−1.93091) | (−6.56308) | (−2.45289) | (−8.20085) | |
| tuition fee square | 0.09578 *** | 0.08202 ** | −0.31302 ** | 0.03089 | 0.21609 *** | −0.55498 ** | −0.04482 | −0.81707 ** |
| (−0.01818) | (−0.02537) | (−0.1442) | (−0.03832) | (−0.05339) | (−0.18149) | (−0.06783) | (−0.22678) | |
| government subsidies | −0.07617 *** | −0.05399 ** | −0.2761 ** | −0.01689 | −0.11722 ** | −0.37141 ** | −0.08345 | 0.04165 |
| (−0.01381) | (−0.01927) | (−0.10951) | (−0.0291) | (−0.04055) | (−0.13782) | (−0.05151) | (−0.17221) | |
| government subsidies square | 0.00556 *** | 0.00461 *** | 0.01864 ** | 0.00252 | 0.01198 *** | 0.01965 ** | 0.00558 | −0.00302 |
| (−0.00082) | (−0.00115) | (−0.00654) | (−0.00174) | (−0.00242) | (−0.00823) | (−0.00307) | (−0.01028) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.-H.; Kim, K.-S.; Lee, K.-H. The Effect of Tuition Fee Constraints on Financial Management: Evidence from Korean Private Universities. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5066. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12125066
Lee Y-H, Kim K-S, Lee K-H. The Effect of Tuition Fee Constraints on Financial Management: Evidence from Korean Private Universities. Sustainability. 2020; 12(12):5066. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12125066
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Young-Hwan, Kwon-Sik Kim, and Kwang-Hoon Lee. 2020. "The Effect of Tuition Fee Constraints on Financial Management: Evidence from Korean Private Universities" Sustainability 12, no. 12: 5066. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12125066
APA StyleLee, Y.-H., Kim, K.-S., & Lee, K.-H. (2020). The Effect of Tuition Fee Constraints on Financial Management: Evidence from Korean Private Universities. Sustainability, 12(12), 5066. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12125066





