Global Nighttime Light Change from 1992 to 2017: Brighter and More Uniform
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- What are the evolutionary characteristics of global nighttime lights over the past 26 years?
- What economic and sociological characteristics and processes does the change in nighttime lights reflect?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
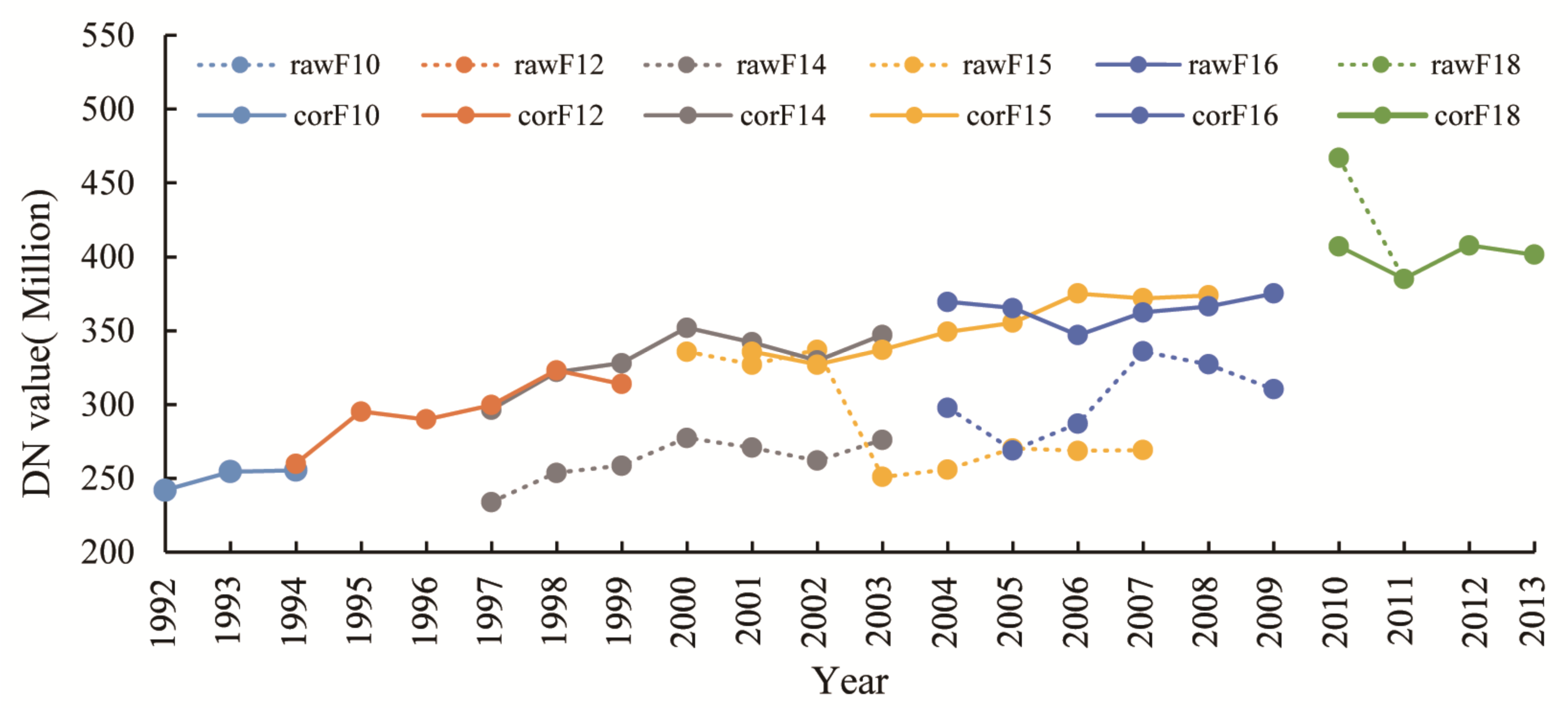
2.2. Preparation of the Long Time Series Nighttime Light Data
2.3. Analytical Method
3. Results
3.1. The World Is Getting Brighter
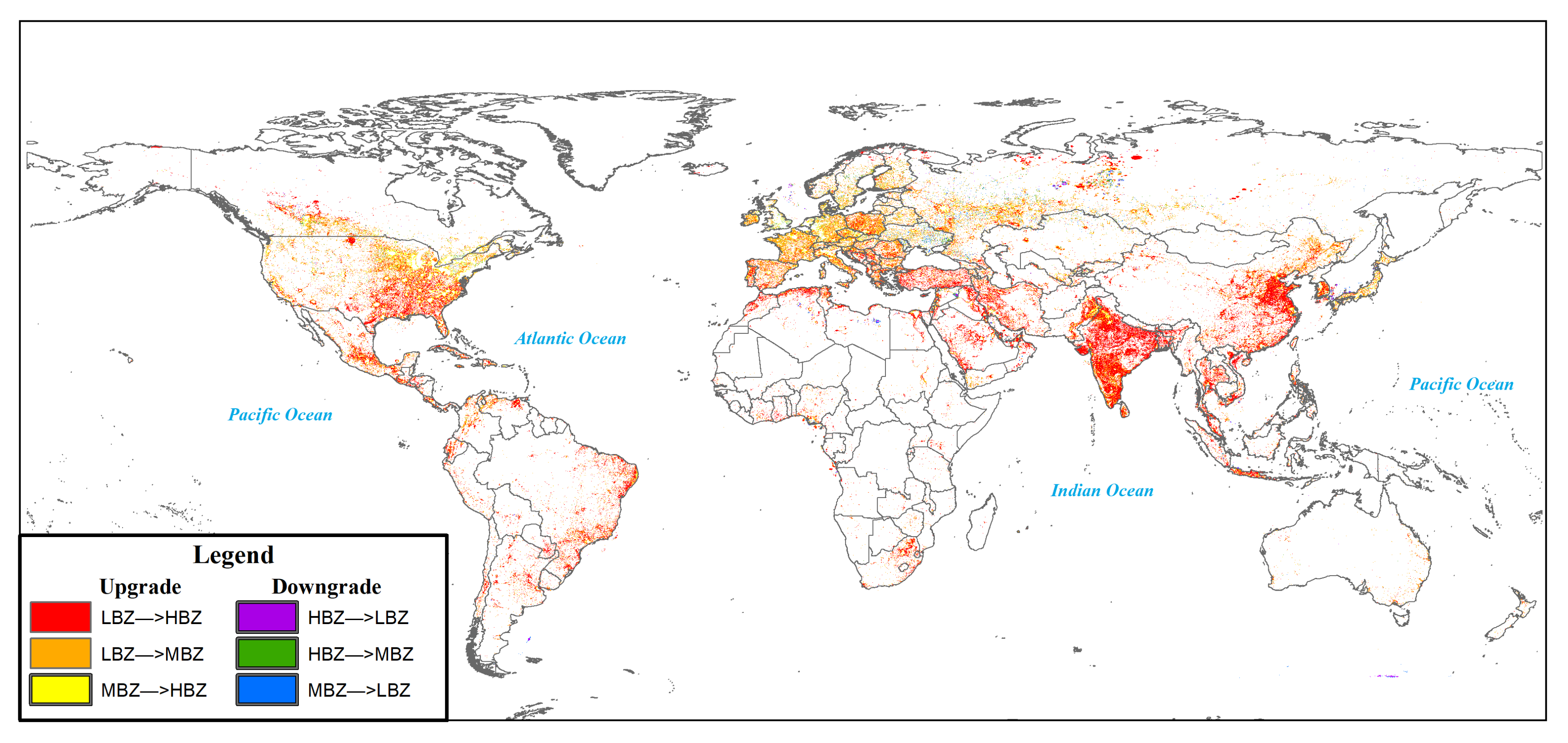
3.2. Low-Brightness Zones Quickly Brightened, and The Global Brightness Became More Uniform
3.3. China, India, and the United States Lead Global Brightening
4. Discussion
4.1. Relationship between Nighttime Lights and Economic Development
4.2. Relationship between the LBZ Area and Global Poverty Reduction
4.3. Uncertainty
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DN | Digital number |
| TNL | Total nighttime lights |
| NLA | Nighttime lighting area |
| LBZ | Low-brightness zone |
| MBZ | Medium-brightness zone |
| HBZ | High-brightness zone |
| SSF | Sub-Saharan Africa |
| MEA | Middle East and North Africa |
| SAS | South Asia |
| LCN | Latin America and the Caribbean |
| NAC | North America |
| EAS | East Asia and the Pacific |
| ECS | Europe and Central Asia |
References
- Hu, K.; Qi, K.; Guan, Q.; Wu, C.; Yu, J.; Qing, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wu, H.; Li, X. A Scientometric Visualization Analysis for Night-Time Light Remote Sensing Research from 1991 to 2016. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doll, C.N.; Muller, J.P.; Morley, J.G. Mapping regional economic activity from night-time light satellite imagery. Ecol. Econ. 2006, 57, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, G. The Suitability of Different Nighttime Light Data for GDP Estimation at Different Spatial Scales and Regional Levels. Sustainability 2017, 9, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Witmer, F.D.W.; O’Loughlin, J. Detecting the Effects of Wars in the Caucasus Regions of Russia and Georgia Using Radiometrically Normalized DMSP-OLS Nighttime Lights Imagery. GIScience Remote Sens. 2011, 48, 478–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Pozzi, F.; Elvidge, C. Spatial analysis of global urban extent from DMSP-OLS night lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Weng, Q. Spatiotemporally enhancing time-series DMSP/OLS nighttime light imagery for assessing large-scale urban dynamics. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 128, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennie, J.; Davies, T.; Duffy, J.; Inger, R.; Gaston, K.J. Contrasting trends in light pollution across Europe based on satellite observed nighttime lights. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Letu, H.; Nakajima, T.; Nishio, F. Regional-Scale Estimation of Electric Power and Power Plant CO2 Emissions Using Defense Meteorological Satellite Program Operational Linescan System Nighttime Satellite Data. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2014, 1, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhan, C.; Tao, J.; Li, L. Long-Term Monitoring of the Impacts of Disaster on Human Activity Using DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data: A Case Study of the 2008 Wenchuan, China Earthquake. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coscieme, L.; Sutton, P.; Anderson, S.; Liu, Q.; Elvidge, C.D. Dark Times: Nighttime satellite imagery as a detector of regional disparity and the geography of conflict. GIScience Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 118–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Yu, B.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yin, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Wu, J. Evaluating the Ability of NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Data to Estimate the Gross Domestic Product and the Electric Power Consumption of China at Multiple Scales: A Comparison with DMSP-OLS Data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1705–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, N.; Zhou, Y.; Samson, E.L. Correcting Incompatible DN Values and Geometric Errors in Nighttime Lights Time-Series Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 53, 2039–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baugh, K.; Hsu, F.-C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Zhizhin, M. Nighttime Lights Compositing Using the VIIRS Day-Night Band: Preliminary Results. In Proceedings of the 35th Asia-Pacific Advanced Network, Manoa, HI, USA, 13–18 January 2013; Asia-Pacific Advanced Network: Manoa, HI, USA, 2013; Volume 35, pp. 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.C.; Ghosh, T. VIIRS night-time lights. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 5860–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, H.; Chen, X.; Li, C. Potential of NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Imagery for Modeling the Regional Economy of China. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3057–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elvidge, C.; Hsu, F.-C.; Baugh, K.; Ghosh, T. National Trends in Satellite-Observed Lighting: 1992–2012. Remote Sens. Nat. Res. 2014, 20144266, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; He, S.; Peng, J.; Li, W.; Zhong, X. Intercalibration of DMSP-OLS night-time light data by the invariant region method. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 7356–7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, B.; Zhang, Q.; Seto, K.C. Comparative evaluation of relative calibration methods for DMSP/OLS nighttime lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 195, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y. A stepwise calibration of global DMSP/OLS stable nighttime light data (1992–2013). Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 637. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Peng, J.; Cao, Q. The Uncertainty of Nighttime Light Data in Estimating Carbon Dioxide Emissions in China: A Comparison between DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, X.; Cao, C.; Zhang, B.; Qiu, S.; Elvidge, C.; von Hendy, M. Radiometric calibration of DMSP-OLS sensor using VIIRS day/night band. In Earth Observing Missions and Sensors: Development, Implementation, and Characterization III; SPIE: Beijing, China, 2014; Volume 92640A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ma, M.-G.; Yang, H.; Ge, W. Modeling the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Gross Domestic Product in China Using Extended Temporal Coverage Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Li, D.; Xu, H.; Wu, C. Intercalibration between DMSP/OLS and VIIRS night-time light images to evaluate city light dynamics of Syria’s major human settlement during Syrian Civil War. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 5934–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pok, S.; Matsushita, B.; Fukushima, T. An easily implemented method to estimate impervious surface area on a large scale from MODIS time-series and improved DMSP-OLS nighttime light data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 133, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Li, G.; Zhu, Y.; Ge, Y.; Kung, H.-T.; Wu, Y. A likelihood-based spatial statistical transformation model (LBSSTM) of regional economic development using DMSP/OLS time-series nighttime light imagery. Spat. Stat. 2017, 21, 421–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Zhao, J.; Yang, X.; Yue, Y.; Wang, Z. Exploring China’s 21-year PM10 emissions spatiotemporal variations by DMSP-OLS nighttime stable light data. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 191, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Yu, B.; Huang, C.; Wu, J.; Sun, X. Exploring spatiotemporal patterns of electric power consumption in countries along the Belt and Road. Energy 2018, 150, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Ziskin, D.; Baugh, K.E.; Tuttle, B.T.; Ghosh, T.; Pack, D.W.; Erwin, E.H.; Zhizhin, M. A Fifteen Year Record of Global Natural Gas Flaring Derived from Satellite Data. Energies 2009, 2, 595–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Hubacek, K.; Roberts, M. Analysis of spatial patterns of urban growth across South Asia using DMSP-OLS nighttime lights data. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 63, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Luan, Y.; Liu, X.; Yu, X.; Miao, L.; Cui, X. A new global anthropogenic heat estimation based on high-resolution nighttime light data. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, B.R.; Tiwari, V.; Pandey, V.; Elvidge, C.D.; Rawat, J.S.; Sharma, M.P.; Prawasi, R.; Kumar, P. Estimation of Urban Population Dynamics Using DMSP-OLS Night-Time Lights Time Series Sensors Data. IEEE Sensors J. 2017, 17, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Seto, K.C. Mapping urbanization dynamics at regional and global scales using multi-temporal DMSP/OLS nighttime light data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2320–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, S.; Weiss, S.; Liang, C. VIIRS day/night band (DNB) stray light characterization and correction. In Earth Observing Systems XVIII; SPIE: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; Volume 88661P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Yang, D.; Dong, J.; Zhang, L.; Xia, F. Regional Inequality in China Based on NPP-VIIRS Night-Time Light Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; He, C.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Y. Extracting the dynamics of urban expansion in China using DMSP-OLS nighttime light data from 1992 to 2008. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 106, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, B.; Hu, Y.; Huang, C.; Shi, K.; Wu, J. Estimating House Vacancy Rate in Metropolitan Areas Using NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Composite Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 2188–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Leung, Y. A study of urban expansion of prefectural-level cities in South China using night-time light images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 5557–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, S.; Ashby, D.; Kerry, S. Sample size for cluster randomized trials: Effect of coefficient of variation of cluster size and analysis method. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 35, 1292–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houser, K.W.; Wei, M.; Royer, M. Illuminance Uniformity of Outdoor Sports Lighting. Leukos 2011, 7, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiroh, K.J. Information Technology and the U.S. Productivity Revival: What Do the Industry Data Say? Am. Econ. Rev. 2002, 92, 1559–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neely, A.; Neely, A.D. Exploring the financial consequences of the servitization of manufacturing. Oper. Manag. Res. 2008, 1, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Li, R. Drivers for energy consumption: A comparative analysis of China and India. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 62, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Nordhaus, W. Using luminosity data as a proxy for economic statistics. In Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences; National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; pp. 8589–8594. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, P.; Costanza, R. Global estimates of market and non-market values derived from nighttime satellite imagery, land cover, and ecosystem service valuation. Ecol. Econ. 2002, 41, 509–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Group, W.B. Poverty and Shared Prosperity 2018: Piecing Together the Poverty Puzzle; World Bank Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Li, Z.-L. Scale Issues in Remote Sensing: A Review on Analysis, Processing and Modeling. Sensors 2009, 9, 1768–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Shi, K.; Hu, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. Poverty Evaluation Using NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Composite Data at the County Level in China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y. Urban mapping using DMSP/OLS stable night-time light: A review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 6030–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.; Smith, L.C. Advances in using multitemporal night-time lights satellite imagery to detect, estimate, and monitor socioeconomic dynamics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 176–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Hu, Y. Spatial Identification of Multi-dimensional Poverty in Rural China: A Perspective of Nighttime-Light Remote Sensing Data. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2018, 46, 1093–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. Explaining Subnational Infant Mortality and Poverty Rates: What Can We Learn from Night-Time Lights? Spat. Demogr. 2015, 3, 27–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Sutton, P.; Ghosh, T.; Tuttle, B.T.; Baugh, K.; Bhaduri, B.; Bright, E. A global poverty map derived from satellite data. Comput. Geosci. 2009, 35, 1652–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, L. Poverty assessment using DMSP/OLS night-time light satellite imagery at a provincial scale in China. Adv. Space Res. 2012, 49, 1253–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proville, J.; Zavala-Araiza, D.; Wagner, G. Night-time lights: A global, long term look at links to socio-economic trends. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noor, A.; Alegana, V.A.; Gething, P.W.; Tatem, A.J.; Snow, R.W. Using remotely sensed night-time light as a proxy for poverty in Africa. Popul. Health Metrics 2008, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Rank | TNL in 2017 (Million) | Largest Lighting Area (Million km2) | TNL Increase (Million) | Ratio of the TNL Increase (%) | Ratio of the Bright Area (%) | Ratio of the Darkening Area (%) | Area from Unlighted to Lighted (million km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | United States (83.8) | United States (6.6) | China (34.9) | China (13.7) | United States (13.3) | Russia (22.8) | China (1.48) |
| 2 | China (44.1) | Russia (5.6) | India (30.9) | India (12.1) | China (12.6) | United States (22.1) | United States (1.39) |
| 3 | Russia (40.0) | China (4.0) | United States (28.6) | United States (11.2) | India (10.8) | Canada (11.8) | Russia (1.38) |
| 4 | India (38.4) | India (2.9) | Russia (14.7) | Russia (5.8) | Russia (7.2) | Ukraine (7.1) | India (1.24) |
| 5 | Canada (17.03) | Canada (2.0) | Brazil (12.8) | Brazil (5.0) | Brazil (4.1) | United Kingdom (3.5) | Brazil (0.66) |
| 6 | Brazil (16.98) | Brazil (1.5) | Iran (8.6) | Iran (3.4) | Iran (3.1) | Sweden (3.2) | Canada (0.40) |
| 7 | Iran (12.0) | Iran (0.98) | Turkey (7.8) | Turkey (3.1) | Mexico (2.6) | Japan (2.7) | Turkey (0.38) |
| 8 | France (10.0) | Mexico (0.94) | Saudi Arabia (6.7) | Saudi Arabia (2.6) | France (2.5) | India (2.3) | Iran (0.33) |
| 9 | Mexico (9.6) | France (0.88) | Mexico (6.3) | Mexico (2.5) | Turkey (2.3) | China (1.8) | Mexico (0.30) |
| 10 | Saudi Arabia (9.2) | Ukraine (0.82) | Canada (4.3) | Canada (1.7) | Poland (2.2) | Finland (1.5) | Poland (0.25) |
| Rank | 1993 | 2015 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LBZ Area (Million km2) | Proportion of the LBZ (%) | Poverty Rate (%) | People Living in Extreme Poverty (Billion) | LBZ Area (Million km2) | Proportion of the LBZ (%) | Poverty Rate (%) | LBZ Area (Million km2) | |
| 1 | ECS 10.5 | SAS 87.3 | SSF 59.6 | EAS 10.2 | ECS 7.5 | SSF 59.3 | SSF 41 | SSF 4.1 |
| 2 | EAS 5.6 | SSF 86.2 | EAS 53.7 | SAS 5.4 | EAS 3.3 | LCN 50.0 | SAS 12.4 | SAS 2.2 |
| 3 | NAC 5.2 | EAS 84.6 | SAS 44.9 | SSF 3.3 | NAC 3.1 | EAS 49.2 | MEA 4.2 | EAS 0.53 |
| 4 | LCN 3.6 | LCN 83.7 | LCN 14 | LCN 0.66 | LCN 2.1 | ECS 48.5 | LCN 3.9 | LCN 0.25 |
| 5 | SAS 3.1 | MEA 80.6 | MEA 7 | ECS 0.44 | MEA 1.4 | MEA 42.4 | EAS 2.3 | MEA 0.18 |
| 6 | MRA 2.7 | ECS 67.2 | ECS 5.2 | MEA 0.19 | SAS 1.0 | NAC 36.4 | ECS 1.5 | ECS 0.14 |
| 7 | SSF 1.1 | NAC 60.0 | NAC 0 | NAC 0 | SSF 0.7 | SAS 28.6 | NAC 0 | NAC 0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Global Nighttime Light Change from 1992 to 2017: Brighter and More Uniform. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4905. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12124905
Hu Y, Zhang Y. Global Nighttime Light Change from 1992 to 2017: Brighter and More Uniform. Sustainability. 2020; 12(12):4905. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12124905
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Yunfeng, and Yunzhi Zhang. 2020. "Global Nighttime Light Change from 1992 to 2017: Brighter and More Uniform" Sustainability 12, no. 12: 4905. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12124905
APA StyleHu, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2020). Global Nighttime Light Change from 1992 to 2017: Brighter and More Uniform. Sustainability, 12(12), 4905. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12124905






