Classifying Pathways for Smart City Development: Comparing Design, Governance and Implementation in Amsterdam, Barcelona, Dubai, and Abu Dhabi
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Research Background
2.1. Design Choices for the Resources of Smart City Development
2.2. Design Choices for the Throughputs
2.3. Design Choices for the Applications of Smart City Development
3. Research Design and Methodology
3.1. Case Selection
3.2. Data Collection
3.3. Data Analysis and Operationalization
4. A Brief Description of the Cases
4.1. Masdar City
4.2. Amsterdam Smart City
4.3. Barcelona Digital (Smart) City
4.4. Smart Dubai
5. Results
5.1. Design Input Choices
5.1.1. Masdar
5.1.2. Amsterdam
5.1.3. Barcelona
5.1.4. Dubai
5.2. Design Throughput Choices
5.2.1. Masdar
5.2.2. Amsterdam
5.2.3. Barcelona
5.2.4. Dubai
5.3. Applications and Externalities
5.3.1. Masdar
5.3.2. Amsterdam
5.3.3. Barcelona
5.3.4. Dubai
6. Towards a Classification of Smart City Development Pathways
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Input-Output Modelling for Smart City Development. J. Urban Technol 2020, Author Omitted for Review in press.
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Foth, M.; Sabatini-Marques, J.; da Costa, E.; Ioppolo, G. Can cities become smart without being sustainable? A systematic review of the literature. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 45, 348–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprotti, F. Spaces of visibility in the smart city: Flagship urban spaces and the smart urban imaginary. Urban Stud. 2019, 56, 2465–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, A.; Thaens, M. Urban Technological Innovation: Developing and Testing a Sociotechnical Framework for Studying Smart City Projects. Urban Aff. Rev. 2018, 54, 363–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, R.; Caprotti, F. Smart city as anti-planning in the UK. Environ. Plan. D Soc. Sp. 2019, 37, 428–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anthopoulos, L.; Janssen, M.; Weerakkody, V. Comparing smart cities with different modeling approaches. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on World Wide Web, Florence, Italy, 18–22 May 2015; pp. 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giffinger, R.; Lu, H. The Smart City Perspective A Necessary Change from Technical to Urban Innovation; Fondazione Giangiacomo Feltrinelli: Milan, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Fong, P.S.W.; Dai, S.; Li, Y. Towards sustainable smart cities: An empirical comparative assessment and development pattern optimization in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 730–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, S. Are smart cities global cities? A European perspective. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2019, 27, 759–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tok, E.; McSparren, J.J.; Merekhi, M.A.; Elghaish, H.; Ali, F.M. Crafting smart cities in the gulf region: A comparison of masdar and lusail. In Handbook of Research on Digital Media and Creative Technologies; IGI Global: Hershey PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Hancock, M.G.; Hu, M.C. Towards an effective framework for building smart cities: Lessons from Seoul and San Francisco. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2014, 89, 80–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dameri, R.P.; Benevolo, C. Governing Smart Cities: An Empirical Analysis. Soc. Sci. Comput. Rev. 2016, 34, 693–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidou, M. The Role of Smart City Characteristics in the Plans of Fifteen Cities. J. Urban Technol. 2017, 24, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raven, R.; Sengers, F.; Spaeth, P.; Xie, L.; Cheshmehzangi, A.; de Jong, M. Urban experimentation and institutional arrangements. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2019, 27, 258–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzada, I. The Techno-Politics of Data and Smart Devolution in City-Regions: Comparing Glasgow, Bristol, Barcelona, and Bilbao. Systems 2017, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calzada, I.; Cobo, C. Unplugging: Deconstructing the smart city. J. Urban Technol. 2015, 22, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capra, C.F. The Smart City and its Citizens. Int. J. E Plan. Res. 2016, 5, 20–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascó, M.; Trivellato, B.; Cavenago, D. How Do Southern European Cities Foster Innovation? Lessons from the Experience of the Smart City Approaches of Barcelona and Milan. In Smarter as the New Urban Agenda. Public Administration and Information Technology; Gil-Garcia, J., Pardo, T., Nam, T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 11, pp. 191–206. [Google Scholar]
- Confer, V.; Madeira, T. Barcelona as a Smart City Lessons Learned from the Evolution of the Concept and the Influence in the City Attractiveness, VIII Conferência Anualdo Turismo Madeira. 2014. Available online: https://docplayer.net/1494769-Barcelona-as-a-smart-city-lessons-learned-from-the-evolution-of-the-concept-and-the-influence-in-the-city-attractiveness.html (accessed on 13 May 2020).
- Mora, L.; Deakin, M.; Reid, A. Strategic principles for smart city development: A multiple case study analysis of European best practices. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 142, 70–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, S.; Sovacool, B.K. Rethinking the future low-carbon city: Carbon neutrality, green design, and sustainability tensions in the making of Masdar City. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2020, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badran, A. Smart-Governments for Smart Cities: The Case of Dubai Smart-Government. In Smart Cities in the Gulf; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 59–82. [Google Scholar]
- Breslow, H. The smart city and the containment of informality: The case of Dubai. Urban Stud. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtudes, A.; Abbara, A.; Sá, J. Dubai: A Pioneer Smart City in the Arabian Territory. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 245, 052071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caprotti, F.; Cowley, R. Varieties of smart urbanism in the UK: Discursive logics, the state and local urban context. Trans. Inst. Br. Geogr. 2019, 44, 587–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, R.; Joss, S.; Dayot, Y. The smart city and its publics: Insights from across six UK cities. Urban Res. Pract. 2018, 11, 53–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niederer, S.; Priester, R. Smart Citizens: Exploring the Tools of the Urban Bottom-Up Movement. Comput. Support. Coop. Work CSCW An Int. J. 2016, 25, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancebo, F. Smart city strategies: Time to involve people. Comparing Amsterdam, Barcelona and Paris. J. Urbanism. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Han, H.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Ioppolo, G.; Sabatini-Marques, J. The making of smart cities: Are Songdo, Masdar, Amsterdam, San Francisco and Brisbane the best we could build? Land Use Policy 2019, 88, 104–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, G.; Brinkman, J.; Wenzler, I. Supporting sustainability through smart infrastructures: The case for the city of Amsterdam. Int. J. Crit. Infrastruct. 2012, 8, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, L. How to Become a Smart City: Learning from Amsterdam. In Smart and Sustainable Planning for Cities and Regions; Bisello, A., Vettorato, D., Laconte, P., Costa, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 251–266. [Google Scholar]
- Angelidou, M. Four European Smart City Strategies. Int. J. Soc. Sci. Stud. 2016, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Winden, W.; van den Buuse, D. Smart City Pilot Projects: Exploring the Dimensions and Conditions of Scaling Up. J. Urban Technol. 2017, 24, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, M.; Hoppe, T.; Noori, N. City Branding, Sustainable Urban Development and the Rentier State. How Do Qatar, Abu Dhabi and Dubai Present Themselves in the Age of Post Oil and GlobalWarming? Energies 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joss, S.; Sengers, F.; Schraven, D.; Caprotti, F.; Dayot, Y. The Smart City as Global Discourse: Storylines and Critical Junctures across 27 Cities. J. Urban Technol. 2019, 26, 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juniper Research, Smart Cities—What’s in it for Citizens? 2017. Available online: https://newsroom.intel.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/11/2018/03/smart-cities-whats-in-it-for-citizens.pdf (accessed on 13 May 2020).
- Eden Strategy Institute, Top 5 Smart City Governments Rankings 2018/9. 2018. Available online: https://www.smartcitygovt.com/ (accessed on 24 February 2020).
- Berrone, P.; Ricart, J.E.; Carrasco, C.; Duch, A. IESE Cities in Motion Index 2018, IESE, ST-471-E. 2018. Available online: https://www.ieseinsight.com/fichaMaterial.aspx?pk=148539&idi=2&origen=3 (accessed on 13 May 2020).
- Bay, O. Singapore Beats Dubai and London to Top Spot in Smart City Rankings. ABI Research. 2018. Available online: https://www.abiresearch.com (accessed on 24 February 2020).
- Checkland, P.; Haynes, M.G. Varieties of systems thinking: The case of soft systems methodology. Manag. Control Theory 1994, 3, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, D. Systems theory in political science. World Polit. 1957, 9, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlaky, T.; Curtis, F.E. Modeling and Optimization: Theory and Applications—Selected Contributions from the MOPTA 2010 Conference; Springer Nature: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, J.S. Optimum Design Problem Formulation. Introd. Optim. Des. 2004, 15–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, T.; Pardo, T.A. Conceptualizing smart city with dimensions of technology, people, and institutions. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual International Digital Government Research Conference: Digital Government Innovation in Challenging Times, College Park, MD, USA, 12–15 June 2011; pp. 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appio, F.P.; Lima, M.; Paroutis, S. Understanding Smart Cities: Innovation ecosystems, technological advancements, and societal challenges. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 142, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borri, D.; Camarda, D.; Grassini, L. Learning and sharing technology in informal contexts: A multiagent-based supporting approach. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE 12th International Conference on Mobile Data Management, Lulea, Sweden, 6–9 June 2011; Volume 2, pp. 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negre, E.; Rosenthal-Sabroux, C.; Gasco, M. A knowledge-based conceptual vision of the smart city. In Proceedings of the Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Kauai, HI, USA, 5–8 January 2015; pp. 2317–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Garcia, J.R.; Pardo, T.A.; De Tuya, M. Information Sharing as a Dimension of Smartness: Understanding Benefits and Challenges in Two Megacities. Urban Aff. Rev. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbate, T.; Cesaroni, F.; Cinici, M.C.; Villari, M. Business models for developing smart cities. A fuzzy set qualitative comparative analysis of an IoT platform. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 142, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchin, R. The real-time city? Big data and smart urbanism. GeoJournal 2014, 79, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meijer, A.; Bolívar, M.P.R. Governing the smart city: A review of the literature on smart urban governance. Int. Rev. Adm. Sci. 2016, 82, 392–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fistola, R.; La Rocca, R.A. Smart City Planning: A Systemic Approach. In Proceedings of the 6th Knowledge Cities World Summit, Istanbul, Turkey, 9–13 September 2013; pp. 520–530. [Google Scholar]
- Pattberg, P.; Widerberg, O. Transnational Multi-Stakeholder Partnerships for Sustainable Development: Building Blocks for Success. SSRN Electron. J. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huston, S.; Rahimzad, R.; Parsa, A. ‘Smart’ sustainable urban regeneration: Institutions, quality and financial innovation. Cities 2015, 48, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engelbert, J.; van Zoonen, L.; Hirzalla, F. Excluding citizens from the European smart city: The discourse practices of pursuing and granting smartness. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 142, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkandari, A.; Alnasheet, M.; Alshekhly, I.F.T. Smart Cities Survey. In Proceedings of the IEEE 20th International Conference on High Performance Computing and Communications; IEEE 16th International Conference on Smart City; IEEE 4th International Conference on Data Science and Systems (HPCC/SmartCity/DSS), Exeter, UK, 28–30 June 2018; Volume 2, pp. 1726–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winters, J.V. Why are smart cities growing? Who moves and who stays. J. Reg. Sci. 2011, 51, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Garcia, J.R.; Pardo, T.A.; Nam, T. What makes a city smart? Identifying core components and proposing an integrative and comprehensive conceptualization. Inf. Polity 2015, 20, 61–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zygiaris, S. Smart City Reference Model: Assisting Planners to Conceptualize the Building of Smart City Innovation Ecosystems. J. Knowl. Econ. 2013, 4, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanyi, M. Sense-Giving and Sense-Reading. Philosophy 1967, 42, 301–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Anez, V.; Fernández-Güell, J.M.; Giffinger, R. Smart City implementation and discourses: An integrated conceptual model. The case of Vienna. Cities 2017, 78, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, S.; Shankaranarayanan, G.; Even, A. Data quality assessment in context: A cognitive perspective. Decis. Support Syst. 2009, 48, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkers, M.P. A beginner’s guide to data stewardship and data sharing. Spinal Cord 2019, 57, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chierici, R.; Mazzucchelli, A.; Garcia-Perez, A.; Vrontis, D. Transforming big data into knowledge: The role of knowledge management practice. Manag. Decis. 2019, 57, 1902–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samosudova, N.V. Modern leadership and management methods for development organizations. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 106, 08062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orlowski, A.; Romanowska, P. Smart Cities Concept: Smart Mobility Indicator. Cybern. Syst. 2019, 50, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walnum, H.T.; Hauge, Å.L.; Lindberg, K.B.; Mysen, M.; Nielsen, B.F.; Sørnes, K. Developing a scenario calculator for smart energy communities in Norway: Identifying gaps between vision and practice. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 46, 101418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, H.; Østergaard, P.A.; Connolly, D.; Mathiesen, B.V. Smart energy and smart energy systems. Energy 2017, 137, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutitas, G. The smart grid: Anchor of the Smart City. In Smart Cities; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 53–74. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.S.; Muhammad, G.; Alamri, A. Smart healthcare monitoring: A voice pathology detection paradigm for smart cities. Multimed. Syst. 2017, 25, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayar, D.Y. Smart Citizens: Smart cities from a different point of view. In Proceedings of the Inspire Conference.
- Doody, L. Smart citizens need smart government. In Smart Citizens; Hemet, D., Townsend, A., Eds.; FutureEverything: Manchester, UK, 2013; pp. 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith, S.; Crawford, S. The responsive city: Engaging communities through data-smart governance. Public Adm. Rev. 2014, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholl, H.J.; Scholl, M.C. Smart Governance: A Roadmap for Research and Practice. In iConference 2014 Proceedings; iSchools: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lor, P.J. International and Comparative Librarianship Concepts and Methods for Global Studies. Rev. Educ. Res. 2019, 37, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapporto Smart City Index; Ernst & Young Global Limited: Rome, Italy, 2016.
- Abdulla, H. Behind the Scenes at Masdar City. 2019. Available online: https://www.arabianbusiness.com/ (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- Cugurullo, F. How to Build a Sandcastle: An Analysis of the Genesis and Development of Masdar City. J. Urban Technol. 2013, 20, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArdle, M. Is Masdar City a Ghost Town or a Green Lab? 2018. Available online: https://www.popsci.com/masdar-city-ghost-town-or-green-lab (accessed on 20 February 2020).
- Solomon, E. Masdar Institute and Huawei Partner to Leverage the Internet-of- Things for Development of ‘Smart City’ Applications. 2017. Available online: https://www.ku.ac.ae/ (accessed on 4 January 2019).
- Vermast, F.A. Frans Anton Vermast: Amsterdam has been at the Forefront of Smart Mobility for Many Years. 2019. Available online: https://www.themayor.eu/en/frans-anton-vermast-amsterdam-has-been-at-the-forefront-of-smart-mobility-for-many-years (accessed on 20 April 2019).
- Colau, A. Barcelona Smart City Visions; Ajuntament de Barcelona: Barcelona, Spain, 2018.
- Al-Azzawi, A. Dubai Happiness Agenda: Engineering the Happiest City on Earth. In Smart Cities in the Gulf; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 195–221. [Google Scholar]
- Smart Dubai Officie, Our Vision Is to Make Dubai The Happiest City on Earth. 2018. Available online: https://www.smartdubai.ae/ (accessed on 21 February 2020).
- I amsterdam, About StartupAmsterdam. 2019. Available online: https://www.iamsterdam.com/ (accessed on 21 February 2020).
- Amsterdam a City of Opportunity; PWC: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; p. 48.
- Söderström, O.; Paasche, T.; Klauser, F. Smart cities as corporate storytelling. City 2014, 18, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, J.R. Barcelona’s Smart City vision: An opportunity for transformation. J. Field Actions 2017, 16, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- KPMG, G.P. Global Cities Investment Monitor. 2013, p. 28. Available online: https://gp-investment-agency.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/GlobalCitiesInvestmentMonitor2019web-compressed.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2019).
- Smart Dubai Officie, Government Resource Planning Portal. 2019. Available online: https://grpportal.dubai.gov.ae/ (accessed on 15 December 2019).
- UAE vision 2021. Ministry of Cabinet Affairs and the Future. 2014. Available online: http://fgccc.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/UAE_Vision_2021.pdf (accessed on 13 May 2020).
- Dameri, R.P. Comparing Smart and Digital City: Initiatives and Strategies in Amsterdam and Genoa. Are They Digital and/or Smart? In Smart City; Dameri, R.P., Rosenthal-Sabroux, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Van Winden, M.; Oskam, W.; van den Buuse, I.; Schrama, D.; va Dijck, W.; Frederiks, E.J. Organising Smart City Projects Lessons from Amsterdam: Lessons for Amsterdam; Hogeschool van Amsterdam: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 37, p. 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, K.; Van Bueren, E. Urban Living Labs: A Living Lab Way of Working, 4th ed.; Amsterdam Institute for Advanced Metropolitan Solutions: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- De Barcelona, A. 22@Barcelona, The Innovation District; Ayuntament de Barcelona: Barcelona, Spain, 2012.
- Calzada, I. (Smart) citizens from data providers to decision-makers? The case study of Barcelona. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ajuntament de Barcelona. City Data Commons. Available online: www.barcelona.cat (accessed on 17 April 2020).
- Ajuntament de Barcelona. Ethical Digital Standards: A Policy ToolKit. Available online: www.barcelona.cat (accessed on 17 April 2020).
- Lootah, W.; Miailhe, N. Dubai’s Artificial Intelligence Roadmap. J. Field Actions 2017, 17, 44–46. [Google Scholar]
- Neirotti, P.; De Marco, A.; Cagliano, A.C.; Mangano, G.; Scorrano, F. Current trends in smart city initiatives: Some stylised facts. Cities 2014, 38, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chourabi, H.; Nam, T.; Walker, S.; Gil-Garcia, J.R.; Mellouli, S.; Nahon, K.; Pardo, T.A.; Scholl, H.J. Understanding smart cities: An integrative framework. In Proceedings of the 2012 45th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Maui, HI, USA, 4–7 January 2012; pp. 2289–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Brandt, T.; Neumann, D. Smart city planning—Developing an urban charging infrastructure for electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 22nd European Conference on Information Systems (ECIS), Tel Aviv, Israel, 9–11 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sengers, F. Smart-Eco Cities in the Netherlands: Trends and City Profiles. 2016. Available online: http://www.smart-eco-cities.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/03/Smart-eco-Cities-Netherlands-2016.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2019).
- De Barcelona, A. More Solar Energy for a Sustainable and Self-Sufficient City. 2018. Available online: https://ajuntament.barcelona.cat/ (accessed on 22 February 2020).
- De Barcelona, A. Smart City Week. 2019. Available online: www.barcelona.cat (accessed on 24 April 2020).
- Dubai Electricity and Water Authority. DEWA Announces 222 Buildings with Photovoltaic Installations as Part of Shams Dubai. 2016. Available online: https://www.dewa.gov.ae/ (accessed on 22 February 2020).
- Gemeente Amsterdam. Plan Amsterdam #5: De stad duurzaam; Gemeente Amsterdam: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Masdar Mubadala Company, the Masder Report on Technologies for Future Smart City Transit. 2018. Available online: https://masdar.ae/-/media/corporate/downloads/about-us/masdar-annual-sustainabilityeports/masdar_report_on_technologies_for_future_smart_city_transit.pdf?la=en&hash=52CAA6DF141DA067E174F91976DC6F4B7DE9F578 (accessed on 13 May 2020).
- Pontin, J. Technology and Optimism: Why Technologists are So Confident. 2009. Available online: https://www.technologyreview.com/2009/02/24/215197/technology-and-optimism/ (accessed on 18 January 2020).
- Vergragt, P.J.; Quist, J. Backcasting for sustainability: Introduction to the special issue. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2011, 78, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
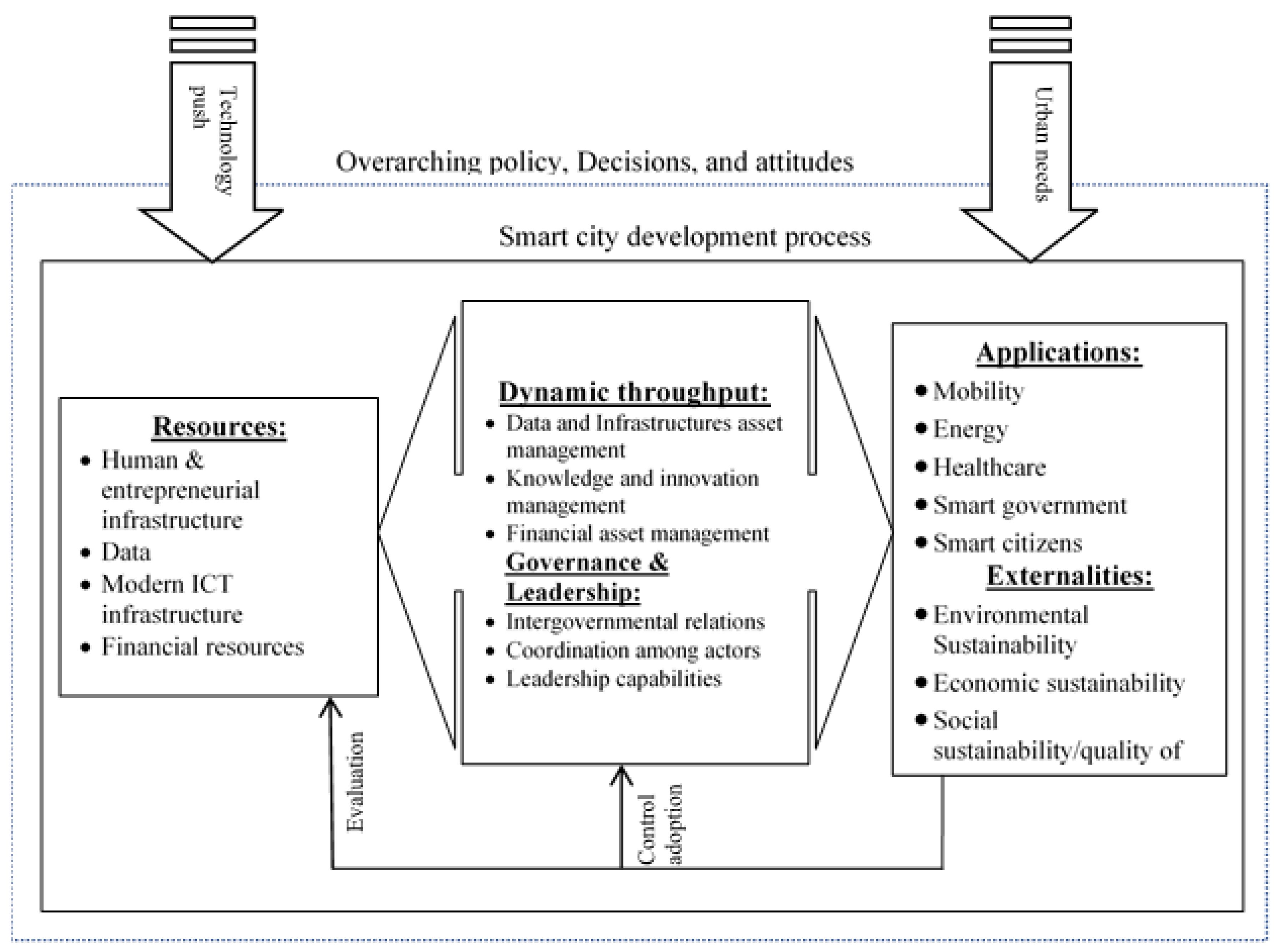
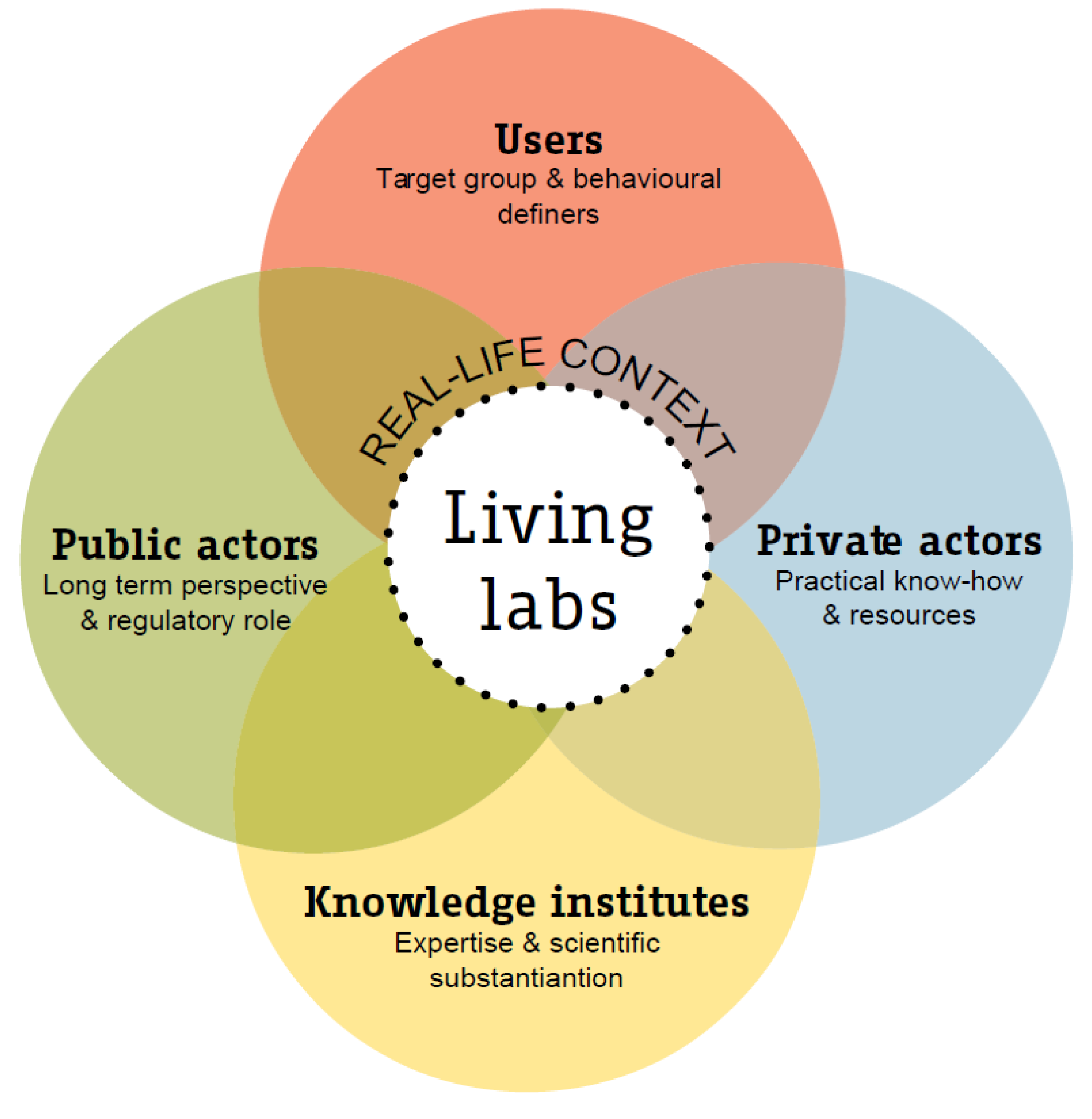
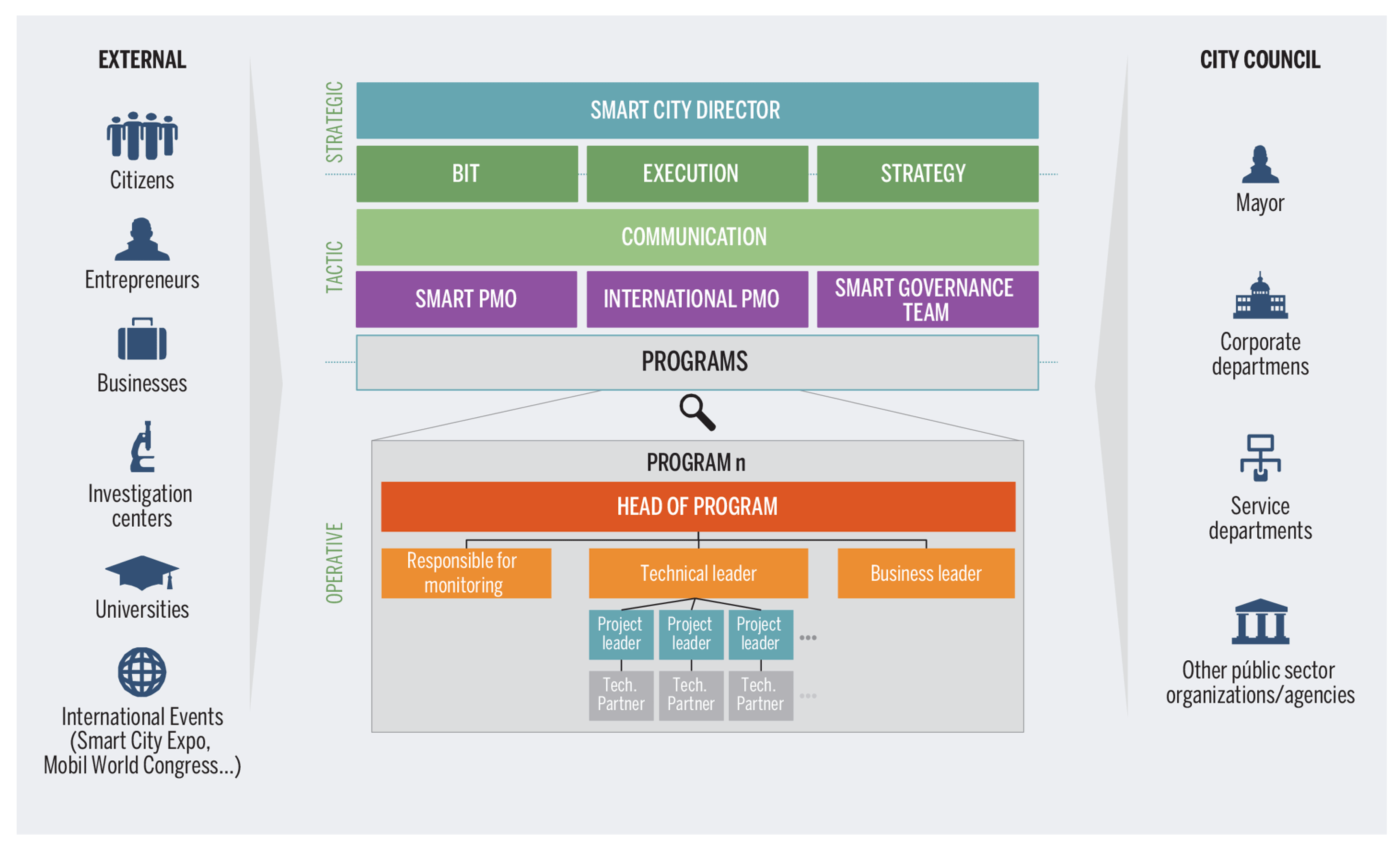
| Smart City Attributes | Design Variables | Indicators (Presence of) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inputs | HR and Entrepreneurship | Educating and training people | Supporting and strengthening universities and research centers (HR1) |
| Transferring (attracting) educated and skilled people | Launching knowledge transfer projects (e.g., scholarships, sabbaticals) (HR2) | ||
| Nurturing the innovation environment | Specific policy in place to promote innovation (HR3) | ||
| Attracting innovative companies | Supporting and encouraging programs for innovative companies (Science and technology parks, free zones) (HR4) | ||
| Information and Communication Technology (ICT) and Data | Data aggregation | Big data establishment (D1) | |
| Data processing | Data science centers (D2) | ||
| Data real-time analysis | Data visualization (D3) | ||
| Financial resources | Supra-national and national investment | Supra-national and national smart city development policy and budget (F1) | |
| Local government investment | Smart city profile and allocated budget (F2) | ||
| Public–private investment | Collaboration with the private sector (F3) | ||
| Foreign investment | International brand and investors | ||
| Throughputs | Governance | Governance structures; technocratic, citizen-centric, socio-technical, hierarchical, surveillance | Role of the government and decision-making process (G1) |
| Actors are involved and engaged (G2) | |||
| Knowledge and Innovation management | Open innovation | Living Labs, idea-sharing champions (KI1) | |
| In-house R&D | Innovation Centers, Smart City R&D department (KI2) | ||
| Data management | Establishing a data authorization | Data Laws (DM1) | |
| Open/closed/ or shared data platform | Data accessibility (DM2) | ||
| Financial management | Redirecting funds away from inadequate, inefficient urban infrastructure development | Alignment of the urban master plan with smart city policies (FM1) | |
| Raising private funds | Having a collaboration platform (FM2) | ||
| Leadership | Leadership styles | Vision creation and the bigger image (L1) | |
| Motivating and empowering people (L2) | |||
| Collaborating with people and influencing them (L3) | |||
| Outputs | Smart Mobility | Smart transportation infrastructures | Smart (sensor and actuator equipped) roads and traffic lights, smart parking, bicycle routes (SM1) |
| Smart public transportation | Interconnected public transportation, smart vehicles, information application (SM2) | ||
| Smart private transportation | EVs (Electric Vehicles), autonomous driving, car-sharing (SM3) | ||
| Smart energy | Renewable energy | Stationary energy use to be supplied from renewable energy sources (SE1) | |
| Energy-efficient buildings | Building regulations, energy certificates (SE2) | ||
| New technology for utilities | Smart grids, smart meters (SE3) | ||
| Smart health | Smart health monitoring systems | Remote health monitoring, mobile health monitoring, or wearable health monitoring (SH1) | |
| Smart health management and information applications | Mobile applications for medication information, weight management, information regarding hospitals and clinics (SH2) | ||
| Smart citizens | One-way communication | A participation platform for data sharing (SC1) | |
| Two-way communication | A participation platform for idea sharing (SC2) | ||
| Co-creating and co-designing | A participation platform for cooperative policies (SC3) | ||
| Smart governance | Smart administration | Redesigning norms based on smart solutions (technologies) (SG1) | |
| Smart interaction | Participation and collaboration via social media and social networking (SG2) | ||
| Smart security and safety | Using smart devices and data analytics for surveillance (SG3) | ||
| Smart policies | Using big data analytics for decision-making (SG4) |
| Indicators | Absence (0) | Plan Without Implementation (+) | Plan Has Begun (++) | Implementation Completed (+++) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR1 | ||||
| HR2 | ||||
| HR3 | ||||
| . | ||||
| . | ||||
| Etc. |
| Design Choices/Cases | Amsterdam | Barcelona | Dubai | Masdar |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Educating and training people | +++ | +++ | ++ | + |
| Transferring (attracting) educated and skilled people | +++ | +++ | ++ | + |
| Nurturing the innovation environment | +++ | +++ | + | + |
| Attracting innovative companies | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ |
| Data aggregation | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ |
| Data processing | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Data real-time analysis | + | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Supra-national and national investment | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++ |
| Local government investment | ++ | ++ | +++ | +++ |
| Public–private investment | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Foreign investment | ++ | +++ | +++ | + |
| Design Choices/Cases | Amsterdam | Barcelona | Dubai | Masdar |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smart transportation infrastructures | +++ | +++ | ++ | + |
| Smart public transportation | +++ | +++ | + | + |
| Smart private transportation | +++ | ++ | ++ | + |
| Renewable energy | ++ | ++ | + | + |
| Building energy efficiency | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ |
| New technologies for utilities | + | ++ | + | ++ |
| Smart health monitoring systems | + | + | ++ | 0 |
| Smart health management and information applications | + | + | ++ | + |
| One-way communication | ++ | ++ | ++ | + |
| Two-way communication | +++ | ++ | + | + |
| Co-creating and co-designing | ++ | ++ | + | 0 |
| Smart administration | 0 | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Smart interaction | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| Smart security and safety | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Smart policies | ++ | ++ | ++ | + |
| Case | Main Driver (Core Element) | Development Path | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amsterdam | Innovation | Innocratic (Startup and business-driven) | Competition, entrepreneurial Innovative, Bottom-up approach |
| Barcelona | Inclusion | Sociocratic (Participation-driven) | Democracy, Citizen empowerment through technology and citizens’ data sovereignty Participatory, Co-creation |
| Dubai | Visionary-ambitious leadership | Aristocratic (State and service-driven) | Being first, being best, Top-down Happiness, government services, branding |
| Masdar | Technological optimism | Technocratic (Investment and branding-driven) | Visibility, lighthouse projects, branding |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noori, N.; Hoppe, T.; de Jong, M. Classifying Pathways for Smart City Development: Comparing Design, Governance and Implementation in Amsterdam, Barcelona, Dubai, and Abu Dhabi. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4030. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12104030
Noori N, Hoppe T, de Jong M. Classifying Pathways for Smart City Development: Comparing Design, Governance and Implementation in Amsterdam, Barcelona, Dubai, and Abu Dhabi. Sustainability. 2020; 12(10):4030. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12104030
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoori, Negar, Thomas Hoppe, and Martin de Jong. 2020. "Classifying Pathways for Smart City Development: Comparing Design, Governance and Implementation in Amsterdam, Barcelona, Dubai, and Abu Dhabi" Sustainability 12, no. 10: 4030. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12104030
APA StyleNoori, N., Hoppe, T., & de Jong, M. (2020). Classifying Pathways for Smart City Development: Comparing Design, Governance and Implementation in Amsterdam, Barcelona, Dubai, and Abu Dhabi. Sustainability, 12(10), 4030. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12104030






