Barriers for the Sustainable Development of Entertainment Tourism in Macau
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Entertainment Tourism Development
2.2. Barriers for Tourism Development
3. Methods
4. Findings and Discussion
4.1. Characteristics of Interviewees
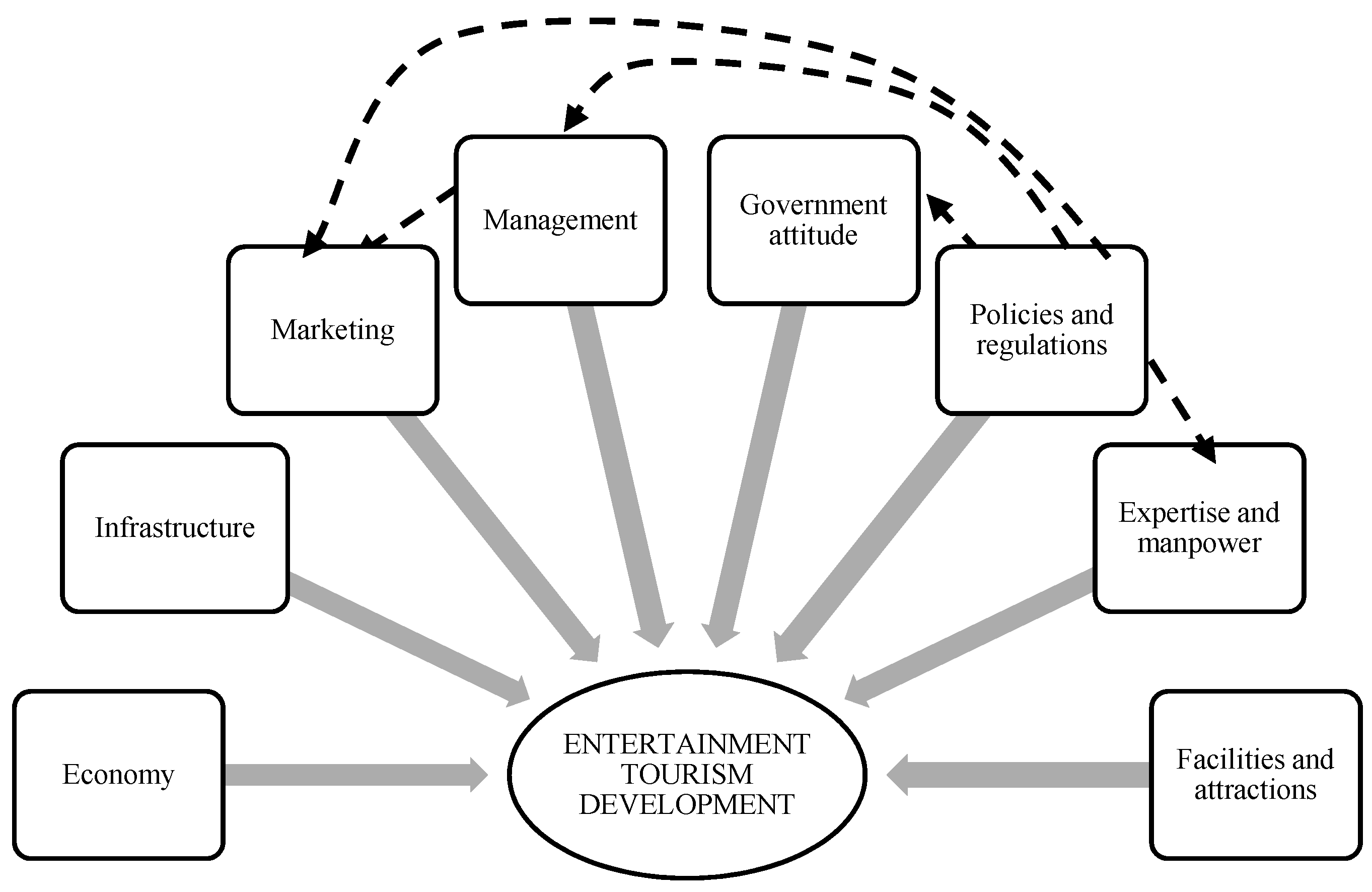
4.2. Framework of the Study
4.3. Barriers for the Development of Entertainment Tourism
4.3.1. Policies and Regulations
4.3.2. Economy (Costs)
4.3.3. Marketing
4.3.4. Management
4.3.5. Infrastructure
4.3.6. Government Attitudes
4.3.7. Facilities and Attractions
4.3.8. Expertise and Manpower
5. Discussion and Implications
6. Conclusions and Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, J.M.; Lam, C.F. Entertainment Tourism; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, J. Entertainment-LED Regeneration: The Case of Detroit. Cities 2002, 19, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.M.; Lam, C.F.; Li, X.; Shen, H. Corporate Social Responsibility in Macau Gambling Industry. J. Qual. Assur. Hosp. Tour. 2016, 17, 237–256. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.M. A Measurement Scale of Corporate Social Responsibility in Gambling Industry from Customer Perspective. J. Qual. Assur. Hosp. Tour. 2018, 19, 461–476. [Google Scholar]
- Blanke, J.; Chiesa, T. The Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Report 2013; World Economic Forum: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013; Available online: http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_TT_Competitiveness_Report_2013.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2017).
- Cohen, M. Macau needs decades to go beyond gambling. Asia Time Online. 30 June 2011. Available online: http://www.atimes.com/atimes/Southeast_Asia/MF30Ae02.html (accessed on 1 June 2018).
- UNWTO. UNWTO World Tourism Barometer. 2018. Available online: https://www.e-unwto.org/doi/pdf/10.18111/wtobarometereng.2019.17.1.1 (accessed on 2 February 2019).
- PwC. Global Entertainment & Media Outlook 2018–2022. 2019. Available online: https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/industries/tmt/media/outlook.html (accessed on 2 February 2019).
- Minton, E. For your amusement: What the entertainment industry is doing for places large and small. Planning 1998, 64, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- “Utopia, Missouri” (1994, December 24). The Economist 1994, 333, 25–29.
- Besciu, I.G. Behvior of the consumer of tourist entertainment services. Cactus Tour. J. 2013, 4, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, H.; Benn, D. Tourism and cultural policy: The case of seaside entertainment in Britain. Eur. J. Cult. Policy 1997, 3, 235–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeboye, C.A. The Impact of Enterainmnet on Tourism. Case Study: Agency Remarc in Greece; Central Ostrobothnia University of Applied: Kokkola, Finland, 2012; Available online: https://www.theseus.fi/bitstream/handle/10024/47217/Adeboye_Christopher.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 2 February 2018).
- Vogel, H.L. Entertainment Industry Economics: A Guide for Financial Analysis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, H. Arts, Entertainment and Tourism; Butterworth Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.B. Perception of tourism products. Tour. Manag. 2010, 31, 607–610. [Google Scholar]
- Loi, K.I.; Pearce, P.L. Powerful stakeholders’ views of entertainment in Macao’s future. J. Bus. Res. 2012, 65, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, E.; West, J.J. Estimating the impact of entertainment on the restaurant revenues of a Las Vegas hotel casino: An exploratory study. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2010, 29, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benston, L. Park Place Betting on Dion Success. 2003. Available online: http://m.lasvegassun.com/news/2003/mar/21/park-place-betting-on-dion-success/ (accessed on 3 February 2019).
- Luo, J.M.; Lam, C.F.; Fan, D.X. The development of measurement scale for entertainment tourism experience: A case study in Macau. Curr. Issues Tour. 2018, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatipoglu, B.; Alvarez, M.D.; Ertuna, B. Barriers to stakeholder involvement in the planning of sustainable tourism: The case of the Thrace region in Turkey. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 111, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formica, S.; Uysal, M. Destination attractiveness based on supply and demand evaluations: An analytical framework. J. Travel Res. 2006, 44, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyser, H. Tourism Development; Oxford University Press: Cape Town, South Africa, 2002; Volume 374. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, K.K. Tourism and Socio-Cultural Development; Sarup & Sons: New Delhi, India, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, P.L.; Wong, E.; Polonsky, M.J. Marketing cultural attractions: Understanding non-attendance and visitation barriers. Mark. Intell. Plan. 2009, 27, 833–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzo-Navarro, M.; Pedraja-Iglesias, M. Wine tourism development from the perspective of the potential tourist in Spain. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2009, 21, 816–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heung, V.C.; Kucukusta, D.; Song, H. Medical tourism development in Hong Kong: An assessment of the barriers. Tour. Manag. 2011, 32, 995–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokni, L.; Turgay, A.V.; Park, S.H. Barriers of developing medical tourism in a destination: A case of South Korea. Iran. J. Public Health 2017, 46, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Momeni, K.; Janati, A.; Imani, A.; Khodayari-Zarnaq, R. Barriers to the development of medical tourism in East Azerbaijan province, Iran: A qualitative study. Tour. Manag. 2018, 69, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.H.; Gu, Z. Ride on the gaming boom: How can Hong Kong, Macau and Zhuhai join hands to develop tourism in the region? Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2010, 15, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, V.A.; Dwyer, L. Reinventing Macau tourism: Gambling on creativity? Curr. Issues Tour. 2017, 20, 580–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsas, C.J. Gaming anyone? A comparative study of recent urban development trends in Las Vegas and Macau. Cities 2013, 31, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macauhub.com. Macao Tourism Growing Stronger. April 2013. Available online: https://macauhub.com.mo/feature/macao-tourism-growing-stronger/ (accessed on 10 March 2019).
- Inskeep, E. Tourism planning: An emerging specialization. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1988, 54, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, A.; Corbin, J. Basics of Qualitative Research: Procedures and Techniques for Developing Grounded Theory; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Macao Government Tourism Office (MGTO). Shows & Entertainment. 2019. Available online: http://en.macaotourism.gov.mo/showentertainment/showentertainment.php?c=1 (accessed on 10 March 2019).
- Glaser, B.; Strauss, A. The Discovery of Grounded Theory: Strategies for Qualitative Research; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mabuza, L.H.; Govender, I.; Ogunbanjo, G.A.; Mash, B. African Primary Care Research: Qualitative data analysis and writing results. Afr. J. Prim. Health Care Fam. Med. 2014, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, G. Tourism Research; John Wiley & Sons Australia Ltd.: Milton, Australia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, L. Foreign investment and urban development: A perspective from tourist cities. Habitat Int. 2011, 35, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaming Inspection and Coordination Bureau (DICJ). Information; 2019. Available online: http://www.dicj.gov.mo/web/en/information/index.html (accessed on 10 March 2019).
- Hu, Y.; Ritchie, J.B. Measuring destination attractiveness: A contextual approach. J. Travel Res. 1993, 32, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Andreu, L.; Kozak, M.; Avci, N.; Cifter, N. Market segmentation by motivations to travel: British tourists visiting Turkey. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2006, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandampully, J. The impact of demand fluctuation on the quality of service: A tourism industry example. Manag. Serv. Qual. Int. J. 2000, 10, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubbe, B.A.; Douglas, A.; Fairer-Wessels, F.; Kruger, E.; Geldenhuys, E.; Francis, C. Matching Tourism Supply and Demand: An analysis of how tourism products meet the needs of emerging domestic market segments in selected regions in South Africa. In Tourism Travel and Research Association: Advancing Tourism Research Globally; Travel and Tourism Research Association: Whitehall, MI, USA, 2016; p. 25. Available online: http://scholarworks.umass.edu/ttra/2013/AcademicPapers_Oral/25 (accessed on 1 September 2019).
- Leitao, L. The Casino City Where Staff Keep Disappearing. 2016. Available online: https://www.bbc.com/news/business-35351416 (accessed on 5 March 2019).
- Macao Statistics and Census Bureau (DSEC). Tourism and Gaming. 2019. Available online: http://www.dsec.gov.mo/default.aspx# (accessed on 1 March 2019).
- Sheng, M.; Gu, C. Economic growth and development in Macau (1999–2016): The role of the booming gaming industry. Cities 2018, 75, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macau Times. News. 2017. Available online: http://www.jornalsisi.com/news-cd.asp?id=23567 (accessed on 1 March 2019).
- Whitfield, R. Macau Matters. 2017. Available online: https://macaudailytimes.com.mo/macau-matters-another-way-supporting-new-small-medium-enterprises.html (accessed on 1 March 2019).
- Luo, J.M.; Lam, C.F.; Qiu, H.; Fan, D.X. The Impact of Climate on Outbound Tourism in Hong Kong: Resident’s Mode of Transport. J. Manag. Sustain. 2015, 5, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, M. Pushing the Frontier—Macao Seeks Extra Land on Fast-Growing Hengqin Island. 2014. Available online: https://macauhub.com.mo/feature/pushing-the-frontier-macao-seeks-extra-land-on-fast-growing-hengqin-island/ (accessed on 1 December 2018).
- Luo, J.M.; Lam, C.F. Corporate Social Responsibility and Responsible Gambling in Gaming Destination; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
| No. | Sex | Working Experience (Years) | Industry Sector | Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | 4 | Gambling | Manager |
| 2 | F | 10 | Gambling | Manager |
| 3 | M | 15 | Gambling | Senior Manager |
| 4 | M | 12 | Gambling | Manager |
| 5 | F | 7 | Gambling | Manager |
| 6 | F | 10 | Gambling | General Manager |
| 7 | M | 12 | Gambling | Senior Manager |
| 8 | M | 20 | Gambling | General Manager |
| 9 | F | 10 | Gambling | Senior Manager |
| 10 | M | 7 | Gambling | Manager |
| 11 | F | 11 | Spa | Senior Manager |
| 12 | M | 2 | Entertainment Production | Manager |
| 13 | F | 3 | Spa | General Manager |
| 14 | F | 10 | Theater | Senior Manager |
| 15 | F | 20 | Spa | General Manager |
| 16 | F | 10 | Dance Club | Manager |
| Themes | Sub-Themes | Frequency Count |
|---|---|---|
| Economy | Costs are high for entertainment in Macau | 5 |
| Infrastructure | Land scarcity | 5 |
| Traffic congestion | 2 | |
| Lack of middle-scale hotels | 1 | |
| Physical environment is unsuitable | 3 | |
| Marketing | Lack of a local brand of entertainment | 2 |
| Poor communication of entertainment tourism with local and international media | 3 | |
| Promotion of old towns | 5 | |
| Management | Lack of strategic planning | 3 |
| Lack of effective coordination among VIP junket operators | 4 | |
| Lack of customer service in casinos for mass market | 2 | |
| Government attitude | Support and promotion on entertainment development | 6 |
| New investment should be encouraged | 2 | |
| Community innovation should be encouraged | 3 | |
| Policies and regulations | Central government policy towards Macau | 7 |
| Restrictions on entertainment development | 9 | |
| Complex procedures on entertainment license | 5 | |
| Expertise and manpower | Limited number of experts | 6 |
| Lack of local specialists | 5 | |
| Facilities and attractions | Lack of entertainment tourism destinations | 5 |
| Old town improvements | 3 | |
| Lack of entertainment facilities | 8 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, J.M.; Lam, C.F.; Ye, B.H. Barriers for the Sustainable Development of Entertainment Tourism in Macau. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2145. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11072145
Luo JM, Lam CF, Ye BH. Barriers for the Sustainable Development of Entertainment Tourism in Macau. Sustainability. 2019; 11(7):2145. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11072145
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Jian Ming, Chi Fung Lam, and Ben Haobin Ye. 2019. "Barriers for the Sustainable Development of Entertainment Tourism in Macau" Sustainability 11, no. 7: 2145. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11072145
APA StyleLuo, J. M., Lam, C. F., & Ye, B. H. (2019). Barriers for the Sustainable Development of Entertainment Tourism in Macau. Sustainability, 11(7), 2145. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11072145





