An Empirical Analysis of Brand as Symbol, Perceived Transaction Value, Perceived Acquisition Value and Customer Loyalty Using Structural Equation Modeling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Brand as Symbol
2.2. Perceived Value
2.3. Message-Response Involvement
2.4. Consumer Loyalty
3. Study Methods
3.1. Study Framework
3.2. Study Hypotheses
3.3. Operational Definition and Measurement of Variables in the Study
3.3.1. Brand as Symbol
3.3.2. Message-Response Involvement
3.3.3. Perceived Value
3.3.4. Customer Loyalty
3.4. Study Design
3.5. Analytic Methods Used in the Study
4. Data Analysis
4.1. Analysis Using Descriptive Statistics
4.2. The Pearson Correlation Test
4.3. Confirmatory Factor Analysis
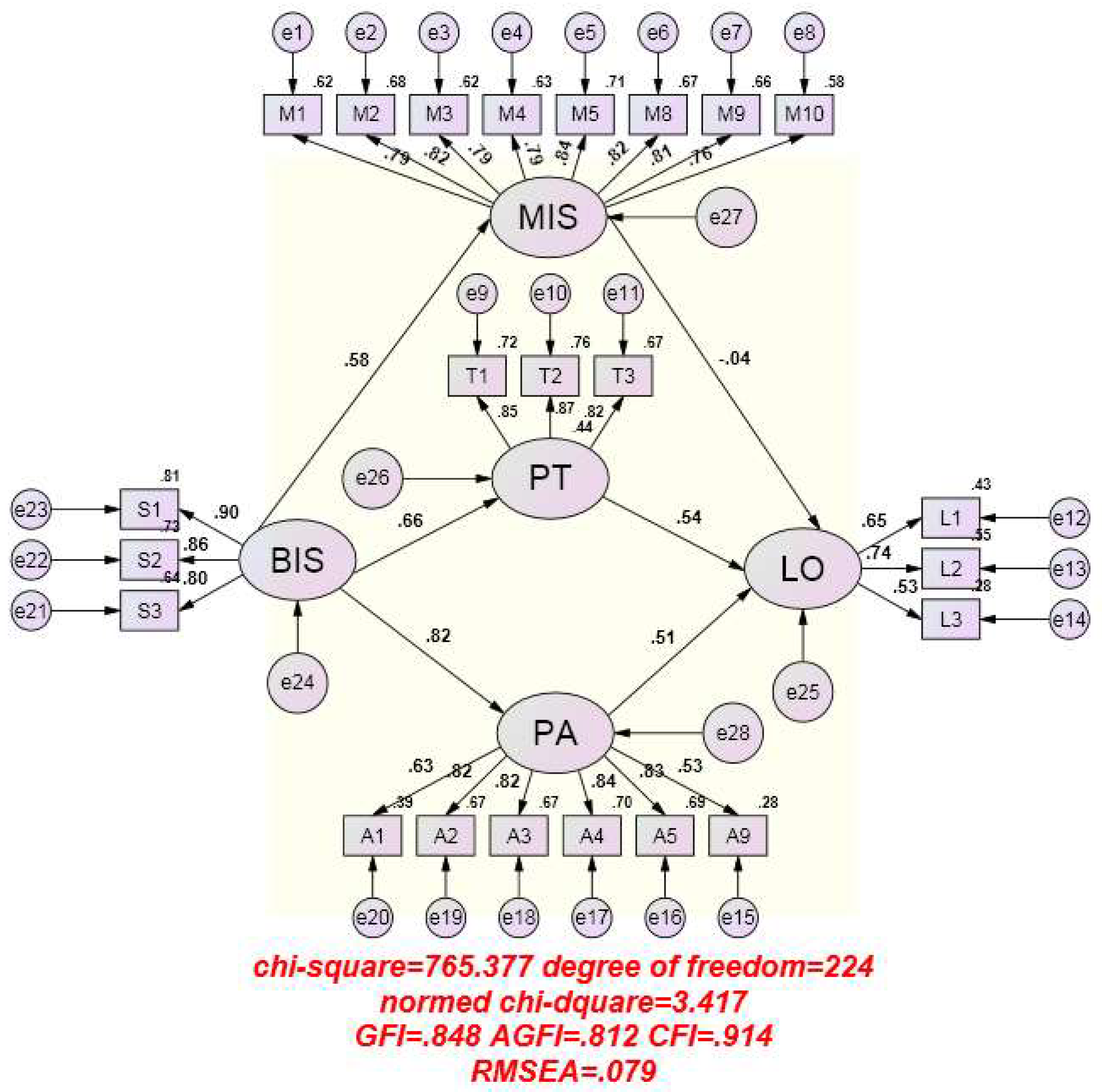
4.4. SEM Goodness-of-Fit Analysis
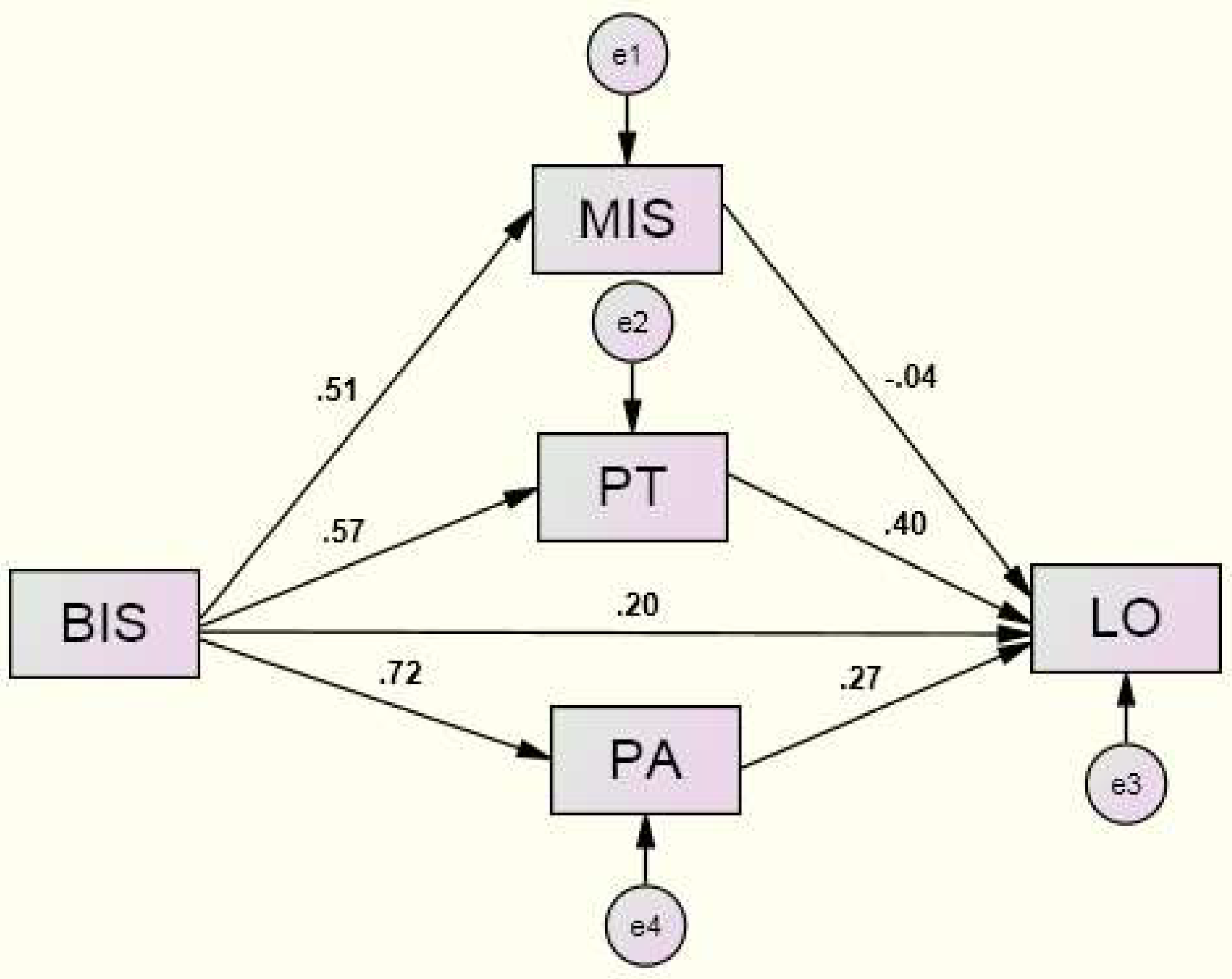
4.5. Path Analysis of Brand as Symbol, Perceived Transaction Value, Perceived Acquisition Value, Message-Response Involvement and Customer Loyalty
5. Conclusions and Discussion
5.1. Managerial Implications
5.2. Research Limitations and Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, K.T. The Application of Similarity Association for Brand Symbolism Design: Vividö Brand Symbolism. J. Des. Stud. 2007, 10, 53–71. [Google Scholar]
- Krippendorff, K.; Butter, R. Product Semantics-Exploring the Symbolic Qualities of Form. Innovation 1984, 3, 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kotler, P.; Keller, K.L. Marketing Management, 12th ed.; Pearson Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Aaker, D. Improve your brand ID. Mark. News 2010, 44, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Azoulay, A.; Kapferer, J.N. Do brand personality scales really measure brand personality? Brand Manag. 2003, 11, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, M.; Dorosti, A.; Rahnama, A.; Hoseinpour, A. Evaluation of factors affecting customer loyalty in the restaurant industry. Afr. J. Bus. Manag. 2012, 6, 5039–5046. [Google Scholar]
- Hallowell, R. The relationships of customer satisfaction, customer loyalty, and profitability: An empirical study. Int. J. Serv. Ind. Manag. 1996, 7, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heskett, J.L.; Jones, T.O.; Loveman, G.W.; Sasser, W.E.; Schlesinger, L.A. Putting the service-profit chain to work. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1994, 72, 164–174. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, X.; Moutinho, L. The role of brand image, product involvement, and knowledge in explaining consumer purchase behaviour of counterfeits: Direct and indirect effects. Eur. J. Mark. 2011, 45, 191–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruwer, J.; Buller, C. Country-of-origin (COO) brand preferences and associated knowledge levels of Japanese wine consumers. J. Prod. Brand Manag. 2012, 21, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaker, J.L.; Benet-Martinez, V.; Garolera, J. Consumption symbols as carriers of culture: A study of Japanese and Spanish brand personality constucts. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2001, 81, 492–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aaker, D.A. Building Strong Brands; The Free Press—A division of Simon & Schuster Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.W.; Jaworski, B.J.; Maclnnis, D.J. Strategic brand concept-image management. J. Mark. 1986, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.H.; Hsu, T.K.; Chiu, C.W. The Effect of Functional and Symbolic Brand Concept on Brand Extension Evaluation. Manag. Inf. Comp. 2017, 6, 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Aufahrt, H.; Franz, H. The Evolution of Loyalty Intentions. J. Mark. 2006, 70, 122–132. [Google Scholar]
- Zeithaml, V.A. Consumer Perceptions of Price, Quality, and Value: A Means-End Model and Synthesis of Evidence. J. Mark. 1988, 52, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, W.B.; Monroe, K.B.; Grewal, D. Effects of price, brand, and store information on buyers’ product evaluations. J. Mark. Res. 1991, 28, 307–319. [Google Scholar]
- McDougall, G.H.G.; Levesque, T. Customer satisfaction with services: Putting perceived value into the equation. J. Serv. Mark. 2000, 14, 392–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, D.; Monroe, K.B.; Krishnan, R. The effects of price-comparison advertising on buyers’ perceptions of acquisition value, transaction value, and behavioral intentions. J. Mark. 1998, 62, 46–59. [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff, R.B. Customer value: The next source for competitive advantage. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 1997, 25, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, Y.C.; Li, C.Y.; Huang, H.L. Is Service Quality Enough? The Impact of Customer Experience on Website Satisfaction. Sun Yat-Sen Manag. Rev. 2013, 21, 479–509. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.H. An Introduction to Consumer Behavior; Hwatai Publishing: Taipei, Taiwan, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zaichkowsky, J.L. Measuring the involvement construct. J. Consum. Res. 1985, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.M.; Kuo, K.T. The Impact of Music Type in TV Commercial at Different Degrees of Advertising Involvement on Advertising Effect. J. Des. 2013, 18, 25–47. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.F. Consumer Behavior: Life and Marketing; Future Career Publishing Corporation: Taipei, Taiwan, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, T.K.; Chen, C.L.; Chung, H.H. The effects of ad appealing, ad message presentation and consumer involvement on restaurant’s advertisement purchasing intention. J. Hosp. Home Econ. 2006, 3, 269–287. [Google Scholar]
- Tepeci, M. Increasing brand loyalty in the hospitality industry. Int. J. Cont. Hosp. Manag. 1999, 11, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.O.; Sasser, W.E. Why satisfied customers defect. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1995, 73, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Ryu, K. The roles of the physical environment, price perception, and customer satisfaction in determining customer loyalty in the restaurant industry. J. Hosp. Tour. Res. 2009, 33, 487–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, K.; Han, H.; Kim, T.H. The relationships among overall quick-casual restaurant image, perceived value, customer satisfaction, and behavioral intentions. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2008, 27, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cretu, A.E.; Brodie, R.J. The influence of brand image and company reputation where manufacturers market to small firms: A customer value perspective. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2007, 36, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Peterson, R.T. Customer perceived value, satisfaction, and loyalty: The role of switching costs. Psychol. Mark. 2004, 21, 799–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunnally, J.C. Psychometric Theory, 2nd ed; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, D.; Banerjee, S. CARE- ing Strategy for Integrat ion of Brand Identity with Brand Image. Int. J. Commun. Manag. 2007, 17, 140–148. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, J.E. The Effect of Family Restaurant Brand Identity on the Purchase Intention of Consumer. J. Korean Soc. Food Cult. 2009, 24, 245–255. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J.; Park, M. The effects of e-mass customization on consumer perceived value, satisfaction, and loyalty toward luxury brands. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 5775–5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

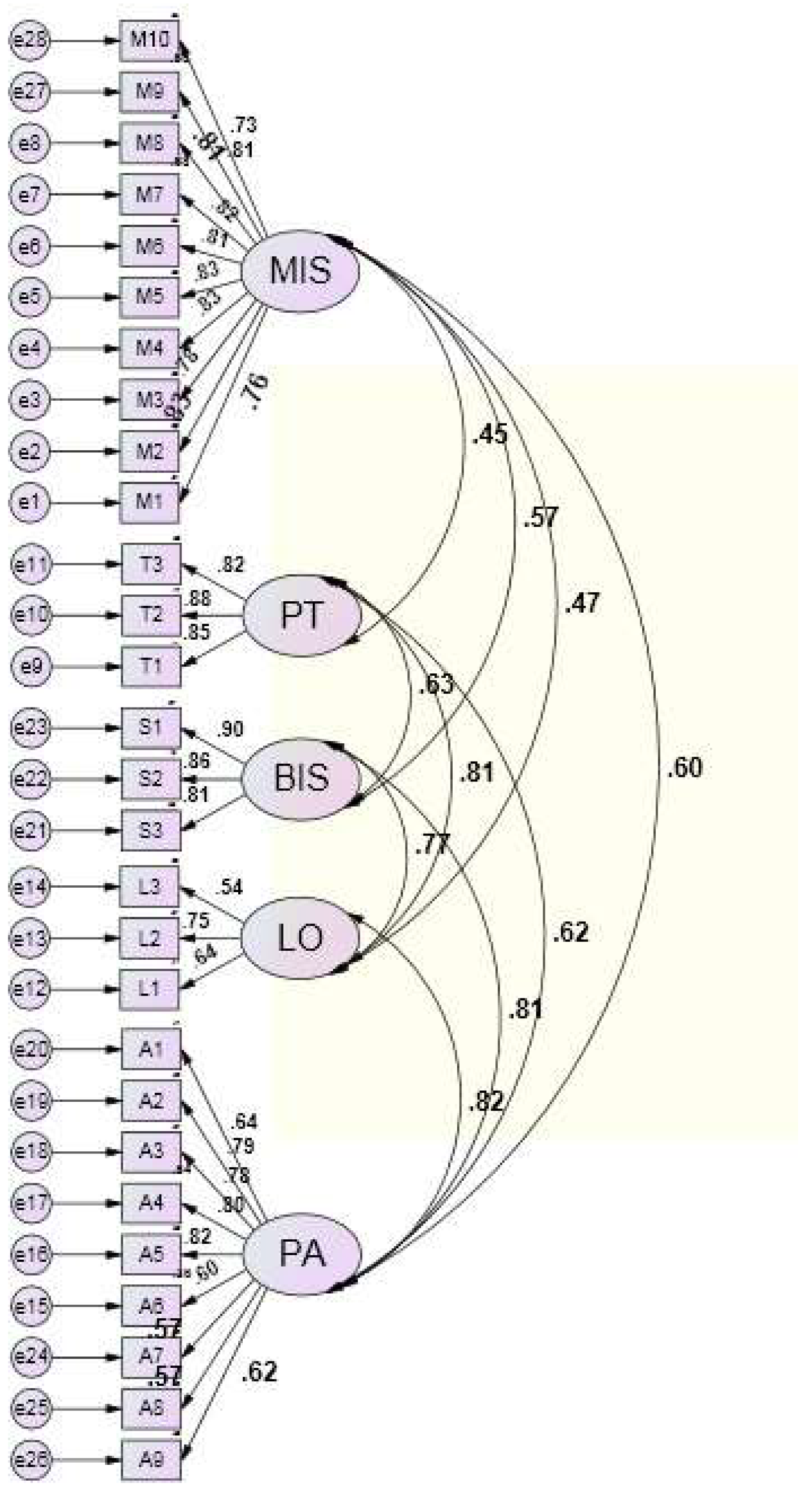
| Study Dimension | Question No. | Factor Loading |
|---|---|---|
| Message-response Involvement (MIS) | M1 | 0.76 |
| M2 | 0.83 | |
| M3 | 0.78 | |
| M4 | 0.83 | |
| M5 | 0.83 | |
| M6 | 0.81 | |
| M7 | 0.82 | |
| M8 | 0.81 | |
| M9 | 0.81 | |
| M10 | 0.73 | |
| Perceived Transaction Value (PT) | T1 | 0.85 |
| T2 | 0.88 | |
| T3 | 0.82 | |
| Brand as Symbol (BS) | S1 | 0.90 |
| S2 | 0.86 | |
| S3 | 0.81 | |
| Customer Loyalty (LO) | L1 | 0.64 |
| L2 | 0.75 | |
| L3 | 0.54 | |
| Perceived Acquisition Value (PA) | A1 | 0.64 |
| A2 | 0.79 | |
| A3 | 0.78 | |
| A4 | 0.80 | |
| A5 | 0.82 | |
| A6 | 0.60 | |
| A7 | 0.57 | |
| A8 | 0.57 | |
| A9 | 0.62 |
| Model Goodness-of-Fit Index | RMSEA | χ2/df | GFI | CFI | AGFI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <0.08 | 1~5 | >0.8 | >0.9 | >0.8 | |
| Before modification | 0.096 | 4.566 | 0.747 | 0.848 | 0.701 |
| After modification | 0.079 | 3.417 | 0.848 | 0.914 | 0.812 |
| Estimate | S.E. | C.R. | p | Standardized Regression Weights | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIS | → | MIS | 0.535 | 0.046 | 11.628 | *** | 0.51 |
| BIS | → | PT | 0.532 | 0.039 | 13.582 | *** | 0.57 |
| BIS | → | PA | 0.629 | 0.031 | 20.572 | *** | 0.72 |
| PT | → | LO | 0.308 | 0.033 | 9.357 | *** | 0.40 |
| MIS | → | LO | −0.028 | 0.028 | −0.996 | 0.319 | −0.04 |
| PA | → | LO | 0.226 | 0.042 | 5.364 | *** | 0.27 |
| BIS | → | LO | 0.146 | 0.043 | 3.370 | *** | 0.20 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.N.; Lee, A.S.; Liang, Y.W. An Empirical Analysis of Brand as Symbol, Perceived Transaction Value, Perceived Acquisition Value and Customer Loyalty Using Structural Equation Modeling. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2116. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11072116
Lee HN, Lee AS, Liang YW. An Empirical Analysis of Brand as Symbol, Perceived Transaction Value, Perceived Acquisition Value and Customer Loyalty Using Structural Equation Modeling. Sustainability. 2019; 11(7):2116. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11072116
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Huang Ning, An Sheng Lee, and Yo Wen Liang. 2019. "An Empirical Analysis of Brand as Symbol, Perceived Transaction Value, Perceived Acquisition Value and Customer Loyalty Using Structural Equation Modeling" Sustainability 11, no. 7: 2116. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11072116
APA StyleLee, H. N., Lee, A. S., & Liang, Y. W. (2019). An Empirical Analysis of Brand as Symbol, Perceived Transaction Value, Perceived Acquisition Value and Customer Loyalty Using Structural Equation Modeling. Sustainability, 11(7), 2116. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11072116




