Research on the Application of Palm Mat Geotextiles for Sand Fixation in the Hobq Desert
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Physical Performance Tests of the Palm Mat Geotextiles in the Lab
2.3. Field Experiments
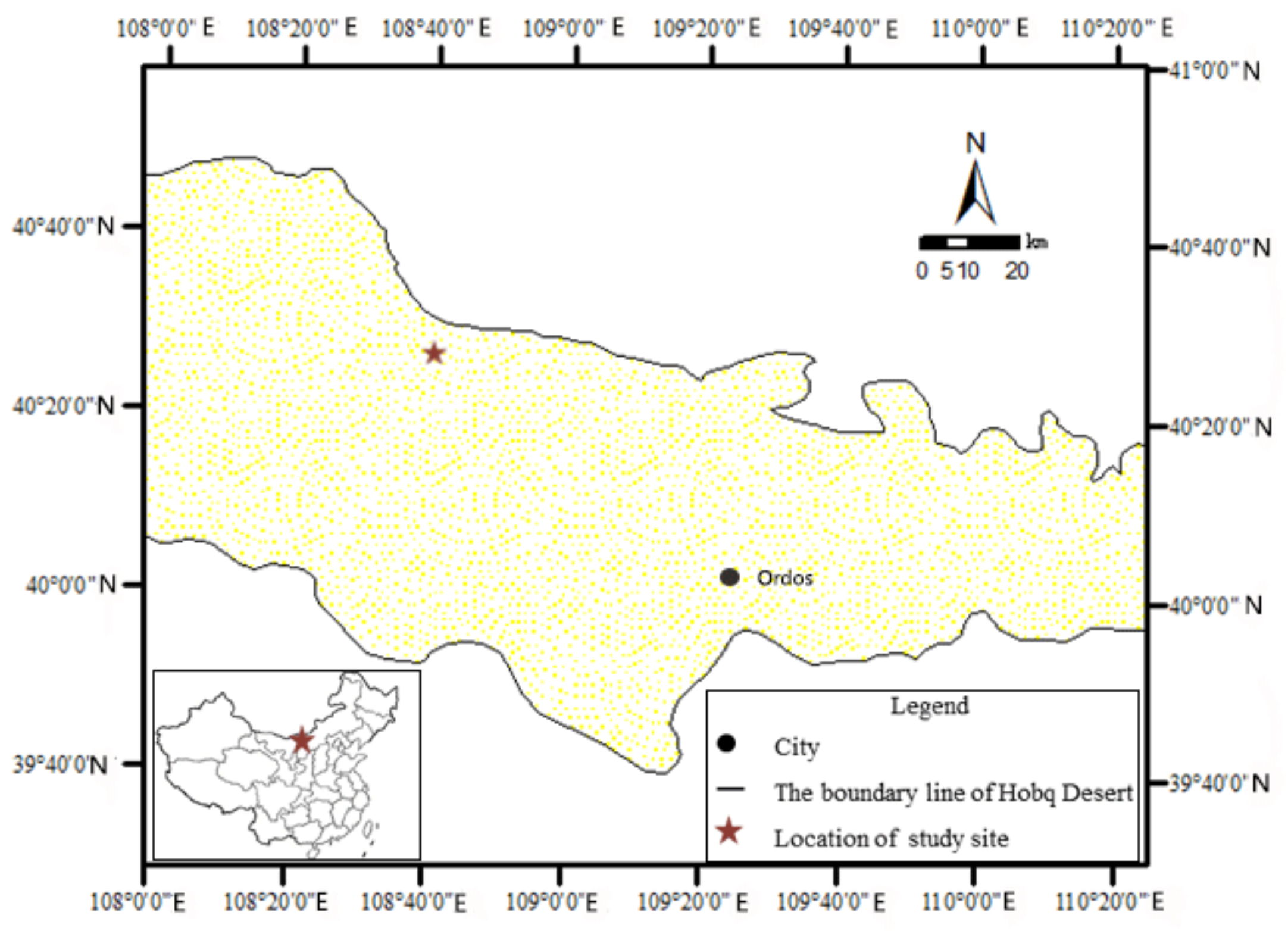
2.3.1. Location of the Experimental Site
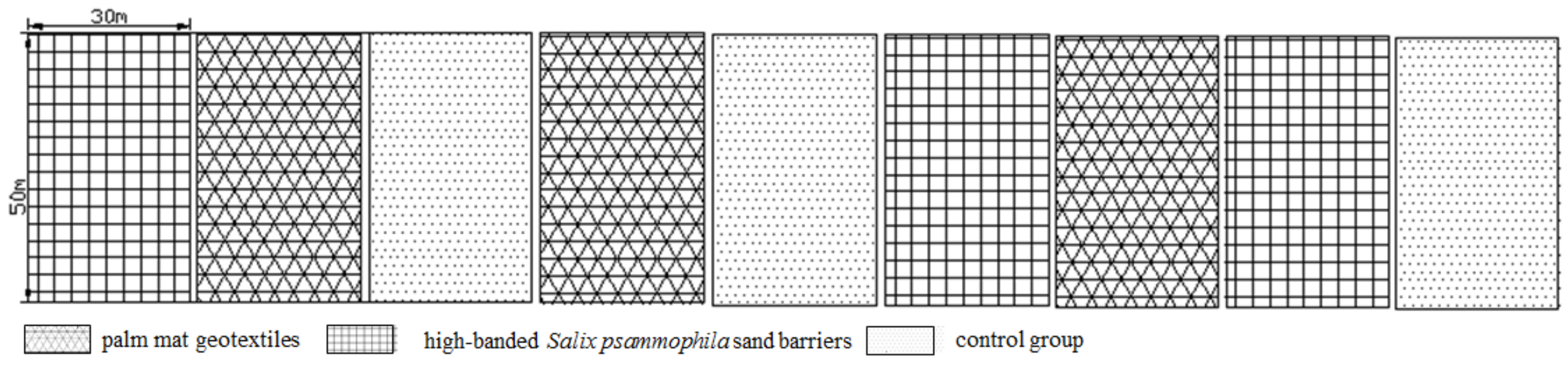
2.3.2. Experimental Setting
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
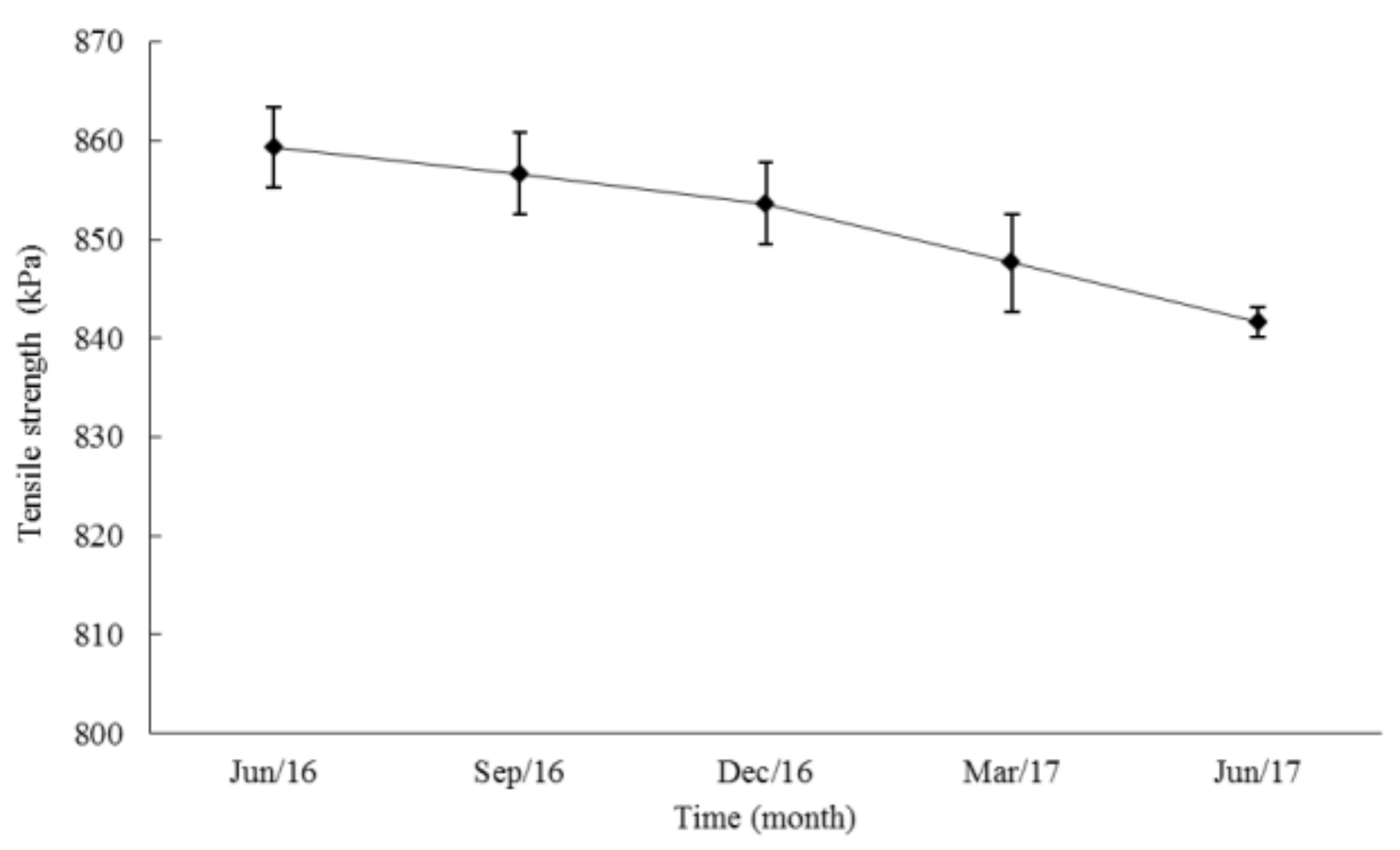
3.1. Physical Performance of the Palm Mat Geotextiles
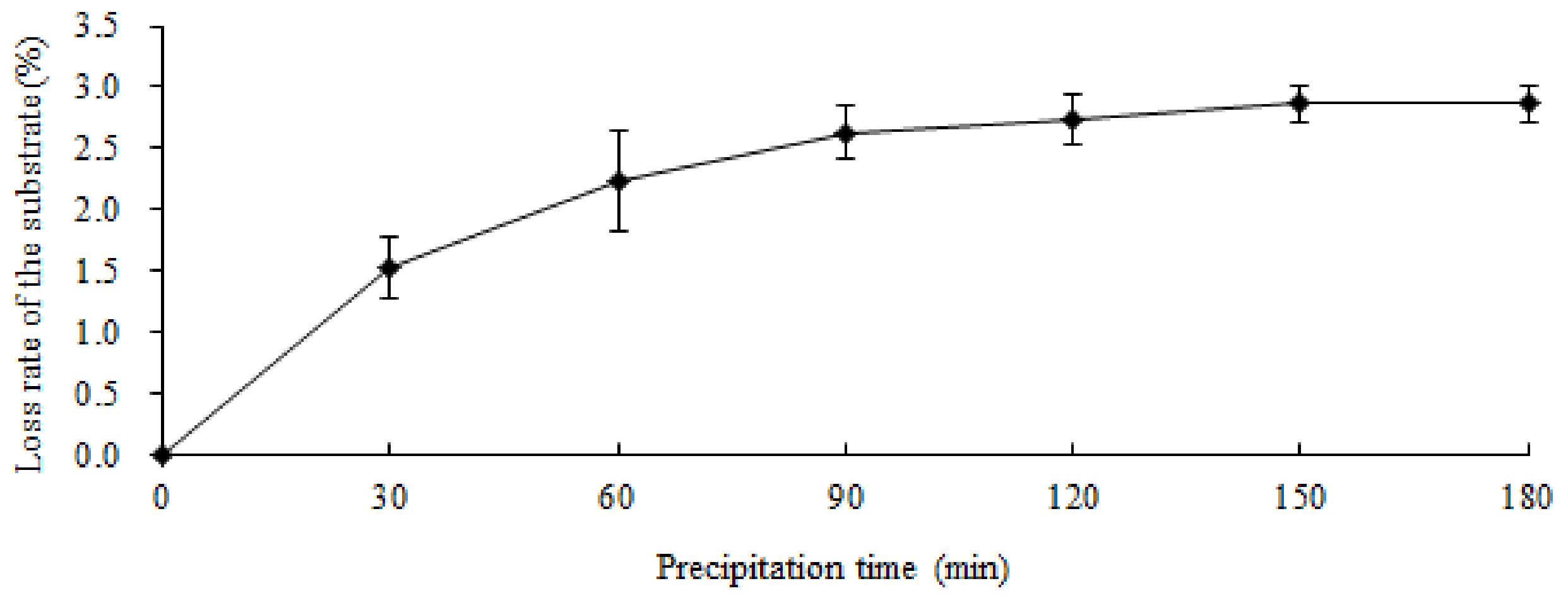
3.2. Water Permeability, Saturated Water Content, and Structural Stability
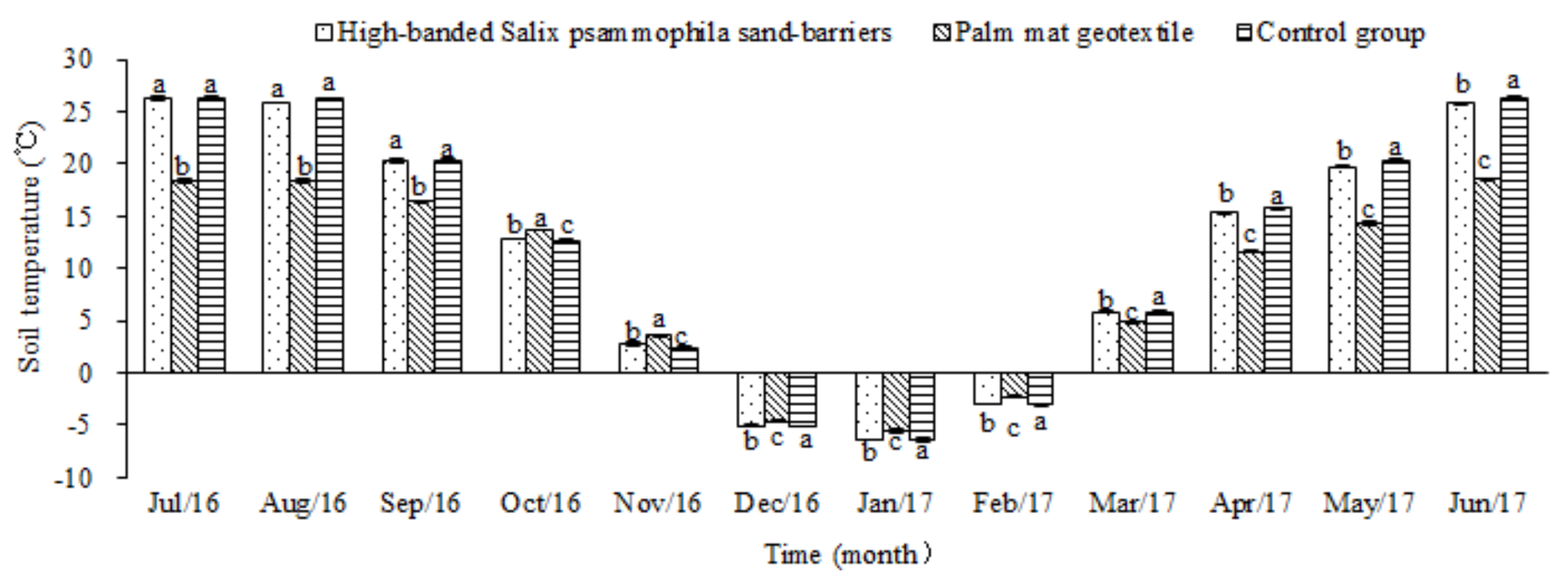
3.3. Effects of the Palm Mat Geotextiles on Soil Temperature
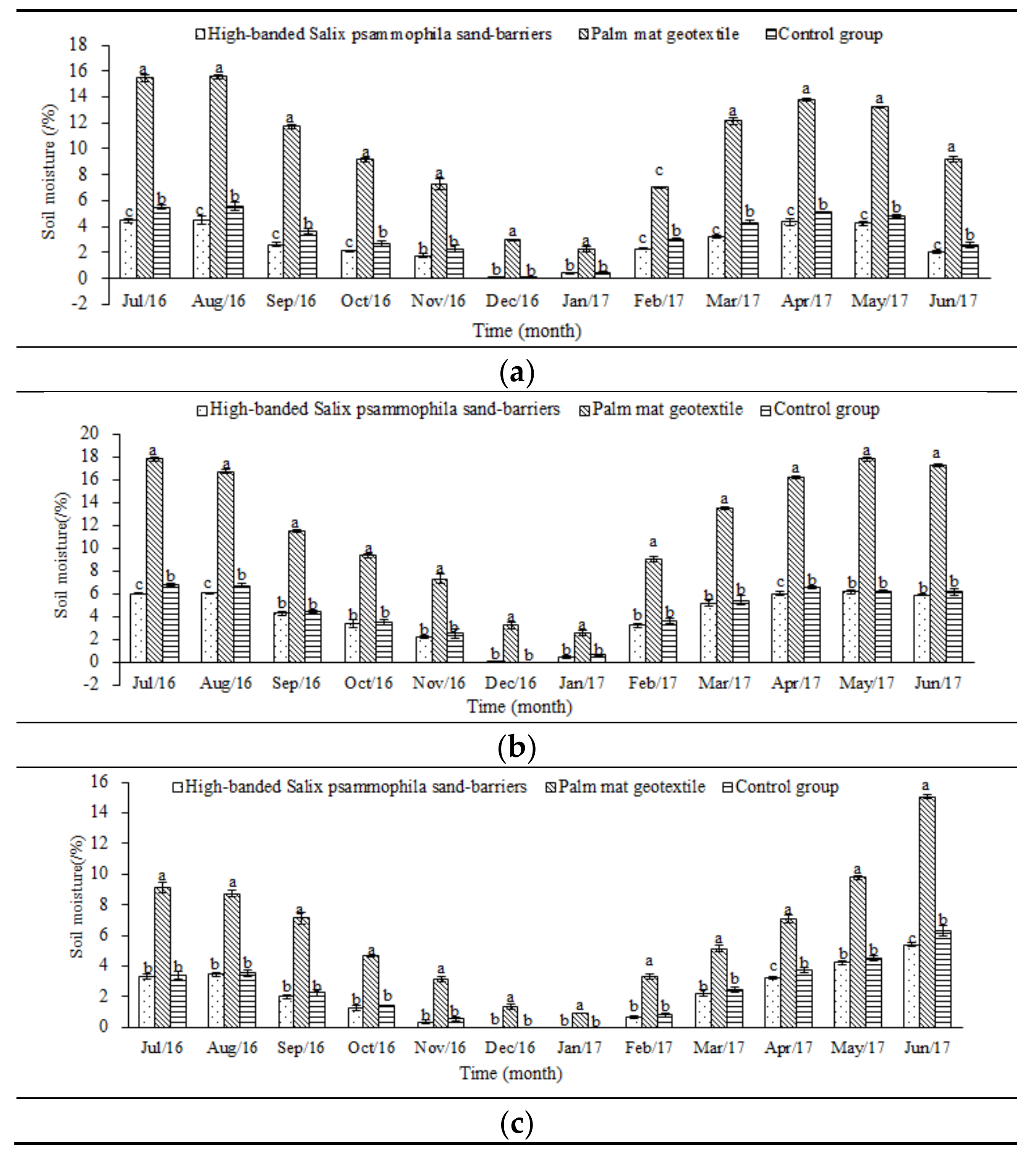
3.4. Effects of the Palm Mat Geotextiles on Soil Moisture
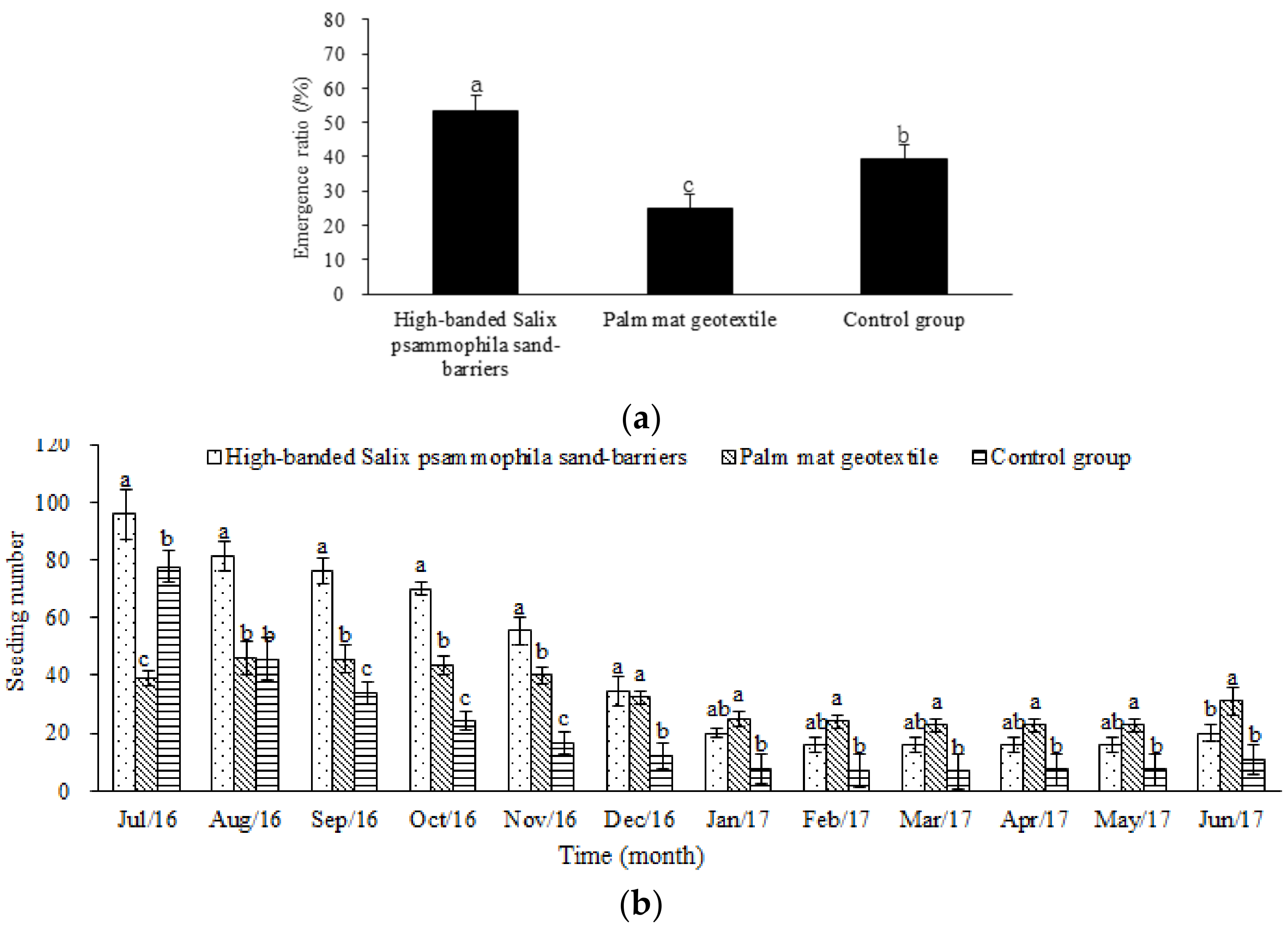
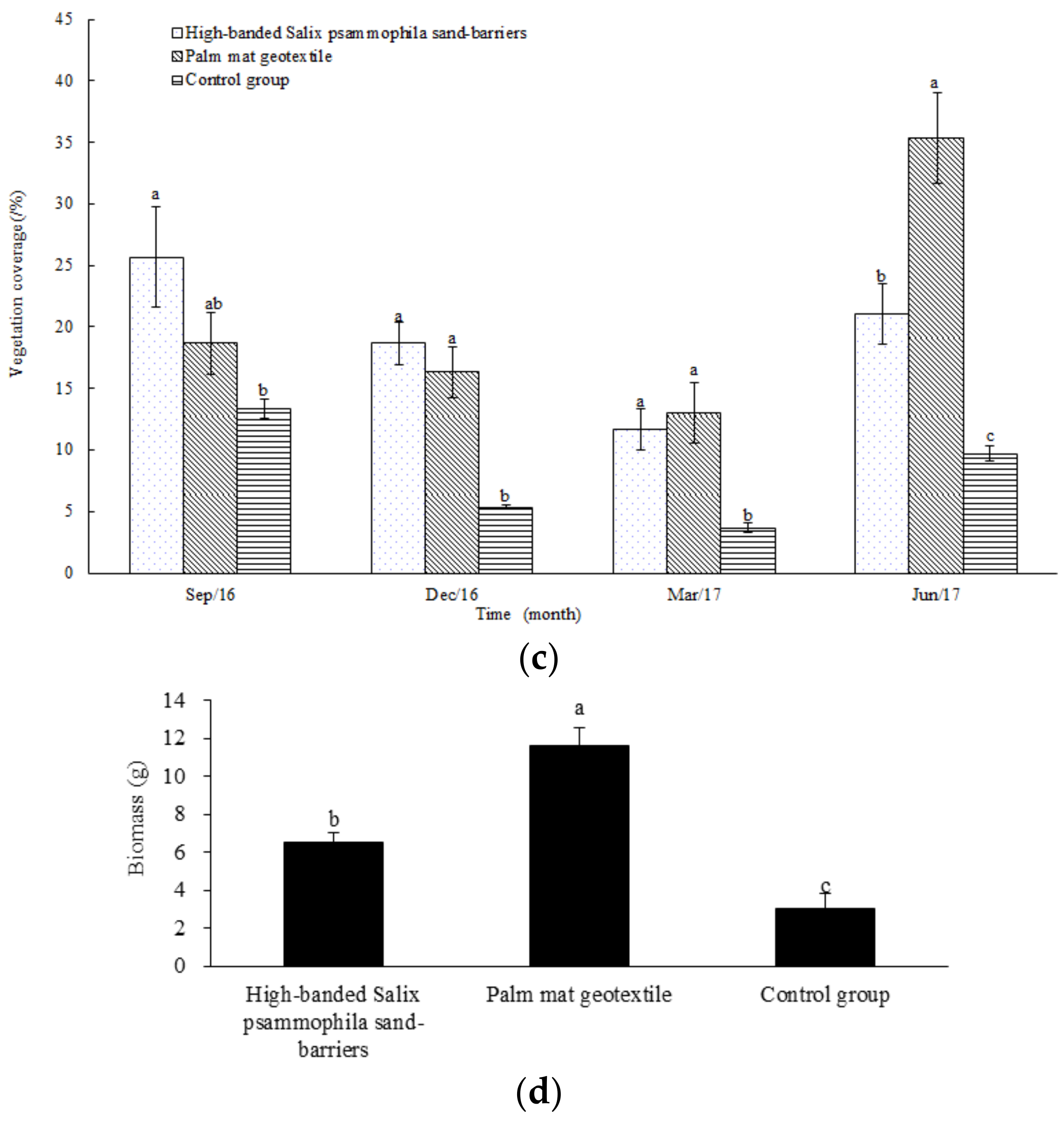
3.5. Effects of the Palm Mat Geotextiles on Plant Growth
4. Discussion
4.1. Physical Performance of the Palm Mat Geotextiles
4.2. Water Permeability and Saturated Water Content of the Palm Mat Geotextiles
4.3. The Effects of Palm Mat Geotextiles on Soil Temperature and Moisture
4.4. Effects of the Palm Mat Geotextiles on Plant Growth
4.5. The Cost and Application of Palm Mat Geotextiles
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNCCD. United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification in Those Countries Experiencing Serious Drought and/or Desertification, Particularly in Africa; United Nations Environment Programme for the Convention to Combat Desertification (CCD): Geneva, Switzerland, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- State Forestry Administration of China. China’s Fifth National bulletin on desertification. China Environmental News, 30 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T. Progress in sandy desertification research of China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2004, 14, 387–400. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.D.; Chen, G.T. Sandy Desertification in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1994; pp. 7–15. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, W. Sandy desertification in the north of China. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2002, 45, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wu, W.; Xue, X.; Sun, Q.; Chen, G. Study of spatial distribution of sandy desertification in North China in recent 10 years. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2004, 47, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Sun, J.-G.; Han, H.; Yan, C.-Z. The relative role of climate change and human activities in the desertification process in Yulin region of northwest China environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 7165–7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Y.Q.; Jin, J.; Zou, B.G.; Cong, Z.; Weng, X.; Tu, X.; Ye, J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, H. Effect of fence techniques in leveling sand accumulation around sandbreaks-case study in Shapotou district. J. Desert Res. 1984, 4, 16–21, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Gao, Y.; Gao, Q.; Yan, X.B. Effects of Salix psammophila checkboard of physical and characteristics of sandy soil. J. Inn. Mong. Agric. Univ. 2006, 27, 39–42, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Liu, L.; Gong, J. Influence of pebble mulch on soil erosion by wind and trapping capacity for windblown sediment. Soil Tillage Res. 2001, 59, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L. Effect of gravel mulch on soil and water conversation—A case study in the northern edge of Hobq desert. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 24, 172–178, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Wang, T.; Fan, J.S.; Zhang, W.M.; Qu, J.J.; Agnew, N.; Lin, B.M. Effect of nylon net fence on preventing blown sand at top of Mogao Grottoes, Dunhuang. J. Desert Res. 2005, 25, 640–648, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Qu, J.; Yu, W.; Qin, X. Wind-protecting efficiency of HDPE functional sand-fixing barriers. J. Desert Res. 2014, 34, 1185–1193, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tong, W.; Han, J.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, H.O.; Zhao, X. Sand-fixing effect of compound soil by mixing feldspathic sandstone and sand in the Mu Us Sand Land. J. Desert Res. 2015, 35, 1467–1472, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.J.; Yuan, H.B.; Guo, C.X.; Xu, X.Y.; Wang, D.Z.; Li, X.M.; Liu, K.L. Windbreak efficiency of two types of simulated shrub forest equally planted in field. J. Desert Res. 2015, 35, 8–13, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T.; Liu, H.J.; Zhu, G.Q.; Zhang, Y.H.; Ma, R.; Man, D.Q. Timeliness of reducing wind and stabilizing sand functions of three mechanical sand barriers in Arid Region. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 26, 13, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.B.; Qu, J.J.; Pang, Y.J. Causes and controlling mode of sand hazards in Honglainghe section of Qinghai-Tibet Railway. J. China Railw. Soc. 2014, 36, 99–105, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R.J.; Liu, X.K.; Lin, J.F.; Zhao, C. Effects of typical sand-fixing plant on soil improvement in Qinhai Lake area. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 39, 177–181, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Q.J.; Xu, X.J.; Chen, Y.Z.; Hu, S.G. The research advances of chemical sand-fixing materials. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. 1980, 1, 33–37, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.; Hu, Y.; Chen, G.; Yao, Z.; Shao, G. The suitability of chemical engineering stabilization in controlling aeolian hazard along the highway in Tarim Basin. Environ. Sci. 2000, 21, 86–88, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya, R.; Fullen, M.A.; Booth, C.A.; Kertesz, A.; Toth, A.; Szalai, Z.; Jakab, G.; Kozma, K.; Jankauskas, B.; Jankauskiene, G.; et al. Effectiveness of biological geotextiles for soil and water conservation in different agro-environments. Land Degrad. Dev. 2011, 22, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembicki, E.; Niespodzinska, L. Geotextiles in coastal engineering practice. Geotext. Geomembr. 1991, 10, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zhao, T.; Dong, M.; Gao, J.; Peng, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liang, C. Field studies on the effects of three geotextiles on runoff and erosion of road slope in Beijing, China. Catena 2013, 109, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Mozos, J.; Abad, E.; Goñi, M.; Giménez, R.; Campo, M.A.; Díez, J.; Casalí, J.; Arive, M.; Diego, I. Evaluation of erosion control geotextiles on steep slopes. Part 2: Influence on the establishment and growth of vegetation. Catena 2014, 121, 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Z.; Kang, N.; Wu, X.; Shang, T. Research on the soilless turfgrass mat production. J. Wuhan Bot. Res. 1994, 12, 236–269, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Rickson, R.J. Controlling sediment at source an evaluation of erosion control geotextiles. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2006, 31, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smets, T.; Poesen, J.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Fullen, M.A.; Subedi, M.; Booth, C.A.; Kertesz, A.; Szalai, Z.; Toth, A.; Jankauskas, B.; et al. Evaluation of biological geotextiles for reducing runoff and soil loss under various environment conditions using laboratory and field plot data. Land Degrad. Dev. 2011, 22, 480–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smets, T.; Poesen, J.; Langhans, C.; Knapen, A.; Fullen, M.A. Concentrated flow erosion rates reduced through biological geotextiles. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2009, 34, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, R.; Fullen, M.A.; Davies, K.; Booth, C.A. Use of palm-mat geotextiles for rainsplash erosion control. Geomophology 2010, 119, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, R.; Davies, K.; Fullen, M.A.; Booth, C.A. Effects of palm mat geotextiles on the conservation of loamy sand soils in east Shropshire. Adv. Geoecol. 2008, 39, 527–538. [Google Scholar]
- Smets, T.; Poesen, J. Effectiveness of palm and simulated geotextiles in reducing run-off and inter-rill erosion on medium and steep slopes. Soil Use Manag. 2007, 23, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Ren, Z.; Cao, M. Apparatus and method of geotextile tensile testing. Water Conserv. Sci. Technol. Econ. 2012, 18, 109–112, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Niu, J.; Li, H.; Yang, Z.; Peng, Y. Research on liquid oxidative degradation of polyethylene and polypropylene. J. Zhengjiang Unv. Sci. Technol. 2008, 20, 110–114, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. The Effects of Geotextiles on Ecological Protection Technology on the Road Slope; Beijing Forest University: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, S.; Deng, A. Three-dimensional vegetation net prefabricated the meaning of the carpet and develop a technology. J. Hunan Environ. Biol. Polytech. 2012, 18, 6–9, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Li, N.; Lu, X. Application of straw checkerboard in wind-proof and sand-fixing engineering. J. Liaoning For. Sci. Technol. 2014, 3, 67–68. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, D.; Xue, Y.; Zhao, C. Present study on biological soil crusts in China. J. Inn. Mong. For. Sci. Technol. 2007, 33, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, G.; Shen, W.; Ding, L. Strength charteristics of sand fixated by SH. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2003, 22, 2883–2887. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, S.; Han, Z.; Li, A. Effects of performance and concentration of GS-3 sand-fixing agent on plant growth. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L. Study on Effects of Soil Physical Properties and Protection Benefits by PLA Sand Barrier; Inner Mongolia Agriculture University: Inner Mongolia, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
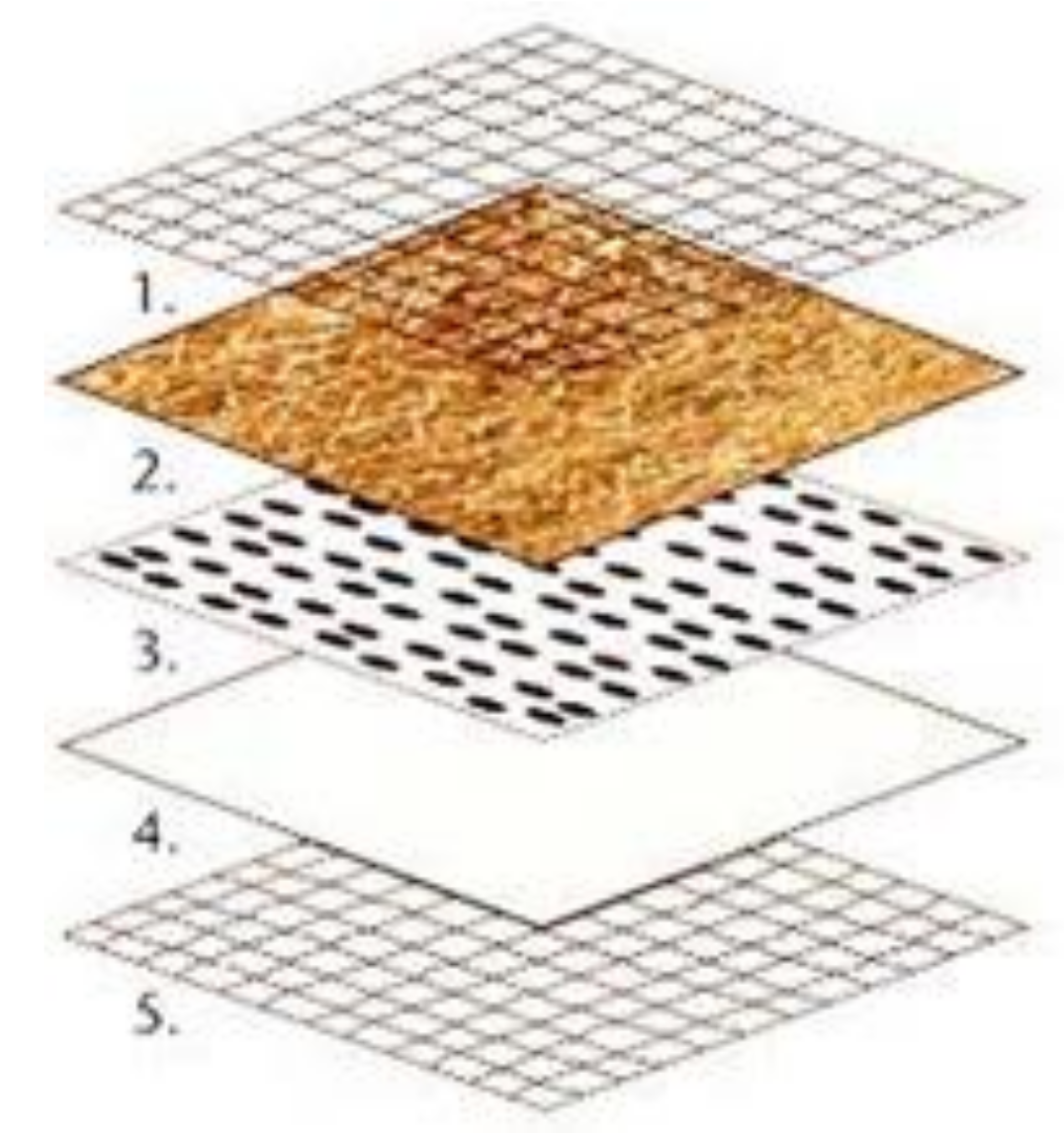

| Types | Materials | Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| Raw material | Palm fiber | 15–25 cm |
| Cushion | Nonwoven fabric | 100 g/m2 |
| Fixed net | Polypropylene (PP) | 5 × 5 mm |
| Sewing thread | Polypropylene (PP) | d ≥ 0.3 mm |
| Species | Germination Ration (%) | 1000 Seed Weight (g) | Purity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriophyllum squarrosum (L.) Moq. | 79.77 | 0.92 | 92.75 |
| Artemisia desertorum Spreng. Syst. Veg. | 81.35 | 0.86 | 89.73 |
| Hedysarum mongolicum Turcz. | 67.67 | 27.44 | 91.62 |
| Hedysarum scoparium Fisch. et Mey. | 72.33 | 16.35 | 93.47 |
| pH | CL− | HCO3− | Ca2+ | N | P | K | Organic Matter | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.85 | 6.63 | 0.43 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.53 | 0.21 | 0.78 | 15.79 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, S.; Han, Z.; Li, A.; Du, H. Research on the Application of Palm Mat Geotextiles for Sand Fixation in the Hobq Desert. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1751. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061751
Zhong S, Han Z, Li A, Du H. Research on the Application of Palm Mat Geotextiles for Sand Fixation in the Hobq Desert. Sustainability. 2019; 11(6):1751. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061751
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Shuai, Zhiwen Han, Aimin Li, and Heqiang Du. 2019. "Research on the Application of Palm Mat Geotextiles for Sand Fixation in the Hobq Desert" Sustainability 11, no. 6: 1751. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061751
APA StyleZhong, S., Han, Z., Li, A., & Du, H. (2019). Research on the Application of Palm Mat Geotextiles for Sand Fixation in the Hobq Desert. Sustainability, 11(6), 1751. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061751




