Quantifying Grazing Intensity Using Remote Sensing in Alpine Meadows on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
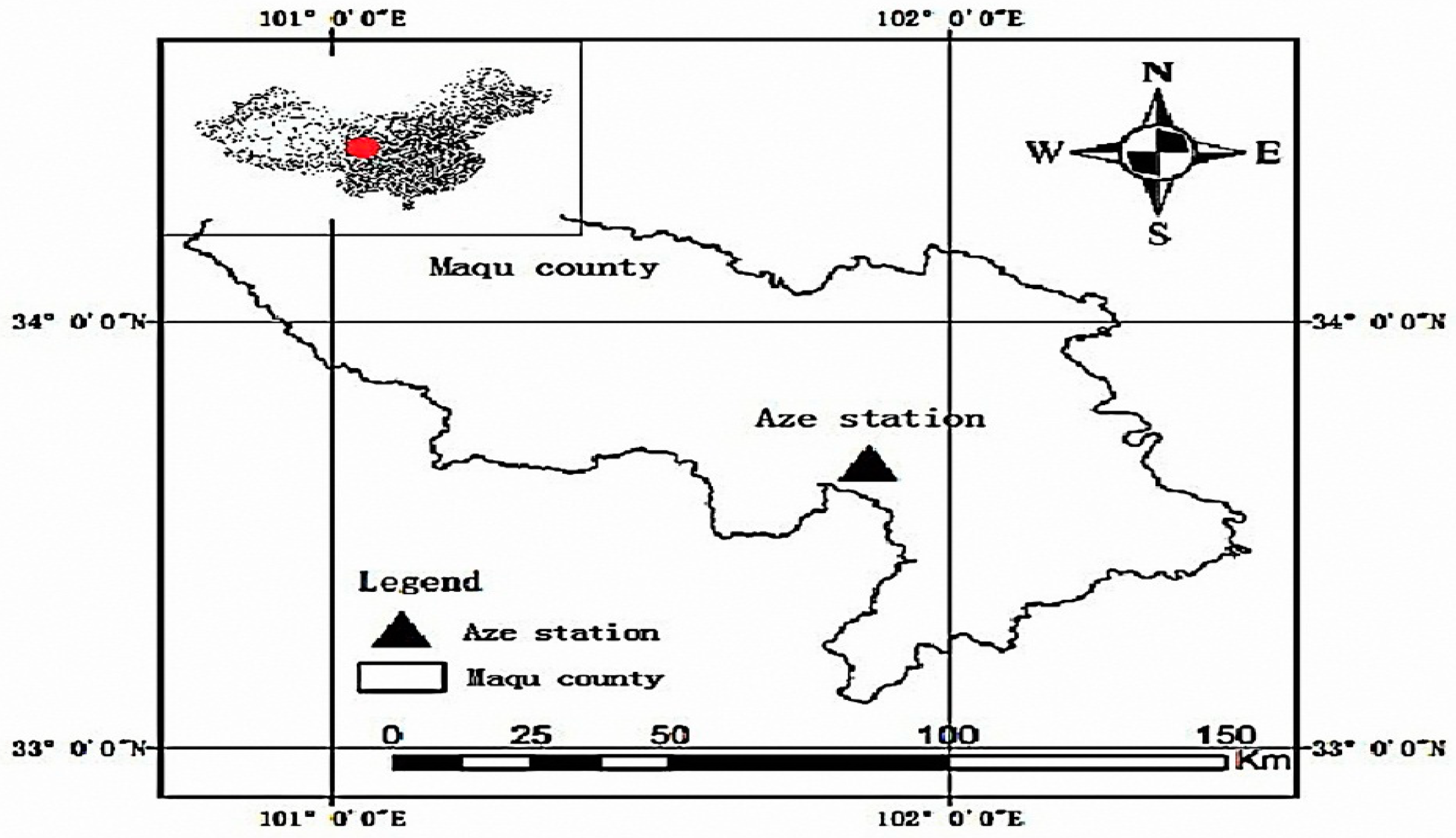
2.1. Study Area
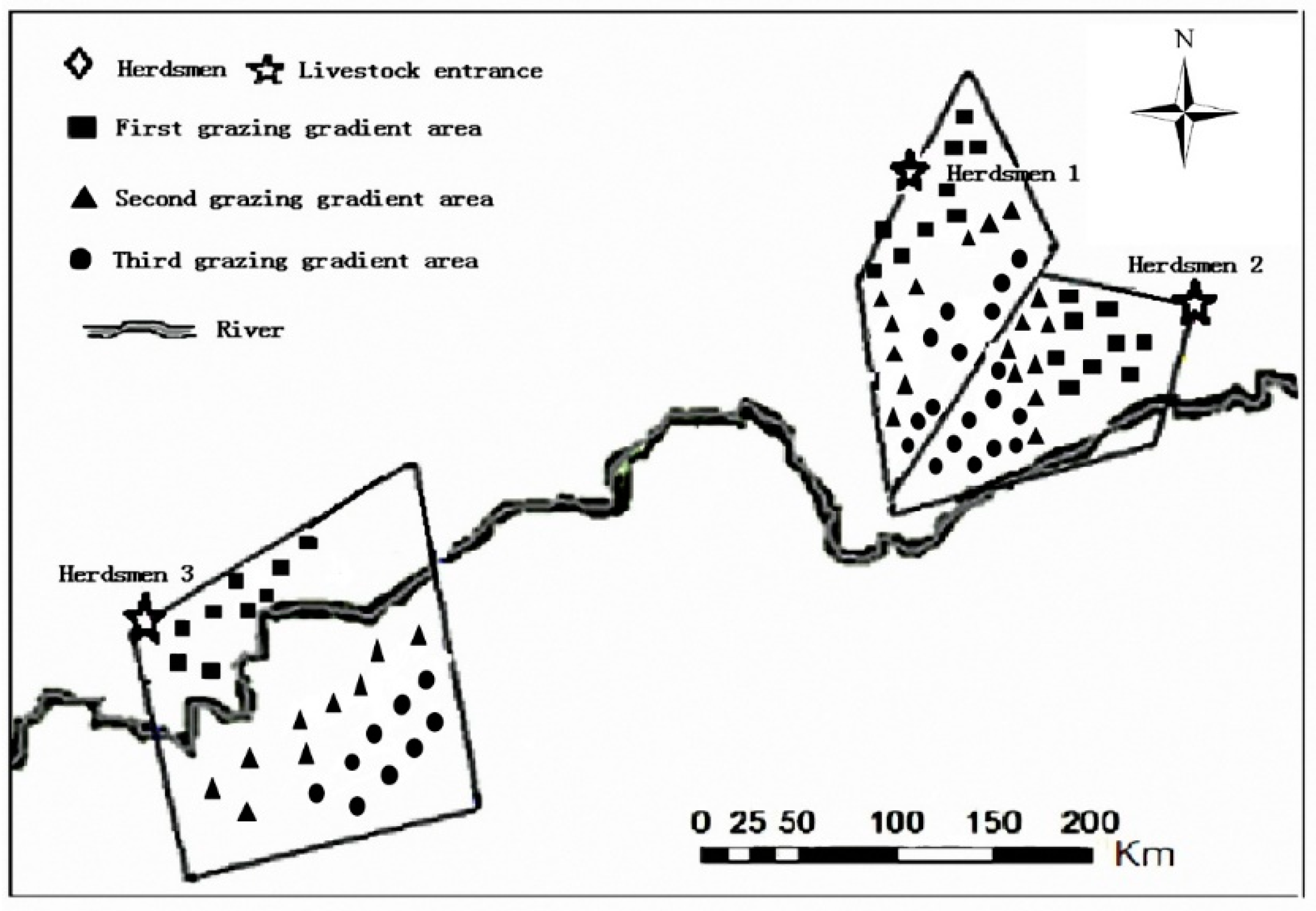
2.2. Ground-Measured Data
2.3. Vegetation Index Extraction and Calculation of Relative Grazing Intensity
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
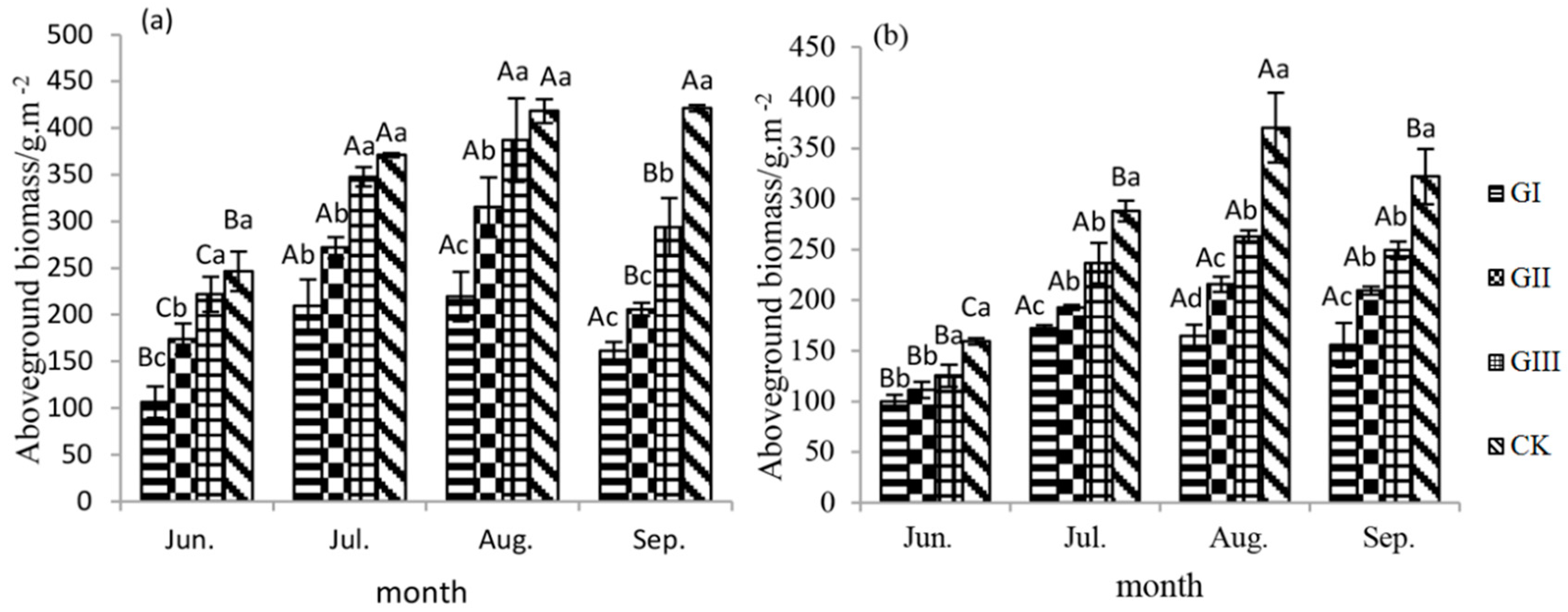
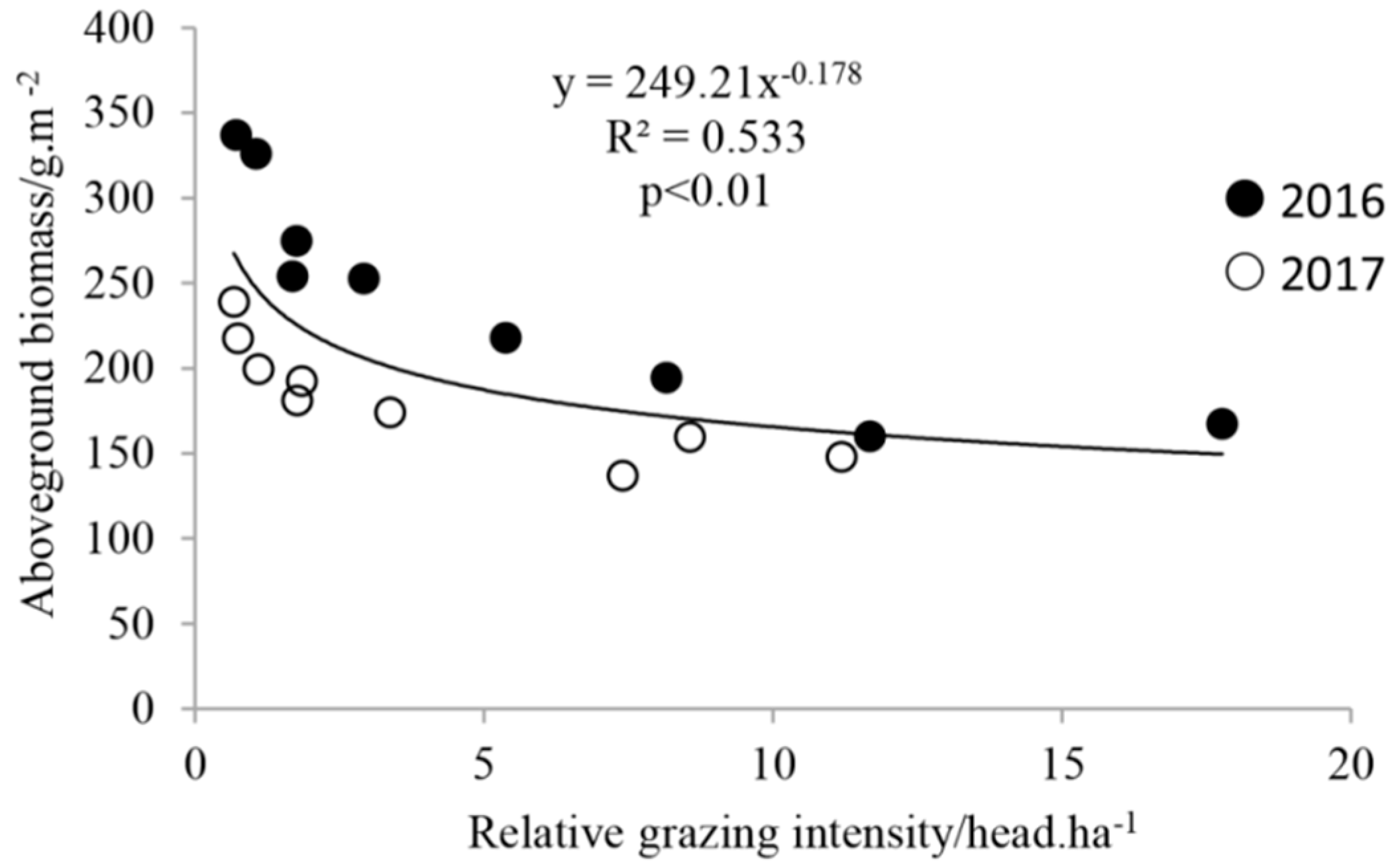
3.1. Correlation Analysis of Measured Aboveground Biomass and Relative Grazing Intensity
3.2. Correlation Analysis between Vegetation Index and Aboveground Biomass
3.3. Correlation Analysis of Relative Grazing Intensity and Vegetation Index
4. Discussion
4.1. Aboveground Biomass under Different Grazing Intensities
4.2. Correlation between Different Vegetation Indices and Aboveground Biomass
4.3. Correlation between Grazing Intensity and Vegetation Index
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramankutty, N.; Evan, A.T.; Monfreda, C.; Foley, J.A. Farming the planet:1. Geographic distribution of global agricultural lands in the year 2000. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2008, 22, GB1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grime, J.P. Competitive exclusion in herbaceous vegetation. Nature 1973, 242, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connell, J.H. Diversity in tropical rain forests and coralreefs. Science 1978, 199, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baoyinhexige. Effect of grazing on grassland ecosystem. Anim. Husb. Feed Sci. 2013, 34, 71–74. [Google Scholar]
- Kemp, D.R.; Michalk, D.L. Sustainable grassland and livestock management. J. Agric. Sci. 2007, 145, 543–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeel, Z.; Safriel, U.; Niemeijer, D.; White, R. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Desertification Synthesis. Millennium Ecosystems Assessment; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, R.; Long, R.; Shang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Dong, S.; Wang, Y. Establishment of Elymus natans, improves soil quality of a heavily degraded alpine meadow in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Plant Soil 2010, 327, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, G.; Peng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Zhu, Q.; Hu, J.; Wang, M.; Zhan, W.; Zhu, E.; et al. The carbon stock of alpine peatlands on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau during the Holocene and their future fate. Quat. Sci. Res. 2014, 95, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhu, J.; Wimberly, M.C.; Yu, G.; Niu, S.; Xi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. Light-intensity grazing improves alpine meadow productivity and adaption to climate change on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, S.; Gao, Q.; Liu, S.; Liang, Y.; Cao, X. Responses of alpine vegetation and soils to the disturbance of plateau pika (Ochotona curzoniae) at burrow level on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau of China. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 88, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.K.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, X.Q.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.N.; Gu, S.; Zhou, X.M. Study on the stability of alpine meadow ecosystem in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.K.; Zhao, X.Q.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.N.; Wang, S.P.; Xu, S.X.; Zhou, L. Restoration capability of alpine meadow ecosystem on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Chin. J. Ecol. 2008, 27, 697–704. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, R.B. Rangeland degradation on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau: A review of the evidence of its magnitude and causes. J. Arid Environ. 2010, 74, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Lassoie, J.P.; Morreale, S.J.; Dong, S. A critical review of socioeconomic and natural factors in ecological degradation on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Rangel. J. 2015, 37, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.B.; Samberg, L.H.; Yeh, E.T.; Smith, A.T.; Wenying, W.; Junbang, W. Rangeland responses to pastoralists’ grazing management on a Tibetan steppe grassland, Qinghai Province, China. Rangel. J. 2016, 38, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Fassnacht, F.E.; Storch, I.; Bürgi, M. Land-use regime shift triggered the recent degradation of alpine pastures in Nyanpo Yutse of the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 2187–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, A.D.; Pech, R.P.; Davey, C.; Jie, B.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H. Livestock grazing, plateau pikas and the conservation of avian biodiversity on the Tibetan plateau. Biol. Conserv. 2008, 141, 1972–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.K.; Zhao, X.Q.; Zhou, L.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.N.; Tang, Y.H. A study on correlations between vegetation degradation and soil degradation in the ‘alpine meadow’ of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Pratacult. Sci. 2005, 14, 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Zhan, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, E.; Gao, Y.; Li, S.; Zheng, Q.; Zhu, D.; He, Y.; et al. The linkage between vegetation and soil nutrients and their variation under different grazing intensities in an alpine meadow on the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 110, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.J.; Han, G.D.; Cui, G.W.; Zhao, M.L. Effects of grazing intensity on the biodiversity and productivity of meadow steppe. Chin. J. Ecol. 2010, 29, 862–868. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.; Dong, Q.M.; Shi-Xiong, L.I.; Hong-Tao, L.I.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.H. Impact of grazing intensities on community biodiversity and production of Alpine grassland in Qinghai lake region. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2012, 20, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.J. Effects of Different Grazing Intensities on Grassland Ecosystem Health of Leymus Chinensis Meadow Steppe; Inner Mongolia Agricultural University: Hohhot, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.G. Influence of grazing on community characteristics of alpine meadow. Guizhou Agric. Sci. 2010, 38, 128–132. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.T.; Zhang, S.H.; Chen, D.D.; Tan, Y.R.; Sun, D.S.; Du, G.Z. The effects of natural grazing intensity on plant community and soil nutrients in alpine meadow. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2010, 18, 510–516. [Google Scholar]
- Cupal, J.J.; Lacy, L.J.; Lindzey, A.F.G. GPS animal tracking system. In Proceedings of the Twelfth International Symposium Biotelemetry, Anrome, Italy, 31 August–5 September 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Turker, C.J.; Sellers, P.J. Satellite remote sensing of primary production. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1986, 7, 1395–1416. [Google Scholar]
- Schimel, D.S.; Participants, V.E.M.A.P.; Braswell, B.H. Continental scale variability in ecosystem processes: Models, data, and the role of disturbance. Ecol. Monogr. 1997, 67, 251–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, A.C.; Andrew, K.S.; Fabio, C.; Sip, V.W.; Istiak, S. Estimation of green grass/herb biomass from airborne hyperspectral imagery using spectral indices and partial least squares regression. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2007, 9, 414–424. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, M.J. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Stipa purpurea Alpine Grassland Biomass under the Grazing Disturbance in Northern Tibet. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.M.; Zhao, Y.S. Grazing intensity monitoring in Northern China steppe: Integrating CENTURY model and MODIS data. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, S. Grazing Gradient versus Restoration Succession of Leymus chinensis (Trin.) Tzvel. Grassland in Inner Mongolia. Restor. Ecol. 2008, 16, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Han, J. The study of method about monitoring grazing intensity in Xilingol rangeland using RS data. Chin. J. Grassl. 2007, 2, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. Research on a Remote Sensed-Based NPP Model and Environment Response for Semiarid Grassland Ecosystem; Institute of Remote Sensing Application Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- McNaughton, S.J. Grazing as an optimization process: Grass-ungulate relationships in the Serengeti. Am. Nat. 1979, 113, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oñatibia, G.R.; Aguiar, M.R. Continuous moderate grazing management promotes biomass production in Patagonian arid rangelands. J. Arid Environ. 2016, 125, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ri, J.; Mu, S. The Influence of Different Grazing Intensity to Typical Grassland Soil Nematodes Communites; Inner Mongolia University: Inner Mongolia, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, S.W.; Zeng, M.M.; Liu, Z.G.; Wu, W.H. The Valuation of Ecosystem Services and the Design of Policies on Ecological Management in Maqu County in the Upper Reaches of Yellow River. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2006, 16, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Huete, A.R.; Justice, C. MODIS Vegetation Index (MOD13) Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document, version 3; NASA Goddard Space Flight Centre: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.Q.; Huete, A.R. A feedback based modification of the NDVI to minimize canopy background and atmospheric noise. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 457–465. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Q.J.; Wu, G.L.; Ren, G.H. Effect of grazing intensity on characteristics of alpine meadow communities in the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2009, 18, 256–261. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.L.; Xu, P.; Meng, L.; Wang, J.H. The comprehensive effects of different rotational grazing intensities (DRGI) on the soil, grassland and sheep production in a spring-autumn pasture of sagebruch desert in the northern slope of tianshan mountain. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 1993, 2, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.H.; Guan, S.Y.; Li, Y.J. Effect of grazing capacity on water content, nutrient and biomass of steppe soil. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2000, 14, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, G.Y. The Influence of Different Grazing Intensities on the Above-Biomass and Root Distribution Character of Stipa baicalensis Grassland. Master’s Thesis, Gansu Agricultural University, Lanzhou, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Johnson, D.A.; Rong, Y. Grazing effects on soil characteristics and vegetation of grassland in northern China. Solid Earth Discuss. 2016, 7, 2283–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, F. Effects of different grazing intensities on grassland production in china: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, Z.; Akiyama, T.; Mo, W.; Fukuo, A. Modeling the spatial pattern of normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) under a post-nomadic sedentary grazing system. Acta Phytoecol. Sin. 2000, 24, 662–666. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Z. The effects of hyper spectral change on grassland biomass after damage by Callipta-mus abbreviates populations of different densities. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2015, 24, 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Tao, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Tian, L.; Zhang, Y. The spatial pattern of grassland aboveground biomass on Xizang Plateau and its climatic controls. J. Plant Ecol. 2015, 8, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Tang, Y.; Klein, J.; Zhang, P.; Gu, S.; Shimono, A.; Chen, J. Estimation of aboveground biomass using in situ hyperspectral measurements in five major grassland ecosystems on the Tibetan Plateau. J. Plant Ecol. 2008, 1, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.E.; Liu, B.K.; Guo, Z.G. Changes of forage biomass of grasslands during the growing season in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau based on MODIS data. Pratacult. Sci. 2011, 28, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, T.; Yang, S.; Feng, Q.; Liu, B.; Zhang, R.; Huang, X.; Xie, H. Multi-factor modeling of above-ground biomass in alpine grassland: A case study in the Three-River Headwaters Region, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.N.; Niu, J.M.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Dong, J.J. A discussion on applications of vegetation index for estimating aboveground biomass of typical steppe. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2012, 21, 229–238. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Huang, X.; Qin, X.; Ding, Y.; Wang, G.; Cao, G.; Nong, X.; Zhang, Z. The effect of different grazing intensities on hyper spectral remote sensing and locust abundance in typical steppe. Plant Prot. 2017, 43, 6–10, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Yi, S.; Qin, Y.; Chen, J. Habitat environment affects the distribution of plateau pikas: A study based on an unmanned aerial vehicle. Pratacult. Sci. 2017, 34, 1306–1313. [Google Scholar]
- Behnke, R.; Robinson, S.; Milnergulland, E.J. Governing open access: Livestock distributions and institutional control in the Karakum Desert of Turkmenistan. Land Use Policy 2016, 52, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, T. In search of forage: Predicting dynamic habitats of Mongolian gazelles using satellite-based estimates of vegetation productivity. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 45, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.Y.; Miura, N.; Lhagvasuren, B.; Enkhbileg, D.; Takatsuki, S.; Tsunekawa, A.; Jiang, Z. Satellite tracking of Mongolian gazelles (Procapra gutturosa) and habitat shifts in their seasonal ranges. J. Zool. 2006, 269, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmshurst, J.F.; Fryxell, J.F.; Farm, B.P.; Sinclair, A.R.E.; Henschel, C.P. Spatial distribution of Serengeti wilde beest in relation to resources. Can. J. Zool. 1999, 77, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryxell, J.M. Forage quality and aggregation by large herbivores. Am. Nat. 1991, 138, 478–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.W. The Study on Simple Estimation Method of Aboveground Biomass of Grassland. Master’s Thesis, Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, Yangling, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.X.; Zhang, W.J.; Feng, Q.S.; Meng, B.P.; Gao, J.L.; Liang, T.G. Monitoring of grassland herbage accumulation by remote sensing using MODIS daily surface reflectance data in the Qingnan region. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2016, 25, 14–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.H. Study on the Effect of the Plant Community and Soil Nutrient of Alpine Grassland on Yak Grazing Intensity. Master’s Thesis, Gansu Agricultural University, Lanzhou, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.Y.; Yan, R.R.; Yan, Y.C.; Chen, B.R.; Xin, X.P. The relationship between temperate meadow steppe soil’s biological properties and aboveground vegetation under different grazing intensities. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2014, 47, 4658–4667. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, G.M.; Wu, Q.; Li, D.; Hu, Q.W.; Li, Y.M.; Wang, X. Effects of nitrogen supply and demand status of soil and herbage system on vegetation succession and grassland degradation in alpine meadow. Chin. J. Ecol. 2004, 23, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.X.; Zhao, M.L. Influence of Overgrazing on Soil Erosion of Grassland. Grassl. China 2001, 23, 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.H.; Zhao, H.L.; Ohkuro, T.; Shirato, Y. Soil characteristics and spatial pattern of vegetation after successive grazing in Horpin Sandy Land, Inner Mongolia. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2003, 4, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.M. Reseach on the Effect of the Plant of Desert Grassland on Different Grazing Intensity. Master’s Thesis, Ningxia University, Yinchuan, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, L.; Bo, T.; Du, G.; Zheng, X. Modeling the responses of grassland vegetation coverage to grazing disturbance in an alpine meadow. Ecol. Model. 2012, 247, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Herdsmen | Distance from the Ring Entrance (m) | Relative Grazing Intensity (head·ha−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 2017 | ||
| 1 | 220 | 17.77 | 11.19 |
| 400 | 5.37 | 3.38 | |
| 700 | 1.75 | 1.10 | |
| 2 | 250 | 8.15 | 8.56 |
| 550 | 1.68 | 1.77 | |
| 850 | 0.71 | 0.74 | |
| 3 | 300 | 11.68 | 7.40 |
| 600 | 2.92 | 1.85 | |
| 1000 | 1.05 | 0.67 | |
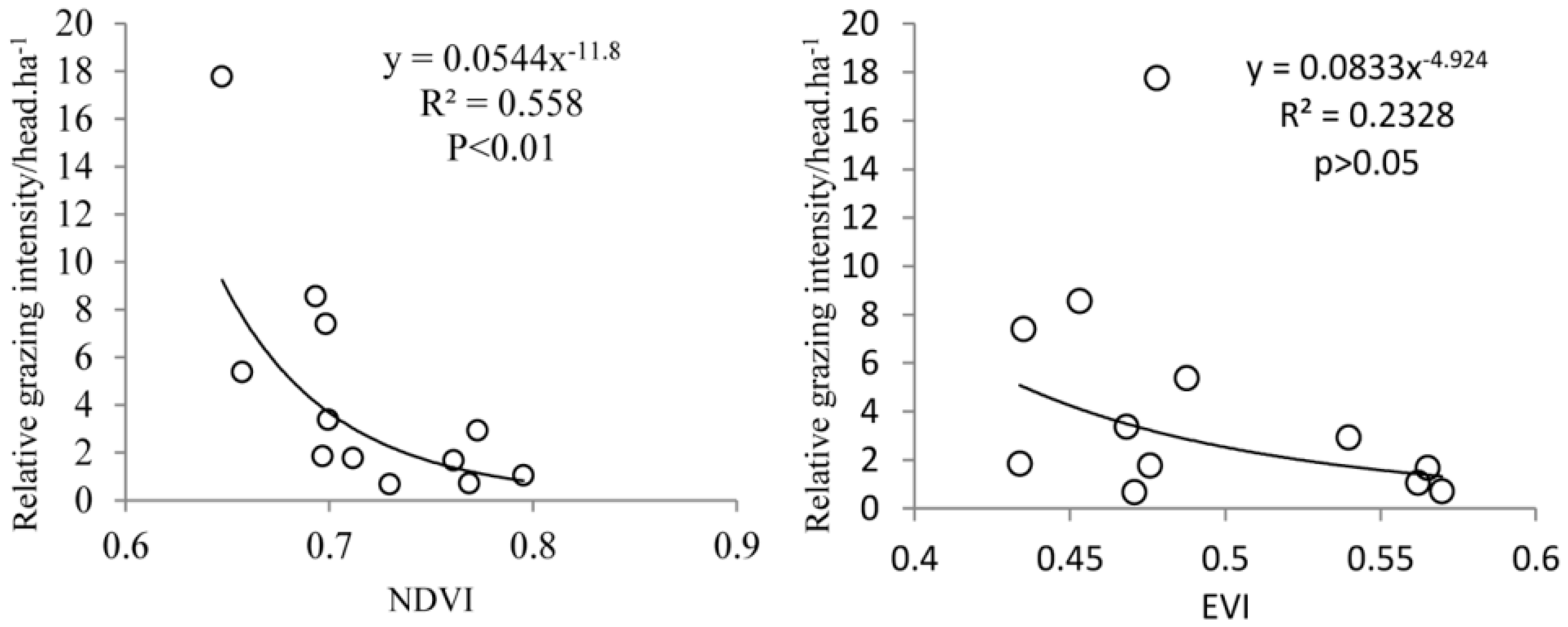
| Vegetation Index | Model | R-Squared | MAE | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI | y = 0.0544x−11.8 | 0.558 | 2.246 | 0.005 |
| EVI | y = 0.0833−4.924 | 0.233 | 2.831 | 0.112 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Q.; Chai, L.; Hou, F.; Chang, S.; Ma, Y.; Tsunekawa, A.; Cheng, Y. Quantifying Grazing Intensity Using Remote Sensing in Alpine Meadows on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Sustainability 2019, 11, 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11020417
Ma Q, Chai L, Hou F, Chang S, Ma Y, Tsunekawa A, Cheng Y. Quantifying Grazing Intensity Using Remote Sensing in Alpine Meadows on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Sustainability. 2019; 11(2):417. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11020417
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Qingqing, Linrong Chai, Fujiang Hou, Shenghua Chang, Yushou Ma, Atsushi Tsunekawa, and Yunxiang Cheng. 2019. "Quantifying Grazing Intensity Using Remote Sensing in Alpine Meadows on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau" Sustainability 11, no. 2: 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11020417
APA StyleMa, Q., Chai, L., Hou, F., Chang, S., Ma, Y., Tsunekawa, A., & Cheng, Y. (2019). Quantifying Grazing Intensity Using Remote Sensing in Alpine Meadows on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Sustainability, 11(2), 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11020417






