Tradeoff between Hydropower and River Visual Landscape Services in Mountainous Areas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
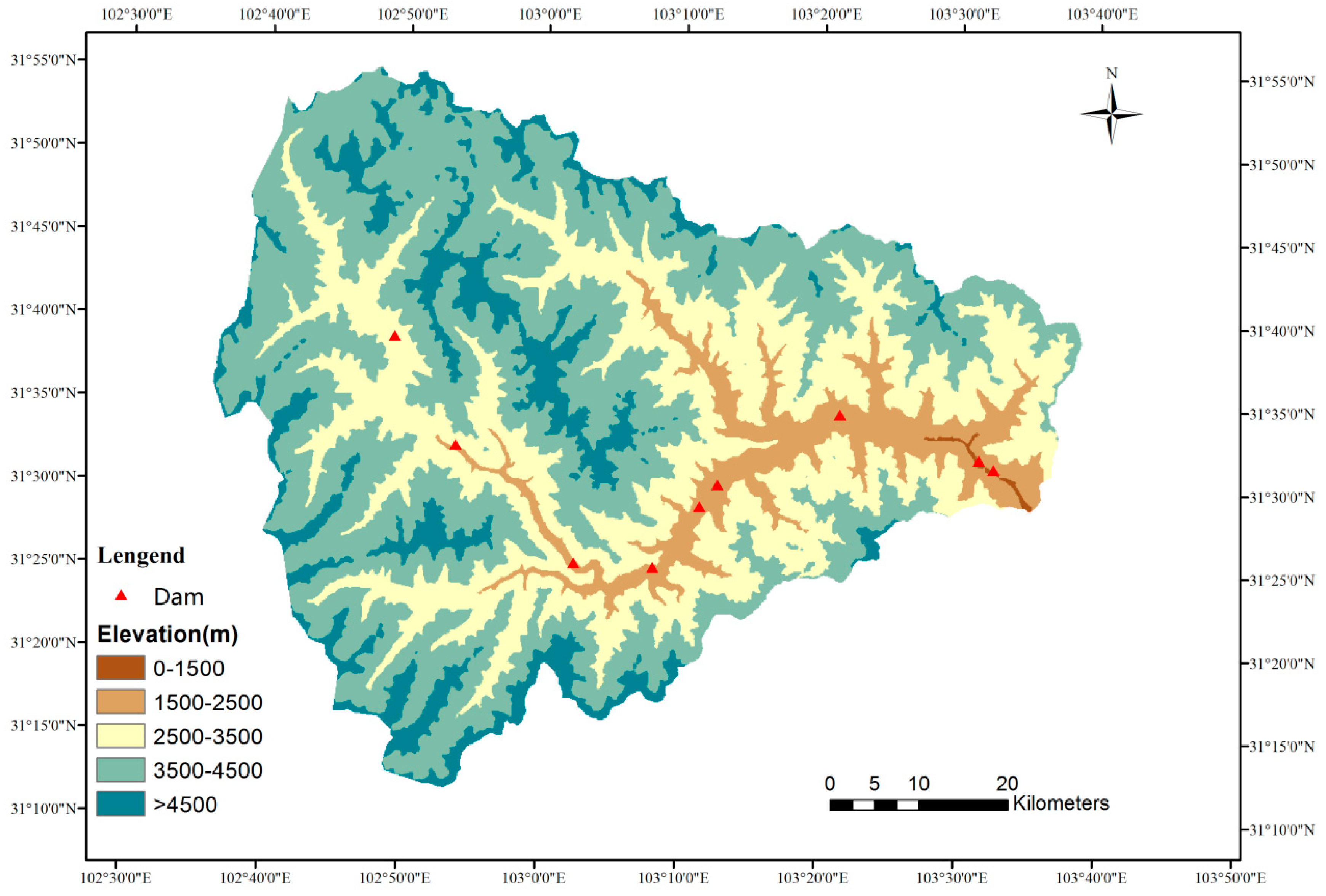
2.1. Study Area
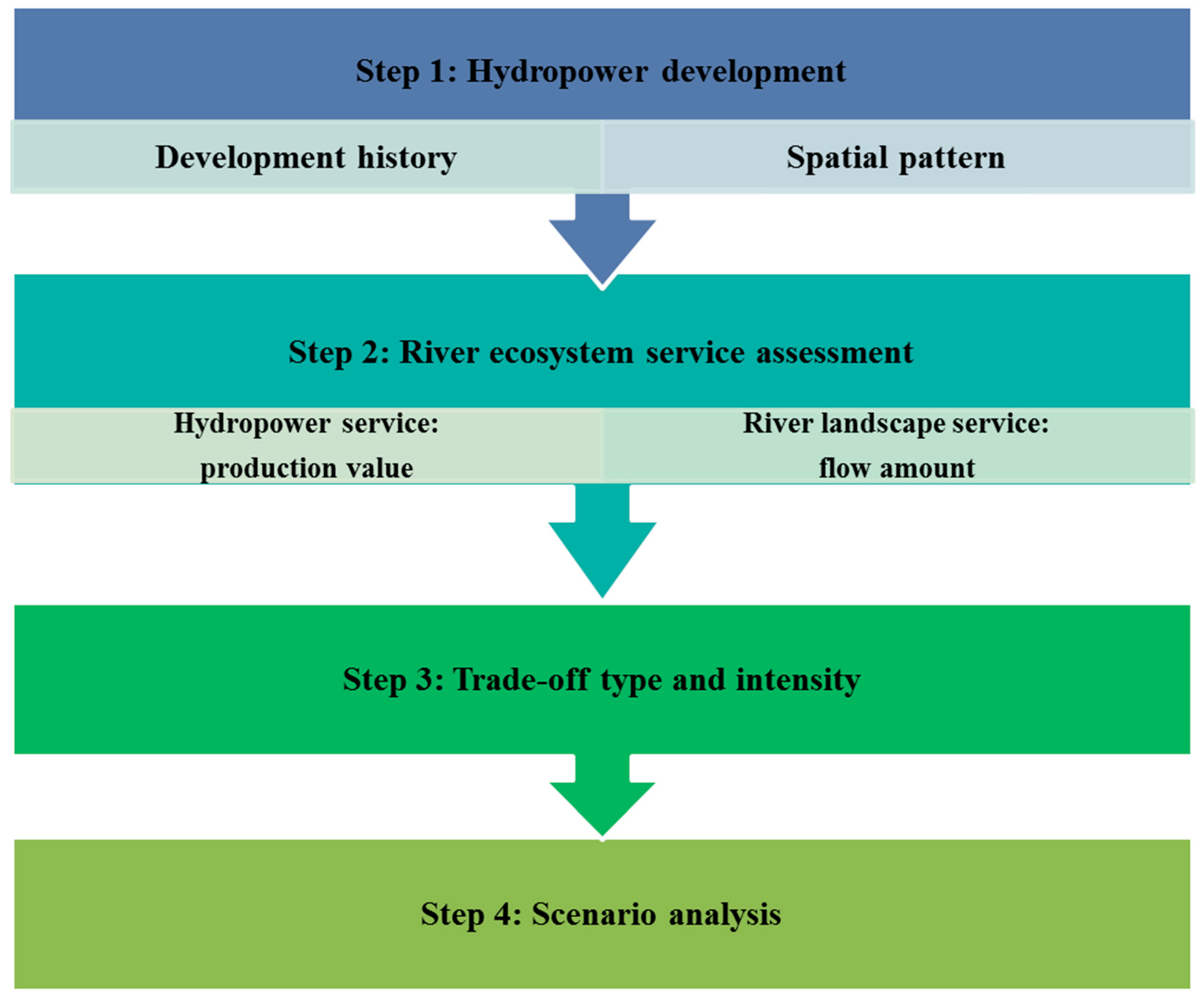
2.2. Research Framework
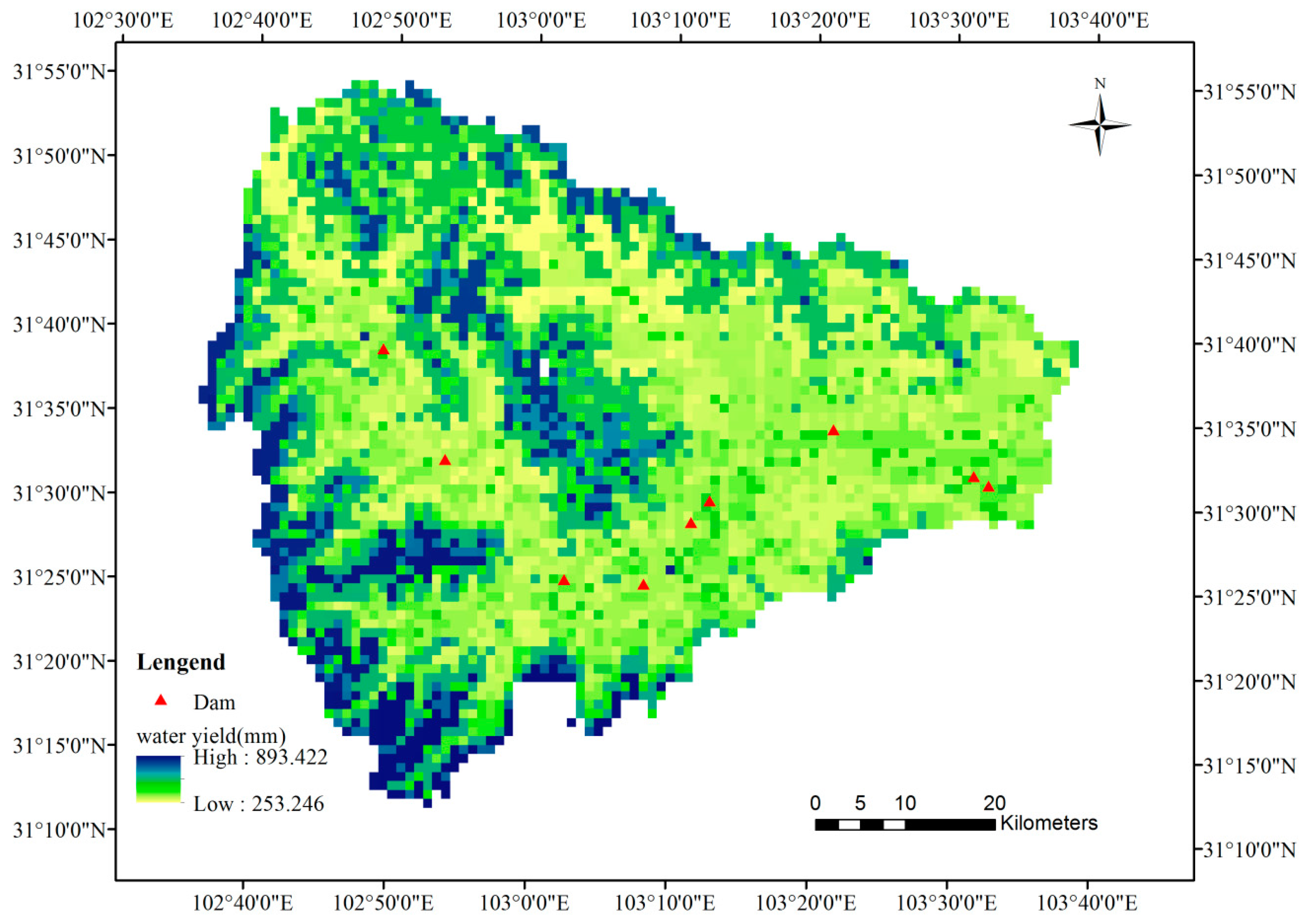
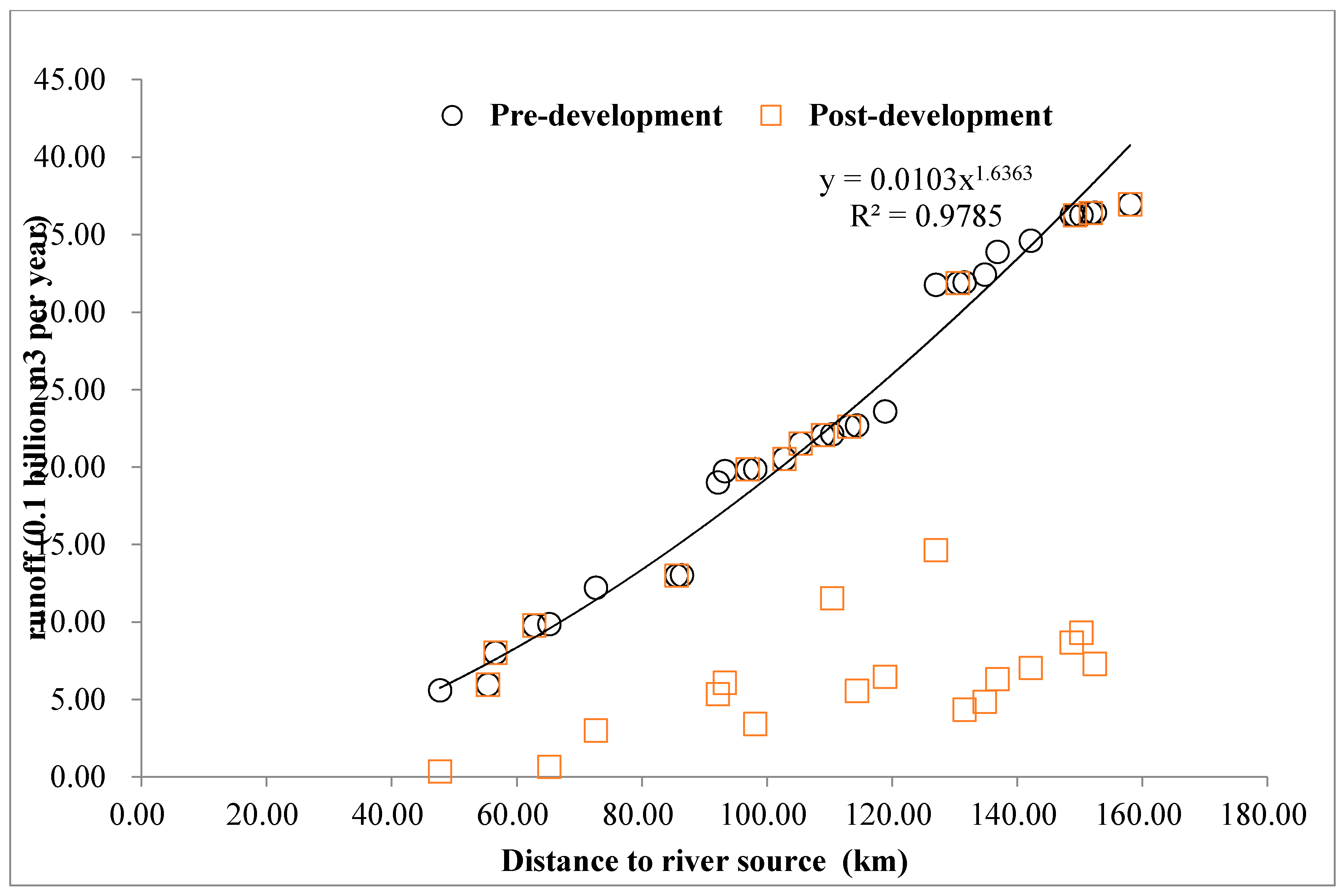
2.3. Water Retention Assessment
2.4. Valuation Hydropower Services
2.5. River Visual Landscape Services
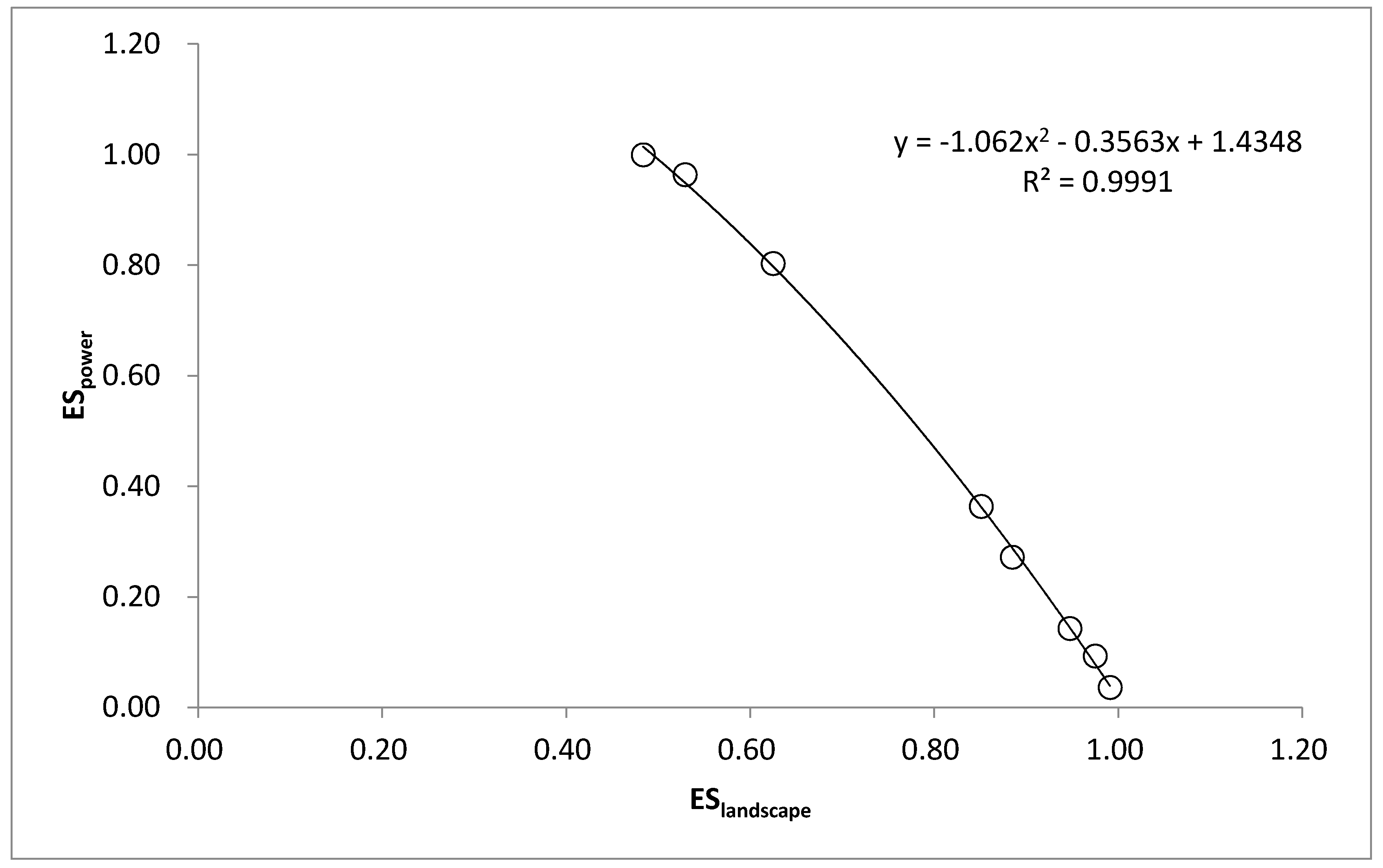
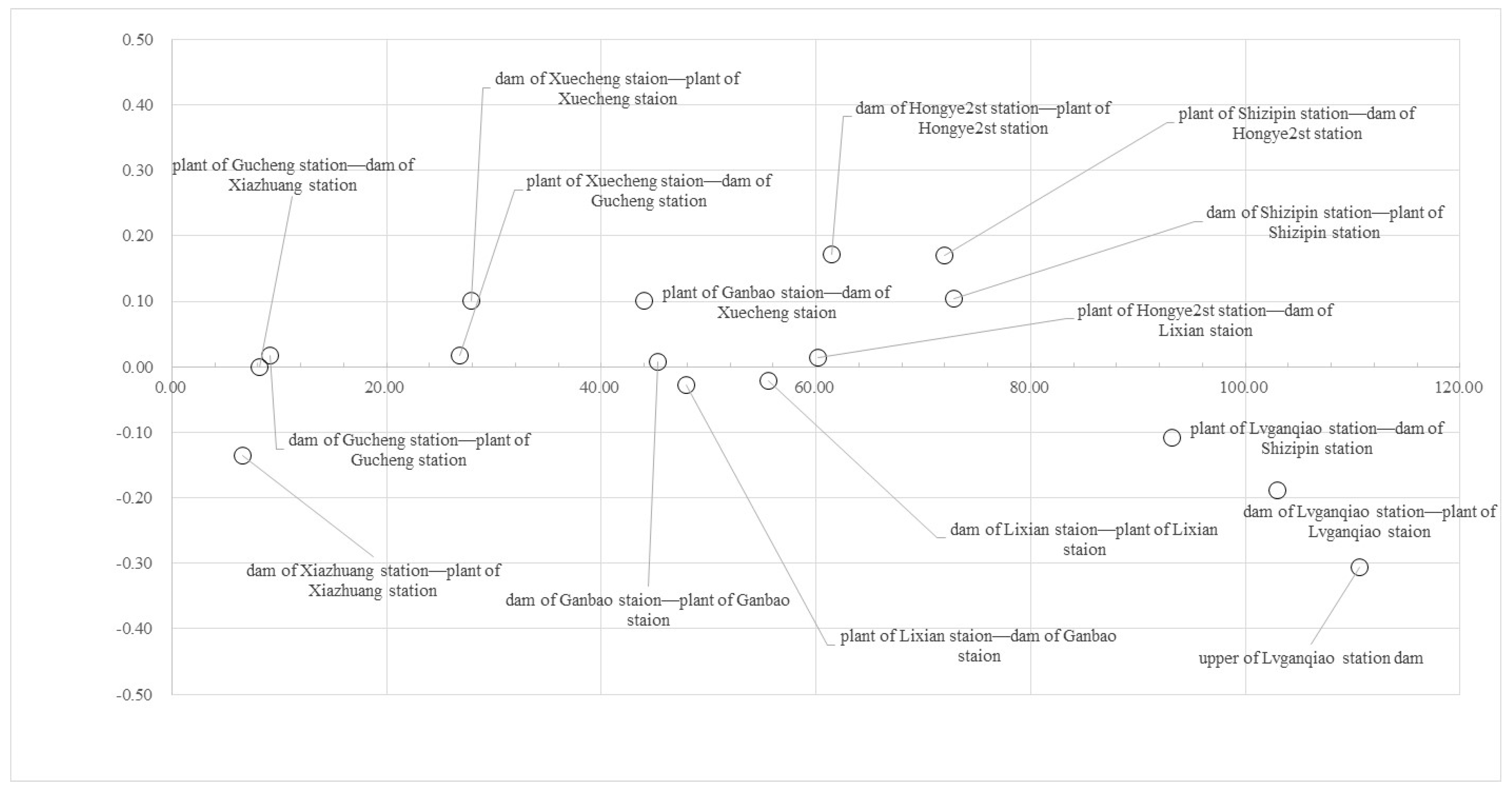
2.6. Tradeoffs
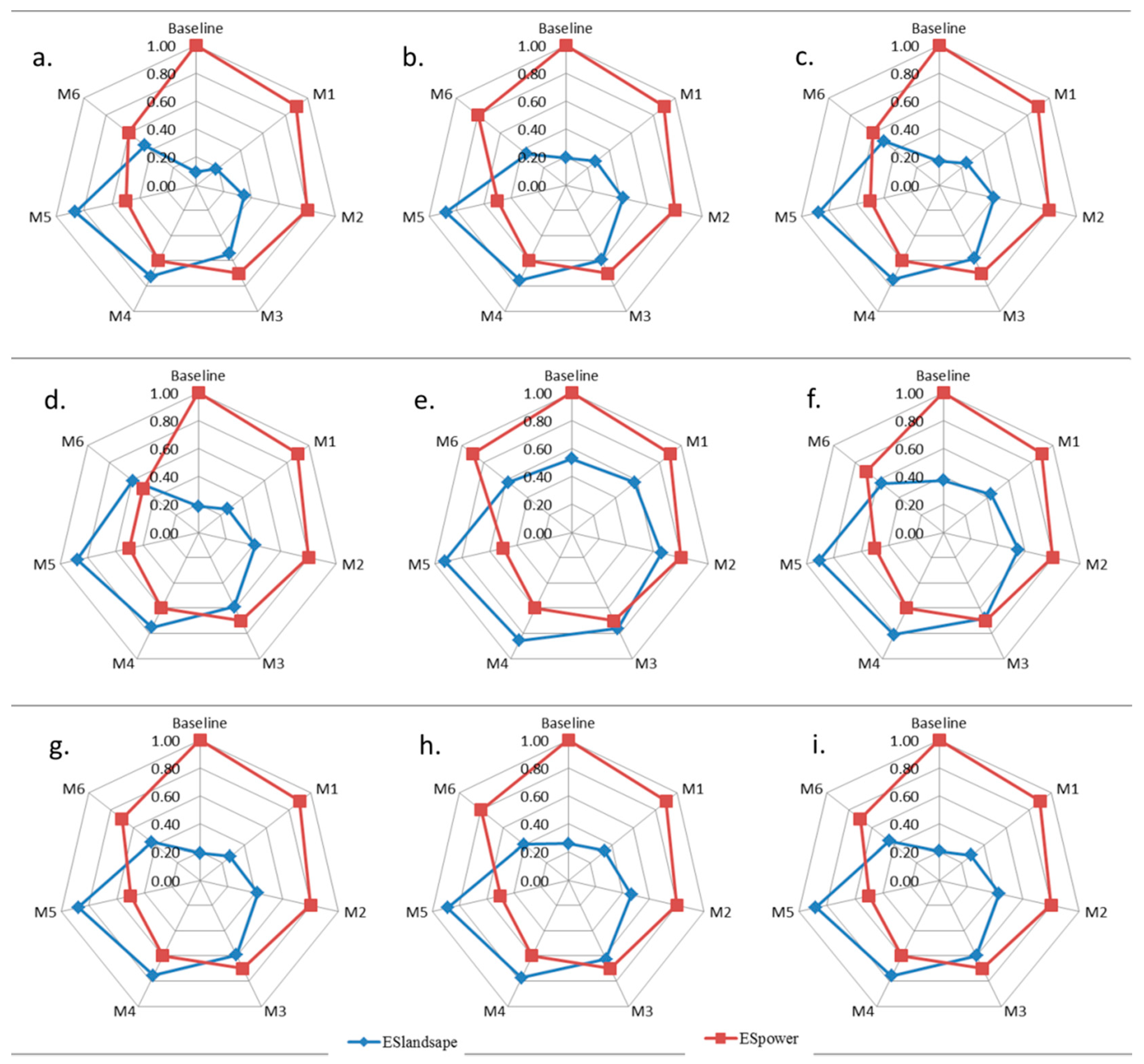
2.7. Scenario Analysis
3. Results
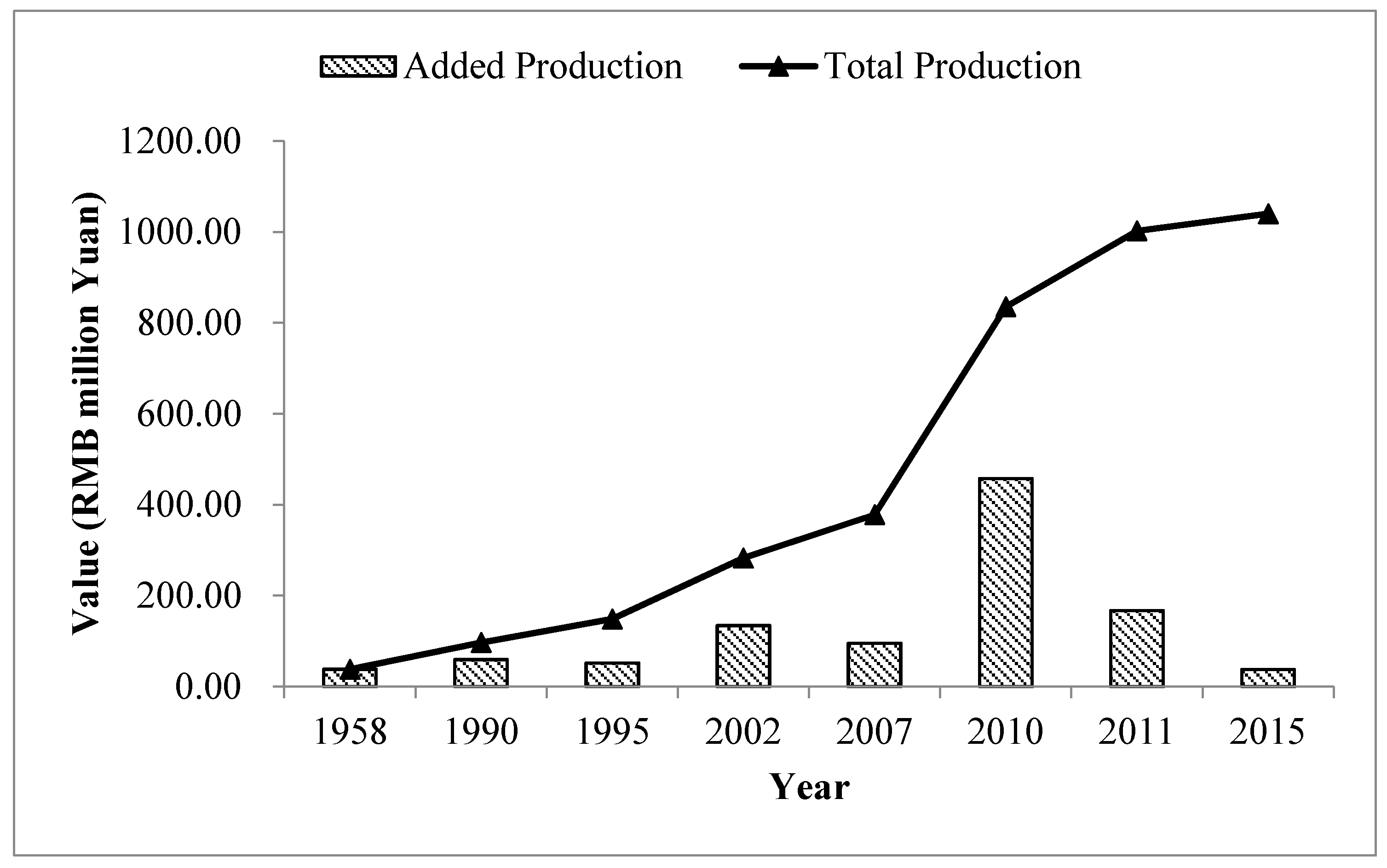
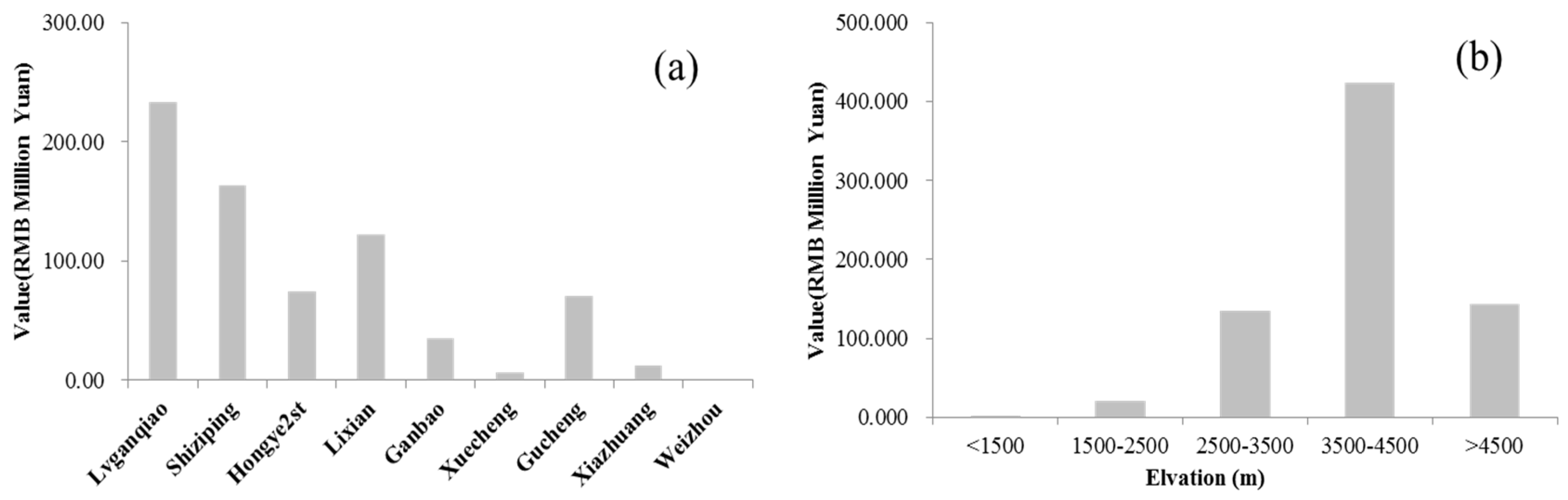
3.1. Hydropower Service
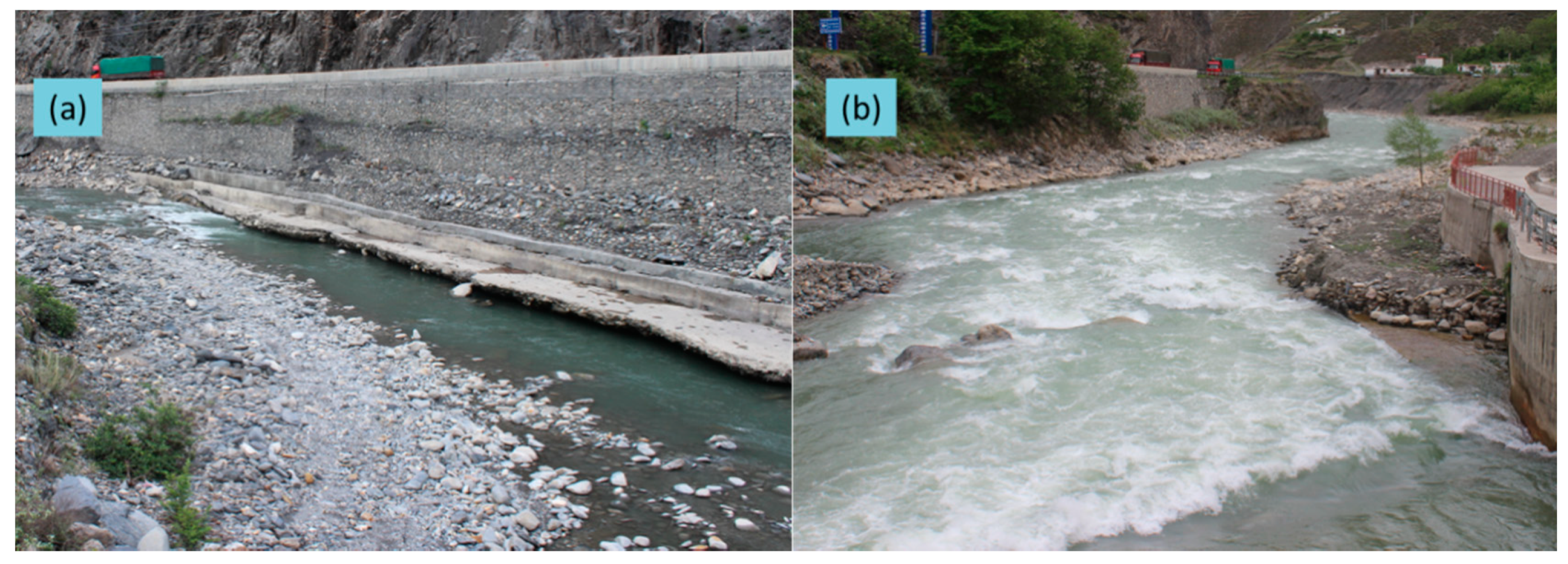
3.2. River Visual Landscape Services
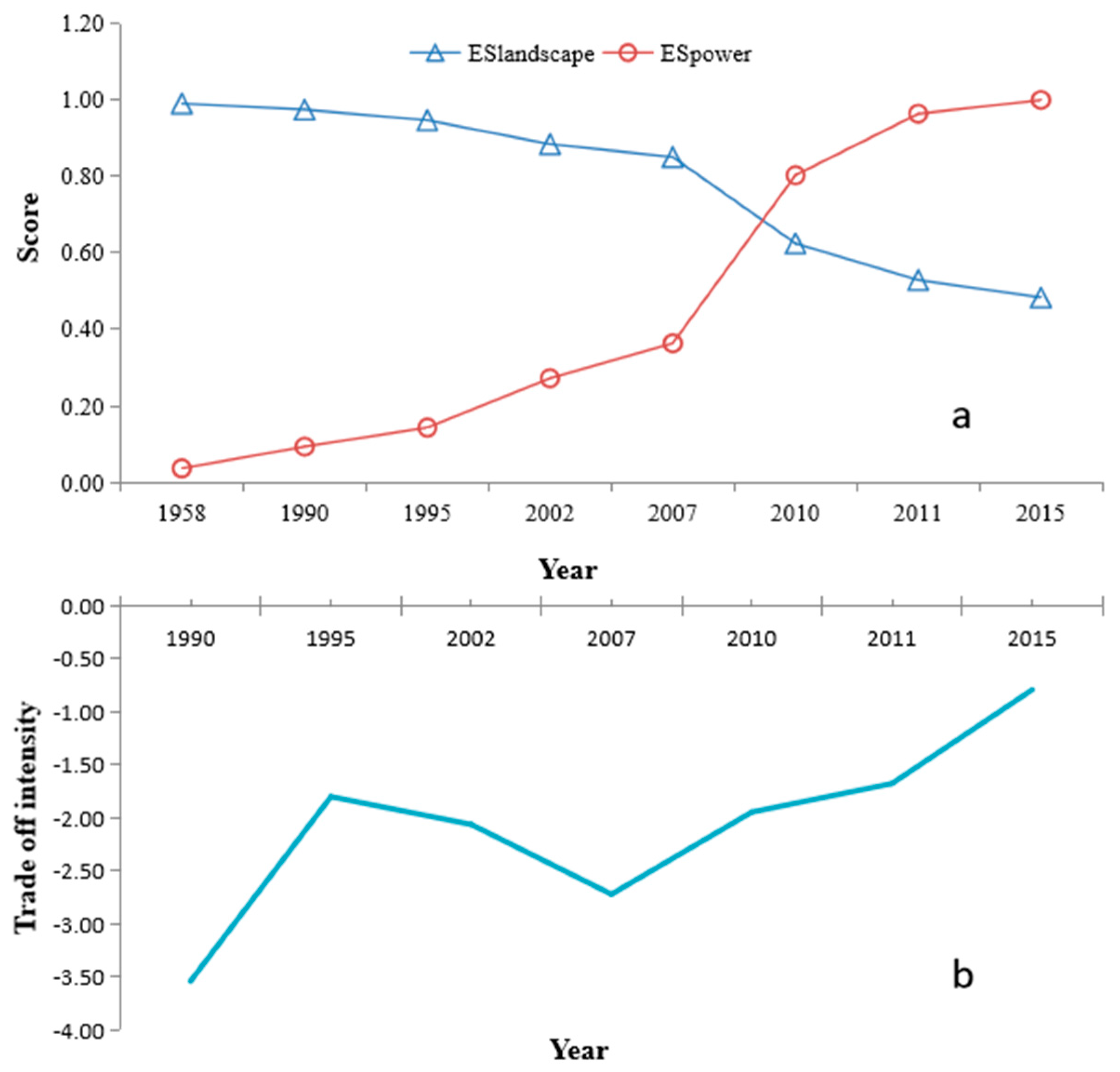
3.3. Tradeoff of the Two Services
3.4. Flow Management Scenario
4. Discussion
4.1. Tradeoff between Hydropower Service and RVLS
4.2. Policy Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daily, G.C. Nature’s Service; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- MEA. Millennium Ecosystem Assessment 2005. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Synthesis; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Jianjia, Z. Characteristic of tradeoffs between timber production and carbon storage for plantation under harvesting impact: Acasestudy of HuitongNational Research Station of Forest Ecosystem. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 73, 1085–1098. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, W. Stream Ecology: Structure and Function of Running Waters. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2010, 125, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamududu, B.; Killingtveit, A. Assessing climate change impacts on global hydropower. Energies 2012, 5, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, J.A.; Moore, R.D. Above-stream microclimate and stream surface energy exchanges in a wildfire-disturbed riparian zone. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 2369–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayyeri, H.; Zandi, S. Evaluation of the effect of river style framework on water quality: Application of geomorphological factors. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutcheson, W.; Hoagland, P.; Di, J. Valuing environmental education as a cultural ecosystem service at Hudson River Park. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 31, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermaat, J.E.; Wagtendonk, A.J.; Brouwer, R.; Sheremet, O.; Ansink, E.; Brockhoff, T.; Plug, M.; Hellsten, S.; Aroviita, J.; Tylec, L. Assessing the societal benefits of river restoration using the ecosystem services approach. Hydrobiologia 2015, 769, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.R.A.; Wong, G.Y.; Metcalfe, D.J.; Honzák, M.; Pert, P.L.; Rao, N.; Grieken, M.E.V.; Lawson, T.; Bruce, C.; Kroon, F.J. An analysis of trade-offs between multiple ecosystem services and stakeholders linked to land use and water quality management in the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 180, 176–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.P.; Beard, T.D., Jr.; Bennett, E.M.; Cumming, G.S. Trade-offs across Space, Time, and Ecosystem Services. Ecol. Soc. 2006, 11, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aillery, M.; Shoemaker, R.; Caswell, M. Agriculture and Ecosystem Restoration in South Florida: Assessing Trade-Offs from Water-Retention Development in the Everglades Agricultural Area. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2001, 83, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, S.E.; Costello, C.; Halpern, B.S.; Gaines, S.D.; White, C.; Barth, J.A. Evaluating tradeoffs among ecosystem services to inform marine spatial planning. Mar. Policy 2013, 38, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, K.G.; Odgaard, M.V.; Bøcher, P.K.; Dalgaard, T.; Svenning, J.C.; Landurbplan, J. Bundling ecosystem services in Denmark: Trade-offs and synergies in a cultural landscape. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 125, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisholm, R.A. Trade-offs between ecosystem services: Water and carbon in a biodiversity hotspot. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 1973–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvill, R.; Lindo, Z. The inclusion of stakeholders and cultural ecosystem services in land management trade-off decisions using an ecosystem services approach. Landsc. Ecol. 2016, 31, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Min, Q.; Liu, M.; Cheng, S. Ecosystem service tradeoff between traditional and modern agriculture: A case study in Congjiang County, Guizhou Province, China. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2012, 6, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divinsky, I.; Becker, N.; Bar, P. Ecosystem service tradeoff between grazing intensity and other services—A case study in Karei-Deshe experimental cattle range in northern Israel. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 24, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, W.; Halpern, B.S.; Kappel, C.V. Ecosystem service tradeoff analysis reveals the value of marine spatial planning for multiple ocean uses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 4696–4701. [Google Scholar]
- Deines, A.M.; Bee, C.A.; Katongo, C.; Jensen, R.; Lodge, D.M. The potential trade-off between artisanal fisheries production and hydroelectricity generation on the Kafue River, Zambia. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 640–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbu, I.; Lau, P.C.K. Trade-Off Decisions in Streamflow Forecasting for Multiobjective River Basins—The Ottawa River Case. Can. Water Resour. J. 1984, 9, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhuang, C.; Ouyang, Z.; Hua, Z.; Bo, J. Spatial characteristics between biodiversity and ecosystem services in a human-dominated watershed. Ecol. Complex. 2011, 8, 177–183. [Google Scholar]
- Onaindia, M.; de Manuel, B.F.; Madariaga, I.; Rodríguez-Loinaz, G. Co-benefits and trade-offs between biodiversity, carbon storage and water flow regulation. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 289, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudsepp-Hearne, C.; Peterson, G.D.; Bennett, E.M. Ecosystem service bundles for analyzing tradeoffs in diverse landscapes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5242–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, J.A.; Fallon Scura, L.; van’t Hof, T. Meeting ecological and economic goals: Marine parks in the Caribbean. AMBIO 1993, 22, 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- Bagstad, K.J.; Semmens, D.J.; Winthrop, R. Comparing approaches to spatially explicit ecosystem service modeling: A case study from the San Pedro River, Arizona. Ecosyst. Serv. 2013, 5, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.V.; Malard, F.; Tockner, K. Landscape ecology: A framework for integrating pattern and process in river corridors. Landsc. Ecol. 2002, 17, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datry, T.; Pella, H.; Leigh, C.; Bonada, N.; Hugueny, B. A landscape approach to advance intermittent river ecology. Freshw. Biol. 2016, 61, 1200–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Zhang, L.; Cong, C.; Deal, B.; Wang, Y. A dynamic and spatially explicit modeling approach to identify the ecosystem service implications of complex urban systems interactions. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 102, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuro Theta, B.M. Pedotransfer Functions for Predicting Soil Hydraulic Properties for Australia Soil; The University of Sydney: Sydney, Australia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Tallis, H.T.; Ricketts, T.; Guerry, A.D.; Wood, S.A.; Sharp, R.; Nelson, E.; Ennaanay, D.; Wolny, S.; Olwero, N.; Vigerstol, K.; et al. InVEST 2.4.1 User’s Guide; The Natural Capital Project, Stanford: Stanford, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Grêt-Regamey, A.; Brunner, S.H.; Kienast, F. Mountain Ecosystem Services: Who Cares? Mt. Res. Dev. 2012, 32, S23–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauman, K.A.; Daily, G.C.; Duarte, T.K.E.; Mooney, H.A. The Nature and Value of Ecosystem Services: An Overview Highlighting Hydrologic Services. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2007, 32, 67–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.X.; Xie, G.D.; Cheng, S.K. Economic Evaluation of River Ecosystem Service in Recreation. Resour. Sci. 2001, 23, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Mach, M.E.; Martone, R.G.; Chan, K.M.A. Human impacts and ecosystem services: Insufficient research for trade-off evaluation. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015, 16, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yue, T.; Xinsheng, C.; Feng, L.; Zhengmiao, D. The impact of Three Gorges Dam on the downstream eco-hydrological environment and vegetation distribution of East Dongting Lake. Ecohydrology 2015, 8, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloranta, A.P.; Finstad, A.G.; Helland, I.P.; Ugedal, O.; Power, M. Hydropower impacts on reservoir fish populations are modified by environmental variation. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intralawan, A.; Wood, D.; Frankel, R.; Costanza, R.; Kubiszewski, I. Tradeoff analysis between electricity generation and ecosystem services in the Lower Mekong Basin. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 30, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Wang, Y.K.; Xu, P.; Yan, K.; Li, M. Value of ecosystem hydropower service and its impact on the payment for ecosystem services. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, E.; Mendoza, G.; Regetz, J.; Polasky, S.; Tallis, H.; Cameron, D.R.; Chan, K.M.A.; Daily, G.C.; Goldstein, J.; Kareiva, P.M. Modeling Multiple Ecosystem Services, Biodiversity Conservation, Commodity Production, and Tradeoffs at Landscape Scales. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2009, 7, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrouse, B.C.; Semmens, D.J.; Ancona, Z.H.; Brunner, N.M. Analyzing land-use change scenarios for trade-offs among cultural ecosystem services in the Southern Rocky Mountains. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 26, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukoski, J.J.; Broadhead, J.S.; Donato, D.C.; Murdiyarso, D.; Gregoire, T.G. The Use of Mixed Effects Models for Obtaining Low-Cost Ecosystem Carbon Stock Estimates in Mangroves of the Asia-Pacific. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagstad, K.J.; Johnson, G.W.; Voigt, B.; Villa, F. Spatial dynamics of ecosystem service flows: A comprehensive approach to quantifying actual services. Ecosyst. Serv. 2013, 4, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, N.; Tsigaris, P. Illustrating Environmental Issues by Using the Production-Possibility Frontier: A Classroom Experiment. J. Econ. Edu. 2011, 42, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ager, A.A.; Day, M.A.; Vogler, K. Production possibility frontiers and socioecological tradeoffs for restoration of fire adapted forests. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 176, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Deng, X.; Wu, F.; Hasan, S. Scenario Analysis for Water Resources in Response to Land Use Change in the Middle and Upper Reaches of the Heihe River Basin. Sustainability 2015, 7, 3086–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, P.A. Growth, degrowth and climate change: A scenario analysis. Ecol. Econ. 2012, 84, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, G.; Feng, L.; Hui, G.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, X. The impact of land-use change on water-related ecosystem services: A study of the Guishui River Basin, Beijing, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 163, 148–155. [Google Scholar]
- Bouguerra, S.; Jebari, S. Identification and prioritization of sub-watersheds for land and water management using InVEST SDR model: Rmelriver basin, Tunisia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentelhas, P.C.; Gillespie, T.J.; Santos, E.A. Evaluation of FAO Penman-Monteith and alternative methods for estimating reference evapotranspiration with missing data in Southern Ontario, Canada. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.S.; Allen, R.G.; Smith, M.; Raes, D. Crop evapotranspiration estimation with FAO56: Past and future. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 147, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, G.S. Evapotranspiration characteristics and crop coefficient of rain-fed maize agroecosystem. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2010, 21, 647–653. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.Q.; Cai, H.J.; Wang, J. Experimental Study on Crop Coefficient of Maize in Guanzhong Region of Shaanxi Province. Water Sav. Irrig. 2011, 12, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Sharp, R.; Tallis, H.T.; Ricketts, T.; Guerry, A.D.; Wood, S.A.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Nelson, E.; Ennaanay, D.; Wolny, S.; Olwero, N.; et al. InVEST User’s Guide; The Natural Capital Project, Stanford: Stanford, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, M.G.E.; Bennett, E.M.; Gonzalez, A. Linking Landscape Connectivity and Ecosystem Service Provision: Current Knowledge and Research Gaps. Ecosystems 2013, 16, 894–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Jing, L.I.; Xin, F.U.; Xingmin, M.U.; Ting, L.I. Trade-offs between carbon sequestration, soil retention and water yield in the Guanzhong-Tianshui Economic Region of China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1449–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziv, G.; Baran, E.; Nam, S.; Rodrígueziturbe, I.; Levin, S.A. Trading-off fish biodiversity, food security, and hydropower in the Mekong River Basin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5609–5614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winemiller, K.O.; Mcintyre, P.B.; Castello, L.; Fluetchouinard, E.; Giarrizzo, T.; Nam, S.; Baird, I.G.; Darwall, W.; Lujan, N.K.; Harrison, I. Balancing hydropower and biodiversity in the Amazon, Congo, and Mekong. Science 2016, 351, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B. Great Policy Benefits for the Hydropower Development in China. Hydropower New Energy 2018, 32, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, M.; Jorde, K.; Buffington, J.M.; Tullos, D.; Tilt, B.; Liermann, C.R. Application of a hierarchical framework for assessing environmental impacts of dam operation: Changes in streamflow, bed mobility and recruitment of riparian trees in a western North American river. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, S224–S236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahrenkamp-Uppenbrink, J. Reducing the ecosystem impacts of dams. Science 2016, 353, 1109–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L.; Olden, J.D. Can dams be designed for sustainability? Science 2017, 358, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bednarek, A.T. Undamming rivers: A review of the ecological impacts of dam removal. Environ. Manag. 2001, 27, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurford, A.P.; Huskova, I.; Harou, J.J. Using many-objective trade-off analysis to help dams promote economic development, protect the poor and enhance ecological health. Environ. Sci. Policy 2014, 38, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharrazi, A.; Akiyama, T.; Yu, Y.; Li, J. Evaluating the evolution of the Heihe River basin using the ecological network analysis: Efficiency, resilience, and implications for water resource management policy. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Vorste, R.; Mermillod-Blondin, F.; Hervant, F.; Mons, R.; Forcellini, M.; Datry, T. Increased depth to the water table during river drying decreases the resilience of Gammarus pulex and alters ecosystem function. Ecohydrology 2016, 9, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Shao, Q.; Liu, J. Forest restoration to achieve both ecological and economic progress, Poyang Lake basin, China. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 44, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, W.D.; Wlodarz, M. Ecosystems, Ecological Restoration, and Economics: Does Habitat or Resource Equivalency Analysis Mean Other Economic Valuation Methods Are Not Needed? AMBIO 2013, 42, 628–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berga, L. The Role of Hydropower in Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation: A Review. Engineering 2016, 2, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demarty, M.; Bastien, J. GHG emissions from hydroelectric reservoirs in tropical and equatorial regions: Review of 20 years of CH emission measurements. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 4197–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, Y.; Xu, L.; Yang, Z. Ecological compensation for inundated habitats in hydropower developments based on carbon stock balance. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 114, 334–342. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Page, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S.; Cong, C.; Destouni, G.; Kalantari, Z.; Deal, B.M. Using comparative socio-ecological modeling to support Climate Action Planning (CAP). J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Power Station | Scenario | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 | M6 | |
| Lvganqiao | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 40 |
| Shiziping | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 20 |
| Hongye 2nd | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 40 |
| Lixian | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 50 |
| Ganbao | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 10 |
| Xuecheng | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 30 |
| Gucheng | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 30 |
| Xiazhuang | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 20 |
| Weizhou | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 30 |
| No | Station | Annual Production (RMB Million Yuan) | Annual Flow Extracted (108 m3) | Efficiency (Yuan/m3) | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Luganqiao | 37.47 | 5.25 | 0.07 | 5 |
| 2 | Shiziping | 238.46 | 9.22 | 0.26 | 1 |
| 3 | Hongye 2nd | 134.21 | 13.66 | 0.10 | 2 |
| 4 | Lixian | 51.84 | 16.46 | 0.03 | 8 |
| 5 | Ganbao | 59.04 | 10.59 | 0.06 | 6 |
| 6 | Xuecheng | 167.04 | 17.13 | 0.10 | 3 |
| 7 | Gucheng | 218.88 | 27.58 | 0.08 | 4 |
| 8 | Xiazhuang | 37.78 | 26.96 | 0.01 | 9 |
| 9 | Weizhou | 95.27 | 29.14 | 0.03 | 7 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, B.; Li, N. Tradeoff between Hydropower and River Visual Landscape Services in Mountainous Areas. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5509. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11195509
Fu B, Li N. Tradeoff between Hydropower and River Visual Landscape Services in Mountainous Areas. Sustainability. 2019; 11(19):5509. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11195509
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Bin, and Naiwen Li. 2019. "Tradeoff between Hydropower and River Visual Landscape Services in Mountainous Areas" Sustainability 11, no. 19: 5509. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11195509
APA StyleFu, B., & Li, N. (2019). Tradeoff between Hydropower and River Visual Landscape Services in Mountainous Areas. Sustainability, 11(19), 5509. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11195509





