A Review on Ecosystem Health Research: A Visualization Based on CiteSpace
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
2.1. Data Acquisition
2.2. CiteSpace
2.3. Co-Citation Analysis
2.4. Keyword Co-Occurrence Analysis
3. Results
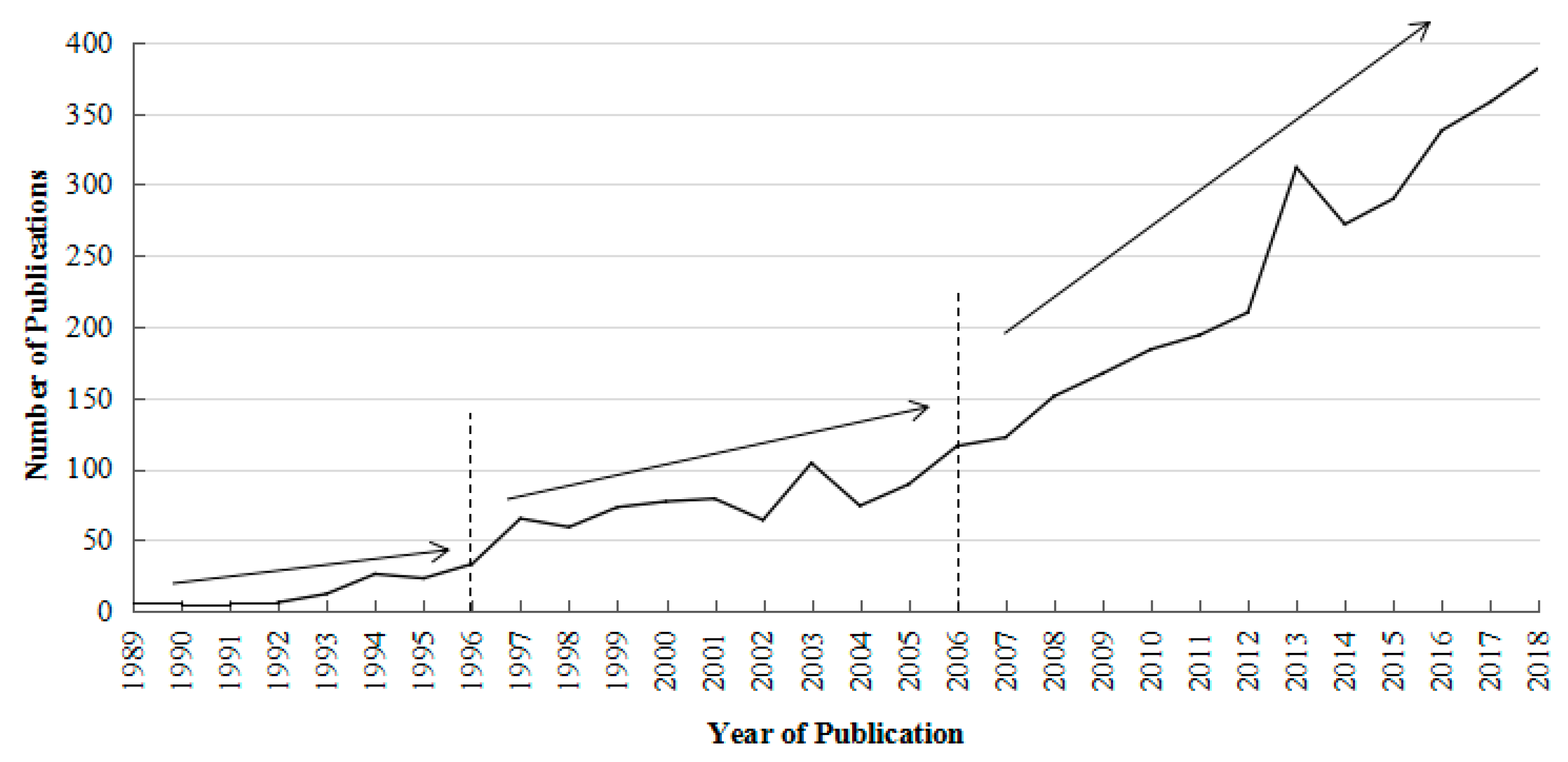
3.1. Annual Variations of Publications and Their Categories
- (1)
- Initial phase (1989–1996). Published papers prior to 1996 for each year were below 40, and increased in frequency slowly. The formation of the First International Workshop on Ecosystem Health and the International Society for Ecosystem Health (ISEH), followed by the publication of the first graduate textbook on ecosystem health, made scholars begin to pay attention to the concept and the importance of ecosystem health, and conduct relevant research.
- (2)
- Development phase (1996–2006). The annual number of published papers increased gradually and fluctuated until 2006. The reason might be related to influential international conferences, symposium, and publications, such as the First Eco-summit, co-convened by D. Rapport and S. E. Jorgensen, the Indo-Pacific Conference on Ecosystem Health, sponsored by Edith Cowan University, and the publication of Managing for Healthy Ecosystems.
- (3)
- Rapid-development phase (2006–2018). Correspondingly, published papers for each year have been increasing rapidly after 2006. This might be relevant to the background of environmental stress and deterioration, resulting from populations’ increasing and growing economies, along with EcoHealth Conferences sponsored by scholars focused on the intersection of health and ecology [1]. Achieving a condition that can reflect a healthy ecosystem is an ongoing global priority for governments, scientists, and managers [29]. Following this, scholars have been paying increasing attention to this research area.
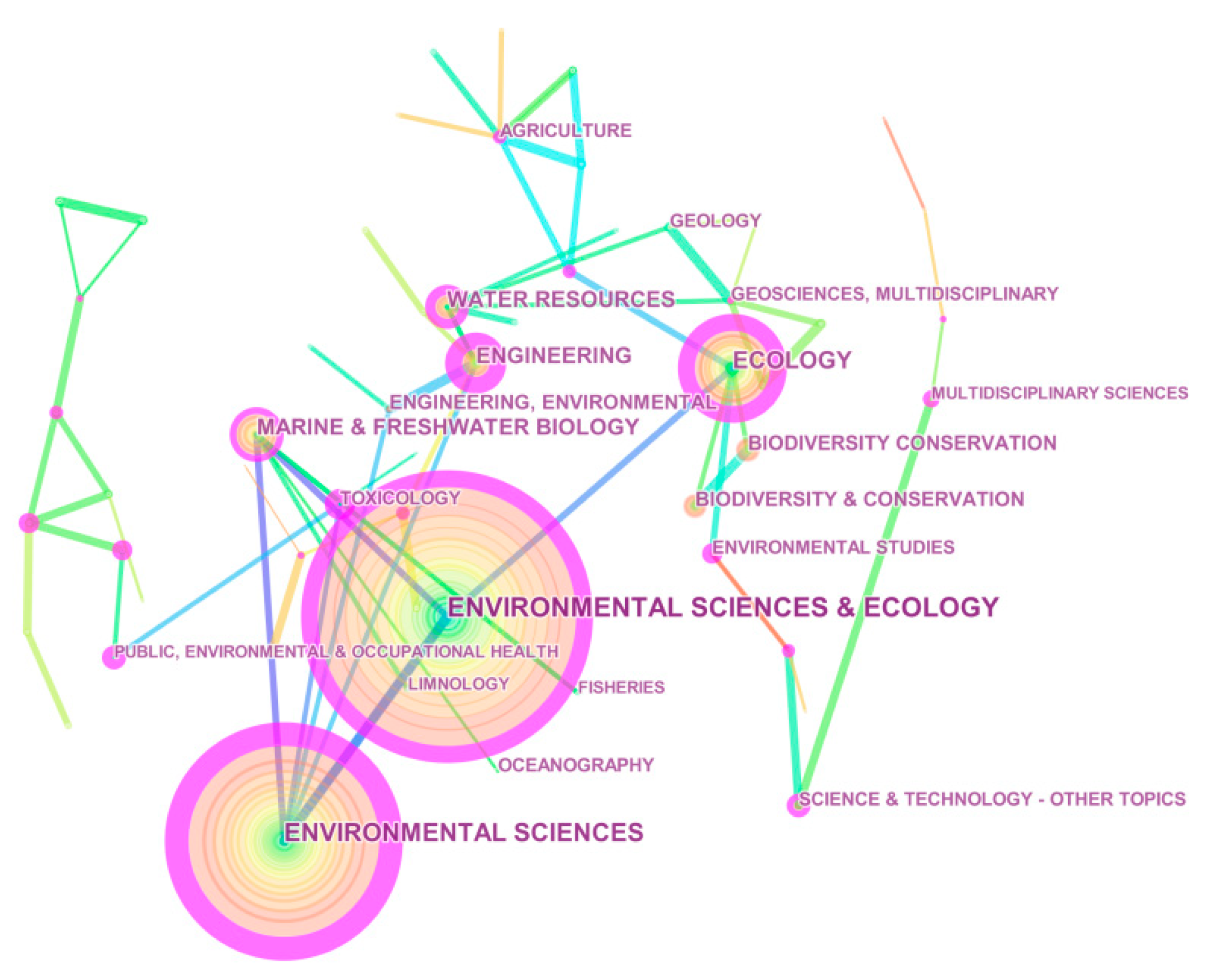
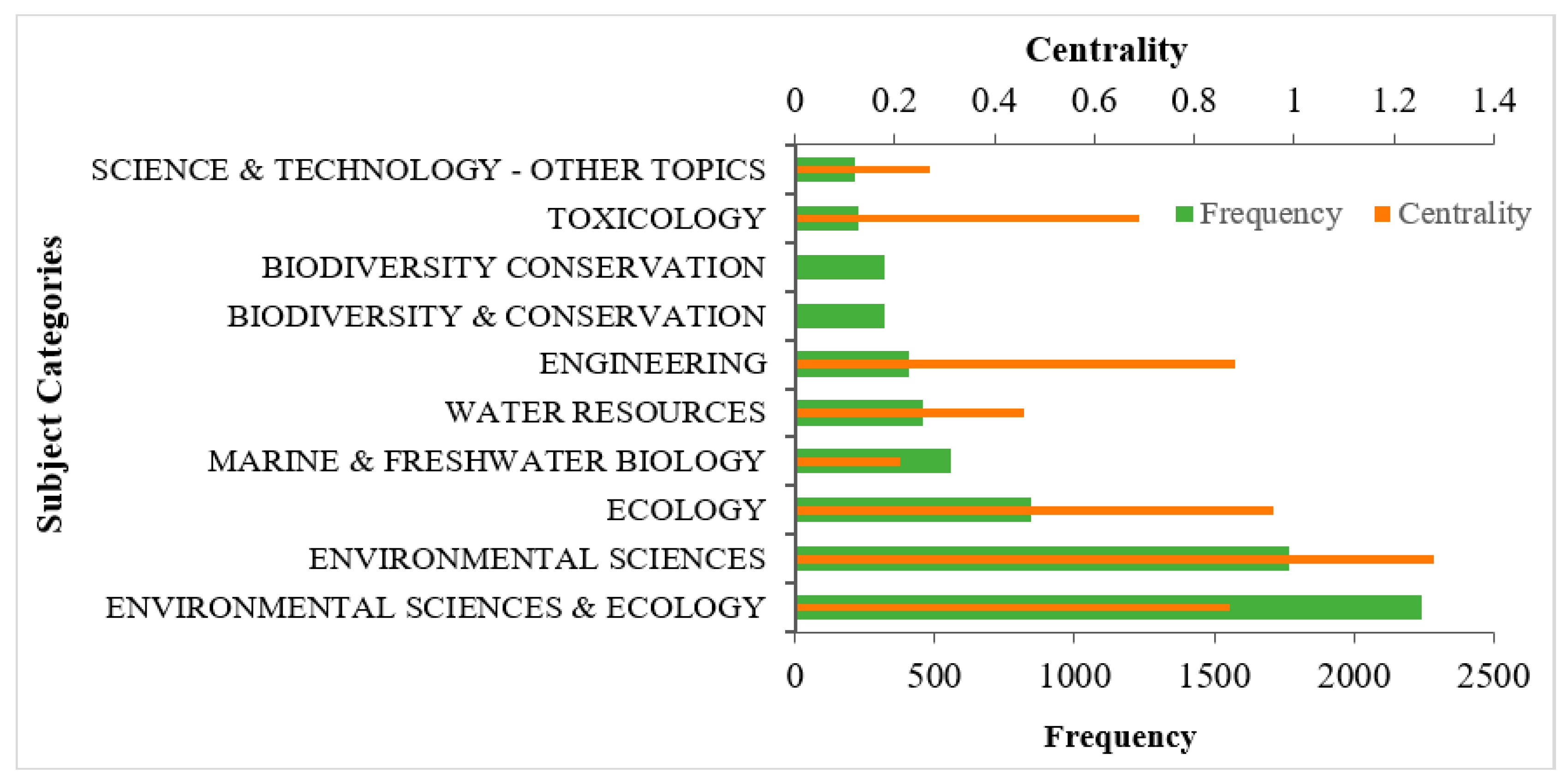
- (1)
- Environmental sciences & ecology, the largest node with a frequency of 2241 (Figure 3), is the most popular subject category, followed by environmental sciences (1768), ecology (844), marine & freshwater biology (556), and water resources (460), which signifies scholars in the field are most concerned about the environmental, ecological, and water-resource aspects.
- (2)
- Among the top 10 most frequently appearing subject categories, environmental sciences has the highest centrality, which means environmental sciences plays an important pivotal role in ecological health and it is the key connection hub in communicating different subjects in the area. Ecology comes second, followed by engineering, and environmental sciences & ecology. Thus, environmental sciences, ecology, and engineering have an intermediary role, and play a critical role in the research of the network structure.
- (3)
- According to the circles’ colors, we can judge the age of the research subjects. As we can see, the earliest studies on ecological health were mainly in environmental sciences & ecology, and environmental sciences, which have blue inner circles. In addition, relatively new areas, such as marine and freshwater biology, and engineering, have yellow inner circles. Thus, ecological-health research is multifaceted and covers quite a wide range of interests, from environmental science and water, to engineering, biodiversity, and toxicology.
3.2. Co-Citation Analysis of Ecosystem Health Research
3.2.1. Author Co-Citation Analysis
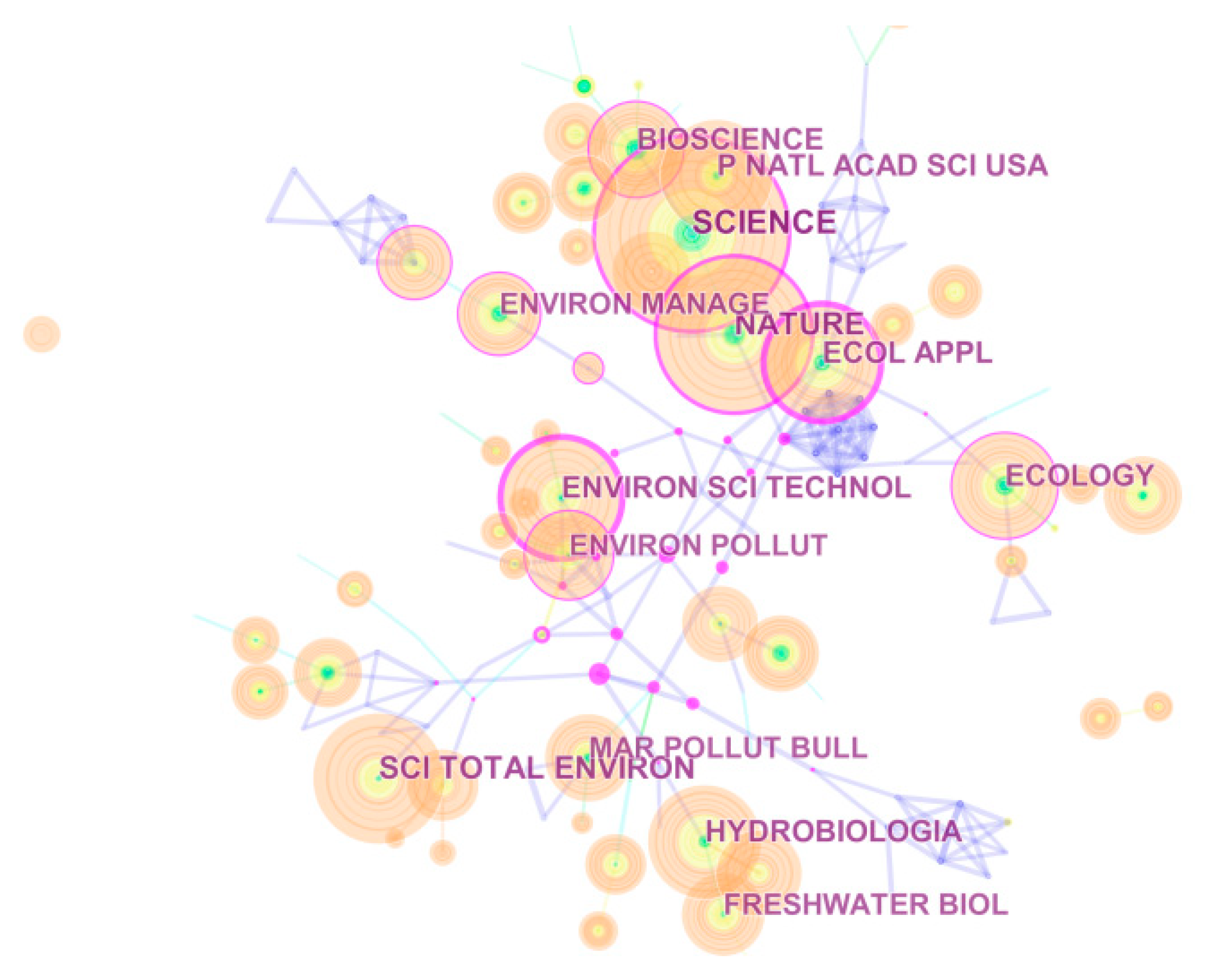
3.2.2. Journal Co-Citation Analysis
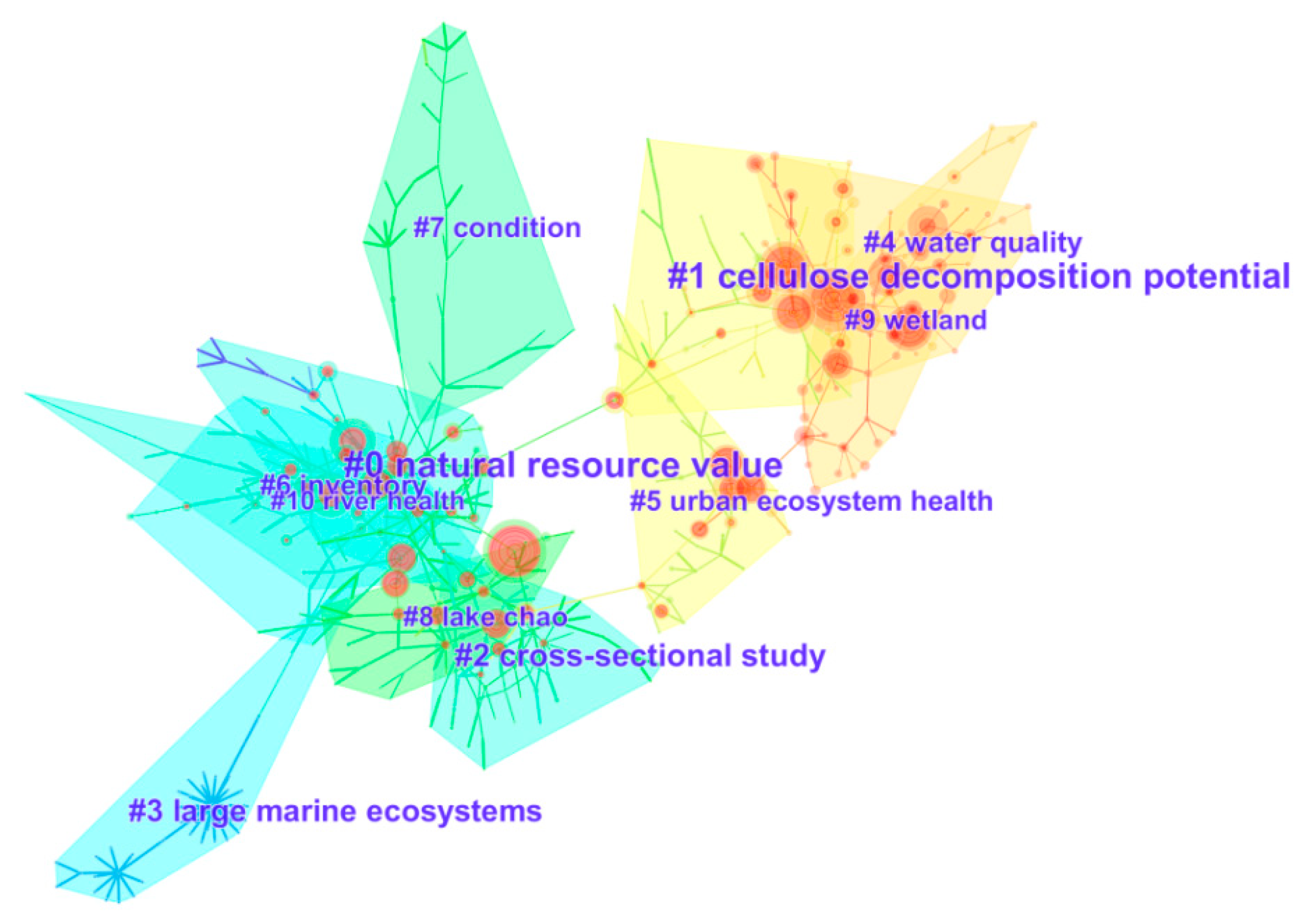
3.2.3. Cluster Analysis
3.2.4. Landmark References
3.3. Emerging Ecosystem Health Trends
3.3.1. References with Citation Bursts
3.3.2. Keyword Co-Occurrence Analysis
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rapport, D.J.; Maffi, L. Eco-cultural health, global health, and sustainability. Ecol. Res. 2011, 26, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, M.S.; Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Hintz, W.D.; Dyack, B.; Birk, S.; Relyea, R.A. Regulations are needed to protect freshwater ecosystems from salinization. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2018, 374, 20180019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costanza, R. Toward an operational definition of ecosystem health. Ecosyst. Health New Goals Environ. Manag. 1992, 239, 269. [Google Scholar]
- Mageau, M.T. The development and initial testing of a quantitative assessment of ecosystem health. Ecosyst. Health 1995, 1, 201–213. [Google Scholar]
- Rapport, D.; Böhm, G.; Buckingham, D.; Cairns, J.; Costanza, R.; Karr, J.; De Kruijf, H.; Levins, R.; McMichael, A.; Nielsen, N. Ecosystem health: The concept, the ISEH, and the important tasks ahead. Ecosyst. Health 1999, 5, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tett, P.; Gowen, R.; Painting, S.; Elliott, M.; Forster, R.; Mills, D.; Bresnan, E.; Capuzzo, E.; Fernandes, T.; Foden, J. Framework for understanding marine ecosystem health. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 494, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, A.; Townsend, K.; Hale, R.; Sharley, D.; Pettigrove, V. How is ecosystem health defined and measured? A critical review of freshwater and estuarine studies. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, D.; Guo, X. Remote sensing of ecosystem health: Opportunities, challenges, and future perspectives. Sensors 2014, 14, 21117–21139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Fath, B.D.; Yang, Z. Urban ecosystem health assessment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 2425–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingers, J.; Leydesdorff, L. A review of theory and practice in scientometrics. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 246, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Staab, S.; Studer, R.; Schnurr, H.-P.; Sure, Y. Knowledge processes and ontologies. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2001, 16, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Song, I.-Y.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, J. The thematic and citation landscape of data and knowledge engineering (1985–2007). Data Knowl. Eng. 2008, 67, 234–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.-H.; Liu, L.-G. A study on the evolution of carbon capture and storage technology based on knowledge mapping. Energies 2018, 11, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Xu, C. Mapping research on carbon emissions trading: A co-citation analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 74, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. Science mapping: A systematic review of the literature. J. Data Inf. Sci. 2017, 2, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Hou, L.; Shi, T.; Gui, Q. A review of urban planning research for climate change. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X. Land use policy as an instrument of rural resilience–The case of land withdrawal mechanism for rural homesteads in China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 87, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.X.; Tong, P.S. Ananalysis of ecological security of the urban agglomeration development trend based on Cite Space econometric analysis. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 8234–8246. [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer, D.J.; Herricks, E.E.; Kerster, H.W. Ecosystem health: I. Measuring ecosystem health. Environ. Manag. 1988, 12, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapport, D.J. What constitutes ecosystem health? Perspect. Biol. Med. 1989, 33, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Yin, J.; Wu, B. Climate change and tourism: A scientometric analysis using CiteSpace. J. Sustain. Tour. 2017, 26, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. Searching for intellectual turning points: Progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 5303–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, C. CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2006, 57, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sun, Y.P.; Gao, X.L.; Sui, Y. Knowledge domain and emerging trends in Alzheimer’s disease: A scientometric review based on CiteSpace analysis. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 1643–1650. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Small, H. Co-citation in the Scientific Literature: A New Measure of the Relationship Between Two Documents. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 1973, 24, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafee, N.; Katsaliaki, K.; Fishwick, P. Exploring the modelling and simulation knowledge base through journal co-citation analysis. Scientometrics 2014, 98, 2145–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Hua, W. Visualizing the knowledge domain of sustainable development research between 1987 and 2015: A bibliometric analysis. Scientometrics 2017, 110, 893–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Li, C.; Sun, J.; Zhang, L. Knowledge domain and emerging trends in organic photovoltaic technology: A scientometric review based on CiteSpace analysis. Front. Chem. 2017, 5, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.; Tsipoura, N.; Gochfeld, M.; Greenberg, M.R. Ecological considerations for evaluating current risk and designing long-term stewardship on Department of Energy lands. In Long-Term Management of Contaminated Sites; Emerald Group Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2006; pp. 139–162. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H. A scientometrics review on nonpoint source pollution research. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 99, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapport, D.J. Evolution of indicators of ecosystem health. In Ecological Indicators; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 121–134. [Google Scholar]
- Callicott, J.B.; Crowder, L.B.; Mumford, K. Current normative concepts in conservation. Conserv. Biol. 1999, 13, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairweather, P.G. Determining the ‘health’of estuaries: Priorities for ecological research. Aust. J. Ecol. 1999, 24, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairweather, P.G. State of environment indicators of ‘river health’: Exploring the metaphor. Freshw. Biol. 1999, 41, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkes, M.; Panelli, R. Integrating catchment ecosystems and community health: The value of participatory action research. Ecosyst. Health 2001, 7, 85–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, G.; Myers, W.L. Environmental and ecological health assessment of landscapes and watersheds with remote sensing data. Ecosyst. Health 1999, 5, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, K. Sustainability, Biomass Yields, and Health of Coastal Ecosystems: An Ecological Perspective; Marine Ecology Progress Series: Oldendorf, Germany, 1994; Volume 112, pp. 277–301. [Google Scholar]
- Sherman, K. Coastal Ecosystem Health A Global Perspective. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1994, 740, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karr, J.R. Defining and measuring river health. Freshw. Biol. 1999, 41, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vora, R.S. Developing programs to monitor ecosystem health and effectiveness of management practices on Lakes States National Forests, USA. Biol. Conserv. 1997, 80, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.-L.; Dawson, R.W.; Tao, S.; Cao, J.; Li, B.-G. A method for lake ecosystem health assessment: An Ecological Modeling Method (EMM) and its application. Hydrobiologia 2001, 443, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Lam, K.; Zhao, Z.; Zhan, W.; Chen, Y.D.; Tao, S. Marine coastal ecosystem health assessment: A case study of the Tolo Harbour, Hong Kong, China. Ecol. Model. 2004, 173, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarts, B.G. Ecological sustainability and biodiversity. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 1999, 6, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.-L.; Tao, S.; Dawson, R.; Li, B.-G. A GIS-based method of lake eutrophication assessment. Ecol. Model. 2001, 144, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jørgensen, S.E.; Tan, C.O.; Beklioglu, M. A structurally dynamic modelling—Lake Mogan, Turkey as a case study. Ecol. Model. 2003, 164, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.-L.; Tao, S.; Dawson, R.W.; Li, P.-g.; Cao, J. Lake ecosystem health assessment: Indicators and methods. Water Res. 2001, 35, 3157–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapcott, J.E.; Young, R.G.; Goodwin, E.O.; Leathwick, J.R. APPLIED ISSUES: Exploring the response of functional indicators of stream health to land-use gradients. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 2181–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hladyz, S.; Tiegs, S.D.; Gessner, M.O.; Giller, P.S.; RÎŞNOVEANU, G.; Preda, E.; Nistorescu, M.; Schindler, M.; Woodward, G. Leaf-litter breakdown in pasture and deciduous woodland streams: A comparison among three European regions. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 1916–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feio, M.; Alves, T.; Boavida, M.; Medeiros, A.; Graça, M. Functional indicators of stream health: A river-basin approach. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 1050–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunn, S.; Abal, E.; Smith, M.; Choy, S.; Fellows, C.; Harch, B.; Kennard, M.; Sheldon, F. Integration of science and monitoring of river ecosystem health to guide investments in catchment protection and rehabilitation. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clapcott, J.E.; Barmuta, L.A. Forest clearance increases metabolism and organic matter processes in small headwater streams. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2010, 29, 546–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Yang, Z.; Chen, B. Relative urban ecosystem health assessment: A method integrating comprehensive evaluation and detailed analysis. Ecohealth 2010, 7, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Huang, G.; Duan, N. An evaluation of dynamic mutuality measurements and methods in cyclic time series. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2010, 15, 4020–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Chen, H.; Li, S. Resources use and greenhouse gas emissions in urban economy: Ecological input–output modeling for Beijing 2002. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2010, 15, 3201–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, G.; Ji, X. Cosmic emergy based ecological systems modelling. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2010, 15, 2672–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Death, R.G.; Death, F.; Stubbington, R.; Joy, M.K.; van den Belt, M. How good are Bayesian belief networks for environmental management? A test with data from an agricultural river catchment. Freshw. Biol. 2015, 60, 2297–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hartmann, M.; Frey, B.; Mayer, J.; Mäder, P.; Widmer, F. Distinct soil microbial diversity under long-term organic and conventional farming. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, S.J.; Barmuta, L.A.; Chessman, B.C.; Davies, P.E.; Dyer, F.J.; Harrison, E.T.; Hawkins, C.P.; Jones, I.; Kefford, B.J.; Linke, S. The imperative need for nationally coordinated bioassessment of rivers and streams. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2017, 68, 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lallias, D.; Hiddink, J.G.; Fonseca, V.G.; Gaspar, J.M.; Sung, W.; Neill, S.P.; Barnes, N.; Ferrero, T.; Hall, N.; Lambshead, P.J.D. Environmental metabarcoding reveals heterogeneous drivers of microbial eukaryote diversity in contrasting estuarine ecosystems. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Xu, Z.; Zhan, C.; Yin, X.; Yu, S. A new framework to evaluate ecosystem health: A case study in the Wei River basin, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakew, A.; Moog, O. A multimetric index based on benthic macroinvertebrates for assessing the ecological status of streams and rivers in central and southeast highlands of Ethiopia. Hydrobiologia 2015, 751, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Yao, P.; Wang, W.; Yue, B.; Liu, G. Assessment of wetland ecosystem health in the Yangtze and Amazon River Basins. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, A.; Bryan, B.; Overton, I.; Holland, K.; Lester, R.; King, D.; Nolan, M.; Connor, J. Integrated modelling of cost-effective siting and operation of flow-control infrastructure for river ecosystem conservation. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, A.R.; Schlacher, T.A.; Schoeman, D.S.; Weston, M.A.; Withycombe, G.M. Ecological research questions to inform policy and the management of sandy beaches. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2017, 148, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, K.L.; Blahna, D.J.; Brinkley, W.; Romolini, M. Environmental stewardship footprint research: Linking human agency and ecosystem health in the Puget Sound region. Urban Ecosyst. 2013, 16, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Pu, L. Assessment of urban ecosystem health based on matter element analysis: A case study of 13 cities in Jiangsu Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döring, T.F.; Vieweger, A.; Pautasso, M.; Vaarst, M.; Finckh, M.R.; Wolfe, M.S. Resilience as a universal criterion of health. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, H.; Katano, I.; Negishi, J.N.; Sanada, S.; Kayaba, Y. Effects of biodiversity, habitat structure, and water quality on recreational use of rivers. Ecosphere 2013, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapport, D.J.; Costanza, R.; McMichael, A. Assessing ecosystem health. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1998, 13, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; McIntyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Glidden, S.; Bunn, S.E.; Sullivan, C.A.; Liermann, C.R. Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, R.G.; Matthaei, C.D.; Townsend, C.R. Organic matter breakdown and ecosystem metabolism: Functional indicators for assessing river ecosystem health. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2008, 27, 605–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suter, G.W. A critique of ecosystem health concepts and indexes. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 1993, 12, 1533–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L.; Zimmerman, J.K. Ecological responses to altered flow regimes: A literature review to inform the science and management of environmental flows. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenfeld, D.; Costanza, R.; Norton, B.; Haskell, B. Ecosystem Health: New Goals for Environmental Management; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Young, R.G.; Collier, K.J. Contrasting responses to catchment modification among a range of functional and structural indicators of river ecosystem health. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 2155–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, M.; Yang, Z.; Chen, B.; Ulgiati, S. Urban ecosystem health assessment based on emergy and set pair analysis—A comparative study of typical Chinese cities. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 2341–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birk, S.; Bonne, W.; Borja, A.; Brucet, S.; Courrat, A.; Poikane, S.; Solimini, A.; Van De Bund, W.; Zampoukas, N.; Hering, D. Three hundred ways to assess Europe’s surface waters: An almost complete overview of biological methods to implement the Water Framework Directive. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 18, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L.; Richter, B.D.; Arthington, A.H.; Bunn, S.E.; Naiman, R.J.; Kendy, E.; Acreman, M.; Apse, C.; Bledsoe, B.P.; Freeman, M.C. The ecological limits of hydrologic alteration (ELOHA): A new framework for developing regional environmental flow standards. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 147–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B.S.; Longo, C.; Hardy, D.; McLeod, K.L.; Samhouri, J.F.; Katona, S.K.; Kleisner, K.; Lester, S.E.; O’leary, J.; Ranelletti, M. An index to assess the health and benefits of the global ocean. Nature 2012, 488, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B.S.; Walbridge, S.; Selkoe, K.A.; Kappel, C.V.; Micheli, F.; D’agrosa, C.; Bruno, J.F.; Casey, K.S.; Ebert, C.; Fox, H.E. A global map of human impact on marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 319, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanza, R. Ecosystem health and ecological engineering. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 45, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costanza, R.; de Groot, R.; Sutton, P.; Van der Ploeg, S.; Anderson, S.J.; Kubiszewski, I.; Farber, S.; Turner, R.K. Changes in the global value of ecosystem services. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2014, 26, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, D.; Borja, A.; Carstensen, J.; Carvalho, L.; Elliott, M.; Feld, C.K.; Heiskanen, A.-S.; Johnson, R.K.; Moe, J.; Pont, D. The European Water Framework Directive at the age of 10: A critical review of the achievements with recommendations for the future. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 4007–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woodward, G.; Gessner, M.O.; Giller, P.S.; Gulis, V.; Hladyz, S.; Lecerf, A.; Malmqvist, B.; McKie, B.G.; Tiegs, S.D.; Cariss, H. Continental-scale effects of nutrient pollution on stream ecosystem functioning. Science 2012, 336, 1438–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karr, J.R. Using biological criteria to protect ecological health. In Evaluating and Monitoring the Health of Large-Scale Ecosystems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 137–152. [Google Scholar]
- Woodwell, G.M. The Earth in Transition: Patterns and Processes of Biotic Impoverishment; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Karr, J.R.; Chu, E.W. Ecological integrity: Reclaiming lost connections. In Perspectives on Ecological Integrity; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 34–48. [Google Scholar]
- Rapport, D.J. Ecosystem Health: Exploring the Territory; University of Guelph: Guelph, ON, Canada, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; De Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonada, N.; Prat, N.; Resh, V.H.; Statzner, B. Developments in aquatic insect biomonitoring: A comparative analysis of recent approaches. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2006, 51, 495–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, P. Development of a national river bioassessment system (AUSRIVAS) in Australia. In Assessing the Biological Quality of Fresh Waters: RIVPACS and Other Techniques, Proceedings of the International Workshop held in Oxford, UK, 16–18 September 1997; Freshwater Biological Association (FBA): Ambleside, Cumbria, UK, 2000; pp. 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Gessner, M.O.; Chauvet, E. A case for using litter breakdown to assess functional stream integrity. Ecol. Appl. 2002, 12, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandin, L.; Solimini, A.G. Freshwater ecosystem structure–function relationships: From theory to application. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feld, C.K.; Birk, S.; Bradley, D.C.; Hering, D.; Kail, J.; Marzin, A.; Melcher, A.; Nemitz, D.; Pedersen, M.L.; Pletterbauer, F. From natural to degraded rivers and back again: A test of restoration ecology theory and practice. In Advances in Ecological Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 44, pp. 119–209. [Google Scholar]
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.-I.; Knowler, D.J.; Lévêque, C.; Naiman, R.J.; Prieur-Richard, A.-H.; Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L. Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol. Rev. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenhoff, A. Multiple-Stressor Effects Along Gradients of Deposited Fine Sediment and Dissolved Nutrients in Streams. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Otago, Dunedin, New Zealand, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Allan, J.D. Landscapes and riverscapes: The influence of land use on stream ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2004, 35, 257–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewson, Z.S.; James, A.B.; Death, R.G. A review of the consequences of decreased flow for instream habitat and macroinvertebrates. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2007, 26, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.A.; Reidy Liermann, C.A.; Nilsson, C.; Flörke, M.; Alcamo, J.; Lake, P.S.; Bond, N. Climate change and the world’s river basins: Anticipating management options. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Ludwig, D.; Brock, W.A. Management of eutrophication for lakes subject to potentially irreversible change. Ecol. Appl. 1999, 9, 751–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, A.; Richardson, R.E. Studies on the biology of the upper Illinois River. Ill. Nat. Hist. Surv. Bull. 1913, 9, 481–574. [Google Scholar]
- Zinger, L.; Boetius, A.; Ramette, A. Bacterial taxa–area and distance–decay relationships in marine environments. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 954–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| # | Author | Frequency | # | Author | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rapport, D.J. | 354 | 6 | Poff, N.L. | 123 |
| 2 | Costanza, R. | 321 | 7 | Vitousek, P.M. | 121 |
| 3 | Karr, J.R. | 302 | 8 | Bunn, S.E. | 117 |
| 4 | Clarke, K.R. | 126 | 9 | Jorgensen, S.E. | 103 |
| 5 | Barbour, M.T. | 124 | 10 | Cairns, J. | 99 |
| # | Frequency | Centrality | Journals | IF 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1265 | 0.26 | SCIENCE | 41.058 |
| 2 | 1037 | 0.29 | NATURE | 41.577 |
| 3 | 872 | 0 | SCIENCE OF THE TOTAL ENVIRONMENT | 4.61 |
| 4 | 828 | 0.07 | HYDROBIOLOGIA | 2.165 |
| 5 | 822 | 0.43 | ECOLOGICAL APPLICATIONS | 4.393 |
| 6 | 816 | 0.42 | ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY | 6.653 |
| 7 | 733 | 0 | PROCEEDINGS OF THE NATIONAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCES OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA | 9.504 |
| 8 | 732 | 0.13 | ECOLOGY | 4.617 |
| 9 | 698 | 0.2 | BIOSCIENCE | 5.876 |
| 10 | 644 | 0.15 | ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT | 2.177 |
| Cluster ID | Size | Silhouette | Label (LLR) | Mean (Cite Year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 63 | 0.828 | natural resource value | 1994 |
| 1 | 62 | 0.916 | cellulose decomposition potential | 2006 |
| 2 | 49 | 0.945 | cross-sectional study | 1997 |
| 3 | 46 | 0.987 | large marine ecosystems | 1990 |
| 4 | 40 | 0.915 | water quality | 2012 |
| 5 | 39 | 0.990 | urban ecosystem health | 2006 |
| 6 | 39 | 0.941 | inventory | 1993 |
| 7 | 38 | 0.965 | condition | 1998 |
| 8 | 37 | 0.915 | lake chao | 1999 |
| 9 | 36 | 0.862 | wetland | 2011 |
| Frequency | Author | Title | Source | Year | Centrality | Cluster |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 46 | Rapport, D.J., et al. | Assessing ecosystem health | Trends in Ecology and Evolution | 1998 | 0.11 | 8 |
| 44 | Vorosmarty, C.J. et al. | Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity | Nature | 2010 | 0.25 | 1 |
| 37 | Young, R.G. et al. | Organic matter breakdown and ecosystem metabolism: functional indicators for assessing river ecosystem health | Journal of the north American benthological society | 2008 | 0.02 | 1 |
| 33 | Suter, G.W. et al. | A critique of ecosystem health concepts and indexes | Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry | 1993 | 0.05 | 0 |
| 33 | Poff, N.L. et al. | Ecological responses to altered flow regimes: a literature review to inform the science and management of environmental flows | Freshwater Biology | 2010 | 0.01 | 9 |
| 32 | Costanza, R. et al. | Ecosystem health: new goals for environmental management | Ecosystem Health New Goals for Environmental | 1992 | 0 | 6 |
| 32 | Young, R.G. et al. | Contrasting responses to catchment modification among a range of functional and structural indicators of river ecosystem health | Freshwater Biology | 2009 | 0.05 | 1 |
| 30 | Bunn, S.E. et al. | Integration of science and monitoring of river ecosystem health to guide investments in catchment protection and rehabilitation | Freshwater Biology | 2010 | 0.02 | 4 |
| 28 | Su, M.R. et al. | Urban ecosystem health assessment based on emergy and set pair analysis—A comparative study of typical Chinese cities | Ecological Modelling | 2009 | 0.01 | 5 |
| 28 | Birk, S. et al. | Three hundred ways to assess Europe’s surface waters: An almost complete overview of biological methods to implement the Water Framework Directive | Ecological Indicators | 2012 | 0.03 | 4 |
| References | Year | Strength | Begin | End | 1989–2018 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vorosmarty, C.J. et al. | 2010 | 17.77 | 2012 | 2018 |  |
| Birk, S. et al. | 2012 | 14.57 | 2015 | 2018 |  |
| Poff, N.L. et al. | 2010 | 12.58 | 2012 | 2018 |  |
| Halpern, B.S. et al. | 2012 | 10.08 | 2013 | 2018 |  |
| Poff, N.L. et al. | 2010 | 9.82 | 2012 | 2016 |  |
| Halpern, B.S. et al. | 2008 | 9.26 | 2013 | 2016 |  |
| Costanza, R. et al. | 2012 | 7.77 | 2015 | 2018 |  |
| Hering, D. et al. | 2010 | 7.25 | 2015 | 2018 |  |
| Costanza, R. et al. | 2014 | 6.73 | 2015 | 2018 |  |
| Woodward, G. et al. | 2012 | 6.16 | 2013 | 2016 |  |
| Period | Keyword | Burst | Begin | End | 1989–2018 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1989–1999 | ecosystem health | 32.71 | 1993 | 2004 |  |
| stress | 11.97 | 1993 | 2002 |  | |
| ecology | 9.54 | 1996 | 2004 |  | |
| integrity | 11.20 | 1997 | 2004 |  | |
| ecosystem management | 7.68 | 1998 | 2001 |  | |
| 2000–2010 | ecological indicator | 6.41 | 2000 | 2007 |  |
| ecotoxicology | 4.75 | 2002 | 2008 |  | |
| risk | 5.23 | 2003 | 2009 |  | |
| sustainable development | 4.76 | 2004 | 2009 |  | |
| bioassessment | 8.93 | 2006 | 2010 |  | |
| forest | 5.44 | 2008 | 2011 |  | |
| set pair analysis | 8.20 | 2009 | 2012 |  | |
| ecosystem health assessment | 5.91 | 2010 | 2013 |  | |
| 2011–2018 | surface water | 8.33 | 2013 | 2018 |  |
| river basin | 5.72 | 2014 | 2018 |  | |
| oxidative stress | 7.04 | 2014 | 2018 |  | |
| waste water | 8.11 | 2016 | 2018 |  | |
| ecological restoration | 4.26 | 2016 | 2018 |  | |
| aquatic ecosystem | 4.24 | 2016 | 2018 |  |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Shao, X.; Wu, M. A Review on Ecosystem Health Research: A Visualization Based on CiteSpace. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4908. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11184908
Yang H, Shao X, Wu M. A Review on Ecosystem Health Research: A Visualization Based on CiteSpace. Sustainability. 2019; 11(18):4908. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11184908
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Hui, Xuexin Shao, and Ming Wu. 2019. "A Review on Ecosystem Health Research: A Visualization Based on CiteSpace" Sustainability 11, no. 18: 4908. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11184908
APA StyleYang, H., Shao, X., & Wu, M. (2019). A Review on Ecosystem Health Research: A Visualization Based on CiteSpace. Sustainability, 11(18), 4908. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11184908




