The Prediction and Assessment of the Impacts of Soil Sealing on Agricultural Land in the North Nile Delta (Egypt) Using Satellite Data and GIS Modeling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
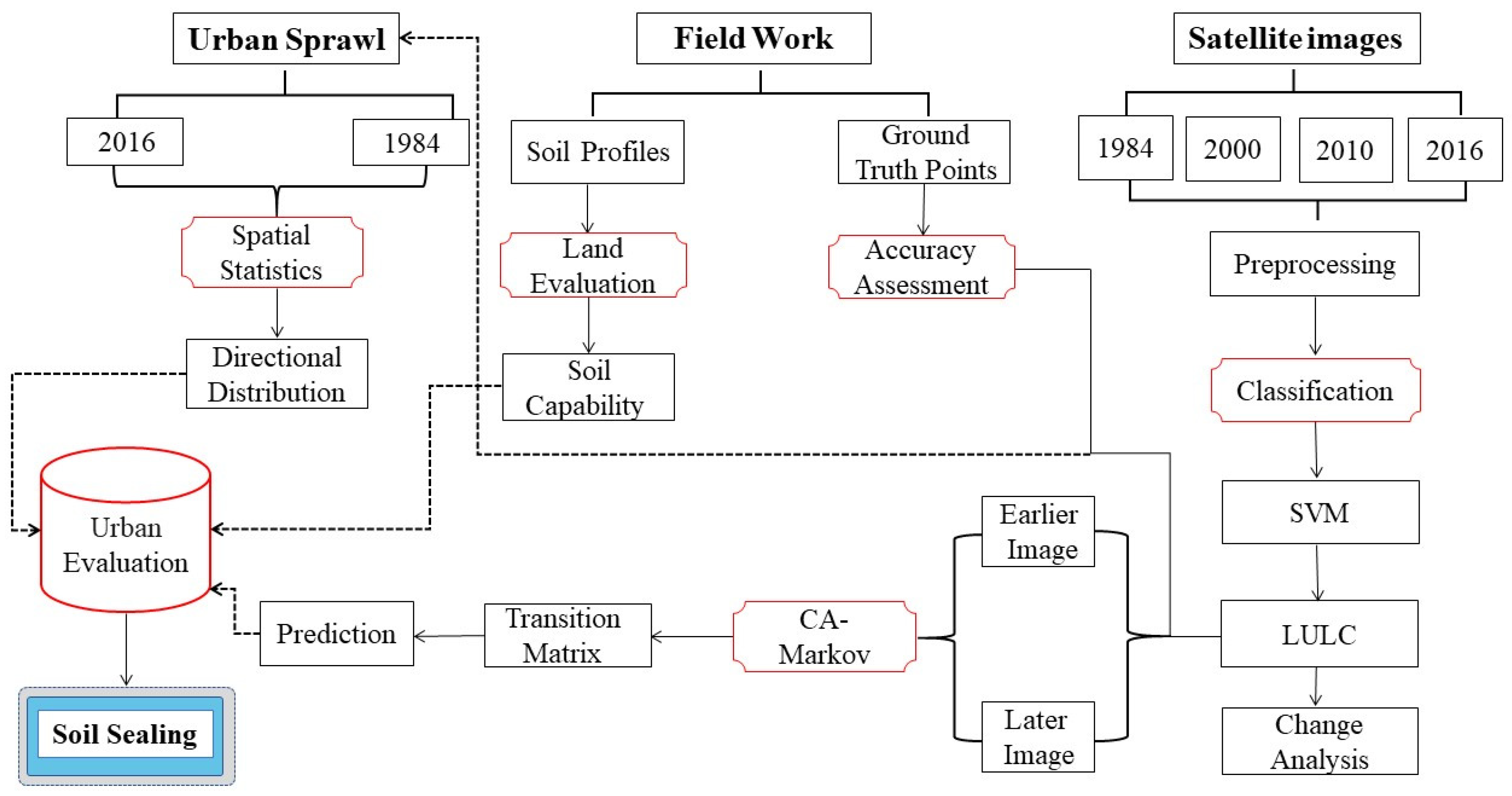
2. Materials and Methods
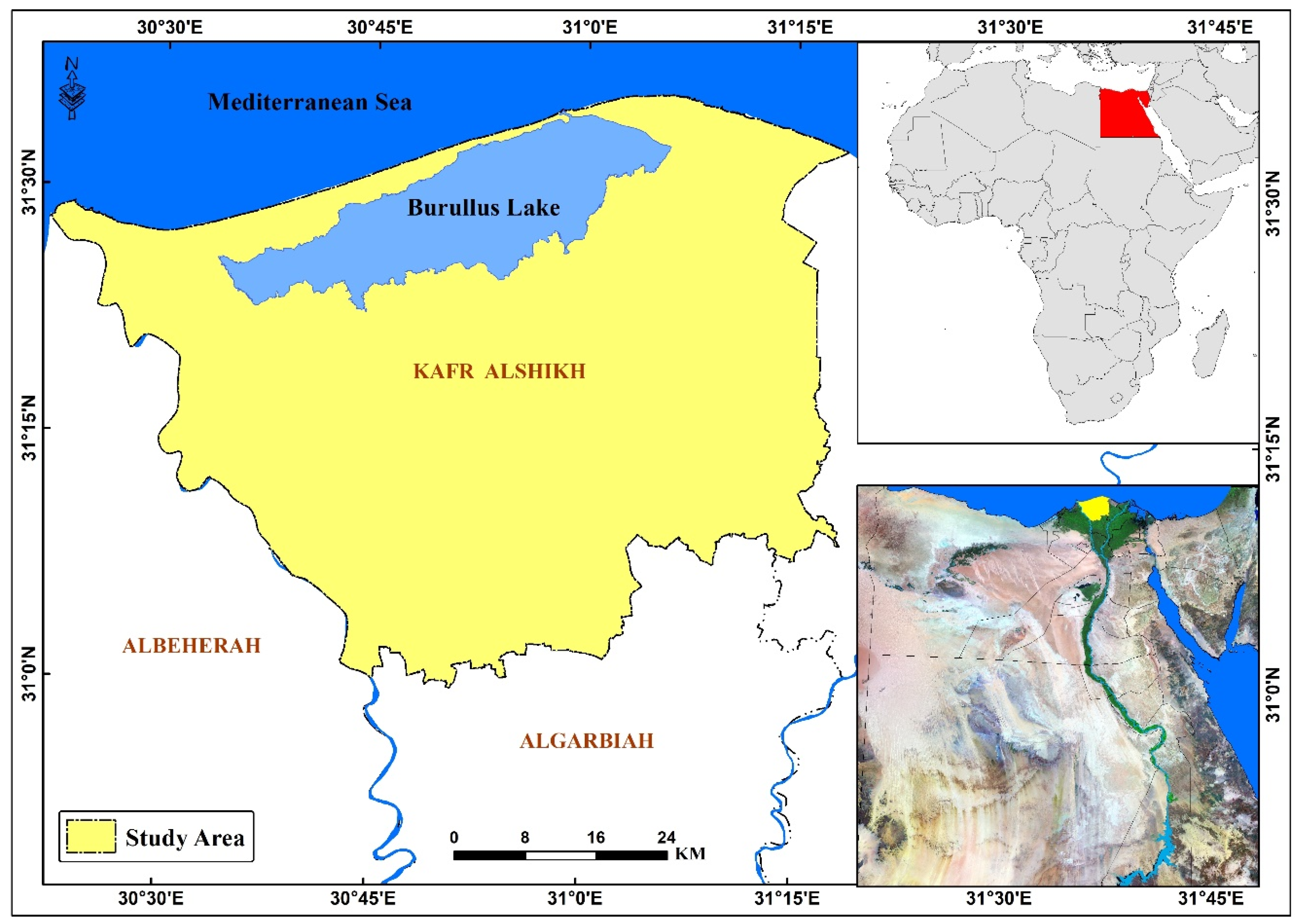
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection and Image Processing
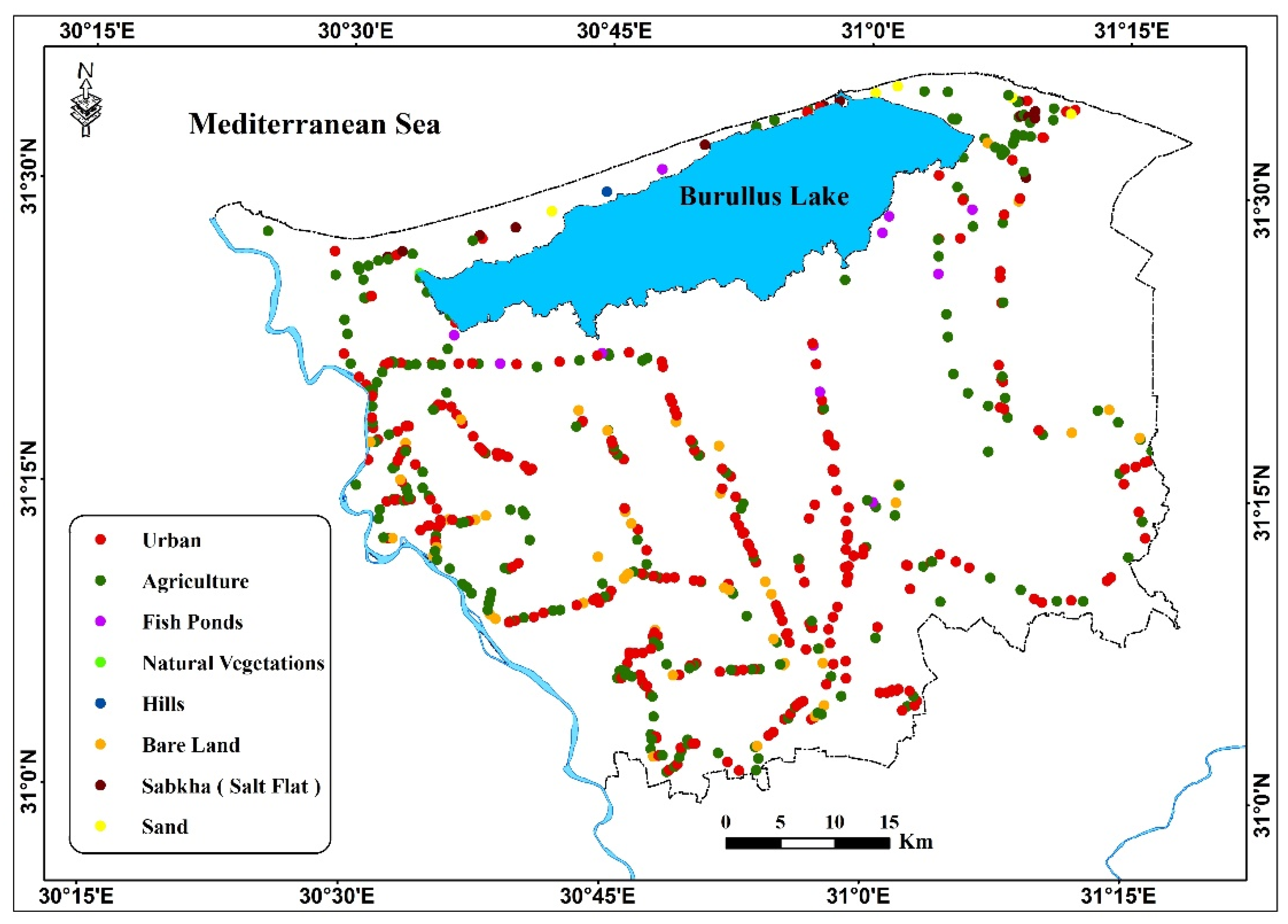
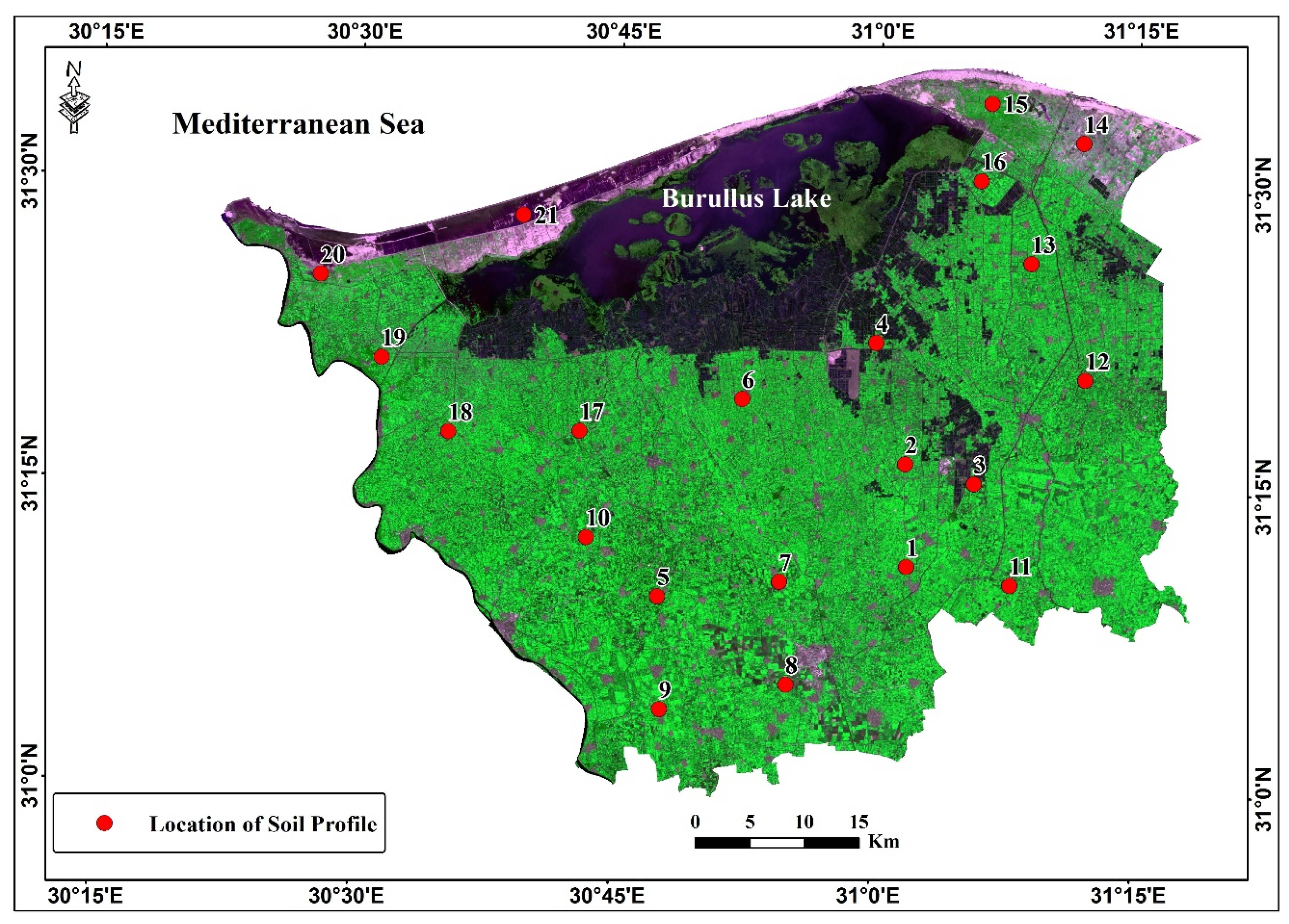
2.3. Field Survey
2.4. Evaluation of Soil Capability
2.5. CA–Markov Model
3. Results and Discussions
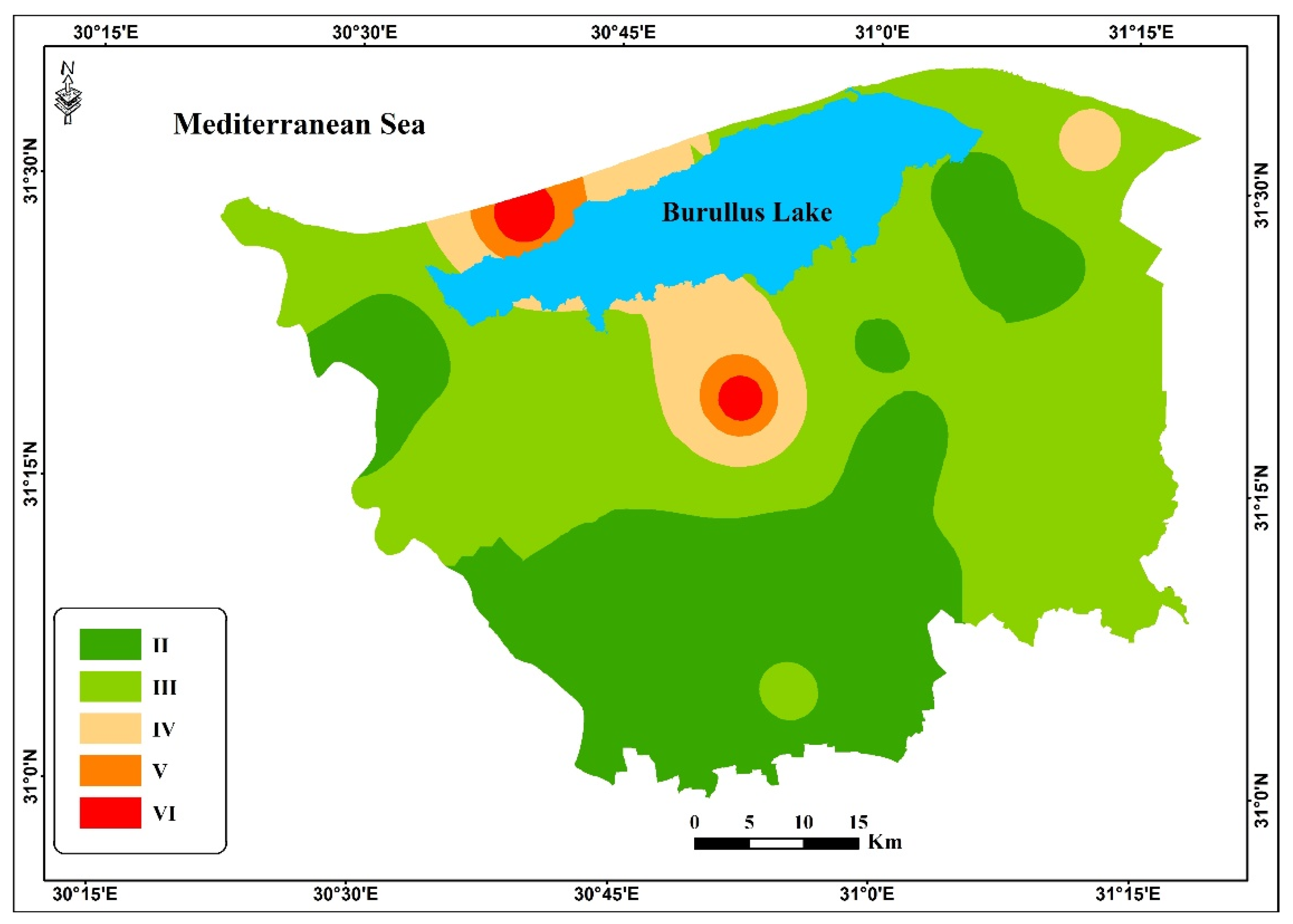
3.1. Soil Capability in the Study Area
3.2. Accuracy Assessment
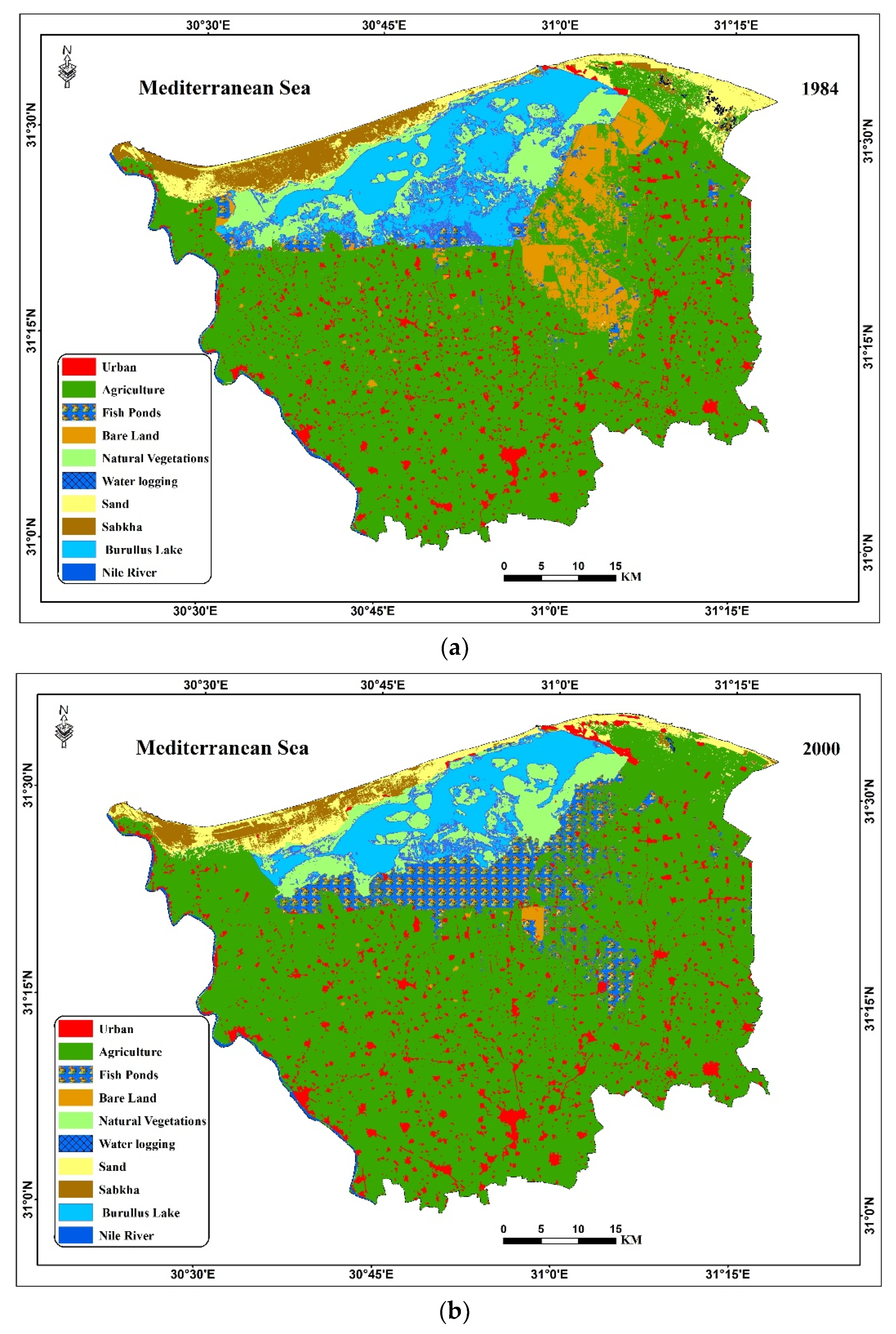
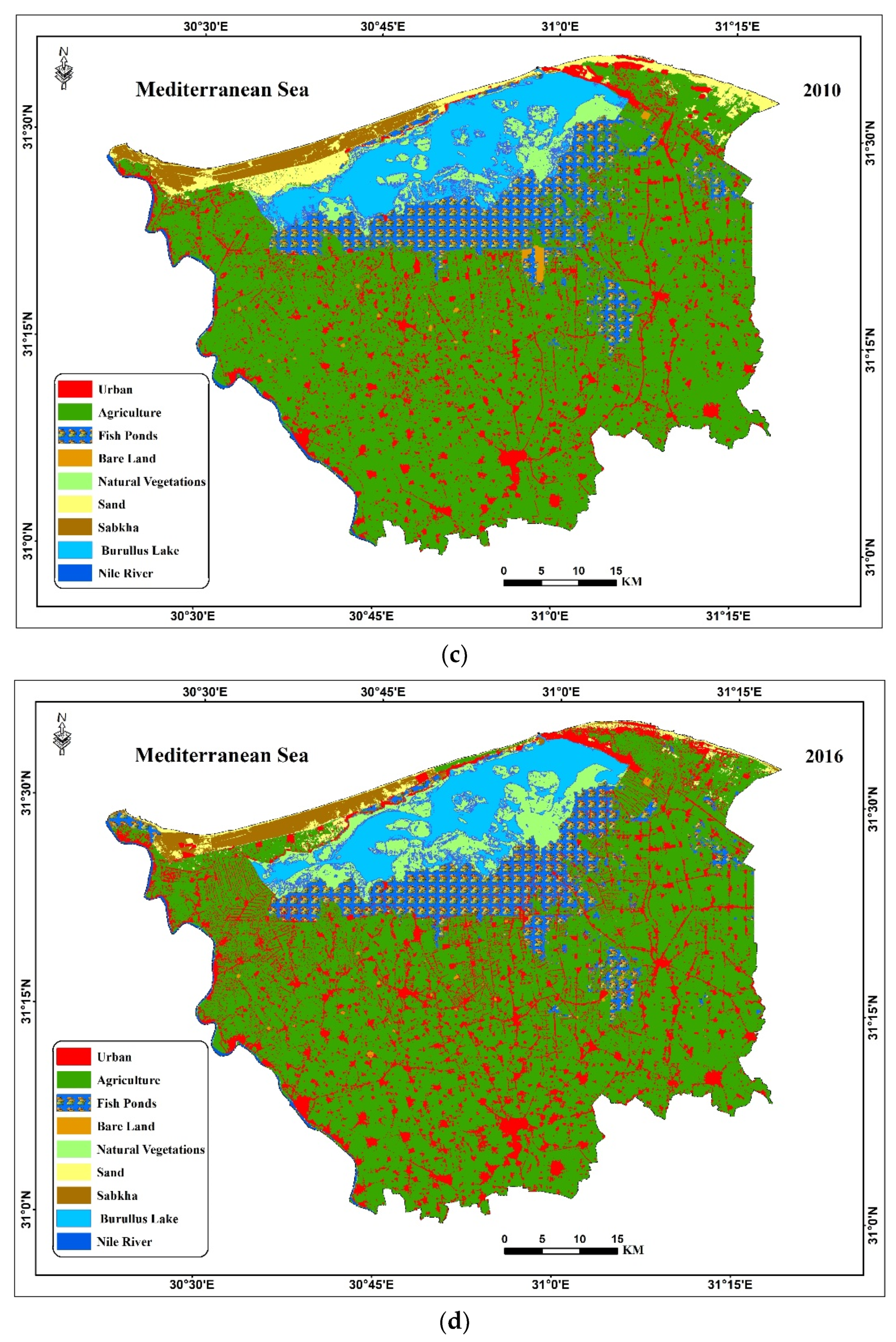
3.3. Detection of Changes in Land Use and Land Cover (LULC)
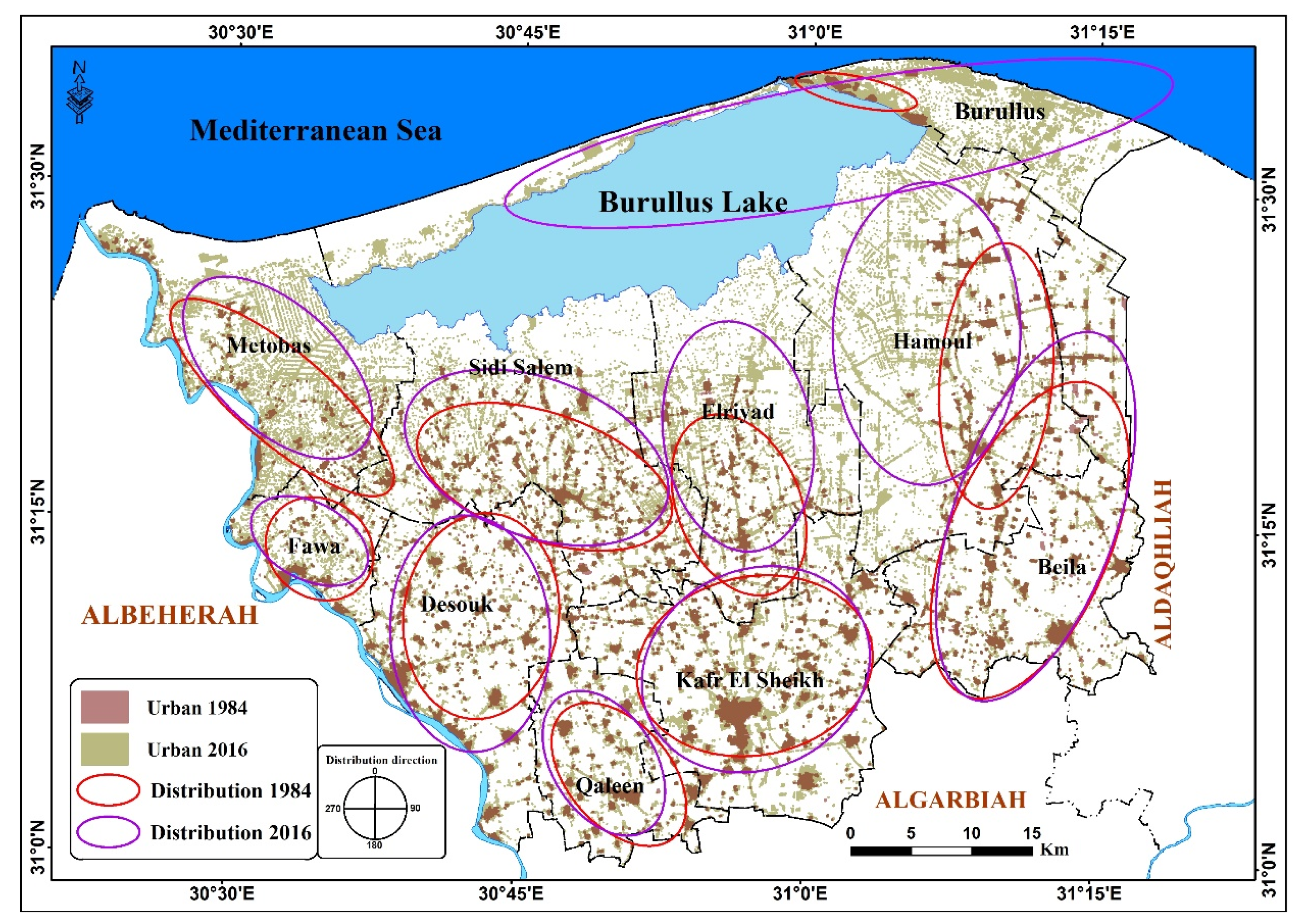
3.4. Spatial Distribution of Soil Sealing Patterns
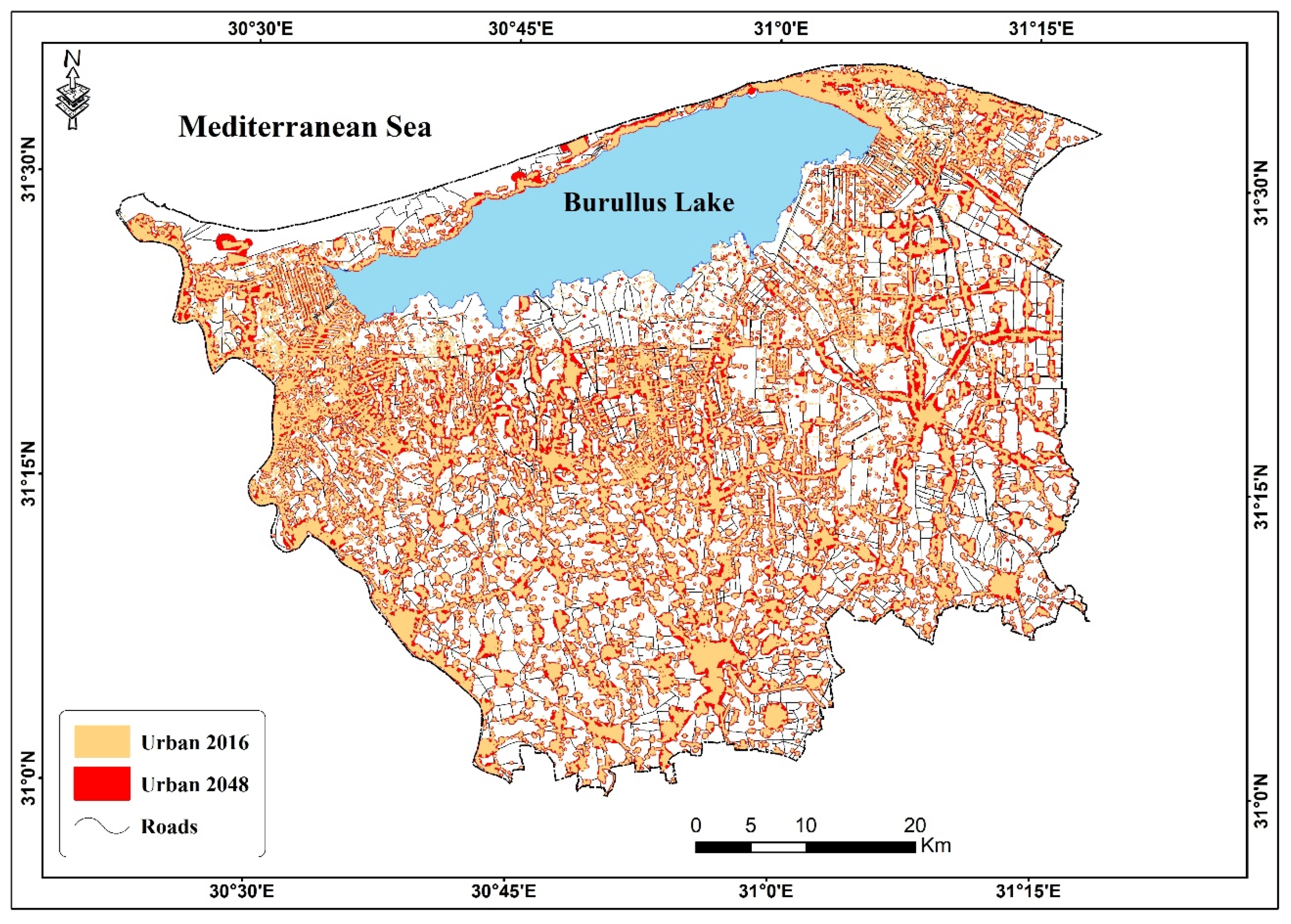
3.5. Expected Changes in Soil Sealing between 2016 and 2048
4. Recommendations
- increase cooperation between governmental authorities, stakeholders, and educational and research institutions to combat soil sealing;
- reactivate past laws that combat soil sealing;
- increase awareness of citizens of the hazards posed by soil sealing via different media;
- the government should oblige the population not to establish any urban communities in the agricultural areas.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prokop, G.; Jobstmann, H.; Schonbauer, A. Report on Best Practices for Limiting Soil Sealing and Mitigating its Effects; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, E.S. Spatial assessment of desertification in north Sinai using modified MEDLAUS model. Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 6, 4647–4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, W.; Lu, D. Challenges and the way forward in China’s new-type urbanization. Land Use Policy 2016, 55, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desa, U.N. World Urbanization Prospects, the 2011 Revision. Population Division, Department of Economic and Social Affairs; United Nations Secretariat: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- World’s Population Increasingly Urban with More than Half Living in Urban Areas. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/news/population/world-urbanization-prospects-2014.html (accessed on 5 July 2019).
- Xiao, R.; Su, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, D.; Wu, J. Local spatial modeling of paddy soil landscape patterns in response to urbanization across the urban agglomeration around Hangzhou Bay, China. Appl. Geogr. 2013, 39, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasioli, M.; Barberis, R.; Ajmonemarsan, F. The influence of a large city on some soil properties and metals content. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 356, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martellozzo, F.; Amato, F.; Murgante, B.; Clarke, K.C. Modelling the impact of urban growth on agriculture and natural land in Italy to 2030. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 91, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cosentino, C.; Amato, F.; Murgante, B. Population-Based Simulation of Urban Growth: The Italian Case Study. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Güneralp, B.; Hutyra, L.R. Global forecasts of urban expansion to 2030 and direct impacts on biodiversity and carbon pools. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16083–16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Yang, L.; Ren, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Z. Impacts of Urban Sprawl on Soil Resources in the Changchun–Jilin Economic Zone, China, 2000–2015. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.G.; Dent, D.L.; Olsson, L.; Schaepman, M.E. Global Assessment of Land Degradation and Improvement: 1. Identification by Remote Sensing (No. 5); ISRIC-World Soil Information: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hamdi, H.; Abdelhafez, S. Agriculture and Soil Survey in Egypt. Soil Resources of Southern and Eastern Mediterranean Countries; Zdruli, P., Steduto, P., Lacirignola, L., Montanarella, L., Eds.; OPTIONS Méditerranéennes: Bari, Italy, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, E.; Saleh, A.; Belal, A. Sustainability indicators for agricultural land use based on GIS spatial modeling in North of Sinai-Egypt. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2014, 17, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foley, J.A.; Ramankutty, N.; Brauman, K.A.; Cassidy, E.S.; Gerber, J.S.; Johnston, M.; Mueller, N.D.; O’Connell, C.; Ray, D.K.; West, P.C.; et al. Solutions for a cultivated planet. Nature 2011, 478, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tilman, D.; Cassman, K.G.; Matson, P.A.; Naylor, R.; Polasky, S. Agricultural sustainability and intensive production practices. Nature 2002, 418, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.S.; Belal, A.; Shalaby, A. Impacts of soil sealing on potential agriculture in Egypt using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2015, 48, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.S.; Abu-Hashim, M.; Belal, A.A.A. Sustainable Indicators in Arid Region: Case Study—Egypt. In The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 273–293. [Google Scholar]
- Ceccarelli, T.; Bajocco, S.; Salvati, L.; Perini, L. Investigating syndromes of agricultural land degradation through past trajectories and future scenarios. Soil Sci. Plant. Nutr. 2014, 60, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prokop, G.; Jobstmann, H.; Schönbauer, A. Overview of Best Practices for Limiting Soil Sealing or Mitigating Its Effects in EU-27; European Communities: Brussels, Belgium, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- El-Ramady, H.; Alshaal, T.; Bakr, N.; Elbana, T.; Mohamed, E.; Belal, A.A. The Soils of Egypt. 2018. Available online: https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9783319955155 (accessed on 5 July 2019).
- Elfadaly, A.; Attia, W.; Lasaponara, R. Monitoring the Environmental Risks Around Medinet Habu and Ramesseum Temple at West Luxor, Egypt, Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2018, 25, 587–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfadaly, A.; Lasaponara, R.; Murgante, B.; Qelichi, M.M. Cultural Heritage Management Using Analysis of Satellite Images and Advanced GIS Techniques at East Luxor, Egypt and Kangavar, Iran (A Comparison Case Study). Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-62401-3_12 (accessed on 22 August 2019).
- Lasaponara, R.; Elfadaly, A.; Attia, W. Low Cost Space Technologies for Operational Change Detection Monitoring Around the Archaeological Area of Esna-Egypt. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-42108-7_48 (accessed on 22 August 2019).
- Saleh, N.H.S. Monitoring the Agriculture Land Change and its Impact on Water Consumption Between branches damietta and rosetta, Egypt Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques. Ph.D. Thesis, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, E.; Belal, A.A.; Ali, R.R.; Saleh, A.; Hendawy, E.A. Land degradation. In The Soils of Egypt; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2019; pp. 159–174. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Hashim, M.; Mohamed, E.; Belal, A.-E. Identification of potential soil water retention using hydric numerical model at arid regions by land-use changes. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2015, 3, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassan, A.; Belal, A.; Hassan, M.; Farag, F.; Mohamed, E.; Hassaan, A. Potential of thermal remote sensing techniques in monitoring waterlogged area based on surface soil moisture retrieval. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2019, 155, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.S.; Abu-Hashim, M.; Abdelrahman, M.A.E.; Schütt, B.; Lasaponara, R. Evaluating the Effects of Human Activity over the Last Decades on the Soil Organic Carbon Pool Using Satellite Imagery and GIS Techniques in the Nile Delta Area, Egypt. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammam, A.; Mohamed, E. Mapping Soil Salinity in the East Nile Delta Using Several Methodological Approaches of Salinity Assessment. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1110982318301339 (accessed on 22 August 2019).
- Abu-Hashim, M.; Elsayed, M.; Belal, A.E. Effect of land-use changes and site variables on surface soil organic carbon pool at Mediterranean Region. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2016, 114, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfadaly, A.; Lasaponara, R. On the Use of Satellite Imagery and GIS Tools to Detect and Characterize the Urbanization around Heritage Sites: The Case Studies of the Catacombs of Mustafa Kamel in Alexandria, Egypt and the Aragonese Castle in Baia, Italy. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanakis, S.H.; Solomon, A.; Wishart, N.; Dublish, S. Multi-attribute decision making: A simulation comparison of select methods. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1998, 107, 507–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belal, A.A.; El-Ramady, H.R.; Mohamed, E.S.; Saleh, A.M. Drought risk assessment using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savin, I.Y. Sealed soils (ecranozems) mapping in Moscow agglomeration based on Landsat images. Issled Zemli Kosm. 2013, 5, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Elfadaly, A.; Attia, W.; Qelichi, M.M.; Murgante, B.; Lasaponara, R. Management of Cultural Heritage Sites Using Remote Sensing Indices and Spatial Analysis Techniques. Surv. Geophys. 2018, 39, 1347–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsanjani, J.J.; Kainz, W.; Mousivand, A.J. Tracking dynamic land-use change using spatially explicit Markov Chain based on cellular automata: the case of Tehran. Int. J. Image Data Fusion 2011, 2, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfadaly, A.; Wafa, O.; AbouArab, M.A.R.; Guida, A.; Spanu, P.G.; Lasaponara, R. Geo-Environmental Estimation of Land Use Changes and Its Effects on Egyptian Temples at Luxor City. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2017, 6, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasaponara, R.; Murgante, B.; Elfadaly, A.; Qelichi, M.M.; Shahraki, S.Z.; Wafa, O.; Attia, W. Spatial Open Data for Monitoring Risks and Preserving Archaeological Areas and Landscape: Case Studies at Kom el Shoqafa, Egypt and Shush, Iran. Sustainability 2017, 9, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, E.D.N.; Nijkamp, P.; Painho, M.; Caetano, M. A multi-scenario forecast of urban change: A study on urban growth in the Algarve. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 104, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muller, M.R.; Middleton, J. A Markov model of land-use change dynamics in the Niagara Region, Ontario, Canada. Landsc. Ecol. 1994, 9, 151–157. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Forsythe, W.; Waters, N. Modeling Urban Land Use Change and Urban Sprawl: Calgary, Alberta, Canada. Netw. Spat. Econ. 2007, 7, 353–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.R. IDRISI Taiga, Guide to GIS and Remote Processing. Guide to GIS and Remote Processing; Clark University: Worcester, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Myint, S.W.; Wang, L. Multicriteria decision approach for land use land cover change using Markov chain analysis and a cellular automata approach. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 32, 390–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Li, H.; Inohae, T.; Su, W.; Nagaie, T.; Hokao, K. Modeling urban land use change by the integration of cellular automaton and Markov model. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 3761–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, J.; Gharagozlou, A.; Arjmandi, R.; Faryadi, S.; Adl, M. Predicting Urban Land Use Changes Using a CA–Markov Model. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2014, 39, 5565–5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, M.A.E.; Shalaby, A.; Aboelsoud, M.H.; Moghanm, F.S. GIS spatial model based for determining actual land degradation status in Kafr El-Sheikh Governorate, North Nile Delta. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2017, 4, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, L.S.; Adler-Golden, S.M.; Sundberg, R.L.; Levine, R.Y.; Perkins, T.C.; Berk, A.; Ratkowski, A.J.; Felde, G.; Hoke, M.L. Validation of the QUick Atmospheric Correction (QUAC) algorithm for VNIR-SWIR multi-and hyperspectral imagery. In Algorithms and Technologies for Multispectral, Hyperspectral, and Ultraspectral Imagery XI. Int. Soc. Opt. Photonics 2005, 5806, 668–679. [Google Scholar]
- Chander, G.; Markham, B.L.; Helder, D.L. Summary of current radiometric calibration coefficients for Landsat MSS, TM, ETM+, and EO-1 ALI sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Stow, D.A.; Gong, P. Examining the effect of spatial resolution and texture window size on classification accuracy: an urban environment case. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 2177–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, P.; Foody, G.M.; Herold, M.; Stehman, S.V.; Woodcock, C.E.; Wulder, M.A. Good practices for estimating area and assessing accuracy of land change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 148, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carletta, J. Assessing agreement on classification tasks: the kappa statistic. Comput. Linguist. 1996, 22, 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Burt, R. Soil Survey Laboratory Methods Manual. Soil Survey Investigations Report 42, Version 4.0. United States Department of Agriculture; Natural Resources Conservation Service, National Soil Survey Center: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, B.; Bai, Z. Simulating land use/cover changes of Nenjiang County based on CA–Markov model. Comput. Comput. Technol. Agric. 1984, 1, 321–329. [Google Scholar]
- Megahed, Y.; Cabral, P.; Silva, J.; Caetano, M. Land Cover Mapping Analysis and Urban Growth Modelling Using Remote Sensing Techniques in Greater Cairo Region—Egypt. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2015, 4, 1750–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, W.L. A review of models of landscape change. Landsc. Ecol. 1989, 2, 111–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, R.; Balzter, H.; Kolo, K. Predicting Land Use/Land Cover Changes Using a CA-Markov Model under Two Different Scenarios. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, L.; Zhang, C.; Yang, J.; Zhu, D.; Yun, W. Simulation of land use spatial pattern of towns and villages based on CA–Markov model. Math. Comput. Model. 2011, 54, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, Y.H.; Cabral, P. Analysis and Modeling of Urban Land Cover Change in Setúbal and Sesimbra, Portugal. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 1549–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.S.; Belal, A.; Saleh, A. Assessment of land degradation east of the Nile Delta, Egypt using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 6, 2843–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zeiny, A.M.; Effat, H.A. Environmental analysis of soil characteristics in El-Fayoum Governorate using geomatics approach. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbeih, S.F.; El-Zeiny, A.M. Qualitative assessment of groundwater quality based on land use spectral retrieved indices: Case study Sohag Governorate, Egypt. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2018, 10, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zeiny, A.M.; Effat, H.A. Environmental monitoring of spatiotemporal change in land use/land cover and its impact on land surface temperature in El-Fayoum governorate, Egypt. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2017, 8, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| LULC | 1984 | 2000 | 2010 | 2016 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Producer (%) | User (%) | Producer (%) | User (%) | Producer (%) | User (%) | Producer (%) | User (%) | |
| Agricultural land | 92.5 | 96.1 | 95.4 | 95.2 | 95.8 | 95.1 | 99 | 98.8 |
| Urban land | 88.1 | 88.1 | 91.7 | 92 | 94.9 | 90.7 | 98.1 | 98.5 |
| Fish ponds | 90.4 | 77.5 | 92.9 | 87.5 | 96.6 | 96.6 | 97.9 | 98.3 |
| Lake Burullus | 73.6 | 93.3 | 69.2 | 88.2 | 76 | 91.8 | 93.3 | 91.8 |
| Overall accuracy | 89 | 92 | 94 | 98.1 | ||||
| Kappa statistic | 0.84 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.97 | ||||
| LULC | 1984 (km2) | 2000 (km2) | 2010 (km2) | 2016 (km2) | Change (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1984–2000 | 2000–2010 | 2010–2016 | |||||
| Urban land | 114.9 | 148.3 | 213.1 | 274.0 | 29.1 | 43.6 | 28.6 |
| Agricultural land | 2389.8 | 2582.7 | 2477.1 | 2485.0 | 8.1 | −4.1 | 0.3 |
| Fish farms | 71.0 | 303.6 | 373.8 | 381.9 | 327.7 | 23.1 | 2.2 |
| Lake Burullus | 391.9 | 239.5 | 304.8 | 243.6 | –38.9 | 27.3 | –20.1 |
| Natural Vegetation | 274.9 | 235 | 150 | 210.4 | –14.5 | –36.2 | 40.3 |
| Sabkha (salt flat) | 130.1 | 81.9 | 87.4 | 74.7 | –37.1 | 6.8 | –14.5 |
| Sand | 133.3 | 122.5 | 108.5 | 49.9 | −8.1 | −11.4 | −54.0 |
| Bare land | 217.6 | 11.1 | 10.3 | 7.8 | −94.9 | −7.2 | −24.4 |
| Water logging | 2.7 | 0.8 | - | - | −71.9 | - | - |
| Nile River | 15.9 | 16.6 | 17.1 | 14.7 | −4.4 | 3.1 | −14.4 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hendawy, E.; Belal, A.A.; Mohamed, E.S.; Elfadaly, A.; Murgante, B.; Aldosari, A.A.; Lasaponara, R. The Prediction and Assessment of the Impacts of Soil Sealing on Agricultural Land in the North Nile Delta (Egypt) Using Satellite Data and GIS Modeling. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4662. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11174662
Hendawy E, Belal AA, Mohamed ES, Elfadaly A, Murgante B, Aldosari AA, Lasaponara R. The Prediction and Assessment of the Impacts of Soil Sealing on Agricultural Land in the North Nile Delta (Egypt) Using Satellite Data and GIS Modeling. Sustainability. 2019; 11(17):4662. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11174662
Chicago/Turabian StyleHendawy, Ehab, A. A. Belal, E. S. Mohamed, Abdelaziz Elfadaly, Beniamino Murgante, Ali A. Aldosari, and Rosa Lasaponara. 2019. "The Prediction and Assessment of the Impacts of Soil Sealing on Agricultural Land in the North Nile Delta (Egypt) Using Satellite Data and GIS Modeling" Sustainability 11, no. 17: 4662. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11174662
APA StyleHendawy, E., Belal, A. A., Mohamed, E. S., Elfadaly, A., Murgante, B., Aldosari, A. A., & Lasaponara, R. (2019). The Prediction and Assessment of the Impacts of Soil Sealing on Agricultural Land in the North Nile Delta (Egypt) Using Satellite Data and GIS Modeling. Sustainability, 11(17), 4662. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11174662








