Spatial-Temporal Changes in Soil Organic Carbon and pH in the Liaoning Province of China: A Modeling Analysis Based on Observational Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
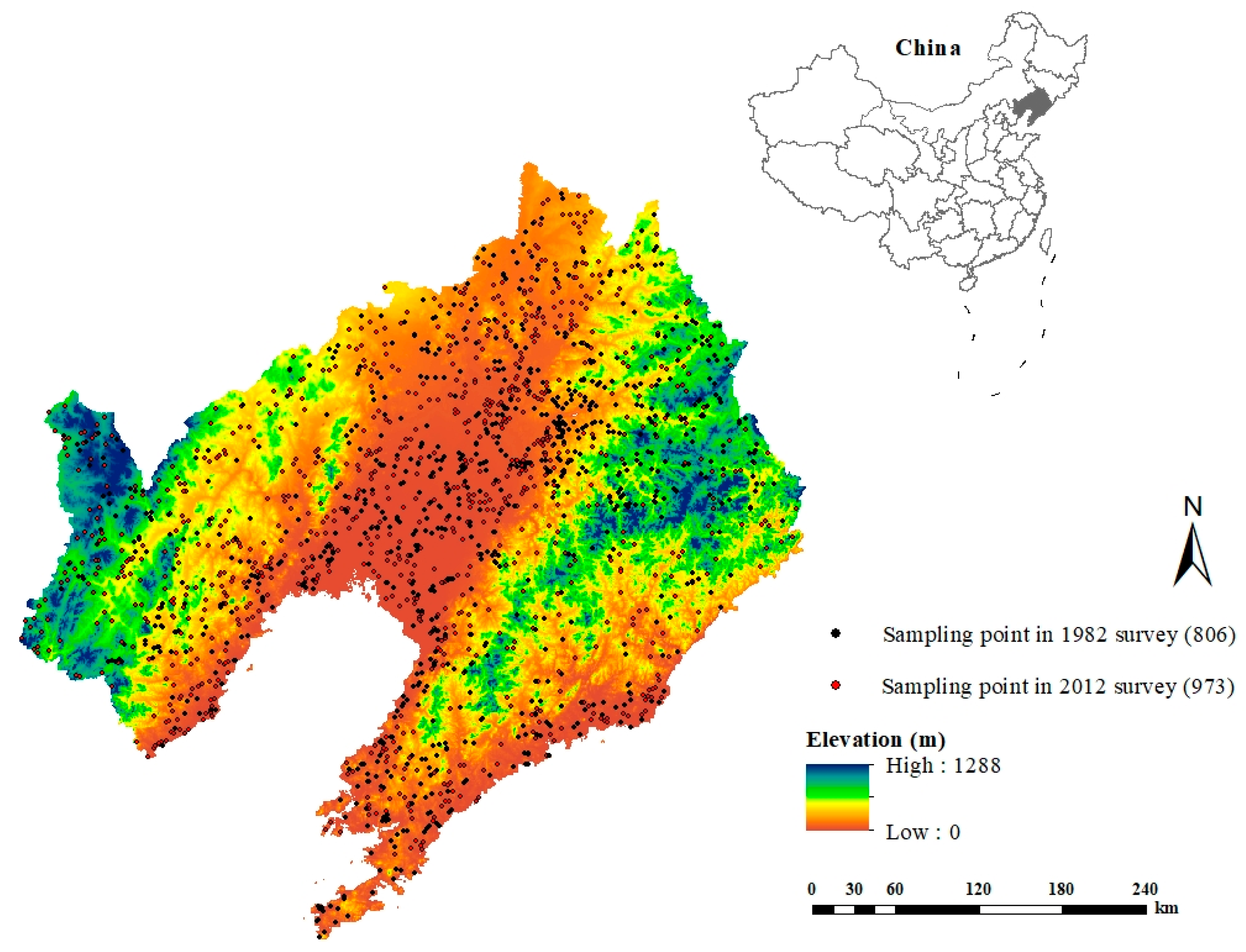
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Experimental Design
2.2.1. Soil Survey Data for 1982
2.2.2. Soil Sampling and Analysis
2.2.3. Environmental Variables
2.3. Random Forest Model
2.4. Model Validation
3. Results
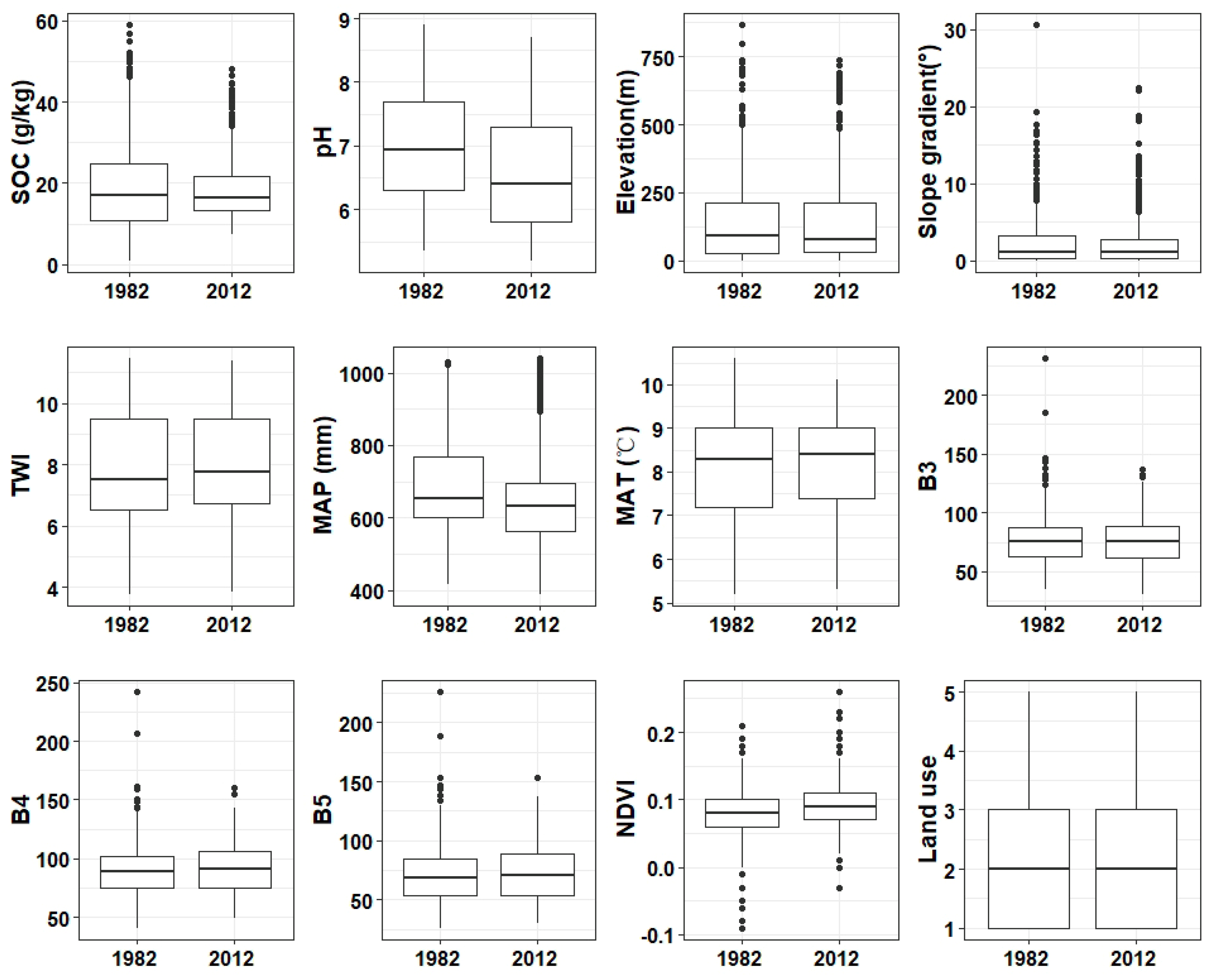
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
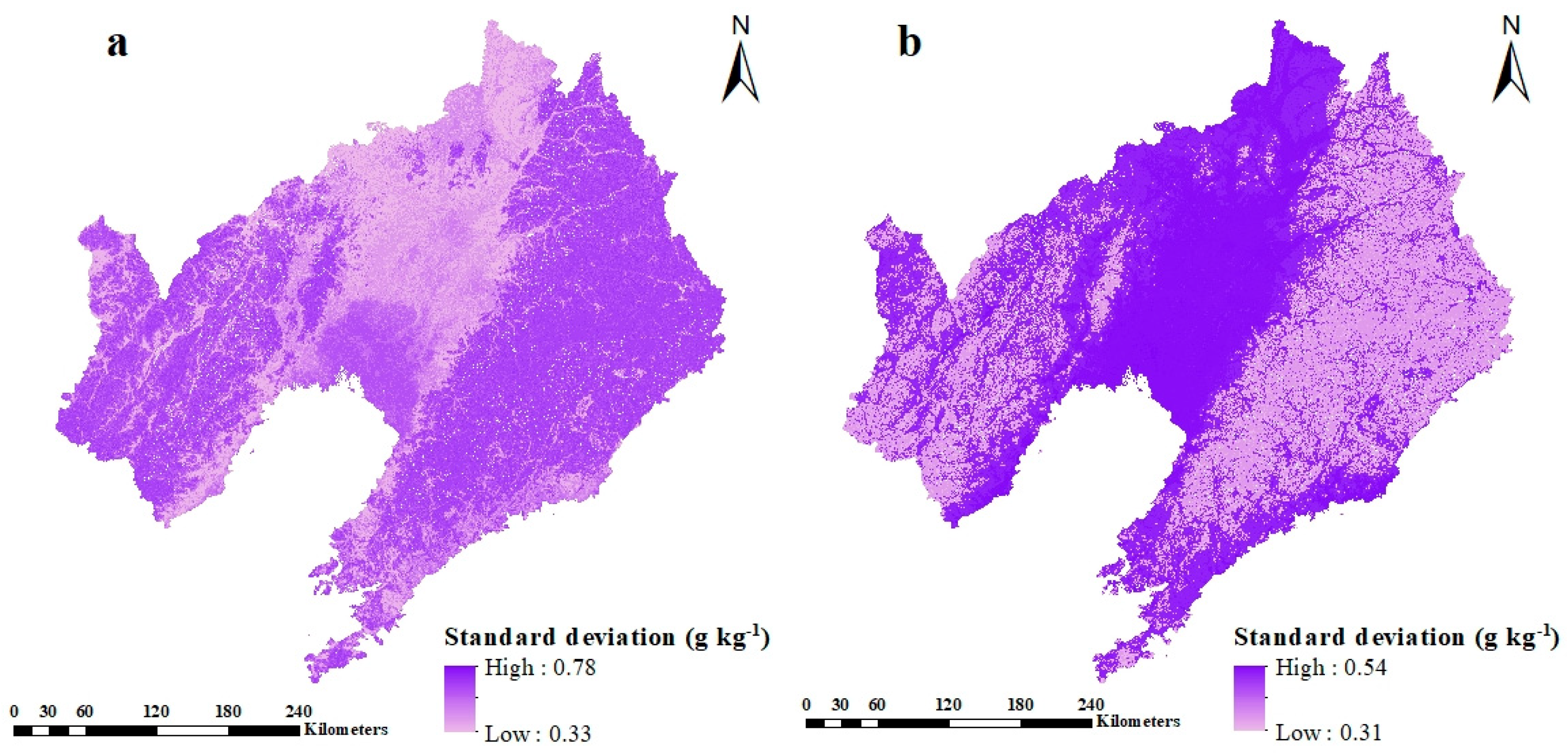
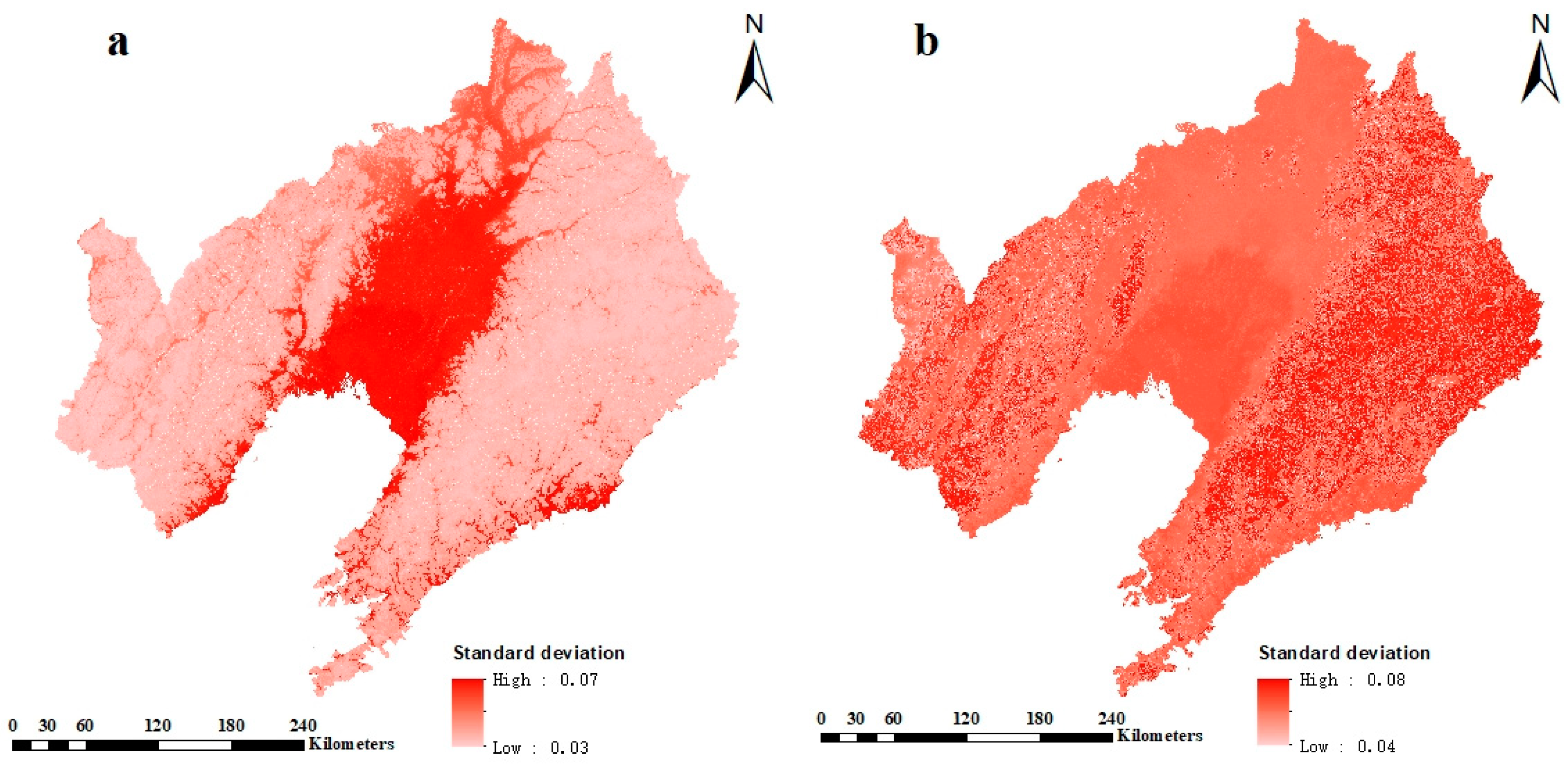
3.2. Uncertainties in the Present Study
3.3. Importance of the Covariates
3.4. Spatial Prediction of SOC and pH
4. Discussion
4.1. Model Performance
4.2. Effects of Covariates on SOC and pH
4.3. Estimates of SOC and pH
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dick, W.A. Organic Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus Concentrations and pH in Soil Profiles as Affected by Tillage Intensity 1. Soil Sci. Soc Am. J. 1982, 47, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Xu, D.; Chen, S.; Li, H.; Shi, Z. Evaluation of Machine Learning Approaches to Predict Soil Organic Matter and pH Using vis-NIR Spectra. Sensors 2019, 19, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, J.F.; Prasad, R. Soil Fertility Management for Sustainable Agriculture; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, C.A. Soil organic carbon, nitrogen and fertility. Dev. Soil Sci. 1978, 8, 173–271. [Google Scholar]
- Tiessen, H.; Cuevas, E.; Chacon, P. The role of soil organic matter in sustaining soil fertility. Nature 1994, 371, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaurov, D.E.; Perdomo, P.; Raskin, I. Optimizing soil fertility and pH to maximize cadmium removed by Indian mustard from contaminated soils. J. Plant Nutr. 1999, 22, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R.J.; Naidu, R. Influence of lime, fertilizer and manure applications on soil organic matter content and soil physical conditions: A review. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 1998, 51, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, Q. Evaluation of spatial and temporal changes of soil quality based on geostatistical analysis in the hill region of subtropical China. Geoderma 2003, 115, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; He, T.; Lu, X.; Luo, Y.; Smith, P. Extent to which pH and topographic factors control soil organic carbon level in dry farming cropland soils of the mountainous region of Southwest China. Catena 2018, 163, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudie, A.S. Human Impact on the Natural Environment; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vågen, T.G.; Winowiecki, L.A.; Tondoh, J.E.; Desta, L.T.; Gumbricht, T. Mapping of soil properties and land degradation risk in Africa using MODIS reflectance. Geoderma 2016, 263, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengl, T.; Heuvelink, G.B.; Kempen, B.; Leenaars, J.G.; Walsh, M.G.; Shepherd, K.D.; Tondoh, J.E. Mapping soil properties of Africa at 250 m resolution: Random forests significantly improve current predictions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minasny, B.; McBratney, A.B. Digital soil mapping: A brief history and some lessons. Geoderma 2016, 264, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Q.; Adhikari, K.; Jia, S.; Jin, X.; Liu, H. Spatial-temporal changes of soil organic carbon content in Wafangdian, China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosemary, F.; Indraratne, S.P.; Weerasooriya, R.; Mishra, U. Exploring the spatial variability of soil properties in an Alfisol soil catena. Catena 2017, 150, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlavan-Rad, M.R.; Akbarimoghaddam, A. Spatial variability of soil texture fractions and pH in a flood plain (case study from eastern Iran). Catena 2018, 160, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenny, H. Factors of Soil Formation: A System of Quantitative Pedology; McGrawHill: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Jin, X.; Adhikari, K.; Li, W.; Yu, M.; Bian, Z.; Wang, Q. Mapping total soil nitrogen from a site in northeastern China. Catena 2018, 166, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, B.P.; Jha, S.K.; Minasny, B.; McBratney, A.B. Comparing regression-based digital soil mapping and multiple-point geostatistics for the spatial extrapolation of soil data. Geoderma 2016, 262, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, T.; Schmidt, K.; MacMillan, R.A.; Rossel, R.A.V. Multi-scale digital soil mapping with deep learning. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, R.; Sharifi, F.; Bagherpour, B.; Safari, M. Prevalence of intestinal parasites in Isfahan city, central Iran, 2014. J. Parasit. Dis. 2016, 40, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Minasny, B.; Setiawan, B.I.; Arif, C.; Saptomo, S.K.; Chadirin, Y. Digital mapping for cost-effective and accurate prediction of the depth and carbon stocks in Indonesian peatlands. Geoderma 2016, 272, 20–31. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.M.; Zhang, G.L.; Liu, F.; Lu, Y.Y.; Yang, F.; Yang, F.; Li, D.C. Comparison of boosted regression tree and random forest models for mapping topsoil organic carbon concentration in an alpine ecosystem. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Were, K.; Bui, D.T.; Dick, Ø.B.; Singh, B.R. A comparative assessment of support vector regression, artificial neural networks, and random forests for predicting and mapping soil organic carbon stocks across an Afromontane landscape. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 52, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Grunwald, S. Assessment of carbon stocks in the topsoil using random forest and remote sensing images. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 1910–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; He, H.S.; Liang, Y.; Hawbaker, T.J.; Henne, P.D.; Liu, J.; Huang, C. Integrating forest inventory data and MODIS data to map species-level biomass in Chinese boreal forests. Can. J. For. Res. 2018, 48, 461–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau of Statistics Liaoning Province. Statistical Yearbook of Liaoning 2011; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2011. (In Chinese)
- Gong, Z.T. Chinese Soil Taxonomy; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1999; p. 903. [Google Scholar]
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization). International Soil Classification System for Naming Soil and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, A.X.; Yang, L.; Li, B.; Qin, C.; English, E.; Burt, J.E.; Zhou, C. Purposive sampling for digital soil mapping for areas with limited data. In Digital Soil Mapping with Limited Data; Hartemink, A.E., McBratney, A., de Lourdes Mendonça-Santos, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 33–245. [Google Scholar]
- Conrad, O.; Bechtel, B.; Bock, M.; Dietrich, H.; Fischer, E.; Gerlitz, L.; Böhner, J. System for automated geoscientific analyses (SAGA) v. 2.1. 4. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 1991–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, R.; Behrens, T.; Märker, M.; Elsenbeer, H. Soil organic carbon concentrations and stocks on Barro Colorado Island—Digital soil mapping using Random Forests analysis. Geoderma 2008, 146, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, 2013, Vienna, Austria. Available online: https://www.rproject.org/ (accessed on 7 March 2013).
- Lin, L. A concordance correlation coefficient to evaluate reproducibility. Biometrics 1989, 45, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hounkpatin, H.O.; Boyce, C.J.; Dunn, G.; Wood, A.M. Modeling bivariate change in individual differences: Prospective associations between personality and life satisfaction. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2018, 115, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, C.C.; Tsai, C.C.; Chen, Z.S. Soil organic carbon stocks in relation to elevation gradients in volcanic ash soils of Taiwan. Geoderma 2013, 209, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.P.; Orton, T.G.; Lacarce, E.; Meersmans, J.; Saby, N.P.A.; Paroissien, J.B.; Joliveta, C.; Boulonnea, L.; Arrouays, D. Evaluation of modelling approaches for predicting the spatial distribution of soil organic carbon stocks at the national scale. Geoderma 2014, 223, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.W.; De Jong, E.; Verity, G.E.; Gregorich, E.G. The effects of cultivation on the organic matter of soils of the Canadian prairies. In Transactions of the XIII Congress of International Society of Soil Science; Reclam Verlag: Hamburg, Germany, 1986; Volume 7, pp. 1344–1345. [Google Scholar]
- Harden, J.W.; Sharpe, J.M.; Parton, W.J.; Ojima, D.S.; Fries, T.L.; Huntington, T.G.; Dabney, S.M. Dynamic replacement and loss of soil carbon on eroding cropland. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1999, 13, 885–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minasny, B.; McBratney, A.B.; Malone, B.P.; Wheeler, I. Digital mapping of soil carbon. Adv. Agron. 2013, 118, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zhuang, Q.; Jia, S.; Jin, X.; Wang, Q. Spatial variations of soil organic carbon stocks in a coastal hilly area of China. Geoderma 2018, 314, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesmeier, M.; Hübner, R.; Spörlein, P.; Geuß, U.; Hangen, E.; Reischl, A.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Carbon sequestration potential of soils in southeast Germany derived from stable soil organic carbon saturation. Glob. Change Boil. 2014, 20, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, K.; Hartemink, A.E. Digital mapping of topsoil carbon content and changes in the Driftless Area of Wisconsin, USA. Soil Sci. Soc Am. J. 2015, 79, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.S.; Zhang, G.L.; Wu, Y.J.; Li, D.C.; Zhao, Y.G. Driving forces of soil organic matter change in Jiangsu Province of China. Soil Use Manag. 2015, 31, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.L.; Cai, Z.J.; Wang, B.J. Changes in pH and exchangeable acidity at depths of red soils derived from 4 parent materials under 3 vegetations. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2015, 28, 2818–2826. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.E.; Wang, Y.Q.; Ma, Z.M.; Guo, T.; Che, Z.; Huang, G.; Nan, L. Effect of vegetation types on soil salt ions transfer and accumulation in soil profile. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2011, 44, 2711–2729. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Elbasiouny, H.; Abowaly, M.; Abu_Alkheir, A.; Gad, A. Spatial variation of soil carbon and nitrogen pools by using ordinary Kriging method in an area of north Nile Delta, Egypt. Catena 2014, 113, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Adhikari, K.; Wang, Q.; Sui, Y.; Xin, G. Effect of cultivation history on soil organic carbon status of arable land in northeastern China. Geoderma 2019, 342, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
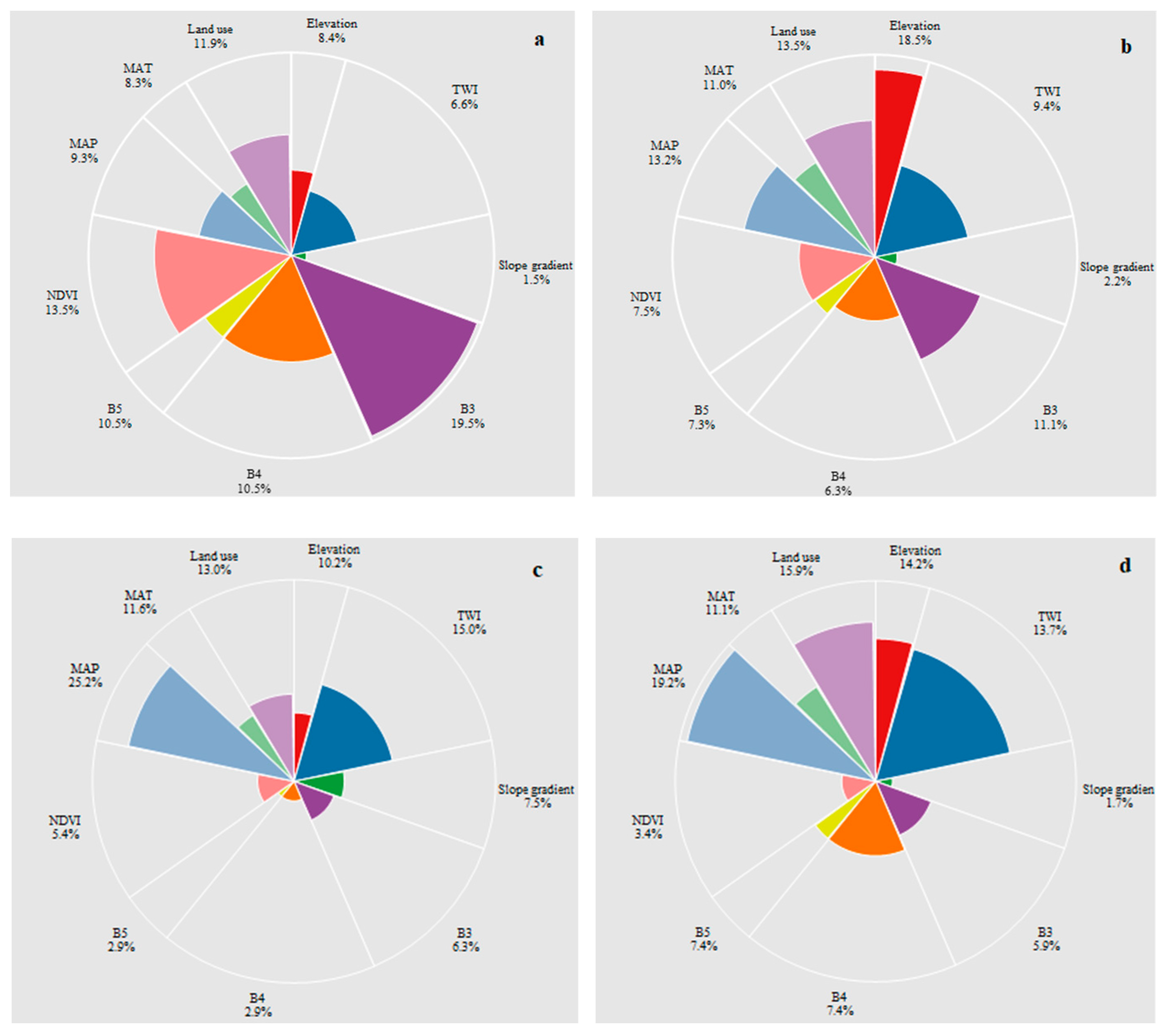

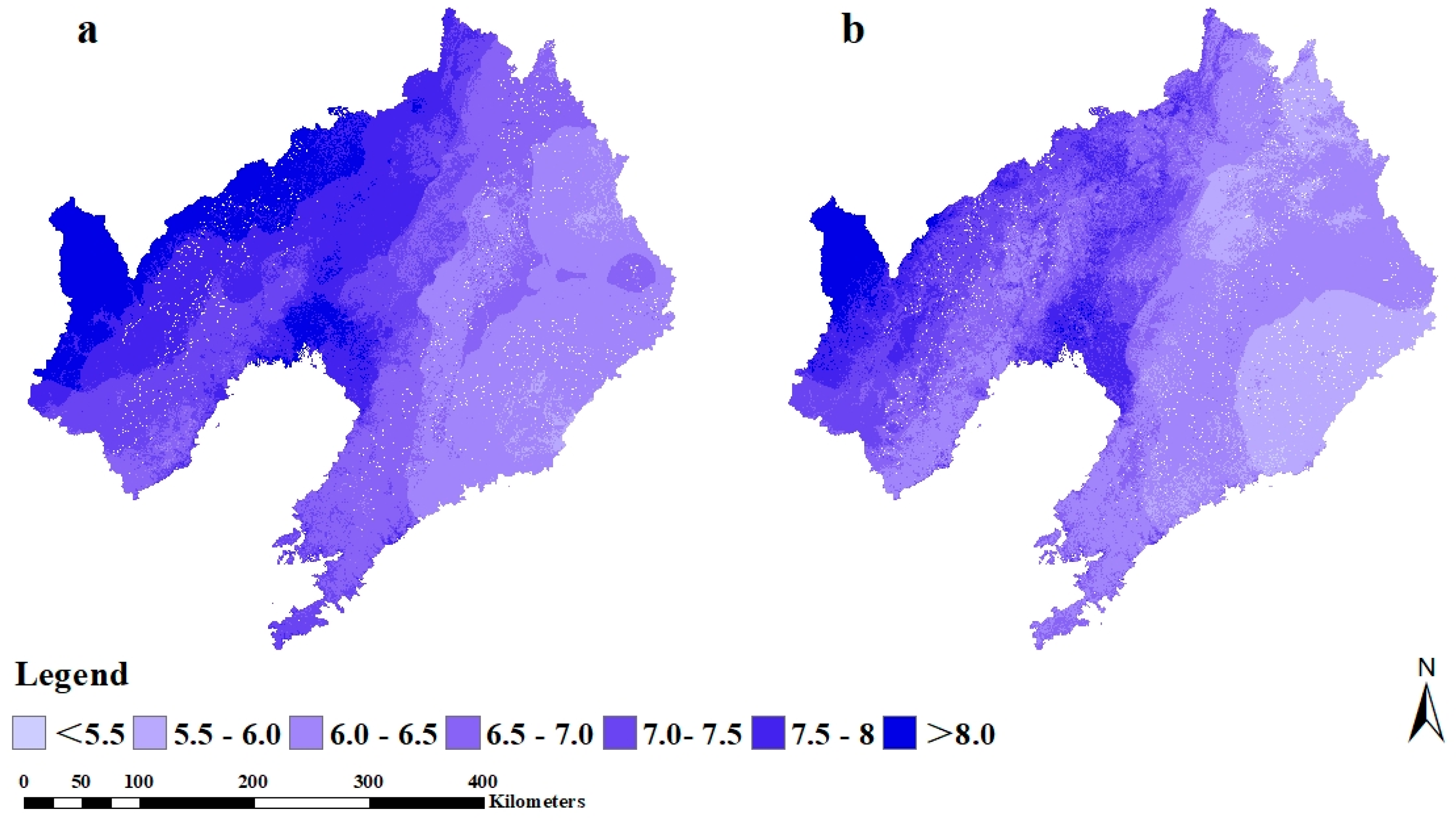
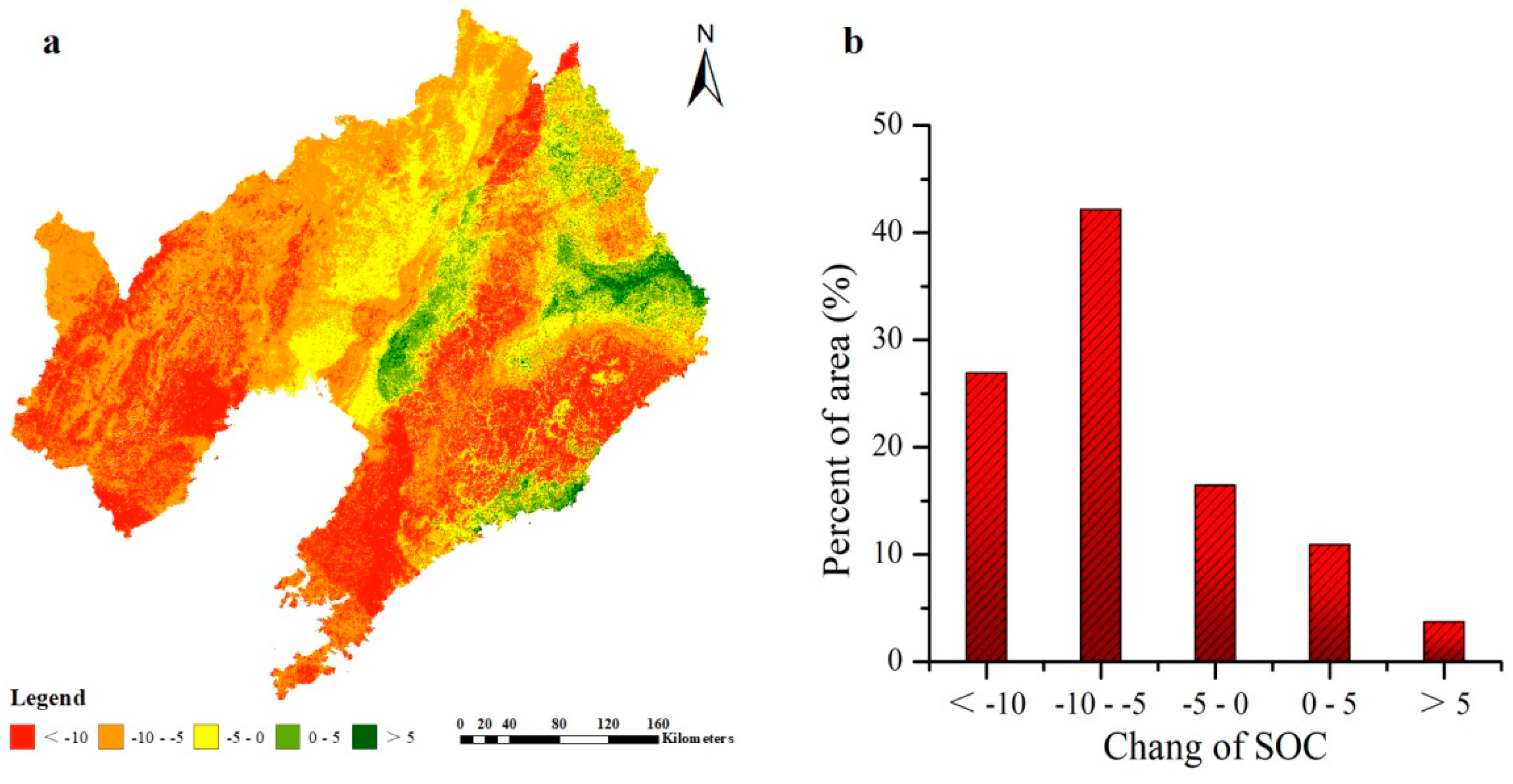
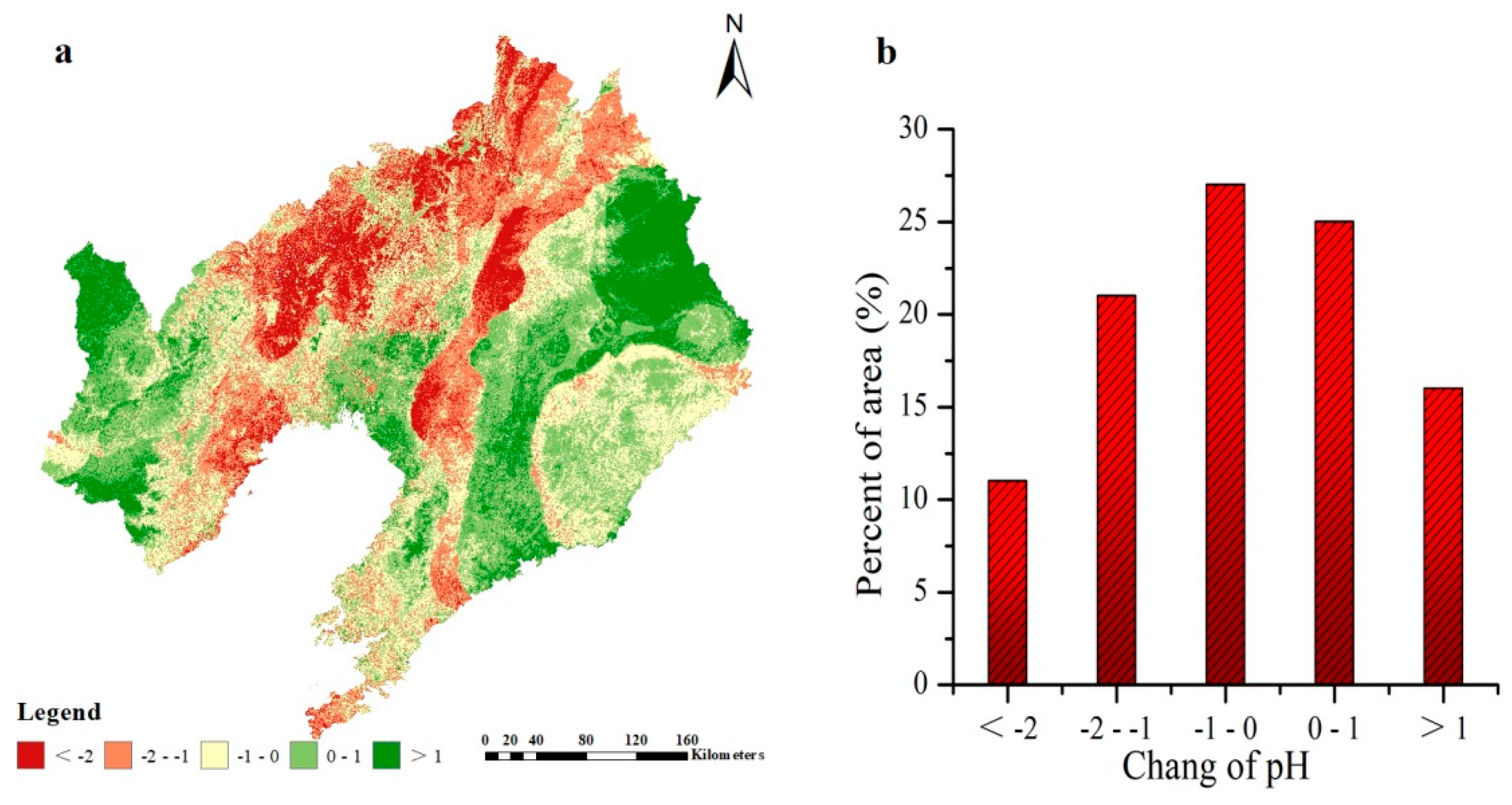
| Year | Property | SOC | pH | Elevation | Slope Gradient | TWI | MAP | MAT | B3 | B4 | B5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1982 | pH | −0.36 ** | |||||||||
| Elevation | 0.25 ** | −0.12 ** | |||||||||
| Slope gradient | 0.12 ** | −0.19 ** | 0.48 ** | ||||||||
| TWI | −0.12 ** | 0.32 ** | −0.54 ** | −0.70 ** | |||||||
| MAP | 0.62 ** | −0.65 ** | 0.25 ** | 0.19 ** | −0.24 ** | ||||||
| MAT | −0.58 ** | 0.27 ** | −0.58 ** | −0.19 ** | 0.21 ** | −0.37 ** | |||||
| B3 | −0.11 ** | 0.034 | −0.14 ** | −0.17 ** | 0.05 | −0.15 ** | 0.14 ** | ||||
| B4 | −0.24 ** | 0.07 * | −0.17 ** | −0.19 ** | 0.05 | −0.25 ** | 0.24 ** | 0.97 ** | |||
| B5 | −0.21 ** | 0.05 | −0.10 ** | −0.15 ** | −0.01 | −0.23 ** | 0.18 ** | 0.94 ** | 0.98 ** | ||
| NDVI | −0.42 ** | 0.16 ** | −0.11 ** | −0.07 | 0.01 | −0.32 ** | 0.36 ** | −0.31 ** | −0.06 | −0.06 | |
| Land use | −0.38 ** | 0.24 ** | −0.17 | −0.24 * | −0.31 ** | −0.15 | 0.11 | −0.34 ** | −0.09 | −0.07 | |
| 2012 | pH | −0.29 ** | |||||||||
| Elevation | 0.18 ** | 0.23 ** | |||||||||
| Slope gradient | 0.12 ** | −0.10 ** | 0.44 ** | ||||||||
| TWI | −0.11 ** | 0.19 ** | −0.55 ** | −0.72 ** | |||||||
| MAP | 0.59 ** | −0.52 ** | −0.24 ** | 0.12 ** | −0.12 ** | ||||||
| MAT | −0.36 ** | 0.11 ** | −0.42 ** | −0.13 ** | 0.15 ** | −0.21 ** | |||||
| B3 | −0.06 | −0.07 * | −0.06 | −0.12 ** | 0.09 ** | −0.12 ** | 0.08 * | ||||
| B4 | −0.15 ** | −0.05 | −0.05 | −0.12 ** | 0.06 | −0.21 ** | 0.17 ** | 0.97 ** | |||
| B5 | −0.14 ** | −0.06 | −0.02 | −0.10 ** | 0.02 | −0.20 ** | 0.13 ** | 0.95 ** | 0.98 ** | ||
| NDVI | −0.33 ** | 0.11 ** | 0.07 * | 0.01 | −0.11 ** | −0.32 ** | 0.32 ** | −0.34 ** | −0.12 ** | −0.11 ** | |
| Land use | −0.32 ** | 0.21 ** | −0.12 | −0.23 * | −0.29 ** | −0.16 | 0.17 | −0.31 ** | −0.05 | −0.08 |
| Property | Year | Index | Min | Median | Mean | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOC | 1982 | MAE | 4.23 | 4.34 | 4.35 | 4.41 |
| RMSE | 5.61 | 5.62 | 5.71 | 5.82 | ||
| R2 | 0.63 | 0.68 | 0.69 | 0.71 | ||
| LCCC | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.83 | ||
| 2012 | MAE | 3.21 | 3.25 | 3.26 | 3.29 | |
| RMSE | 4.31 | 4.38 | 4.39 | 4.43 | ||
| R2 | 0.58 | 0.62 | 0.63 | 0.64 | ||
| LCCC | 0.75 | 0.78 | 0.79 | 0.81 | ||
| pH | 1982 | MAE | 0.46 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 0.47 |
| RMSE | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.59 | ||
| R2 | 0.52 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.55 | ||
| LCCC | 0.71 | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.72 | ||
| 2012 | MAE | 0.52 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.53 | |
| RMSE | 0.66 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.67 | ||
| R2 | 0.48 | 0.48 | 0.48 | 0.49 | ||
| LCCC | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.67 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, L.; Wang, S.; Zhuang, Q.; Yang, Z.; Bai, S.; Jin, X.; Lei, G. Spatial-Temporal Changes in Soil Organic Carbon and pH in the Liaoning Province of China: A Modeling Analysis Based on Observational Data. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3569. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11133569
Qi L, Wang S, Zhuang Q, Yang Z, Bai S, Jin X, Lei G. Spatial-Temporal Changes in Soil Organic Carbon and pH in the Liaoning Province of China: A Modeling Analysis Based on Observational Data. Sustainability. 2019; 11(13):3569. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11133569
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Li, Shuai Wang, Qianlai Zhuang, Zijiao Yang, Shubin Bai, Xinxin Jin, and Guangyu Lei. 2019. "Spatial-Temporal Changes in Soil Organic Carbon and pH in the Liaoning Province of China: A Modeling Analysis Based on Observational Data" Sustainability 11, no. 13: 3569. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11133569
APA StyleQi, L., Wang, S., Zhuang, Q., Yang, Z., Bai, S., Jin, X., & Lei, G. (2019). Spatial-Temporal Changes in Soil Organic Carbon and pH in the Liaoning Province of China: A Modeling Analysis Based on Observational Data. Sustainability, 11(13), 3569. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11133569







