Tensile Behavior and Diffusion of Moisture through Flax Fibers by Desorption Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
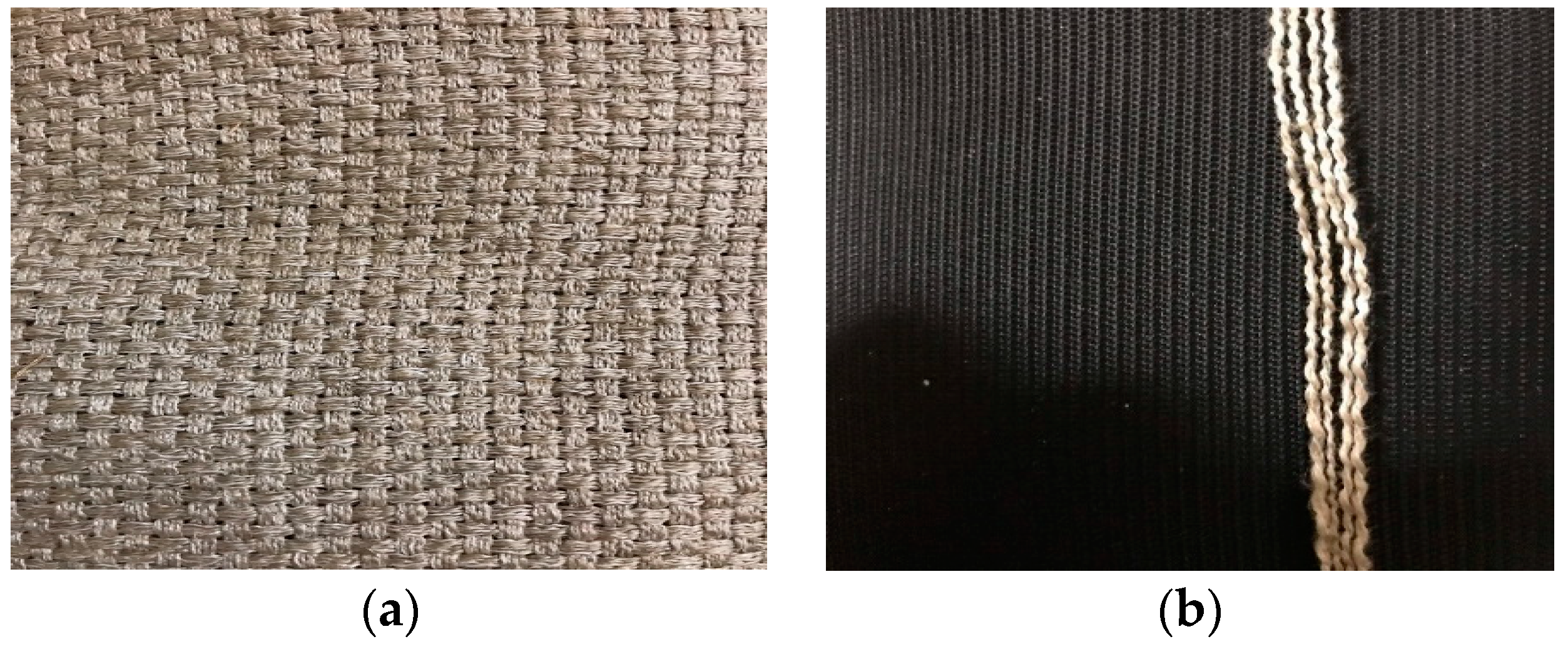
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Moisture Diffusion Testing
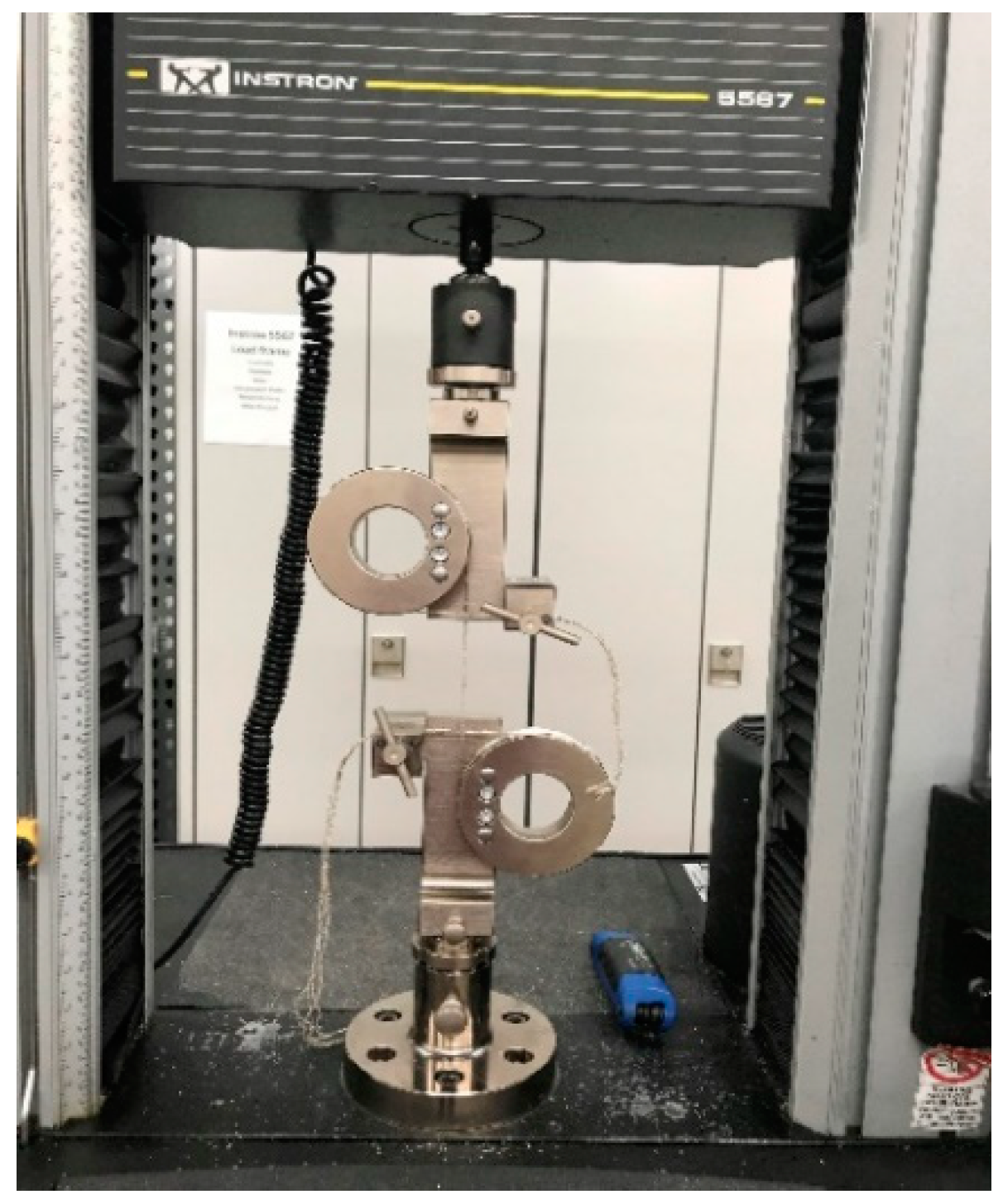
2.2. Tow Tensile Testing
3. Results
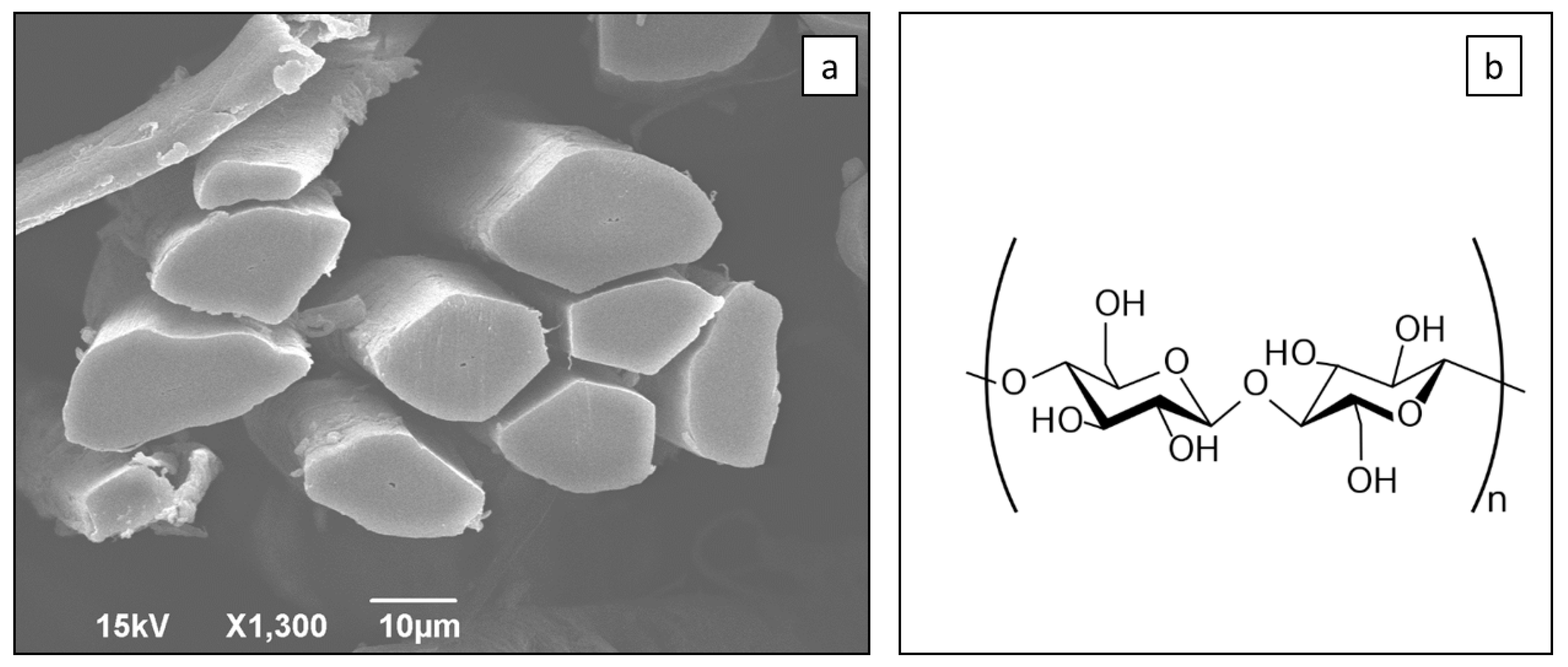
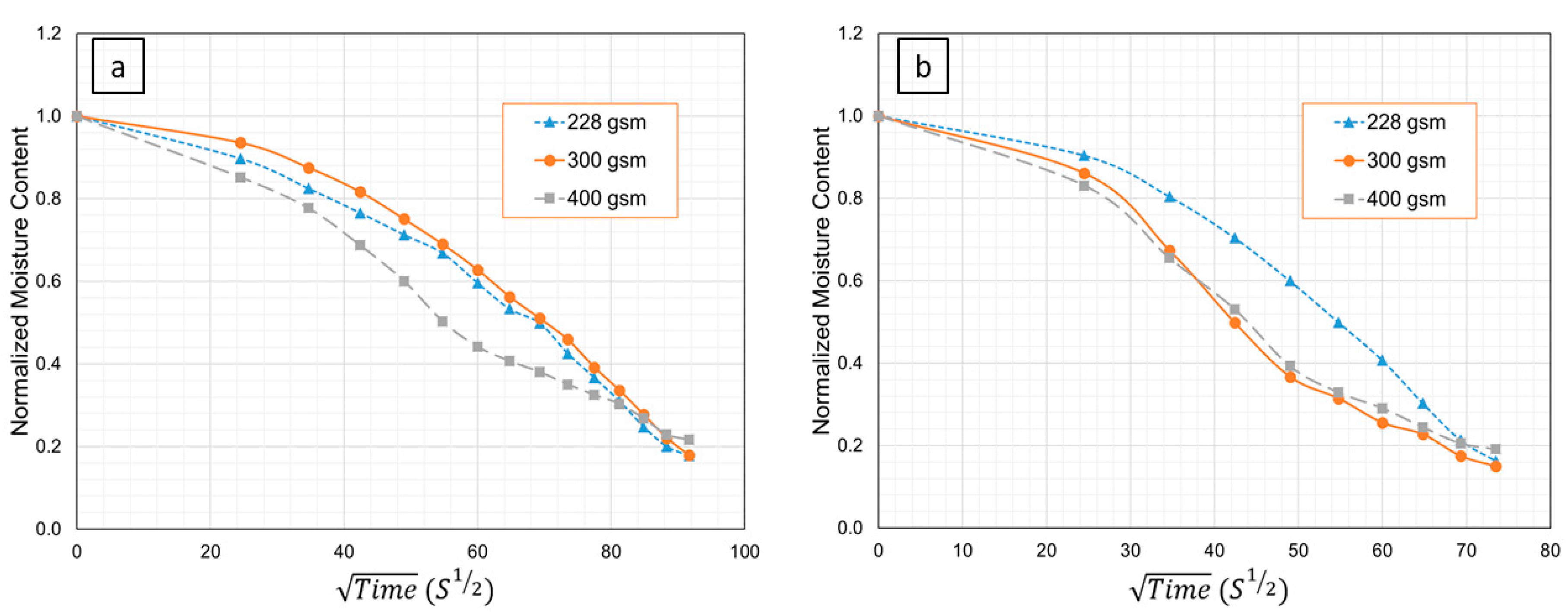
3.1. Moisture Desorption in Flax Fiber Non-Woven Random Mats
3.2. Influence of Moisture on Tensile Properties of Flax Fiber Tows
4. Discussion
4.1. Moisture Desorption in Flax Fiber Non-Woven Random Mats
4.2. Influence of Moisture on Tensile Properties of Flax Fiber Tows
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Virta, R.L. Asbestos. In Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fuqua, M.A.; Huo, S.; Ulven, C.A. Natural fiber reinforced composites. Polym. Rev. 2012, 52, 259–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisti, L.; Totaro, G.; Vannini, M.; Celli, A. Retting process as a pretreatment of natural fibers for the development of polymer composites. In Lignocellulosic Composite Materials; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 97–135. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, C.A.; Amiri, A.; Webster, D.C.; Ulven, C.A. Long-term behavior of bio-composites for structural applications. In Proceedings of The Composites and Advanced Materials Conference; CAMX: Anaheim, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fowler, P.A.; Hughes, J.M.; Elias, R.M. Biocomposites: Technology, environmental credentials and market forces. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 1781–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, N.; Tiwary, R.K.; Rohatgi, P.K. Bibliography Resource structure properties of natural cellulosic fibres ? an annotated bibliography. J. Mater. Sci. 1988, 23, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilholt, H.; Lawther, J. Natural organic fibers. In Comprehensive Composite Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; Volume 1, pp. 303–325. [Google Scholar]
- Franck, R.R. Bast and Other Plant Fibres; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bolton, A.J. Natural fibers for plastic reinforcement. Mater. Technol. 1994, 9, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saheb, D.N.; Jog, J.P. Natural fiber polymer composites: A review. Adv. Polym. Technol. 1999, 18, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Studies on jute composites—A literature review. Polym. Technol. Eng. 1995, 34, 729–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledzki, A.K.; Sperber, V.E.; Faruk, O. Natural and Wood Fibre Reinforcement in Polymers; Rapra Technology Limited: Shrewsbury, Shropshire, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Netravali, A.N.; Chabba, S. Composites get greener. Mater. Today 2003, 6, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baillie, C. Green Composites: Polymer Composites and the Environment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M.; Drzal, L.T.; Selke, S.; Harte, B.; Hinrichsen, G. Natural Fibers, Biopolymers, and Biocomposites; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pickering, K.L. Properties and Performance of Natural-Fibre Composites; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- John, M.J.; Thomas, S. Biofibres and biocomposites. Carbohyd. Polym. 2008, 71, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A.; Burkart, V.; Yu, A.; Webster, D.; Ulven, C. The potential of natural composite materials in structural design. In Sustainable Composites for Aerospace Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 269–291. [Google Scholar]
- Amiri, A.; Krosbakken, T.; Schoen, W.; Theisen, D.; Ulven, C.A. Design and manufacturing of a hybrid flax/carbon fiber composite bicycle frame. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part. P J. Sports Eng. Technol. 2018, 232, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, J.; Amiri, A.; Ulven, C. Hybridized carbon and flax fiber composites for tailored performance. J. Mater. Des. 2016, 102, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveen, J.; Sathish Kumar, T.P.; Satheesh Kumar, S. Effect of moisture absorption on the tensile behavior of woven hybrid natural fiber reinforced polymer composites. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2014, 3, 1091–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriu, A.; Mustata, A. Flax and hemp-natural alternatives in the field of medical textiles. Buletin Institutului Politehnic Din Iasi, Tome LVI (LX), Lasi, Romania. 2010. Available online: http://www.tex.tuiasi.ro/BIP/1_2010/17-23_2_Grigoriu_.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2019).
- Austin, D.F. Plants for people. Econ. Bot. 2003, 57, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Flax Production. Available online: http://www.fao.org/tempref/docrep/fao/009/a0439e/a0439e22.pdf (accessed on 16 May 2019).
- Moothoo, J.; Allaoui, S.; Ouagne, P.; Soulat, D. A study of the tensile behaviour of flax tows and their potential for composite processing. Mater. Des. 2014, 55, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A. Characterization, Long-Term Behavior Evaluation and Thermo-Mechanical Properties of Untreated and Treated Flax Fiber-Reinforced Composites. Ph.D. Dissertation, North Dakota State University, Fargo, ND, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Salnikov, V.V.; Ageeva, M.V.; Yumashev, V.N.; Lozovaya, V.V. Ultrastructural analysis of bast fibers. Rus. Plant. Physiol. 1993, 40, 416–421. [Google Scholar]
- Bogoeva-Gaceva, G.; Avella, M.; Malinconico, M.; Buzarovska, A.; Grozdanov, A.; Gentile, G.; Errico, M.E. Natural fiber eco-composites. Polym. Compos. 2007, 28, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldas, D.; Kokta, B.V.; Daneault, C. Influence of coupling agents and treatments on the mechanical properties of cellulose fiber–polystyrene composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1989, 37, 751–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadez-Gonzalez, A.; Cervantes-Uc, J.; Olayo, R.; Herrera-Franco, P. Chemical modification of henequén fibers with an organosilane coupling agent. Compos. Part B Eng. 1999, 30, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, M.Z.; Zhang, M.Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, G.C.; Zeng, H.M. The effect of fiber treatment on the mechanical properties of unidirectional sisal-reinforced epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2001, 61, 1437–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baley, C. Analysis of the flax fibres tensile behaviour and analysis of the tensile stiffness increase. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2002, 33, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallade, J. Endosperme ou albumen? Petite histoire d’un choix terminologique relatif à l’organisation de l’ovule et de la graine chez les Phanérogames. Acta Bot. Gallica 2004, 151, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bowes, B.G. A Colour Atlas of Plant Structure; Manson Publishing Ltd.: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Bos, H.L.; Donald, A.M. In situ ESEM study of the deformation of elementary flax fibres. J. Mater. Sci. 1999, 34, 3029–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledzki, A. Composites reinforced with cellulose based fibres. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1999, 24, 221–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustata, A. Factors influencing fiber-fiber friction in the case of bleached flax. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 1997, 31, 405–413. [Google Scholar]
- John, M.J.; Anandjiwala, R.D. Recent developments in chemical modification and characterization of natural fiber-reinforced composites. Polym. Compos. 2008, 29, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fangueiro, R.; Rana, S. Natural Fibres: Advances in Science and Technology Towards Industrial Applications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ehresmann, M.; Amiri, A.; Ulven, C. The effect of different variables on in-plane radial permeability of natural fiber mats. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2018, 37, 1191–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafeiropoulos, N.; Baillie, C. A study of the effect of surface treatments on the tensile strength of flax fibres: Part II. Application of Weibull statistics. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersons, J.; Spārniņš, E.; Joffe, R.; Wallstrom, L. Strength distribution of elementary flax fibres. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffe, R.; Andersons, J.; Wallström, L. Strength and adhesion characteristics of elementary flax fibres with different surface treatments. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2003, 34, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, H.L.; Oever, M.J.A.V.D.; Peters, O.C.J.J. Tensile and compressive properties of flax fibres for natural fibre reinforced composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2002, 37, 1683–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assarar, M.; Scida, D.; El Mahi, A.; Poilâne, C.; Ayad, R. Influence of water ageing on mechanical properties and damage events of two reinforced composite materials: Flax–fibres and glass–fibres. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A.; Ulven, C. Surface treatment of flax fiber. In Proceedings of the 65th Flax Institute of the United States, Fargo, ND, USA, 27–28 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Stamboulis, A.; Baillie, C.A.; Garkhail, S.K.; Van Melick, H.G.H.; Peijs, T. Environmental durability of flax fibres and their composites based on polypropylene matrix. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2000, 7, 273–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, C.T.; Waldron, K.W. Physiology and Biochemistry of Plant Cell Walls; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, W.; Hearle, J. Physical Properties of Textile Fibers, 4th ed.; Wood Head Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Stamboulis, A.; Baillie, C.; Peijs, T. Effects of environmental conditions on mechanical and physical properties of flax fibers. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2001, 32, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, G. Environmental Effects on Composite Materials; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1981; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D2256-02 Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Yarns by the Single-Strand Method. In Annual Book of ASTM Standards; D. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1972.
- Feng, H.; Li, J.; Wang, L. Preparation of biodegradable flax shive cellulose-based superabsorbent polymer under microwave irradiation. BioResources 2010, 5, 1484–1495. [Google Scholar]
- Warner, S.B. Fiber Science; Pearson College Division: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]




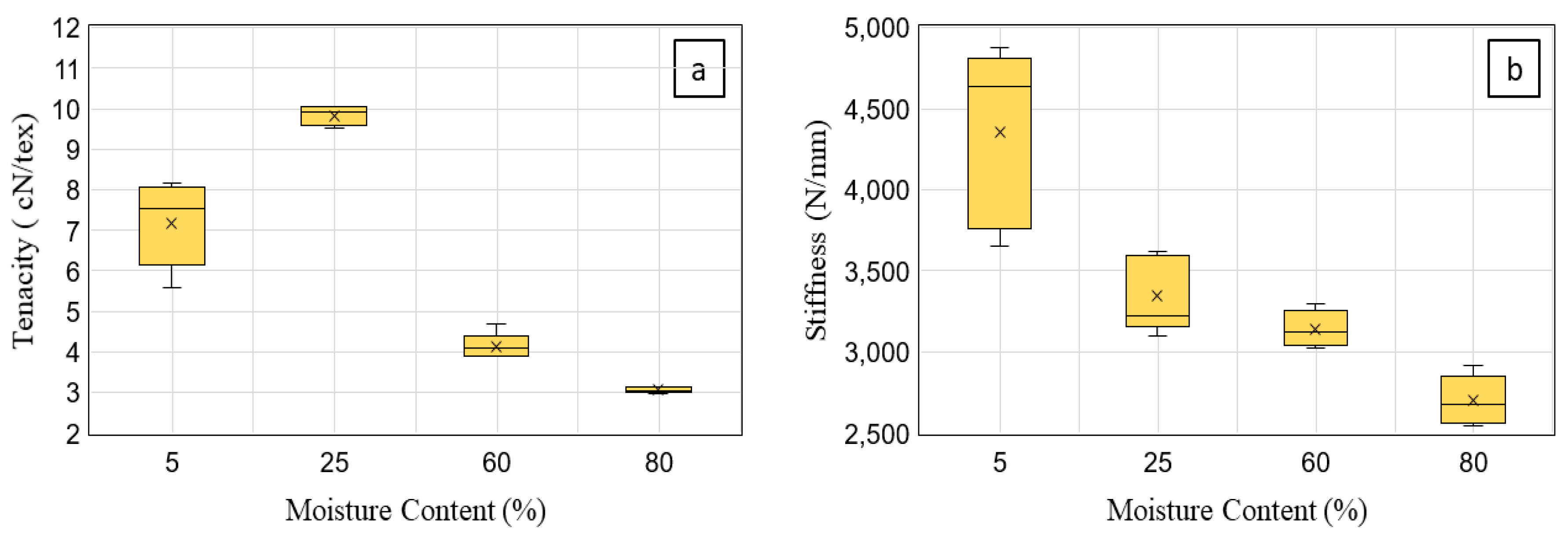
| Moisture (%) | Tenacity (cN/tex) | Stiffness (N/mm) | Elongation at Failure (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 7.18 ± 0.94 | 4352.80 ± 495.69 | 12.78 ± 0.98 |
| 25 | 9.83 ± 0.21 | 3342.28 ± 208.27 | 22.74 ± 3.67 |
| 60 | 4.13 ± 0.29 | 3141.40 ± 100.95 | 21.49 ± 3.23 |
| 80 | 3.06 ± 0.07 | 2700.88 ± 135.42 | 28.27 ± 0.34 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radkar, S.S.; Amiri, A.; Ulven, C.A. Tensile Behavior and Diffusion of Moisture through Flax Fibers by Desorption Method. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3558. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11133558
Radkar SS, Amiri A, Ulven CA. Tensile Behavior and Diffusion of Moisture through Flax Fibers by Desorption Method. Sustainability. 2019; 11(13):3558. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11133558
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadkar, Swarda S., Ali Amiri, and Chad A. Ulven. 2019. "Tensile Behavior and Diffusion of Moisture through Flax Fibers by Desorption Method" Sustainability 11, no. 13: 3558. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11133558
APA StyleRadkar, S. S., Amiri, A., & Ulven, C. A. (2019). Tensile Behavior and Diffusion of Moisture through Flax Fibers by Desorption Method. Sustainability, 11(13), 3558. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11133558






