The Effect of Quality Attributes on Visiting Consumers’ Patronage Intentions of Green Restaurants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Green Restaurants
2.2. Quality Attributes of Restaurants
3. Theoretical Model and Hypotheses
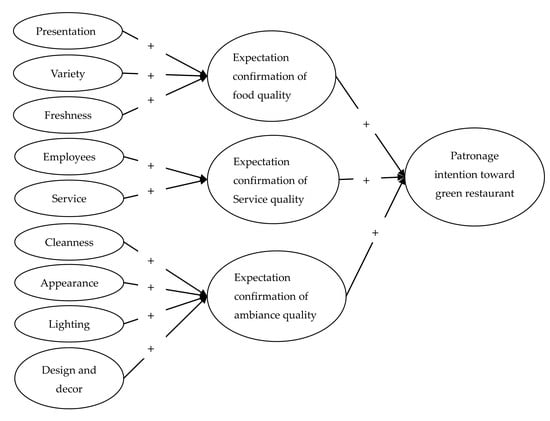
3.1. Theoretical Model
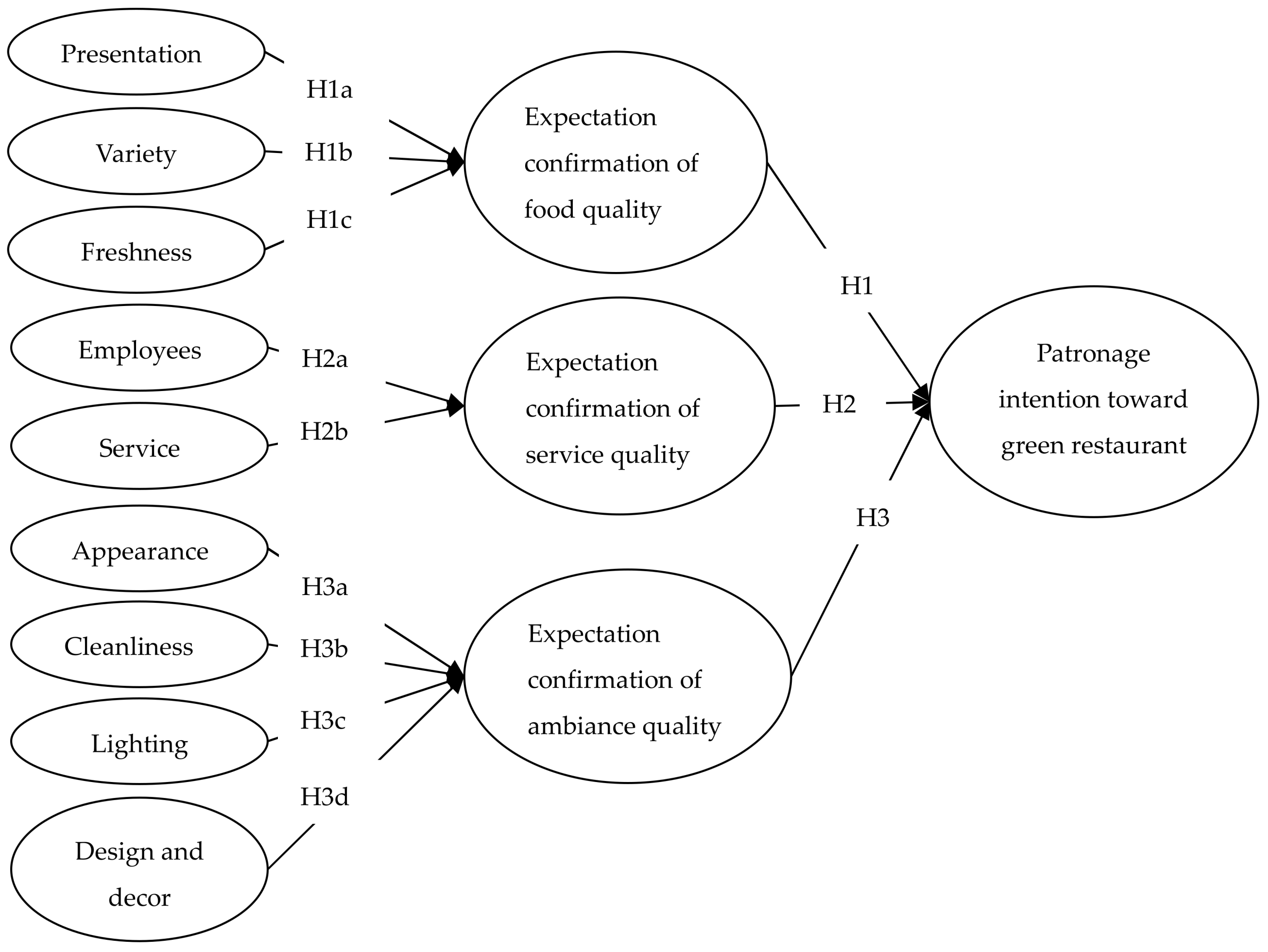
3.2. Hypotheses
4. Methodology
4.1. Data Collection
4.2. Measurement
4.3. Common Method Bias
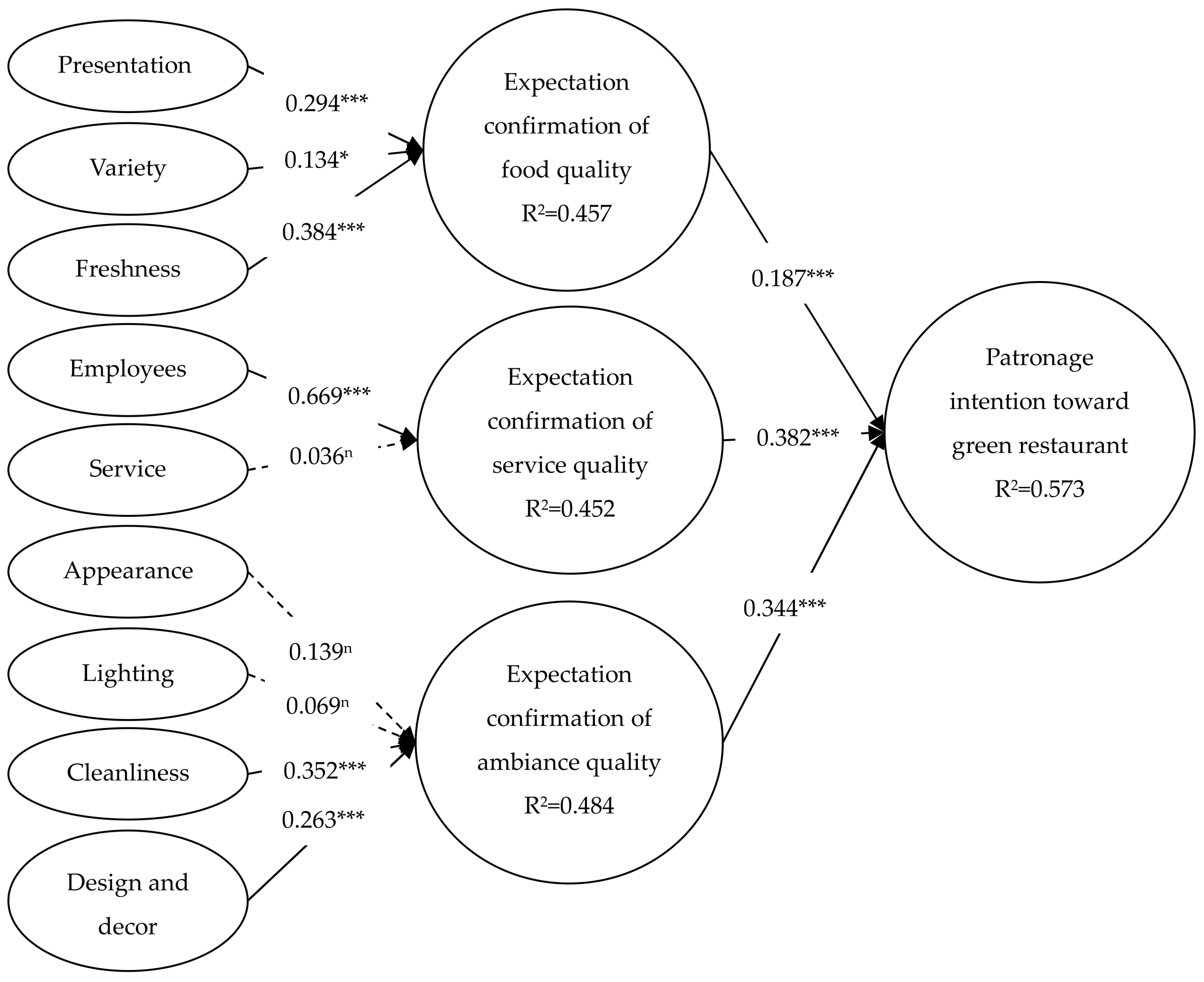
5. Result
5.1. Measurement Model
5.2. Structural Model
6. Discussion
7. Implications and Limitations
7.1. Implications
7.1.1. Theoretical Implications
7.1.2. Practical Implications
7.2. Limitations and Further Study
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, C.H.; Kao, S.C.; Wu, C.C.; Huang, S. Location-aware service applied to mobile short message advertising: Design, development, and evaluation. Inf. Process. Manag. 2015, 51, 625–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.H.; Chang, Y.P.; Luo, J.J.; Li, X. Understanding the adoption of location-based recommendation agents among active users of social networking sites. Inf. Process. Manag. 2014, 50, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.H.; Sun, H.; Chang, Y.P. How the content of location-based advertisings influences consumers’ store patronage intention. J. Consum. Mark. 2017, 34, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Line, N.D.; Hanks, L.; Kim, W.G. Hedonic adaptation and satiation: Understanding switching behavior in the restaurant industry. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2016, 52, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.; Jang, S.C. Attributes, consequences, and consumer values A means-end chain approach across restaurant segments. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2013, 25, 383–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujisic, M.; Hutchinson, J.; Parsa, H.G. The effects of restaurant quality attributes on customer behavioral intentions. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2014, 26, 1270–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.H.; Parsa, H.G.; Self, J. The Dynamics of Green Restaurant Patronage. Cornell Hosp. Q. 2010, 51, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yu, Y.F. The Impact of Consumers’ Beliefs on Attitudes and Patronage Intention toward Green Restaurant in Taiwan. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 524–527, 3501–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.-M.; Wu, K.-S.; Huang, D.-M. The Influence of Green Restaurant Decision Formation Using the VAB Model: The Effect of Environmental Concerns upon Intent to Visit. Sustainability 2014, 6, 8736–8755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.-J.; Chen, K.-S.; Wang, Y.-Y. Green practices in the restaurant industry from an innovation adoption perspective: Evidence from Taiwan. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2012, 31, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiPietro, R.B.; Yang, C.; Charles, P. Green practices in upscale foodservice operations: Customer perceptions and purchase intentions. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2013, 25, 779–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namkung, Y.; Jang, S. Are Consumers Willing to Pay more for Green Practices at Restaurants? J. Hosp. Tour. Res. 2017, 41, 329–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-T.; Cheng, C.-C.; Hsu, F.-S. GRSERV scale: An effective tool for measuring consumer perceptions of service quality in green restaurants. Total Qual. Manag. Bus. Excell. 2015, 26, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, L.; Huang, Y.-K.; Hu, L. Green attributes of restaurants: What really matters to consumers? Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2016, 55, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namkung, Y.; Jang, S. Does food quality really matter in restaurant? Its impact on customer satisfaction and behavioral intentions. J. Hosp. Tour. Res. 2007, 31, 387–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jang, S. Perceptions of Chinese restaurants in the US: What affects customer satisfaction and behavioral intentions? Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2009, 28, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.H.; Chang, Y.P.; Chang, A. Effects of free gifts with purchase on online purchase satisfaction: The moderating role of uncertainty. Internet Res. 2015, 25, 690–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, N.; Goodman, R.J.; Goh, B.K. Restaurant consumers repeat patronage: A service quality concern. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2011, 30, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.; Parasuraman, A.; Grewal, D.; Voss, G.B. The Influence of Multiple Store Environment Cues on Perceived Merchandise Value and Patronage Intentions. J. Mark. 2002, 66, 120–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.P.; Zhu, D.H. The role of perceived social capital and flow experience in building users’ continuance intention to social networking sites in China. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2012, 28, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayans, A.; Herath, T.C.; O’Brien, N. Understanding continuance intentions of physicians with electronic medical records (EMR): An expectancy-confirmation perspective. Decis. Support. Syst. 2015, 77, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.Y.; Huang, F.; Hou, H.P.; Chen, Y.; Bulysheva, L. Customized logistics service and online shoppers’ satisfaction: An empirical study. Internet Res. 2016, 26, 484–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, R.L. A cognitive model of the antecedents and consequences of satisfaction decisions. J. Mark. Res. 1980, 17, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacherjee, A. Understanding information systems continuance: An expectation confirmation model. MIS Q. 2001, 25, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.M.; Kim, E.; Tang, R.; Bosselman, R. Exploring the determinants of e-commerce by integrating a technology-organization-environment framework and an expectation-confirmation model. Tour. Anal. 2015, 20, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.-L. Intentions to continue using a digital mammography vehicle based on the technology acceptance model and expectation confirmation theory. Asian Women 2017, 33, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, B. The formation of consumer attitudes and intentions towards fast food restaurants: How do teenagers differ from adults? Manag. Serv. Qual. 2012, 22, 260–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swimberghe, K.R.; Wooldridge, B.R. Drivers of Customer Relationships in Quick-Service Restaurants: The Role of Corporate Social Responsibility. Cornell Hosp. Q. 2014, 55, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zinkhan, G.M. Determinants of retail patronage: A meta-analytical perspective. J. Retail. 2006, 82, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Prybutok, V.R. Determinants of customer-perceived service quality in fast-food restaurants and their relationship to customer satisfaction and behavior intentions. Qual. Manag. J. 2008, 15, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajic, T.; Dado, J. Modelling the relationships among retail atmospherics, service quality, satisfaction and customer behavioural intentions in an emerging economy context. Total Qual. Manag. Bus. Excell. 2013, 24, 1096–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyewole, P. The role of frequency of patronage and service quality of all-you-can-eat buffet restaurant: A perspective of socio-economic and demographic characteristics of African American consumers. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2013, 34, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andaleeb, S.S.; Conway, C. Customer satisfaction in the restaurant industry: An examination of the transaction-specific model. J. Serv. Mark. 2006, 20, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, N.Y.M.; Wanb, P.Y.K.; Dongc, P. The impact of the servicescape on the desire to stay in convention and exhibition enters: The case of Macao. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2012, 31, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.H.; Chang, Y.P. Effects of interactions and product information on initial purchase intention in product placement in social games: The moderating role of product familiarity. J. Electron. Commer. Res. 2015, 16, 22–33. [Google Scholar]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; Organ, D.W. Self-reports in organizational research: Problems and prospects. J. Manag. 1986, 12, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringle, C.M.; Wende, S.; Will, A. SmartPLS 2. SmartPLS. 2005. Available online: http://www.smartpls.com (accessed on 2 February 2018).
- Chin, W.W. The partial least squares approach for structural equation modeling. In Modern Methods for Business Research; Marcoulides, G.A., Ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1998; pp. 295–336. [Google Scholar]
- Nunnally, J.C. Psychometric Theory; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, W.W.; Gopal, A. Adoption intention in GSS: Relative importance of beliefs. Data Base Data Base Adv. Inf. Syst. 1995, 26, 42–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement errors. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakefield, K.L.; Blodgett, J.G. The effect of the servicescape on customers’ behavioral intentions in leisure service settings. J. Serv. Mark. 1996, 10, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, J.-Z.; Hsieh, C.-C. The impact of restaurants’ green supply chain practices on firm performance. Sustainability 2016, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaker, D.; Walker, J.L. Revealing the value of “green” and the small group with a big heart in transportation mode choice. Sustainability 2013, 5, 2913–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiPietro, R.B.; Parsa, H.G.; Gregory, A. Restaurant QSC inspections and financial performance: An empirical investigation. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2011, 23, 982–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author | Findings |
|---|---|
| Hu et al., 2010 [7] | Knowledge of a restaurant’s sustainable practices and environmental concerns is an important antecedent of consumers’ green restaurant patronage intentions. |
| Liu & Yu, 2012 [8] | Consumers’ beliefs affect attitudes and patronage intentions towards green restaurants. |
| Chou et al., 2012 [10] | Perceived innovation characteristics affect the intention to adopt green practices in restaurants through attitude, and perceived behavioral control affects the intention to adopt. |
| DiPietro et al., 2013 [11] | Female customers and people with higher education are more conscious regarding green practices. In addition, customers who utilize green practices at home intend to visit green restaurants more often. |
| Teng et al., 2014 [9] | Consumer values and attitudes affect their intentions to visit green restaurants. Attitude is affected by consumer values and environmental concerns. |
| Chen et al., 2015 [13] | The service quality of green restaurants includes seven dimensions: tangible, empathetic, reliable, responsive, assuring, environmentally-oriented, and food quality. |
| Kwok et al., 2016 [14] | Environment-focused attributes are the most important green attributes of restaurant. Consumers who value food-focused and administration-focused attributes and younger consumers are more likely to pay more, wait longer, and/or go farther to dine at a green restaurant. Females tend to rate higher than males in all three categories of green attributes. Families with children value food-focused attributes more than those without children. |
| Namkung & Jang, 2017 [12] | Age, previous experience, involvement and self-perception affect consumers’ willingness to pay more for green practices in restaurants. |
| Source | Food Attributes | Service Attributes | Ambiance Attributes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liu & Jang [16] | Food taste | Serve food as ordered | Cleanliness of environment * |
| Food safety | Accurate guest check | Employee appearance * | |
| Food freshness * | Dependable and consistent service | Odor | |
| Food temperature | Prompt service * | Room temperature | |
| Food variety * | Friendly and helpful employees * | Lighting | |
| Food presentation * | Attentive employees | Interior design and décor * | |
| Healthy options | Employees have knowledge of menu | Music |
| Variable | Item | Loading | AVE | CR | α |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Presentation (PR) | Food looks tasty. | 0.840 | 0.776 | 0.912 | 0.855 |
| Food looks delicious. | 0.909 | ||||
| Food presentation is visually attractive. | 0.892 | ||||
| Freshness (FR) | Food looks fresh. | 0.929 | 0.815 | 0.898 | 0.773 |
| The restaurant offers fresh food. | 0.936 | ||||
| Variety (VA) | The restaurant offers wide variety of green food. | 0.904 | 0.869 | 0.930 | 0.869 |
| The restaurant offers a lot of choices of green food. | 0.901 | ||||
| Expectation confirmation of food quality (ECFQ) | The food provided by the green restaurant is better than what I expected. | 0.800 | 0.714 | 0.882 | 0.799 |
| The food quality of the green restaurant is better than what I expected. | 0.882 | ||||
| Overall, most of my food expectations are confirmed. | 0.850 | ||||
| Employee (EM) | The employees are friendly. | 0.911 | 0.835 | 0.910 | 0.802 |
| The employees are helpful. | 0.917 | ||||
| Service (SE) | The employees are attentive. | 0.713 | 0.751 | 0.854 | 0.790 |
| The restaurant offers prompt service. | 0.997 | ||||
| Expectation confirmation of service quality (ECSQ) | The service provided by the green restaurant is better than what I expected. | 0.886 | 0.808 | 0.927 | 0.881 |
| The service quality of the green restaurant is better than what I expected. | 0.906 | ||||
| Overall, most of my service expectations are confirmed. | 0.905 | ||||
| Appearance (AP) | The employees dress appropriately. | 0.864 | 0.719 | 0.837 | 0.610 |
| The employees have neat appearance. | 0.831 | ||||
| Design and décor (DD) | A lot of green plants are planted in the restaurant. | 0.829 | 0.735 | 0.892 | 0.822 |
| Decorative materials are green. | 0.866 | ||||
| The design and décor are appealing. | 0.876 | ||||
| Lighting (LI) | The lighting is appropriate. | 0.890 | 0.820 | 0.901 | 0.782 |
| The lights are natural. | 0.921 | ||||
| Cleanliness (CL) | The facility is clean. | 0.898 | 0.845 | 0.916 | 0.819 |
| The restaurant is a clean environment. | 0.939 | ||||
| Expectation confirmation of ambiance quality (ECAQ) | The ambiance provided by the green restaurant is better than what I expected. | 0.882 | 0.748 | 0.899 | 0.832 |
| The ambiance quality of the green restaurant is better than what I expected. | 0.863 | ||||
| Overall, most of my ambiance expectations are confirmed. | 0.850 | ||||
| Patronage intention (PI) | The likelihood of eating in the green restaurant is high. | 0.913 | 0.819 | 0.931 | 0.889 |
| The probability that I would consider eating in the green restaurant is high. | 0.900 | ||||
| My willingness to eat in the green restaurant is high. | 0.902 |
| PR | FR | VA | EM | SE | DD | LI | CL | AP | ECFQ | ECSQ | ECAQ | INT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PR | 0.881 | ||||||||||||
| FR | 0.559 | 0.903 | |||||||||||
| VA | 0.434 | 0.444 | 0.932 | ||||||||||
| EM | 0.435 | 0.416 | 0.188 | 0.914 | |||||||||
| SE | 0.134 | 0.040 | 0.141 | 0.064 | 0.867 | ||||||||
| DD | 0.525 | 0.468 | 0.264 | 0.476 | 0.077 | 0.857 | |||||||
| LI | 0.312 | 0.421 | 0.223 | 0.458 | 0.004 | 0.563 | 0.906 | ||||||
| CL | 0.470 | 0.567 | 0.391 | 0.440 | 0.088 | 0.537 | 0.458 | 0.919 | |||||
| AP | 0.552 | 0.564 | 0.335 | 0.598 | −0.016 | 0.640 | 0.582 | 0.694 | 0.848 | ||||
| ECFQ | 0.566 | 0.607 | 0.432 | 0.420 | 0.046 | 0.387 | 0.387 | 0.436 | 0.448 | 0.845 | |||
| ECSQ | 0.423 | 0.448 | 0.153 | 0.671 | 0.079 | 0.518 | 0.364 | 0.452 | 0.523 | 0.449 | 0.899 | ||
| ECAQ | 0.438 | 0.546 | 0.232 | 0.589 | 0.009 | 0.579 | 0.458 | 0.620 | 0.591 | 0.454 | 0.572 | 0.865 | |
| INT | 0.571 | 0.569 | 0.340 | 0.543 | 0.066 | 0.634 | 0.431 | 0.584 | 0.640 | 0.515 | 0.663 | 0.648 | 0.905 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Y.S.; Luo, M.; Zhu, D.H. The Effect of Quality Attributes on Visiting Consumers’ Patronage Intentions of Green Restaurants. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10041187
Yu YS, Luo M, Zhu DH. The Effect of Quality Attributes on Visiting Consumers’ Patronage Intentions of Green Restaurants. Sustainability. 2018; 10(4):1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10041187
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Yi Shan, Min Luo, and Dong Hong Zhu. 2018. "The Effect of Quality Attributes on Visiting Consumers’ Patronage Intentions of Green Restaurants" Sustainability 10, no. 4: 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10041187
APA StyleYu, Y. S., Luo, M., & Zhu, D. H. (2018). The Effect of Quality Attributes on Visiting Consumers’ Patronage Intentions of Green Restaurants. Sustainability, 10(4), 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10041187