An Analysis of Housing Structures’ Earthquake Vulnerability in Two Parts of Dhaka City
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Earthquake Vulnerability of Dhaka’s Housing Structures
1.2. Earthquake Concern in Dhaka
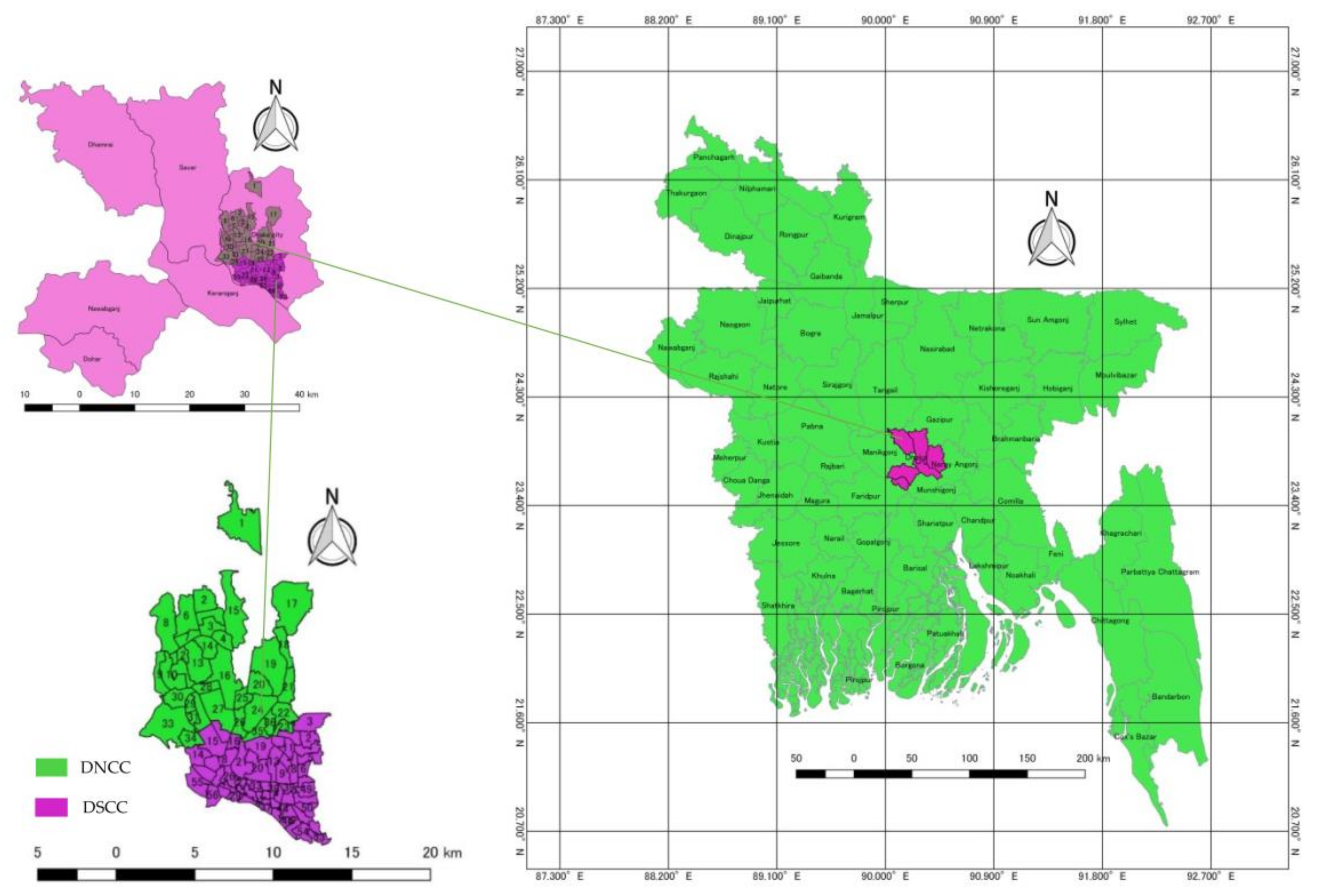
1.3. Dhaka North City Corporation (DNCC)
1.4. Dhaka South City Corporation
2. Materials and Methods
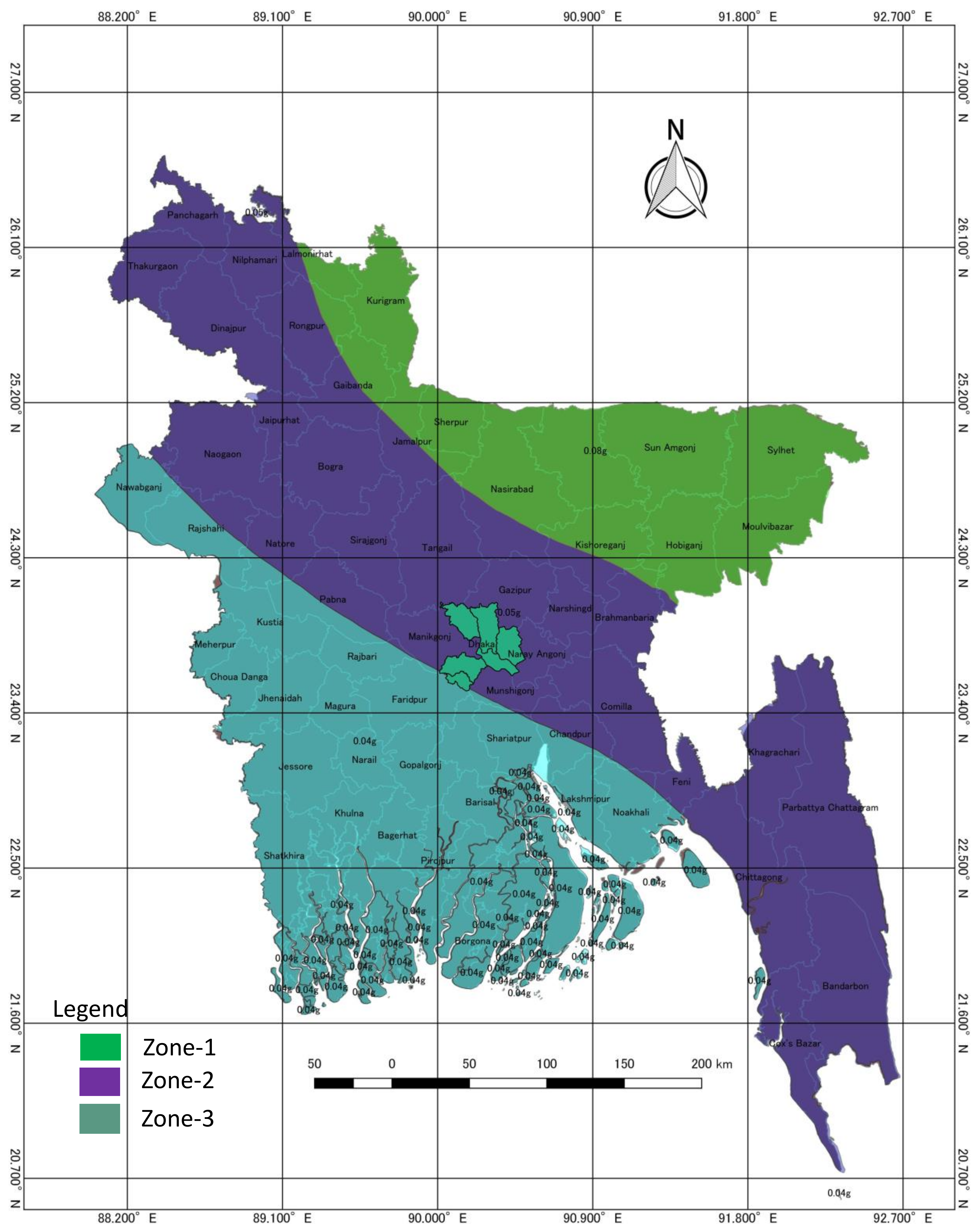
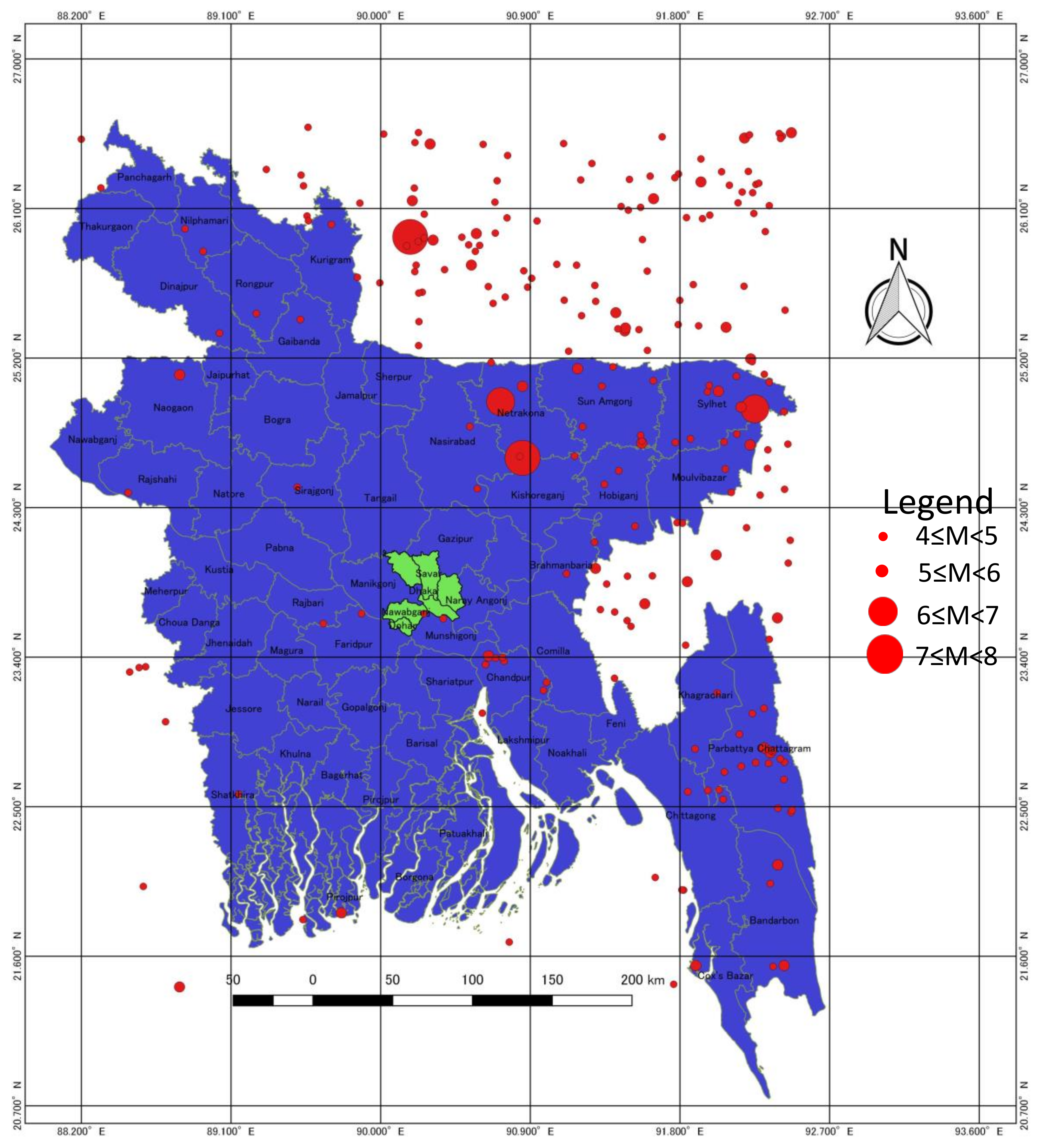
2.1. Data Sources and Selection of the Research Area
2.2. Data Analysis and Mapping
2.3. Decision Tree
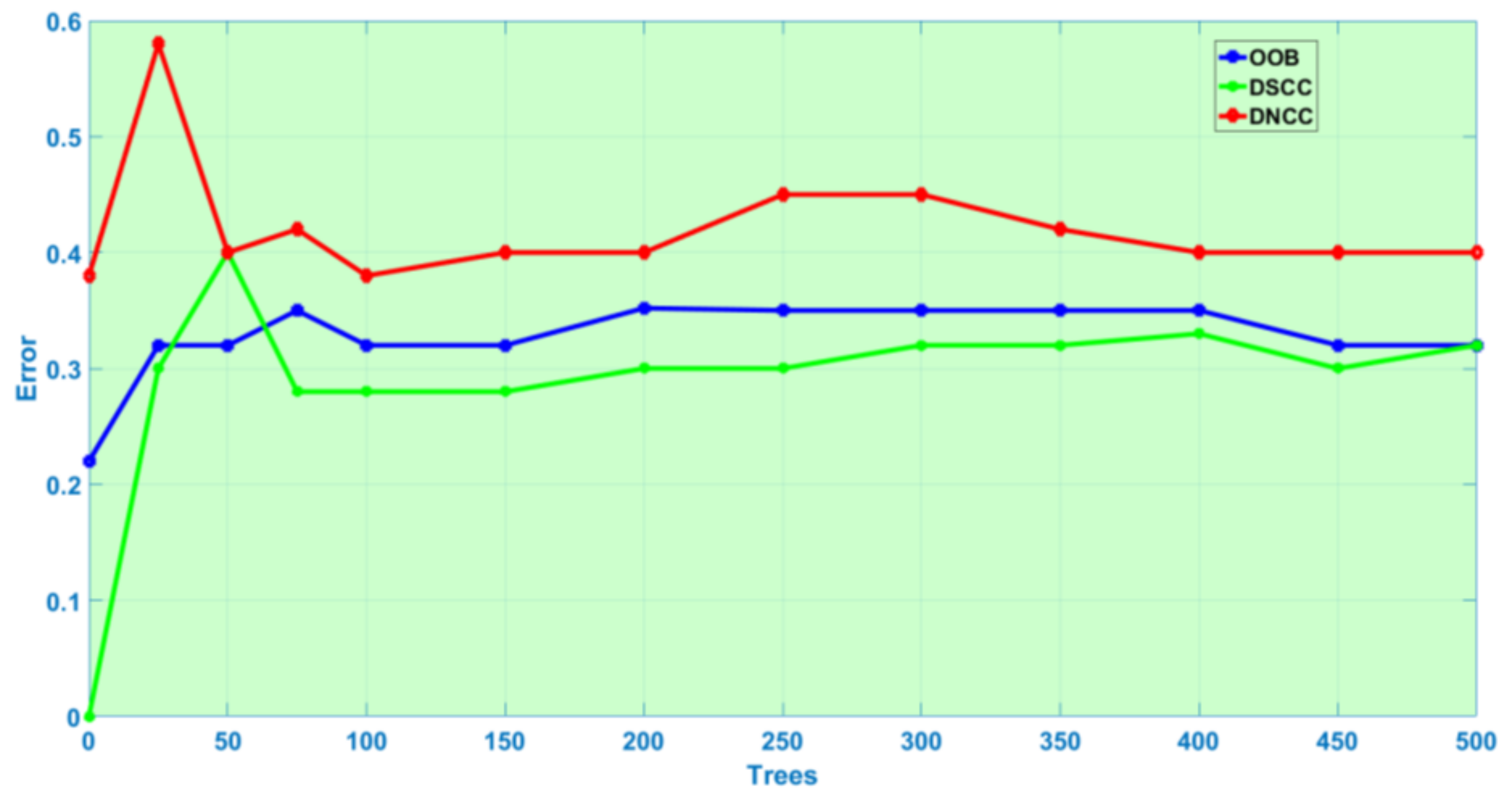
2.4. Random Forest
3. Results
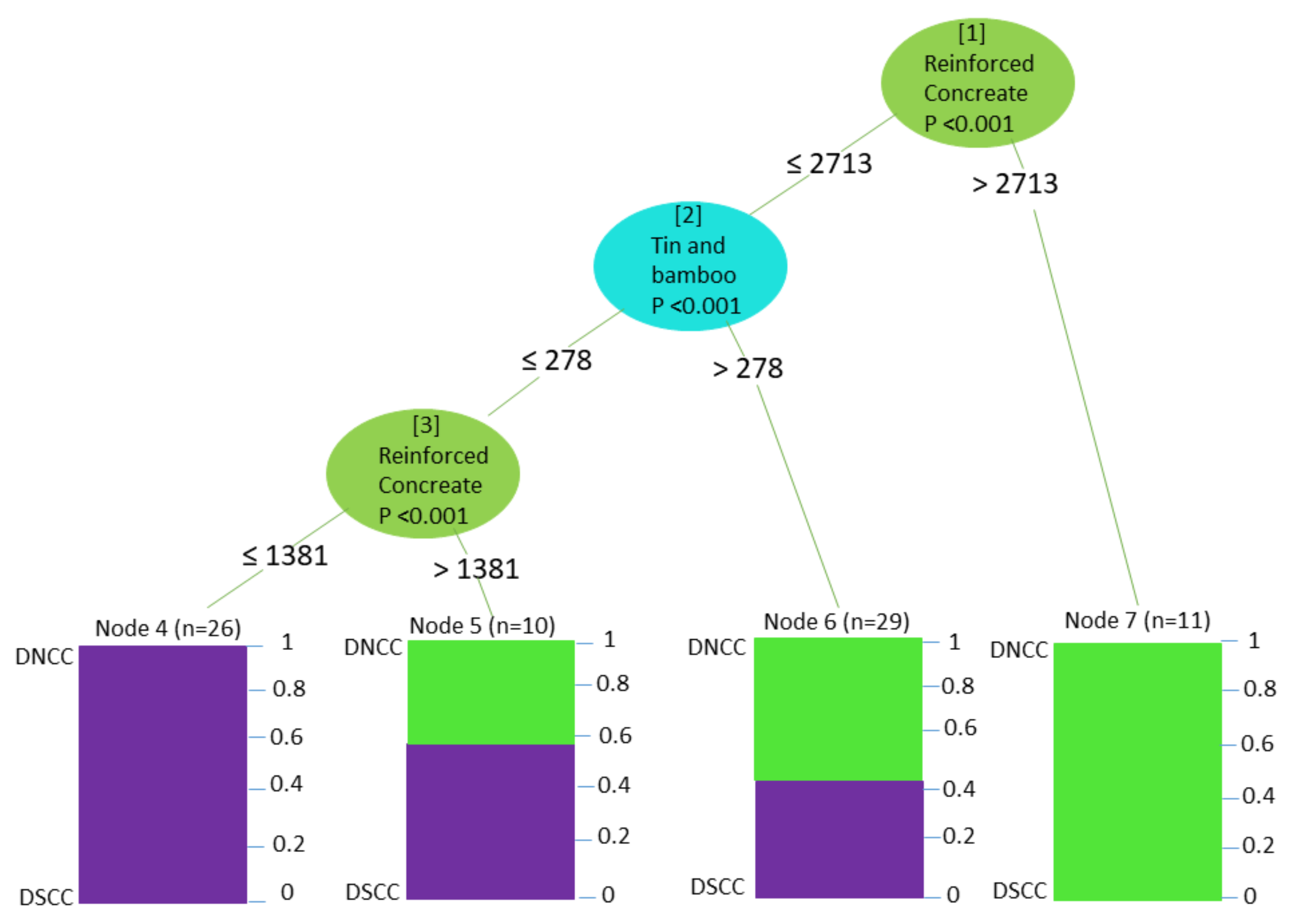
3.1. Decision Tree
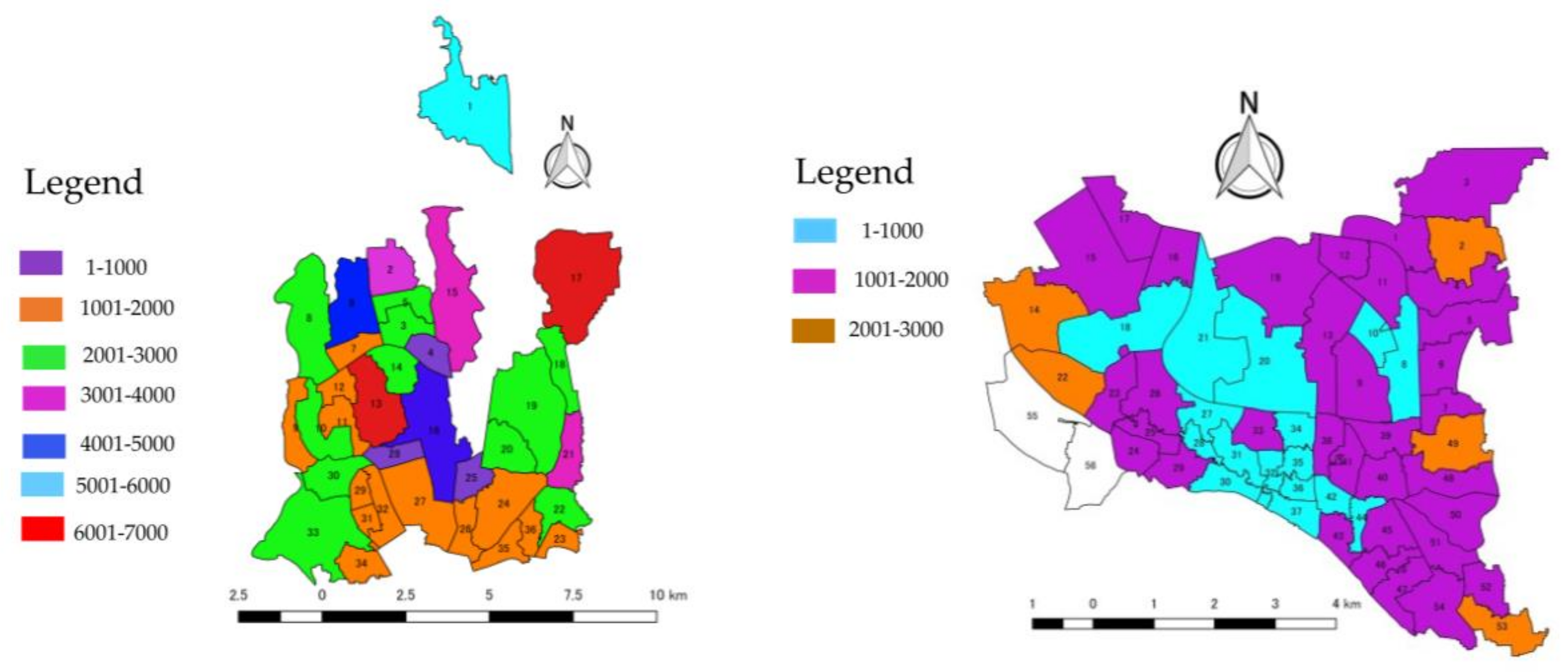
3.1.1. Housing Structure
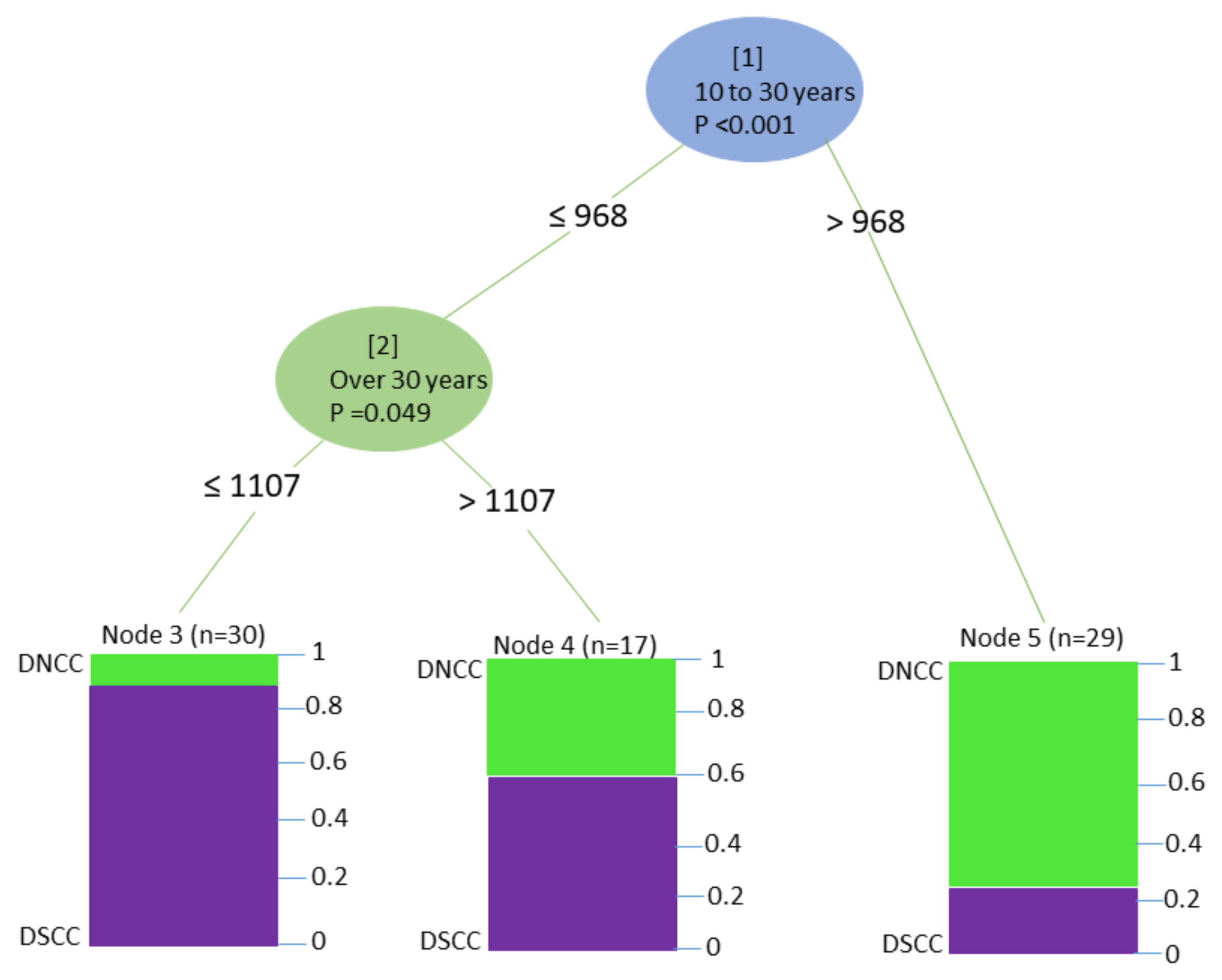
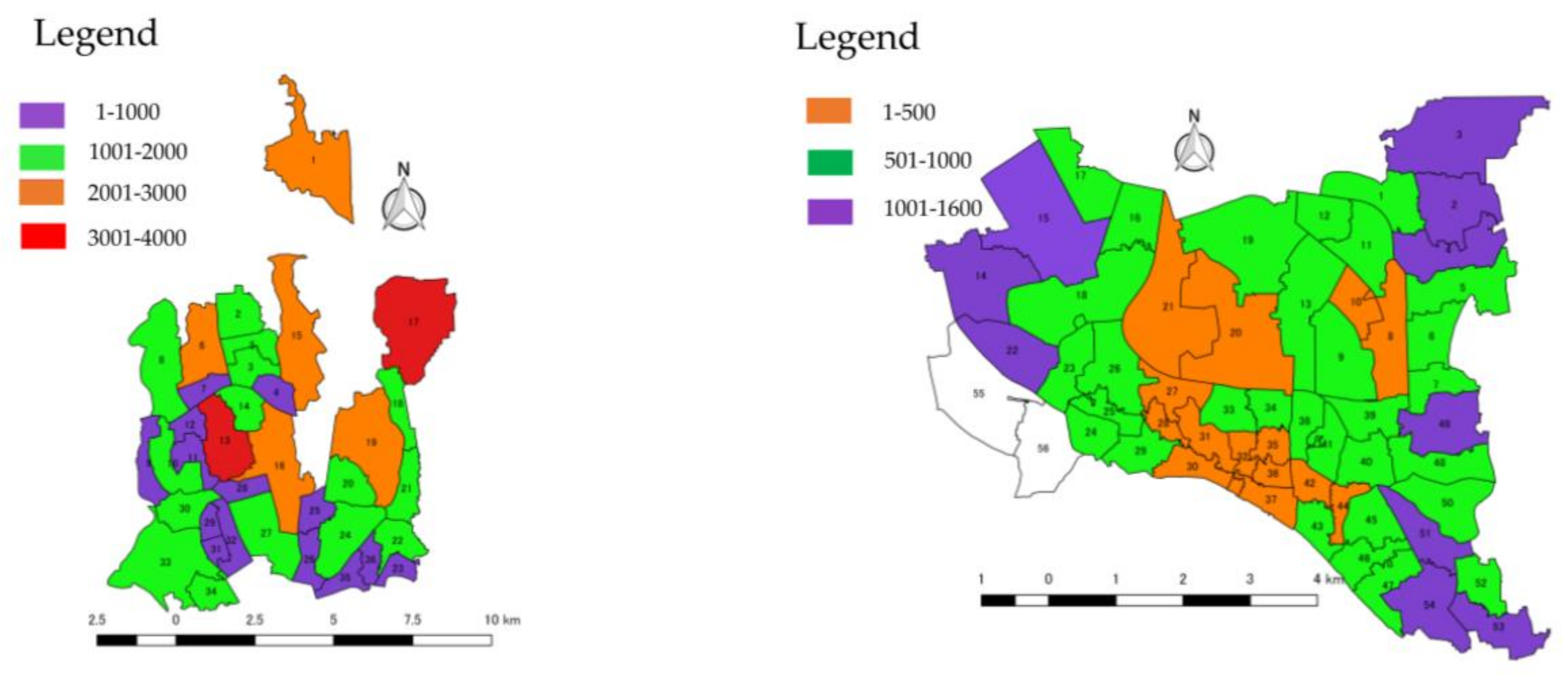
3.1.2. Building Age
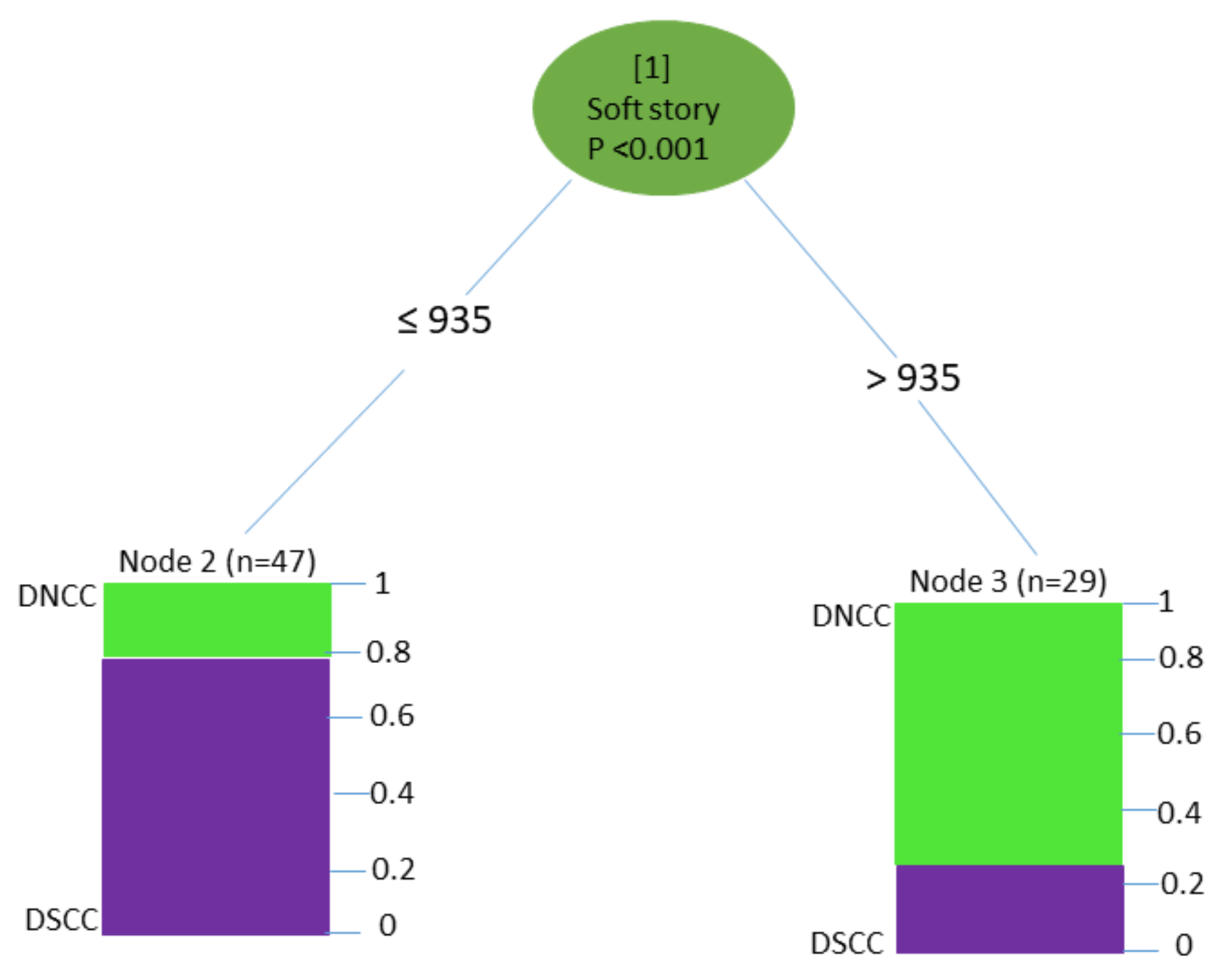
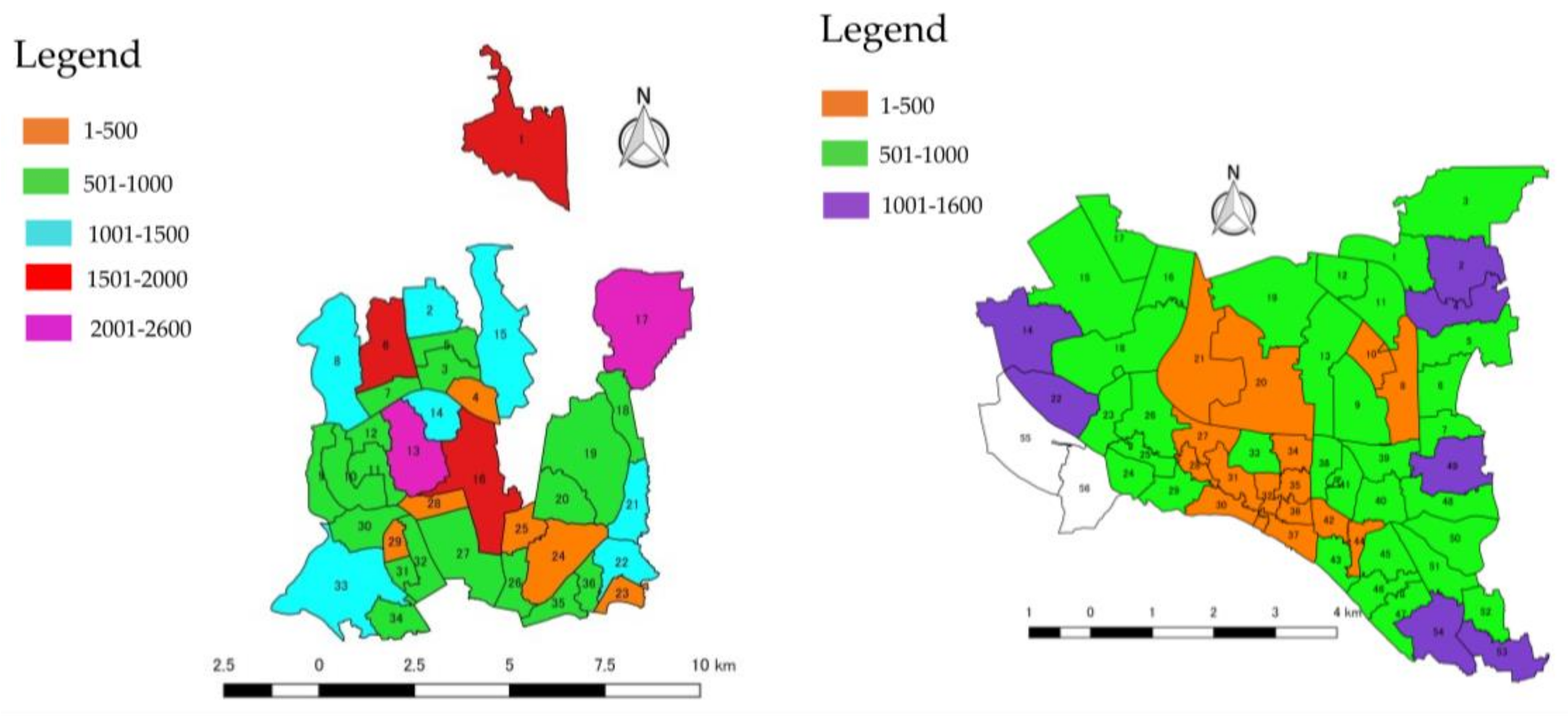
3.1.3. Earthquake Vulnerability Factors
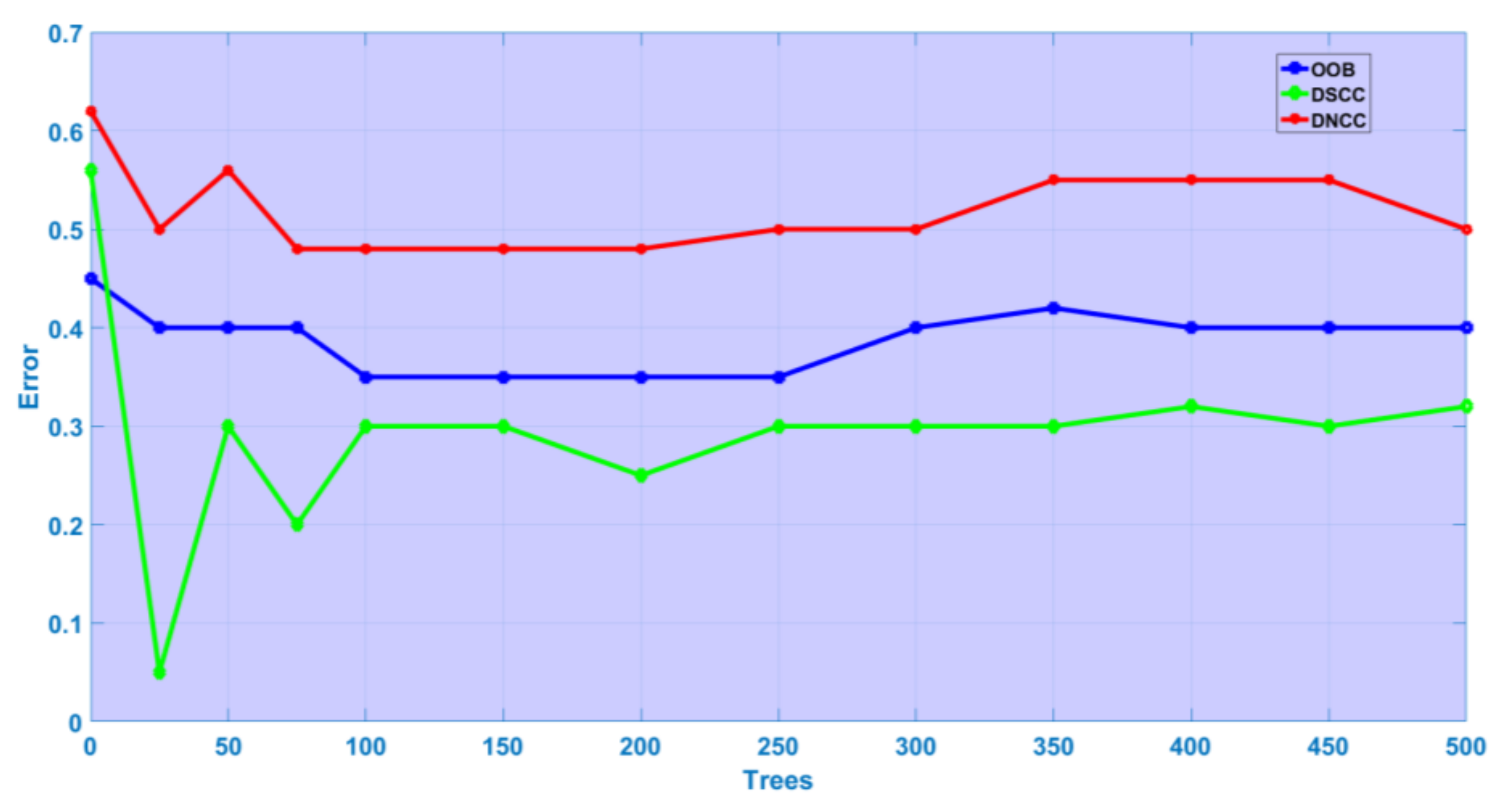
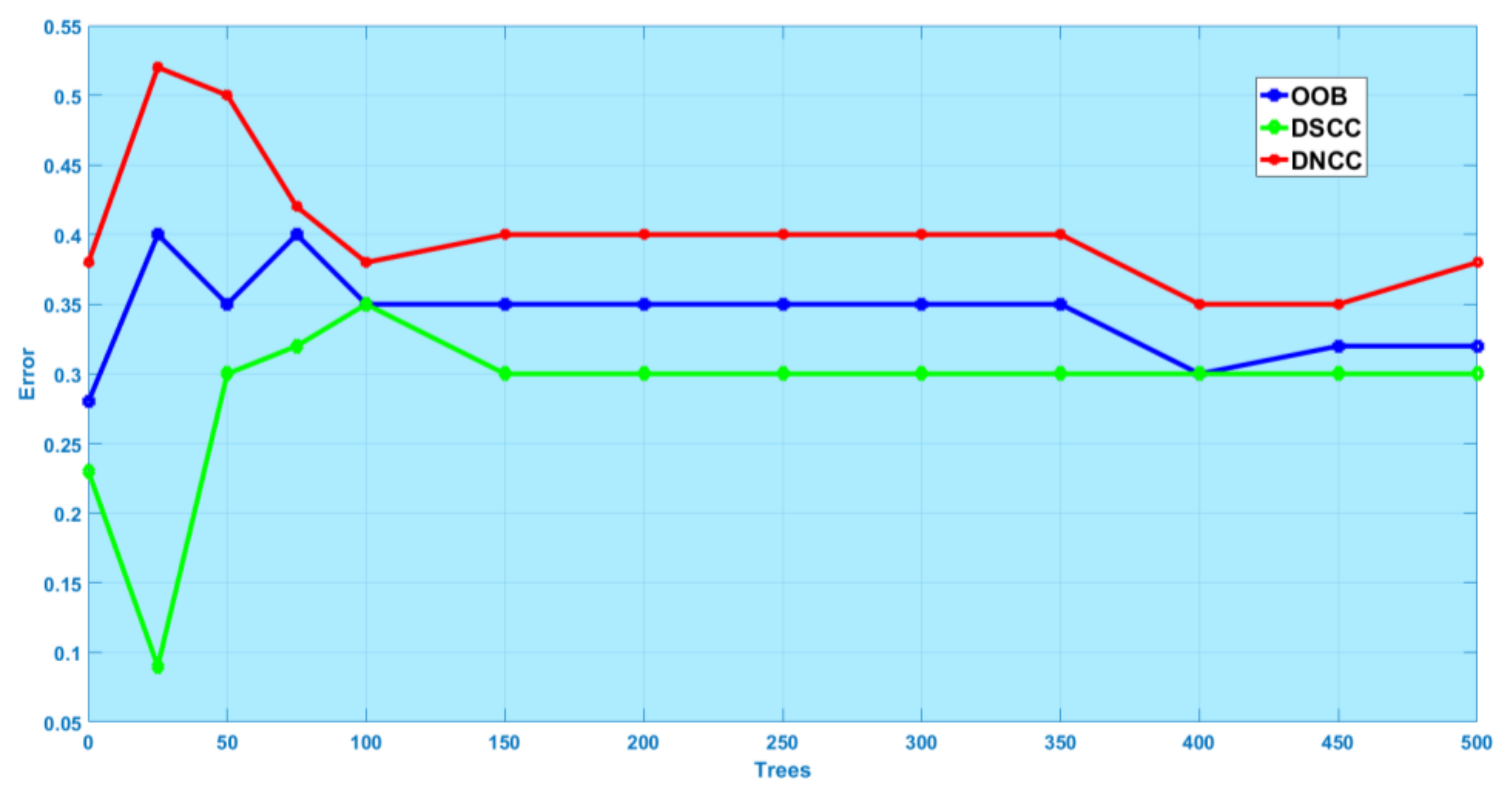
3.2. Random Forest
3.2.1. Housing Structure
3.2.2. Building Age
3.2.3. Earthquake Vulnerability Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Structural Type
4.2. Building Age
4.3. Vulnerability Factors
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahman, M.Z.; Siddiqua, S.; Kamal, A.S.M.M. Liquefaction hazard mapping by liquefaction potential index for Dhaka City, Bangladesh. Eng. Geol. 2015, 188, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.Z.; Islam, K.; Roy, K.S.; Arafat, M.S.; Al-Hussaini, T.M. Seismic vulnerability assessment of RCF buildings in old town of Dhaka city. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Earthquake Symposium, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 5–6 March 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, S.; Khan, M.S.R.; Ahmad, S.I. Comparative Cost Analysis of Possible Seismic Retrofitting Schemes for Multi-Story Unreinforced Masonry Building. Procedia Eng. 2013, 54, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Fabio, T.; Tiziana, R. Field investigation on the performance of building structures during the 12 May 2008 Wenchuan earthquake in China. Eng. Struct. 2009, 31, 1707–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adanur, S. Performance of masonry buildings during the 20 and 27 December 2007 Bala (Ankara) earthquakes in Turkey. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 10, 2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Ueda, T. Seismic rehabilitation of masonry structure strengthening by two distinct FRPs. In Proceedings of the IABSE-JSCE Joint Conference on Advances in Bridge Engineering-III, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 21–22 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Solberg, C.; Rossetto, T.; Joffe, H. The social psychology of seismic hazard adjustment: Re-evaluating the international literature. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 10, 1663–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, H. Application of high performance fiber reinforced cementitious composites for damage mitigation of building structures. J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 2006, 4, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdik, M.; Durukal, E. Earthquake risk and its mitigation in Istanbul. Nat. Hazards 2008, 44, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, P.; Begum, M.; Nasrin, S. Fiber reinforced polymers for structural retrofitting: A review. J. Civ. Eng. 2011, 39, 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Housing—Banglapedia. Available online: http://en.banglapedia.org/index.php?title=Housing (accessed on 8 November 2017).
- Comprehensive Disaster Management Programme (CDMP). Seismic Hazard and Vulnerability Assessment of Dhaka, Chittagong and Sylhet City Corporation Areas; Final Report; Ministry of Food and Disaster Management: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2009.
- Barua, U.; Akhter, M.S.; Ansary, M.A. District-wise multi-hazard zoning of Bangladesh. Nat. Hazards 2016, 82, 1895–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitsi-Selmi, A.; Murray, V.; Wannous, C.; Dickinson, C.; Johnston, D.; Kawasaki, A.; Yeung, T. Reflections on a Science and Technology Agenda for 21st Century Disaster Risk Reduction: Based on the Scientific Content of the 2016 UNISDR Science and Technology Conference on the Implementation of the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015–2030. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2016, 7, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I. Factors in building resilience in urban slums of Dhaka, Bangladesh. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2014, 18, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asian Disaster Preparedness Center (ADPC). Earthquake Contingency Plan for Dhaka City Corporation (DCC); Comprehensive Disaster Management Programme (CDMP): Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.S.; Morita, H. Earthquake disaster management analysis in Dhaka. In Proceedings of the Humanitarian Technology Conference (IHTC), Toronto, ON, Canada, 21–22 July 2017; pp. 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa, Y. The lived experience of preparing for earthquakes in households: A phenomenological psychological study. Nat. Hazards 2017, 88, 1825–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hussaini, T.M.; Chowdhury, I.N.; Noman, M.N. Seismic hazard assessment for Bangladesh-old and new perspectives. In Proceedings of the First International conference on CICM, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 14–15 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- DDC. Bangladesh National Building Code 1993; Development Design Consultants for Housing and Building Research Institute: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 1993.
- URP- phase 1. Bangladesh Urban Resilience Project, Environmental Management Framework (EMF) Draft; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.A. Geophysical characterization and earthquake hazard vulnerability of Dhaka Mega City, Bangladesh, vis-à-vis impact of scenario earthquakes. Nat. Hazards 2016, 82, 1147–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Search Earthquake Catalog. Available online: https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/search/ (accessed on 16 February 2018).
- Alam, E.; Dominey-Howes, D. An analysis of the AD1762 earthquake and tsunami in SE Bangladesh. Nat. Hazards 2014, 70, 903–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BBS Statistical Yearbook of Bangladesh; Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (BBS), Government of Bangladesh: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2012; ISBN 9789849005599.
- Rizvi, S.N.H. East Pakistan District Gazetteers: Dacca; East Pakistan Government Press: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 1969; p. 353.
- Rizvi, S.N.H. East Pakistan District Gazetteers: Chittagong; East Pakistan Government Press: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 1970; p. 344.
- Del Gobbo, G.M.; Williams, M.S.; Blakeborough, A. Seismic Performance Assessment of a Conventional Multi-storey Building. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2017, 8, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hussaini, T. Critical Elements for Earthquake Disaster in Dhaka City. New Technology for Urban Safety of Mega Cities in Asia. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on New Technologies for Urban Safety of Mega Cities in Asia, Tokyo, Japan, 30–31 October 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Barua, U.; Ansary, M.A. Workplace safety in Bangladesh ready-made garment sector: 3 years after the Rana Plaza collapse. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2017, 23, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansary, M.A.; Barua, U. Workplace safety compliance of RMG industry in Bangladesh: Structural assessment of RMG factory buildings. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2015, 14, 424–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansary, M.A.; Rahman, M.S. Site amplification investigation in Dhaka, Bangladesh, using H/V ratio of microtremor. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 559–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Location and Area, Dhaka North City Corporation. Available online: http://www.dncc.gov.bd/site/page/c0b6953f-16d3-405b-85e9-dece13bb98de/Location-and-Area (accessed on 4 April 2018).
- Uddin Ahmeda, S.; Mohuyab, F.A. Growth and Development of Dhaka North: 1971–2011. J. Asiat. Soc. Bangladesh Hum. 2013, 58, 303–334. [Google Scholar]
- Dhaka South City Corporation. Available online: http://www.dhakasouthcity.gov.bd/ (accessed on 4 April 2018).
- Ferdous, I.; Rahman, M. Citizens at risk from earthquake hazard in Dhaka city: Scaling risk factors from household to city region level. J. Geogr. Inst. Jovan Cvijic SASA 2015, 65, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, I.; Ansary, M.A.; Ara, S.; Islam, I. Assessing social vulnerability to earthquake hazard in old Dhaka, Bangladesh. Asian J. Environ. Disaster Manag. 2011, 3, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Comparison of decision tree methods for finding active objects. Adv. Space Res. 1959, 41, 1955–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.; Johnson, K. Applied Predictive Modeling; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; ISBN 9781461468493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, J.P.; Burdon, D.; Allen, J.H. An application of contingent valuation and decision tree analysis to water quality improvements. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 55, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 45, pp. 5–32. [Google Scholar]
- Reinforced Concrete. Wikipedia (2018). Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Reinforced_concrete&oldid=830231868 (accessed on 3 April 2018).
- Mohuya. Climate change and city: An utopian debate or white truth. In Souvenir of the World Habitat Day 2011- Cities and Climate Change; Kalam, A.A., Nazem, N.I., Eds.; Ministry of Housing and Public Works, Government of Bangladesh and UN-HABITAT: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2011; pp. 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Doğangün, A.; Ural, A.; Livaoğlu, R. Seismic performance of masonry buildings during recent earthquakes in Turkey. In Proceedings of the 14th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Beijing, China, 12–17 October 2008; pp. 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Passmore, A.C. Twenty Styles of Architecture. In Handbook of Technical Terms Used in Architecture and Building and Their Allied Trades and Subjects; Scott, Greenwood, and Co.: London, UK, 1904. [Google Scholar]
- Bruneau, M. Building damage from the Marmara, Turkey earthquake of August 17, 1999. J. Seismol. 2002, 6, 357–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, S. Earthquake resistant design of reinforced concrete buildings. J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 2004, 2, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
| Source | Estimated Maximum Magnitude |
|---|---|
| Madhupur Fault | 7.5 |
| Dauki Fault | 8.0 |
| Plate Boundary Fault 1 | 8.5 |
| Plate Boundary Fault 2 | 8.0 |
| Plate Boundary Fault 3 | 8.3 |
| Variable | Mean Gini Decrease |
|---|---|
| Reinforced concrete building | 7.107414 |
| Lightly reinforced concrete building | 5.385688 |
| Brick in cement mortar with concrete floor | 5.945903 |
| Brick in cement mortar with flexible roof | 4.944385 |
| Tin and bamboo mixed | 6.594351 |
| Variable | Mean Gini Decrease |
|---|---|
| 10 years | 9.965379 |
| 10–30 years | 10.390261 |
| Over 30 years | 9.566955 |
| Variable | Mean Gin Decrease |
|---|---|
| Soft first story | 6.911157 |
| Heavy overhang | 7.043463 |
| Short columns | 7.693125 |
| Pounding effects | 6.615364 |
| Topographic effects | 1.714052 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, M.S.; Morita, H. An Analysis of Housing Structures’ Earthquake Vulnerability in Two Parts of Dhaka City. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10041106
Ahmed MS, Morita H. An Analysis of Housing Structures’ Earthquake Vulnerability in Two Parts of Dhaka City. Sustainability. 2018; 10(4):1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10041106
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Md Sohel, and Hiroshi Morita. 2018. "An Analysis of Housing Structures’ Earthquake Vulnerability in Two Parts of Dhaka City" Sustainability 10, no. 4: 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10041106
APA StyleAhmed, M. S., & Morita, H. (2018). An Analysis of Housing Structures’ Earthquake Vulnerability in Two Parts of Dhaka City. Sustainability, 10(4), 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10041106





