Abstract
Due to the upward trend in the globalization of sustainability issues and the intense competitive environment, it is evident that higher education institutions need new strategic approaches to succeed. To this end, the inquiry for this paper has been made into the debate about student relationship management. Going through the literature indicates that institutions have mainly perceived the concept as a technological initiative for solving the problems in individual domains, accompanied by uncoordinated efforts. Thus, the aims of this study are to theoretically present the critical success factors of this strategic approach and to empirically examine the recognized factors. To do so, a confirmatory factor analysis that is a quantitative analytic method was performed. The results and analyses revealed that there has been a significant correlation between the four critical success factors including knowledge management, student relationship management technology, student orientation, and employees’ involvement. It was also found that these factors are significantly correlated with the construct of student relationship management success. The findings have consequently highlighted that in addition to the technological tool, the role of knowledge management, employees’ involvement, and student orientation appeared to be particularly important for the implementation of the application.
1. Introduction
Sustainability and competitiveness are now totems in higher educational establishments [1]. On the one hand, a significant number of public universities, university colleges, and private universities and colleges across the world compete for the identical pool of the local and international qualified students’ groups, who are the most valuable customers in requesting service ‘education’ [2] as well as the most important stakeholders in shaping a sustainable future [3]. On the other hand, the growing scientific communities and institutions are increasingly engaging themselves in maximizing value for both students and universities to go beyond the triple-bottom line, seizing the initiative to embed and develop sustainability into higher education systems in order to expedite the transition to sustainable development. Due to these totems, it is evident that universities need new strategic approaches and leadership to succeed [1,4,5,6,7].
In pursuit of this aim, it is believed that the establishment of a successful student relationship management (SRM), which has been coined by Hilbert et al. [2] and Ackerman and Schibrowsky [8], in higher education institutions is strategic and crucial for the sake of the aforementioned totems [7,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. Implementing such an approach offers numerous benefits to universities, as thoroughly enumerated in the theoretical framework of this article. Gholami et al. [7], by reviewing the relational managerial literature, found that an effective SRM can contribute to constituting “a strategic orientation for maximizing the student value through meeting the students’ needs as well as for advancing the institutional sustainability through sustainable relationships development” (p. 2).
As the discourse on this topic is insufficient [7,13], the inquiry for this investigation is made into the debate about SRM due to its importance, capability, and philosophy. By reviewing the literature, it is found that institutions have mainly perceived the concept as a technological initiative for solving the problems in individual domains, accompanied by uncoordinated efforts. However, there is a lack of understanding about the impacts of other critical factors on the success of SRM. A study has theoretically analyzed the vital role played by knowledge management (KM) initiatives as determinants of the SRM success [7], along with other factors (organizational and technological factors); however, they have yet to address the concept empirically. This indicates that a generally accepted model to guide universities to their successful implementation is still missing, which accords with the investigations of [2,7]. Thus, the aims of this study are to theoretically present the SRM’s critical success factors and to empirically examine the recognized factors based on a research model, which was proposed by Gholami et al. [7]. The proposed model was made on the basis of customer relationship management (CRM) conceptual lenses, whereby confirmatory examinations should be carried out. Consequently, this article contributes to a field which has no empirical evidence in this context.
To do so, this article proceeds with a literature review to present the theoretical insights into SRM’s critical success factors. The next section clarifies the research method, providing an empirical analysis of the recognized factors. Then, the research results and findings, which are finally pursued by the conclusions and future research directions, are discussed.
2. Literature Review
Due to the upward trend in the globalization of sustainability issues and the intense competitive environment, higher education institutions have recently undergone a change in their systems’ attitude and have become much more cooperative. The role of the student is accordingly changing from that of a mere consumer to that of a consumer, cooperator, co-producer, co-creator of value, and co-developer of knowledge, implying a much more important position of the student than ever, i.e., as a partner. This attitude was clearly described by Wardley et al. [17], that students are not just consumers of education, but they are co-creators. The special issues established in journals, a new journal dedicated solely to ‘students as partners’, a practitioner journal of reflective essays, an international institute on this scope (reported by Reference [18]), and the research attention given in creating and delivering of the value to students and the effective management of student relationship (e.g., References [2,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,19] make this matter obvious. The point of the issue has consequently been how to perform and develop such an attitude.
The concept of student relationship management (SRM), which was coined by References [2,8] as an emergent theme of inquiry with a distinct identity, has been gradually progressing over the past few years. It is aimed at advancing the university-student relational development for the sake of higher education sustainability. Hilbert et al. [2], by drawing on customer relationship management in the context of higher education in Germany, defined that SRM is a fundamental strategy to generate a superior value for both the students and the university across the lifecycle of relationship. Ackerman and Schibrowsky [8], by reviewing the student retention and relationship marketing literature and based on a relational managerial model, have theoretically argued that SRM is not only a business tool, but also an institutional philosophy to improve the interactions between the institution and the students. These leading studies are in accord with the investigations that view students as customers, for instance, Seeman and O’Hara [19], who enumerated the benefits obtained by implementing an actual customer relationship management project in an educational system in the USA.
Going through the SRM literature indicates that the implementation of an effective SRM offers numerous advantages including enabling universities to pursue the ‘best processes’ in educating, collaborating, and managing [2,8,14,16,19]; involving students in the co-creation of value [2,7]; increasing student satisfaction, retention, and loyalty to institutional programs and commitments [2,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,19]; improving institutional efficiency and effectiveness [8,9,12]; advancing the interactions between the institution and the students [8]; growing the student-centric focus [8,19]; improving student-employee integration [7,8]; enhancing the capability to create sustainable partnerships [7,8,13]; developing the service and meeting the students’ needs [7,8,16]; enabling better allocation of resources across the student portfolio [10]; elevating the student experience [12]; minimizing dropout rates [9,12]; optimizing the cost to serve and maximizing financial benefits [9,13]; enhancing long-term profitability [8]; heightening the university’s reputation [13]; and assisting in gathering competitive intelligence [9,13].
Despite the research attention paid to the importance and capability of SRM, there is a lack of studies on clarifying a comprehensive definition, conceptualizing a generally accepted framework, identifying and analyzing critical success factors to succeed in its implementation, developing valid scales to examine and measure, recognizing the barriers, and investigating on the topic empirically that is essential for conceptual richness. However, the general consensus in the literature is that discourse upon this initiative is rather limited, indicating that it is a missing link in higher education systems. According to Ackerman and Schibrowsky [8], few institutions take that initiative into careful consideration or act in holistic ways while every campus claims to have a student-centered approach. Notably, in some cases, it is observed that SRM technology is equated with SRM while considering SRM as an exclusively technological initiative and ignoring other key components is the main reason for its failure in implementation [7], highlighting the principal gap in the contemporary knowledge of SRM strategy. Gholami et al. [7] argued that SRM is much more than technological innovations and technology is not all for its success. They have clearly proposed a conceptual model by reviewing the relational managerial literature, consisting mainly of four critical success factors and five hypotheses which will be explained in the ensuing segments. The proposed model is according to the principles and ideals that reflect SRM as a multi-dimensional strategic approach and involves three key components—technology, people, and process. Figure 1 demonstrates a comprehensive perspective for the sake of SRM success based on the aforementioned notion. It is believed that these four critical success factors are more tangible and would guarantee the SRM success if become fully integrated.
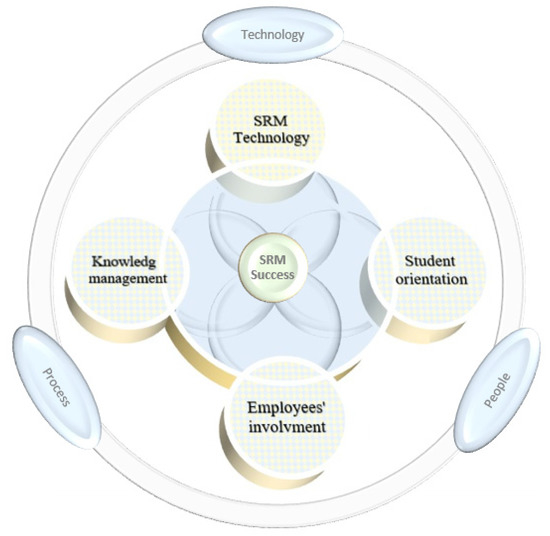
Figure 1.
A comprehensive perspective for the sake of SRM success.
2.1. Knowledge Management
Various descriptions abound in the literature regarding knowledge management (KM). According to the descriptive perspectives of Alavi and Leidner [20], KM is outlined in (a) advancing the individual understanding and learning through presenting information, viewing knowledge as a ‘state of mind’; (b) developing and managing the knowledge stocks, viewing knowledge as an ‘object’; (c) acquiring, sharing, and applying knowledge, viewing knowledge as a ‘process’; (d) accessing and retrieving information systematically, viewing knowledge as an ‘access to information’; and (e) developing core competencies and understanding strategic know-how, viewing knowledge as a ‘capability’. This agrees with References [21,22], which label knowledge as a justified belief which expands the individual’s competence for effective action.
KM has widely appeared in the managerial literature, which has had a long history [23]. There are no limitations for applying KM, depending on the organizational specification [24]. Wong and Aspinwall [25], by drawing on References [26,27,28], enumerated its main potential advantages, representing KM as a potent mechanism towards enhancing the decision-making by just-in-time intelligence, improving the productivity and efficiency of the work, increasing the innovations in products, services and operations, improving the managerial competencies and competitiveness, enabling the generation of technical solutions to customers’ problems, and increasing responses to the clients. However, it is often recognized as a means to improve organizational performance [29].
Higher education institutions are not separate from organizations [30]; they should take this key component into careful consideration [7]. Tan [31] affirmed that KM is an indispensable prerequisite for the research in universities and should be identified and encouraged by top management. It is observed by [31] that knowledge sharing takes place once the apt KM scene happens. Shahbudin et al. [32] believe KM enhances the effectiveness, competitiveness, and quality of education globally. They stressed the importance of monitoring the KM practices and evaluating its performance in such institutes. Shoham and Perry [33] described it as a mechanism for managing the organizational and technological change, enabling universities to adapt themselves to the environment. It is argued that KM provides a systemic strategic approach for complex organizational management as well as a foundation for designing and managing change and innovation strengthened by co-operation, collaboration, and knowledge sharing as relying on and utilizing information technology and furthering co-operation [33]. However, knowledge management is a challenging and relatively new concept for such institutions [32,33], various scholars and authors have appealed to utilizing a strategic approach/planning/framework during the last few years [34]. In this context, there are studies [31,32,33,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43] which focus on practices, tools, initiatives, resources, and frameworks to implement and develop this critical factor in higher education institutions. In many cases, the concentration has been on the frameworks, which comprise a set of knowledge processes to support and improve knowledge activities and resources. In other cases, there has been a bias towards the implementation of information systems (in terms of social networks), KM practices, workflow systems or institutional methodologies, so as to manage the creation and transmission of structured and unstructured knowledge. In these scenarios, KM is intrinsically associated with the concepts that contribute to continuous learning, innovation, communication, collaboration, and the culture of sharing.
In common sense, KM from the viewpoint of SRM can be summarized as a systematic comprehensive ‘process’ which delivers a continuous development towards institutional learning and excellence due to its unique ‘capability’. It can propel a university to be more adaptive, innovative, intelligent, competitive, and sustainable. On this basis, the following hypothesis is formulated:
Hypothesis 1 (H1).
Knowledge management and SRM success are significantly correlated.
2.2. Employees’ Involvement
From the viewpoint of an employee who plays a critical role in a system as a neuron performs in brain functioning, being an asset has gathered momentum [44]. Thereby, it should carefully be dealt with by providing sufficient space and participation within a system via employees’ involvement (EI). This factor (in terms of employees’ engagement, participation, and recognition) can be viewed as a conceptual opposition to burn-out [45,46,47]. Harter et al. [48] described it as ‘the individual’s involvement and satisfaction with as well as enthusiasm for work’. It is also likened to a positive manner, carried by the employee for the sake of the organization and its value [49].
Going through the literature, EI has been touted as essential for the existing organizations, which face many challenges [45]; a key to achieving the organizational competitiveness and success [46,50]; a driving force towards individual behavior, attitudes, and performance and also organizational productivity, efficiency, and effectiveness [45,48]; a critical importance for keeping up with the increasing transitions of economy and society, described by technological development and universal competitiveness [51]; and, also, a corporate social responsibility which finally considers the commitment of employees [45,52]. It resulted in employees being more motivated to participate in future developmental activities when they experience that their learning has been appreciated, valued, and supported [51]. This motivational level is determined by the employees’ involvement.
Becoming a co-operative and co-creative institution is not possible without the active involvement of the employees who interact with students [17]. EI in the design, implementation, and evaluation of the SRM activities in a university are regarded to be vital to vertical integration. According to Ackerman and Schibrowsky [8], ‘while front-line employees at colleges and universities such as administrative assistants, office receptionists, advisors, and classroom instructors are often the key to the successful implementation of SRM programs, the efforts of all are needed’. This agrees with Reference [2], which states that SRM should be pursued by all members of an academy. However, employees have a fundamental role in the relationship between institutions and their students. Therefore, the below hypothesis has been formulated:
Hypothesis 2 (H2).
Employees’ involvement and SRM success are significantly correlated.
2.3. Student Orientation
To accomplish the pinnacle of excellence, employees should be involved in an exceptional working culture [53]. According to Lindner and Wald [54], culture acts out a fundamental function throughout the early stages of a project whilst in the following stages the embedded cultural basis permits a greater level of impersonal communication. To meet student needs, the development of a cultural approach to be student-oriented is necessary. Such an approach contributes to establishing the student satisfaction-retention-loyalty chain to advance long-term relationships with the students who are (potentially) valuable in the co-creation process [7]. Curran [55] implied that encouraging a cultural initiative of student-as-partner that can lead to personal development may empower both employees and students.
Student orientation (SO) is an institutional cultural approach, making universities more responsive to student needs and, consequently, creating superior value for them continuously. Gholami et al. [7], by drawing on the relational managerial literature particularly the investigations of References [56,57,58,59], revealed that SO is a fundamental factor of the institutional climate needed for SRM success and reflects an institution’s culture on students’ focus, needs, and feedbacks. It is believed a university that is strongly oriented to the student will be able to design its processes better since that institutional culture is conducive to improved employee understanding of the students.
SO can be progressively considered a part of the social legitimacy of an institution that may lead to progress towards reputation, performance, talent attainment, student engagement and retention, cost-effectiveness, market extension and access to human capital. Moreover, a student-oriented cultural approach is vital to the quality and expansion of creating and disseminating student-knowledge, which, in turn, is a pivotal concept in relational management. There are many studies in the literature on KM that have taken culture as a most important enabler of knowledge acquisition and diffusion into consideration [25,31,54]. Base on Tan [31], knowledge sharing approaches among the educational staff in universities would positively increase if this initiative is increased. Therefore, higher education systems must meet SO as a key component for building long-term relationships with students. Additionally, it relies on the delivered quality of the value-added services. A significant relation between service quality and student satisfaction have empirically been tested and confirmed by previous investigations [11,60,61]. Satisfied students comprise a source of competitive advantage [61] as well as a contributing factor in determining both the student loyalty and the university’s image [11]. Accordingly, SO has been taken into account as an indispensable prerequisite to the success of SRM.
Hypothesis 3 (H3).
Student orientation and SRM success are significantly correlated.
2.4. SRM Technology
Student-oriented activities would be possible with the right technology [1,2,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,19]. SRM technological tools have been observed as a main component in the implementation of this kind of strategy. Seeman and O’Hara [19] discussed how technology facilitates this approach, asserting when the relational managerial approach is improved by technology; an integrated synthesis of each area of the academy that involves the student is made. Technological tools provide the interplay and communication between the various members of an organization and also perform the personalized operations automatically [9,13,14]. Fontaine [15] affirmed that the implementation of technology is vital to attracting students, and regarded it as one of the driving forces behind the future of higher education institutions. Moreover, technological systems are specifically considered as one of the main enablers for KM [25,31] and the system change processes [33].
Consequently, higher education institutions must possess the proper technology to advance the processes associated with student relationships to succeed in implementation. SRM technological tools offer many benefits to such institutions, for instance, to present an individual view of the students, to handle the student relationship in a holistic manner regardless of the utilized communication channel, to improve the processes’ effectiveness and efficiency included in student relationships, and to customize the service with greater quality and cheaper cost.
In spite of all the above-mentioned, however, paying an excessive attention to the technology is regarded as inappropriate—the institutions must employ it as an enabler of its SRM instead. We have accordingly acknowledged technology as a necessary condition (but not sufficient) to succeed in the SRM implementation.
Hypothesis 4 (H4).
SRM technology and SRM success are significantly correlated.
In order to examine the research model, a hypothesis in addition to the aforementioned four hypotheses was developed that allows for the exploration of the relationship between the four critical success factors, as shown below. It should be noted that the following hypothesis is in pursuit of Reference [7], who argued there is a strong correlation between KM, EI, SO, and SRM technology. The mentioned study was conducted based on the investigations that regard the student as a customer; however, there was a body of relevant literature that theoretically and empirically demonstrates the presence of this hypothesis. To be more exact, the findings of Sin et al. [62] supported that these critical factors are significantly correlated. In the current knowledge of SRM strategy, a web of interlocking initiatives, which can institutionalize the concept over time, has also been affirmed [8,9]. Moreover, to succeed in examining the research model (Figure 2), it is necessary to take it into our hypothetical account.
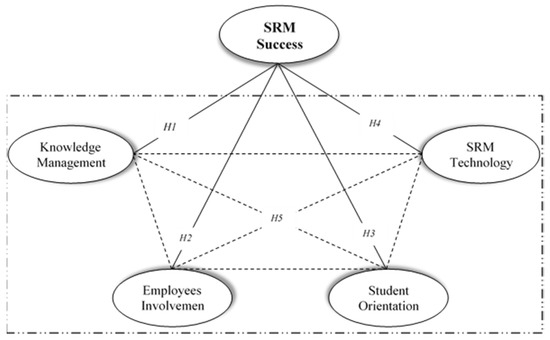
Figure 2.
The SRM research model.
Hypothesis 5 (H5).
The critical success factors are interrelated, i.e., there has been a significant correlation between them.
Based on this literature review and the resultant five hypotheses, the research model that helps with identifying the critical success factors is presented in Figure 2. The conceptual model connects the construct of SRM success and the recognized four critical success factors of SRM (i.e., H1–H4), and also show the potential correlations among the four SRM’s critical success factors (i.e., H5).
3. Methods
As the research model (Figure 2) is involved in the theoretical relations between the observed and unobserved variables, a confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) that is a quantitative analytic method was employed, which allows the authenticity of the model and its hypotheses to be tested through the empirical dataset. Based on Hair et al. [63], CFA is the appropriate technique if the factorial structure is to be analyzed. It is likened to theory (or hypothesis)-driven [64,65]. This method, which is widely utilized in psychological, economic, managerial, educational research, and other areas, and can provide a more specific framework for proving a prior structural model [66]. The main advantage of CFA is to examine a conceptually grounded theory, analyzing how the theoretical designation of the factors harmonizes with the actual data (in reality). In other words, it permits us to either accept or reject our hypotheses [63]. Thus, the research model presented with the resultant five hypotheses (Figure 2) is evaluated using CFA. Three main steps for the implementation of this method have been taken out in this study, as explained below.
3.1. Specifying the Measurement Model
Two basic questions should be addressed in this step [63]: (1) What is the factorial structure to be analyzed? and (2) What are the items included as the measurement scales? Due to lack of research on the topic, both questions have been answered based on the investigation of Reference [7], which have systematically defined the individual constructs as well as methodically developed and specified the measurement scale and model for implementing a successful SRM. As presented in Figure 2, the model has a theoretical basis, whereby a confirmatory investigation should be carried out. Accordingly, the item-based checklist (consisted mainly of 26 items) by Gholami et al. [7] was applied to analyze. The measurement scales along with the respondents’ answers on them, after a thorough survey which is discussed in the next step, have been presented in Appendix A (Figure A1).
3.2. Designing A Confirmatory Survey
In order to design a confirmatory, survey three main questions should be addressed [63]: (1) What has been the desired sample size to measure? (2) How has it been collected? and (3) What is the technique of sampling? Concerning the sample size, Hair et al. [63] suggested that the minimum sample size should exceed 150 in the confirmatory perspectives if the model involves seven constructs or less with modest communalities. Moreover, Nejati and Nejati [67] supported their confirmatory survey on data collected from an investigation with 185 completed questionnaires (response rate = 72.8%). Questionnaires are one of the main methods in the survey research among other procedures and sources to collect data [68]. There are a variety of techniques and routines for sampling, the non-probabilistic convenience sampling has often been regarded to collect primary data regarding the particular matters such as obtaining the respective customers’ opinions in connection with a new design of a service or product. In this type of sampling, which was widely employed in the operational and managerial fields, the sample collection process proceeds to the required sample size be fulfilled [68].
In this study, the data were collected through 260 distributed questionnaires (10:1) in a non-probabilistic convenience sampling among the students of Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM), which is a top-ranking public research university in Malaysia. A total of 231 out of the completed 260 questionnaires with a response rate of 88.85% were deemed usable. To administer the participants, the Likert-scaled items on a continuum from one (strongly disagree) to five (strongly agree) were performed, as illustrated in Figure A1. The respective participants’ demographic profile, which is based on [67], has been summarized below.
Based on gender, 42.9% and 57.1% of the total respondents were female and male, respectively. Based on the age group, 49.4%, 45.4%, and 5.2% of the total respondents were under 25, 26 to 35, and 36 to 45 years old, respectively. Based on nationality, 51.9% and 48.1% of the total respondents were international and local students, respectively. Based on the higher educational level, 40.3%, 43.3%, and 16.4% of the total respondents had undergone a bachelor’s degree, master’s degree, and Ph.D. study, respectively. According to the study’s period in the current institution, 13%, 44.2%, 24.2%, 13.4%, and 5.2% of the total respondents had less than 1 years,1 to 2 years, 2 to 3 years, 3 to 4 years, and more than 4 years’ experience in their occupations.
3.3. Assessing the Measurement Model Reliability and Validity
After specifying the model and collecting sufficient data, the reliability and validity of the measurement scales and model are assessed by performing this step, which is in pursuit of the criteria set by Hair et al. [63] and the investigations of References [29,67,69,70,71].
Firstly, the Cronbach’s Alpha (α) technique was applied using SPSS to examine the survey instrument’s internal consistency. According to its outcome, as indicated in Figure A1, the reliability of all factors is considered acceptable and the total reliability of the structure was calculated to be 0.94, which is regarded as excellent.
Next, CFA was implemented as a way to test the Goodness-of-fit of the hypothetical model (Figure 2), which involves five factors and 26 measurement scales. In doing so, the software package of IBM®SPSS®AMOS™22 was utilized due to its integrity— the data format supported in AMOS is the SPSS format [64]. Additionally, it systematically allows for considering robust goodness-of-fit indicators, analyzing the standardized residuals, and appraising modification indices (M.I.) to the factorial models. In pursuit of the criteria set by the mentioned researchers, various fit indices have been employed to examine the fitness of the model, as shown in Table 1. Based on the model fit summary of AMOS, the initial CFA did not appear to be acceptable (Table 1), displaying that there is a need for few modifications in the specification to dress up the appropriate model. After evaluating the content and nature of the variables, the regression weights associated with some of the variables within each pair that denoted an extremely high—KM3, KM4, EI4, SO3, SMRT4, SMRT5, and SMRT6—were omitted from the revised CFA (see Figure A2).

Table 1.
The goodness-of-fit indexes for the CFA models.
Hence, after omitting the seven variables of SRM, CFA with 19 variables was re-performed to examine the model validity. Table 1 shows that all the values exceed the recommended criteria for the acceptable goodness-of-fit of the model, proving that the revised model has outlined an appropriate goodness-of-fit. All the path coefficients had been significant (p < 0.001) in the revised model, demonstrating an important contribution of each variable to the relevant factor. The standardized loadings of the variables in the five constructs were found to be higher than 0.5 (Figure A2), representing the high convergent validity of the constructs. The standardized residuals were also determined to be satisfactory, distributing a standard normal which was smaller than two in the absolute value. Moreover, the construct reliability (CR) value was utilized to examine the reliability of constructs, which should be higher than 0.6. In this study, the CR for the constructs of KM, EI, SO, and SRMT were estimated to be 0.9, 0.7, 0.7, and 0.7, respectively. These evaluations verify the satisfactory results regarding the structural reliability and validity of the SRM strategy, which are classified into an articulated five-factor model. Therefore, how the instrument with 19 variables has a high consistency or even harmonizes with respect to its utilization in the new version of the SRM scale as a developed standard scale may be mentioned. Consequently, the construct of the SRM success and the presented four critical success factors of SRM were significantly permitted to correlate with one another, as evidenced in Figure 3.
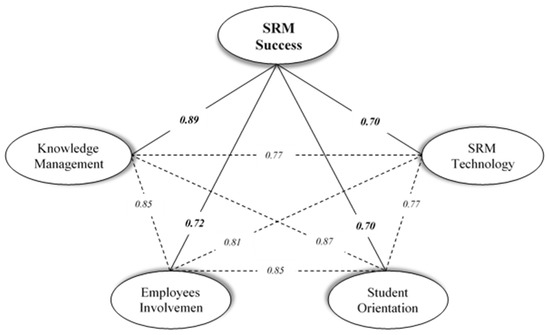
Figure 3.
The research hypotheses testing results (all coefficients are significant at 0.001 or better).
4. Results and Discussion
The results of this study are in accord with the research purpose—presenting and examining the critical success factors of SRM. To address this, a theoretical and empirical contribution was explicitly made that would provide a valuable source to taper off the existing gap in the contemporary knowledge of SRM strategy.
Theoretically, a comprehensive perspective for the sake of SRM success was presented (Figure 1), highlighting that SRM technology is not equated with SRM. In this perspective that reflects SRM as a multi-dimensional strategic approach, the importance of four critical success factors, i.e., knowledge management (KM), employees’ involvement (EI) student orientation (SO), and SRM technology (SRMT) has been stressed to succeed in implementation. It is believed that these factors involve three key components including technology, people, and process [7]. Consequently, a research model with five hypotheses (Figure 2) was formulated for further analysis. This paper described these critical factors underpinning a structure in detail; however, to date, there is no any investigation in this context.
Empirically, confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) (that is, a quantitative analytic method) was implemented in three steps. Specifying the measurement model was discussed in the first step. The second step led to designing a confirmatory survey—the data were collected and deemed usable through the completed 231 questionnaires in a non-probabilistic convenience sampling among the students, who are the major stakeholders. Finally, assessing the measurement model reliability and validity is taken into careful consideration—the regression weights (modification indices) associated with some of the variables within each pair that were extremely high, were suggested by the CFA output to revise the model. After revision, the goodness-of-fit indices, standardized loadings, standardized residuals, and other diagnostic tests were found to be satisfactory.
Upon confirmation of the research model (Figure 3), the results indicated that there has been a significant correlation between the SRM success and the four critical success factors since all p-values were found to be less than 0.001 (p < 0.001), as shown in Table 2. However, these factors correlate with SRM success significantly where the strongest correlation coefficient belongs to the “knowledge management” factor (0.886), while the weakest correlation coefficient belongs to “SRM technology” factor (0.696). Furthermore, it is noted that the SRM critical success factors correlate with SRM success significantly in a descending order; knowledge management (ϕ = 0.886), employees’ involvement (ϕ = 0.715), Student Orientation (ϕ = 0.704), and SRM technology (ϕ = 0.696). Table 3 shows that the SRM critical success factors possess a significant correlation with each other as all p-values were less than 0.001 (p < 0.001) and all correlation coefficients exceeded 0.5. Therefore, the resultant five hypotheses in this research are empirically accepted, as illustrated in Figure 3.

Table 2.
The correlation coefficients between SRM critical success factors and SRM Success.

Table 3.
The correlation coefficients among SRM critical success factors.
5. Conclusions and Future Research Directions
SRM has recently been established as a strategic approach to developing sustainability issues and generating a significant competitive advantage in higher education institutions. However, institutions do not take the full potential of SRM into careful consideration while claiming to have a student-centered approach. More studies are accordingly needed to develop the concept. This study contributes valuable insights into critical success factors of SRM implementation. It has theoretically identified and clarified these factors, as well as empirically formulated and examined them, which may provide a guide for decision-makers in institutions to become better acquainted with SRM applications and also for the state-of-the-art research towards constituting a comprehensive successful SRM system.
The research results and analyses revealed that there are four critical success factors to succeed in the SRM implementation. These factors, which are knowledge management, employees’ involvement, student orientation, and SRM technology, were found to be interrelated, i.e., there was a significant correlation between them. Additionally, they were significantly correlated to the SRM success. These findings highlight that SRM is not equated with SRM technology, but a multi-dimensional strategic approach which should also involve the key components associated with people and process in order to succeed. In addition to the technological tool, it is consequently confirmed that the role of knowledge management, employees’ involvement, and student orientation appear to be especially important for implementation. Therefore, the educational establishments must take technology into account as an enabling factor without assigning to it a solo driver in the implementation of SRM.
As the discourse upon SRM has just started to develop with a distinct identity, an opportunity exists for innovative research. Despite the studies that make the contributions to this subject, new research is needed to conceptualize and operationalize the concept based on the following perspectives.
- The SRM strategy has primarily emerged from the customer relationship management (CRM) theoretical lens (cf. References [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]), implying that students are prime customers of higher education institutions. This issue has clearly been addressed by the findings of References [19,72], stating that the adoption of the student-as-customer perspective by such institutions will contribute to improving “the universities’ service quality” and “the degradation of educational quality in terms of the instructors’ neglect of teaching, the impairment of instructor-student relationship, and the ease of course achievement” [72] and including a “student-centric focus”, “improved customer data and process management”, “increased student loyalty”, “retention”, and “satisfaction with the college’s programs and services” [19].
- Besides, it should be taken into careful consideration that the student relationship is somewhat different from the customer relationship in the industrial and general service sectors. In these sectors, the customers are well-defined while in universities the definition of students as customers is quite broad [73,74]. Although students are recognized as prime customers by many researchers [7,74], due to the dynamic and interactive nature of these institutions, they are also considered as cooperators, co-producers, co-creators of value, and co-developers of knowledge, which reflects a much more important perspective, i.e., the student-as-partner perspective.
Thus, it is recommended that future studies reconcile the aforementioned perspectives for the sake of developing a modern SRM. This article represented an attempt to examine the SRM’s critical success factors. However, the confirmatory analysis performed by this study provides merely a snapshot of the institution in Malaysia. So as to consolidate the issues encountered in this research, the additional follow-up investigations is undoubtedly an opportunity that could be pursued. Since SRM initiative is a long-term academic strategy, longitudinal research could be undertaken with the same institutions to observe if the same findings hold over time.
Another important topic for further research arising from this article is: to identify and analyze the barriers that would contribute to the clearer implementation of the SRM concept. However, the barriers, which hinder implementing SRM, pose serious challenges to the practitioners.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.G.; Formal analysis, H.G; Funding acquisition, S.R.A. and F.A.; Investigation, H.G.; Methodology, H.G. and N.Z.; Project administration, M.Z.M.S. and S.S.; Resources, H.G. and F.A.; Software, H.G.; Supervision, M.Z.M.S., S.S. and N.Z.; Validation, H.G.; Visualization, H.G.; Writing – original draft, H.G.; Writing – review & editing, M.Z.M.S. and S.S.
Funding
This research was funded by the Research Management Centre (RMC) at Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM) under the post-doctoral fellowship scheme (PDRU Grant), grant number. Q.J130000.21A2.04E01 and the APC was funded by the fundamental research grant scheme (FRGS), grant number. R.J.130000.7809.4F935.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Research Management Centre (RMC) at Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM) and the Ministry of Higher Education (Malaysia) for supporting and funding this research under the post-doctoral fellowship scheme (PDRU Grant), Vot No. Q.J130000.21A2.04E01 as well as the fundamental research grant scheme (FRGS), Vot No. R.J.130000.7809.4F935.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
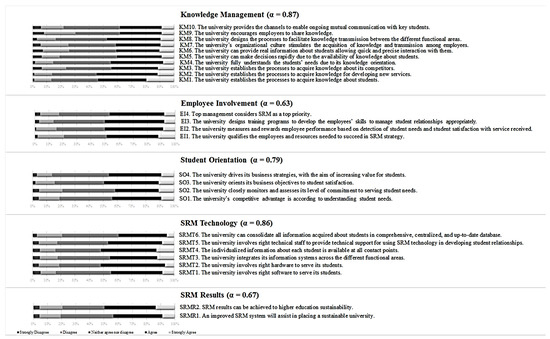
Figure A1.
Confirmatory survey respondents’ answers (N = 231).
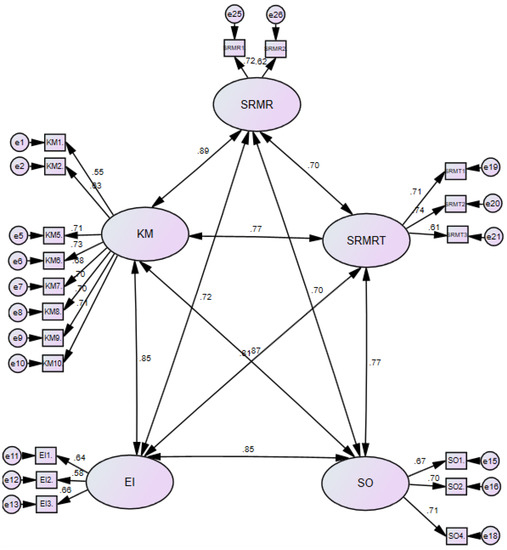
Figure A2.
The standardized estimates of the revised CFA model; all coefficients are significant (p < 0.001).
References
- Carter, S.; Yeo, A.C.M. Students-as-customers’ satisfaction, predictive retention with marketing implications: The case of Malaysian higher education business students. Int. J. Educ. Manag. 2016, 30, 635–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilbert, A.; Schönbrunn, K.; Schmode, S. Student relationship management in Germany: Foundations and opportunities. Manag. Rev. 2007, 18, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckler, C.; Creech, H. Shaping the Future We Want: UN Decade of Education for Sustainable Development (2005–2014) Final Report; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Foo, K.Y. A vision on the role of environmental higher education contributing to the sustainable development in Malaysia. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 61, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, T.; Vuorisalo, T.; Sammalisto, K. Integrated management systems for enhancing education for sustainable development in universities: A memetic approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 106, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, M.; Lindgren, M.; Packendorff, J. Universities need leadership, academics need management: Discursive tensions and voids in the deregulation of Swedish higher education legislation. High. Educ. 2018, 75, 299–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, H.; Zameri Mat Saman, M.; Mardani, A.; Streimikiene, D.; Sharif, S.; Zakuan, N. Proposed Analytic Framework for Student Relationship Management based on a Systematic Review of CRM Systems Literature. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, R.; Schibrowsky, J. A business marketing strategy applied to student retention: A higher education initiative. J. Coll. Stud. Retent. 2007, 9, 307–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piedade, M.B.; Santos, M.Y. Business intelligence in higher education: Enhancing the teaching-learning process with a SRM system. In Proceedings of the 5th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies, Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 16–19 June 2010; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shannaq, B.; Rafael, Y.; Alexandro, V. Student relationship in higher education using data mining techniques. Glob. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2010, 10, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Drapińska, A. A concept of student relationship management in High Education. Prace Instytutu Lotnictwa 2012, 6, 35–49. [Google Scholar]
- Kongsakun, K.; Fung, C.C. Neural Network Modeling for an Intelligent Recommendation System Supporting SRM for Universities in Thailand. WSEAS Trans. Comput. 2012, 11, 34–44. [Google Scholar]
- Lechtchinskaia, L.; Friedrich, I.; Breitner, M.H. Requirements Analysis for a Student Relationship Management System—Results from an Empirical Study in Ivy League Universities. In Proceedings of the IEEE 45th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Washington, DC, USA, 4–7 January 2012; pp. 5132–5141. [Google Scholar]
- Radenković, B.; Despotović-Zrakić, M.; Bogdanović, Z.; Labus, A.; Milutinović, M. Providing services for student relationship management on cloud computing infrastructure. In Proceedings of the IEEE 11th International Conference on Telecommunications in Modern Satellite, Cable and Broadcasting Services (TELSIKS), Nis, Serbia, 16–19 October 2013; Volume 2, pp. 385–388. [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine, M. Student Relationship Management (SRM) in Higher Education: Addressing the Expectations of an Ever Evolving Demographic and Its Impact on Retention. J. Educ. Hum. Dev. 2014, 3, 105–119. [Google Scholar]
- Vulić, M.; Petrović, P.; Kovačević, I.; Živanović, V.R. Student Relationship Management Using Social Clouds. In Handbook of Research on High Performance and Cloud Computing in Scientific Research and Education; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2014; pp. 173–194. [Google Scholar]
- Wardley, L.J.; Bélanger, C.H.; Nadeau, J. A co-creation shift in learning management: Work design for institutional commitment and personal growth. High. Educ. 2017, 74, 997–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, K.E.; Dwyer, A.; Hine, L.; Turner, J. Conceptions of students as partners. High. Educ. 2018, 76, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeman, E.D.; O’Hara, M. Customer relationship management in higher education: Using information systems to improve the student-school relationship. Campus-Wide Inf. Syst. 2006, 23, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, M.; Leidner, D.E. Review: Knowledge management and knowledge management systems: Conceptual foundations and research issues. MIS Q. 2001, 25, 107–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, G.P. Organizational learning: The contributing processes and the literatures. Organ. Sci. 1991, 2, 88–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, I. A dynamic theory of organizational knowledge creation. Organ. Sci. 1994, 5, 14–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepeda-Carrion, I.; Martelo-Landroguez, S.; Leal-Rodríguez, A.L.; Leal-Millán, A. Critical processes of knowledge management: An approach toward the creation of customer value. Eur. Res. Manag. Bus. Econ. 2017, 23, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.Y.; Tan, L.P.; Lee, C.S.; Wong, W.P. Knowledge Management performance measurement: Measures, approaches, trends and future directions. Inf. Dev. 2015, 31, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.Y.; Aspinwall, E. Development of a knowledge management initiative and system: A case study. Expert Syst. Appl. 2006, 30, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skyrme, D.; Amidon, D. The knowledge agenda. J. Knowl. Manag. 1997, 1, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beijerse, R.P. Questions in knowledge management: Defining and conceptualising a phenomenon. J. Knowl. Manag. 1999, 3, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrar, Y.F. Knowledge management: Learning for organisational experience. Manag. Audit. J. 2002, 17, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.R.; Huang, C.F.; Hsu, T.J. Knowledge leadership to improve project and organizational performance. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2014, 32, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, R. Incorporation and institutionalization of SD into universities: Breaking through barriers to change. J. Clean. Prod. 2006, 14, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.N.L. Enhancing knowledge sharing and research collaboration among academics: The role of knowledge management. High. Educ. 2016, 71, 525–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbudin, A.S.M.; Nejati, M.; Amran, A. Sustainability-based knowledge management performance evaluation system (SKMPES): Linking the higher learning institutes with the bottom billions. Afr. J. Bus. Manag. 2011, 5, 9530–9540. [Google Scholar]
- Shoham, S.; Perry, M. Knowledge management as a mechanism for technological and organizational change management in Israeli universities. High. Educ. 2009, 57, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.N.; Gomes, A.M. Review of knowledge management in higher education institutions. Eur. J. Bus. Manag. 2014, 6, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Bhusry, M.; Ranjan, J. Implementing knowledge management in higher educational institutions in India: A conceptual framework. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2011, 29, 34–46. [Google Scholar]
- Sedziuviene, N.; Vveinhardt, J. The paradigm of knowledge management in higher educational institutions. Eng. Econ. 2009, 65, 79–90. [Google Scholar]
- Kidwell, J.J.; Vander, L.K.; Johnson, S.L. Applying corporate knowledge management practices in Higher Education. Educ. Q. 2000, 23, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Suciu, M.C.; Piciorus, L.; Imbrisca, C.I. Intellectual capital, trust, cultural traits and reputation in the Romanian education system. Electronic J. Knowl. Manag. 2012, 10, 223–235. [Google Scholar]
- Helm-Stevens, R.; Brown, K.C.; Russell, J.K. Introducing the Intellectual Capital Interplay Model: Advancing Knowledge Frameworks in the Not-for-Profit Environment of Higher Education. Int. Educ. Stud. 2011, 4, 126–140. [Google Scholar]
- Trivella, L.; Dimitrios, N.K. Knowledge management strategy within the High. Educ. The case of Greece. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 175, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, W.; Nawe, J. Knowledge Management (KM) Practices in Institutions of Higher Learning in Tanzania with Reference to Mbeya University of Science and Technology. Univ. Dar es Salaam Libr. J. 2017, 12, 48–65. [Google Scholar]
- Cranfield, D.J.; Taylor, J. Knowledge management and higher education: A UK case study. Electronic J. Knowl. Manag. 2008, 6, 85–100. [Google Scholar]
- Rees, S.J.; Protheroe, H. Value, Kaizen and Knowledge Management: Developing a Knowledge Management Strategy for Southampton Solent University. The Electronic J. Knowl. Manag. 2009, 7, 135–144. [Google Scholar]
- Tariq, S.; Jan, F.A.; Ahmad, M.S. Green employee empowerment: A systematic literature review on state-of-art in green human resource management. Qual. Quant. 2016, 50, 237–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslach, C.; Schaufeli, W.B.; Leiter, M.P. Job burnout. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2001, 52, 397–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaufeli, W.B.; Salanova, M.; González-Romá, V.; Bakker, A.B. The measurement of engagement and burnout: A two sample confirmatory factor analytic approach. J. Happiness Stud. 2002, 3, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruman, J.A.; Saks, A.M. Performance management and employee engagement. Hum. Resour. Manag. Rev. 2011, 21, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harer, J.K.; Schmidt, F.L.; Hayes, T.L. Business-unit-level relationship between employee satisfaction, employee engagement, and business outcomes: A meta-analysis. J. Appl. Psychol. 2002, 87, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kompaso, S.M.; Sridevi, M.S. Employee engagement: The key to improving performance. Int. J. Bus. Manag. 2010, 5, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macey, W.H.; Schneider, B.; Barbera, K.M.; Young, S.A. Employee Engagement: Tools for Analysis, Practice, and Competitive Advantage; Wiley-Blackwell: Malden, WA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kyndt, E.; Baert, H. Antecedents of employees’ involvement in work-related learning: A systematic review. Rev. Educ. Res. 2013, 83, 273–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, I.A.; Crane, A. Corporate social responsibility in small-and medium-size enterprises: Investigating employee engagement in fair trade companies. Bus. Ethics: A Eur. Rev. 2010, 19, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, G.; Gholami, H.; Shaharou, A.B.M.; Saman, M.Z.M.; Zakuan, N.; Najmi, M. Relationship among culture of excellence, organisational performance and knowledge sharing: Proposed conceptual framework. Int. J. Prod. Qual. Manag. 2016, 19, 446–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, F.; Wald, A. Success factors of knowledge management in temporary organizations. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2011, 29, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, R. Students as Partners—Good for Students, Good for Staff: A Study on the Impact of Partnership Working and How This Translates to Improved Student-Staff Engagement. Int. J. Stud. Partn. 2017, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Moreno, A.; Padilla-Meléndez, A. Analyzing the impact of knowledge management on CRM success: The mediating effects of organizational factors. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2011, 31, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullateef, A.O.; Salleh, S.M. Does customer relationship management influence call centre quality performance? An empirical industry analysis. Total Qual. Manag. Bus. Excell. 2013, 24, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narver, J.C.; Slater, F.S. The effect of a market orientation on business profitability. J. Mark. 1990, 54, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentum, R.V.; Stone, M. Customer relationship management and the impact of corporate culture—A European study. J. Database Mark. Cust. Strategy Manag. 2005, 13, 28–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brown, R.M.; Mazzarol, T.W. The importance of institutional image to student satisfaction and loyalty within higher education. High. Educ. 2009, 58, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dužević, I.; Časni, A.Č. Student and faculty perceptions of service quality: The moderating role of the institutional aspects. High. Educ. 2015, 70, 567–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, L.Y.; Tse, A.C.; Yim, F.H. CRM: Conceptualization and scale development. Eur. J. Mark. 2005, 39, 1264–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Black, W.C.; Babin, B.J.; Anderson, R.E. Multivariate Data Analysis: A Global Perspective, 7th ed.; Pearson-Hall International: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber, J.B.; Nora, A.; Stage, F.K.; Barlow, E.A.; King, J. Reporting structural equation modeling and confirmatory factor analysis results: A review. J. Educ. Res. 2006, 99, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albright, J.J.; Park, H.M. Confirmatory factor analysis using Amos, LISREL, Mplus, and SAS/STAT CALIS; Working Paper; The Trustees of Indiana University: Indianapolis, IN, USA, 2009; Volume 1, pp. 1–85. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, D.R.; Lachos, V.H.; Bazan, J.L.; Azevedo, C.L. Estimation methods for multivariate Tobit confirmatory factor analysis. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2014, 79, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejati, M.; Nejati, M. Assessment of sustainable university factors from the perspective of university students. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 48, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forza, C. Survey research in operations management: A process-based perspective. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2002, 22, 152–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayles, J.G.; Rockenbach, A.B.; Davis, H.A. Civic responsibility and the student athlete: Validating a new conceptual model. J. High. Educ. 2012, 83, 535–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, G.; Gholami, H.; Shaharou, A.B.M.; Zameri Mat Saman, M.; Sadeghi, L.; Zakuan, N. Shared knowledge mediated correlation between cultural excellence and organisational performance. Total Qual. Manag. Bus. Excell. 2017, 28, 427–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, H.; Rezaei, G.; Saman, M.Z.M.; Sharif, S.; Zakuan, N. State-of-the-art Green HRM System: Sustainability in the sports center in Malaysia using a multi-methods approach and opportunities for future research. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 124, 142–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watjatrakul, B. Factors affecting students’ intentions to study at universities adopting the “student-as-customer” concept. Int. J. Educ. Manag. 2014, 28, 676–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madu, C.N.; Chu-Hua, K. Dimensions of quality teaching in higher institutions. Total Qual. Manag. 1993, 4, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandaviya, M.; Dwivedi, V.V. A critical review on paradigms of sustainable development in higher education: An international perspective. Int. J. Appl. Res. 2016, 2, 312–320. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).