Constructing the Green Supply Chain for Rural Tourism in China: Perspective of Front–Back Stage Decoupling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Supply Chain in Tourism Industry: From Distribution Channel to Destination-Based Service Network
2.2. Green Supply Chain: Balance Thinking for Both Efficiency and Environment
2.3. Green Supply Chain in Tourism Studies: Lack of Consideration on Service Features
2.4. Front–Back Stage Decoupling: Solution to Both Efficiency and Environment in Service Operations
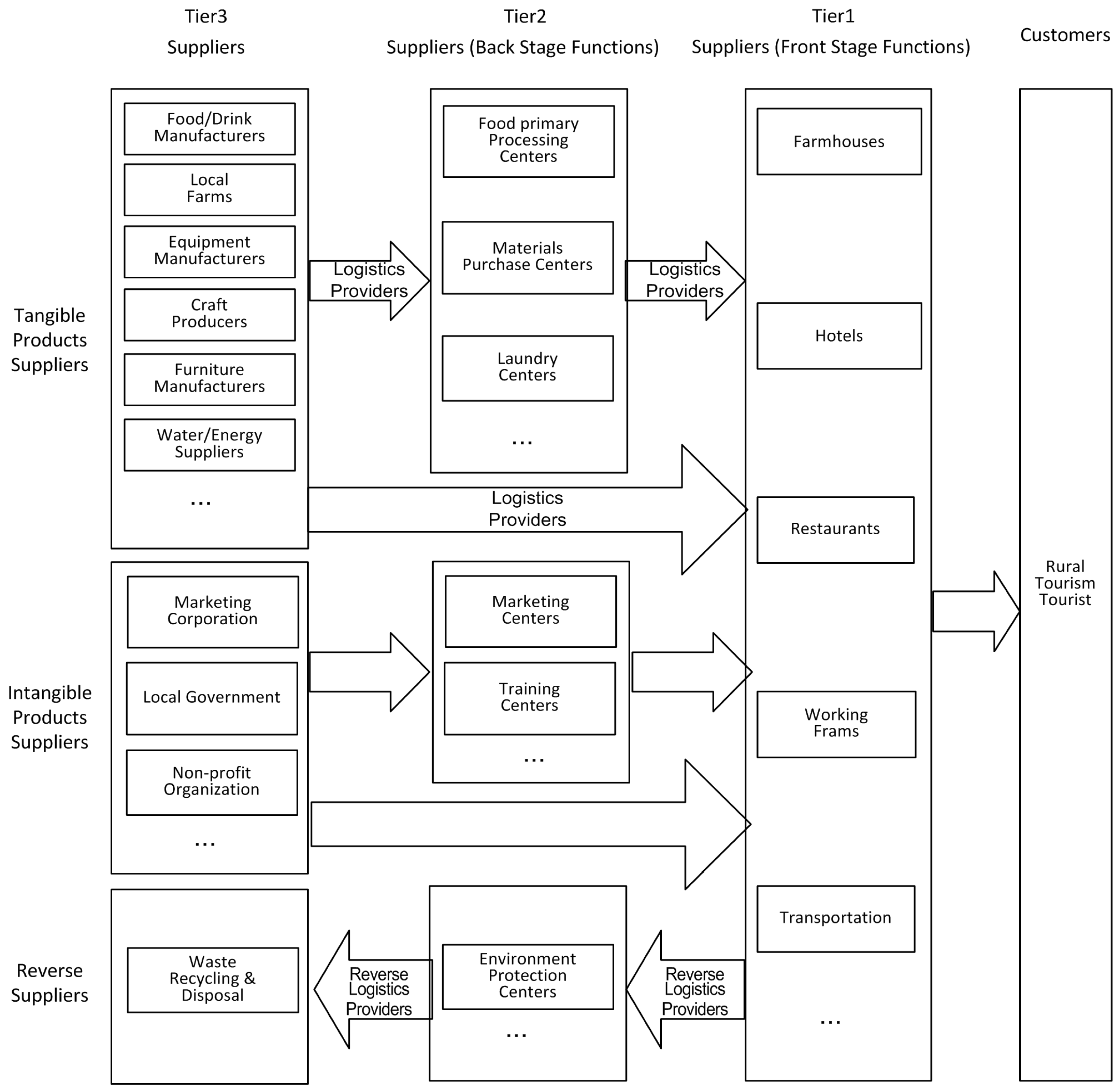
3. Constructing a Green Rural Tourism Supply Chain Model Based on Front–Back Stage Decoupling Concept
4. Methods
4.1. Research Context
4.2. Methodology: Data Collection and Analysis
4.3. Validity of the Case Study
5. Findings
5.1. Problem Diagnose of Rural Tourism in Baofu Town
5.1.1. Environment Pollution and the Vicious Circle It Caused
5.1.2. Analysis of Causes
5.2. Process of Green TSC Construction for Baofu Town’s Rural Tourism
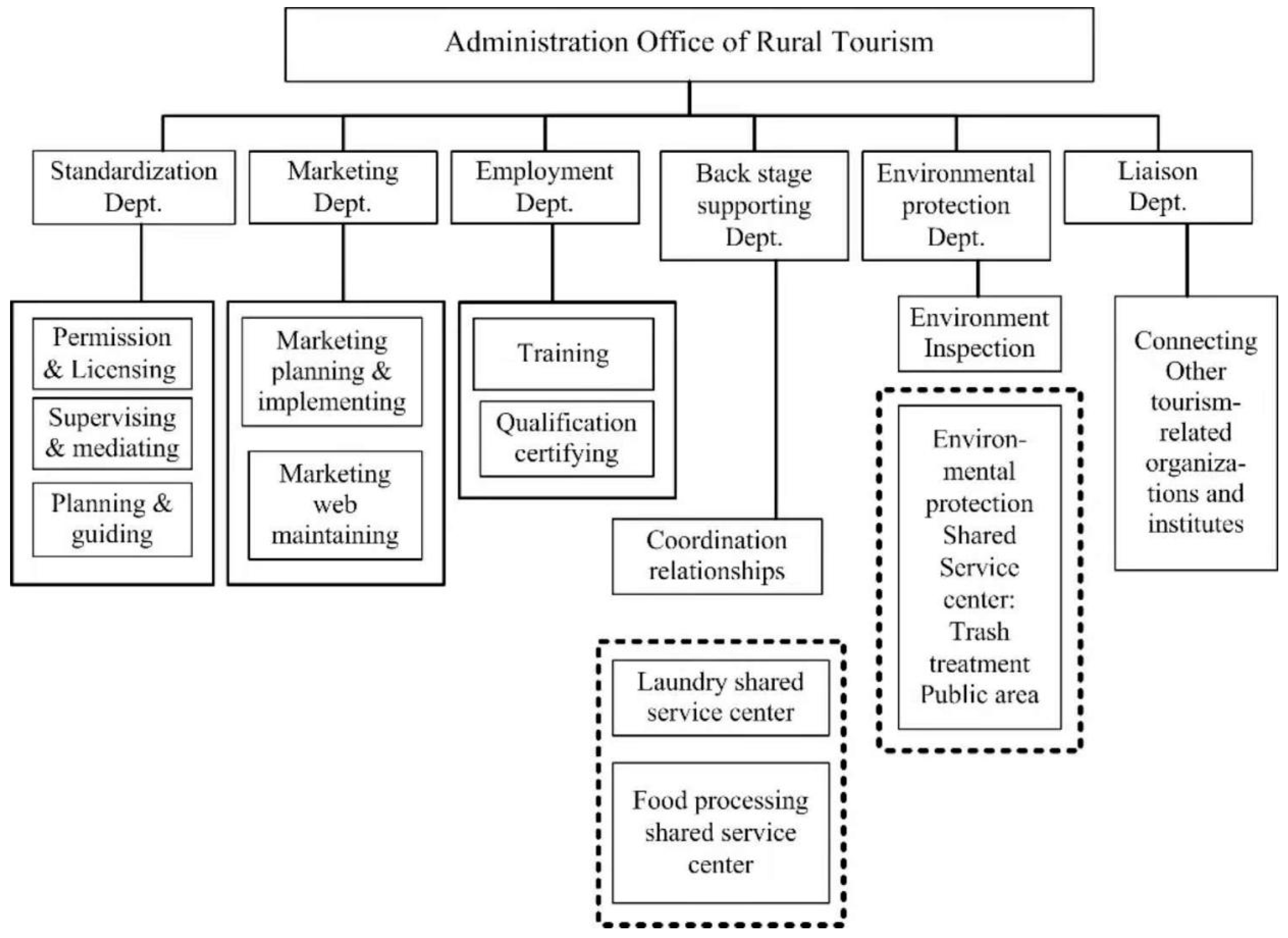
5.2.1. The Implementation of Green TSC’s New Structure
5.2.2. Operations of Shared Service Centers
5.2.3. A Top-Down Approach to Construction
5.3. The Effects of New Green TSC Structure in Baofu Town
6. Discussion and Conclusions
6.1. Academic Implications
6.2. Practical Implications
6.3. Limitations and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharpley, R. Rural tourism and the challenge of tourism diversification: The case of Cyprus. Tour. Manag. 2002, 23, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, R. Flagship attractions and sustainable rural tourism development: The case of the Alnwick Garden, England. J. Sustain. Tour. 2007, 15, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, V.D.; Hall, C.M.; Garry, T. Tourism and poverty alleviation: Perceptions and experiences of poor people in Sapa, Vietnam. J. Sustain. Tour. 2014, 22, 1071–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, R.; Roberts, L. Rural tourism—10 years on. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2004, 6, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyim, P. Tourism and rural development in western China: A case from Turpan. Community Dev. J. 2016, 51, 534–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaranta, G.; Citro, E.; Salvia, R. Economic and social sustainable synergies to promote innovations in rural tourism and local development. Sustainability 2016, 8, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.M. Rural eco-environmental problems and countermeasures in China. Agric. Econ. 2017, 4, 38–40. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bramwell, B. Rural tourism and sustainable rural tourism. J. Sustain. Tour. 1994, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva-Álvaro, J.J.; Mondéjar-Jiménez, J.; Sáez-Martínez, F.J. Rural tourism: Development, management and sustainability in rural establishments. Sustainability 2017, 9, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Ministry of Agriculture. Research Report on China’s Leisure Agriculture and Rural Tourism Development; China Ministry of Agriculture: Hangzhou, China, 2017; (In Chinese).
- Liao, Y.; Nong, D. Analysis of the impact of rural tourism on Farmers’ income and environment—Taking Fuxian Lake in Jiangchuan County of Yunnan Province as an example. Glob. Hum. Geogr. 2016, 6, 168–169. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Hu, W. A study on the impact of rural tourism development on Tourist Destinations—A case study of Guan Hou Village, Xianju County, Zhejiang Province. Rural Econ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 28, 77–79. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chi, J.; Cui, F.J. A Study on “The Tragedy of the Commons” in the Process of the Development of On-limits Rural Tourism Destinations—A Case of Meijiawu, Longwu and Shangougou in Hangzhou. Tour. Trib. 2006, 21, 17–23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Choo, H.; Jamal, T. Tourism on organic farms in South Korea: A new form of ecotourism? J. Sustain. Tour. 2009, 17, 431–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsen, J.; Getz, D.; Ali-Knight, J. The environmental attitudes and practices of family businesses in the rural tourism and hospitality sectors. J. Sustain. Tour. 2001, 9, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Meiwei, W.; Rongde, L. Goodbye, Dali: Hip Tourist Spot Turns Into Ghost Town as Sewage Scare Prompts Shutdown. Available online: https://www.caixinglobal.com/2017-05-18/goodbye-dali-hip-tourist-spot-turns-into-ghost-town-as-sewage-scare-prompts-shutdown-101092172.html (accessed on 3 April 2018).
- Bitner, M.J.; Ostrom, A.L.; Morgan, F.N. Service blueprinting: A practical technique for service innovation. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2008, 3, 66–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon-itt, S.; Wong, C.Y.; Wong, C.W. Service supply chain management process capabilities: Measurement development. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, S.E.; Spring, M. Service supply chains: Introducing the special topic forum. J. Supply Chain Manag. 2012, 4, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maull, R.S.; Geraldi, J.; Johnston, R. Service supply chains: A customer perspective. J. Supply Chain Manag. 2012, 4, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, W.S.; Pohlen, T.L.; Hanna, J.B. Evolving a theory of performance-based logistics using insights from service dominant logic. J. Bus. Logist. 2010, 2, 35–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selviaridis, K.; Matopoulos, A.; Szamosi, L.T.; Psychogios, A. Reverse resource exchanges in service supply chains: The case of returnable transport packaging. Supply Chain Manag. 2016, 21, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhou, X. The construction of conceptual model of tourist destination supply chain. Tour. Sci. 2009, 23, 15–20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tapper, R.; Font, X. Tourism supply chains: Report of a desk research project for the travel foundation. Available online: http://www.icrtourism.com.au/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/TourismSupplyChains.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2018).
- Zhang, X.; Song, H.; Huang, G.Q. Tourism supply chain management: A new research agenda. Tour. Manag. 2009, 30, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkis, J.; Zhu, Q.; Lai, K.H. An organizational theoretic review of green supply chain management literature. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2011, 130, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, C.R.; Rogers, D.S. A framework of sustainable supply chain management: Moving toward new theory. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. 2008, 38, 360–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K. Green supply chain management: A state-of-the art literature view. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2007, 9, 53–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Sarkis, J. An inter-sectoral comparison of green supply chain management in China: Drivers and practices. J. Clean. Prod. 2006, 14, 472–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, F.; Iraldo, F. Shadows and lights of GSCM (green supply chain management): Determinants and effects of these practices based on a multinational study. J. Clean. Prod. 2010, 18, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laari, S.; Töyli, J.; Solakivi, T.; Ojala, L. Firm performance and customer-driven green supply chain management. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1960–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.L.; Bui, T.D. Identifying eco-innovation in industrial symbiosis under linguistic preferences: A novel hierarchical approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 1376–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islama, M.S.; Tseng, M.L.; Kariaa, N.; Leed, C.H. Assessing green supply chain practices in Bangladesh using fuzzy importance and performance approach. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 131, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigala, M. A supply chain management approach for investigating the role of tour operators on sustainable tourism: The case of TUI. J. Clean. Prod. 2008, 16, 1589–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Research on the impact of supply and demand environment change on the connotation of tourism destination supply chain. J. Beijing Int. Stud. Univ. 2009, 173, 14–19. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Gursoy, D. A conceptual framework of sustainable hospitality supply chain management. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2015, 24, 229–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadeeva, Z. Translation of sustainability ideas in tourism networks: Some roles of cross-sectoral networks in change towards sustainable development. J. Clean. Prod. 2005, 13, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgell Sr, D.L. Managing Sustainable Tourism: A Legacy for the Future, 2nd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 9781138918634. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D. Supply chain construction in low carbon tourism. Spec. Zone Econ. 2011, 11, 178–180. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F. The Operation Research about Green Tourism Supply Chain with Scenic Spots as Core-enterprises. Zhejiang Ocean. Univ. Hum. Sci. 2010, 27, 52–55. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H. Applying the green supply chain management on the development of ecotourism products. Product. Res. 2007, 2, 132–134. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.Q. The study on the rural tourism green supply chain in the urban economy influencing zone. Res. Admin. Sci. 2013, 6, 1–4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, J.D. Organizations in Action: Social Science Bases of Administrative Theory, 7th ed.; Transaction Publishers: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010; ISBN 0765809915. [Google Scholar]
- Chase, R.B. The customer contact approach to services: Theoretical bases and practical extensions. Oper. Res. 1981, 29, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metters, R.; Vargas, V. A typology of decoupling strategies in mixed services. J. Oper. Manag. 2002, 18, 663–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safizadeh, M.H.; Field, J.M.; Ritzman, L.P. An empirical analysis of financial services processes with a front-office or back-office orientation. J. Oper. Manag. 2003, 21, 557–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hao, Y. Front-back stage decoupling of service system from traditional operation to mass customization. China Ind. Econ. 2009, 10, 108–117. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, V.; Brenner, W. Characteristics of shared service centers. Transform. Gov. People Process Policy 2010, 4, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, U.M.; Mason, R.O. Global disaggregation of information-intensive services. Manag. Sci. 1995, 41, 1250–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breathnach, P. Globalisation, information technology and the emergence of niche transnational cities: The growth of the call centre sector in Dublin. Geoforum 2000, 31, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacity, M.; Willcocks, L.; Teeny, D. Commercializing the back office at Lloyds of London: Outsourcing and strategic partnerships revisited. Eur. Manag. J. 2004, 22, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zomerdijk, L.G.; de Vries, J. Structuring front office and back office work in service delivery systems: An empirical study of three design decisions. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2007, 27, 108–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D. The Development of Tourist Dissipative Structure System: Theory and Practice; China Market Press: Beijing, China, 2006; ISBN 9787509200438. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Tang, D.; Wang, J. A Comprehensive Cost Analysis on New System Structure for Nature-Based Tourism Destination: Perspective of Front and Back Stage Decoupling. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2014, 19, 1345–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, B. Essentials of Shared Service Centers; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2003; ISBN 978-0471250791. [Google Scholar]
- Utting, P. Social and political dimensions of environmental protection in Central America. Dev. Chang. 1994, 25, 231–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creswell, J. Qualitative Inquiry & Research Design: Choosing among Five Approaches; Sage: Riverside County, CA, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-1412995306. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, R.K. Discovering the future of the case study. Method in evaluation research. Eval. Pract. 1994, 15, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.M. Counter Measures to environmental and ecological problems in rural tourism in China. Agric. Econ. 2017, 4, 38–40. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.L.; Guo, J.; Li, X.F. Rural tourism and environmental pollution problems. Rural Econ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 11, 72–73. [Google Scholar]
- Wanhill, S. Sustaining Tourism SMEs. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.138.480&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 8 April 2018).
- Tseng, M.L.; Tan, R.R.; Siriban-Manalang, A.B. Sustainable consumption and production for Asia: Sustainability through green design and practice. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 40, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangzhou Tianchuan Environmental Technology Co. Environment impact assessment of rural tourism in Shiling village, BaofuTown. Available online: http://www.doc88.com/p-9089790309806.html (accessed on 25 October 2018).
- Neto, F. A new approach to sustainable tourism development: Moving beyond environmental protection. Nat. Resour. Forum 2003, 27, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amemba, C.S.; Nyaboke, P.G.; Osoro, A.; Mburu, N. Elements of green supply chain management. Eur. J. Bus. Manag. 2013, 5, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Font, X.; Tapper, R.; Schwartz, K.; Kornilaki, M. Sustainable supply chain management in tourism. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2008, 17, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, J.; Moreno, P.; Tejada, P. The tourism SMEs in the global value chains: The case of Andalusia. Serv. Bus. 2008, 2, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, L.J.; Lockwood, A. Understanding the challenges of implementing best practices in hospitality and tourism SMEs. Benchmarking Int. J. 2006, 13, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sako, M. Outsourcing and offshoring: Implications for productivity of business services. Oxf. Rev. Econ. Policy 2006, 22, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Stage | Research Objectives | Examples of Research Questions | Information Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before the project | Construct theoretical logic and define the requirement of research sample | Why did town government launch the project? | Public information |
| Understand the context of the project | How serious is the environmental problem in local tourism? | Archival documentation | |
| Collect basic information of the sample town and validate the archival information | How do you describe the local environment comparing that before tourism development? | Interviews | |
| During the project | Understand environmental and efficiency issues in rural tourism development and details in promoting TSC from perspective of government, industry, tourists and residents. | What are the main reasons causing the environmental and cost problems? | Interviews |
| Know the actual situation of the efficiency and environmental effects | Observations | ||
| Collect documentary data to understand the cost efficiency of TSC and also to validate the information from other sources | Archival documentation | ||
| After the project | Understand the green TSC influences on environment and efficiency from different perspectives | Does Green TSC boost tourism development in both efficiency and environment? | Panel Discussion |
| Type | No | Title | Gender | Age | Affiliation/Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Local authority | L1 | Manager of project for tourism improvement | M | 39 | Economy development office of Baofu town |
| L2 | Vice mayor | M | 41 | Baofu town government | |
| L3 | Senior officer | M | 42 | Administration office of rural tourism in Baofu town | |
| L4 | Officer | F | 33 | Administration office of rural tourism in Baofu town | |
| L5 | Director | F | 35 | Economy development office of Baofu town government | |
| Environmental experts | E1 | Chef environmental engineer | M | 46 | Environmental Protection bureau of Anji county |
| E2 | Director of environment supervision | M | 40 | Environmental Protection bureau of Anji county | |
| SSC managers | M1 | Vice general manager | M | 37 | Kaidi Laundry company |
| M2 | Sales manager | F | 35 | Zhengong Food Supply company | |
| Indigenous business owner | I1 | Owner | M | 50 | Fengshou Farm restaurant and accommodation in Baofu |
| I2 | Owner | F | 47 | Le Hui Agri-restaurant | |
| I3 | Owner | M | 39 | Zhuyuan leisure services | |
| I4 | Vice director | M | 40 | Committee of tourism development of Anji county | |
| Local residents | L1 | M | 52 | Baofu Town | |
| L2 | M | 45 | Baofu Town | ||
| L3 | M | 33 | Baofu Town | ||
| L4 | M | 27 | Baofu Town | ||
| L5 | M | 29 | Baofu Town | ||
| L6 | F | 34 | Baofu Town | ||
| L7 | F | 55 | Baofu Town | ||
| L8 | F | 30 | Baofu Town | ||
| Tourists | T1 | F | 37 | Shanghai | |
| T2 | M | 40 | Shanghai | ||
| T3 | M | 33 | Hangzhou | ||
| T4 | M | 36 | Jiaxing | ||
| T5 | F | 28 | Jiashan | ||
| T6 | M | 30 | Changxing | ||
| T7 | M | 33 | Shaoxing | ||
| T8 | M | 29 | Deqing | ||
| T9 | M | 34 | Huzhou | ||
| T10 | M | 38 | Tongxiang | ||
| Scholars | S1 | M | 47 | Zhejiang University of technology | |
| S2 | M | 42 | Zhejiang University of Finance & economics |
| Sources of Pollution | Pollution Description | Pollution Types | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Front stage | Dining facilities | Trash and waste water from the left-over and packages | SP, WP |
| Accommodation facilities | Trash from the one-off toiletries, stationaries, waste water for day use | SP, WP | |
| Leisure facilities | Noise and some trash from food/drinks | NP, SP | |
| Toilets for tourists | Drainage water and residue | WP, SP | |
| Back stage | Food processing | Waste water and oil, oil fume, smell and smoke, food/materials and residue and packages, noise produced in kitchen operations | WP, SP, NP, AP |
| Heating and air conditioning | Waste gas, water dust and noise in heating or cooling conditioning operations | AP, WP, NP | |
| Laundry | Waste water and noise | WP, NP | |
| Storage | Trash in storing goods | SP | |
| Operation offices | Trash from everyday office work | SP | |
| Toilets for employees | Drainage water and residue | WP, SP | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Guan, J.; Xu, J.; Clergeau, C. Constructing the Green Supply Chain for Rural Tourism in China: Perspective of Front–Back Stage Decoupling. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4276. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10114276
Chen J, Guan J, Xu J, Clergeau C. Constructing the Green Supply Chain for Rural Tourism in China: Perspective of Front–Back Stage Decoupling. Sustainability. 2018; 10(11):4276. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10114276
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jue, Jingjing Guan, Jing (Bill) Xu, and Cecile Clergeau. 2018. "Constructing the Green Supply Chain for Rural Tourism in China: Perspective of Front–Back Stage Decoupling" Sustainability 10, no. 11: 4276. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10114276
APA StyleChen, J., Guan, J., Xu, J., & Clergeau, C. (2018). Constructing the Green Supply Chain for Rural Tourism in China: Perspective of Front–Back Stage Decoupling. Sustainability, 10(11), 4276. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10114276




