Abstract
Ecologically fragile cropland soils and intensive agricultural production are characteristic of the valley area of the Tibetan Plateau. A systematic assessment of soil quality is necessary and important for improving sustainable cropland management in this area. This study aims to establish a minimum data set (MDS) for soil quality assessment and generate an integrated soil quality index for sustainable cropland management in the Tibetan Plateau. Soil samples were collected from the 0–20 cm depths of agricultural land in the middle and lower reaches of the Lhasa River. These samples were analyzed by routine laboratory methods. Significant differences were identified via statistical test between different soil types and land use types for each soil property. Principal component analysis was used to define a MDS of indicators that determine soil quality. Consequently, effective porosity, pH, total organic C, total N, available P, and catalase were identified as the final MDS. The soil quality index was obtained by the fuzzy-set membership function and the linear weighted additive method. The soil quality index differed significantly between the soil types and land use types. The soil quality can be ranked based on their indices in the following order: 1. Grain land with meadow soils, 2. Grain land with steppe soils, 3. Greenhouse vegetable land with fluvo-aquic soils, 4. Grain land with fluvo-aquic soils. The soils with higher soil quality indices exhibited better soil structure, higher nutrient contents, and superior resistance to water and nutrient loss. While the intensive tillage practices associated with vegetable production could reduce the values for effective porosity, pH and catalase, the application of appropriate fertilizers increased the values for total organic C, total N and available P. Therefore, the MDS method is an effective and useful tool to identify the key soil properties for assessing soil quality, and provides guidance on adaptive cropland management to a variety of soil types and land use types.
1. Introduction
Land degradation is a pervasive and systemic phenomenon that impacts approximately 30% of the total global land area across all parts of the terrestrial world []. Human-induced soil degradation, i.e., the temporary or permanent reduction of the productive capacity of lands as a result of soil fertility declines and deterioration in plant growth conditions [], has gained considerable attention as a serious global environmental problem, especially in the Tibetan Plateau. Because soil is the basis of all terrestrial ecosystems, soil degradation exacerbates shortages in land resources, poses a threat to food security, and hinders poverty reduction.
The Tibetan Plateau has relatively few agricultural land resources due to its low temperatures and complex geography. Suitable cropland accounts for approximately 0.3% of the total land area of Tibet, and it is mainly distributed in the valley area of the Yarlung Zangbo River and its tributaries. The cropland in the valley area accounts for more than 70% of the total cropland area in the Tibetan Plateau []. However, the quality of cropland in these areas is relatively low overall, with a low cultivation index and a shortage of cropland resource reserves. Although alpine soils, as the dominant soil type in the cropland region, are often characterized by a deep topsoil layer, good soil structure, and a relatively high organic matter content, these soils are young with a low content of soil available N. In addition, the soil ecosystem is extremely fragile and sensitive given the poor natural conditions and severe environmental threats, such as overgrazing and climate change []. Therefore, a systematic assessment of soil quality is necessary and important for improving sustainable cropland management in the Tibetan Plateau.
Soil quality plays an important role in reducing agricultural costs, maintaining land output and protecting the quality of the ecological environment. In recent decades, the research on soil quality assessment has mainly focused on soil quality indicators, the assessment index system, and assessment methods. Soil quality indicators represent the characteristics, functions or conditions of soil and aid in assessing the soil health status from the perspective of soil productivity and environmental management. Because soil research has not yet formed a unified concept and assessment criteria for soil quality, there is no set of defined basic soil quality indicators that have received widespread adoption []. In early studies, some relatively simple indicators have usually been selected, such as plant biomass, crop yield and status of plant growth []. Subsequently, various indicators of soil nutrients were selected to reflect soil fertility []. With the expansion of the concept of soil fertility quality, comprehensive indices that incorporate physical properties, biochemical properties and environmental conditions have been developed, but studies still concentrate on soil nutrient indicators []. In recent years, more attention has been paid to biological indicators, among which soil microbial biomass and soil enzyme activity are the most widely used [,]. Soil enzyme activities have been identified as a quantifiable soil quality indicator for early responses to changes in soil management [].
In order to fully reflect all aspects of soil quality and to avoid collinearity between soil indicators, a minimum data set (MDS) of soil indicators was adopted to assess soil quality []. The introduction of the MDS method has greatly facilitated soil quality assessment and the selection of soil indicators []. On the one hand, soil data redundancy can be reduced by using a general approach for choosing the most representative indicators from large existing data sets. On the other hand, the weight for each soil quality indicator was obtained by its communality, calculated by mathematical statistics of standardized factor analysis [], thus helping to avoid subjective judgments. Moreover, a number of methods for quantitative determination of MDS have been proposed, and the principal component analysis method is the most widely used [,].
Ecologically fragile cropland soils and intensive agricultural production are characteristic of the valley area of the Tibetan Plateau. The current research focuses on the ecological effects from climate change, soil erosion, land desertification and grassland degradation []. Our previous study shows that the physical and chemical properties of soils in this area have changed significantly, especially the decrease of soil organic matter content [,]. Unfortunately, there are few studies on soil quality in the study area. The present study is conducted in the Lhasa River valley, a typical cropland region of the Tibetan Plateau. The primary objective of our study is to generate a soil quality index with establishing an index system for soil quality assessment based on the MDS method and fuzzy sets in the Lhasa River valley. This research will help to provide support for decision-making about sustainable cropland management in this region.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
This study was conducted in an area of the Lhasa River basin located in the south of the Tibetan Plateau (Figure 1). The Lhasa River is a branch of the Yarlung Zangbo River. The basin covers an area of 32.9 thousand km2 which accounts for about 13.5% of the total area of the Yarlung Zangbo River basin []. The topography is characterized by the transition from riverbeds to valley slopes. Alluvial flats and channel bars are frequent and widely distributed. Terraces are developed along the main stream of the river. Large alluvial fans are formed by the deposition of sediment at the mouth of the tributary. The study area is characterized by a plateau cold monsoon and semi-arid climate, with a mean annual temperature of −1.5 to 7.8 °C and a mean annual precipitation of 430–700 mm []. Over 85% of the annual rainfall is distributed in a summer wet period lasting from June to September. According to Chinese soil classification, the soil of the study area is classified as fluvo-aquic soils, meadow soils, and steppe soils (Fluvisols and Cambisols in the World Reference Base for Soil Resources).
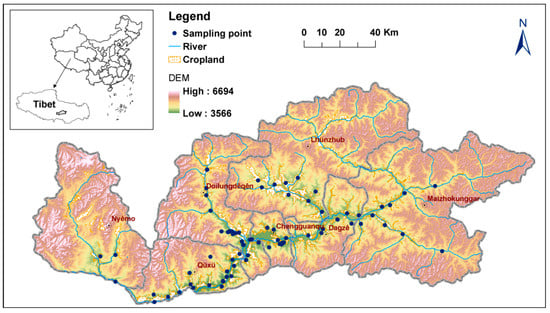
Figure 1.
Location of study area, sampling points, distribution of cropland, and elevation (expressed as meters above sea level).
This study focused exclusively on cropland in the middle and lower reaches of the Lhasa River (Figure 1). This area is dominated largely by valley agriculture where grains and vegetables are widely cropped. The cropland is mainly distributed in strips in the terraces along the river and around the alluvial flats, with an elevation range between 3300 and 4000 m a.s.l. The soil texture in this area is suitable for cultivation and there are favorable conditions for irrigation.
2.2. Soil Sampling and Laboratory Analysis
A total of 93 sampling points were selected over the cropland in the middle and lower reaches of the Lhasa River (Figure 1). The selection of sampling points was based on soil type, topography, and agricultural land use. Soil samples were collected from the 0–20 cm depth at these points. Among these samples, there were 53 in fluvo-aquic soils, 14 in meadow soils, and 26 in steppe soils. Exact positions for each sampling point were acquired by portable GPS (Global Position System) units and topographic maps. A portion of 3 kg composite sample was collected at each sampling point within a 50 m × 50 m area. The soil samples were air-dried and then plant roots and residues were picked out. After that, these samples were ground in an agate mortar and passed through a 2 mm, 0.25 mm or 0.149 mm mesh sieve, which were preparing for the analysis of soil properties.
According to common indicators in previous studies, 23 soil items covering physical, chemical, and biological properties were analyzed and considered as potential indicators for soil quality assessment in the study (Table 1). Particle size distributions of sand (0.02–2 mm), silt (0.002–0.02 mm), and clay (<0.002 mm), was determined via the hydrometer method []. Bulk density was assayed by the core method []. Microaggregates were measured via the pipette method []. Total porosity was calculated by using the measured bulk density and assuming particle density of 2.65 Mg m−3. Effective porosity was obtained by subtracting water content at 10 kPa from that at saturation. This was determined with ground and sieved soil (<2 mm) using a pressure plate []. Field capacity and permanent wilting point was measured at 30 kPa and 1.5 MPa respectively and the difference between these values was taken as the available water capacity []. The pH was assayed via the potentiometric method using a 1:2.5 soil/water ratio extract []. Total organic C was determined by dichromate wet combustion []. Total N was measured via the Kjeldahl method []. Total P was measured by dissolving soil phosphorus with HClO4 and H2SO4 and using a spectrophotometer for detection []. Total K was determined by the digestion of soil potassium with HF and HClO4 and then using flame photometer for detection []. Available N was assayed via alkaline hydrolysis diffusion []. Available P was determined by extraction with NaHCO3 and subsequent colorimetric analysis []. Available K was measured by extraction using 1 mol L−1 NH4OAc and then using a flame photometer for detection []. Cation exchange capacity (CEC) was determined after soil treatment with an ammonium acetate solution at a pH of 7.0 []. Urease activity was assayed by adding toluene to moist soils and incubating soils with 1 mol L−1 citric acid buffer (pH = 6.7) and 10% urea for 3 h at 38 °C and then measuring the amount of NH4+ with a spectrophotometer at 578 nm []. Catalase activity was determined by first adding 3 mol L−1 of H2SO4 and 0.3% hydrogen peroxide solution to moist soils. This mixture was then incubated via a 30-min oscillation. After incubation, the mixture was then filtrated with compact filter paper and titrated with KMnO4. Catalase activity was therefore expressed as mL g−1 of KMnO4 []. To measure alkaline phosphatase, toluene was added to moist soils and the mixture was then incubated with 0.003 mol L−1 borate buffer (pH = 9.6) and 0.03 mol L−1 C6H5PO4Na2 for 3 h at 38 °C. Alkaline phosphatase was then assayed by measuring the amount of phenol via a spectrophotometer at 578 nm []. β-glucosidase was measured by incubating soil samples in McIlvaine buffer (pH 4.8) with p-nitrophenyl-β-d-glucopyranoside and toluene at 30 °C for 1 h and then subjecting the samples to colorimetric estimation of p-nitrophenol that was released by enzyme activity [].

Table 1.
Soil physical, chemical, and biological properties that were considered as potential soil quality indicators in this study.
2.3. Indicator Selection for Soil Quality Assessment and Factor Analysis
2.3.1. Assessment Objectives
The selection of soil quality indicator should vary depending on the particular evaluation purpose and soil functions that are being studied. Therefore, the identification of the primary management goal for the study area should be the first step in the development of a suitable index system for soil quality assessment. The assumption in this study is that our soil quality assessment should be aimed at guiding sustainable farming practices to maximize grain and vegetable production and minimize soil fertility degradation. Andrews et al. [] reported that the productivity goal was defined as enhancing or maintaining the production quantity, quality, and stability of economically important plants as a primary management concern. This goal is associated with nutrient cycling, water relations, physical stability and support, as well as resistance and resilience.
2.3.2. Initial Filter for Soil Indicators
Soil indicators were initially filtered by grouping soil sampling points according to soil types and land use types. We then tested for significant differences via multivariate statistical methods. Soil sampling points were classified according to the following soil types: fluvo-aquic soils (), meadow soils (), and steppe soils (). These points were further subdivided into five groups according to agricultural land use types. The grain land (Group 1, ), conventional vegetable land (Group 2, ), and greenhouse vegetable land (Group 3, ) were classed as fluvo-aquic soils areas. Both meadow soils areas (Group 4, ) and steppe soils (Group 5, ) areas were occupied by the grain land (See Supplementary Materials).
Statistical analysis was implemented by the SPSS® 16.0 software (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). For each soil property, the Kolmogorov-Smirnov (K-S) test was performed to determine if the data exhibited a normal distribution () []. If the data passed the normality test, a parametric method (one-way ANOVA) with least significant difference tests were used to compare the groups to determine whether groups exhibited significant differences []. Meanwhile, a nonparametric method (Kruskal-Wallis test) was chosen for the data with non-normal distribution. Only soil properties with significant differences among groups () were retained as potential candidates to generate a minimum data set (MDS) of soil quality indicators [].
2.3.3. Defining a Minimum Data Set with Factor Analysis
Soil indicators which were sensitive to soil quality were selected from physical, chemical, and biological properties to constitute a MDS for soil quality assessment. A factor analysis method has been widely used in previous studies in relation to soil quality assessment [,,,]. Factor analysis is a statistical method based on the correlation analysis of multiple variables to reduce the dimensionality of a set of data. The basic model of factor analysis is as follows:
where are the observed soil properties, are factors; (; ) are constants called factor loadings; and () are error terms.
Principal component analysis (PCA) is a frequently used method for factor extraction. PCA uses orthogonal transformation to convert a set of possibly correlated soil properties into a set of linearly uncorrelated variables called principal components []. The PCA method can scale down the number of soil quality indicators via dimensionality reduction. This aids in avoiding the problem of data redundancy.
First, a correlation matrix was constructed by calculating the correlation coefficient between selected soil indicators. The following is the calculation equation:
where () are the correlation coefficients between and of the selected soil indicators.
Second, an appropriate number of principal components were extracted depending on the calculated eigenvalue and eigenvector, the variance percentage of the principal component and the cumulative variance percentage. The factor loadings can be calculated via the equation below:
To clarify the relationship between the soil indicators and principal components, a factor rotation was done via the varimax method with orthogonal rotation. This process maximizes the variance of the squared loadings of a factor on all the soil indictors in a factor matrix, and makes it as easy as possible to identify each indicator with a single factor.
Most previous studies have reached a consensus that principal components with eigenvalue ≥1 and soil indicators with high factor loadings best represent the original data of soil properties [,]. Therefore, only principal components that explained at least 5% of the variation in the data and 85% of the cumulative variation were examined []. For each principal component, only highly weighted soil indicators were retained for the MDS, i.e., factor loadings with absolute values within 10% of the highest weight [,,].
Finally, correlation coefficients between soil indicators in the MDS were calculated to examine the possible further reductions in the number of these indicators []. We assumed that soil indicators in the MDS with coefficients more than 0.7 were highly correlated, these indicators were regarded redundant and candidates for elimination from the MDS []. Among highly correlated indicators, the indicator with the highest absolute value of factor loading was selected for the MDS.
2.4. Soil Quality Index Generation Using Fuzzy Set
Generally, soil quality indicators are not directly comparable due to different units. Therefore, the values of these indicators should be transformed into scores between 0 and 1. In view of the fuzziness and gradualness of soil quality indicator scoring, fuzzy set techniques were used in this study.
Fuzzy sets are based on imprecise reasoning and can be used for classification of objects when classes do not have rigidly defined boundaries []. Soil quality assessment with fuzzy set techniques includes three steps: determination of the membership function for scoring soil quality indicators, weight assignment for selected soil quality indicators, and integration of weighted membership values of soil quality indicators into a soil quality index. Wang [] reported that indicators were scored along an ascending or descending membership curve depending on the relationship between soil quality indicator and crop yield. It should be noted that a lower half trapezoid curve was not used and showed in this study because no indicator from the MDS has an inverse relationship with crop yield [].
Indicators that have a positive correlation with contributions to crop yield (i.e., higher values of the indicator indicate higher contributions to crop yield) were termed ‘more is better’ soil quality indicators. Thus, an upper half trapezoid curve was used to score these indicators:
where, x is the value of soil quality indicator, while a and b are the lower and upper thresholds for a given indicator respectively.
Indicators that exhibited positive contributions to the growth of crops within an optimum range of values were termed ‘mid-point optimum’ indicators. Thus, a trapezoid curve was used to score these indicators.
where, , , , and are the thresholds of soil quality indicators.
The method of integrating of various soil properties allows for the quantification of interactions between soil quality indicators, and it can also account for the importance of each soil quality indicator relative to the integrated evaluation of soil quality. According to previous studies, linear weighted sum method was adopted to calculate a general index from the soil quality indicators []:
where, SQI represents the integrated value of the soil quality index, and represents the index value and its weight for the ith soil quality indicator.
Correctly assigning a weight for each of selected soil quality indicators is crucial for the determination of the overall soil quality index. In view of intrinsic relationship between soil properties, value of communality for each indicator was obtained via PCA. The communality represents the contribution to overall determination of soil quality. For each soil quality indicator, weight is therefore the ratio of the communality value for the indicator to the total value of communality for all indicators []:
where and are the weight and value of community for ith soil indicator, respectively.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Descriptive Statistics of Soil Properties
A total of 23 soil properties were analyzed as potential soil quality indicators. Table 2 exhibits minima, maxima, means, standard deviations, and coefficient of variations (CV) for these properties.

Table 2.
Minimum, maximum, mean, standard deviation, and coefficient of variation of soil properties as potential soil quality indicators in the Lhasa River valley.
Physical soil properties mainly refer to texture, structure, and drainage, which determine the ventilation conditions and thermal properties of soils. These physical properties play an important role in the migration process of water and chemicals in soils. As shown in Table 2, most soils sampled in this study were classified as sandy loam according to the international system of soil texture classification. The mean proportion of sand, silt and clay in soils from the study area were 71.92%, 18.42%, and 9.32%, respectively. The main issues limiting crop production in these soils are water and nutrient deficiency, and these can be solved via clay application to increase water use efficiency and water conservation []. The bulk density of the soils ranged from 1.11 to 1.59 g cm−3, with an average value of 1.34 g cm−3. These values are appropriate for crop root growth in the study area. Studies have shown that root growth was limited when bulk density exceeded 1.5 g cm−3 due to the high penetration resistance. However, a bulk density less than 1.4 g cm−3 could effectively alleviate the inhibition of root growth, improve moisture absorption, and increase crop yields []. Soil microaggregates, widely accepted as an indicator of soil structure stability, varied between 58.79% and 95.45% with a mean value of 85.77%. Total porosity as determined by the bulk density, ranged from 0.4 to 0.581 m3 m−3 with an average value of 0.49 m3 m−3. The minimum value (0.119 m3 m−3) of effective porosity was found in fluvo-aquic soils at a height of 3710 m a.s.l. The maximum value (0.274 m3 m−3) was obtained from steppe soils at an elevation of 4275 m a.s.l. Water content at field capacity ranged from 0.188 to 0.425 m3 m−3, while water content at the permanent wilting point varied between 0.069 and 0.287 m3 m−3. Among the 93 sampling points in the study area, 10 had low available water capacity at less than 0.1 m3 m−3.
Chemical soil properties related to soil fertility and nutrient management that were analyzed in this study include pH, C, N, P, K, and CEC. Table 2 shows that there was a fair amount of variation in the soil pH. The soil pH ranged from 4.5 to 8.65, with a mean value of 7.15. The results revealed that only 18 samples from grain agricultural soils exhibited moderately alkaline pH levels. However, almost a third of total samples exhibited acidic pH (<6.5) levels and six samples even exhibited a moderately acidic pH. The acidification of cropland soils in Lhasa Chengguanqu District may be attributed to fertilizer application in the greenhouse systems that grow vegetables []. Total organic C varied between 9.77 and 56.08 g kg−1, with an average value of 25.44 g kg−1. Approximately 25.81% of total samples exhibited a total organic C that exceeded 30 g kg−1, indicating good soil fertility that can support crop growth. The total organic C was significantly correlated with the height above sea level in the study area, with a correlation coefficient of 0.3 (). A similar relationship was found by Zhang et al. [] who reported an increase in total organic C with a rise in the height above sea level. This trend was likely due to the use of animal-derived organic fertilizer in some higher regions. Total N was high across the study area, where 82.80% of soil samples had values more than 1.2 g kg−1. Among the 93 soil samples analyzed for available N, almost 37% of the samples exhibited high values (>150 mg kg−1), 53% exhibited medium values (90–150 mg kg−1), and 10% exhibited low values (<90 mg kg−1). Total P also exhibited high levels. Total P ranged from 0.44 to 2.88 g kg−1, with a mean value of 0.89 g kg−1. Sixty-two sampling points exhibited available P values that exceeded 20 mg kg−1, while only 5 points had values less than 10 mg kg−1. The entire study area exhibited medium (15–25 g kg−1) to high (>25 g kg−1) levels of total K, and available K exhibited basically similar characteristics. The higher levels of soil nutrients could be attributed to a significant increase in use of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizer that accompanied the comprehensive agricultural development in southern valley area of Tibet that began in 1990. Cation exchange capacity varied between 3.89 and 19.89 cmol kg−1 of soil, with an average value of 10.74 cmol kg−1. This indicates a medium capacity for nutrient retention [].
For the nutrient cycling process assessment, total organic C was considered as the primary organic matter indicator, with soil enzymes including urease, catalase, alkaline phosphatase, and β-glucosidase. Urease activity ranged from 0.11 to 1.36 mg g−1 with a mean value of 0.56 mg g−1. Catalase activity varied between 15.01 and 59.25 mg g−1, with an average value of 39.00 mg g−1. Alkaline phosphatase activity varied between 1.36 and 47.28 mg g−1, with a mean of 17.75 mg g−1. β-glucosidase activity ranged from 0.27 to 2.71 mg g−1, with an average value of 1.70 mg g−1. The average values were similar to those found in previous reports [], and are typical for the Lhasa River valley.
Among the 23 soil properties analyzed in this study, bulk density, microaggregates, and total porosity exhibited the least dispersion, with CVs less than 9%. The most variable property was available P, with a CV of 111.61%. The properties with moderate dispersion were silt content, clay content, total P, available K, urease, and alkaline phosphatase. These factors with moderate dispersion exhibited CVs ranging from 40% to 60%.
3.2. Minimum Data Set for Determining Soil Quality
First, the K-S test for goodness of fit was performed to check the normality of soil property data. We used a parametric method if data passed this test, and we used a nonparametric method if data failed the test. Table 2 shows the parameters of the data distributions and the significance levels of the K-S test. It is obvious that a subset of soil properties, such as bulk density, pH, total C, and catalase, passed the K-S test for normality at a significance level 0.05. However, the data distribution of other soil properties including microaggregates, effective porosity, field capacity, permanent wilting point, total P, available P, available K, and urease were skewed positively or negatively and exhibited leptokurtosis.
Furthermore, comparisons were drawn among groups divided by soil type and agricultural land use for each soil property from the total sampling points as described in Section 2.3 and statistically significant differences were also identified. For the soil properties with normal distributions, the results of one-way ANOVA revealed that pH, total organic C, total N, available N, CEC, catalase, alkaline phosphatase, and β-glucosidase had significant differences between the groups. There were no significant differences between these groups for any of the physical properties with normal distribution. For the data with non-normal distributions, the results of Kruskal-Wallis test showed that there were significant differences between agricultural land uses and soil types for several physicochemical properties including effective porosity, total P, available P, and available K. As a result, a data set that included the soil properties that exhibited significant differences between the groups was created in preparation for the factor analysis.
The value of the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin measure of sampling adequacy and Bartlett’s test of sphericity for this set of soil properties are 0.749 and 857.7 respectively []. This implies that the degree of common variance among these indicators was moderate. Therefore, we concluded that the correlations in the soil property data are appropriate for factor analysis. The PCA method with varimax rotation was performed and three principal components were extracted with eigenvalues >1. Most of the common variance shared by the twelve soil indicators was explained by the three principal components, with the cumulative percentage accounting for 68.81% of the variance in the data (Table 3). Soil indicators associated with each principal component were defined and these indicators exhibited low contributions to other principal components. The first PC, which explained 31.323% of the total variance in the data, was related to pH, available P, catalase, and alkaline phosphatase. The pH, catalase, and alkaline phosphatase are positively loaded on the first PC, while only available P exhibited a negative loading. These indicators revealed that the first PC comprehensively reflected the biochemical status of soils. The second PC explained 28.608% of the total variance and variables that were positively loaded on this factor were total organic C, total N, and available N. Obviously, this set of properties represented soil nutrient status because the variables were mainly related to the nutrients necessary for plants growth. The third PC explained 8.879% of the total variance and effective porosity was positively loaded on this factor. The third PC was principally associated with soil moisture status.

Table 3.
Results of the principal component analysis of soil quality indicators.
Finally, Pearson’s correlation coefficients were calculated with Equation (2) in Section 2.4. for the soil indicators in Table 4. Results show that available P is not significantly correlated with other highly weighted soil indicators in PC1. This lack of collinearity and the high absolute value of factor loading in PC1 indicate that available P is strongly represented in PC1 and should be included in the MDS. In view of the large variance explained by PC1, pH and catalase were also included in MDS to represent the PC1 due to their lower correlation coefficients and high absolute value of factor loading. Because all three highly weighted indicators in PC2 were highly correlated with each other, total organic C and total N were the only variables included in the MDS due to their higher absolute value of factor loading and importance to soil fertility. Effective porosity was directly retained in the MDS because it was the only highly weighted indicator in the PC3. Consequently, the final MDS for determining soil quality in the study area comprised six indicators: effective porosity, pH, total organic C, total N, available P, and catalase.

Table 4.
Correlation coefficients for highly weighted variables under principal components.
Almost all the soil properties have been identified in previous studies as important indicators for soil quality evaluation under different agricultural land uses. Shukla et al. [] reported effective porosity as an important indicator for assessing soil quality in the surface layer of soil under different land uses and management practices. Effective porosity has also been mentioned as one of the major determining factors that controls yield variability [], and it has been suggested as an indicator for routine evaluation and monitoring of soil physical quality []. pH was identified as a soil quality indicator by Andrews et al. [], Shukla et al. [], and Bautista-Cruz et al. []. Meng et al. [] also suggested that pH is an important evaluation indicator due to its significant impact on the availability and form of soil nutrients. However, pH was the first factor eliminated in the study of Rezaei et al. [] because its range of values within the study area was insufficient to result in substantial differences in plant growth. Soil properties related to organic matter or organic carbon were regarded as the most dominant indicator for soil quality [,,,]. These factors can be monitored over time to determine if soil quality has improved, degraded, or remained stable []. Pan et al. [] reported that total organic C plays a crucial role in sequestration of C, enhancement of crop productivity, and stabilization of yield in China’s croplands. In the Tibetan Plateau, higher total organic C in cropland soils usually implies superior soil quality. Total N has been reported as an important soil quality indicator for different management system treatments such as crop rotation and use of external inputs []. Total N at a soil depth of 10–20 cm is more important for assessing soil quality in comparison with total N at soil depths in the range of 0–10 cm []. However, total N was reported as a key soil quality indicator to represent soil fertility at the 0–20 cm soil depth for coastal tidal lands []. Liu et al. [] also reported that total N was a major determinant and indicator of soil fertility and quality in agricultural ecosystems. Available P was identified as one of the most important indicators for assessing soil quality within an agricultural watershed []. Chen et al. [] reported that available P was selected as an important soil quality indicator and had considerable effect on soybean yield. Available P was regarded as the primary limiting factor for rice growth in the red soil region, and it was included in the MDS of soil quality created by Li et al. [] and Meng et al. []. Catalase exhibited a strong positive correlation with the content of soil nutrients, and it can be regarded as an important soil quality indicator in the desertification process []. Similar results were reported by Zhang et al. [], and catalase was selected in previous study that calculated a soil quality index in the Loess Plateau [].
3.3. Soil Quality Index under Different Soil Types and Land Use Types
The soil indicators in the final MDS were transformed via the membership function as described in Section 2.4 with Equations (4) and (5). The critical values of the soil quality indicators were determined according to the ecological requirements of local crops in the study area in conjunction with the previous research results (Table 5). Effective porosity is indispensable to ensure soil air quality for normal growth of plants and microorganism activities, and a upper half trapezoid curve function was therefore used to calculate scores for the indicator []. The optimum pH range for most crops in Tibet is between 6.9 and 7.1 [], and this range of pH values received a score of 1. Scores for pH values <6.9 or >7.1 were determined by a trapezoid curve function []. The scores for total organic C were determined by the upper half trapezoid curve function based on the critical role for soil fertility [,,]. For total N and available P, scores were assigned by the upper half trapezoid curve function because these are the nutrients that most frequently limit crop productivity [,]. Catalase activity reflects the intensity of soil microbial activity in the study area which has a positive effect on soil quality. Therefore, the upper half trapezoid curve function was used for scoring [].

Table 5.
Model types and fuzzy set membership function parameters for soil quality indicator scoring.
The soil quality index (SQI) was obtained via a linear weighted sum of the scores of all six indicators for each of the 93 sampling points as described in Section 2.4 with Equation (6). The average SQI value was 0.603, while the minimum and maximum was 0.350 and 0.816, respectively, for points situated in grain land with fluvo-aquic soils and meadow soils. The SQI results in Figure 2 show the following order of the groups according to soil types and land use types: grain land with fluvo-aquic soils < conventional vegetable land with fluvo-aquic soils < greenhouse vegetable land with fluvo-aquic soils < grain land with steppe soils < grain land with meadow soils. Soil quality indices were affected by the coupling of soil types and land use types in the study area.
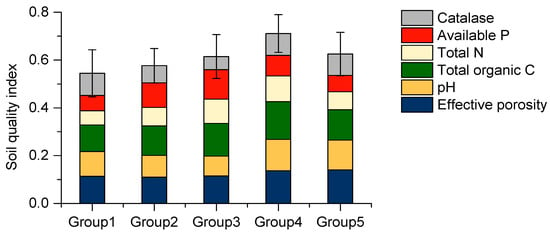
Figure 2.
Weighted soil quality indices using minimum data set as determined by principal component analysis for each group of sampling points in the Lhasa River valley. Vertical bars represent standard errors from the mean soil quality index values for each group. Group 1 to Group 5 represent the groups of sampling points divided by soil types and land use types as described in Section 2.3.
The SQI values were significantly higher in grain land with meadow soils with an average value 0.711. The SQI of other groups ranged from 0.545 in grain land with fluvo-aquic soils to 0.625 in grain land with steppe soils. SQI values less than 0.5 were almost all located in grain land with fluvo-aquic soils. Conventional vegetable land with fluvo-aquic soils exhibited moderate SQI values. The difference in SQI indices between these groups can be attributed to different soil characteristics, tillage practices, and fertilizer application.
Both the meadow soils and steppe soils developed from calcareous parent material originating from alluvial deposits. These soils were characterized by a thick tillage layer, fine soil structure, and high soil nutrient content. These soils were highly suitable for the growth of barley, wheat, peas, and rapeseed. Meadow soils had a higher capability to retain water and nutrients, while N and P content in steppe soils were slightly insufficient []. Although fluvo-aquic soils were located in valley terraces with superior irrigation conditions, these soils formed in noncalcareous parent material from alluvial deposits and exhibited high sand contents. This results in a low ability to retain nutrients or water. Furthermore, these soils exhibited lower values of nutrient content and a notable lack of available nutrients. It is obvious that the soil quality with meadow soils was superior to steppe soils and fluvo-aquic soils given that these soils were not cultivated.
When considering land use types, 68% sampling points of fluvo-aquic soils, all of meadow soils, and all of steppe soils were from the grain land areas, while 11% of fluvo-aquic soils were from the conventional vegetable land areas and 21% of fluvo-aquic soils were from the greenhouse vegetable land areas, respectively. In Table 6, all the soil quality indices except catalase for fluvo-aquic soils were significantly lower in the grain land areas when compared with the conventional vegetable land areas and the greenhouse vegetable land areas. Compared to the soils from grain land, soils from vegetable land exhibited lower values of effective porosity, pH and catalase as well as higher values of total organic C, total N and available P (Table 6). Oliveira et al. [] found that conventional tillage with mineral fertilizer and pig slurry application increased the bulk density and penetration resistance, resulting in the reduction of effective porosity. Reynolds et al. [] observed that effective porosity was critically low under a system of long-term (48 years) cropping, fertilization and fall moldboard plow tillage. The main reason for the low pH value in vegetable land may be due to the excessive application of N fertilizer. It has been observed that average soil pH values declined significantly over time as N application rates have slightly increased []. Lower catalase activities were found in vegetable land. This is attributed to the application of acid fertilizer and unleavened manure, resulting in enhancements of harmful bacteria and element activity []. The total organic C, total N and available P were significantly higher in vegetable land This was caused by the application of N and phosphorus fertilizer and organic fertilizer. Soil organic C accumulates gradually with long-term cultivation and fertilizer application []. Significantly higher accumulation of available N and P were observed under application of inorganic fertilizers and manure either alone or in combination [].

Table 6.
Average soil quality indices for different soil types and agricultural land uses in the Lhasa River valley.
4. Conclusions
In the present study, we investigated the statistical characteristics of soil properties under different soil types and land use types in the Lhasa River valley. We produced a MDS for soil quality assessment as well as a soil quality index with the management goals of maximizing crop production and minimizing soil fertility degradation. Grain land with meadow soils exhibited superior soil quality than grain land with steppe soils and all kinds of land use types with fluvo-aquic soils. Some areas where conventional vegetable and greenhouse vegetable agriculture were practiced had meadow soils and steppe soils that exhibited superior soil quality to fluvo-aquic soils. These areas with higher soil quality indices exhibited superior soil structure, higher nutrient contents, and greater resistance to water and nutrient loss. The intensive tillage practices with vegetable production could reduce the effective porosity, pH and catalase levels. However, the application of appropriate fertilizer improved soil quality by increasing the total organic C, total N and available P.
In this study, the final MDS for determining soil quality was composed of effective porosity, pH, total organic C, total N, available P, and catalase. The use of factor analysis to define MDS for soil quality assessment has the potential to integrate physical, chemical, and biological data for sustainable cropland management. By using factor analysis, the intrinsic correlation and difference between the soil quality indicators were revealed, and the primary components that determine soil quality were identified. Fuzzy sets can be a useful tool to score soil quality indicators. The fuzzy and gradual nature of soil quality indicator scoring was fully considered in the soil quality assessment. The soil quality assessment also considered the joint influence of the weighted index and the interaction between soil indicators. Therefore, soil quality assessment can be used to identify and evaluate trends and the spatial extent of soil impacts from cropland management in the Lhasa River valley on the Tibetan Plateau. Soil properties from the MDS were recommended to be observed primarily in future field experiment for soil quality assessment in similar alpine valley agroecosystems. Planting cereal crops could be suitable agricultural land use in meadow soils and steppe soils for grain production in the study area. The application of organic fertilizer is the key to improve the effectiveness of soil fertility, while it is necessary to gradually increase soil microbial activity.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/10/10/3477/s1, Figure S1: Statistical characteristics of soil properties under different groups in the Lhasa River valley. Group 1 to Group 5 represent the groups of sampling points that were divided by soil types and land use types as described in Section 2.3.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.D. and G.L.; Methodology, F.D.; Software, F.D.; Validation, F.D., Z.L. and G.L.; Formal Analysis, F.D.; Investigation, F.D. and Z.L.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, F.D. and Z.L.; Writing—Review and Editing, G.L.; and Supervision, G.L.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41301351).
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Scientific Research Foundation of Chongqing Technology and Business University (No. 2013-56-05), Chongqing Research Program of Basic Research and Frontier Exploration (No. cstc2018jcyjAX0497), and the Scientific and Technological Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (No. KJ1600611). We thank LetPub (www.letpub.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Nkonya, E.; Mirzabaev, A.; von Braun, J. Economics of Land Degradation and Improvement: An Introduction and Overview. In Economics of Land Degradation and Improvement—A Global Assessment for Sustainable Development; Nkonya, E., Mirzabaev, A., von Braun, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zika, M.; Erb, K.H. The global loss of net primary production resulting from human-induced soil degradation in drylands. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 69, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Shen, W.; Wang, T. Spatial-temporal characteristics of cultivated land in Tibet in recent 30 years. Trans. CSAE 2015, 31, 264–271, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Dai, F.Q.; Su, Z.A.; Liu, S.Z.; Liu, G.C. Temporal variation of soil organic matter content and potential determinants in Tibet, China. Catena 2011, 85, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Li, H.Y.; Yang, L.M.; Ren, Y.X. Assessment of Soil Quality of Croplands in the Corn Belt of Northeast China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.S.; Carroll, C.R. Designing a soil quality assessment tool for sustainable agroecosystem management. Ecol. Appl. 2001, 11, 1573–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.S.; Karlen, D.L.; Cambardella, C.A. The soil management assessment framework: A quantitative soil quality evaluation method. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 1945–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo-Mbogba, M.; Yemefack, M.; Nyeck, B. Assessing soil quality under different land cover types within shifting agriculture in South Cameroon. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 150, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastida, F.; Zsolnay, A.; Hernandez, T.; Garcia, C. Past, present and future of soil quality indices: A biological perspective. Geoderma 2008, 147, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiesi, F.; Kabiri, V. Identification of soil quality indicators for assessing the effect of different tillage practices through a soil quality index in a semi-arid environment. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 71, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, B.R.; Udawatta, R.P.; Anderson, S.H. Agroforestry and grass buffer effects on soil quality parameters for grazed pasture and row-crop systems. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2011, 48, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, J.W.; Parkin, T.B.; Jones, A. Quantitative indicators of soil quality: A minimum data set. In Methods for Assessing Soil Quality; SAAA: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 25–37. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaei, S.A.; Gilkes, R.J.; Andrews, S.S. A minimum data set for assessing soil quality in rangelands. Geoderma 2006, 136, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, M.K.; Lal, R.; Ebinger, M. Determining soil quality indicators by factor analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 87, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, U.K.; Ramachandran, K.; Sharma, K.L.; Satyam, B.; Venkanna, K.; Bhanu, M.U.; Mandal, M.; Masane, R.N.; Narsimlu, B.; Rao, K.V.; et al. Assessing Soil Quality in a Semiarid Tropical Watershed Using a Geographic Information System. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 1144–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosrati, K. Assessing soil quality indicator under different land use and soil erosion using multivariate statistical techniques. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 2895–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Z.; Wang, X.D.; Gao, Q.Z.; Hou, T.P.; Shen, Z.X.; Fang, J.P. Research in ecological restoration and reconstruction technology for degraded alpine ecosystem, boosting the protection and construction of ecological security barrier in Tibet. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 7083–7087. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, F.Q.; Zhou, Q.G.; Lv, Z.Q.; Wang, X.M.; Liu, G.C. Spatial prediction of soil organic matter content integrating artificial neural network and ordinary kriging in Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 45, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, Z.; Gong, T.; Wang, H.; Chu, D.; Liu, L.; Zhang, F. The trend on runoff variations in the Lhasa River Basin. J. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.Q.; Yao, L.N.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, C.L. Spatial-temporal dynamics of cultivated land in recent 35 years in the Lhasa River basin of Tibet. J. Nat. Resour. 2014, 29, 623–632. [Google Scholar]
- Gee, G.W.; Bauder, J.W. Particle Size Analysis; Agron. Monogr. 9; ASA and SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, G.R.; Hartge, K.H. Bulk Density; ASA and SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; pp. 364–367. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.S.; Jiang, N.H.; Zhang, L.D.; Liu, Z.L. Soil Physical and Chemical Analysis & Description of Soil Profiles; Chinese Standard Press: Beijing, China, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total Carbon, Organic Carbon, and Organic Matter; ASA-SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, J.M. Determination of nitrogen in soil by the Kjeldahl method. J. Agric. Sci. 1960, 55, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.R.; Sommers, L.E. Phosphorus; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley, D.; Cornforth, I.S. Methods of measuring available nutrients in West Indian soils. Plant Soil 1973, 39, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G.W. Exchangeable Cations; ASA and SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Rhoades, J.D. Cation Exchange Capacity; ASA and SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.F.; Yang, J.S.; Yao, R.J.; Liu, G.M. Soil quality in east coastal region of China as related to different land use types. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.G.; Luo, Y.M.; Teng, Y. Soil and Environmental Microbiology Research Method; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hayano, K. A method for the determination of β-glucosidase activity in soil. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1973, 19, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilliefors, H.W. On the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for normality with mean and variance unknown. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1967, 62, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olive, D.J. One Way Anova. In Linear Regression; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 175–211. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, S.S.; Karlen, D.L.; Mitchell, J.P. A comparison of soil quality indexing methods for vegetable production systems in Northern California. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 90, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, T.L.; Wang, X.X.; Yu, D.S. Development of biological soil quality indicator system for subtropical China. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 126, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, R.; Oliver, M.A. Statistical Methods in Soil and Land Resource Survey; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, H.F. The application of electronic computers to factor analysis. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wander, M.M.; Bollero, G.A. Soil quality assessment of tillage impacts in Illinois. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brejda, J.J.; Moorman, T.B.; Karlen, D.L.; Dao, T.H. Identification of regional soil quality factors and indicators: I. Central and southern high plains. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 2115–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Cruz, A.; del Castillo, R.F.; Etchevers-Barra, J.D.; Gutierrez-Castorena, M.D.; Baez, A. Selection and interpretation of soil quality indicators for forest recovery after clearing of a tropical montane cloud forest in Mexico. For. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 277, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inform. Control 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-G.; Yang, L.-Z.; Shan, Y.-H. Application of fuzzy mathematics to soil quality evaluation. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2001, 38, 176–183. [Google Scholar]
- Doran, J.W.; Parkin, T.B. Defining and assessing soil qualit. In Defining Soil Quality for a Sustainable Environment; Doran, J.W., Coleman, D.C., Bezdicek, D.F., Stewart, B.A., Eds.; SSSA Special Publication: Madison, WI, USA, 1994; Volume 35, pp. 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, S.M.; Ozawa, K. Improvement of crop yield, soil moisture distribution and water use efficiency in sandy soils by clay application. Appl. Clay Sci. 2007, 37, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, C.H.; Hao, S.P.; Zhang, Y.E.; Han, J.F. Effects of subsoil bulk density on late growth stage photosynthetic characteristics and grain yield of maize. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 19, 787–793. [Google Scholar]
- Barak, P.; Jobe, B.O.; Krueger, A.R.; Peterson, L.A.; Laird, D.A. Effects of long-term soil acidification due to nitrogen fertilizer inputs in Wisconsin. Plant Soil 1997, 197, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhou, Z.H.; Zhang, B.; Du, S.H.; Liu, G.C. The effects of agricultural management on selected soil properties of the arable soils in Tibet, China. Catena 2012, 93, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortoluzzi, E.C.; Tessier, D.; Rheinheimer, D.S.; Julien, J.L. The cation exchange capacity of a sandy soil in southern Brazil: An estimation of permanent and pH-dependent charges. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2006, 57, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.L.; Zhou, Z.H.; Liu, G.C. Physico-chemical properties and enzyme activities of the arable soils in Lhasa, Tibet, China. J. Mount. Sci. 2012, 9, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obade, V.D.; Lal, R. Soil quality evaluation under different land management practices. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 4531–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moebius, B.N.; van Es, H.M.; Schindelbeck, R.R.; Idowu, O.J.; Clune, D.J.; Thies, J.E. Evaluation of laboratory-measured soil properties as indicators of soil physical quality. Soil Sci. 2007, 172, 895–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.B.; Darilek, J.L.; Huang, B.A.; Zhao, Y.C.; Sun, W.X.; Gu, Z.Q. Evaluating soil quality indices in an agricultural region of Jiangsu Province, China. Geoderma 2009, 149, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.J.; Yang, J.S.; Gao, P.; Zhang, J.B.; Jin, W.H. Determining minimum data set for soil quality assessment of typical salt-affected farmland in the coastal reclamation area. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 128, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Smith, P.; Pan, W. The role of soil organic matter in maintaining the productivity and yield stability of cereals in China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 129, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.J.; Zhou, W.; Shen, J.B.; Li, S.T.; Liang, G.Q.; Wang, X.B.; Sun, J.W.; Ai, C. Soil Quality Assessment of Acid Sulfate Paddy Soils with Different Productivities in Guangdong Province, China. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.D.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhou, J.M.; Xing, L.; Zhu, B.S.; Zhao, Y.C.; Chen, X.Q. Minimum Data Set for Assessing Soil Quality in Farmland of Northeast China. Pedosphere 2013, 23, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, T.; Wen, H. Change of the Biological Properties of Soil Quality in the Desertification Process. Arid Zone Res. 2002, 19, 64–68. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Xue, S.; Liu, G.-B.; Song, Z.-L. A comparison of soil qualities of different revegetation types in the Loess Plateau, China. Plant Soil 2011, 347, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Yue, X.; Ge, X.; Wang, X. Evaluation of soil quality on gully region of loess plateau based on principal component analysis. Agric. Res. Arid Areas 2010, 28, 141. [Google Scholar]
- The Scientific Expedition to Qing-zang Plateau. In Soils of Tibet; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1985.
- Marzaioli, R.; D’Ascoli, R.; De Pascale, R.A.; Rutigliano, F.A. Soil quality in a Mediterranean area of Southern Italy as related to different land use types. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 44, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgoz, E.; Gunal, H.; Acir, N.; Gokmen, F.; Birol, M.; Budak, M. Soil quality and spatial variability assessment of land use effects in a typic haplustoll. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, J.; Sharma, S.P.; Sharma, S.K.; Sharma, G.D.; Sankhyan, N.K. Indexing Soil Quality under Long-Term Maize-Wheat Cropping System in an Acidic Alfisol. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2015, 46, 1841–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Zhang, X.N.; Ran, Q.Y. Quality assessment of oasis soil in the upper reaches of Tarim River based on minimum data set. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2015, 52, 682–689. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, D.M.S.; de Lima, R.P.; Verburg, E.E.J. Physical quality of soil under different systems of tillage and application of pig slurry. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agric. Ambient. 2015, 19, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, W.D.; Drury, C.F.; Yang, X.M.; Tan, C.S.; Yang, J.Y. Impacts of 48 years of consistent cropping, fertilization and land management on the physical quality of a clay loam soil. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 94, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, R.L.; Wilson, S.; Shafii, B.; Price, W. Long-Term Trends of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Use and Soil pH Change in Northern Idaho and Eastern Washington. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2016, 47, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.H.; Zheng, J.W. Soil Organic Carbon, Black Carbon, and Enzyme Activity Under Long-Term Fertilization. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.T.; He, X.H.; Xu, M.G.; Zhang, W.J.; Yang, X.Y.; Huang, S.M. Long-term fertilization increases soil organic carbon and alters its chemical composition in three wheat-maize cropping sites across central and south China. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 177, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.; Panday, S.C.; Meena, V.S.; Singh, S.; Yadav, R.P.; Mahanta, D.; Mondal, T.; Mishra, P.K.; Bisht, J.K.; Pattanayak, A. Long-term effects of organic manure and inorganic fertilization on sustainability and chemical soil quality indicators of soybean-wheat cropping system in the Indian mid-Himalayas. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 257, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).