The Race to Document Archaeological Sites Ahead of Rising Sea Levels: Recent Applications of Geospatial Technologies in the Archaeology of Polynesia
Abstract
“In coastal regions around the world, we need to accelerate our own efforts to inventory, investigate, and interpret the history of endangered coastal sites … We must pull our heads from the proverbial sand for we are literally racing a rising tide.”[1]
1. Introduction
2. Remote Sensing
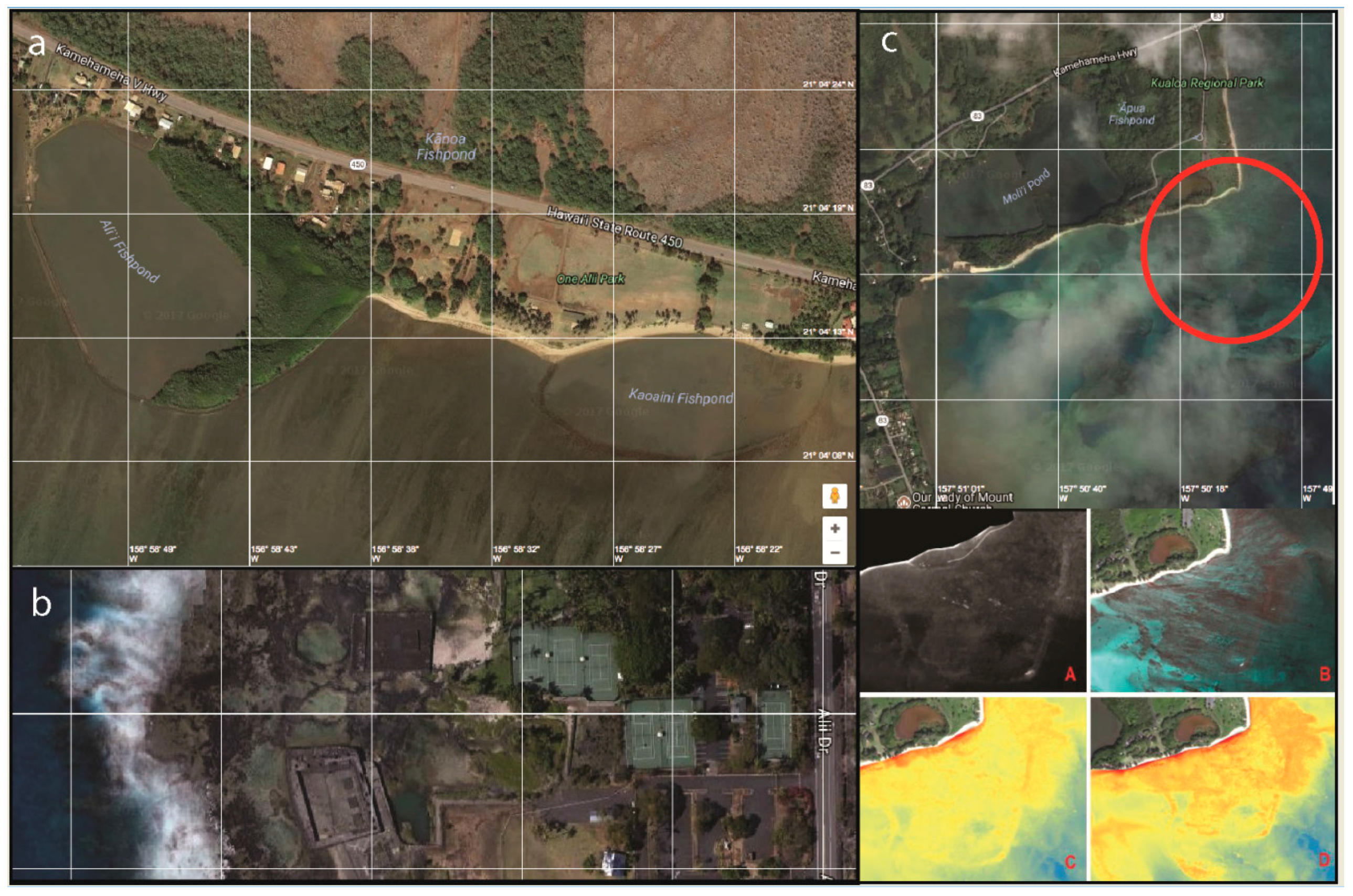
2.1. Airborne and Satellite Imagery
2.2. Airborne LiDAR
2.3. Geophysical Survey
2.4. Near-Shore Maritime Survey
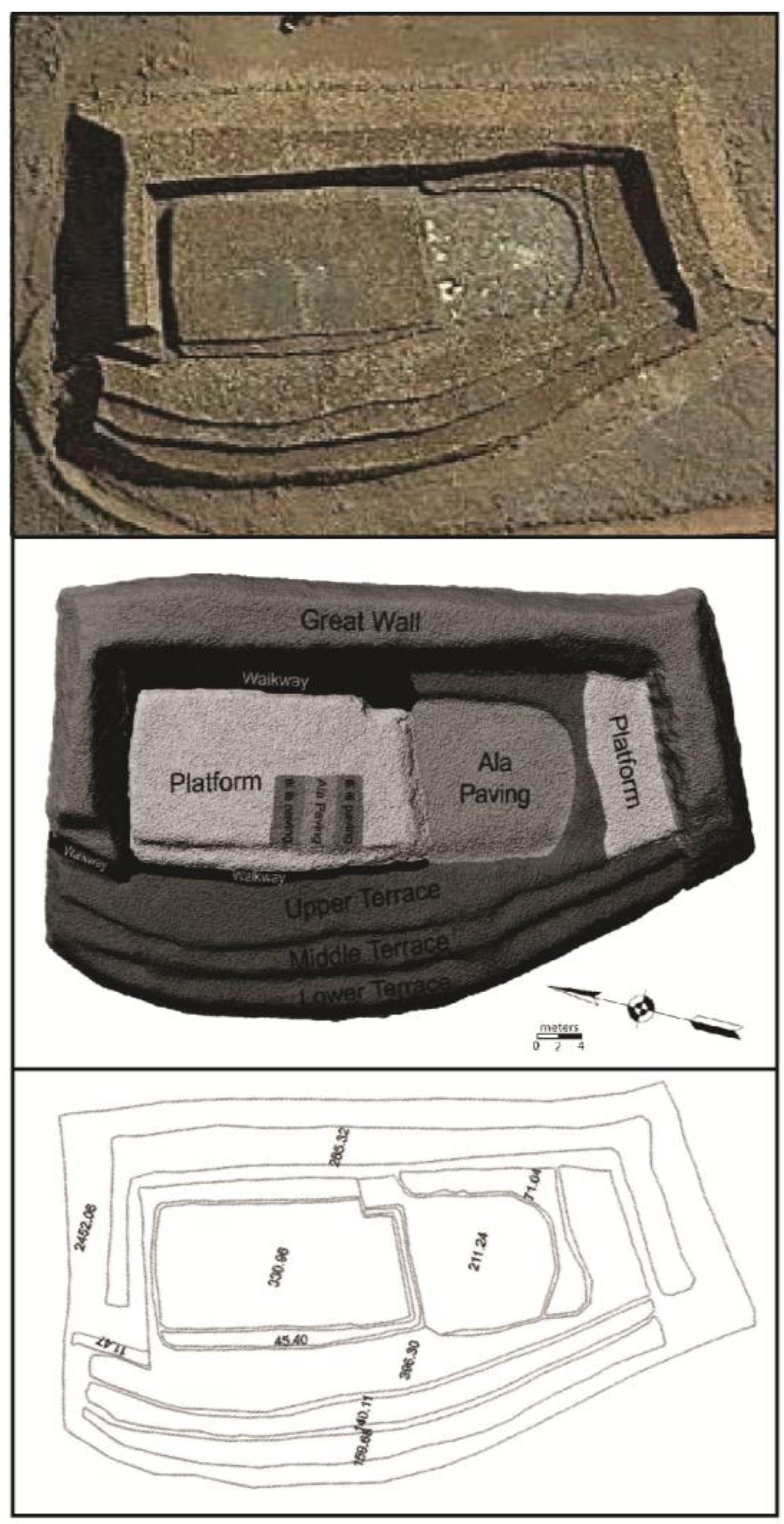
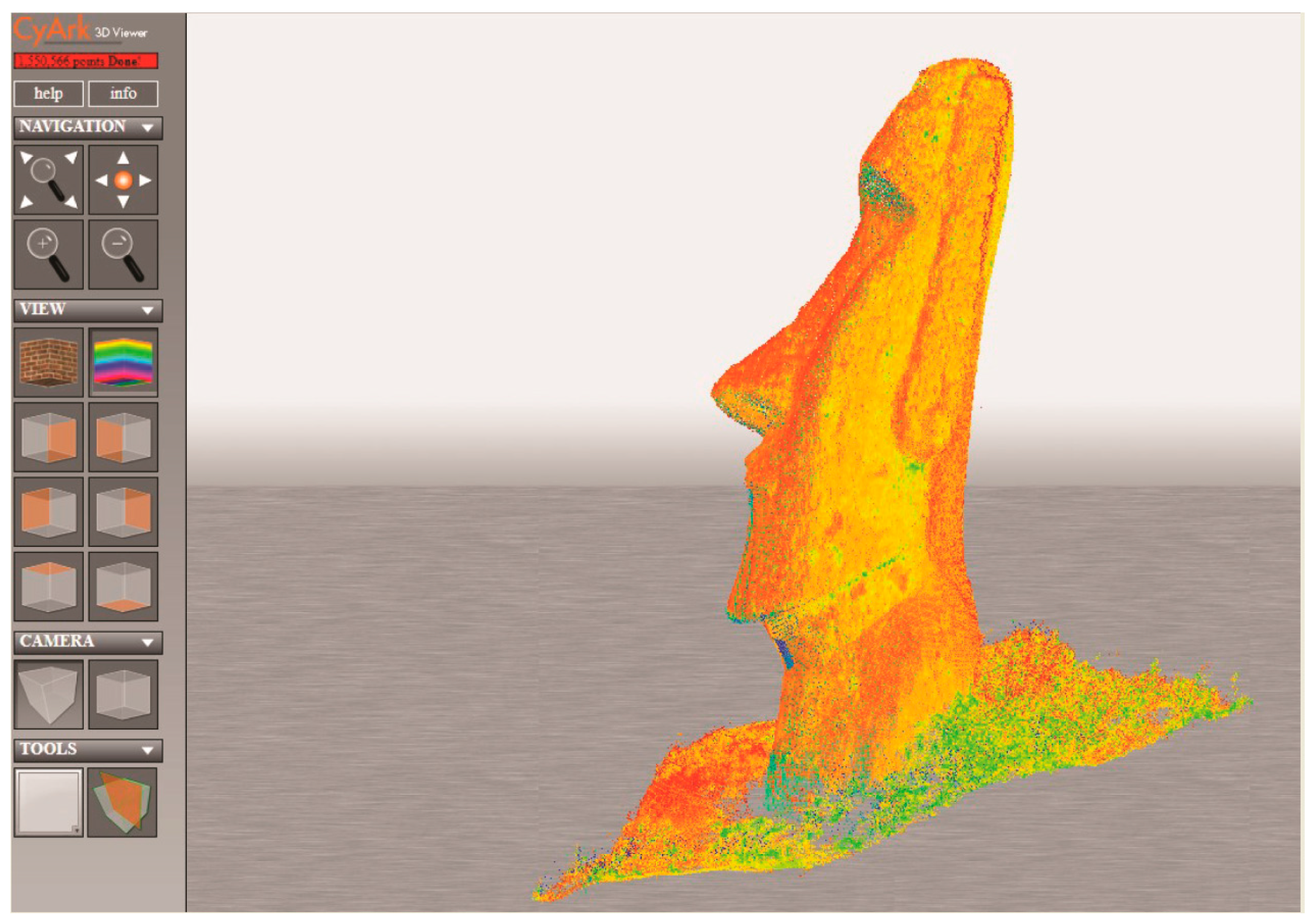
3. High-Resolution Documentation
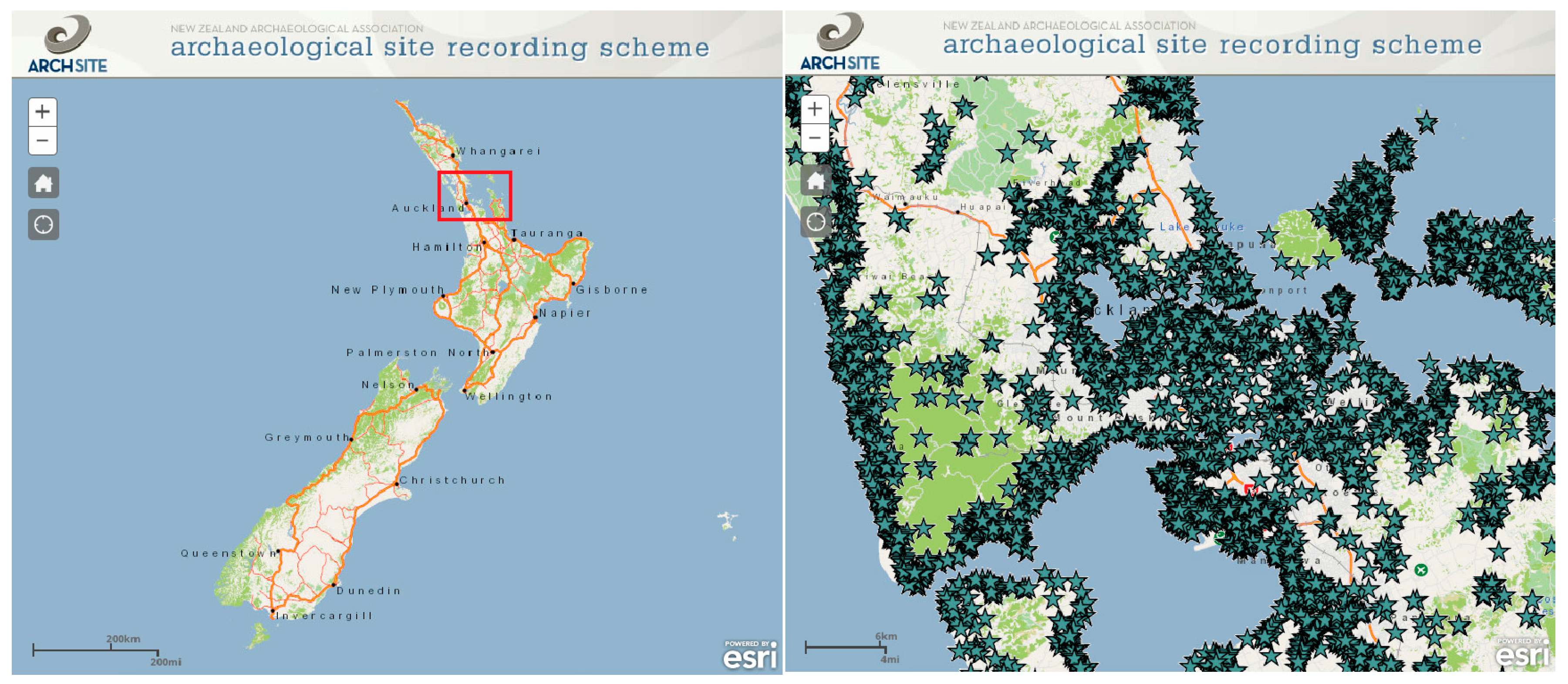
4. Archaeological Site Geodatabases
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Erlandson, J.M. Racing a Rising Tide: Global warming, rising seas, and the erosion of human history. J. Isl. Coast. Archaeol. 2008, 3, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeradino, A. On the origins and significance of Pleistocene coastal resource use in southern Africa with particular reference to shellfish gathering. J. Anthropol. Archaeol. 2017, 41, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- What are “Cultural Resources”? Available online: www.npi.org/NEPA/what-are (accessed on 12 January 2018).
- Allison, I.; Bindoff, N.; Bindschadler, R.; Cox, P.; de Noblet, N.; England, M.; Francis, J.; Gruber, N.; Haywood, A.; Karoly, D.; et al. The Copenhagen Diagnosis 2009: Updating the World on the Latest Climate Science; The University of New South Wales Climate Change Research Centre (CCRC): Sydney, Australia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Church, J.A.; Clark, P.U.; Cazenave, A.; Gregory, J.M.; Jevrejeva, S.; Levermann, A.; Merrifield, M.A.; Milne, G.A.; Nerem, R.S.; Nunn, P.D.; et al. Sea Level Change. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report; Core Writing Team, Pachauri, R.K., Meyer, L.A., Eds.; Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., et al., Eds.; Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmstorf, S.; Perrette, M.; Vermeer, M. Testing the robustness of semi-empirical sea level projections. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 39, 861–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrette, M.; Landerer, F.; Riva, R.; Frieler, K.; Meinshausen, M. A scaling approach to project regional sea level rise and its uncertainties. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2013, 4, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeer, M.; Rahmstorf, S. Global sea level linked to global temperature. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21527–21532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, J.; Weuebbles, D.; Hayhoe, K.; Kossin, J.; Kunkel, K.; Stephens, G.; Thorne, P.; Vose, R.; Wehner, M.; Willis, J.; et al. Chapter 2: Our changing climate. In Climate Change Impacts in the United States: The Third National Climate Assessment; Melillo, J., Richmond, T., Yohe, G., Eds.; U.S. Global Change Research Program: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; pp. 19–67. [Google Scholar]
- Bruun, P. Sea-level rise as a cause of shoreline erosion. J. Waterw. Harb. Div. 1962, 88, 117–139. [Google Scholar]
- Leatherman, S.P.; Zhang, K.; Douglas, B.C. Sea level rise shown to drive coastal erosion. EOS Trans. 2000, 81, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Douglas, B.C.; Leatherman, S.P. Global warming and coastal erosion. Clim. Chan. 2004, 64, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatorić, S.; Seekamp, E. Are Cultural Heritage and Resources threatened by Climate Change? A systematic literature review. Clim. Chan. 2017, 142, 227–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.G.; Bissett, T.G.; Yerka, S.J.; Wells, J.J.; Kansa, E.C.; Kansa, S.W.; Myers, K.N.; DeMuth, R.C.; White, D.A. Sea-level rise and archaeological site destruction: An example from the southeastern United States using DINAA (Digital Index of North American Archaeology). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, M.K. The impact of tropical cyclones on the archaeological record: An Australian example. Archaeol. Ocean. 1992, 27, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, M.J. Climate change, sea-level rise and the archaeological record. Aust. Archaeol. 1992, 34, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
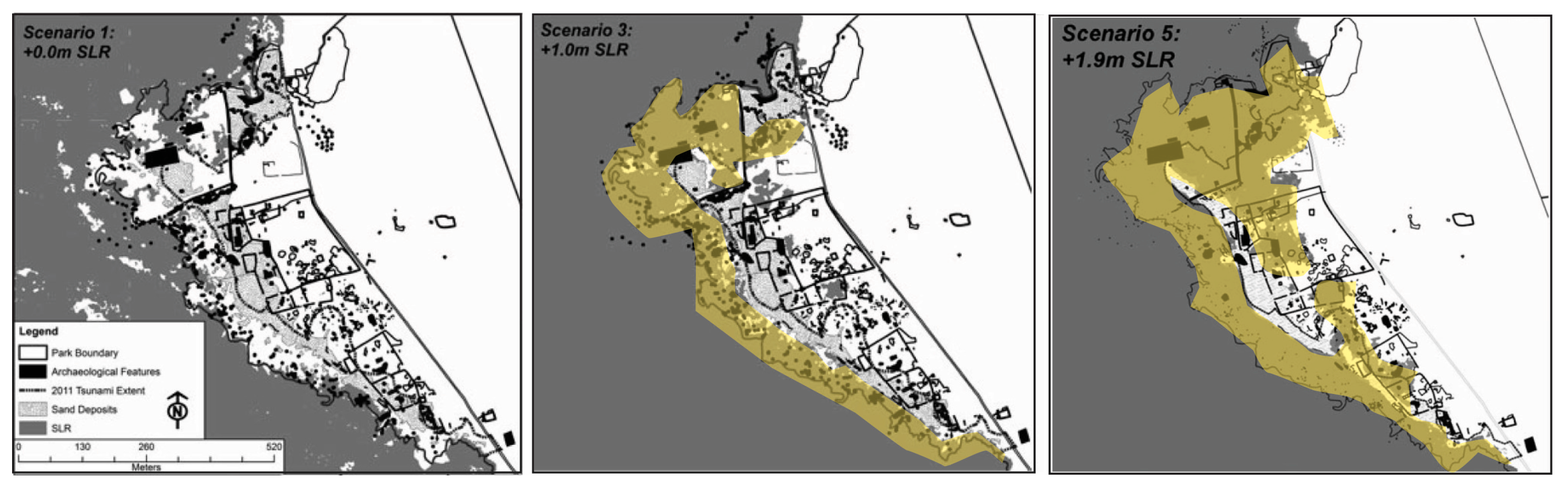
- Johnson, A.; Marrack, L.; Dolan, S. Threats to Coastal Archaeological Sites and the Effects of Future Climate Change: Impacts of the 2011 Tsunami and an Assessment of Future Sea-Level Rise at Hōnaunau, Hawai‘i. J. Isl. Coast. Archaeol. 2015, 10, 232–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knott, S.; Szabó, K.; Ridges, M.; Fullagar, R. Vulnerability of Indigenous Heritage Sites to Changing Sea Levels: Piloting a GIS-Based Approach in the Illawarra, New South Wales, Australia. Archaeol. Rev. Camb. 2017, 32, 78–97. [Google Scholar]
- Kvamme, K. Recent directions and developments in geographical information systems. J. Archaeol. Res. 1999, 7, 153–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, M.D.; Ladefoged, T.N. New developments in the use of spatial technology in archaeology. J. Archaeol. Res. 2009, 17, 263–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlandson, J.M.; Fitzpatrick, S.M. Oceans, islands, and coasts: Current perspectives on the role of the sea in human prehistory. J. Isl. Coast. Archaeol. 2006, 1, 5–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, S.M.; Rick, T.C.; Erlandson, J.M. Recent progress, trends, and developments in island and coastal archaeology. J. Isl. Coast. Archaeol. 2015, 10, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rick, T.C.; Erlandson, J.M. (Eds.) Human Impacts on Ancient Marine Ecosystems: A global Perspective; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Burley, D.; Weisler, M.I.; Zhao, J. High precision U/Th dating of first Polynesian settlement. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dye, T.S. Dating human dispersal in Remote Oceania: A Bayesian view from Hawai’i. World Archaeol. 2015, 47, 661–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawelu, K.L. Kuleana and Commitment: Working Toward a Collaborative Hawaiian Archaeology; University of Hawaii Press: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, G.B. New Zealand archaeology and air photography. J. Polyn. Soc. 1947, 57, 233–241. [Google Scholar]
- Gorbey, K. Aerial photography in New Zealand archaeology. N. Z. Archaeol. Assoc. Newsl. 1967, 10, 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, K.L. Aerial Photography in New Zealand Archaeology. Aust. Hist. Archaeol. 1996, 14, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, T.S. Hawaiian Fishing and Farming on the Island of Hawaii in A.D. 1778; Hawaii Division of State Parks: Honolulu, HI, USA, 1970.
- Ladefoged, T.N.; Graves, M.W.; Jennings, R.P. Dryland agricultural expansion and intensification in the Kohala, Hawai’i Island. Antiquity 1996, 70, 861–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casana, J.; Cothren, J. The CORONA Atlas Project: Orthorectification of CORONA Satellite Imagery and Regional-Scale Archaeological Exploration in the Near East. In Mapping the Archaeological Landscape from Space; Comer, D.C., Harrower, M.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 33–43. [Google Scholar]
- Lipo, C.P.; Hunt, T.L. Mapping the Prehistoric Statue Roads on Easter Island. Antiquity 2005, 79, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
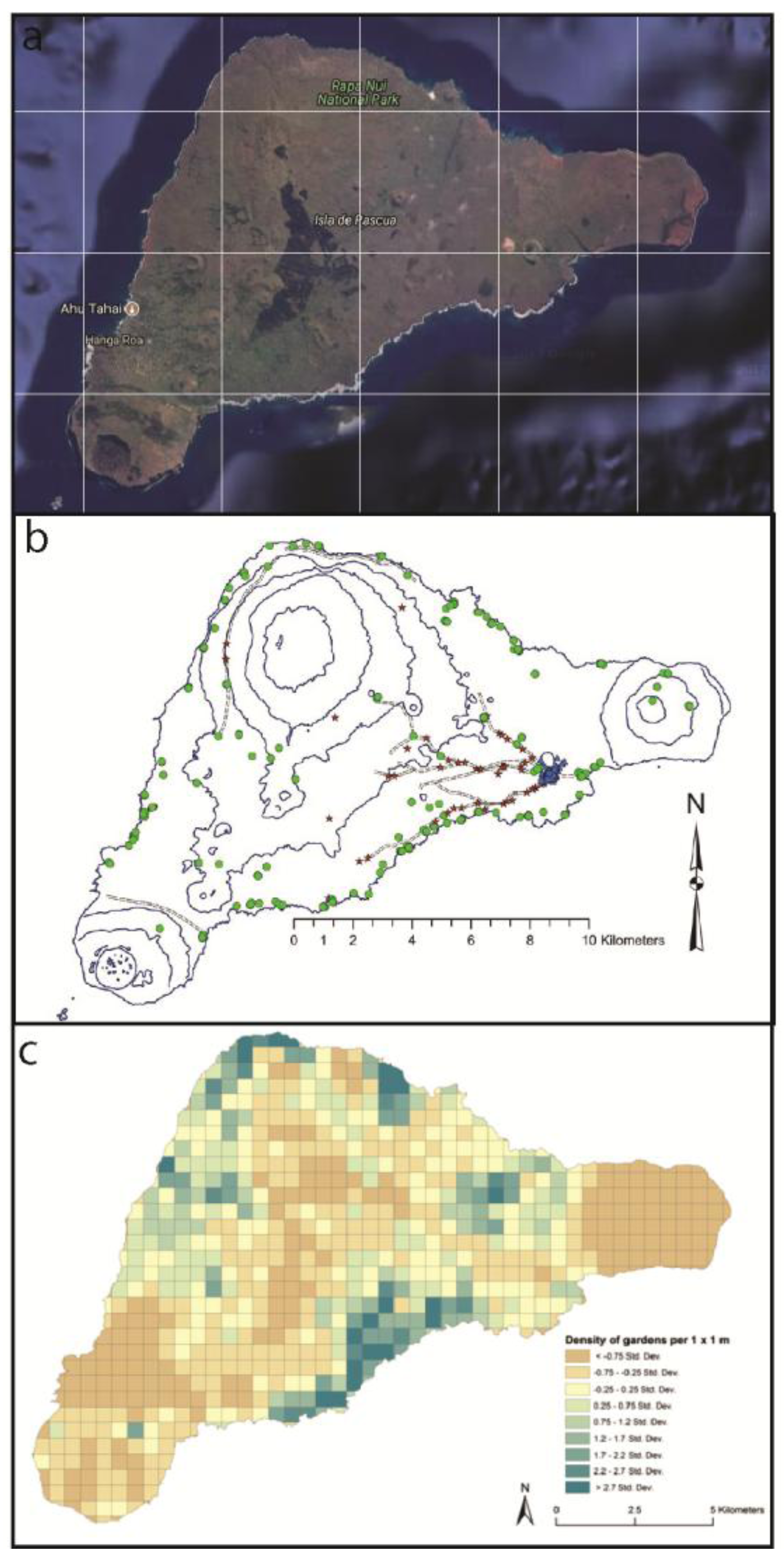
- Ladefoged, T.N.; Flaws, A.; Stevenson, C.M. The distribution of rock gardens on Rapa Nui (Easter Island) as determined from satellite imagery. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rouke, M.J.E. Archaeological Site Vulnerability Modelling: The Influence of High Impact Storm Events on Models of Shoreline Erosion in the Western Canadian Arctic. Open Archaeol. 2017, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
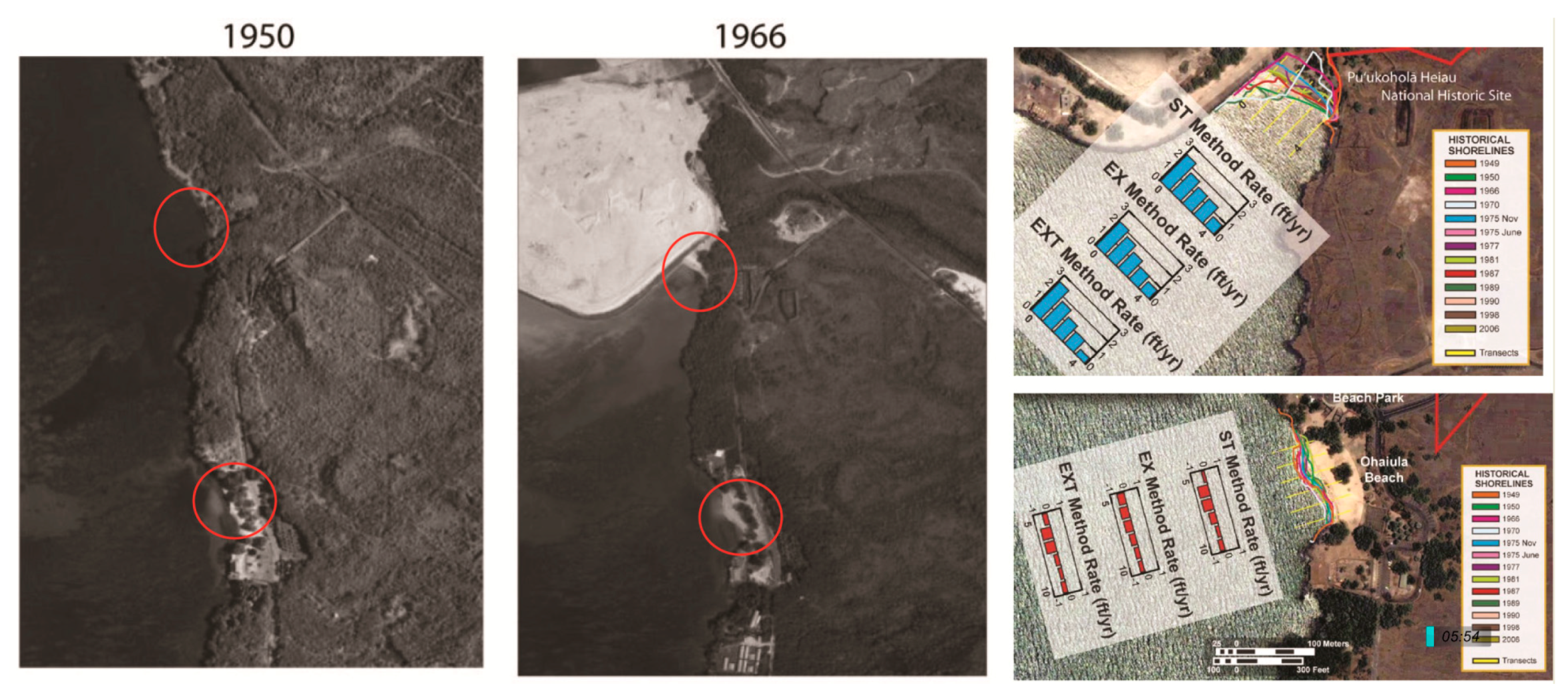
- Vitousek, S.; Barbee, M.M.; Fletcher, C.H.; Richmond, B.M.; Genz, A.S. Pu’ukoholā Heiau National Historic Site and Kaloko Honokōhau Historical Park, Big Island of Hawai’i Coastal Hazard Analysis Report; National Park Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- Chase, A.F.; Chase, D.Z.; Fisher, C.T.; Leisz, S.J.; Weishampel, J.F. Geospatial revolution and remote sensing LiDAR in Mesoamerican archaeology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12916–12921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintus, S.; Day, S.S.; Smith, N.J. The Efficacy and Analytical Importance of Manual Feature Extraction Using Lidar Datasets. Adv. Archaeol. Pract. 2017, 5, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, M.D. Geospatial Big Data in Archaeology: Problems and prospects too great to ignore. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2017, 84, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladefoged, T.N.; McCoy, M.D.; Asner, G.P.; Kirch, P.V.; Puleston, C.O.; Chadwick, O.A.; Vitousek, P.M. Agricultural potential and actualized development in Hawai’i: An airborne LiDAR survey of the leeward Kohala field system (Hawai’i Island). J. Archaeol. Sci. 2011, 38, 3605–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, M.D.; Asner, G.P.; Graves, M.W. Airborne lidar survey of irrigated agricultural landscapes: An application of the slope contrast method. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2011, 38, 2141–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIvor, I.H.; Ladefoged, T.N. Intermittent irrigation in the Waimea Field System, Hawai’i Island: A computational fluid dynamics model. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2018, 17, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeland, T.; Heung, B.; Burley, D.V.; Clark, G.; Knudby, A. Automated Feature Extraction for Prospection and Analysis of Monumental Earthworks from Aerial LiDAR in the Kingdom of Tonga. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2016, 69, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintus, S.; Clark, J.T.; Day, S.S.; Schwert, D.P. Investigating Regional Patterning in Archaeological Remains by Pairing Extensive Survey with a Lidar dataset: The Case of the Manu’a Group, American Samoa. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2015, 2, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2006 FEMA Lidar: Hawaiian Islands. Available online: https://coast.noaa.gov/htdata/lidar1_z/geoid12a/data/1393/2006_HI_fema_metadata.html (accessed on 12 January 2018).
- Irwin, G.J.; Ladefoged, T.N.; Wallace, R.T.; Jones, M.D.; Ross, S.C.; Clout, S.D. Experimental geophysical survey on Motutapu Island 1994–1996. Archaeol. N. Z. 1997, 40, 266–277. [Google Scholar]
- Bickler, S.H.; Low, J.M. “Lies, damned lies and geophysics”: Uses and abuses of remote sensing techniques in New Zealand heritage management. Archaeol. N. Z. 2007, 50, 195–210. [Google Scholar]
- Conyers, L.B.; Connell, S. An analysis of ground-penetrating radar’s ability to discover and map buried archaeological sites in Hawai’i. Hawaii. Archaeol. 2007, 11, 61–76. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, B.; Jacomb, C.; Walter, R. The potential of the fluxgate gradiometer as a research tool in New Zealand. Archaeol. N. Z. 2008, 51, 121–129. [Google Scholar]
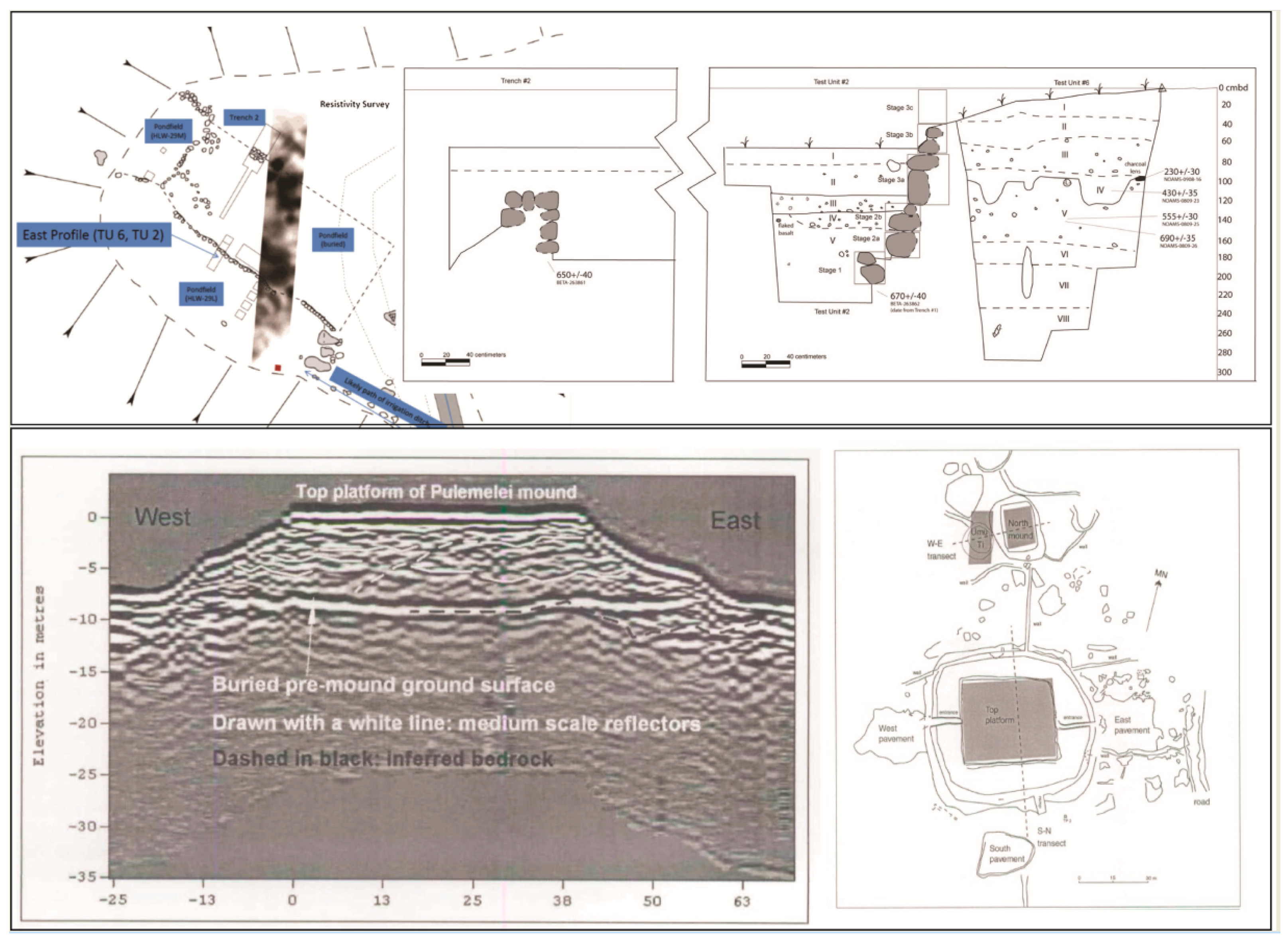
- Pearl, F.B.; Sauck, W.A. Geophysical and geoarchaeological investigations at Aganoa Beach, American Samoa an early archaeological site in Western Polynesia. Geoarchaeology 2014, 29, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, M.D.; Browne Ribeiro, A.T.; Graves, M.W.; Chadwick, O.A.; Vitousek, P.M. Taro (Colocasia esculenta) farming in ancient Hawaii: Sedimentology and soil nutrient analyses of irrigated pondfield soils. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 1528–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, G.; de Biran, A. Geophysical investigations at the Pulemelei mound. Archaeol. Ocean. 2007, 42, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, E.; Jacomb, C.; Walter, R. Archaeological investigations at Wairau Bar. Archaeol. N. Z. 2009, 52, 259–268. [Google Scholar]
- Van Tilburg, H. Underwater archaeology, Hawaii style. In International Handbook of Underwater Archaeology; Ruppe, C.V., Barstad, J.F., Eds.; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 247–266. [Google Scholar]
- Sailors, D.; Honda, S.S. Remote Survey of a Near-Coastal Archaeological Alignment at Kualoa, Hawai’i Using Worldview 2 Satellite, LiDAR and UAV Imagery. 2014. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/16518333/Remote_Survey_of_a_Near-Coastal_Archaeological_Alignment_at_Kualoa_Hawaii_Using_Worldview_2_Satellite_LiDAR_and_UAV_Imagery (accessed on 12 January 2018).
- Pfeffer, M. Distribution and design of Pacific octopus lures: The Hawaiian octopus lure in regional context. Hawaii. Archaeol. 1995, 4, 47–56. [Google Scholar]
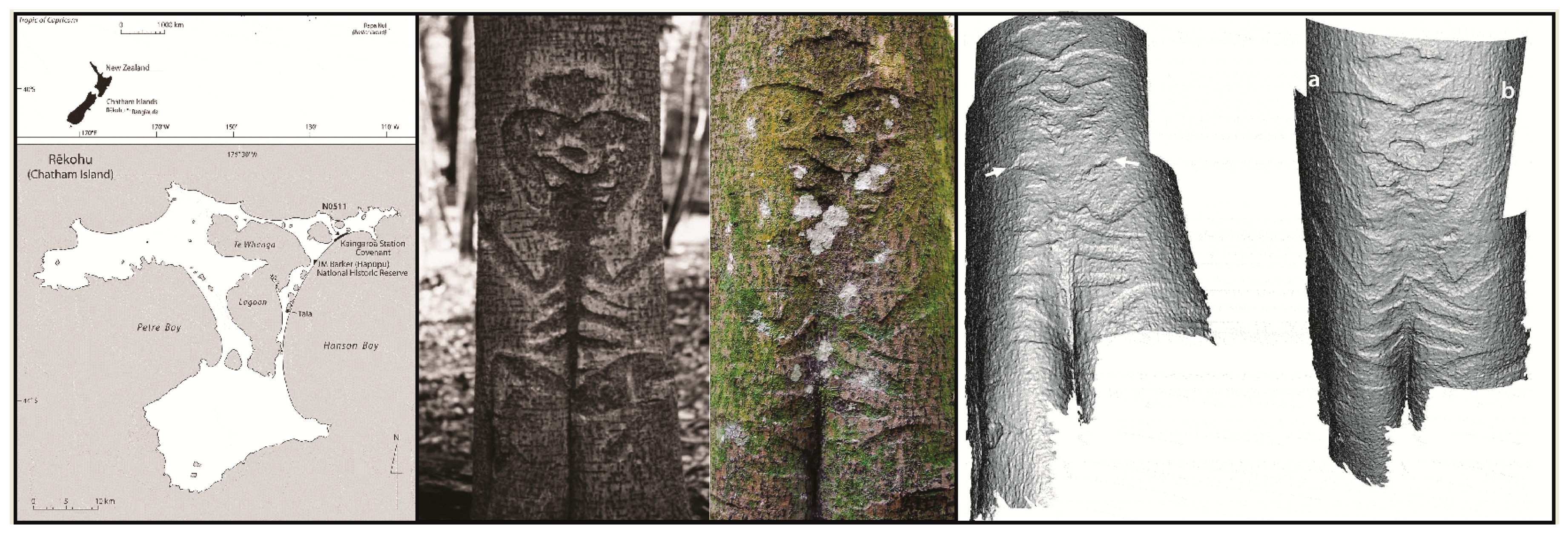
- Barber, I.G.; Maxwell, J.J.; Hemi, R. Growing images: Generating 3D digital models to investigate archaeological Moriori carvings on live trees. World Archaeol. 2014, 46, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulrooney, M.A.; Ladefoged, T.N.; Gibb, R.; McCurdy, D. Eight million points per day: Archaeological implications of laser scanning and three-dimensional modeling of Pu‘ukohola Heiau. Hawaii. Archaeol. 2005, 10, 18–28. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, A. Shifting stones and data points: Using terrestrial laser scanning to assess damage to monumental architecture in Hawai‘i. In Proceedings of the Computer Applications and Quantitative Methods in Archaeology Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 14–16 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Foecke, T.; Ma, L.; Russell, M.A.; Conlin, D.L.; Murphy, L.E. Investigating archaeological site formation processes on the battleship USS Arizona using finite element analysis. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2010, 37, 1090–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New Zealand Archaeological Association’s ArchSite: Archaeological Site Recording Scheme. Available online: www.archsite.org.nz (accessed on 12 January 2018).
- Mann, T.; Westphal, H. Assessing Long-Term Changes in the Beach Width of Reef Islands Based on Temporally Fragmented Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 6961–6987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvamme, K.L. Integrating Multiple Geophysical Datasets. In Remote Sensing in Archaeology James Wiseman; El-Baz, F., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 345–374. [Google Scholar]
- Howey, M.C.L.; Brouwer Burg, M. Assessing the state of archaeological GIS research: Unbinding analyses of past landscapes. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2017, 84, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIvor, I.H.; Ladefoged, T.N. A multi-scalar analysis of Māori land use on Ahuahu (Great Mercury Island), New Zealand. Archaeol. Ocean. 2015, 51, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M.; See, L.; Fritz, M.; van der Velde, M.; Perger, C.; Schill, C.; Boyd, D.S. Assessing the Accuracy of Volunteered Geographic Information arising from Multiple Contributors to an Internet Based Collaborative Project. Trans. GIS 2013, 17, 847–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







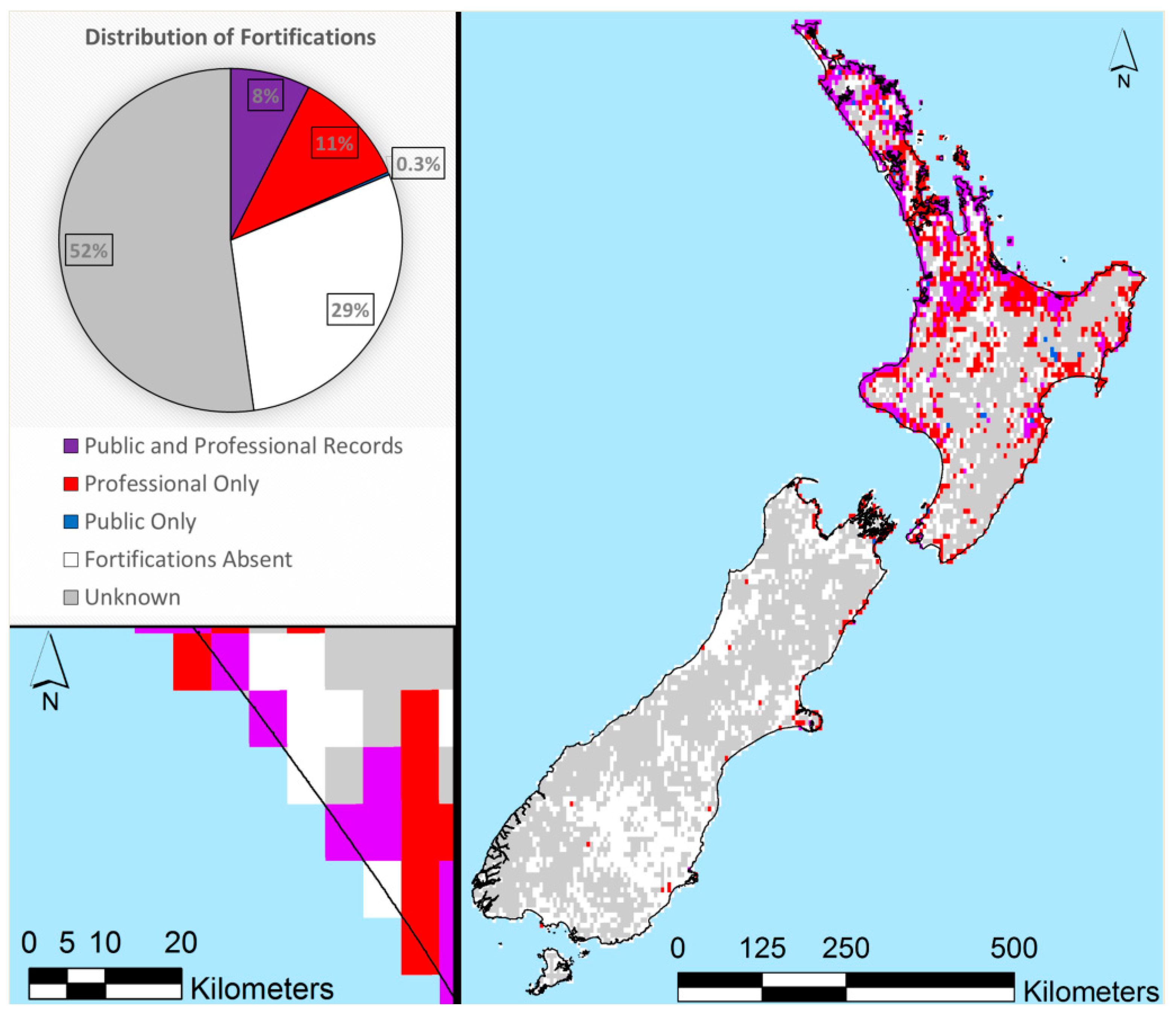
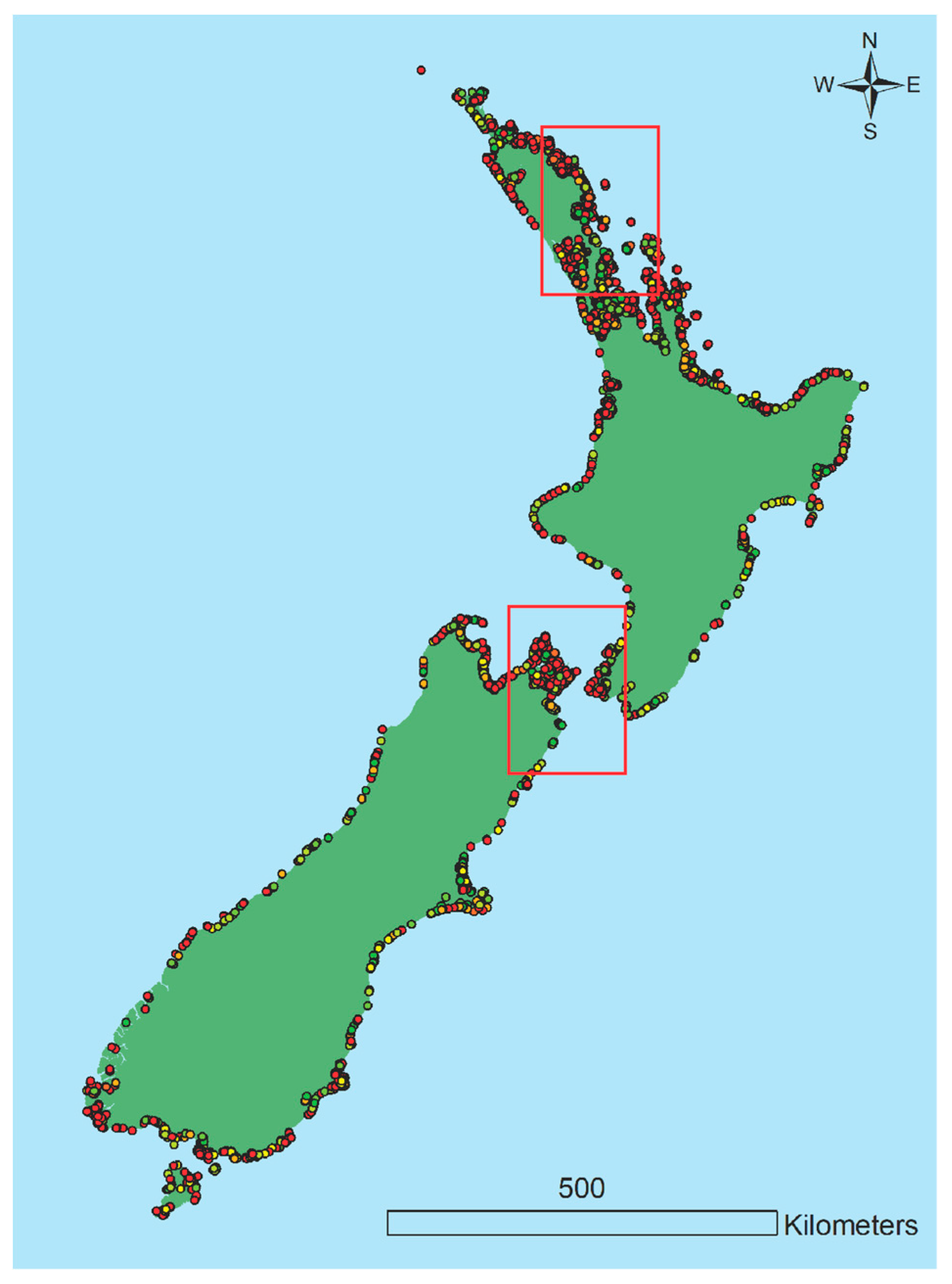
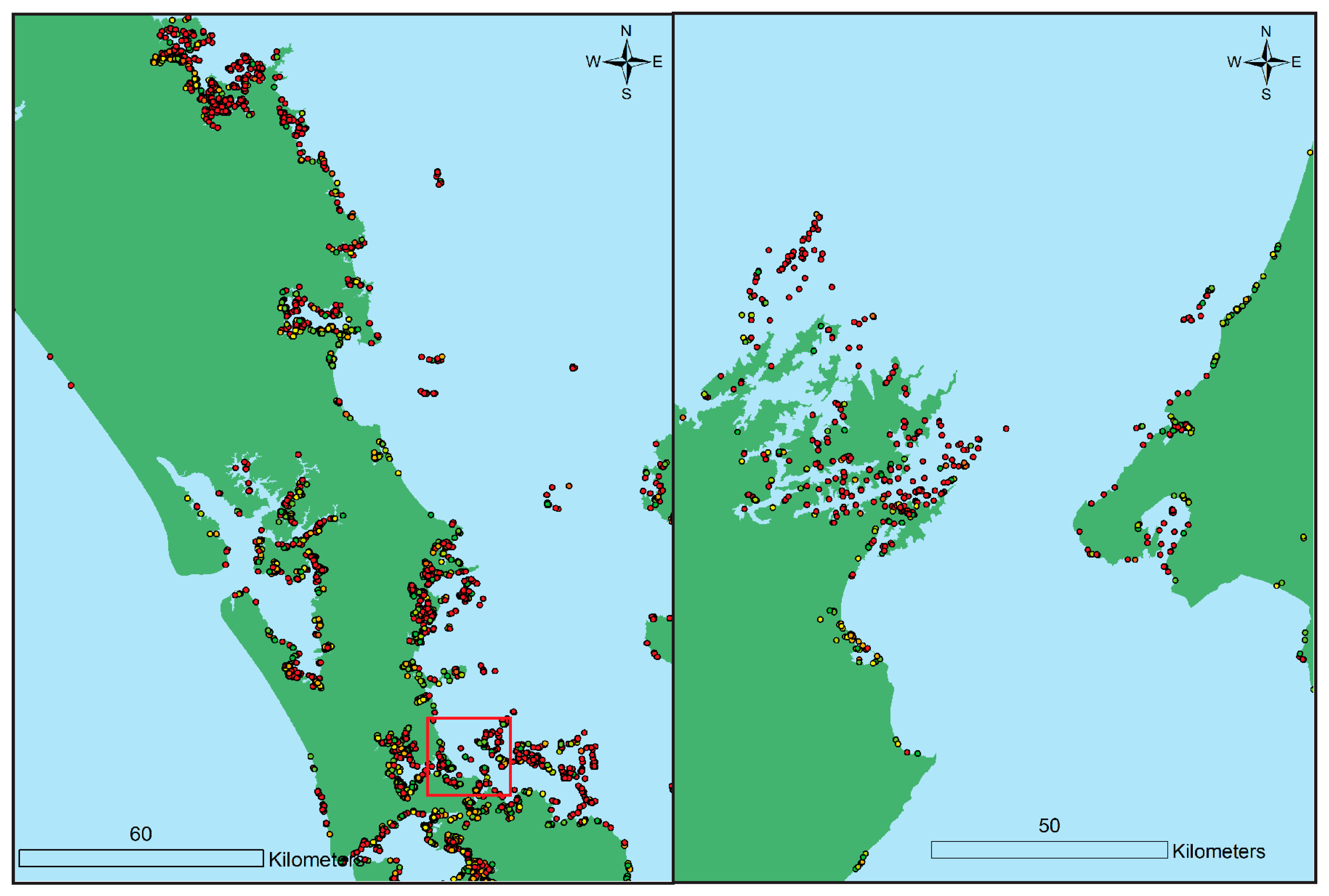
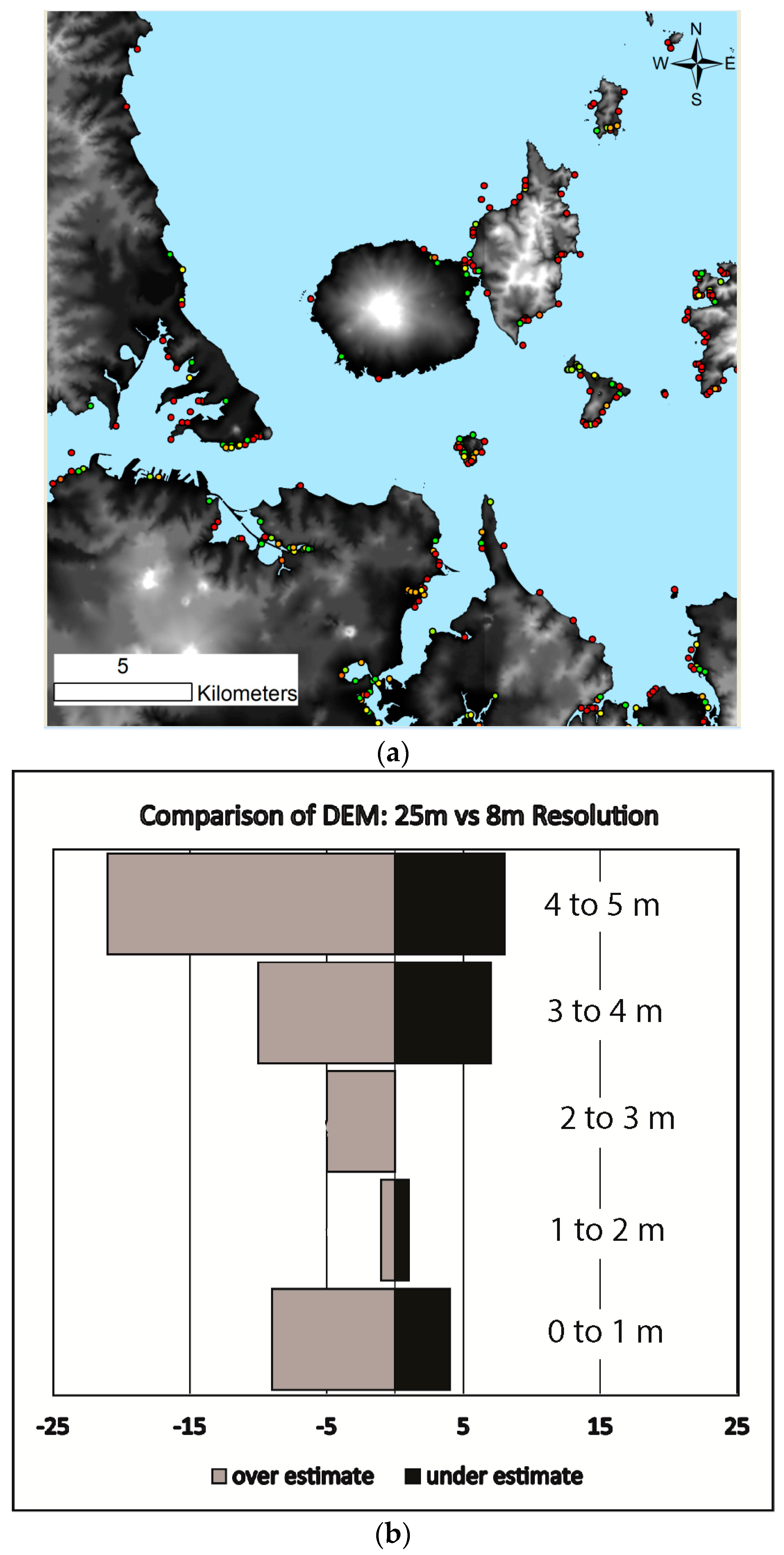
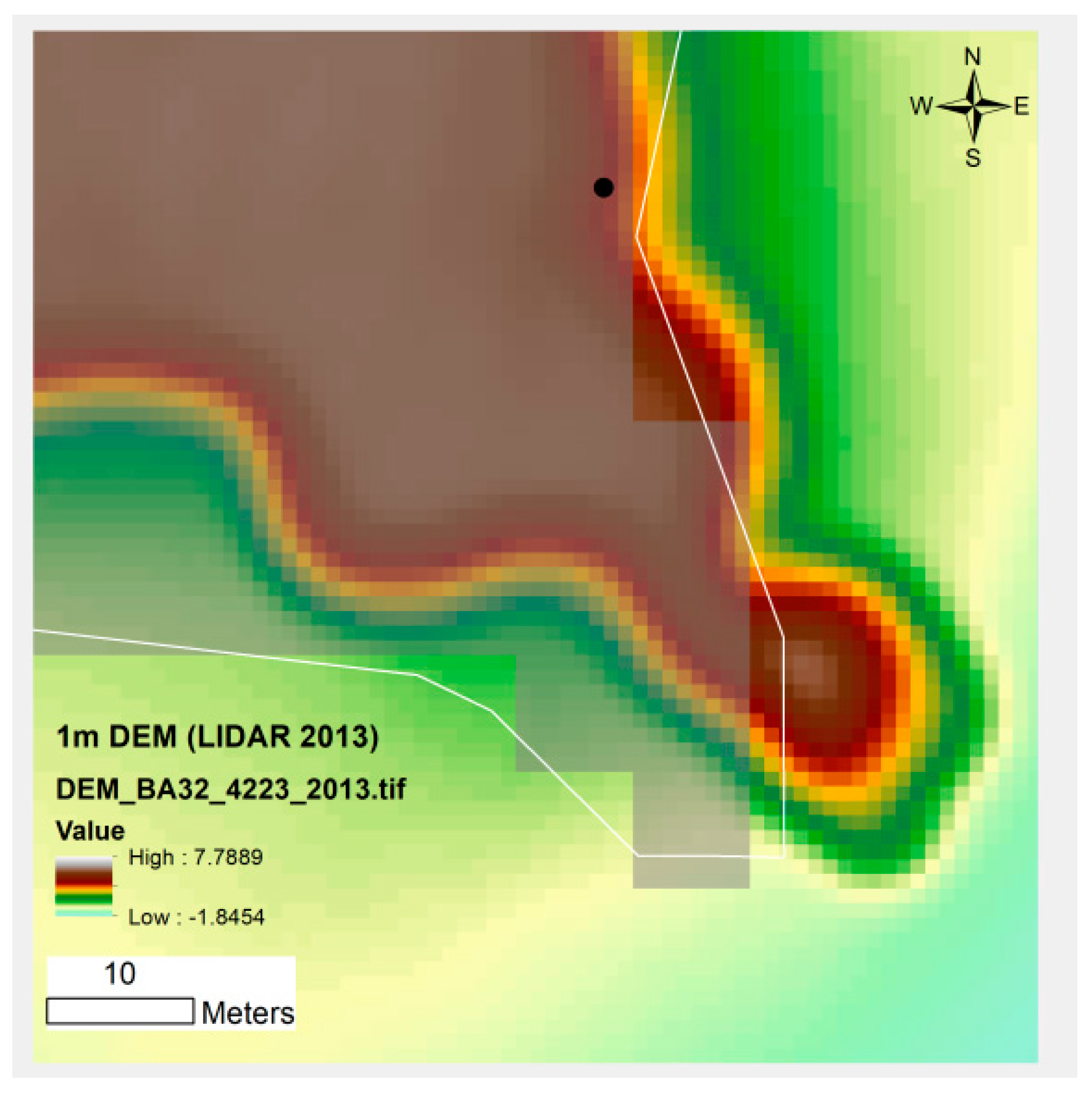
| Elevation (m asl) | Archaeological Sites (n = ) | Archaeological Sites (% Total Sites) | Map Symbol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Less than 0 | 4208 | 6.1% | Red |
| 0–1 | 1096 | 1.6% | Orange |
| 1–2 | 995 | 1.5% | Yellow |
| 2–3 | 951 | 1.4% | Yellow-Green |
| 3–4 | 1043 | 1.5% | Light Green |
| 4–5 | 1137 | 1.7% | Green |
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McCoy, M.D. The Race to Document Archaeological Sites Ahead of Rising Sea Levels: Recent Applications of Geospatial Technologies in the Archaeology of Polynesia. Sustainability 2018, 10, 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10010185
McCoy MD. The Race to Document Archaeological Sites Ahead of Rising Sea Levels: Recent Applications of Geospatial Technologies in the Archaeology of Polynesia. Sustainability. 2018; 10(1):185. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10010185
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcCoy, Mark D. 2018. "The Race to Document Archaeological Sites Ahead of Rising Sea Levels: Recent Applications of Geospatial Technologies in the Archaeology of Polynesia" Sustainability 10, no. 1: 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10010185
APA StyleMcCoy, M. D. (2018). The Race to Document Archaeological Sites Ahead of Rising Sea Levels: Recent Applications of Geospatial Technologies in the Archaeology of Polynesia. Sustainability, 10(1), 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10010185




