Trends and Predictors of Venous Thromboembolism and Major Hemorrhagic Events in Hospitalized Leukemia Patients: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the NIS (2016–2020)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Data Elements
2.2. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics and Primary Outcomes
3.2. Acute Inpatient Events and Secondary Outcomes
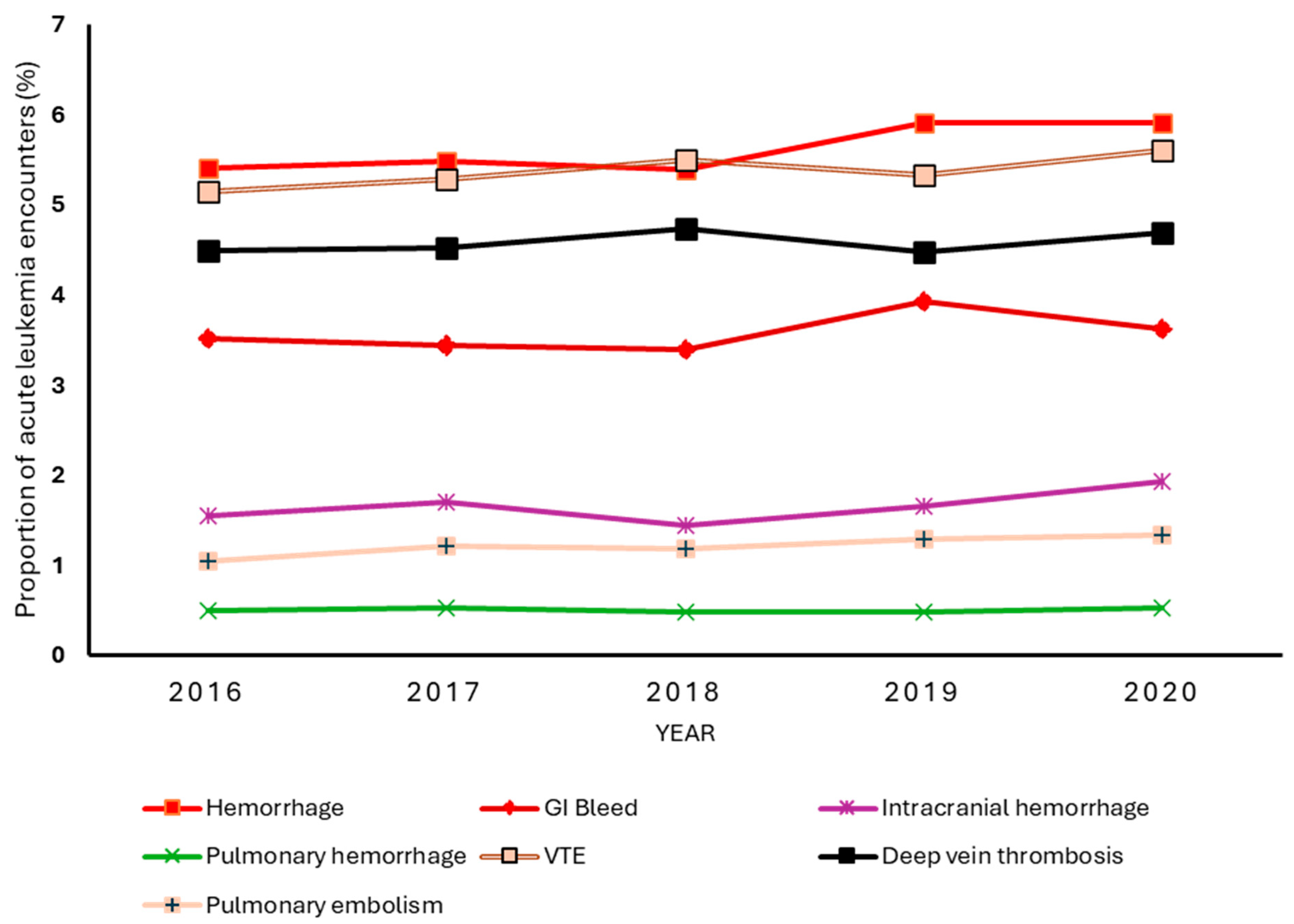
3.3. Trends in VTE and Hemorrhagic Complications
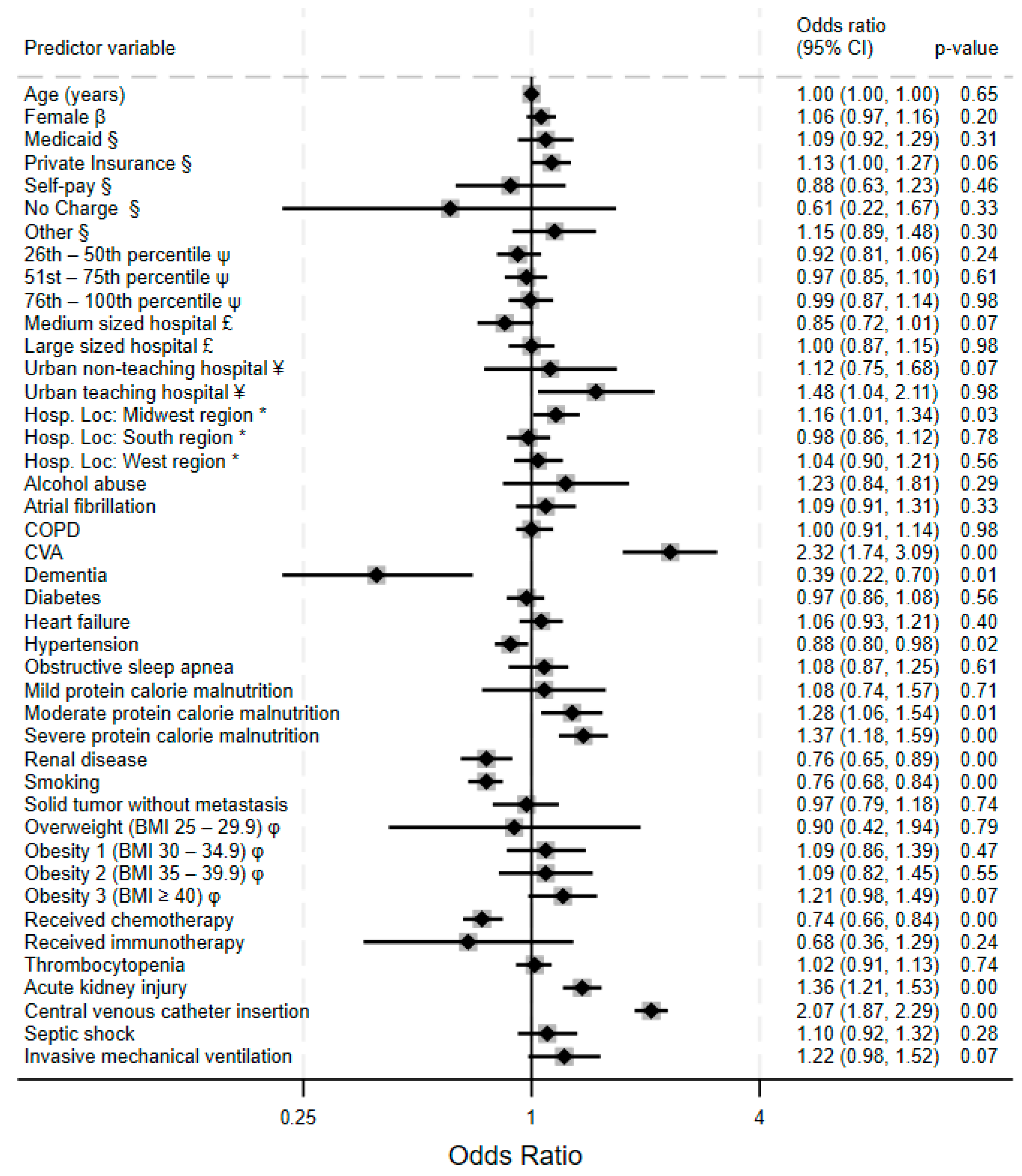
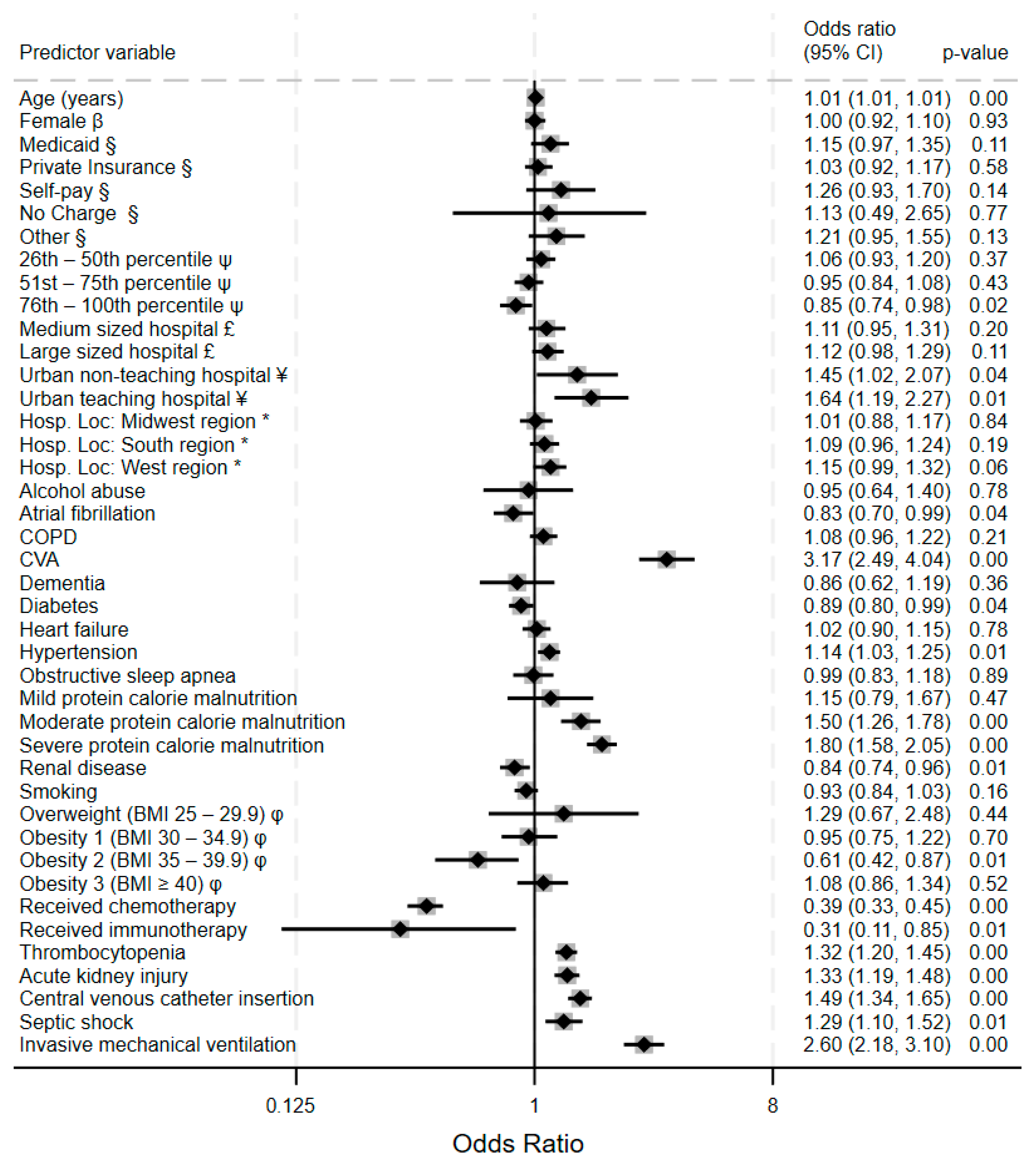
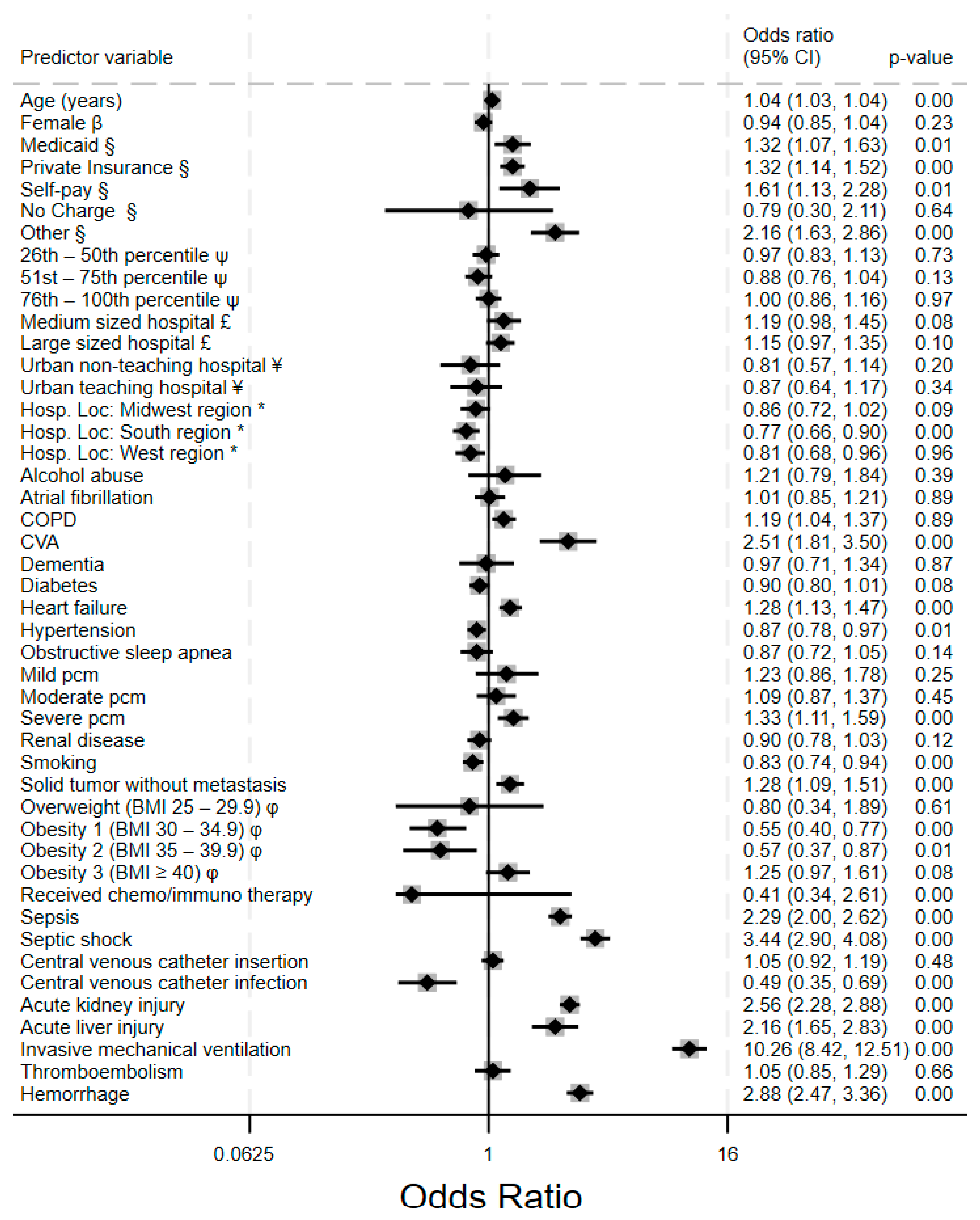
3.4. Predictors of VTE and Hemorrhagic Complications
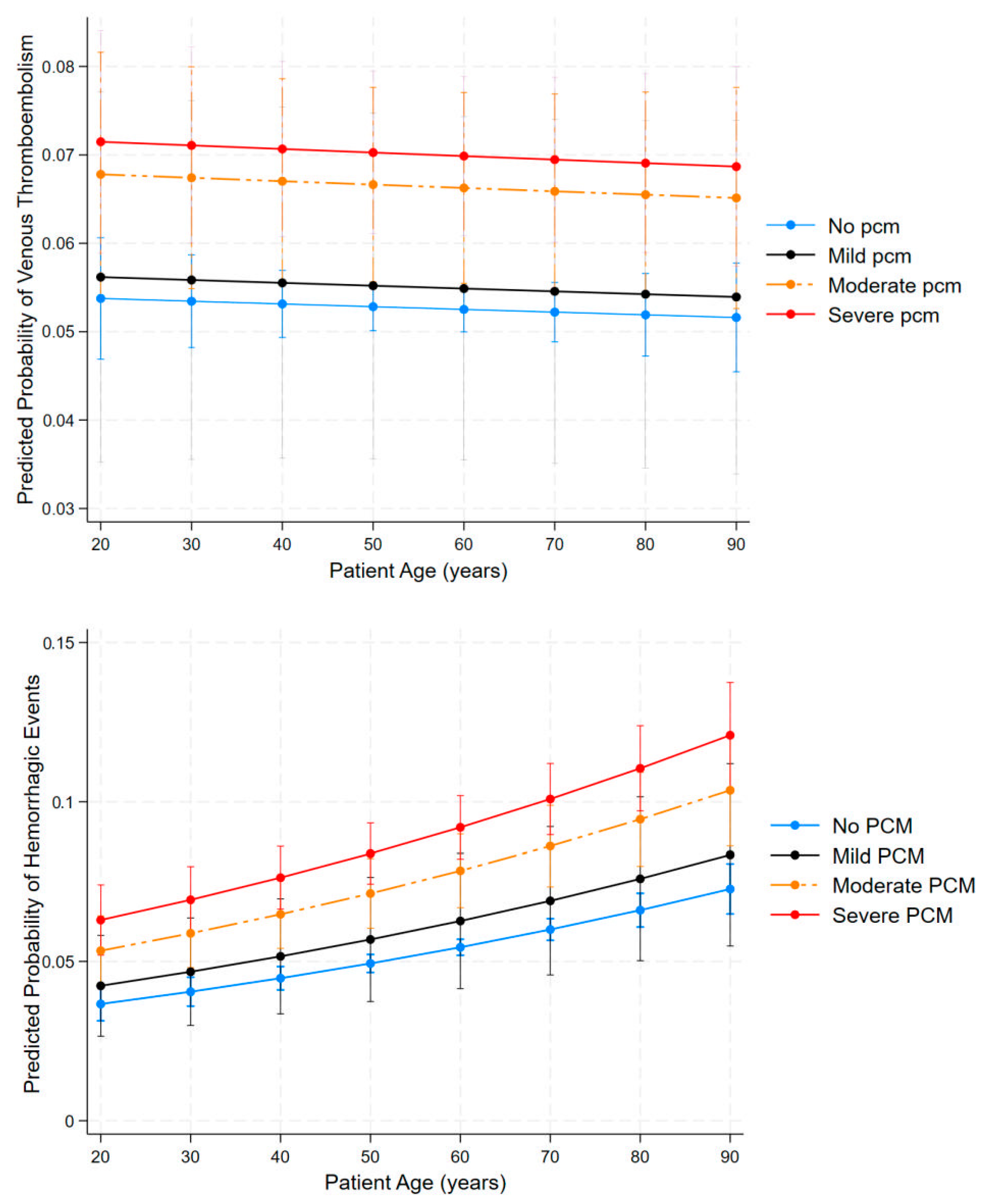
3.5. The Influence of Malnutrition on VTE and Hemorrhagic Risks
3.6. Influence of Malnutrition on the Risk for VTE and/or Major Bleeding
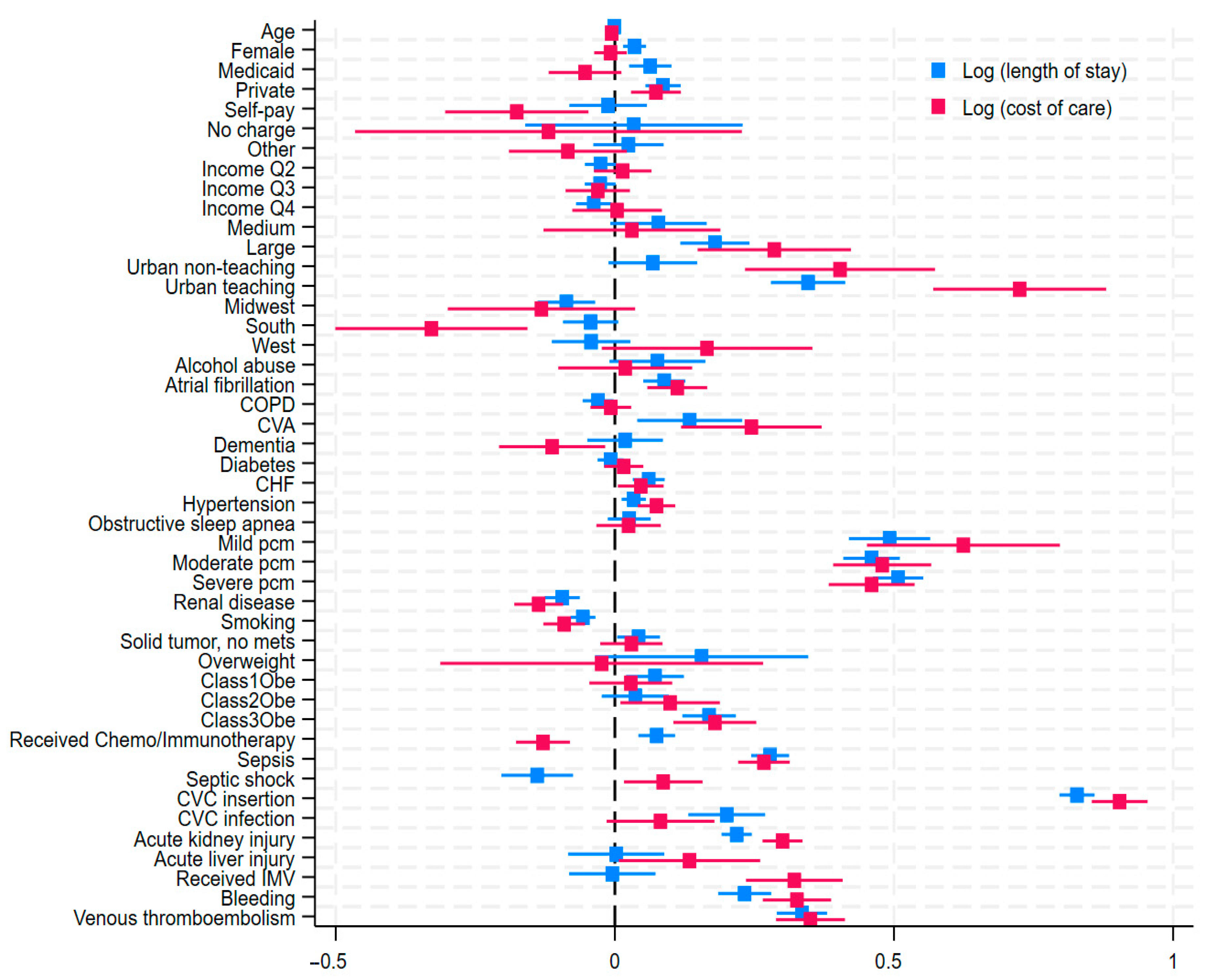
3.7. Predictors of Length of Stay and Cost of Care
3.8. Predictors of Inpatient Mortality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| DOAJ | Directory of Open Access Journals |
| HCUP | Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project |
| TLA | Three-letter acronym |
| LD | Linear dichroism |
| DVT | Deep vein thrombosis |
| VTE | Venous thromboembolism |
| AHRQ | Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality |
| NIS | National Inpatient Sample |
| ICD-10-CM | International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification |
| ICD-10-PCS | International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Procedure Coding System |
References
- Wu, Y.-Y.; Tang, L.; Wang, M.-H. Leukemia and Risk of Venous Thromboembolism: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of 144 Studies Comprising 162,126 Patients. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ani, F.; Wang, Y.P.; Lazo-Langner, A. Development of a Clinical Prediction Rule for Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with Acute Leukemia. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 120, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuger, A.L.; Middelburg, R.A.; Beckers, E.A.M.; de Vooght, K.M.K.; Zwaginga, J.J.; Kerkhoffs, J.-L.H.; van der Bom, J.G. The Identification of Cases of Major Hemorrhage during Hospitalization in Patients with Acute Leukemia Using Routinely Recorded Healthcare Data. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HCUP. US NIS Overview. Available online: https://hcup-us.ahrq.gov/nisoverview.jsp (accessed on 2 May 2025).
- Ulanja, M.B.; Beutler, B.D.; Antwi-Amoabeng, D.; Apanga, P.A.; Moody, A.E.; Willyard, C.E.; Gullapalli, N.; Boampong-Konam, K.; Bowman, A.T. Patient Outcomes in Myeloproliferative Neoplasm-Related Thrombosis: Insights from the National Inpatient Sample. Thromb. Res. 2020, 194, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, G.H.; White, R.H.; Chew, H.K.; Harvey, D.J.; Zhou, H.; Wun, T. Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with Acute Leukemia: Incidence, Risk Factors, and Effect on Survival. Blood 2009, 113, 3911–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakalov, V.; Tang, A.; Yellala, A.; Kaplan, R.; Lister, J.; Sadashiv, S. Risk Factors for Venous Thromboembolism in Hospitalized Patients with Hematological Malignancy: An Analysis of the National Inpatient Sample, 2011–2015. Leuk. Lymphoma 2020, 61, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geffen, D.B.; Man, S. New Drugs for the Treatment of Cancer, 1990–2001. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2002, 4, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, C. A Decade of Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.; Barua, A.; Huang, L.; Ganguly, S.; Feng, Q.; He, B. From Bench to Bedside: The History and Progress of CAR T Cell Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1188049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyman, G.H.; Culakova, E.; Poniewierski, M.S.; Kuderer, N.M. Morbidity, Mortality and Costs Associated with Venous Thromboembolism in Hospitalized Patients with Cancer. Thromb. Res. 2018, 164, S112–S118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gussoni, G.; Frasson, S.; Regina, M.L.; Micco, P.D.; Monreal, M. Three-Month Mortality Rate and Clinical Predictors in Patients with Venous Thromboembolism and Cancer. Findings from the RIETE Registry. Thromb. Res. 2013, 131, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lioutas, V.-A.; Beiser, A.S.; Aparicio, H.J.; Himali, J.J.; Selim, M.H.; Romero, J.R.; Seshadri, S. Assessment of Incidence and Risk Factors of Intracerebral Hemorrhage Among Participants in the Framingham Heart Study Between 1948 and 2016. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 1252–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, M.A.; Luxton, G. Prealbumin Measurement as a Screening Tool for Protein Calorie Malnutrition in Emergency Hospital Admissions: A Pilot Study. Clin. Investig. Med. 1999, 22, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Doley, J.; Phillips, W. Coding for Malnutrition in the Hospital: Does It Change Reimbursement? Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2019, 34, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arney, B.D.; Senter, S.A.; Schwartz, A.C.; Meily, T.; Pelekhaty, S. Effect of Registered Dietitian Nutritionist Order-Writing Privileges on Enteral Nutrition Administration in Selected Intensive Care Units. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2019, 34, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothberg, M.B.; Pekow, P.S.; Lahti, M.; Lindenauer, P.K. Comparative Effectiveness of Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin versus Unfractionated Heparin for Thromboembolism Prophylaxis for Medical Patients. J. Hosp. Med. 2012, 7, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, B.N.; Cain-Nielsen, A.H.; Jakubus, J.L.; Mikhail, J.N.; Fath, J.J.; Regenbogen, S.E.; Hemmila, M.R. Unfractionated Heparin versus Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis in Trauma. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017, 83, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laporte, S.; Liotier, J.; Bertoletti, L.; Kleber, F.-X.; Pineo, G.F.; Chapelle, C.; Moulin, N.; Mismetti, P. Individual Patient Data Meta-analysis of Enoxaparin vs. Unfractionated Heparin for Venous Thromboembolism Prevention in Medical Patients. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellucci, L.A.; Cameron, C.; Le Gal, G.; Rodger, M.A.; Coyle, D.; Wells, P.S.; Clifford, T.; Gandara, E.; Wells, G.; Carrier, M. Clinical and Safety Outcomes Associated with Treatment of Acute Venous Thromboembolism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA 2014, 312, 1122–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, A.; Ellis, A.; Shaffer, N.; Gurwitz, J.; Chandramohan, A.; Saulino, J.; Ishak, A.; Okubanjo, T.; Hylek, E.; Trikalinos, T.A.; et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Options for the Patient Undergoing Total Hip and Knee Replacement: A Network Meta-analysis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, N.D.; Tricarico, L.; Correale, M.; De Gennaro, L.; Santoro, F.; Ieva, R.; Di Biase, M. Direct Oral Anticoagulants More Effective than Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin for Venous Thrombo-Embolism in Cancer: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2020, 50, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wumaier, K.; Li, W.; Chen, N.; Cui, J. Direct Oral Anticoagulants versus Low Molecular Weight Heparins for the Treatment of Cancer-Associated Thrombosis: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis. Thromb. J. 2021, 19, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.T.; Maraveyas, A.; Beyer-Westendorf, J.; Lee, A.Y.Y.; Folkerts, K.; Abdelgawwad, K.; Sanctis, Y.D.; Fatoba, S.; Bamber, L.; Bach, M.; et al. Patient-Reported Outcomes Associated with Changing to Rivaroxaban for the Treatment of Cancer-Associated Venous Thromboembolism–The COSIMO Study. Thromb. Res. 2021, 206, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Garcia, D.A.; Lyman, G.H.; Carrier, M. Direct Oral Anticoagulant (DOAC) versus Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin (LMWH) for Treatment of Cancer Associated Thrombosis (CAT): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Thromb. Res. 2019, 173, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Huang, C.; Yan, V.K.C.; Wei, Y.; Shami, J.J.P.; Li, S.T.H.; Yang, Y.; Ye, X.; Tang, J.; Lee, S.F.; et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Continuous Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin versus Switching to Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Cancer-Associated Venous Thrombosis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.; Al-Horani, R.A. Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis in Major Orthopedic Surgeries and Factor XIa Inhibitors. Med. Sci. 2023, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunsua, A.A.; Touray, S.; Lui, J.K.; Ip, T.; Escobar, J.V.; Gore, J. Body Mass Index Predicts Major Bleeding Risks in Patients on Warfarin. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2015, 40, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | VTE Absent 407,575 (94.6%) | VTE Present 23,205 (5.4%) | p-Value | Hemorrhage Absent 406,710 (94.4%) | Hemorrhage Present 24,300 (5.6%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age Categories (years) | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| 18–39 | 85,560 (21.0) | 4755 (20.5) | 87,025 (21.4) | 3290 (13.5) | ||
| 40–49 | 43,425 (10.7) | 2705 (11.7) | 43,965 (10.8) | 2165 (8.9) | ||
| 50–59 | 66,095 (16.2) | 3990 (17.2) | 66,505 (16.4) | 3580 (14.7) | ||
| 60–69 | 93,805 (23.0) | 6210 (26.8) | 93,800 (23.1) | 6215 (25.6) | ||
| 70–79 | 80,925 (18.9) | 4135 (17.8) | 79,065 (19.4) | 5995 (24.7) | ||
| ≥80 | 37,965 (9.3) | 1415 (17.8) | 36,325 (8.9) | 3055 (12.6) | ||
| Sex | 0.81 | 0.39 | ||||
| Male | 226,115 (55.5) | 12,830 (55.3) | 225,315 (55.4) | 13,630 (56.1) | ||
| Females | 181,460 (44.5) | 10,375 (44.7) | 181,170 (44.6) | 10,665 (43.9) | ||
| Insurance Type | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| Medicare | 173.385 (42.6) | 9180 (39.6) | 170,205 (41.9) | 12,360 (50.9) | ||
| Medicaid | 62,605 (15.4) | 3585 (15.5) | 63,090 (15.5) | 3100 (12.8) | ||
| Private insurance | 146,340 (35.9) | 9070 (39.1) | 148,020 (36.4) | 7390 (30.5) | ||
| Self-pay | 10,575 (2.6) | 540 (2.3) | 10,530 (2.6) | 585 (2.4) | ||
| No charge | 1395 (0.3) | 65 (0.3) | 1400 (0.3) | 60 (0.2) | ||
| Other | 12,985 (3.2) | 745 (3.2) | 12,955 (3.2) | 775 (3.2) | ||
| Household Income | 0.31 | 0.13 | ||||
| 0–25th percentile | 96,090 (23.9) | 5210 (22.8) | 95,330 (23.8) | 5970 (25.0) | ||
| 26th–50th percentile | 99,670 (24.9) | 5875 (25.7) | 99,455 (24.9) | 6090 (25.5) | ||
| 51st–75th percentile | 104,105 (25.9) | 6025 (26.3) | 104,125 (26.0) | 6005 (25.1) | ||
| 76th–100th percentile | 101,245 (25.2) | 5765 (25.2) | 101,170 (25.3) | 5840 (24.4) | ||
| Hospital Bed Size | <0.001 | 0.94 | ||||
| Small | 47,730 (11.7) | 2595 (11.2) | 47,510 (11.7) | 2815 (11.6) | ||
| Medium | 788,220 (19.2) | 3685 (15.9) | 77,325 (19) | 4580 (18.9) | ||
| Large | 281,850 (69.1) | 16,930 (72.9) | 281,875 (69.3) | 16,905 (69.6) | ||
| Hospital Location | <0.001 | 0.05 | ||||
| Rural | 10,655 (26.1) | 350 (1.5) | 10,520 (25.9) | 485 (2.0) | ||
| Urban non-teaching | 37,235 (9.1) | 1390 (6.0) | 36,445 (9.0) | 2180 (9.0) | ||
| Urban teaching | 359,910 (88.3) | 21,470 (92.5) | 359,745 (8.8) | 21,635 (8.9) | ||
| Hospital Region | 0.18 | 0.43 | ||||
| Northeast | 79,385 (19.5) | 4655 (20.1) | 79,120 (19.5) | 4920 (20.3) | ||
| Midwest region | 88,210 (21.6) | 5175 (22.3) | 88,250 (21.7) | 5135 (21.1) | ||
| South region | 152,220 (37.3) | 8210 (35.4) | 151,285 (37.2) | 9145 (37.6) | ||
| West region | 87,985 (21.6) | 5170 (22.3) | 88,055 (21.7) | 5100 (21.0) | ||
| Comorbid Conditions | ||||||
| Alcohol abuse | 2170 (1.2) | 150 (1.5) | 0.36 | 2175 (1.2) | 145 (1.3) | 0.75 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 24,045 (5.9) | 1590 (6.9) | 0.01 | 23,870 (5.9) | 1765 (7.3) | <0.001 |
| COPD | 57,840 (14.2) | 3290 (14.2) | 0.99 | 57,380 (14.1) | 3750 (15.4) | 0.01 |
| CVA | 3995 (1.0) | 595 (2.6) | <0.001 | 3730 (0.9) | 860 (3.5) | <0.001 |
| Dementia | 6310 (1.5) | 205 (0.9) | <0.001 | 6105 (1.5) | 410 (1.7) | 0.29 |
| Diabetes | 40,910 (10.0) | 2210 (9.5) | 0.29 | 40,565 (10.0) | 2555 (10.5) | 0.25 |
| Heart failure | 53,420 (13.1) | 3340 (14.4) | 0.02 | 52,655 (13.0) | 4105 (16.9) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 87,930 (21.6) | 4690 (20.2) | 0.05 | 86,480 (21.3) | 6140 (25.3) | <0.001 |
| Obstructive sleep apnea | 26,585 (6.5) | 1750 (7.5) | <0.001 | 26,850 (6.6) | 1485 (6.1) | 0.19 |
| Mild protein calorie malnutrition | 4405 (1.1) | 255 (1.1) | 0.91 | 4340 (1.1) | 320 (1.3) | 0.11 |
| Moderate protein calorie malnutrition | 16,370 (4.0) | 1200 (5.2) | <0.001 | 16,080 (3.9) | 1490 (6.1) | <0.001 |
| Severe protein calorie malnutrition | 24,670 (6.1) | 2225 (9.6) | <0.001 | 24,090 (5.9) | 2805 (11.5) | <0.001 |
| Renal disease | 48,650 (11.9) | 2295 (9.9) | <0.001 | 47,625 (11.7) | 3320 (13.7) | <0.001 |
| Smoking | 121,095 (29.7) | 5865 (25.7) | <0.001 | 119,860 (29.5) | 7100 (29.2) | 0.72 |
| Solid tumor, no metastasis | 10,430 (5.9) | 550 (5.4) | <0.001 | 10,215 (5.8) | 765 (6.9) | 0.03 |
| BMI Class | <0.001 | 0.02 | ||||
| Normal | 368,645 (90.4) | 20,375 (87.8) | 367,005 (90.2) | 22,015 (90.6) | ||
| Overweight | 1375 (0.3) | 50 (0.2) | 1350 (0.3) | 75 (0.3) | ||
| Class 1 obesity | 12,750 (3.1) | 875 (3.8) | 12,830 (3.1) | 795 (3.3) | ||
| Class 2 obesity | 9085 (2.2) | 610 (2.6) | 9315 (2.3) | 380 (1.6) | ||
| Class 3 obesity | 15,945 (3.9) | 1300 (5.6) | 16,210 (4.0) | 1035 (4.3) |
| Acute Inpatient Events | VTE Absent [407,575 (94.61%)] | VTE Present [23,205 (5.39%)] | p-Value | Hemorrhage Absent [406,710 (94.36%)] | Hemorrhage Present [24,300 (5.64%)] | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute kidney injury | 79,600 (19.5) | 6490 (28.0) | <0.001 | 77,835 (19.1) | 8255 (34.0) | <0.001 |
| Acute liver injury | 5515 (1.4) | 530 (2.3) | <0.001 | 5260 (1.3) | 785 (3.2) | <0.001 |
| Central venous catheter insertion | 73,605 (18.1) | 7775 (33.4) | <0.001 | 75,020 (18.5) | 6640 (27.3 | <0.001 |
| Central venous catheter infection | 10,300 (2.5) | 1220 (5.3) | <0.001 | 10,780 (2.7) | 740 (3.0) | 0.09 |
| Received chemotherapy | 96,585 (23.7) | 4495 (19.4) | <0.001 | 99,000 (24.3) | 2080 (8.6) | <0.001 |
| Received immunotherapy | 2485 (0.6) | 105 (0.5) | <0.001 | 2545 (0.6) | 45 (0.2) | <0.001 |
| Invasive mechanical ventilation | 12,525 (3.1) | 1470 (6.3) | <0.001 | 10,970 (2.7) | 3025 (12.5) | <0.001 |
| Sepsis | 73,430 (18.0) | 5825 (25.1) | <0.001 | 72,250 (17.8) | 7005 (28.8) | <0.001 |
| Septic shock | 21,705 (5.3) | 2245 (9.7) | <0.001 | 2085 (5.1) | 3265 (13.4) | <0.001 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 95,205 (23.4) | 5455 (23.5) | 0.81 | 92,945 (22.9) | 7715 (31.8) | <0.001 |
| Thrombocythemia | 2410 (0.6) | 155 (0.7) | 0.51 | 2410 (0.6) | 155 (0.6) | 0.69 |
| Secondary Outcomes | ||||||
| Length of stay [Median (interquartile range)], days | 5 (3–13) | 11.5 (5–27) | <0.001 | 5 (3–13) | 10 (4–26) | <0.001 |
| Cost of care [MD (IQR)], US Dollars | 21,363 (9530–57,201) | 46,872 (16,473–125,724) | <0.001 | 21,404 (9541–57,250) | 43,663 (15,287–126,279) | <0.001 |
| All-cause inpatient mortality | 28,315 (6.9) | 2365 (10.2) | <0.001 | 24,860 (6.1) | 5820 (24.0) | <0.001 |
| Relative Risk Ratio (95% Confidence Intervals) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome | Mild PCM | Moderate PCM | Severe PCM |
| VTE Only | 1.1 (0.74–1.62) ns | 1.27 (1.04–1.54) * | 1.28 (1.08–1.51) ** |
| Hemorrhage Only | 1.25 (0.85–1.83) ns | 1.48 (1.23–1.78) *** | 1.73 (1.50–1.99) *** |
| VTE & Hemorrhage | 0.37 (0.05–2.73) ns | 2.00 (1.21–3.37) * | 2.88 (2.00–4.14) *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antwi-Amoabeng, D.; Beutler, B.D.; Neelam, V.; Ulanja, M. Trends and Predictors of Venous Thromboembolism and Major Hemorrhagic Events in Hospitalized Leukemia Patients: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the NIS (2016–2020). Clin. Pract. 2025, 15, 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15070117
Antwi-Amoabeng D, Beutler BD, Neelam V, Ulanja M. Trends and Predictors of Venous Thromboembolism and Major Hemorrhagic Events in Hospitalized Leukemia Patients: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the NIS (2016–2020). Clinics and Practice. 2025; 15(7):117. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15070117
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntwi-Amoabeng, Daniel, Bryce D. Beutler, Vijay Neelam, and Mark Ulanja. 2025. "Trends and Predictors of Venous Thromboembolism and Major Hemorrhagic Events in Hospitalized Leukemia Patients: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the NIS (2016–2020)" Clinics and Practice 15, no. 7: 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15070117
APA StyleAntwi-Amoabeng, D., Beutler, B. D., Neelam, V., & Ulanja, M. (2025). Trends and Predictors of Venous Thromboembolism and Major Hemorrhagic Events in Hospitalized Leukemia Patients: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the NIS (2016–2020). Clinics and Practice, 15(7), 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15070117





