Spontaneous Bowel Evisceration Through Umbilical Hernia Sites in Adult Patients: A Systematic Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
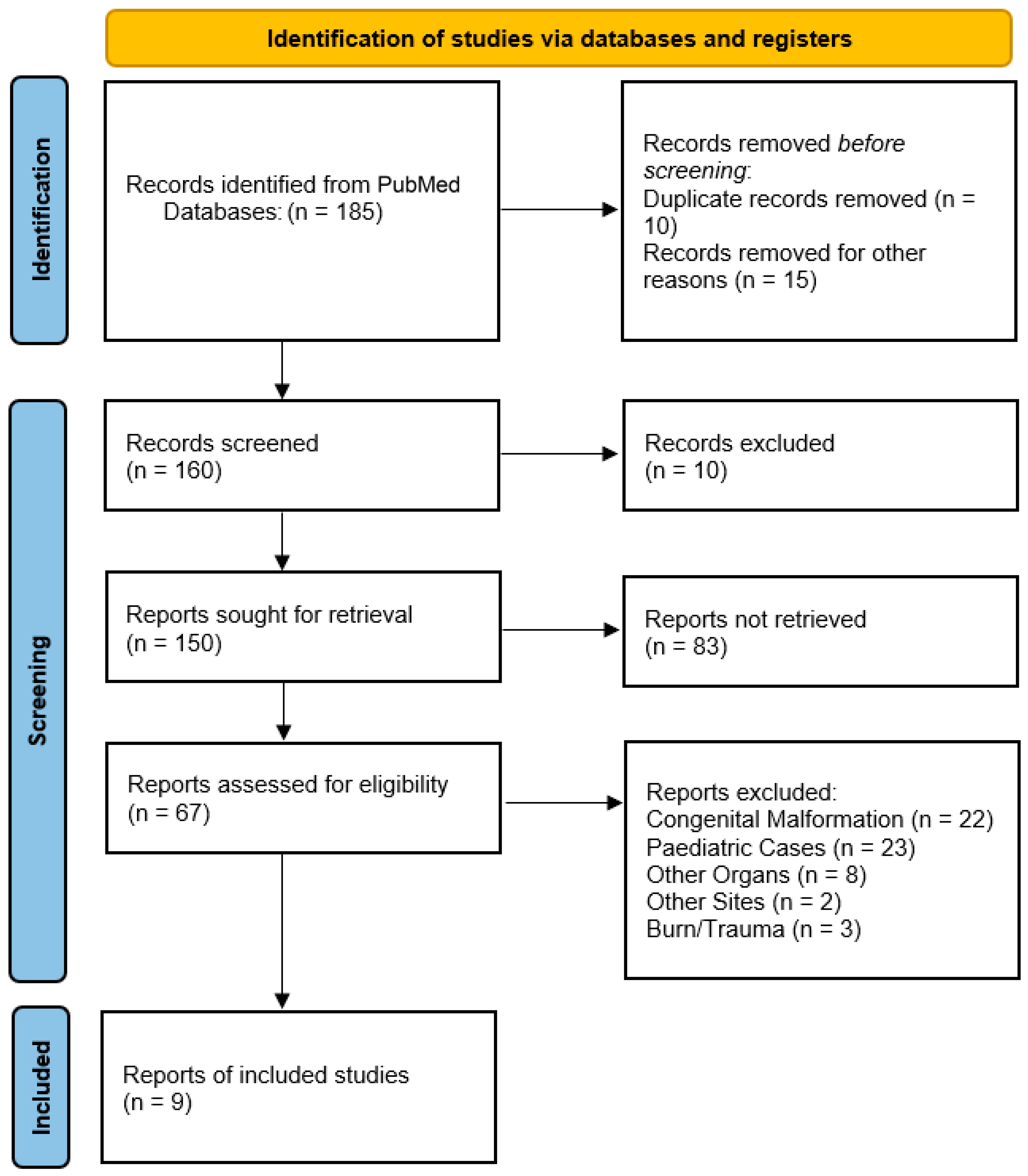
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
- Congenital anomalies (22 records): Congenital anomalies were excluded, including cases of omphalocele, gastroschisis, and umbilical cord hernias, as these represent fundamentally different embryological defects rather than acquired spontaneous ruptures.
- Pediatric cases (23 records): All childhood presentations were removed to maintain our focus on adult pathology.
- Non-umbilical herniations (64 records): Non-umbilical herniations were removed, including vaginal, rectal, and other atypical herniation sites.
- Irrelevant content (six records): Irrelevant content was removed, including one describing umbilical hernias without evisceration, one detailing parastomal hernias, and four involving animal studies.
- Off-topic publications (24 records): Off-topic publications were removed, including incisional hernia complications (8 records), non-umbilical eviscerations (8 records), post-traumatic cases (3 records), and surgical technique papers (5 records).
- Practical exclusions: Non-English publications (19 records), duplicates (10 records), and records with unavailable data (6 records) were excluded.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kingsnorth, A.; LeBlanc, K. Hernias: Inguinal e incisional. Lancet 2003, 362, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.K.; Sah, S.; Agrawal, S.C. Spontaneous rupture of incisional hernia: A rare cause of a life-threatening complication. BMJ Case Rep. 2011, 2011, bcr1120103486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, V.F. Umbilical and other abdominal wall hernias. In Paediatric Surgery, 3rd ed.; Ashcraft, K.W., Ed.; WB Saunders and Co.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2000; pp. 651–652. [Google Scholar]
- Ciley, R.E.; Krummel, T.M. Disorders of the umbilicus. In Paediatric Surgery, 5th ed.; O’Neil, J.A., Jr., Rowe, M.I., Grosfield, J.L., Eds.; Mosby: St Louis, MO, USA, 1998; pp. 1037–1039. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, W.L.; Wood, R.J.; Millar, A.J.W. A literature review of spontaneous evisceration in paediatric umbilical. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2012, 28, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weik, J.; Moores, D. An unusual case of umbilical hernia rupture with evisceration. J. Paediatr. Surg. 2005, 40, E33–E35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eker, H.H.; Van Ramshorst, G.H.; De Goede, B. A prospective study on elective umbilical hernia repair in patients with liver cirrhosis and ascites. Surgery 2011, 150, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albeladi, A.M.; Odeh, A.M.; AlAli, A.H.; Alkhars, A.M.; Buhlaigah, A.M.; Alghadeer, H.A. AlGhadeer Spontaneous Umbilical Hernia Rupture Associated With Omentum Evisceration in a Patient With Advanced Hepatic Cirrhosis and Refractory Ascites. Cureus 2021, 13, e1604. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, E.; Gandhi, S.; Bhandarwar, A.; Quraishi, A.H.M.; Wagh, A.; Tandur, A.; Wakle, D. Umbilical Hernia with Evisceration. Two Cases and a Review of the Literature. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 55, e27–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Good, D.W.; Royds, J.E.; Smith, M.J.; Neary, P.C.; Eguare, E. Umbilical hernia rupture with evisceration of omentum from massive ascites: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2011, 5, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, K.; McElroy, S. Spontaneous bowel evisceration in a patient with alcoholic cirrosi and an umbilical hernia. J. Emerg. Med. 2008, 34, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsburg, Y.; Sharma Adhi, N. Spontaneous rupture of an umbilical hernia with evisceration. J. Emerg. Med. 2006, 30, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugerman, H.; Windsor, A.; Bessos, M.; Wolfe, L. Intra-abdominal pressure, sagittal abdominal diameter and obesity comorbidity. J. Intern. Med. 1997, 241, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.; Longhi, J.; Goldman, C.; McNatt, S. Intra-abdominal pressure and the morbidly obese patients: The effect of body mass index. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2010, 69, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twardowski, Z.J.; Tully, R.J.; Ersoy, F.F.; Dedhia, N.M. Computerized tomography with and without intraperitoneal contrast for determination of intraabdominal fluid distribution and diagnosis of complications in peritoneal dialysis patients. ASAIO J. 1990, 36, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmer, J.H.; Strodel, W.E.; Knol, J.A.; Eckhauser, F.E. Management of spontaneous umbilical hernia disruption in the cirrhotic patient. Ann. Surg. 1983, 198, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolívar-Rodríguez, M.A.; Magaña-Zavala, P.A.; Pamanes-Lozano, A.; Fragoza-Sánchez, E. Evisceration due to spontaneous rupture of umbilical hernia in adult. Cir. Esp. 2021, 99, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.; Stephen, G.; Ukwenya, Y. Spontaneous rupture of umbilical hernia in pregnancy: A case report. Oman Med. J. 2011, 26, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuki, I.; Mayu, H.; Yusuke, S.; Maki, T.; Kazuhiro, S.; Yuichi, H. Intestinal evisceration and Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia due to ruptured umbilical hernia in a patient with liver cirrhosis: A case report and literature review. Oxf. Med. Case Rep. 2022, 7, omac078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogu, U.S.; Valko, J.; Wilhelm, J.; Dy, V. Spontaneous evisceration of bowel through an umbilical hernia in a patient with refractory ascites. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2013, 4, rjt073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central][Green Version]
- Grappolini, N.; Zanchetta, M.; Inversini, D.; Ietto, G. Spontaneous bowel evisceration through umbilical hernia in an adult non-cirrhotic patient. BMJ Case Rep. 2024, 17, e258602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chatzizacharias, N.A.; Bradley, J.A.; Harper, S.; Butler, A.; Jah, A.; Huguet, E. Successful surgical management of ruptured umbilical hernias in cirrhotic patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 3109–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKay, A.; Dixon, E.; Bathe, O.; Sutherland, F. Umbilical hernia repair in the presence of cirrhosis and ascites: Results of a survey and review of the literature. Hernia 2009, 13, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Den Hartog, D.; Dur, A.H.; Tuinebreijer, W.E.; Kreis, R.W. Open surgical procedures for Incisional hernias. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 3, 6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arowojolu, O.A.; Mitchell, O.J.L.; Liu, S. FLOOD Syndrome: Not Your Average Paracentesis; Hospital Medicine: Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
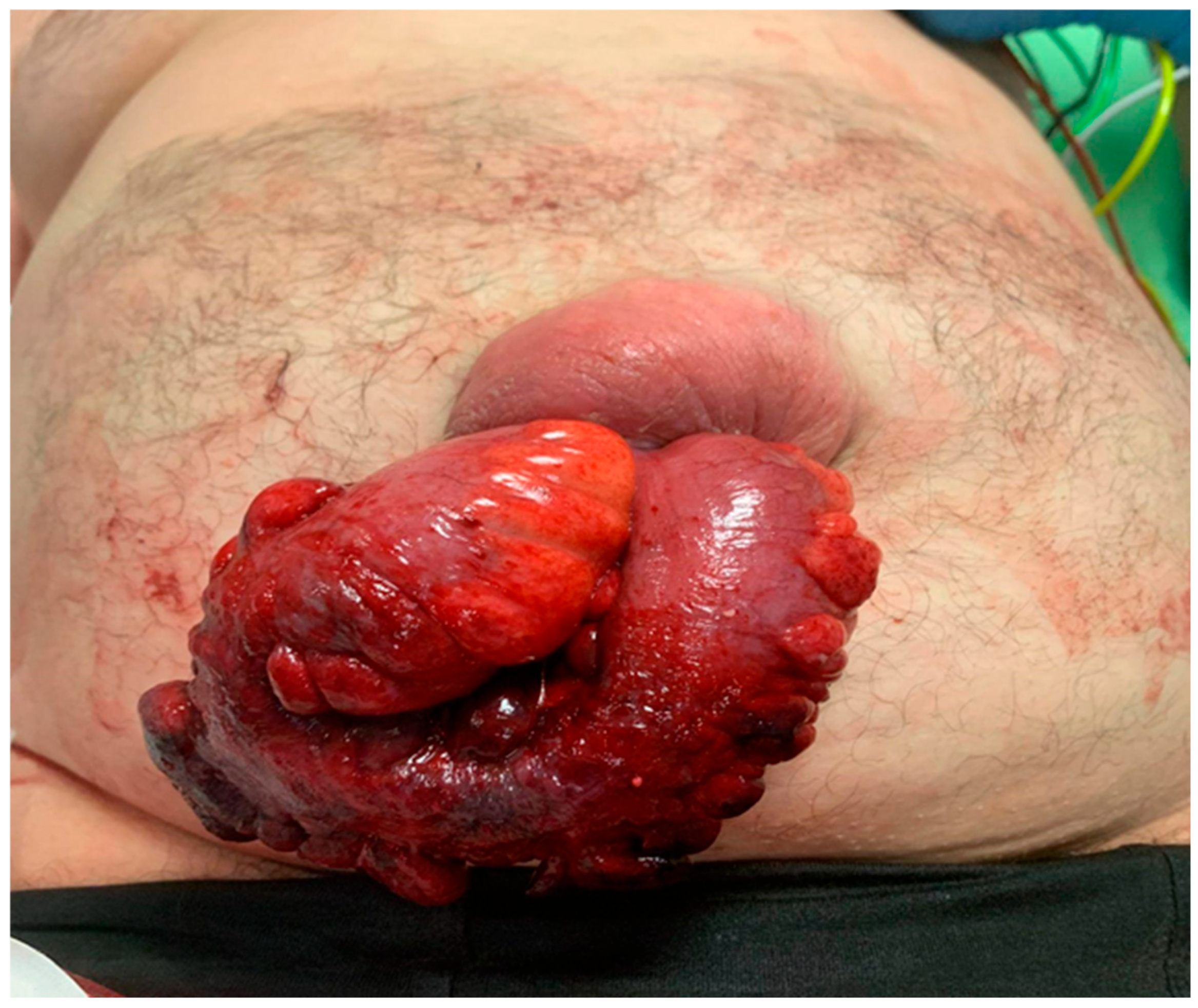
| Author | Age | Sex | Growth | Ulcerations | Leakage | Cirrhosis | Ascites | Viscera | Repair | Resection | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arora | 42 | F | Y | N | Y | Y (Hepatic) | Y | Omentum | Suture | N | Exitus |
| Arora | 40 | M | N | Y | Y | Y (Alcoholic) | Y | Omentum | Suture | N | Exitus |
| Albeladi | 23 | F | Y | Y | N | Y (Hepatic) | Y | Omentum | Mesh | N | Discharged |
| Bolivar R | 46 | F | Y | Y | N | N | N | Ileus | Suture | N | Discharged |
| Good | 81 | M | N | Y | Y | Y (Alcoholic) | Y | Omentum | Suture | N | Discharged |
| Choo | 41 | M | N | Y | Y | Y (Alcoholic) | Y | Ileus | Suture | N | Discharged |
| Ginsburg | 45 | M | Y | Y | N | Y (Both) | Y | Omentum | Suture | Y | Exitus |
| Ahmed | 28 | F | Y | Y | N | N | N | Ileus | Suture | Y | Discharged |
| Iizuka | 42 | F | N | Y | Y | Y (Alcoholic) | Y | Ileus | Suture | N | Discharged |
| Ogu | 50 | M | N | N | Y | Y (Hepatic) | Y | Ileus | Suture | N | Discharged |
| Grappolini | 53 | M | N | Y | N | N | N | Ileus | Suture | Y | Discharged |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gianazza, S.; Grappolini, N.; Morabito, M.; Palillo, A.; Ripamonti, M.; Inversini, D. Spontaneous Bowel Evisceration Through Umbilical Hernia Sites in Adult Patients: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Clin. Pract. 2025, 15, 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15060099
Gianazza S, Grappolini N, Morabito M, Palillo A, Ripamonti M, Inversini D. Spontaneous Bowel Evisceration Through Umbilical Hernia Sites in Adult Patients: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Clinics and Practice. 2025; 15(6):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15060099
Chicago/Turabian StyleGianazza, Simone, Niccolò Grappolini, Marika Morabito, Andrea Palillo, Marta Ripamonti, and Davide Inversini. 2025. "Spontaneous Bowel Evisceration Through Umbilical Hernia Sites in Adult Patients: A Systematic Review of the Literature" Clinics and Practice 15, no. 6: 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15060099
APA StyleGianazza, S., Grappolini, N., Morabito, M., Palillo, A., Ripamonti, M., & Inversini, D. (2025). Spontaneous Bowel Evisceration Through Umbilical Hernia Sites in Adult Patients: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Clinics and Practice, 15(6), 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15060099






