C-Reactive Protein, International Normalized Ratio, and Fibrinogen in Diagnostic Scale of Complicated Acute Appendicitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants, Variables, and Study Design
2.2. Statistical Analysis
2.3. Construction of the Score
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Preoperative Factors Between Complicated and Uncomplicated Acute Appendicitis
3.2. Factors Associated with Complicated Acute Appendicitis
3.3. Plasma Concentrations of C-Reactive Protein, Fibrinogen, and INR Are Individual Factors Associated with CA
3.4. Diagnostic Scale for Complicated Acute Appendicitis
3.5. Performance of the Scale Generated
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borruel, S.; Ibáñez, L.; Sanz, R.; Depetris, M.A.; Martínez, E. Update on acute appendicitis: Typical and untypical findings. Radiología (Engl. Ed.) 2023, 65, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakcak, İ.E.; Türkyılmaz, Z.; Demirel, T. Relationship between SIRI, SII values, and Alvarado score with complications of acute appendicitis during the COVID-19 pandemic. Ulus. Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2022, 28, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Téoule, P.; de Laffolie, J.; Rolle, U.; Reissfelder, C. Acute appendicitis in childhood and adolescence-an everyday clinical challenge. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2020, 117, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quevedo-Fernandez, E.; Gonzalez-Urquijo, M.; Hinojosa-Gonzalez, D.E.; Morales-Flores, L.F.; Morales-Morales, C.A.; Zambrano-Lara, M.; Guajardo-Nieto, D.; Rodarte-Shade, M. Analysis of deferral times in patients diagnosed with acute apendicitis. Asian J. Surg. 2023, 46, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, N.J.; Eaton, S.; Abbo, O.; Arnaud, A.P.; Beaudin, M.; Brindle, M.; Bütter, A.; Davies, D.; Jancelewicz, T.; Johnson, K.; et al. Appendectomy versus non-operative treatment for acute uncomplicated appendicitis in children: Study protocol for a multicentre, open-label, non-inferiority, randomised controlled trial. BMJ Paediatr. Open 2017, 1, bmjpo-2017-000028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brucchi, F.; Bracchetti, G.; Fugazzola, P.; Viganò, J.; Filisetti, C.; Ansaloni, L.; Dal Mas, F.; Cobianchi, L.; Danelli, P.F. A meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis comparing nonoperative versus operative management for uncomplicated appendicitis: A focus on randomized controlled trials. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2024, 19, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçiçek, M.; Ilgar, M.; Ünlü, S. Is acute appendicitis complicated or uncomplicated? Approaching the question via computed tomography. Acta Radiol. 2023, 64, 1755–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bom, W.J.; Scheijmans, J.C.G.; Salminen, P.; Boermeester, M.A. Diagnosis of Uncomplicated and Complicated Appendicitis in Adults. Scand. J. Surg. 2021, 110, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zengin, A.; Bağ, Y.M.; Öğüt, M.Z.; Sağlam, K. The role of C-reactive protein/albumin ratio and prognostic nutritional index in the diagnosis of complicated acute appendicitis. Turk. J. Surg. 2024, 40, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Soto, R.H.; Ponce de León-Ballesteros, G.; Álvarez-Bautista, F.; Trolle-Silva, A.M.; Medina-Franco, H. Thrombocytosis and Hyponatremia as Predictors of Complicated Acute Appendicitis. Predictors of Appendicitis. J. Surg. Res. 2021, 261, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özozan, Ö.V.; Vural, V. High C-reactive protein level as a predictor for appendiceal perforation. Ulus. Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2020, 26, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuaib, A.; Alhamdan, N.; Arian, H.; Sallam, M.A.; Shuaib, A. Hyperbilirubinemia and Hyponatremia as Predictors of Complicated Appendicitis. Med. Sci. 2022, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Y.; Qian, S.; Wu, L.; Liu, X. Fibrinogen as a Marker of Overall and Complicated Acute Appendicitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Surg. Res. 2022, 280, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, Z.G.; Chen, X.Y.; Xu, B.X.; Mao, X.P. Fascial involvement score on unenhanced CT potentially helps predict complicated appendicitis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2025, 182, 111843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahankali, S.K.; Ahamed, S.A.; Gupta, G.S.P.; Razek, A.A.K.A. CT based Acute Appendicitis Severity Index for acute appendicitis and validate its effectiveness in predicting complicated appendicitis. Emerg. Radiol. 2021, 28, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Saverio, S.; Podda, M.; De Simone, B.; Ceresoli, M.; Augustin, G.; Gori, A.; Boermeester, M.; Sartelli, M.; Coccolini, F.; Tarasconi, A.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of acute appendicitis: 2020 update of the WSES Jerusalem guidelines. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2020, 15, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, S.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, K.P.; Lee, H.S.; Ahn, S.; Kim, T.; Hwang, S.S.; et al. Low-Dose Abdominal CT for Evaluating Suspected Appendicitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundappan, S.S.; Karpelowsky, J.; Lam, A.; Lam, L.; Cass, D. Diagnostic accuracy of surgeon performed ultrasound (SPU) for appendicitis in children. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2018, 53, 2023–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meléndez-Negrette, F.; Acosta-Reyes, J. Is ultrasound useful in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis in patients suffering overweight/obesity? Rev. Chil. Cir. 2016, 68, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haak, F.; Kollmar, O.; Ioannidis, A.; Slotta, J.E.; Ghadimi, M.B.; Glass, T.; von Strauss Und Torney, M. Predicting complicated appendicitis based on clinical findings: The role of Alvarado and Appendicitis Inflammatory Response scores. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2022, 407, 251–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiters, A.; Drozd, A.; Parikh, P.; Markert, R.; Shim, J.K. Use of the Alvarado score in elderly patients with complicated and uncomplicated appendicitis. Am. Surg. 2019, 85, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, J.C.; Trimborn, C.P.; Hoffmann, M.; Schröder, R.; Förster, S.; Dirks, K.; Tannapfel, A.; Anthuber, M.; Hollerweger, A. Classification of acute appendicitis (CAA): Treatment directed new classification based on imaging (ultrasound, computed tomography) and pathology. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2021, 36, 2347–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheijmans, J.C.G.; Bom, W.J.; Ghori, U.H.; van Geloven, A.A.W.; Hannink, G.; van Rossem, C.C.; van de Wouw, L.; Huisman, P.M.; van Hemert, A.; Franken, R.J.; et al. Development and Validation of the Scoring System of Appendicitis Severity 2.0. JAMA Surg. 2024, 159, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouali, M.; El Berni, Y.; Moufakkir, A.; El Bakouri, A.; El Hattabi, K.; Bensardi, F.; Fadil, A.M. Value of Alvarado scoring system in diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 77, 103642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, A. A practical score for the early diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1986, 15, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mervak, B.M.; Wilson, S.B.; Handly, B.D.; Altun, E.; Burke, L.M. MRI of acute appendicitis. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 50, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolmers, M.D.M.; Bom, W.J.; Scheijmans, J.C.G.; van Geloven, A.A.W.; Boermeester, M.A.; Bemelman, W.A.; van Rossem, C.C.; SNAPSHOT collaborators. Accuracy of imaging in discriminating complicated from uncomplicated appendicitis in daily clinical practice. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2022, 37, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.M.; Romero, I.; Pereira, C.C.; Soares, F.; Gonçalves, Á.; Costa, S.; da Silva, J.B. Inflammatory parameters as predictive factors for complicated appendicitis: A retrospective cohort study. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 74, 103266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, H.; Meng, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P. A risk score system for predicting complicated appendicitis and aid decision-making for antibiotic therapy in acute appendicitis. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 6133–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atema, J.J.; van Rossem, C.C.; Leeuwenburgh, M.M.; Stoker, J.; Boermeester, M.A. Scoring system to distinguish uncomplicated from complicated acute appendicitis. Br. J. Surg. 2015, 102, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.A.; Tsai, H.W.; Chao, C.C.; Lin, S.F. Periappendiceal fat-stranding models for discriminating between complicated and uncomplicated acute appendicitis: A diagnostic and validation study. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2021, 16, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Clos, T.M. Pentraxins: Structure, Function, and Role in Inflammation. ISRN Inflamm. 2013, 379040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornick, M.G.; Potempa, L.A. Monomeric C-reactive protein as a biomarker for major depressive disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 14, 1325220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sproston, N.R.; Ashworth, J.J. Role of C-reactive protein at sites of inflammation and infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaïni, S.; Koldkjær, O.G.; Pedersen, C.; Pedersen, S.S. Procalcitonin, lipopolysaccharide-binding protein, interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in community-acquired infections and sepsis: A prospective study. Crit. Care 2006, 10, R53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prada-Arias, M.; Gómez-Veiras, J.; Salgado-Barreira, A.; Vázquez, J.L.; Montero-Sánchez, M.; Fernández-Lorenzo, J.R. Value of Fibrinogen to Discriminate Appendicitis from Nonspecific Abdominal Pain in Preschool Children. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2020, 30, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loike, J.D.; Sodeik, B.; Cao, L. CD11c/CD18 on neutrophils recognizes a domain at the N terminus of the Aα chain of fibrinogen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyendyk, J.P.; Schoenecker, J.G.; Flick, M.J. The multifaceted role of fibrinogen in tissue injury and inflammation. Blood 2019, 133, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinod Kumar, M.; Tiwari, T.; Singh, J.; Malik, A. Plasma fibrinogen: An independent predictor of pediatric appendicitis. J. Indian. Assoc. Pediatr. Surg. 2021, 26, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandi, A.; Cipriani, E.; Parolini, F.; Consonni, D.; Calderini, E.; Franzini, S.; Leva, E. The coagulation profile as a marker for acute appendicitis in the paediatric population: Retrospective study. Afr. J. Paediatr. Surg. 2020, 17, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, S.J.; Cho, H.J. International normalized ratio and serum C-reactive protein are feasible markers to predict complicated appendicitis. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2016, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partain, K.N.; Patel, A.U.; Travers, C.; Short, H.L.; Braithwaite, K.; Loewen, J.; Heiss, K.F.; Raval, M.V. Improving ultrasound for appendicitis through standardized reporting of secondary signs. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2017, 52, 1273–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelin, M.; Paquette, B.; Revel, L.; Landecy, M.; Bouveresse, S.; Delabrousse, E. Acute appendicitis: Factors associated with inconclusive ultrasound study and the need for additional computed tomography. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2018, 99, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macri, F.; Greffier, J.; Pereira, F.R.; Mandoul, C.; Khasanova, E.; Gualdi, G.; Beregi, J.P. Ultra-low-dose chest CT with iterative reconstruction does not alter anatomical image quality. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2016, 97, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avanesov, M.; Wiese, N.J.; Karul, M.; Guerreiro, H.; Keller, S.; Busch, P.; Jacobsen, F.; Adam, G.; Yamamura, J. Diagnostic prediction of complicated appendicitis by combined clinical and radiological appendicitis severity index (APSI). Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 3601–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastunen, K.; Leppäniemi, A.; Mentula, P. Perforation rate after a diagnosis of uncomplicated appendicitis on CT. BJS Open 2021, 5, zraa034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldaraca-Moreno, A.; Álvarez Zúñiga, R.; Bustamante-Silva, J.R.; Oest-Dávila, C.W.; Peralta-Pedrero, M.L.; Ochoa-Pineda, F.J.; Rodríguez-Guerrero, A. Clinical Practice Guideline, Treatment of Acute Appendicitis; Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social: Juárez, Mexico, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Yin, W.; Chuanzhou, Z.; Huang, J.; Liao, C.; Nie, L.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, P. Alterations of the Preoperative Coagulation Profile in Patients with Acute Appendicitis. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2011, 49, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlinaric, A.; Milos, M.; Coen-Herak, D.; Fucek, M.; Rimac, V.; Zadro, R.; Rogic, D. Autovalidation and automation of the postanalytical phase of routine hematology and coagulation analyses in a university hospital laboratory. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2018, 56, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, S.T.; van Dijk, A.H.; Dijkgraaf, M.G.; Boermeester, M.A. Meta-analysis of in-hospital delay before surgery as a risk factor for complications in patients with acute appendicitis. Br. J. Surg. 2018, 105, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Kingdom National Surgical Research Collaborative; Bhangu, A. Safety of short, in-hospital delays before surgery for acute appendicitis: Multicentre cohort study, systematic review, and meta-analysis. Ann. Surg. 2014, 259, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, S.; Mandal, N. Evaluation of role of hyperbilirubinemia as a new diagnostic marker of complicated appendicitis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashirekha, C.A.; Vincent, A. Mean Platelet Volume as an Emerging Biomarker for Diagnosing Acute Appendicitis: A Retrospective Study. Cureus 2024, 16, e75247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moons, K.G.; Kengne, A.P.; Grobbee, D.E.; Royston, P.; Vergouwe, Y.; Altman, D.G.; Woodward, M. Risk prediction models: II. External validation, model updating, and impact assessment. Heart 2012, 98, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | CA (n = 52) | UC (n = 80) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Men % (n) Women % (n) | 61.54% (32) 38.46% (20) | 41.25% (33) 58.75% (47) | 0.0227 (*) |
| Age (years) | 31.67 ± 17.48 | 34.85 ± 16.61 | 0.1276 |
| Self-medication with antibiotics | 25.00% (13) | 14.44% (13) | 0.1171 |
| Self-medication with steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | 61.54% (32) | 55.00% (44) | 0.4577 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Diabetes % (n) | 5.77% (3) | 5% (4) | 0.8472 |
| Obesity % (n) | 19.23% (10) | 12.50% (10) | 1.111 |
| Hypertension % (n) | 5.77% (3) | 2.50% (2) | 0.9242 |
| Autoimmune disease % (n) | 0 | 0 | - |
| Signs and symptoms | |||
| Anorexia | 76.92% (40) | 67.50% (54) | 0.2427 |
| Migration of pain | 80.77% (42) | 77.50% (62) | 0.6535 |
| Fever greater than 38 °C | 61.54% (32) | 41.25% (33) | 0.0227 (*) |
| Nausea/Vomiting | 84.62% (44) | 81.25% (65) | 0.6184 |
| Right lower quadrant pain | 98.08% (51) | 100% (80) | 0.2131 |
| Right iliac fossa rebound (Blumberg’s sign) | 96.15% (50) | 86.25% (69) | 0.0621 |
| Laboratory values | |||
| Leukocytes (103/µL) | 16.00 ± 6.119 | 13.88 ± 5.466 | 0.0393 (*) |
| Neutrophils (103/µL) | 13.55 ± 6.183 | 11 ± 5.466 | 0.0142 (*) |
| Lymphocytes (103/µL) | 1.432 ± 1.244 | 1.693 ± 0.7639 | 0.1377 |
| Monocytes (103/µL) | 0.9737 ± 0.5049 | 0.9031 ± 0.4235 | 0.3880 |
| Platelets (103/µL) | 273.6 ± 85.07 | 262 ± 69.66 | 0.3943 |
| MPV | 10.08 ± 1.058 | 10.15 ± 1.001 | 0.6997 |
| aPTT(s) | 29.14 ± 3.356 | 28.95 ± 3.451 | 0.9325 |
| PT(s) | 15.99 ± 2.390 | 14.67 ± 1.551 | 0.0002 (***) |
| INR | 1.233 ± 0.1978 | 1.122 ± 0.1321 | 0.0001 (****) |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) | 577.1 ± 165.7 | 438.3 ± 158.4 | <0.0001 (****) |
| C-reactive protein (mg/dL) | 11.69 ± 8.816 | 6.872 ± 14.32 | 0.0318 (*) |
| Total protein (g/dL) † | 7.410 ± 2.677 | 7.214 ± 1.326 | 0.6836 |
| Albumin (g/dL) † | 4.090 ± 0.6973 | 4.228 ± 0.5568 | 0.4215 |
| Globulin (g/dL) † | 3.275 ± 0.4153 | 3.192 ± 0.3434 | 0.4233 |
| Total Bilirubin (g/dL) † | 1.185 ± 0.5724 | 0.9800 ± 0.6067 | 0.2242 |
| Direct bilirubin (g/dL) † | 0.01500 ± 0.06708 | 0.000 ± 0.000 | 0.3571 |
| Indirect bilirubin (g/dL) † | 1.170 ± 0.5507 | 0.9778 ± 0.5981 | 0.2414 |
| Ultrasound findings | |||
| Appendicolith | 3.85% (2) | 1.25% (1) | 0.3281 |
| Periappendicular Plastontium | 17.31% (9) | 11.25% (9) | 0.3217 |
| Abscess | 9.62% (5) | 1.25% (1) | 0.0242 (*) |
| Free fluid in periappendicular cavity | 13.46% (7) | 2.50% (2) | 0.0146 (*) |
| Scales and ratios | |||
| Alvarado scale points | 7.904 ± 1.376 | 7.375 ± 1.594 | 0.0513 |
| RIPASA scale point | 7.394 ± 1.439 | 6.669 ± 1.522 | 0.0043 (**) |
| NLR | 13.26 ± 10.56 | 8.800 ± 7.338 | 0.0013 (**) |
| PLR | 255.92 ± 174.4 | 188.3 ± 97.95 | 0.0032 (**) |
| MLR | 0.9095 ± 0.7878 | 0.6668 ± 0.5074 | 0.0158 (*) |
| 0.9095 ± 0.7878 | 0.6668 ± 0.5074 | 0.0158 (*) |
| Variable | Odds Ratio | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Biological sex (male) | 0.904 | 0.342 |
| Fever greater than 38 °C | 0.571 | 0.450 |
| Free fluid | 4.612 | 0.032 (*) |
| Abscess | 3.651 | 0.056 |
| Neutrophils count | 0.599 | 0.439 |
| Fibrinogen | 8.277 | 0.004 (**) |
| INR | 4.651 | 0.031 (*) |
| C-reactive protein | 7.533 | 0.006 (**) |
| NLR | 0.339 | 0.560 |
| PLR | 1.055 | 0.304 |
| MLR | 2.903 | 0.088 |
| RIPASA score | 3.644 | 0.056 |
| Variables | Clinical Features | Odds Ratio | Significance | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fibrinogen > 481.5 mg/dL | 4.692 | 0.030 (*) | 2 | |
| INR > 1.15 | 4.479 | 0.034 (*) | 2 | |
| C-reactive protein > 7.15 mg/dL | 4.535 | 0.033 (*) | 2 | |
| Free fluid | 3.861 | 0.049 (*) | 2 | |
| Total score | 8 |
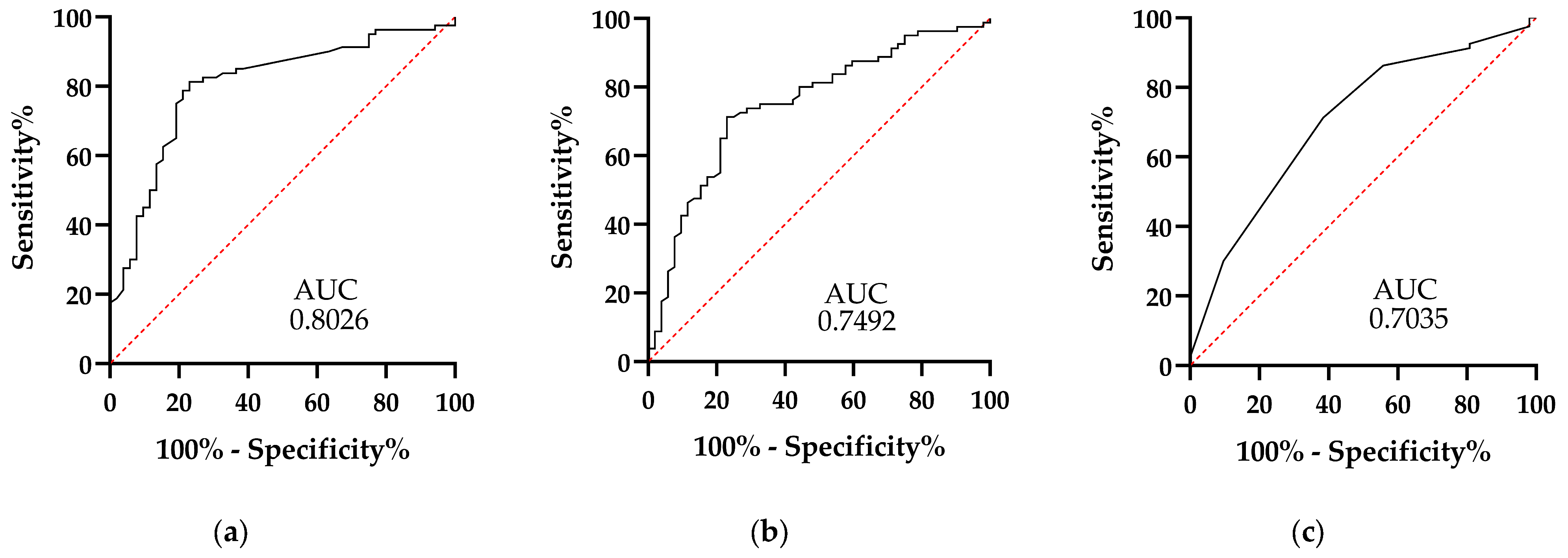
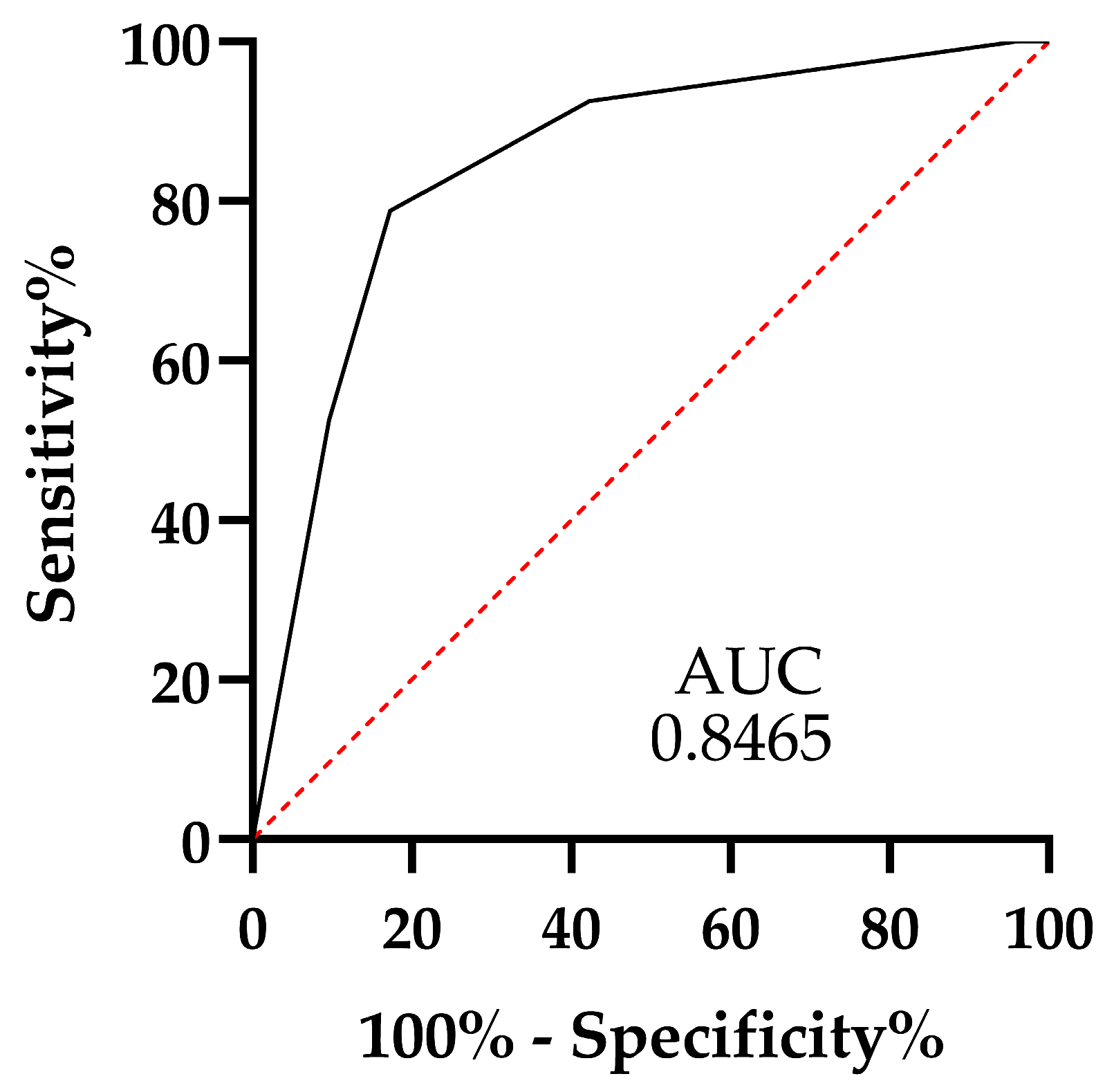
| AUC | C.I. 95% L.L. | C.I. 95% U.L. | Cutoff Point | Sensitivity | Specificity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NLR | 0.6647 | 0.5718 | 0.7575 | 9.342 | 61.25 | 59.62 |
| MLR | 0.6242 | 0.5259 | 0.7224 | 0.6141 | 61.25 | 57.69 |
| PLR | 0.6512 | 0.5562 | 0.7462 | 203.0 | 62.50 | 63.46 |
| Alvarado scale | 0.5958 | 0.4982 | 0.6934 | 7.500 | 51.25 | 63.46 |
| RIPASA scale | 0.6457 | 0.5498 | 0.7416 | 7.250 | 65 | 63.46 |
| scale proposed | 0.8465 | 0.7748 | 0.9182 | 3.0 | 78.75 | 82.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández-González, L.L.; Serrano-Guzmán, S.J.; Guzmán-Ortiz, J.D.; Pérez-Ceballos, H.E.; Cano-Pérez, J.L.; Cruz-Hernández, V.; Bernardino-Hernández, H.U.; Martínez-Martínez, L.L.; Aguilar-Ruiz, S.R. C-Reactive Protein, International Normalized Ratio, and Fibrinogen in Diagnostic Scale of Complicated Acute Appendicitis. Clin. Pract. 2025, 15, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15020025
Hernández-González LL, Serrano-Guzmán SJ, Guzmán-Ortiz JD, Pérez-Ceballos HE, Cano-Pérez JL, Cruz-Hernández V, Bernardino-Hernández HU, Martínez-Martínez LL, Aguilar-Ruiz SR. C-Reactive Protein, International Normalized Ratio, and Fibrinogen in Diagnostic Scale of Complicated Acute Appendicitis. Clinics and Practice. 2025; 15(2):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15020025
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández-González, Leticia Lorena, Said José Serrano-Guzmán, Jesús David Guzmán-Ortiz, Hermelo Esteban Pérez-Ceballos, José Luis Cano-Pérez, Víctor Cruz-Hernández, Héctor Ulises Bernardino-Hernández, Lucía Lourdes Martínez-Martínez, and Sergio Roberto Aguilar-Ruiz. 2025. "C-Reactive Protein, International Normalized Ratio, and Fibrinogen in Diagnostic Scale of Complicated Acute Appendicitis" Clinics and Practice 15, no. 2: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15020025
APA StyleHernández-González, L. L., Serrano-Guzmán, S. J., Guzmán-Ortiz, J. D., Pérez-Ceballos, H. E., Cano-Pérez, J. L., Cruz-Hernández, V., Bernardino-Hernández, H. U., Martínez-Martínez, L. L., & Aguilar-Ruiz, S. R. (2025). C-Reactive Protein, International Normalized Ratio, and Fibrinogen in Diagnostic Scale of Complicated Acute Appendicitis. Clinics and Practice, 15(2), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15020025








