Urinary Tract Infections and Bacterial Multidrug Resistance in Kidney Transplant Impact on Function and Graft Survival
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Definitions and Variables
2.4. Immunosuppression Regimens
2.5. Data Collection
2.6. Microbiological Analysis
2.7. Assessment of Renal Function and Graft Survival
2.8. Statistical Analysis
2.9. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Baseline Renal Function Pathological Characteristics and Outcomes
3.3. Microbiological Profile of UTIs
3.4. Graft Survival
3.5. Risk Factors for Graft Loss
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hariharan, S.; Israni, A.K.; Danovitch, G. Long-Term Survival after Kidney Transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 729–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishman, J.A. Infection in Organ Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2017, 17, 856–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, E.; Torre-Cisneros, J.; Blanes, M.; Montejo, M.; Cervera, C.; Aguado, J.M.; Len, O.; Carratalá, J.; Cordero, E.; Bou, G.; et al. Bacterial urinary tract infection after solid organ transplantation in the RESITRA cohort. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2012, 14, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.R.; Bang, H.; Dadhania, D.; Hartono, C.; Aull, M.J.; Satlin, M.; August, P.; Suthanthiran, M.; Muthukumar, T. Independent Risk Factors for Urinary Tract Infection and for Subsequent Bacteremia or Acute Cellular Rejection. Transplantation 2013, 96, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, L.F.; Esteves, A.B.A.; Ulisses, L.R.S.; Rivelli, G.G.; Mazzali, M. Urinary Tract Infection in Renal Transplant Recipients: Incidence, Risk Factors, and Impact on Graft Function. Transplant. Proc. 2014, 46, 1757–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodro, M.; Sabé, N.; Tubau, F.; Lladó, L.; Baliellas, C.; Roca, J.; Cruzado, J.M.; Carratalà, J. Risk Factors and Outcomes of Bacteremia Caused by Drug-Resistant ESKAPE Pathogens in Solid-Organ Transplant Recipients. Transplantation 2013, 96, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Delden, C.; Blumberg, E.A. Multidrug Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2009, 9, S27–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Delden, C.; Stampf, S.; Hirsch, H.H.; Manuel, O.; Meylan, P.; Cusini, A.; Hirzel, C.; Khanna, N.; Weisser, M.; Garzoni, C.; et al. Burden and Timeline of Infectious Diseases in the First Year After Solid Organ Transplantation in the Swiss Transplant Cohort Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, e159–e169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, R.; Javaid, S.; Khan, M.; Lal, N.; Luxmi, S.; Sarfaraz, S. Multiple Drug Resistant Urinary Tract Infection in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transplant. 2020, 31, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenberger, E.M.; Thaden, J.T. Epidemiology and Mechanisms of Resistance of Extensively Drug Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Origüen, J.; López-Medrano, F.; Fernández-Ruiz, M.; Polanco, N.; Gutiérrez, E.; González, E.; Mérida, E.; Ruiz-Merlo, T.; Morales-Cartagena, A.; Pérez-Jacoiste Asín, M.A.; et al. Should Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Be Systematically Treated in Kidney Transplant Recipients? Results From a Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 2943–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, J.D.; Julian, K. Urinary tract infections in solid organ transplant recipients: Guidelines from the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 33, e13507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguado, J.M.; Silva, J.T.; Fernández-Ruiz, M.; Cordero, E.; Fortún, J.; Gudiol, C.; Martínez-Martínez, L.; Vidal, E.; Almenar, L.; Almirante, B.; et al. Management of multidrug resistant Gram-negative bacilli infections in solid organ transplant recipients: SET/GESITRA-SEIMC/REIPI recommendations. Transplant. Rev. 2018, 32, 36–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS) Report 2022; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolle, L.E.; Bradley, S.; Colgan, R.; Rice, J.C.; Schaeffer, A.; Hooton, T.M. Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, R.; Julian, K. Urinary Tract Infections in Solid Organ Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Jawdeh, B.G.; Me, H.M. Immunosuppression in Kidney Transplant Recipients: An Update for the General Nephrologist. Adv. Kidney Dis. Health 2024, 31, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuetz, A.N.; Ferrell, A.; Hindler, J.A.; Humphries, R.; Bobenchik, A.M. Overview of changes in the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: M100 32nd and 33rd editions. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2025, 63, e0162323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posit Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R. Posit Software. PBC: Boston, MA, USA. Available online: http://www.posit.co/ (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Pinchera, B.; Trucillo, E.; D’Agostino, A.; Gentile, I. Urinary Tract Infections in Kidney Transplant Patients: An Open Challenge-Update on Epidemiology, Risk Factors and Management. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, K.C.; Oliver, J.D., III; Hypolite, I.; Lepler, L.L.; Kirk, A.D.; Ko, C.W.; Hawkes, C.A.; Jones, C.A.; Agodoa, L.Y. Hospitalizations for Bacterial Septicemia after Renal Transplantation in the United States. Am. J. Nephrol. 2001, 21, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiekhani, M.; Shekari, Z.; Zamani, A.; Zare, Z.; Haem, E.; Jalali, S.S.; Akbari, A.; Nikoupour, H.; Shahabinezhad, F. Antimicrobial resistance surveillance of gram-negative bacteria among solid organ transplant recipients, a 4-year retrospective study. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 19371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutzoukas, A.E.; Dai, W.; Cober, E.; Abbo, L.M.; Komarow, L.; Chen, L.; Hill, C.; Satlin, M.J.; Grant, M.; Fries, B.C.; et al. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales in solid organ transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2025, 25, 848–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariza-Heredia, E.J.; Beam, E.N.; Lesnick, T.G.; Kremers, W.K.; Cosio, F.G.; Razonable, R.R. Urinary tract infections in kidney transplant recipients: Role of gender, urologic abnormalities, and antimicrobial prophylaxis. Ann. Transplant. 2013, 18, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, K.C.; Swanson, S.J.; Richter, E.R.; Bohen, E.M.; Agodoa, L.Y.; Peters, T.G.; Barbour, G.; Lipnick, R.; Cruess, D.F. Late urinary tract infection after renal transplantation in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2004, 44, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strohaeker, J.; Aschke, V.; Koenigsrainer, A.; Nadalin, S.; Bachmann, R. Urinary Tract Infections in Kidney Transplant Recipients-Is There a Need for Antibiotic Stewardship? J. Clin. Med. 2021, 11, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huml, A.M.; Sedor, J.R.; Poggio, E.; Patzer, R.E.; Schold, J.D. An opt-out model for kidney transplant referral: The time has come. Am. J. Transplant. 2021, 21, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolley, B.E.; Hong, Y.; Nasim, U.; Iyanna, N.; Dorken-Gallastegi, A.; Machinski, S.N.; Hickey, G.W.; Keebler, M.E.; Horn, E.T.; Kaczorowski, D.J. Center experience is associated with greater survival following donation after circulatory death heart transplantation. J. Hear. Lung Transplant. 2025; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastidas-Caldes, C.; Romero-Alvarez, D.; Valdez-Vélez, V.; Morales, R.D.; Montalvo-Hernández, A.; Gomes-Dias, C.; Calvopiña, M. Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamases Producing Escherichia coli in South America: A Systematic Review with a One Health Perspective. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 5759–5779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Blanco, M.; Labarca, J.A.; Villegas, M.V.; Gotuzzo, E. Extended spectrum β-lactamase producers among nosocomial Enterobacteriaceae in Latin America. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 18, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satlin, M.J.; Jenkins, S.G.; Walsh, T.J. The Global Challenge of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae in Transplant Recipients and Patients With Hematologic Malignancies. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 58, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristic | Overall n = 163 1 | UTI (−) n = 134 1 | UTI (+) n = 29 1 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 44 (18–75) | 44 (30–56) | 40 (18–75) | 0.3 2 |
| Sex | 0.004 3 | |||
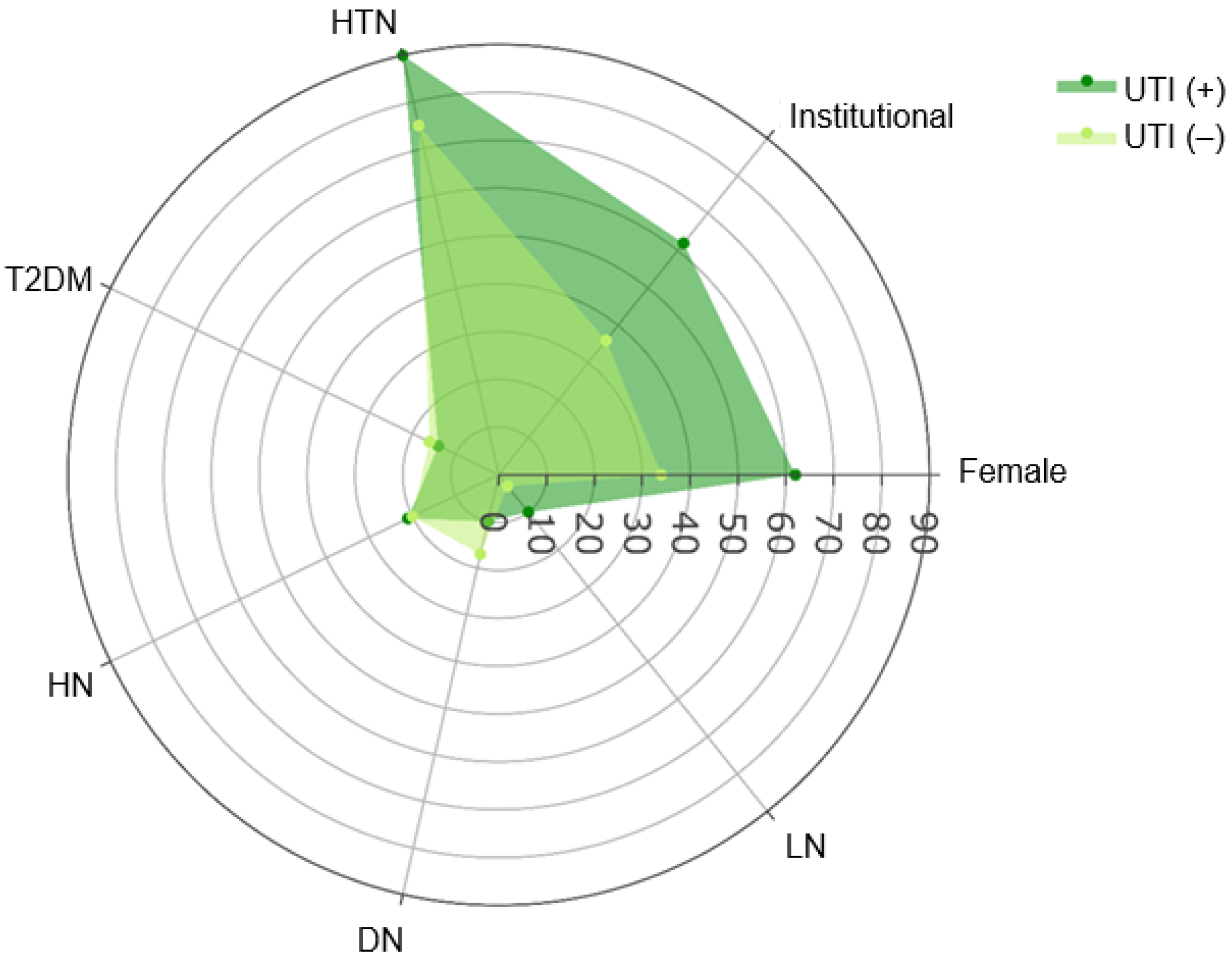
| Female | 63 (39%) | 45 (34%) | 18 (62%) | |
| Male | 100 (61%) | 89 (66%) | 11 (38%) | |
| Referral | 0.009 3 | |||
| External | 97 (60%) | 86 (64%) | 11 (38%) | |
| Institutional | 66 (40%) | 48 (36%) | 18 (62%) | |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Diabetes | >0.9 4 | |||
| DM1 | 3 (1.8%) | 3 (2.2%) | 0 (0%) | |
| DM2 | 26 (16%) | 22 (16%) | 4 (14%) | |
| Hypertension | 127 (78%) | 101 (75%) | 26 (90%) | 0.093 3 |
| Dyslipidemia | 10 (6.1%) | 9 (6.7%) | 1 (3.4%) | >0.9 4 |
| Hyperparathyroidism | 13 (8.0%) | 9 (6.7%) | 4 (14%) | 0.3 4 |
| Hypothyroidism | 7 (4.3%) | 6 (4.5%) | 1 (3.4%) | >0.9 4 |
| Primary Kidney Disease | ||||
| LN | 7 (4.3%) | 4 (3.0%) | 3 (10%) | 0.11 4 |
| DN | 26 (16%) | 23 (17%) | 3 (10%) | 0.6 4 |
| HN | 33 (20%) | 27 (20%) | 6 (21%) | >0.9 3 |
| MPGN | 1 (0.6%) | 1 (0.7%) | 0 (0%) | >0.9 4 |
| MN | 7 (4.3%) | 5 (3.7%) | 2 (6.9%) | 0.6 4 |
| FSGS | 4 (2.5%) | 3 (2.2%) | 1 (3.4%) | 0.5 4 |
| Cystinosis | 1 (0.6%) | 1 (0.7%) | 0 (0%) | >0.9 4 |
| Characteristic | UTI (−) n = 134 1 | UTI (+) n = 29 1 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline eGFR, mL/min/m2 | 60.0 (5.0–134.0) | 35.0 (9.0–94.0) | 0.002 2 |
| Donor type | 0.5 3 | ||
| Deceased | 65 (49%) | 16 (55%) | |
| Living | 69 (51%) | 13 (45%) | |
| Ischemia time, hours | 9.9 (1.0–28.0) | 8.7 (3.0–26.0) | 0.6 2 |
| PRA, % | 0.6 4 | ||
| 0–10 | 130 (97%) | 28 (97%) | |
| 11–50 | 2 (1.5%) | 1 (3.4%) | |
| 51–100 | 2 (1.5%) | 0 (0%) | |
| HLA-A, # matches | >0.9 4 | ||
| 1 | 23 (68%) | 6 (75%) | |
| 2 | 11 (32%) | 2 (25%) | |
| HLA-B, # matches | >0.9 4 | ||
| 1 | 19 (90%) | 5 (100%) | |
| 2 | 2 (9.5%) | 0 (0%) | |
| HLA-DR, # matches | 0.4 4 | ||
| 1 | 28 (93%) | 5 (83%) | |
| 2 | 2 (6.7%) | 1 (17%) | |
| Kidney Graft loss | 11 (8.2%) | 1 (3.4%) | 0.5 4 |
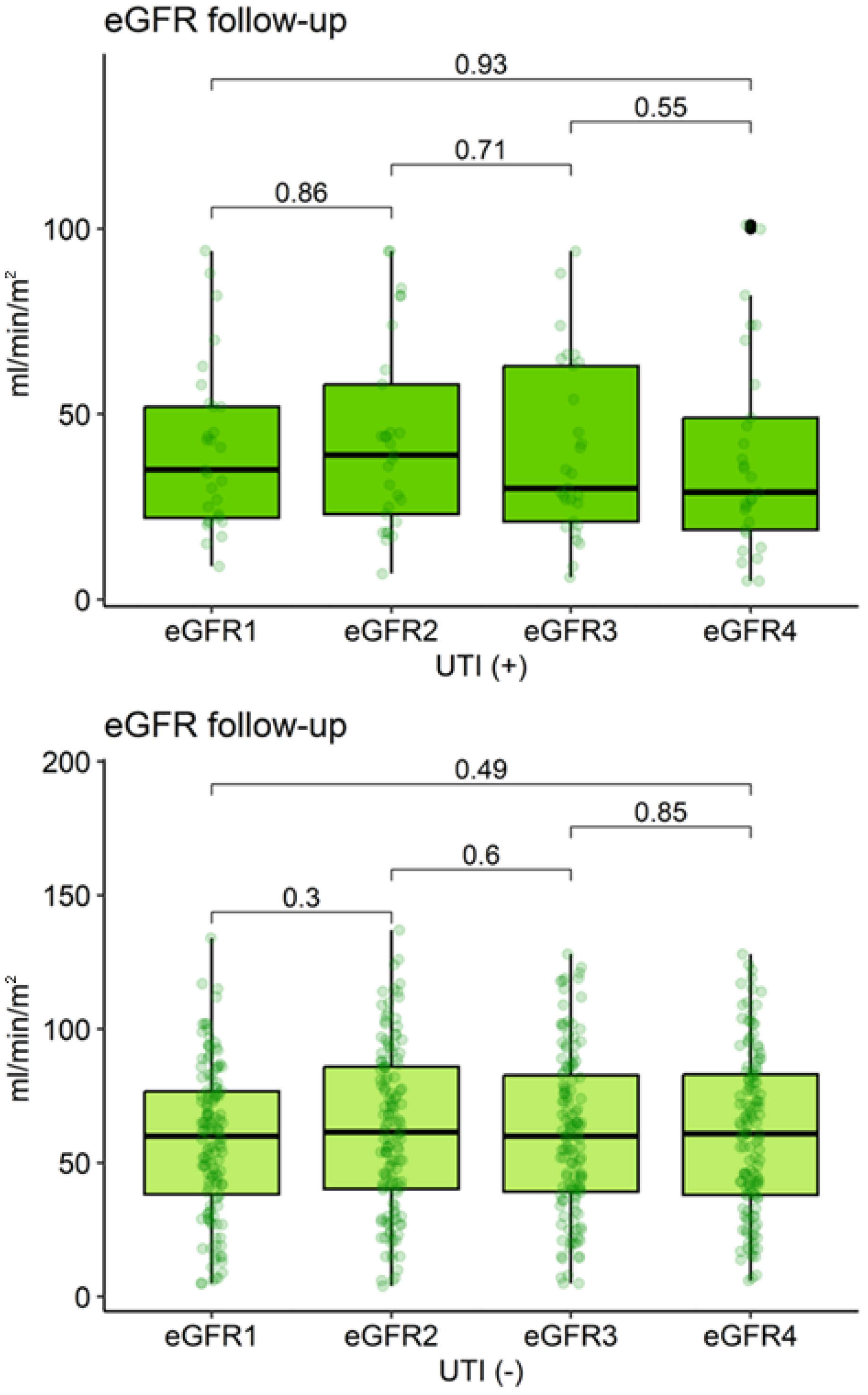
| Characteristic | eGFR1 | eGFR2 | eGFR3 | eGFR4 | p-Value 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UTI (−) (n = 134) | 60.0 (5.0–134.0) | 61.5 (4.0–137.0) | 60.0 (5.0–128.0) | 60.9 (6.0–128.0) | 0.59 |
| UTI (+) (n = 29) | 35.0 (9.0–94.0) | 39.0 (7.0–94.0) | 30.0 (6.0–94.0) | 29.0 (5.0–101.0) | 0.68 |
| p-value 2 | 0.002 | 0.002 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Characteristic | Overall n = 29 1 | Female n = 18 1 | Male n = 11 1 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hospitalization | 3 (10%) | 1 (5.6%) | 2 (18%) | 0.5 2 |
| Sample source | >0.9 2 | |||
| Urine | 13 (45%) | 8 (44%) | 5 (45%) | |
| Bladder catheter | 16 (55%) | 10 (56%) | 6 (55%) | |
| Type of infection | >0.9 2 | |||
| HAI | 20 (69%) | 12 (67%) | 8 (73%) | |
| CAI | 9 (31%) | 6 (33%) | 3 (27%) | |
| Gram | ||||
| Negative | 29 (100%) | 18 (100%) | 11 (100%) | - |
| Microorganism | ||||
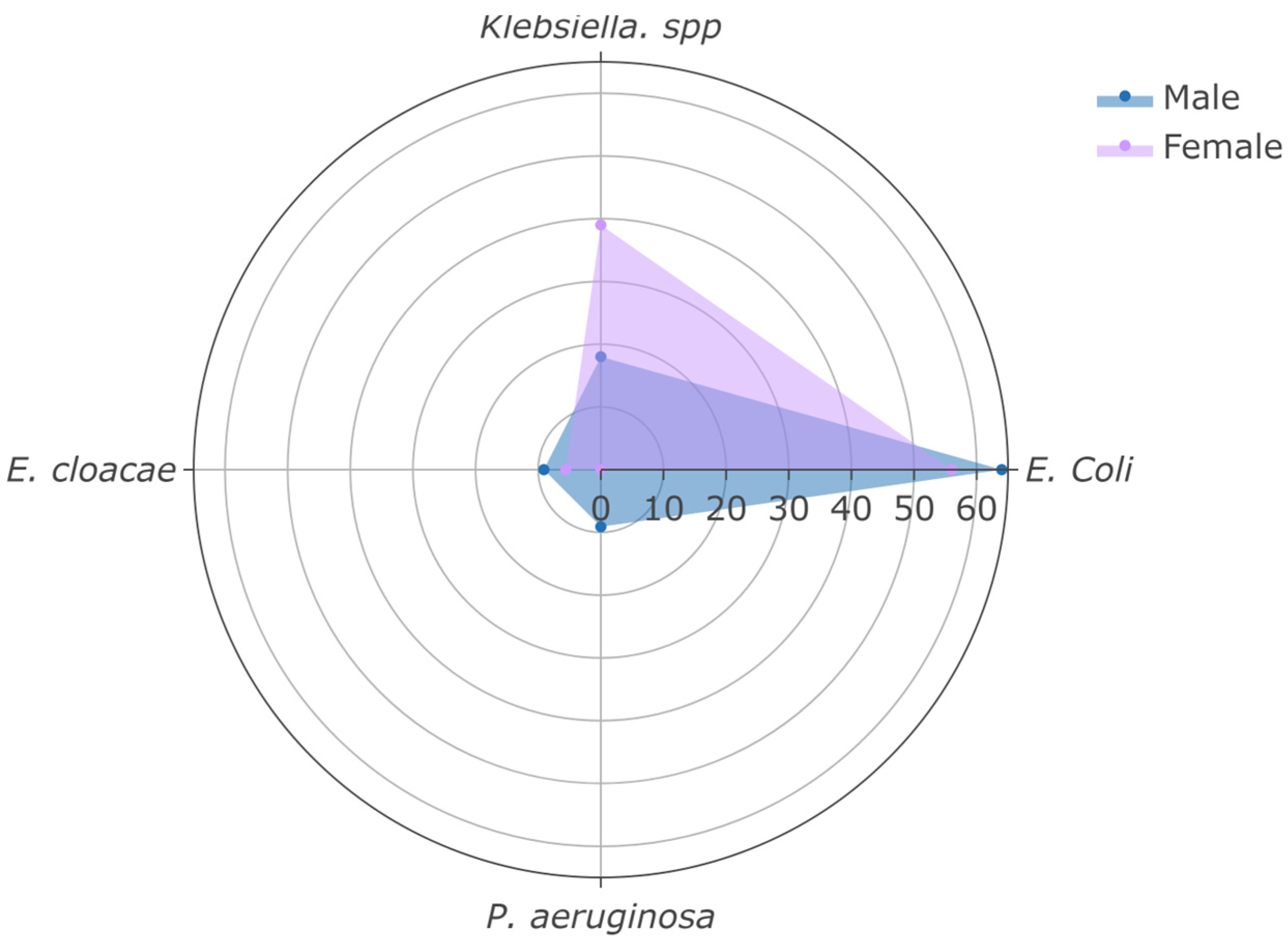
| E. coli | 17 (59%) | 10 (56%) | 7 (64%) | 0.7 2 |
| Klebsiella spp. | 9 (31%) | 7 (39%) | 2 (18%) | 0.4 2 |
| E. cloacae | 2 (6.9%) | 1 (5.6%) | 1 (9.1%) | >0.9 2 |
| P. aeruginosa | 1 (3.4%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (9.1%) | 0.4 2 |
| Characteristic | Overall n = 29 1 | Female n = 18 1 | Male n = 11 1 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Susceptibility profile | ||||
| Fully susceptible | 7 (24%) | 4 (22%) | 3 (27%) | >0.9 2 |
| Amikacin | 24 (83%) | 15 (83%) | 9 (82%) | >0.9 3 |
| Meropenem | 21 (72%) | 14 (78%) | 7 (64%) | 0.4 3 |
| Gentamicin | 16 (55%) | 11 (61%) | 5 (45%) | 0.4 2 |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 15 (52%) | 10 (56%) | 5 (45%) | 0.7 2 |
| Cefepime | 12 (41%) | 8 (44%) | 4 (36%) | 0.7 2 |
| Ceftazidime | 11 (38%) | 7 (39%) | 4 (36%) | >0.9 2 |
| Ampicillin-sulbactam | 11 (38%) | 8 (44%) | 3 (27%) | 0.5 2 |
| Cefotaxime | 10 (34%) | 7 (39%) | 3 (27%) | 0.7 2 |
| Levofloxacin | 8 (28%) | 5 (28%) | 3 (27%) | >0.9 2 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 7 (24%) | 5 (28%) | 2 (18%) | 0.6 2 |
| Resistance profile | ||||
| Nonsusceptible classes | 8 (0, 14) | 6 (0, 13) | 10 (0, 14) | 0.2 3 |
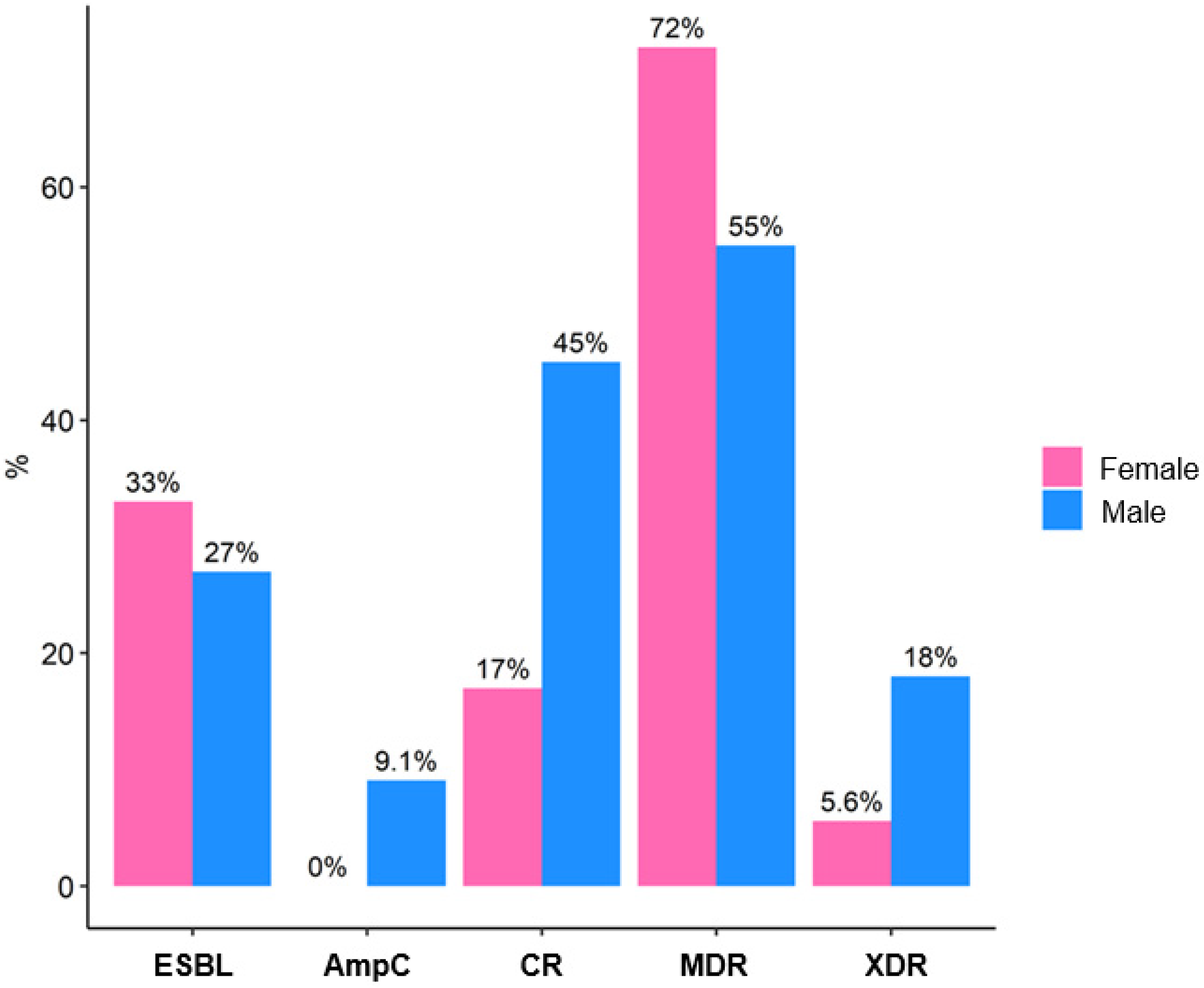
| ESBL | 9 (31%) | 6 (33%) | 3 (27%) | >0.9 2 |
| AmpC | 1 (3.4%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (9.1%) | 0.4 2 |
| CR | 8 (28%) | 3 (17%) | 5 (45%) | 0.2 2 |
| MDR | 19 (66%) | 13 (72%) | 6 (55%) | 0.4 2 |
| XDR | 3 (10%) | 1 (5.6%) | 2 (18%) | 0.5 2 |
| Characteristic | HR 1 | 95% CI 1 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 0.93 | 0.79–1.09 | 0.4 |
| Male sex | 0.65 | 0.13–3.28 | 0.6 |
| Institutional referral | 9.7 | 2.03–17.9 | 0.010 |
| HTN | 0.18 | 0.02–1.53 | 0.12 |
| HN | 2.83 | 0.49–16.2 | 0.2 |
| DN | 2.40 | 0.12–46.0 | 0.6 |
| LN | 0.75 | 0.05–10.8 | 0.8 |
| Baseline eGFR, mL/min/m2 | 0.95 | 0.92–0.97 | <0.001 |
| Living donor | 1.28 | 0.19–8.72 | 0.8 |
| Ischemia time, hours | 0.92 | 0.76–1.10 | 0.4 |
| PRA 0–10% | 10.1 | 0.44–234 | 0.15 |
| UTI (+) | 0.11 | 0.04–2.72 | 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pájaro Huertas, H.J.; Pantoja Echeverri, M.V.; Aroca Martínez, G.; Musso, C.G.; Dominguez Vargaz, A.; González-Torres, H.J. Urinary Tract Infections and Bacterial Multidrug Resistance in Kidney Transplant Impact on Function and Graft Survival. Clin. Pract. 2025, 15, 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15110215
Pájaro Huertas HJ, Pantoja Echeverri MV, Aroca Martínez G, Musso CG, Dominguez Vargaz A, González-Torres HJ. Urinary Tract Infections and Bacterial Multidrug Resistance in Kidney Transplant Impact on Function and Graft Survival. Clinics and Practice. 2025; 15(11):215. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15110215
Chicago/Turabian StylePájaro Huertas, Hernán Javier, María Viviana Pantoja Echeverri, Gustavo Aroca Martínez, Carlos Guido Musso, Alex Dominguez Vargaz, and Henry J. González-Torres. 2025. "Urinary Tract Infections and Bacterial Multidrug Resistance in Kidney Transplant Impact on Function and Graft Survival" Clinics and Practice 15, no. 11: 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15110215
APA StylePájaro Huertas, H. J., Pantoja Echeverri, M. V., Aroca Martínez, G., Musso, C. G., Dominguez Vargaz, A., & González-Torres, H. J. (2025). Urinary Tract Infections and Bacterial Multidrug Resistance in Kidney Transplant Impact on Function and Graft Survival. Clinics and Practice, 15(11), 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15110215








