Impact of an Artificial Intelligence-Guided Pulmonary Embolism Response Team (AIPERT) on Patient Transfers, Diagnosis, and Management: A Healthcare System Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. AI Integration and Workflow
2.3. Patient Inclusion
2.4. Outcomes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
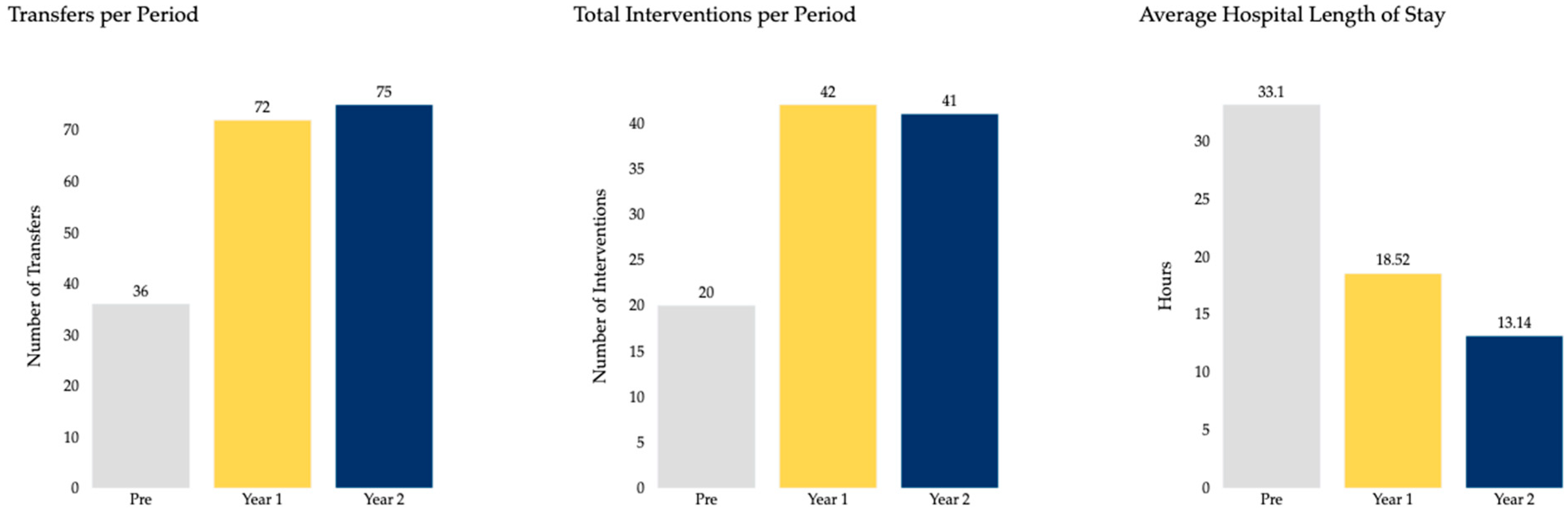
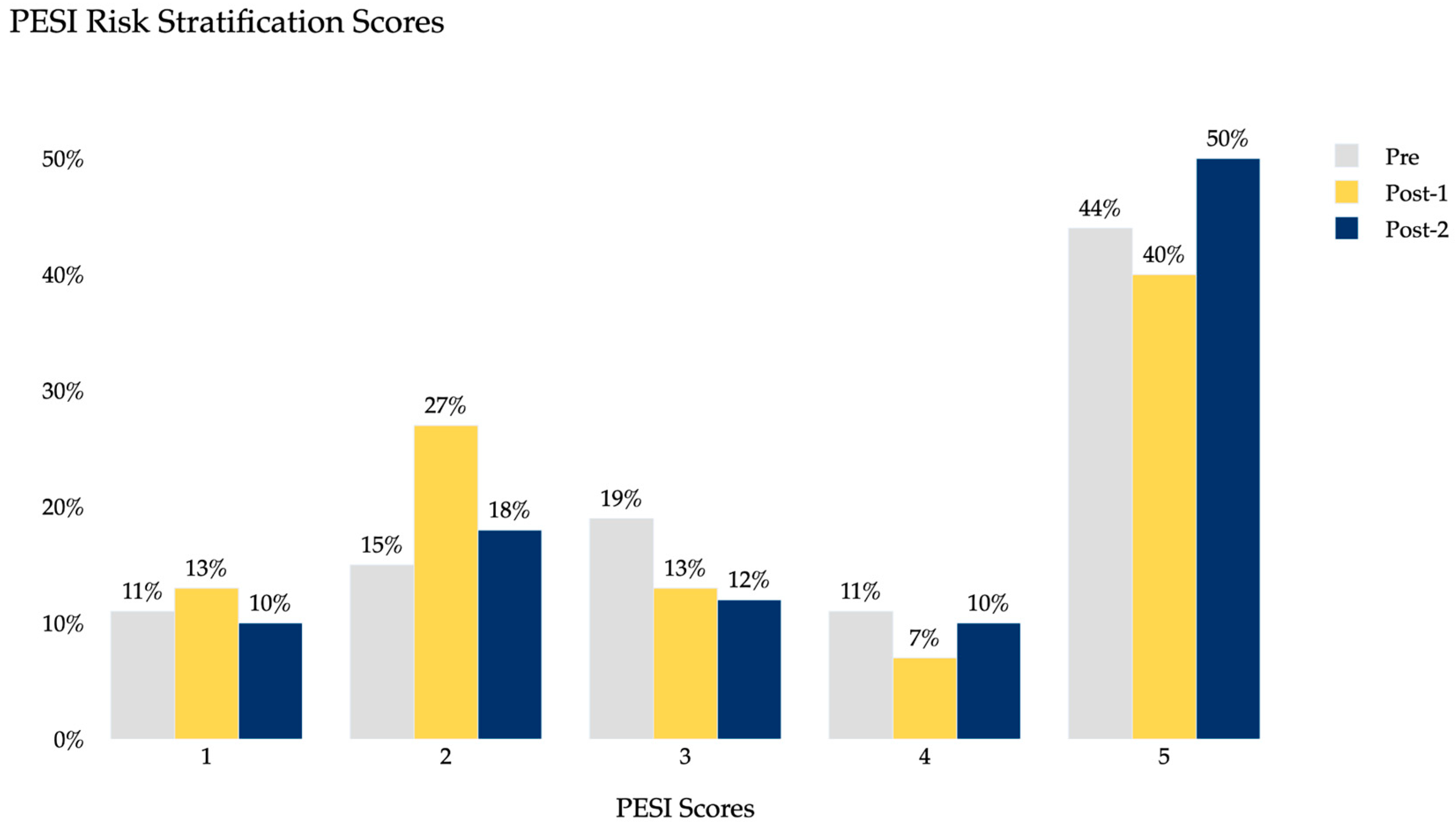
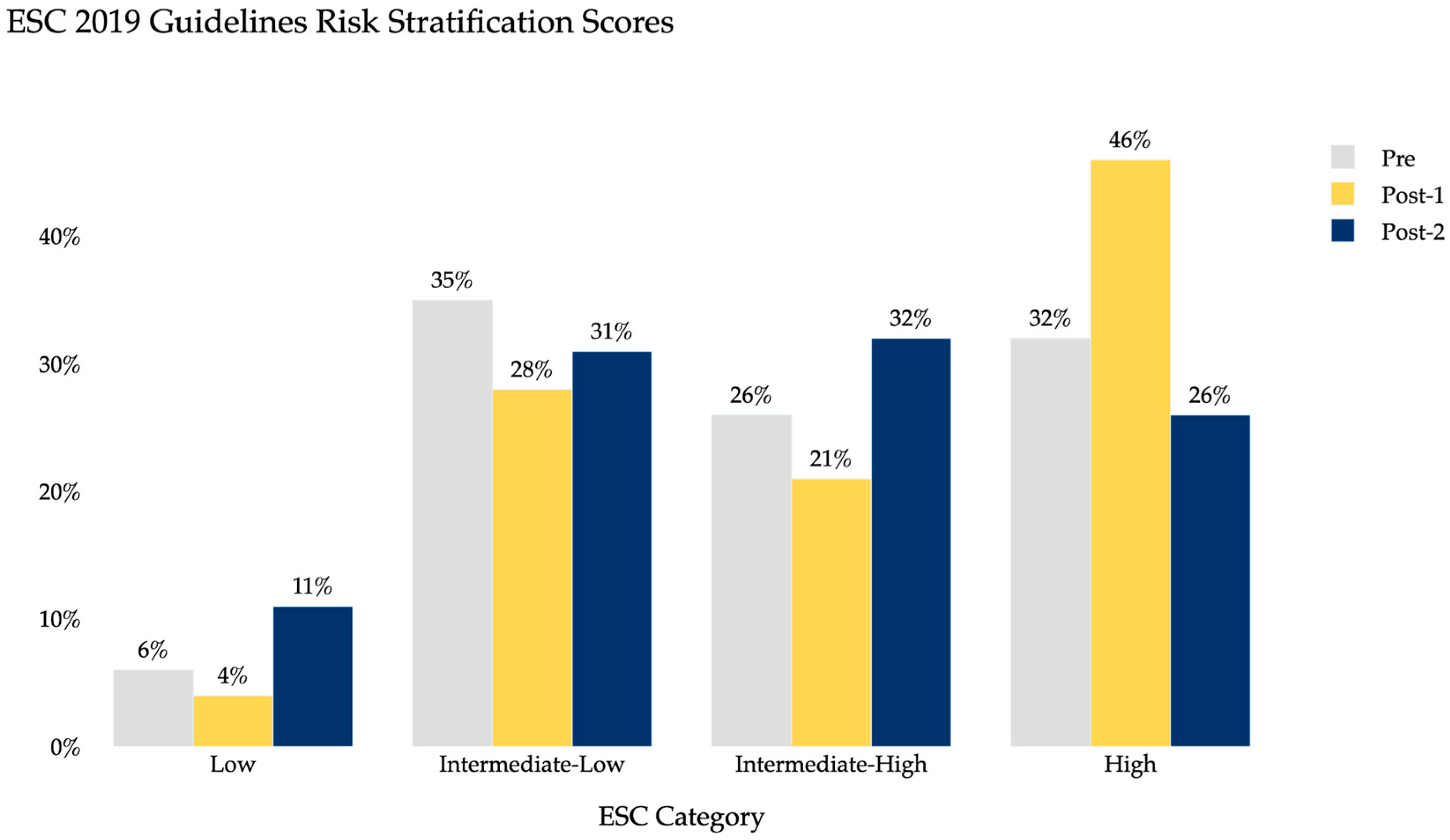
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | artificial intelligence |
| LOS | length of stay |
| PE | pulmonary embolism |
| PERT | pulmonary embolism response team |
| RV | right ventricular |
References
- Goldhaber, S.Z.; Bounameaux, H. Pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis. Lancet 2012, 379, 1835–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinides, S.V.; Meyer, G.; Becattini, C.; Bueno, H.; Geersing, G.J.; Harjola, V.P.; Huisman, M.V.; Humbert, M.; Jennings, C.S.; Jiménez, D.; et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 543–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearon, C.; Akl, E.A.; Ornelas, J.; Blaivas, A.; Jimenez, D.; Bounameaux, H.; Huisman, M.; King, C.S.; Morris, T.A.; Sood, N.; et al. Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease: CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. Chest 2016, 149, 315–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudzinski, D.M.; Piazza, G. Multidisciplinary Pulmonary Embolism Response Teams. Circulation 2016, 133, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazza, G.; Goldhaber, S.Z. The acutely decompensated right ventricle: Pathways for diagnosis and management. Chest 2005, 128, 1836–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, C.; Goldenberg, I.; Schleede, S.; McNitt, S.; Gosev, I.; Elbadawi, A.; Pietropaoli, A.; Barrus, B.; Chen, Y.L.; Mazzillo, J.; et al. Effect of a Multidisciplinary Pulmonary Embolism Response Team on Patient Mortality. Am. J. Cardiol. 2021, 161, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhury, P.; Gadre, S.K.; Schneider, E.; Renapurkar, R.D.; Gomes, M.; Haddadin, I.; Heresi, G.A.; Tong, M.Z.; Bartholomew, J.R. Impact of Multidisciplinary Pulmonary Embolism Response Team Availability on Management and Outcomes. Am. J. Cardiol. 2019, 124, 1465–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosovsky, R.; Zhao, K.; Sista, A.; Rivera-Lebron, B.; Kabrhel, C. Pulmonary embolism response teams: Purpose, evidence for efficacy, and future research directions. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 3, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryan, A.; Tran, Q.K.; Ahari, J.; McLaughlin, E.; Boone, K.; Pourmand, A. Pulmonary Embolism Response Teams—Evidence of Benefits? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosla, A.; Zhao, Y.; Mojibian, H.; Pollak, J.; Singh, I. High-Risk Pulmonary Embolism: Management for the Intensivist. J. Intensive Care Med. 2023, 38, 1087–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, J.; Reichard, A.; Muck, P.E. New Diagnostic Tools for Pulmonary Embolism Detection. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc. J. 2024, 20, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, J.; Giordano, N.; Zheng, H.; Parry, B.A.; Barnes, G.D.; Heresi, G.A.; Jaber, W.; Wood, T.; Todoran, T.; Courtney, D.M.; et al. EXPRESS: A Multidisciplinary Pulmonary Embolism Response Team (PERT)-Experience from a national multicenter consortium. Pulm Circ. 2019, 9, 2045894018824563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Syed, A.B.; Zoga, A.C. Artificial Intelligence in Radiology: Current Technology and Future Directions. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2018, 22, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soffer, S.; Klang, E.; Shimon, O.; Barash, Y.; Cahan, N.; Greenspana, H.; Konen, E. Deep learning for pulmonary embolism detection on computed tomography pulmonary angiogram: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ambrogio, S.; Verdon, I.; Laureano, B.; Ramnarine, K.V.; Fedele, F.; Vilic, D.; Honey, I.; Barton, E.; Goncalves, C.; Mak, S.M.; et al. Independent Evaluation of a Commercial AI Software for Incidental Findings of Pulmonary Embolism (IPE) on a Large Hospital Retrospective Dataset. Radiol. Res. Pract. 2025, 2025, 9091895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becattini, C.; Agnelli, G.; Lankeit, M.; Masotti, L.; Pruszczyk, P.; Casazza, F.; Vanni, S.; Nitti, C.; Kamphuisen, P.; Vedovati, M.C.; et al. Acute pulmonary embolism: Mortality prediction by the 2014 European Society of Cardiology risk stratification model. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleitas Sosa, D.; Lehr, A.L.; Zhao, H.; Roth, S.; Lakhther, V.; Bashir, R.; Cohen, G.; Panaro, J.; Maldonado, T.S.; Horowitz, J.; et al. Impact of pulmonary embolism response teams on acute pulmonary embolism: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2022, 31, 220023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rivera-Lebron, B.; McDaniel, M.; Ahrar, K.; Alrifai, A.; Dudzinski, D.M.; Fanola, C.; Blais, D.; Janicke, D.; Melamed, R.; Mohrien, K.; et al. Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow Up of Acute Pulmonary Embolism: Consensus Practice from the PERT Consortium. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2019, 25, 1076029619853037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naser, A.M.; Vyas, R.; Morgan, A.A.; Kalaiger, A.M.; Kharawala, A.; Nagraj, S.; Agarwal, R.; Maliha, M.; Mangeshkar, S.; Singh, N.; et al. Role of Artificial Intelligence in the Diagnosis and Management of Pulmonary Embolism: A Comprehensive Review. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]

| Pre | Post-1 | Post-2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Patients, number (%) | 36 (100) | 72 (100) | 75 (100) |
| Sex, number (%) | |||
| Males | 15 (41.67) | 41 (56.94) | 32 (42.67) |
| Females | 21 (58.33) | 31 (43.06) | 43 (57.33) |
| Age Ranges, number (%) | |||
| 18–44 | 5 (13.89) | 10 (13.89) | 9 (12.00) |
| 45–64 | 7 (19.44) | 25 (34.72) | 27 (36.00) |
| 65–75 | 12 (33.33) | 20 (27.78) | 23 (30.67) |
| >75 | 12 (33.33) | 17 (23.61) | 16 (21.33) |
| BMI, mean (SD) | 30.39 (7.98) | 29.31 (8.33) | 29.79 (6.80) |
| Pre | Post-1 | Post-2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| OSH Transfer, number (%) | 36 (100) | 72 (100) | 75 (100) |
| FlowTriever, number (%) | 10 (27.78) | 18 (25.00) | 28 (37.33) |
| VA-ECMO, number (%) | 0 (0) | 2 (2.78) | 2 (2.67) |
| Surgical Embolectomy, number (%) | 1 (2.78) | 1 (1.39) | 0 (0) |
| IVC Filter, number (%) | 9 (25.00) | 21 (29.17) | 11 (14.67) |
| After-Hours Diagnosis, number (%) | 25 (69.44) | 51 (70.83) | 58 (77.33) |
| Hospital LOS (Hours), mean (SD) | 33.61 (99.09) | 18.52 (17.28) | 13.14 (14.85) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khosla, A.; Singh, I.; Pollak, J.; Mojibian, H. Impact of an Artificial Intelligence-Guided Pulmonary Embolism Response Team (AIPERT) on Patient Transfers, Diagnosis, and Management: A Healthcare System Experience. Clin. Pract. 2025, 15, 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15110207
Khosla A, Singh I, Pollak J, Mojibian H. Impact of an Artificial Intelligence-Guided Pulmonary Embolism Response Team (AIPERT) on Patient Transfers, Diagnosis, and Management: A Healthcare System Experience. Clinics and Practice. 2025; 15(11):207. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15110207
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhosla, Akhil, Inderjit Singh, Jeffrey Pollak, and Hamid Mojibian. 2025. "Impact of an Artificial Intelligence-Guided Pulmonary Embolism Response Team (AIPERT) on Patient Transfers, Diagnosis, and Management: A Healthcare System Experience" Clinics and Practice 15, no. 11: 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15110207
APA StyleKhosla, A., Singh, I., Pollak, J., & Mojibian, H. (2025). Impact of an Artificial Intelligence-Guided Pulmonary Embolism Response Team (AIPERT) on Patient Transfers, Diagnosis, and Management: A Healthcare System Experience. Clinics and Practice, 15(11), 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15110207






